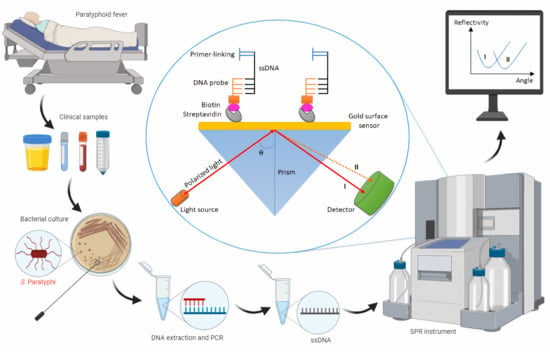
Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Paratyphoid Fever
3. Laboratory Diagnostic Approaches
3.1. Bacterial Culture
3.2. Serology
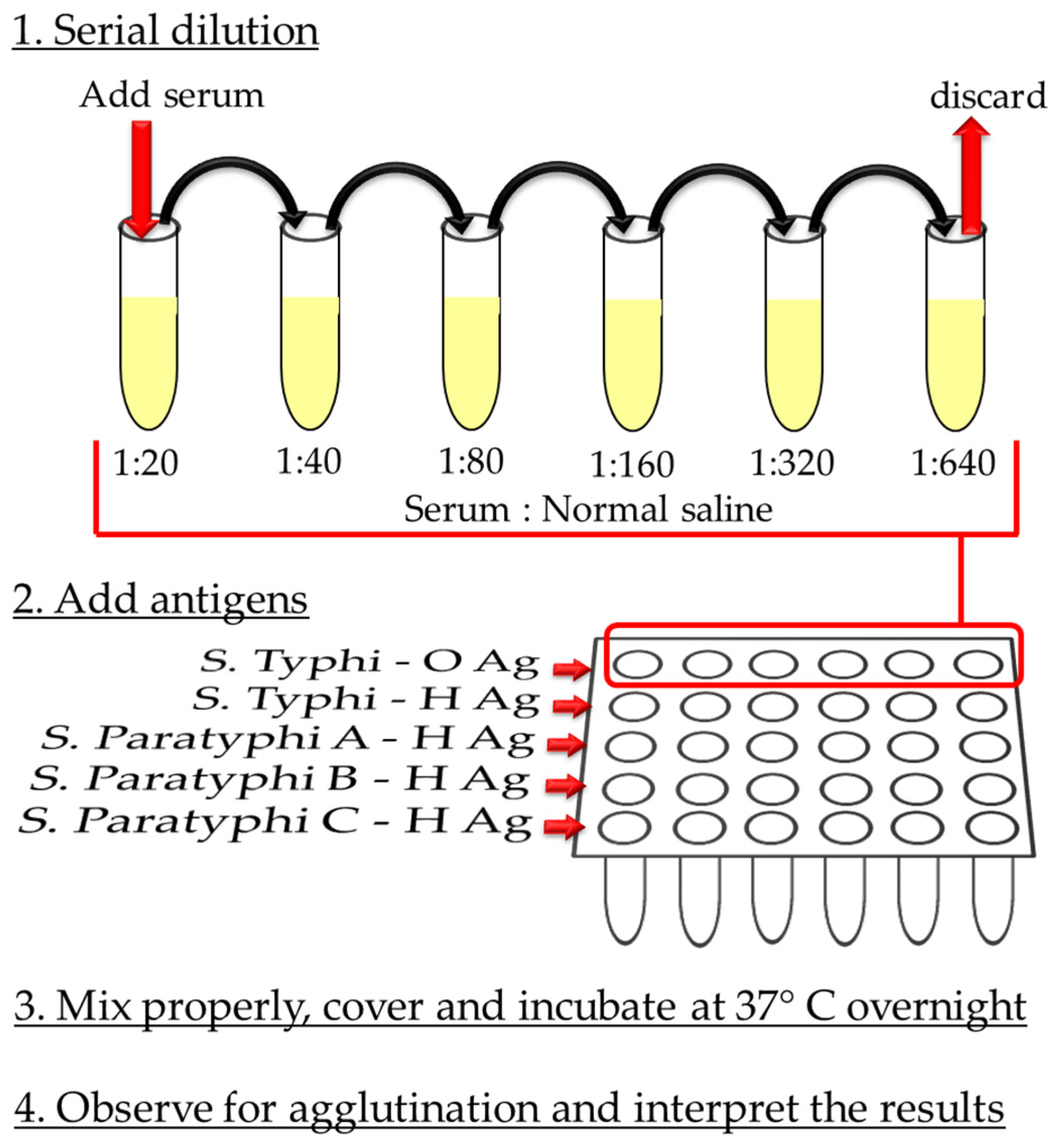
3.2.1. Widal Test
3.2.2. ELISA
3.2.3. Other Tests
3.3. Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostics
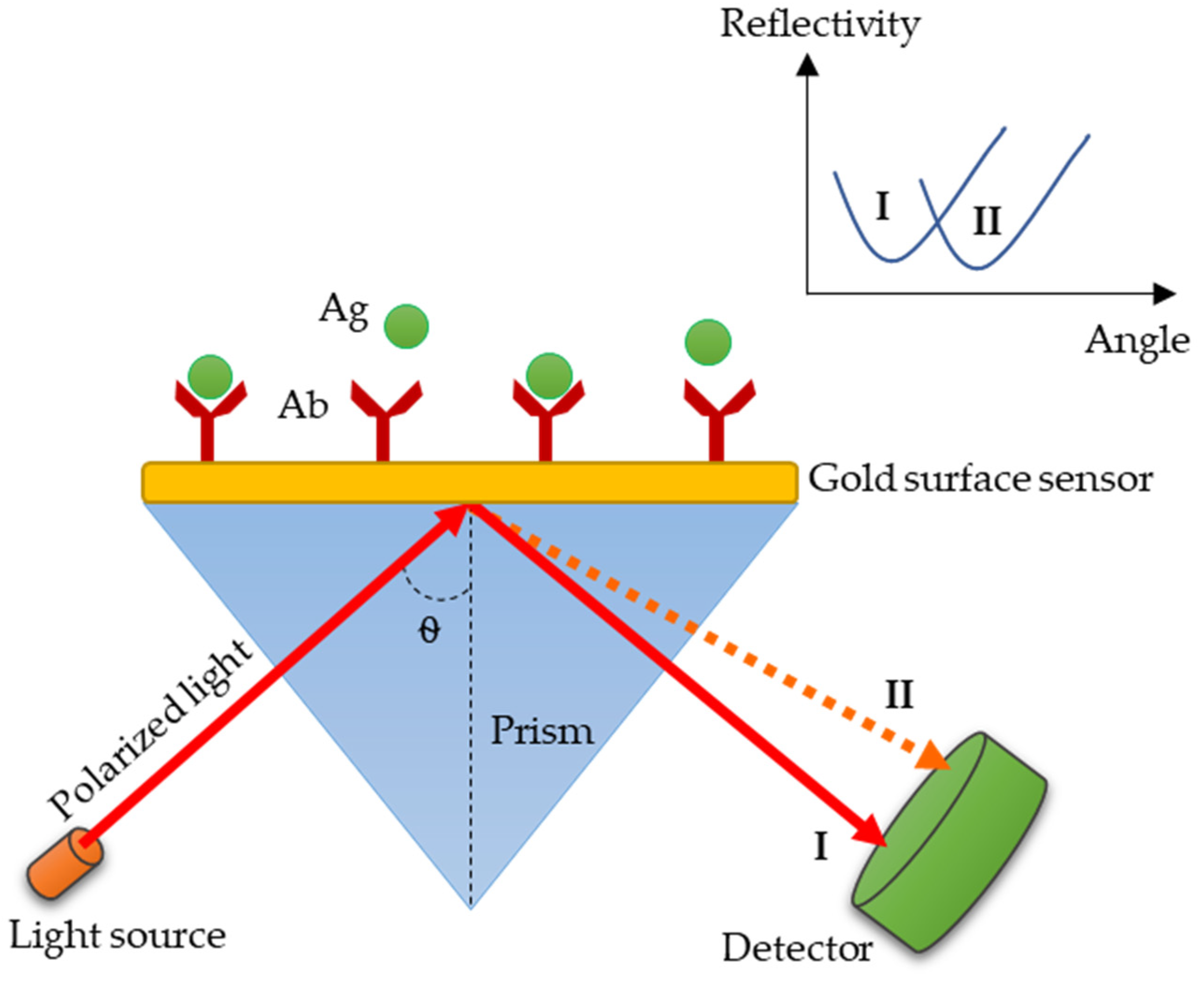
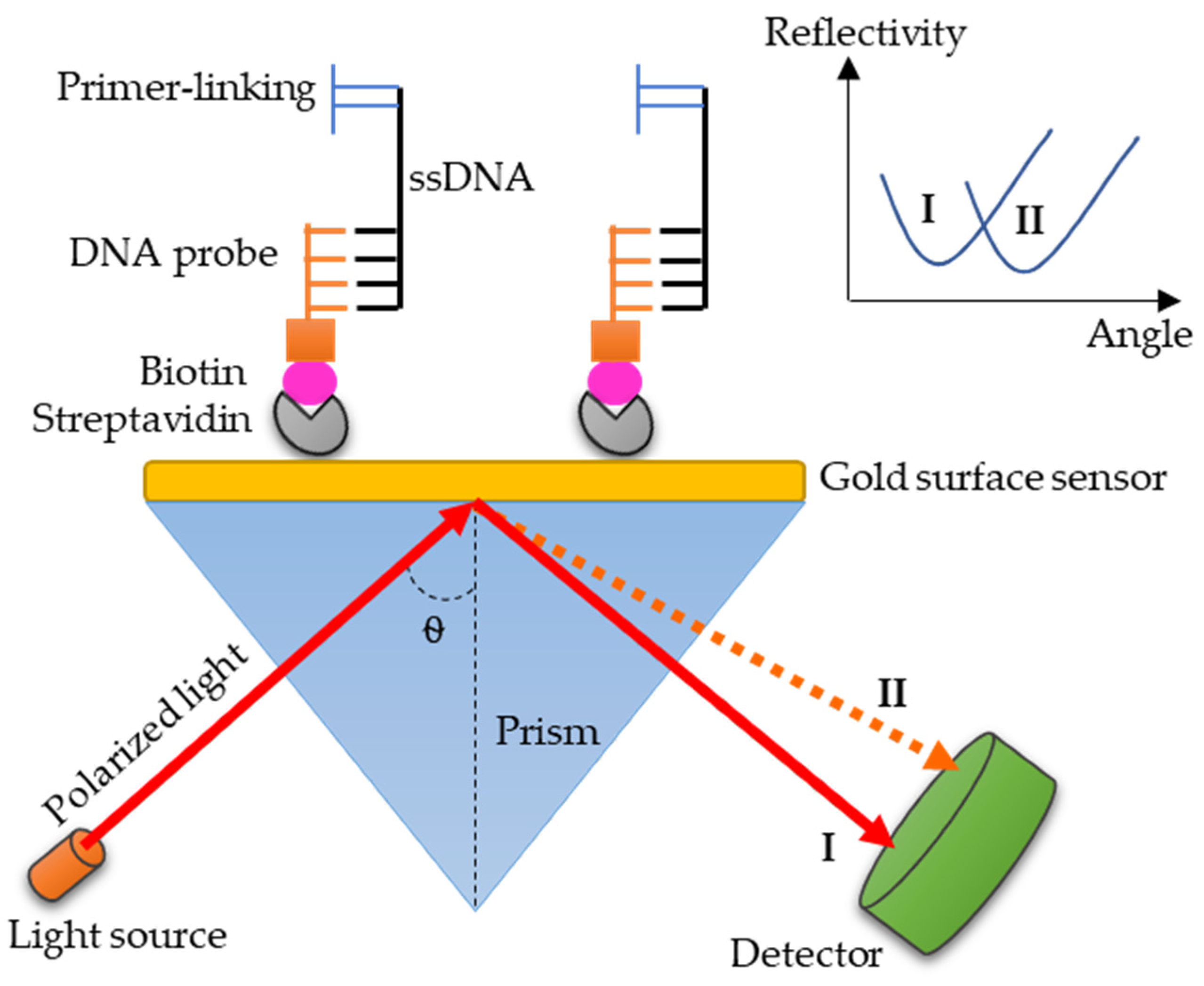
3.4. SPR: A Promising Technology for Paratyphoid Diagnosis
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, M.P.; O’Dwyer, J.; Adley, C.C. Evaluation of the Complex Nomenclature of the Clinically and Veterinary Significant Pathogen Salmonella. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.A.; Mietzner, T.A.; Miller, S.; Riedel, S. Jawetz Melnick & Adelbergs Medical Microbiology 28 E; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grimont, P.A.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2007; pp. 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Centers-for-Disease-Control-and-Prevention. Serotypes and the Importance of Serotyping Salmonella. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/reportspubs/salmonella-atlas/serotyping-importance.html (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Jajere, S.M. A review of Salmonella enterica with focus on the pathogenicity and virulence factors, host specificity and antimicrobial resistance including multidrug resistance. Vet. World 2019, 12, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelobolina, E.S.; Sullivan, S.A.; O’Neill, K.R.; Nevin, K.P.; Lovley, D.R. Isolation, Characterization, and U(VI)-Reducing Potential of a Facultatively Anaerobic, Acid-Resistant Bacterium from Low-pH, Nitrate- and U(VI)-Contaminated Subsurface Sediment and Description of Salmonella subterranea sp. nov. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, F.W.; Villar, R.G.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.; Swaminathan, B. Salmonella Nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2465–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwollik, S.; Boyd, E.F.; Choy, C.; Cheng, P.; Florea, L.; Proctor, E.; McClelland, M. Characterization of Salmonella enterica Subspecies I Genovars by Use of Microarrays. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5883–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Boyle, E.C.; Grassl, G.A. Same species, different diseases: How and why typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars differ. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.E.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M.J. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vollaard, A.M.; Ali, S.; Widjaja, S.; van Asten, H.A.; Visser, L.G.; Surjadi, C.; van Dissel, J.T. Identification of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever cases at presentation in outpatient clinics in Jakarta, Indonesia. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, M.K.; Bahl, R.; Bhatnagar, S. Typhoid, and paratyphoid fever. Lancet 2005, 366, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, A.P.; Day, J.; Tuan, P.Q.; E Thwaites, G.; Campbell, J.I.; Zimmerman, M.; Farrar, J.; Basnyat, B. Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi A and S. enterica Serovar Typhi Cause Indistinguishable Clinical Syndromes in Kathmandu, Nepal. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, J.; van Aart, C.J.C.; Grassly, N.C. The Burden of Typhoid and Paratyphoid in India: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahastrabuddhe, S.; Carbis, R.; Wierzba, T.F.; Ochiai, L. Increasing rates of Salmonella paratyphi A and the status of its vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.; Favorov, M.; Dougan, G. Searching for the elusive typhoid diagnostic. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, M.K.; Panezai, M.; Nawaz, I.; Taj, I.; Panezai, M.; Panezai, N.; Zafar, U.; Muh, D.G.; Esso, S.A.; Muhammad, G. Isolation and Identification of Salmonella Paratyphi from Enteric Fever Patients at Different Hospitals of Quetta City. Pak. J. Boil. Sci. 2018, 21, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antillon, M.; Saad, N.J.; Baker, S.; Pollard, A.J.; Pitzer, V.E. The Relationship Between Blood Sample Volume and Diagnostic Sensitivity of Blood Culture for Typhoid and Paratyphoid Fever: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, S255–S267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.T.; Hill, D.R.; Solomon, T.; Endy, T.P.; Aronson, N. Hunter’s Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brunette, G.W. CDC Yellow Book 2018: Health Information for International Travel; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Waddington, C.S.; Darton, T.C.; Pollard, A.J. The challenge of enteric fever. J. Infect. 2014, 68, S38–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, G.D.; Hughes, M.J.; Chatham-Stephens, K. Typhoid & Paratyphoid Fever, Chapter 4. Travel-Related Infectious Diseases. In CDC Yellow Book; Centers of Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Centers-for-Disease-Control-and-Prevention. Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/typhoid-fever/symptoms.html (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Woh, P.Y.; Thong, K.L.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Behnke, J.M.; Lewis, J.W.; Zain, S.N.M. Microorganisms as an Indicator of Hygiene Status Among Migrant Food Handlers in Peninsular Malaysia. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2017, 29, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollaard, A.; Ali, S.; van Asten, H.A.G.H.; Widjaja, S.; Visser, L.G.; Surjadi, C.; van Dissel, J.T. Risk Factors for Typhoid and Paratyphoid Fever in Jakarta, Indonesia. JAMA 2004, 291, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, C.S.J.; Chua, K.H.; Thong, K.L. Paratyphoid Fever: Splicing the Global Analyses. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, G.J.Y.; Ng, L.M.; Lin, R.T.; Teo, J.W. Development of a novel multiplex PCR for the detection and differentiation of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, B. Recent and the Latest Developments in Rapid and Efficient Detection of Salmonella in Food and Water. Adv. Tech. Boil. Med. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Lim, C.; Chan, Y. Detection of Salmonella typhi by polymerase chain reaction. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1996, 80, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Balakrishna, K.; Batra, H. Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) by selective amplification of invA, viaB, fliC-d and prt genes by polymerase chain reaction in mutiplex format. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, S.M.; Toema, D.; Qamar, F.; Iqbal, N.; Boyd, M.A.; Marshall, J.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Wu, Y.; Quadri, F.; Khan, A.; et al. Detection of Typhoidal and Paratyphoidal Salmonella in Blood by Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, S241–S250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, J.A.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Gordon, M.A.; Parry, C.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijedoru, L.; Mallett, S.; Parry, C.M. Rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid and paratyphoid (enteric) fever. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, CD008892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.A.; Kankwatira, A.M.; Mwafulirwa, G.; Walsh, A.L.; Hopkins, M.J.; Parry, C.M.; Faragher, E.B.; Zijlstra, E.E.; Heyderman, R.S.; E Molyneux, M. Invasive Non-typhoid Salmonellae Establish Systemic Intracellular Infection in HIV-Infected Adults: An Emerging Disease Pathogenesis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, J.; Bay, P.V.B.; Vinh, H.; Duong, N.M.; Diep, T.S.; Walsh, A.L.; Parry, C.M.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ho, V.A.; Hien, T.T.; et al. Quantitation of Bacteria in Bone Marrow from Patients with Typhoid Fever: Relationship between Counts and Clinical Features. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, C.M.; Hien, T.T.; Dougan, G.; White, N.J.; Farrar, J. Typhoid Fever. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Mor, O. Persistent Infection and Long-Term Carriage of Typhoidal and Nontyphoidal Salmonellae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 32, e00088-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, J.; Diep, T.S.; Ho, V.A.; Walsh, A.M.; Hoa, N.T.T.; Parry, C.M.; White, N.J. Quantitation of Bacteria in Blood of Typhoid Fever Patients and Relationship between Counts and Clinical Features, Transmissibility, and Antibiotic Resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogasale, V.; Ramani, E.; Mogasale, V.V.; Park, J. What proportion of Salmonella Typhi cases are detected by blood culture? A systematic literature reviews. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharmoria, A. Typhoid Fever as a Challenge for Developing Countries and Elusive Diagnostic Approaches Available for the Enteric Fever. Int. J. Vaccine Res. 2017, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, K.E.; Liu, S.-L.; Tang, L.; Johnston, R.N. Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A. In Molecular Medical Microbiology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1275–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Pokhrel, B.M.; Karmacharya, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Koirala, J. Distribution of antibody titer against Salmonella enterica among healthy individuals in nepal. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2009, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andualem, G.; Abebe, T.; Kebede, N.; Gebreselassie, S.; Mihret, A.; Alemayehu, H. A comparative study of Widal test with blood culture in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in febrile patients. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, S. Widal Test—Introduction, Principle, Procedure, Interpretation and Limitation. Microbiology Info. 2018. Available online: https://microbiologyinfo.com/widal-test-introduction-principle-procedure-interpretation-and-limitation/ (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Olopoenia, L.; King, A.L. Widal agglutination test—100 years later: Still plagued by controversy. Postgrad. Med. J. 2000, 76, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Balakrishna, K.; Batra, H.V. Enrichment-ELISA for Detection of Salmonella typhi From Food and Water Samples. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.P.; Tsui, C.O.; Roberts, D.; Chau, P.Y.; Ng, M.H. Detection, and serogroup differentiation of Salmonella spp. in food within 30 hours by enrichment-immunoassay with a T6 monoclonal antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 2294–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, K.G.; Falkenhorst, G.; Ceper, T.H.; Dalby, T.; Ethelberg, S.; Moelbak, K.; Krogfelt, K. Detecting non-typhoid Salmonella in humans by ELISAs: A literature review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Sayers, A.; Woodward, M.J. Analysis of expression of flagella by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium by monoclonal antibodies recognising both phase specific and common epitopes. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 78, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Tang, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Highly Sensitive ELISA, and Immunochromatographic Strip for the Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Milk Samples. Sensors 2015, 15, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahi, E.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Detection Methodologies for Pathogen and Toxins: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.; Song, E.K.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.T.; Park, T.J.; Kang, S. A Recombinant Secondary Antibody Mimic as a Target-specific Signal Amplifier, and an Antibody Immobilizer in Immunoassays. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sippel, J.; Bukhtiari, N.; Awan, M.B.; Krieg, R.; Duncan, J.F.; A Karamat, K.; Malik, I.A.; Igbal, L.M.; Legters, L. Indirect immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and IgM capture ELISA for detection of antibodies to lipopolysaccharide in adult typhoid fever patients in Pakistan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadallah, F.; Brighouse, G.; del Giudice, G.; Drager-Dayal, R.; Hodne, M.; Lambert, P.H. Production of Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Salmonella typhi Flagellin and Possible Application to Immunodiagnosis of Typhoid Fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.H.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G.Z.; Quan, W.L.; Gong, H.M.; Szu, S.C. An outbreak of Salmonella Paratyphi A in a boarding school: A community-acquired enteric fever and carriage investigation. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyildiz, A.; Demir, Y.; Tuncel, E.; Babacan, M.; Leloğlu, S. Comparison of the Gruber-Widal and ELISA technics used to study Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi infections in patients. Mikrobiyol. Bulteni 1986, 20, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.-L.; Fang, H.-J.; Fan, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Sun, A. Distribution of Salmonella paratyphi A outer membrane protein X gene and immune-protective effect related to its recombinant expressed products. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2013, 34, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Ge, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, A. Distribution of Salmonella paratyphi A pagC gene and immunoprotective effect of its recombinant expressed products. J. Zhejiang Univ. Med. Sci. 2013, 42, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, P.; Xia, X.-P.; Sun, D.; Ojcius, D.M.; Mao, Y.-F.; Yue, W.-Y.; Yan, J. Recombinant SpaO and H1a as immunogens for protection of mice from lethal infection with Salmonella paratyphi A: Implications for rational design of typhoid fever vaccines. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6639–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, C.M.; Wijedoru, L.; Arjyal, A.; Baker, S. The utility of diagnostic tests for enteric fever in endemic locations. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chart, H.; Cheasty, T.; de Pinna, E.; Siorvanes, L.; Wain, J.; Alam, D.; Nizami, Q.; Bhutta, Z.; Threlfall, E.J. Serodiagnosis of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and S. enterica serovars Paratyphi A, B and C human infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaicumpa, W.; Thin-Inta, W.; Khusmith, S.; Tapchaisri, P.; Echeverria, P.; Kalambaheti, T.; Chongsa-Nguan, M. Detection with monoclonal antibody of Salmonella typhi antigen 9 in specimens from patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appassakij, H.; Bunchuin, N.; Sarasombath, S.; Rungpitarangsi, B.; Manatsathit, S.; Komolpit, P.; Sukosol, T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Salmonella typhi protein antigen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, F.; Sheikh, A.; Sayeed, A.; Bhuiyan, S.; Choudhury, F.K.; Salma, U.; Pervin, S.; Sultana, T.; Ahmed, D.; Goswami, D.; et al. Evaluation of a Typhoid/Paratyphoid Diagnostic Assay (TPTest) Detecting Anti-Salmonella IgA in Secretions of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes in Patients in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastoor, R.; Hatta, M.; Abdoel, T.H.; Smits, H.L. Simple, rapid, and affordable point-of-care test for the serodiagnosis of typhoid fever. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Thorlund, K.; Brenner, D.R.; Andrews, J.R. Comparative accuracy of typhoid diagnostic tools: A Bayesian latent-class network analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Sayeed, A.; Hossen, E.; Khanam, F.; Charles, R.C.; Andrews, J.; Ryan, E.T.; Qadri, F. Comparison of the Performance of the TPTest, Tubex, Typhidot and Widal Immunodiagnostic Assays and Blood Cultures in Detecting Patients with Typhoid Fever in Bangladesh, Including Using a Bayesian Latent Class Modeling Approach. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, M.; E Sanderson, K.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Porwollik, S.; Sabo, A.; Meyer, R.; Bieri, T.; Ozersky, P.; Harkins, C.R.; et al. Comparison of genome degradation in Paratyphi A and Typhi, human-restricted serovars of Salmonella enterica that cause typhoid. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y. PCR in Diagnosis of Infection: Detection of Bacteria in Cerebrospinal Fluids. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2002, 9, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, C.; Cady, N.C.; Batt, C.A. Nucleic Acid-based Detection of Bacterial Pathogens Using Integrated Microfluidic Platform Systems. Sensors 2009, 9, 3713–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, C.; Schielke, A.; Ellerbroek, L.; Johne, R. PCR inhibitors—Occurrence, properties, and removal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abusalah, M.A.H.; Gan, S.H.; Al-Hatamleh, M.; Irekeola, A.A.; Shueb, R.H.; Yean, C.Y. Recent Advances in Diagnostic Approaches for Epstein–Barr Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wages, J.M., Jr. Polymerase chain reaction. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed.; Worsfold, P., Townshend, A., Poole, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Espy, M.J.; Uhl, J.R.; Sloan, L.M.; Buckwalter, S.P.; Jones, M.F.; Vetter, E.A.; Yao, J.D.C.; Wengenack, N.L.; Rosenblatt, J.E.; Cockerill, F.R.; et al. Real-Time PCR in Clinical Microbiology: Applications for Routine Laboratory Testing. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 165–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscarsson, J.; Westermark, M.; Löfdahl, S.; Olsen, B.; Palmgren, H.; Mizunoe, Y.; Wai, S.N.; Uhlin, B.E. Characterization of a Pore-Forming Cytotoxin Expressed by Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5759–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Rhein, C.; Bauer, S.; Sanjurjo, E.J.L.; Benz, R.; Goebel, W.; Ludwig, A. ClyA cytolysin from Salmonella: Distribution within the genus, regulation of expression by SlyA, and pore-forming characteristics. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 299, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.; von Rhein, C.; Bauer, S.; Huüttinger, C.; Goebel, W. Molecular Analysis of Cytolysin A (ClyA) in Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5311–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Haque, A.; Haque, A.; Sarwar, Y.; Mohsin, M.; Bashir, S.; Tariq, A. Multiplex PCR for differential diagnosis of emerging typhoidal pathogens directly from blood samples. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 137, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, S.; D’Auria, S.; Pennacchio, A.; Lacroix, M. A new competitive fluorescence immunoassay for detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Jackeray, R.; Abid, C.Z.; Kohli, G.S.; Singh, H. Highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhi using surface aminated polycarbonate membrane enhanced ELISA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Hirst, N.A.; Millner, P.A. Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors: Fundamental Concepts, Selected Techniques, Materials and Applications. In Advances in Sensors; Yurish, S., Ed.; IFSA Publishing: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; Volume 5, pp. 25–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Versatile Technique for Biosensor Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 10481–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Hu, F. Biomolecule immobilization techniques for bioactive paper fabrication. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, B.; Skoumal, M.J.; Ramunno, B.; Li, X.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Liu, L.; Jia, L. Antifouling Poly(β-peptoid)s. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Sim, S.J.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, J. Characterization of a self-assembled monolayer of thiol on a gold surface and the fabrication of a biosensor chip based on surface plasmon resonance for detecting anti-GAD antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfas, S.; Johnsson, B.; Edström, A.; Hansson, A.; Lindquist, G.; Hillgren, R.