COVID-19 Assessment with Bedside Lung Ultrasound in a Population of Intensive Care Patients Treated with Mechanical Ventilation and ECMO
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistics
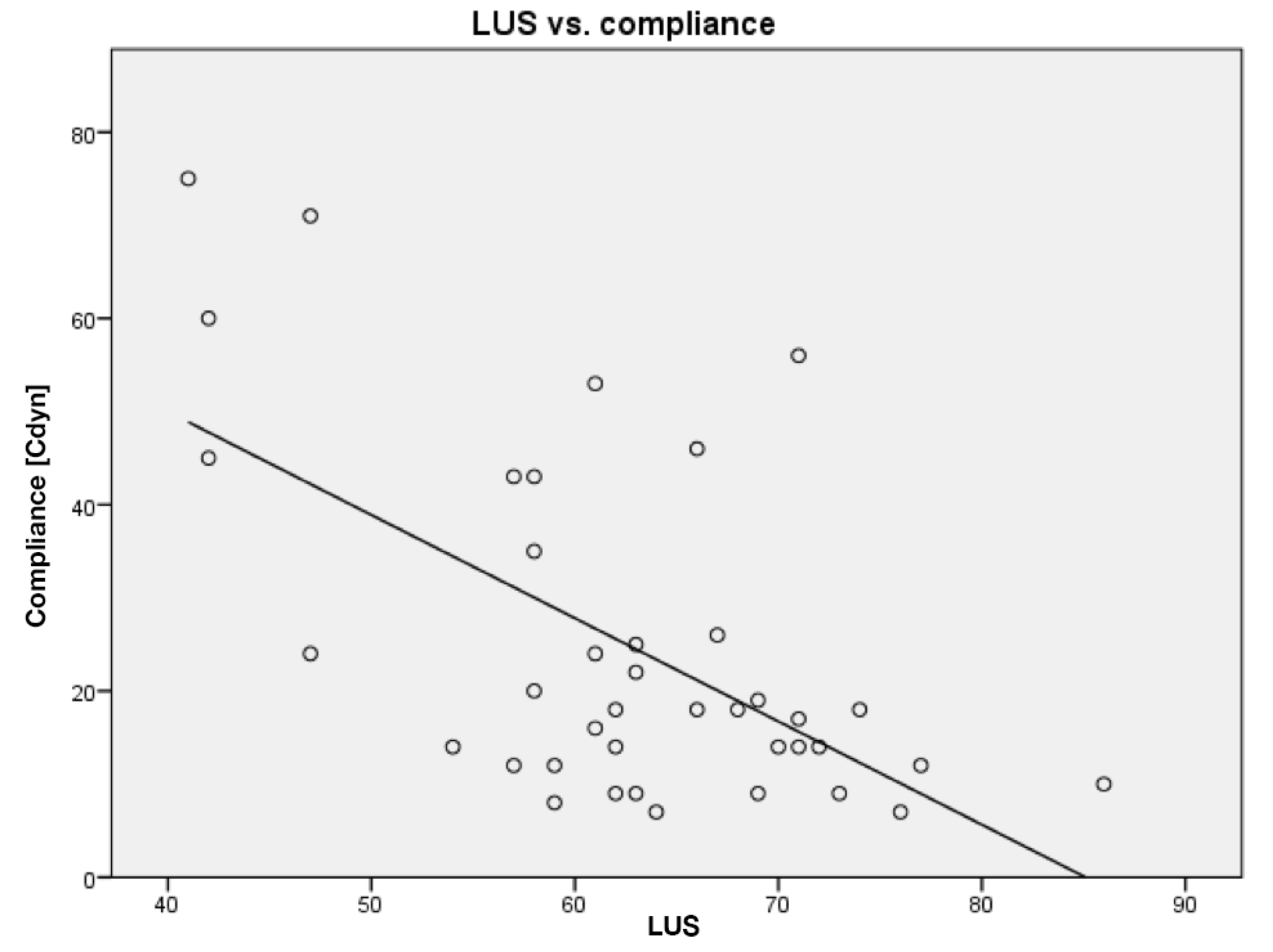
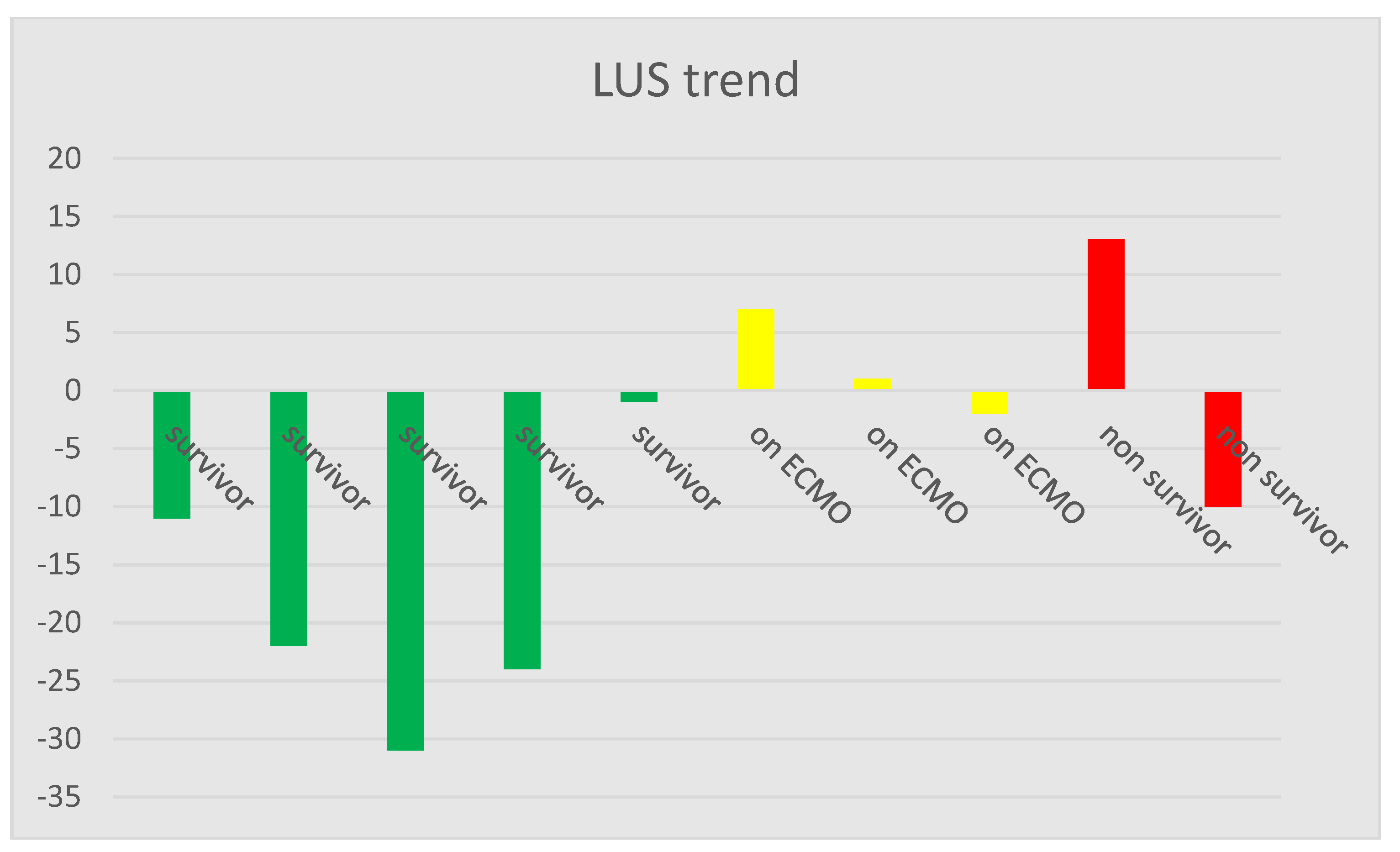
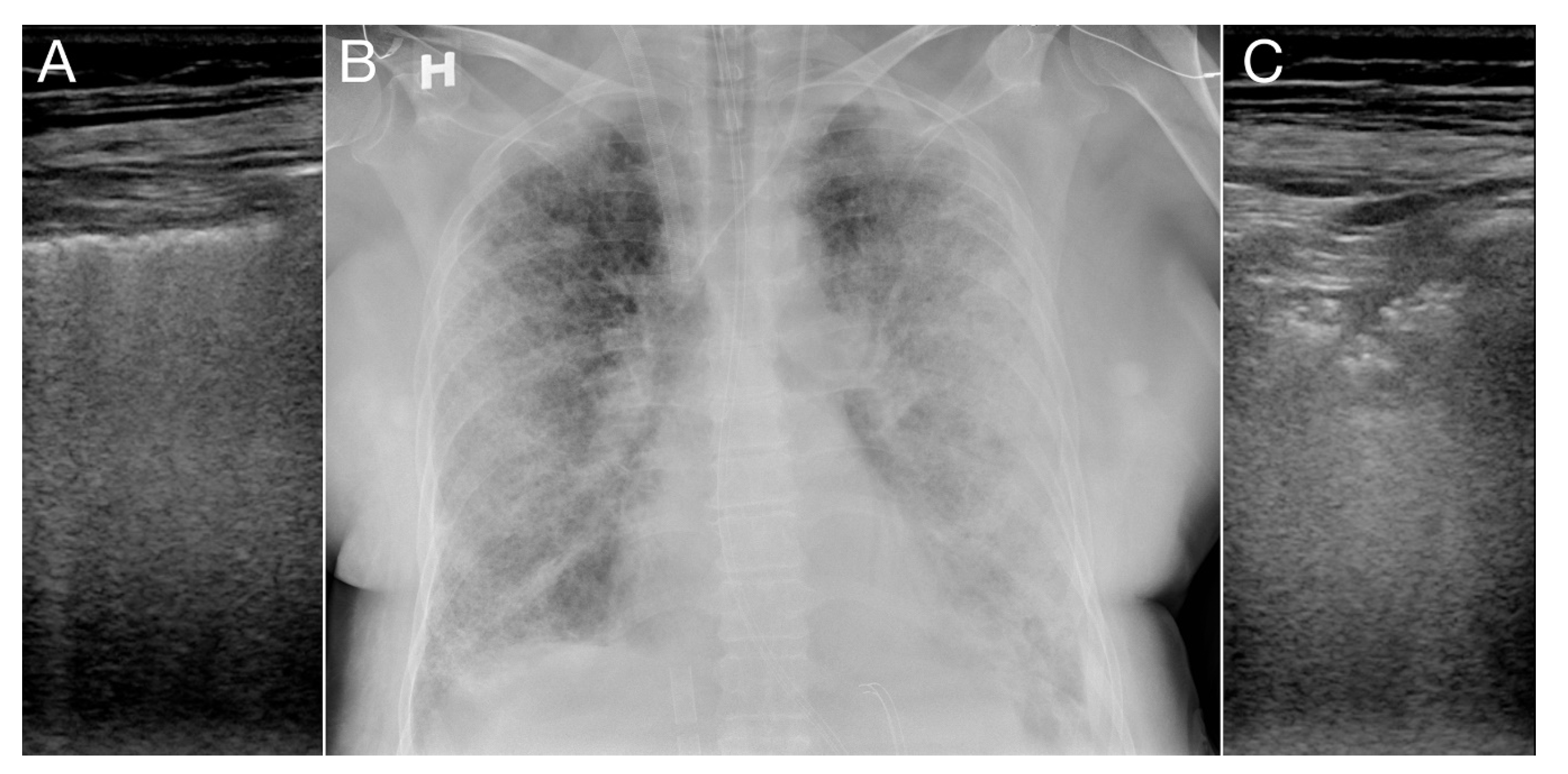
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, china. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-ncov and naming it sars-cov-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lei, P.; Zeng, B.; Li, Z.; Yu, P.; Fan, B.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Hu, S.; et al. Coronavirus disease (covid-19): Spectrum of ct findings and temporal progression of the disease. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Pan, C.; Qin, P.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, M.; Liao, Y.; Li, S. Ct image visual quantitative evaluation and clinical classification of coronavirus disease (covid-19). Eur. Radiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.Y.F.; Lam, H.Y.S.; Fong, A.H.; Leung, S.T.; Chin, T.W.; Lo, C.S.Y.; Lui, M.M.; Lee, J.C.Y.; Chiu, K.W.; Chung, T.; et