Clinical Validation of a Urine Test (Uromonitor-V2®) for the Surveillance of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
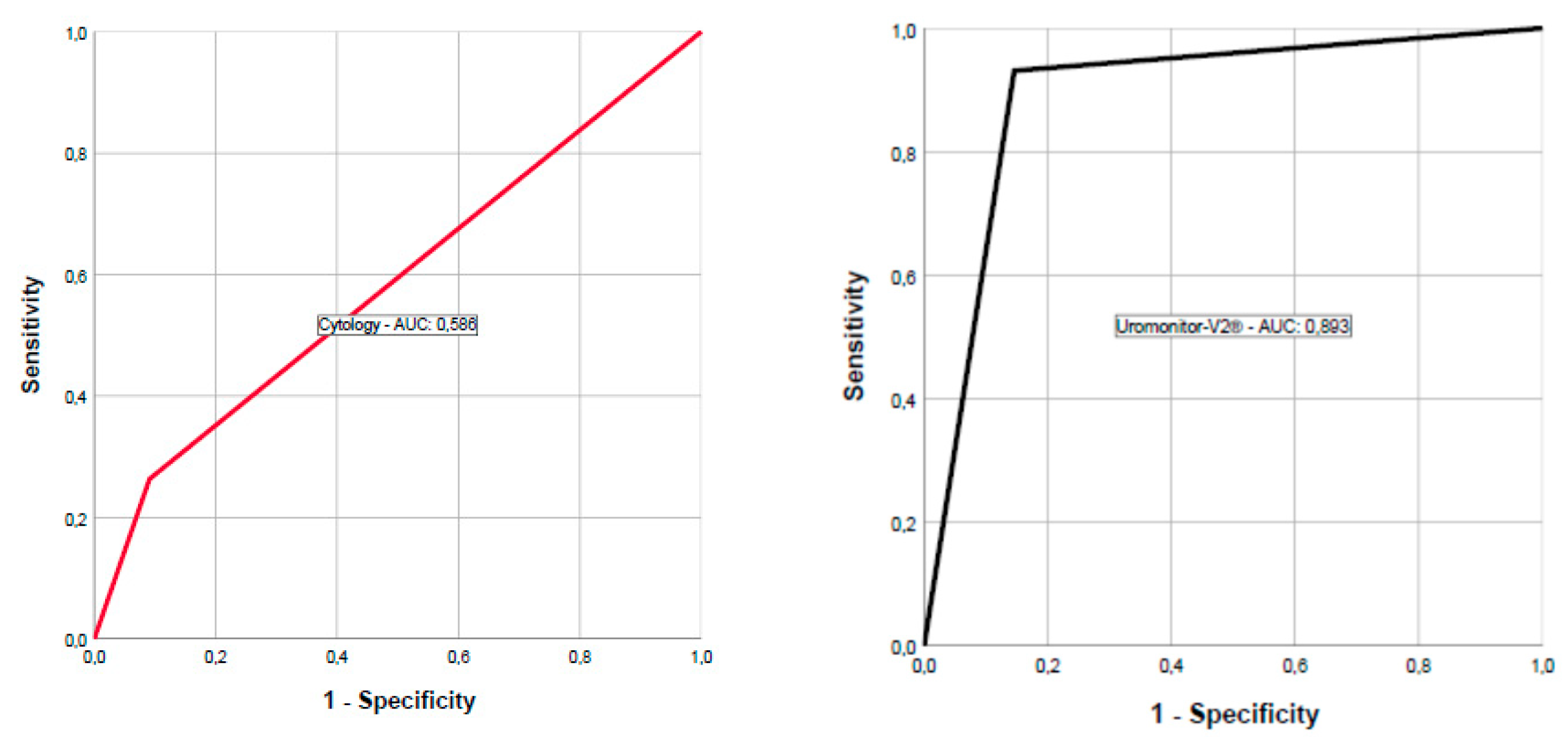
2.2. Test Results
2.3. Cytology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Urine Collection, Sample Handling and Testing
4.3. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burger, M.; Catto, J.W.F.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Herr, H.; Karakiewicz, P.; Kassouf, W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Vecchia, C.L.; Shariat, S. Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambier, S.; Sylvester, R.J.; Collette, L.; Gontero, P.; Brausi, M.A.; Andel, G.V.; Kirkels, W.J.; Silva, F.C.D.; Oosterlinck, W.; Prescott, S.; et al. EORTC Nomograms and Risk Groups for Predicting Recurrence, Progression, and Disease-specific and Overall Survival in Non–Muscle-invasive Stage Ta–T1 Urothelial Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with 1–3 Years of Maintenance Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gontero, P.; Sylvester, R.; Pisano, F.; Joniau, S.; Eeckt, K.V.; Serretta, V.; Larré, S.; Stasi, S.D.; Rhijn, B.V.; Witjes, A.J.; et al. Prognostic Factors and Risk Groups in T1G3 Non–Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Patients Initially Treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin: Results of a Retrospective Multicenter Study of 2451 Patients. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Doyle, W.; Leow, J.J.; Orsola, A.; Chang, S.L.; Bellmunt, J. Improving Selection Criteria for Early Cystectomy in High-Grade T1 Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 15,215 Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.M.; Oosterlinck, W.; Witjes, J.A.; Bouffioux, C.; Denis, L.; Newling, D.W.W.; Kurth, K. Predicting Recurrence and Progression in Individual Patients with Stage Ta T1 Bladder Cancer Using EORTC Risk Tables: A Combined Analysis of 2596 Patients from Seven EORTC Trials. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gomez, J.; Madero, R.; Solsona, E.; Unda, M.; Martinez-Piñeiro, L.; Ojea, A.; Portillo, J.; Montesinos, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Pertusa, C.; et al. The EORTC Tables Overestimate the Risk of Recurrence and Progression in Patients with Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin: External Validation of the EORTC Risk Tables. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gontero, P.; Mostafid, A.H.; Palou, J.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Rouprêt, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Sylvester, R.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and Carcinoma In Situ)—2019 Update. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteman, M.F.; Pashos, C.L.; Redaelli, A.; Laskin, B.; Hauser, R. The health economics of bladder cancer. PharmacoEconomics 2003, 21, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafi, F.A.; Brimo, F.; Steinberg, J.; Aprikian, A.G.; Tanguay, S.; Kassouf, W. Prospective analysis of sensitivity and specificity of urinary cytology and other urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2015, 33, 66.e25–66.