-M.M.; Stigh, L.; Lrofas, S. Methods for site-controlled coupling to carboxymethyldextran surfaces in surface plasmon resonance sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, D.G.; Drescher, M.J.; Ramakrishnan, N.A. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis of Binding Interactions of Proteins in Inner-Ear Sensory Epithelia. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 493, pp. 323–343. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, G.; Mandenius, C.-F. Orientation and capturing of antibody affinity ligands: Applications to surface plasmon resonance biochips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 158, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, R.; Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, H. Characterizing the interaction between aptamers and human IgE by use of surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 390, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szunerits, S.; Rich, S.A.; Coffinier, Y.; Languille, M.-A.; Supiot, P.; Boukherroub, R. Preparation and characterization of thin organosilicon films deposited on SPR chip. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3910–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudpour, M.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Torbati, M.; Homayouni-Rad, A. Nanomaterials based surface plasmon resonance signal enhancement for detection of environmental pollutions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Immobilisation of DNA probes for the development of SPR-based sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. SPR Biosensors: Historical Perspectives and Current Challenges. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-H.; Choi, M.; Kim, T.W.; Choi, W.; Park, S.Y.; Byun, K.M. Sensitivity and Stability Enhancement of Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors based on a Large-Area Ag/MoS2 Substrate. Sensors 2019, 19, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, B.; Stack, E.; Gilmartin, N.; O’Kennedy, R. Antibody-Based Sensors: Principles, Problems and Potential for Detection of Pathogens and Associated Toxins. Sensors 2009, 9, 4407–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedberg, B.; Nylander, C.; Lunström, I. Surface plasmon resonance for gas detection and biosensing. Sens. Actuators 1983, 4, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratamico, P.; Strobaugh, T.; Medina, M.; Gehring, A. Detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biotechnol. Tech. 1998, 12, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, P. Surface Plasmon Resonance: Applications in Understanding Receptor–Ligand Interaction. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 126, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J.; Vaisocherová, H.; Dostálek, J.; Piliarik, M. Multi-analyte surface plasmon resonance biosensing. Methods 2005, 37, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Hillier, A.C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging of Biomolecular Interactions on a Grating-Based Sensor Array. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templier, V.; Roux, A.; Roupioz, Y.; Livache, T. Ligands for label-free detection of whole bacteria on biosensors: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J.; Hegnerová, K.; Vala, M. Surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of foodborne pathogens and toxins. Proceedings of Frontiers in Pathogen Detection: From Nanosensors to Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–29 January 2009; SPIE Digital Library: San Jose, CA, USA, 2009; p. 716705. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumdar, S.D.; Barlen, B.; Kämpfer, P.; Keusgen, M. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) as a rapid tool for serotyping of Salmonella. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlen, B.; Mazumdar, S.D.; Lezrich, O.; Kämpfer, P.; Keusgen, M. Detection of Salmonella by Surface Plasmon Resonance. Sensors 2007, 7, 1427–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perçin, I.; Idil, N.; Bakhshpour, M.; Yılmaz, E.; Mattiasson, B.; Denizli, A. Microcontact Imprinted Plasmonic Nanosensors: Powerful Tools in the Detection of Salmonella paratyphi. Sensors 2017, 17, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.-K.; Lee, W.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor using self-assembled protein G for the detection of Salmonella paratyphi. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Park, B.; Zhao, Y. Limitation of a localized surface plasmon resonance sensor for Salmonella detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aura, A.M. Surface Plasmon Resonamce Imaging Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogens and Toxins in Food; University of Catania: Catania, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, S.; Singh, A.; Naidoo, R.; Wu, P.; McDermott, M.; Evoy, S. Chemically immobilized T4-bacteriophage for specific Escherichia coli detection using surface plasmon resonance. Analyst 2011, 136, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.-C.; Bridgman, R.C. Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in Romaine Lettuce Using a Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.-C.; Hamal, S.; Bridgman, R.C. Kinetic Analysis and Epitope Mapping of Monoclonal Antibodies to Salmonella Typhimurium Flagellin Using a Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Antibodies 2019, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlen, B.; Mazumdar, S.D.; Keusgen, M. Immobilisation of biomolecules for biosensors. Phys. Status Solidi 2009, 206, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokken, G.C.; Corbee, R.J.; van Knapen, F.; A Bergwerff, A. Immunochemical detection of Salmonella group B, D and E using an optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 222, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Park, B. Label-free screening of foodborne Salmonella using surface plasmon resonance imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 410, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, E.; Ekiz, O.Ö.; Çelik, H.; Sülek, S.; Dana, A.; Ekiz, H.İ. Rapid detection of foodborne pathogens by surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Int. J. Biosci. Biochem. Bioinform. 2015, 5, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongerius-Gortemaker, B.G.M.; Goverde, R.; van Knapen, F.; A Bergwerff, A. Surface plasmon resonance (BIACORE) detection of serum antibodies against Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 266, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoung, J.-Y.; Hong, S.; Lee, W.; Choi, J. Immunosensor for the detection of Vibrio cholerae O1 using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Cho, H.S.; Park, N.Y.; Lee, J.I. Serodiagnostic Comparison Between Two Methods, ELISA, and Surface Plasmon Resonance for the Detection of Antibody Titres of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2006, 53, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubová, V.; Brynda, E.; Karasová, L.; Škvor, J.; Homola, J.; Dostálek, J.; Tobiška, P.; Rosický, J. Detection of foodborne pathogens using surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 74, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Wang, S.-Z.; Yin, Y.-G.; Hoffmann, W.C.; Zheng, X. Using a Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in Chicken Carcass. J. Bionic Eng. 2008, 5, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukose, J.; Shetty, V.; Ballal, M.; Chidangil, S.; Sinha, R.K. Real-time and rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using an inexpensive lab-built surface plasmon resonance setup. Laser Phys. Lett. 2018, 15, 075701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, S.D.; Hartmann, M.; Kämpfer, P.; Keusgen, M. Rapid method for detection of Salmonella in milk by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, S.D.; Barlen, B.; Kramer, T.; Keusgen, M. A rapid serological assay for prediction of Salmonella infection status in slaughter pigs using surface plasmon resonance. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 75, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, C.A.; Alocilja, E.C.; Osburn, W.N. Detection of E. Coli O157:H7 Using a Miniaturized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Yi, S.Y.; Woubit, A.; Kim, M. Portable Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 2016, 25, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.-K.; Lee, W.; Chun, B.S.; Bae, Y.M.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J. The fabrication of protein chip based on surface plasmon resonance for detection of pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, E. Development of instrumentation to allow the detection of microorganisms using light scattering in combination with surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 14, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.-H.; Li, X.; Fung, Y.-S.; Zhu, D.-R. Rapid detection of Salmonella enteritidis by piezoelectric immunosensor. Microchem. J. 2001, 68, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Verma, H.N.; Arora, K. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Label-Free Detection of Salmonella using DNA Self Assembly. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 175, 1330–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Irudayaraj, J.; Ryan, T. A mixed self-assembled monolayer-based surface plasmon immunosensor for detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.S.; Irudayaraj, J.M. Surface plasmon resonance based immunosensing of E. coli O157:H7 in apple juice. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Irudayaraj, J.; Ryan, T. Mono, and dithiol surfaces on surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, R.A.; Rezayan, A.H.; Rahimi, F.