al. Frequency and distribution of chest radiographic findings in covid-19 positive patients. Radiology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaivas, M. Update on point of care ultrasound in the care of the critically ill patient. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 1, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A. Lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Ann. Intensive Care 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, C.B.; Sloth, E.; Lassen, A.T.; Christensen, R.; Lambrechtsen, J.; Madsen, P.H.; Henriksen, D.P.; Davidsen, J.R.; Rasmussen, F. Point-of-care ultrasonography in patients admitted with respiratory symptoms: A single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, A.; Tutino, L.; Zagli, G.; Batacchi, S.; Cianchi, G.; Spina, R.; Bonizzoli, M.; Migliaccio, L.; Perretta, L.; Bartolini, M.; et al. The use of point-of-care bedside lung ultrasound significantly reduces the number of radiographs and computed tomography scans in critically ill patients. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, M.A.; Shams, N.; Ellington, L.E.; Naithani, N.; Gilman, R.H.; Steinhoff, M.C.; Santosham, M.; Black, R.E.; Price, C.; Gross, M.; et al. Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, C.; Gunalp, M.; Genc, S.; Acar, N.; Ustuner, E.; Oguz, A.B.; Tanriverdi, A.K.; Demirkan, A.; Polat, O. Diagnostic value of bedside lung ultrasonography in pneumonia. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Xiang, M.; Li, S.; Zhao, D.; Huang, C.; Chen, S. Protecting healthcare personnel from 2019-ncov infection risks: Lessons and suggestions. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.Y.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, L.N. Findings of lung ultrasonography of novel corona virus pneumonia during the 2019–2020 epidemic. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 849–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; et al. Is there a role for lung ultrasound during the covid-19 pandemic? J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, E.; Goffi, A.; Lupia, E.; Tizzani, M.; Porrino, G.; Ferreri, E.; Volpicelli, G.; Balzaretti, P.; Banderali, A.; Iacobucci, A.; et