Performance of Targeted Library Preparation Solutions for SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Controls Generation
2.3. Calculation of Ct for Samples and Controls
2.4. NGS Library Preparation
2.4.1. Library Preparation—1st Attempt NEB+TWIST (NEB+TWIST1)
2.4.2. Library Preparation—2nd Attempt NEB+TWIST (NEB+TWIST2)
2.4.3. Library Preparation—Illumina
2.4.4. Library Preparation—Paragon
2.5. Sequencing
2.6. Reference Mapping and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. NEB+Twist Workflow
3.2. Illumina Workflow
3.3. Paragon Workflow
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.E. Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19). Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J. SARS-CoV-2: An Emerging Coronavirus that Causes a Global Threat. Int. J. Boil. Sci. 2020, 16, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, E.; Broberg, E.K.; Connor, T.R.; Hodcroft, E.B.; Komissarov, A.B.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Melidou, A.; Neher, R.A.; O’Toole, A.; Pereyaslov, D.; et al. Geographical and temporal distribution of SARS-CoV-2 clades in the WHO European Region, January to June 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcoba-Florez, J.; Gil-Campesino, H.; De Artola, D.G.-M.; González-Montelongo, R.; Valenzuela-Fernández, A.; Ciuffreda, L.; Flores, C. Sensitivity of different RT-qPCR solutions for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegova, E.; Fillerova, R.; Kvapil, P. Direct-RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2 without RNA Extraction as Part of a COVID-19 Testing Strategy: From Sample to Result in One Hour. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T. Genetic diversity and evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 81, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dorp, L.; Acman, M.; Richard, D.; Shaw, L.P.; Ford, C.E.; Ormond, L.; Owen, C.J.; Pang, J.; Tan, C.C.; Boshier, F.A.; et al. Emergence of genomic diversity and recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 83, 104351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artesi, M.; Bontems, S.; Göbbels, P.; Franckh, M.; Maes, P.; Boreux, R.; Meex, C.; Melin, P.; Hayette, M.