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Kamali, M. Development of an immunosensor using oriented immobilized anti-OmpW for sensitive detection of Vibrio cholerae by surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Bouma, A.; van Eerden, E.; Landman, W.J.; van Knapen, F.; Stegeman, J.; A Bergwerff, A. Detection of egg yolk antibodies reflecting Salmonella enteritidis infections using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 315, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usachev, E.; Usacheva, O.; Agranovski, I. Surface plasmon resonance-based bacterial aerosol detection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waswa, J.; Debroy, C.; Irudayaraj, J. Rapid detection of Salmonella enteritidis and Escherichia coli using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. J. Food Process. Eng. 2006, 29, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waswa, J.; Irudayaraj, J.; Debroy, C. Direct detection of E. Coli O157:H7 in selected food systems by a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. LWT 2007, 40, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tsuji, S.; Kitaoka, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Tamai, M.; Honjoh, K.-I.; Miyamoto, T. Simultaneous Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enteritidis, and Listeria monocytogenes at a Very Low Level Using Simultaneous Enrichment Broth and Multichannel SPR Biosensor. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-C.; Baig, I.; Lee, S.-C.; Moon, J.-Y.; Yoon, M.Y. Development of ssDNA Aptamers for the Sensitive Detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella enteritidis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, Á.; de Vicente, J.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.F.; Casquel, R.; Santamaria, B.; Maigler, M.V.; Hernandez, A.L.; Ramirez, Y. On the Determination of Uncertainty and Limit of Detection in Label-Free Biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuermann, J.; Fernandez-Gavela, A.; Torres-Cubillo, A.; Postigo, S.; Sánchez-Postigo, A.; Lechuga, L.M.; Halir, R.; Molina-Fernández, Í. Optimizing the Limit of Detection of Waveguide-Based Interferometric Biosensor Devices. Sensors 2019, 19, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, B.A.; Purwidyantri, A.; Liu, K.-C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Optical Sensor: A Review on Light Source Technology. Biosensors 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, E.; Ekiz, H.I. Antibody fragmentation technique for Salmonella detection by SPR based biosensor. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 256, S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, W.; Du, X.; Pan, M.; Wang, J. The SPR detection of Salmonella enteritidis in food using aptamers as recongnition elements. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Singapore, 28–30 July 2017; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 231, p. 12114. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, S.C.; Yuan, Y.J.; Kumar, P.K.R. Regeneration of commercial Biacore chips to analyze biomolecular interactions. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 34402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antigen Name | Antigenic Virulence Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Paratyphi A | S. Paratyphi B | S. Paratyphi C | S. Typhi | |
| H flagellar | a, 1, 5 | b, 1, 2 | c, 1, 5 | d |
| O somatic | 1, 2, 12 | 1, 4, 5, 12 | 6, 7 | 9, 12 |
| Capsular antigen | - | - | Vi | Vi |
| Method | Advantage(s) | Disadvantage(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical adsorption | For study of membrane-associated protein | The immobilized ligands are formed in random oriented order | [84,85] |
| Thiol-based | Covalent binding; thus, provides strong immobilization of ligand with thiol group and in homogenous orientation | Chemical synthesis and protein engineering need to be carried out if thiol group is lacking | [86,87] |
| Self-assembled monolayer based | Covalent binding; thus, provides strong immobilization of ligand with amine-coupling group and in homogenous orientation. This method is the simplest | Efficiency of immobilization can be decreased due to non-specific biding of ligand onto the surface | [88] |
| Capture | This method is used when the covalent immobilization process is not sufficient enough. Common techniques: streptavidin-biotin and antibody-antigen | Both analyte and ligand are removed during regeneration, so a new ligand is required, thus, increasing cost | [89,90] |
| Polymer film deposition | Provides high sensitivity | Weak binding to the sensor chip through non-covalent forces | [91,92] |
| Study ID [Reference] | Detected Bacteria | Sample | Principle of Immobilization | Limit of Detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arya 2011 [110] | Escherichia coli K12 | Bacterial culture | T4-based bioassay | 7 × 102 CFU/mL−1 |
| Aura 2017 [109] | Staphylococcal enterotoxin A, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes | Milk | Ab/Ag immunoassay and PNA/SSO probes-based genoassay | 0.05 µg/mL |
| Bhandari 2019 [111] | S. Typhimurium | Romaine lettuce | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 0.9 log CFU/g |
| Bhandari 2019 [112] | S. Typhimurium | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | - |
| Barlen 2007 [105] | S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis | Milk | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 2.50 × 105 cells/mL−1 |