al. Lung ultrasound-implemented diagnosis of acute decompensated heart failure in the ed: A simeu multicenter study. Chest 2015, 148, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Meziere, G.A. Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure: The blue protocol. Chest 2008, 134, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. Ct imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-ncov). Radiology 2020, 295, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Mussa, A.; Garofalo, G.; Cardinale, L.; Casoli, G.; Perotto, F.; Fava, C.; Frascisco, M. Bedside lung ultrasound in the assessment of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 24, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshavegh, R.; Hansen, K.L.; Moller-Sorensen, H.; Nielsen, M.B.; Jensen, J.A. Automatic detection of b-lines in in vivo lung ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2019, 66, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Jelic, T.; Woo, M.Y.; Heslop, C.; Olszynski, P. Just the facts: Recommendations on point of care ultrasound use and machine infection control during the covid-19 pandemic. Can. J. Emerg. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D. Novel approaches to ultrasonography of the lung and pleural space: Where are we now? Breathe 2017, 13, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Via, G.; Storti, E.; Gulati, G.; Neri, L.; Mojoli, F.; Braschi, A. Lung ultrasound in the icu: From diagnostic instrument to respiratory monitoring tool. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012, 78, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K.L.; Fields, J.M.; Panebianco, N.L.; Jenq, K.Y.; Marin, J.; Dean, A.J. Inter-rater reliability of quantifying pleural b-lines using multiple counting methods. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbia, X.; Chabannon, M.; Chevallier, T.; de La Coussaye, J.E.; Lefrant, J.Y.; Pujol, S.; Claret, P.G.; Zieleskiewicz, L.; Roger, C.; Muller, L. Assessment of five different probes for lung ultrasound in critically ill patients: A pilot study. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koratala, A.; Ronco, C.; Kazory, A. The promising role of lung ultrasound in assessment of volume status for patients receiving maintenance renal replacement therapy. Blood Purif. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
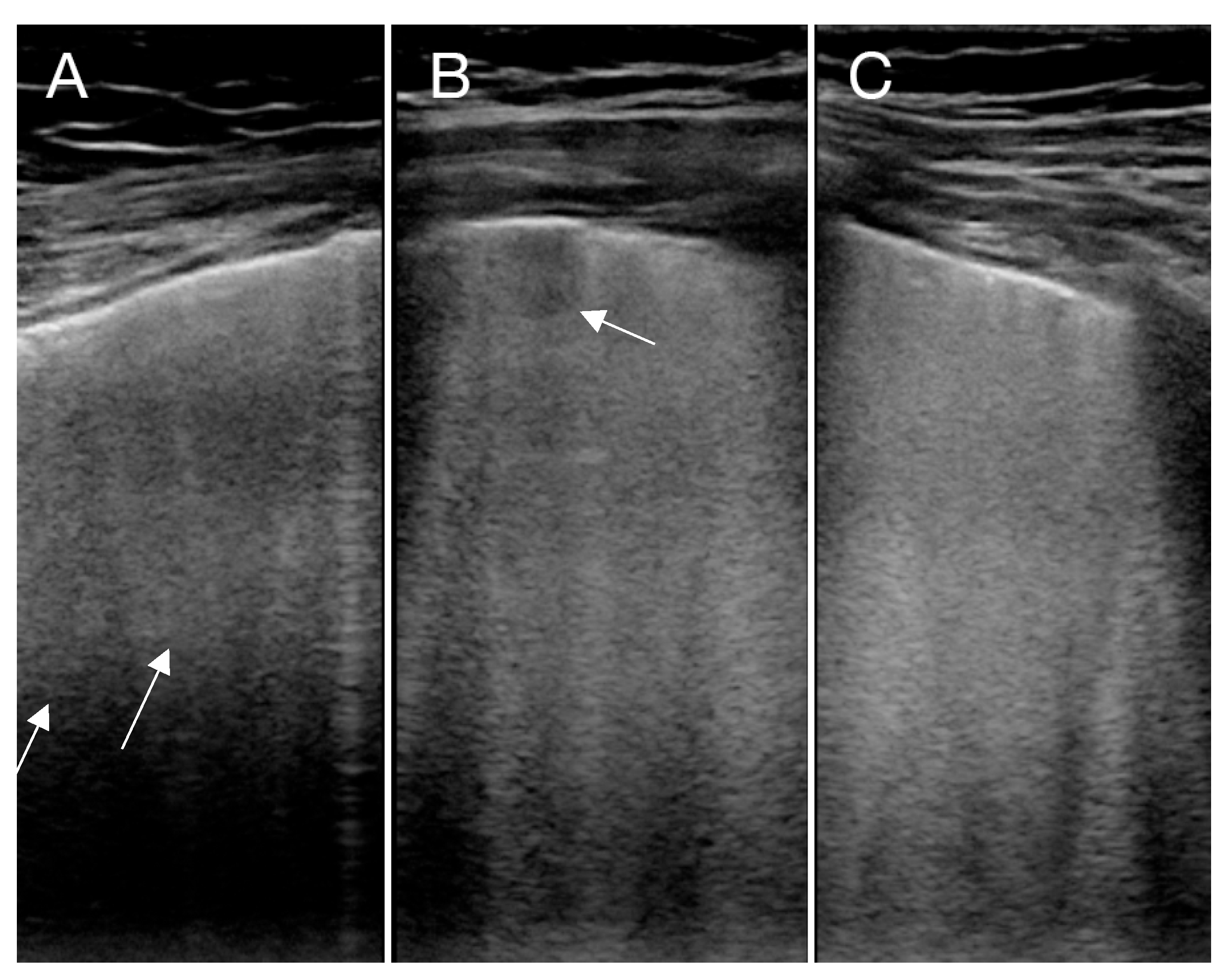
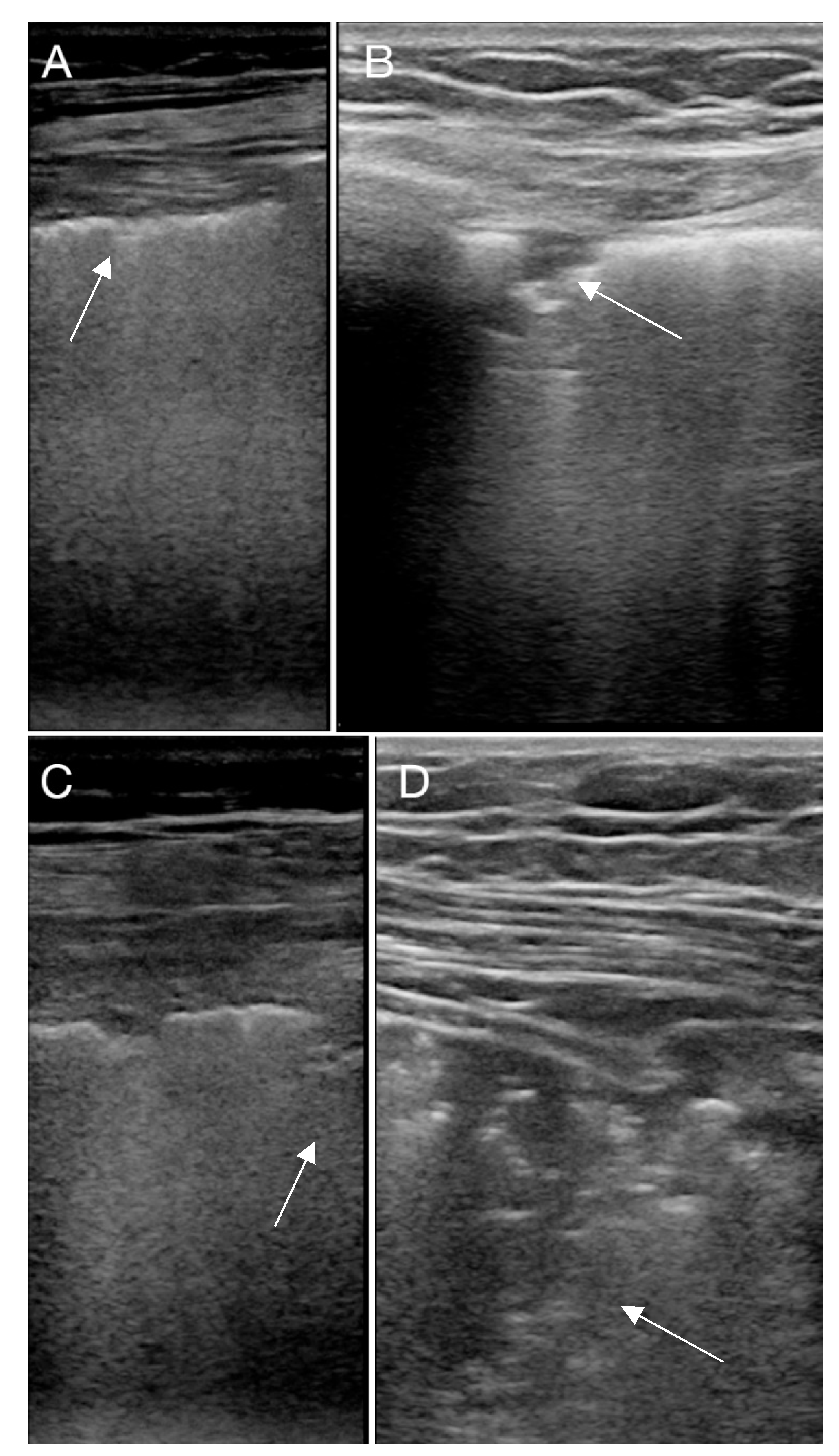
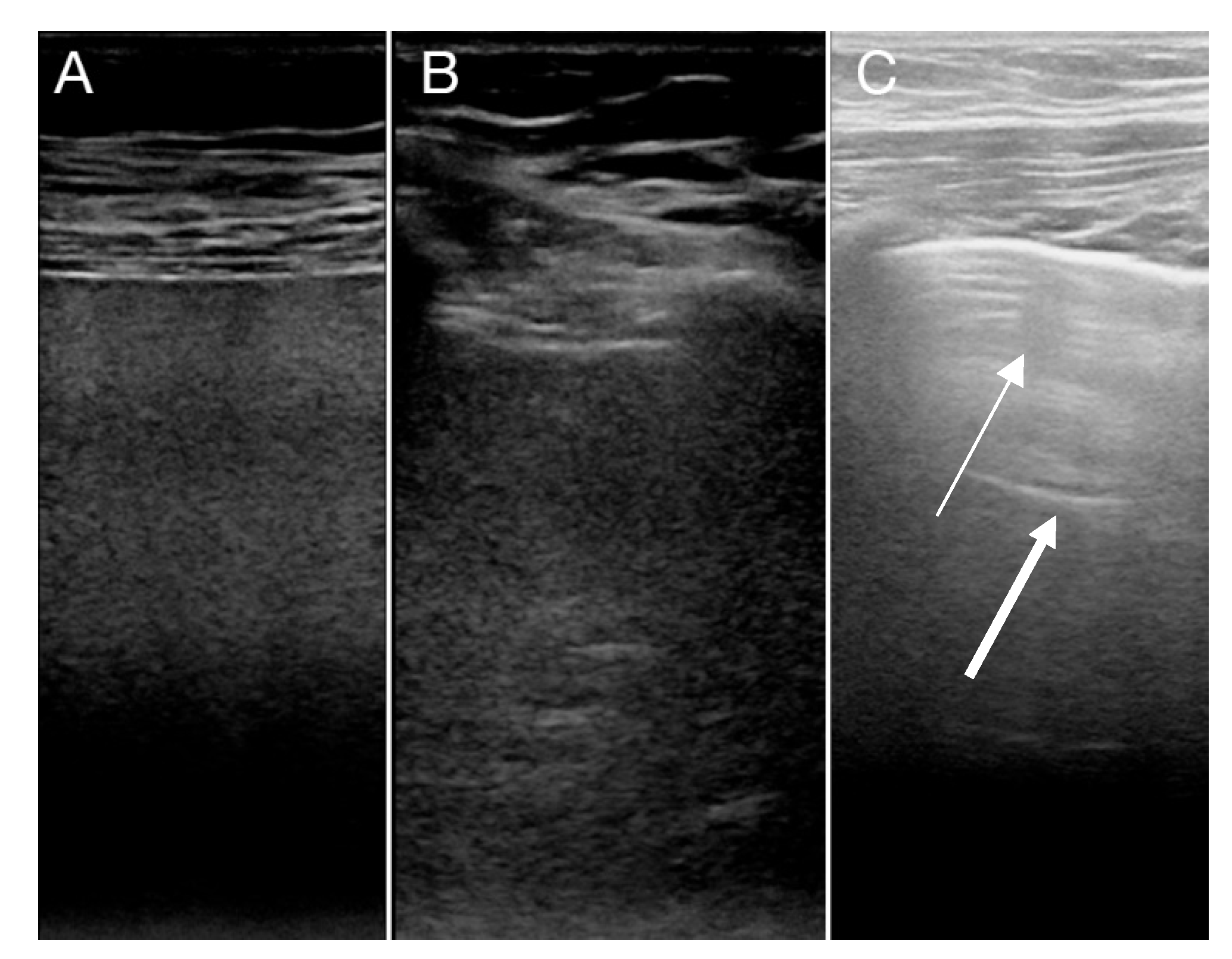
| Table for LUS Findings of Left/Right Lung | Scoring System for LUS Findings | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior | Lateral | Posterior | ||||
| Pleural thickening (Y/N) | Yes +3 | No 0 | ||||
| Lung sliding (Y/N) | No +3 | Yes 0 | ||||
| B-line appearance (none/multifocal/few) | None +3 | Multifocal +2 | Few +1 | |||
| A-line appearance (Y/N) | No +3 | Yes 0 | ||||
| Subpleural consolidation (Y/N) | Yes +2 | No 0 | ||||
| Lobar consolidation (Y/N) | Yes +2 | No 0 | ||||
| Pleural fluid (Y/N) | Yes +1 | No 0 | ||||
| Total (n = 10) | Survivor (n = 5) | On ECMO (n = 3) | Non-Survivor (n = 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
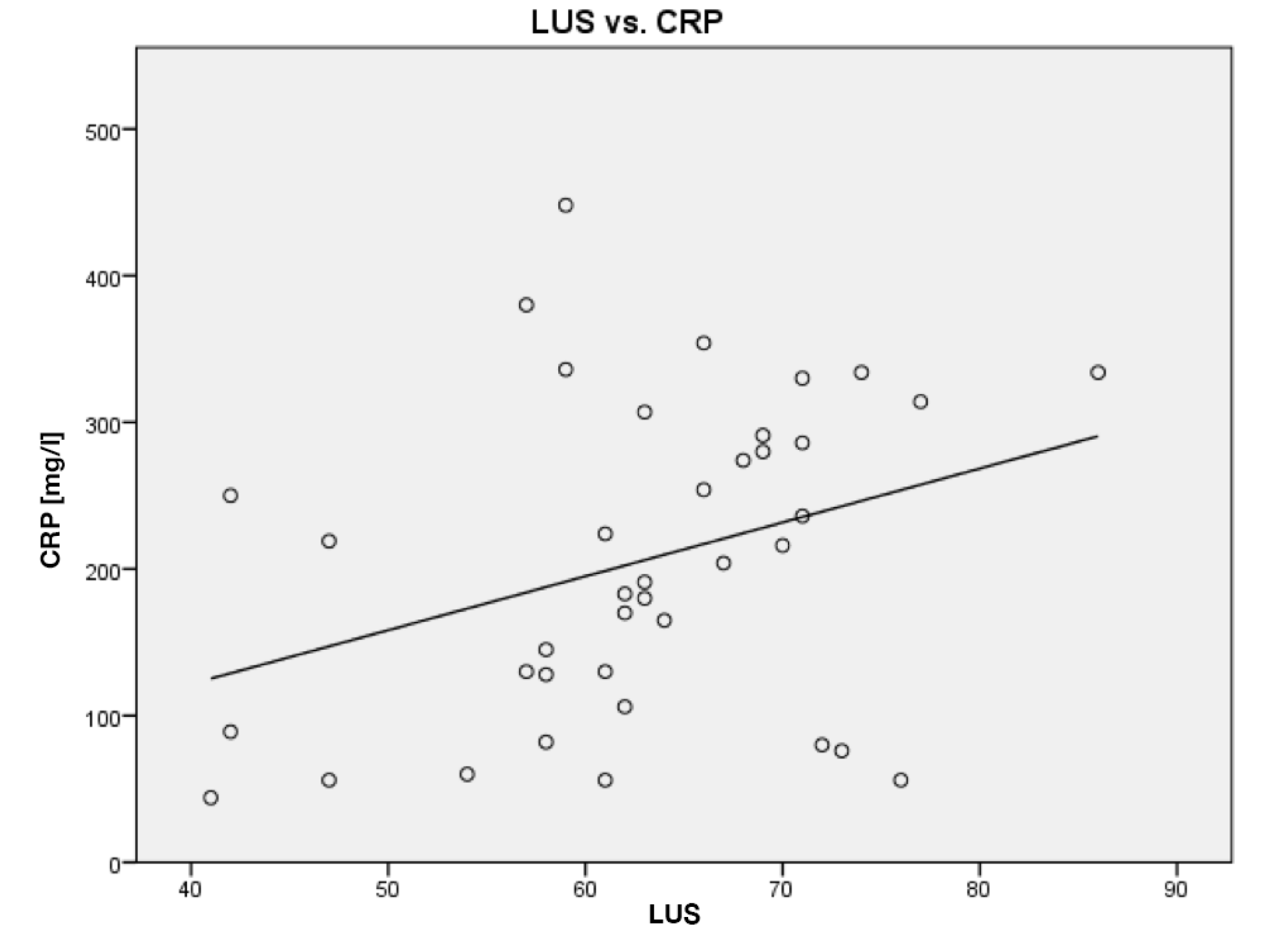