-P.; Bours, V.; et al. A recurrent mutation at position 26,340 of SARS-CoV-2 is associated with failure of the E-gene qRT-PCR utilized in a commercial dual-target diagnostic assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.D.; Muñoz, M.; Hernández, C.; Flórez, C.; Gomez, S.; Turca, A.; Pardo, L.; Barros, E.C.; Mondolfi, A.E.P. Genetic Diversity Among SARS-CoV2 Strains in South America may Impact Performance of Molecular Detection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, F.; Khan, K.S.; Le, T.K.; Paris, C.; Demirbag, S.; Barfuss, P.; Rocchi, P.; Ng, W.-L. Coronavirus RNA proofreading: Molecular basis and therapeutic targeting. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 710–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samorodnitsky, E.; Jewell, B.M.; Hagopian, R.; Miya, J.; Wing, M.R.; Lyon, E.; Damodaran, S.; Bhatt, D.; Reeser, J.W.; Datta, J.; et al. Evaluation of Hybridization Capture Versus Amplicon-Based Methods for Whole-Exome Sequencing. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.S.; Meissner, B.; Chavez, E.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Ennishi, D.; Jones, M.R.; Shulha, H.P.; Chan, F.C.; Boyle, M.; Kridel, R.; et al. Assessment of Capture and Amplicon-Based Approaches for the Development of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Pipeline to Personalize Lymphoma Management. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD). Division of Viral Diseases. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/rt-pcr-panel-primer-probes.html (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- ‘FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data—ScienceOpen’. n.d. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=de674375-ab83-4595-afa9-4c8aa9e4e736 (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ‘Picard Tools—By Broad Institute’. n.d. Available online: https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/ (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-Based Variant Detection from Short-Read Sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907. [Google Scholar]
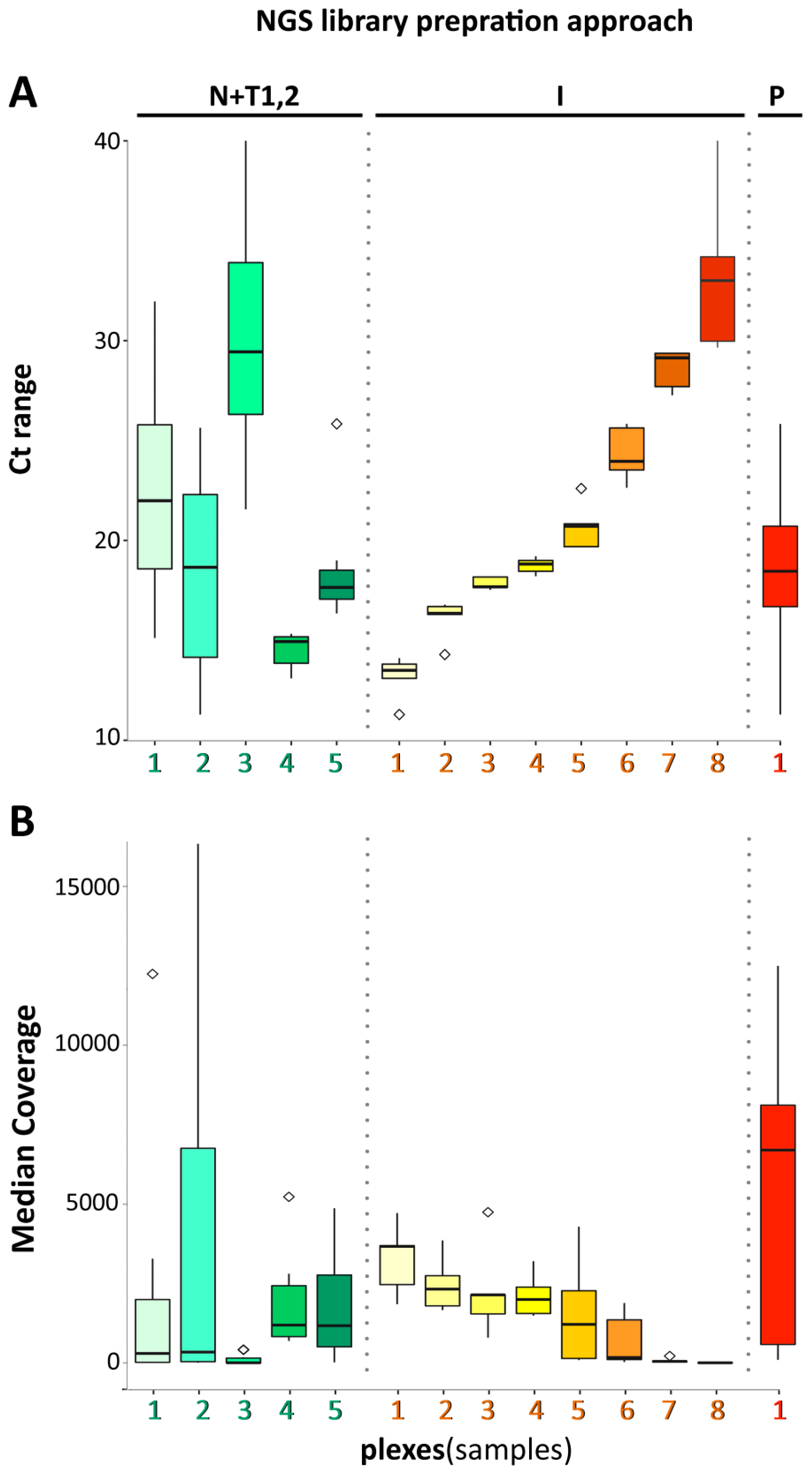
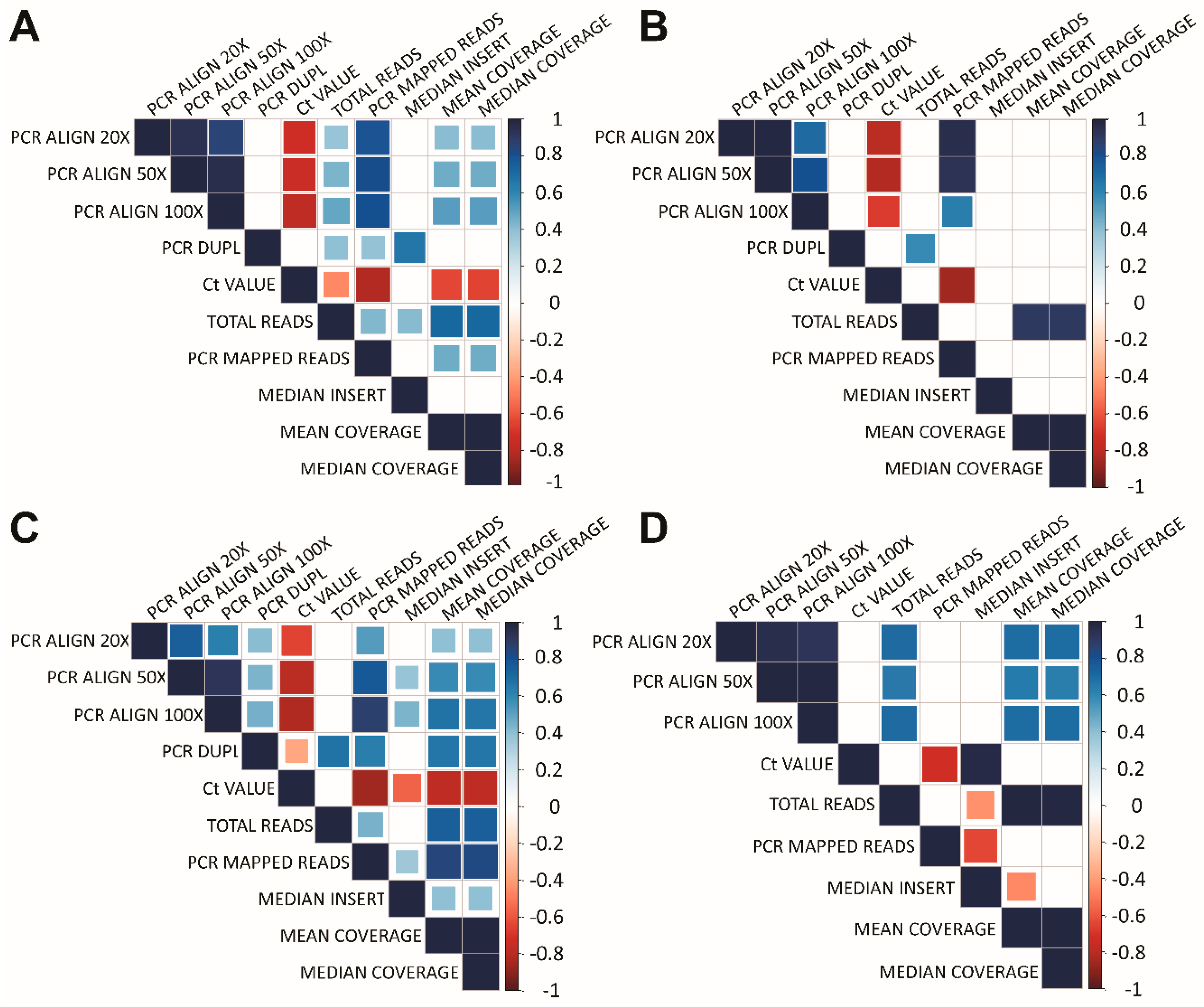



| Position | Twist1 | Coverage | Twist2 | Coverage | Illumina | Coverage | Paragon | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19065 | yes | 390 | yes | 36 | yes | 117 | yes | 66 |
| 22303 | yes | 381 | yes | 62 | yes | 166 | no | 3 |
| 26144 | yes | 217 | yes | 40 | yes | 197 | yes | 45 |
| 29749 | yes | 573 | yes | 22 | yes | 58 | no | 14 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klempt, P.; Brož, P.; Kašný, M.; Novotný, A.; Kvapilová, K.; Kvapil, P. Performance of Targeted Library Preparation Solutions for SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100769
Klempt P, Brož P, Kašný M, Novotný A, Kvapilová K, Kvapil P. Performance of Targeted Library Preparation Solutions for SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Analysis. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(10):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100769
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlempt, Petr, Petr Brož, Martin Kašný, Adam Novotný, Kateřina Kvapilová, and Petr Kvapil. 2020. "Performance of Targeted Library Preparation Solutions for SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Analysis" Diagnostics 10, no. 10: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100769
APA StyleKlempt, P., Brož, P., Kašný, M., Novotný, A., Kvapilová, K., & Kvapil, P. (2020). Performance of Targeted Library Preparation Solutions for SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Analysis. Diagnostics, 10(10), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100769