| Barlen 2009 [113] | S. Enteritidis (antibodies) | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 1010 cells/mL−1 |
| Bokken 2003 [114] | Salmonella group B, D and E | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 107 CFU/mL−1 |
| Chen 2017 [115] | S. Enteritidis, S. Kentucky, S. Infantis, S. Javiana, S. Heidelberg and S. Typhimurium | Chicken carcass | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 2.1 × 106 CFU/mL |
| Eser 2015 [116] | S. Enteritidis | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 102 CFU/mL |
| Fratamico 1998 [98] | E. coli O157:H7 | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 107 CFU/mL |
| Fu 2009 [108] | S. Typhimurium | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 104 CFU/mL |
| Jongerius 2002 [117] | S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium (antibodies) | Serum from infected chickens | Ab/Ag immunoassay | - |
| Jyoung 2006 [118] | Vibrio cholerae O1 | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 105 cells/mL |
| Kim 2006 [119] | Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (antibodies) | Serum from infected pigs | Ab/Ag immunoassay | - |
| Koubova 2001 [120] | S. Typhimurium and L. monocytogenes | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 106 cells/mL |
| Lan 2008 [121] | S. Typhimurium | Chicken carcass | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 106 CFU/mL |
| Lukose 2018 [122] | S. Typhimurium | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 106 CFU/mL−1 |
| Mazumdar 2007 [123] | S. Typhimurium | Milk | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 1.25 × 105 cells/mL−1 |
| Mazumdar 2008 [124] | S. Typhimurium (antibodies) | Serum from infected pigs | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 67.5 µg/mL−1 |
| Mazumdar 2010 [104] | Salmonella group B, C and D | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 1010 cells/mL−1 |
| Meeusen 2005 [125] | E. coli O157:H7 | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 8.7 × 106 CFU/mL |
| Nguyena 2016 [126] | S. Typhimurium | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 107 CFU/mL |
| Oh 2004 [107] | S. Paratyphi | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 102 CFU/mL |
| Oh 2005 [127] | E. coli O157:H7, S. Typhimurium, Legionella pneumophila and Yersinia enterocolitica | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 105 CFU/mL |
| Perçin 2017 [106] | S. Paratyphi | Bacterial culture | A special microcontact imprinted sensor chip programed to detect S. Paratyphi | 2.5 × 106 CFU/mL |
| Perkins 2000 [128] | Bacillus subtilis (spore) | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 107 mL−1 |
| Si 2001 [129] | S. Enteritidis | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 105 cells/mL |
| Singh 2014 [130] | S. Typhi | ssDNA extracted from bacterial culture | DNA self-assembly | 0.019 µg/mL−1 |
| Subramanian 2006 [131] | E. coli O157:H7 | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 104 CFU/mL |
| Subramanian 2006 [132] | E. coli O157:H7 | Apple juice | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 106 CFU/mL |
| Subramanian 2006 [133] | S. aureus | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 105 CFU/mL |
| Taheri 2016 [134] | V. cholerae O1 serovar Ogawa | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 43 cells/mL |
| Thomas 2006 [135] | S. Enteritidis (antibodies) | Eggs from chickens infected with Salmonella enteritidis | Ab/Ag immunoassay | - |
| Usachev 2014 [136] | E. coli K12 | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 1.5 × 103 CFU/mL−1 |
| Waswa 2006 [137] | S. Enteritidis, E. coli O26, K12, NM and H16 | Milk | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 23 CFU/mL |
| Waswa 2007 [138] | E. coli O157:H7 | Milk, apple juice and ground beef | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 102 CFU/mL |
| Zhang 2017 [139] | E. coli O157:H7, S. Enteritidis and L. monocytogenes | Bacterial culture | Ab/Ag immunoassay | 6 CFU/25 g |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhaj-Qasem, D.M.; Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Irekeola, A.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Mohamud, R.; Ismail, A.; Mustafa, F.H. Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070438
Alhaj-Qasem DM, Al-Hatamleh MAI, Irekeola AA, Khalid MF, Mohamud R, Ismail A, Mustafa FH. Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(7):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070438
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhaj-Qasem, Dina M., Mohammad A. I. Al-Hatamleh, Ahmad Adebayo Irekeola, Muhammad Fazli Khalid, Rohimah Mohamud, Aziah Ismail, and Fatin Hamimi Mustafa. 2020. "Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance" Diagnostics 10, no. 7: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070438
APA StyleAlhaj-Qasem, D. M., Al-Hatamleh, M. A. I., Irekeola, A. A., Khalid, M. F., Mohamud, R., Ismail, A., & Mustafa, F. H. (2020). Laboratory Diagnosis of Paratyphoid Fever: Opportunity of Surface Plasmon Resonance. Diagnostics, 10(7), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070438