| LUS score | 62.7 (9.9) | 60.4 (9.1) | 68.8 (8.0) | 61.2 (11.5) |
| CRP [mg/L] | 205.1 (107.6) | 189.5 (116.6) | 238.8 (81.4) | 202.3 (114.7) |
| Compliance [Cdyn] | 24.7 (18.4) | 25.7 (17.0) | 14.8 (5.2) | 33.9 (26.0) |
| Patient No. | Patient Status | LUS Start | LUS End | CRP Start [mg/L] | CRP End [mg/L] | Compliance Start [Cdyn] | Compliance End [Cdyn] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | survivor | 74 | 63 | 334 | 191 | 18 | 25 |
| 2 | survivor | 69 | 47 | 291 | 56 | 19 | 24 |
| 3 | survivor | 72 | 41 | 80 | 44 | 14 | 75 |
| 4 | survivor | 66 | 42 | 354 | 89 | 46 | 45 |
| 5 | survivor | 59 | 58 | 448 | 128 | 12 | 35 |
| 6 | on ECMO | 63 | 70 | 180 | 216 | 22 | 14 |
| 7 | on ECMO | 61 | 62 | 130 | 106 | 16 | 9 |
| 8 | on ECMO | 71 | 69 | 330 | 280 | 14 | 9 |
| 9 | non-survivor | 63 | 76 | 307 | 56 | 9 | 7 |
| 10 | non-survivor | 57 | 47 | 380 | 219 | 43 | 46 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Møller-Sørensen, H.; Gjedsted, J.; Lind Jørgensen, V.; Lindskov Hansen, K. COVID-19 Assessment with Bedside Lung Ultrasound in a Population of Intensive Care Patients Treated with Mechanical Ventilation and ECMO. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070447
Møller-Sørensen H, Gjedsted J, Lind Jørgensen V, Lindskov Hansen K. COVID-19 Assessment with Bedside Lung Ultrasound in a Population of Intensive Care Patients Treated with Mechanical Ventilation and ECMO. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(7):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070447
Chicago/Turabian StyleMøller-Sørensen, Hasse, Jakob Gjedsted, Vibeke Lind Jørgensen, and Kristoffer Lindskov Hansen. 2020. "COVID-19 Assessment with Bedside Lung Ultrasound in a Population of Intensive Care Patients Treated with Mechanical Ventilation and ECMO" Diagnostics 10, no. 7: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070447
APA StyleMøller-Sørensen, H., Gjedsted, J., Lind Jørgensen, V., & Lindskov Hansen, K. (2020). COVID-19 Assessment with Bedside Lung Ultrasound in a Population of Intensive Care Patients Treated with Mechanical Ventilation and ECMO. Diagnostics, 10(7), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070447