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, F.; Droller, M.J.; Lotan, Y.; Gontero, P.; D’Andrea, D.; Gust, K.M.; Rouprêt, M.; Babjuk, M.; Palou, J.; Shariat, S.F. An uptodate catalog of available urinary biomarkers for the surveillance of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1981–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappellen, D.; De Oliveira, C.; Ricol, D.; De Medina, S.; Bourdin, J.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Chopin, D.; Thiery, J.P.; Radvanyi, F. Frequent activating mutations of FGFR3 in human bladder and cervix carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibley, K.; Cuthbert-Heavens, D.; Knowles, M.A. Loss of heterozygosity at 4p16.3 and mutation of FGFR3 in transitional cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2001, 20, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billerey, C.; Chopin, D.; Aubriot-Lorton, M.H.; Ricol, D.; Gil Diez de Medina, S.; Van Rhijn, B.; Bralet, M.P.; Lefrere-Belda, M.A.; Lahay, J.B.; Abbou, C.C.; et al. Frequent FGFR3 mutations in papillary noninvasive bladder (pTa) tumors. Am. J. Pathol 2001, 158, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Vis, A.N.; Van der Kwast, T.H.; Kirkels, W.J.; Radvanyi, F.; Ooms, E.C.M.; Chopin, D.K.; Boevé, E.R.; Jöbsis, A.C.; Zwarthoff, E.C. Molecular grading of urothelial cell carcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 and MIB-1 is superior to pathologic grade for the prediction of clinical outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.; López-Knowles, E.; Lloreta, J.; Kogevinas, M.; Amorós, A.; Tardón, A.; Carrato, A.; Serra, C.; Malats, N.; Real, F.X. Prospective study of FGFR3 mutations as a prognostic factor in nonmuscle invasive urothelial bladder carcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, D.C.; Baldo, O.; Harnden, P.; Knowles, M.A. FGFR3 protein expression and its relationship to mutation status and prognostic variables in bladder cancer. J. Pathol. 2007, 213, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandith, A.A.; Shah, Z.A.; Siddiqi, M.A. Oncogenic role of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in tumorigenesis of urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebar, A.H.; Hurst, C.D.; Tomlinson, D.C.; Johnston, C.; Taylor, C.F.; Knowles, M.A. FGFR3 and Ras gene mutations are mutually exclusive genetic events in urothelial cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5218–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachakonda, P.S.; Hosen, I.; De Verdier, P.J.; Fallah, M.; Heidenreich, B.; Ryk, C.; Wiklund, N.P.; Steineck, G.; Schadendorf, D.; Hemminki, K.; et al. TERT promoter mutations in bladder cancer affect patient survival and disease recurrence through modification by a common polymorphism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17426–17431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allory, Y.; Beukers, W.; Sagrera, A.; Flández, M.; Marqués, M.; Márquez, M.; Van der Keur, K.A.; Dyrskjot, L.; Lurkin, I.; Vermeij, M.; et al. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations in bladder cancer: High frequency across stages, detection in urine, and lack of association with outcome. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurst, C.D.; Platt, F.M.; Knowles, M.A. Comprehensive mutation analysis of the TERT promoter in bladder cancer and detection of mutations in voided urine. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosen, I.P.; Rachakonda, S.; Heidenreich, B.; De Verdier, P.J.; Ryk, C.; Steineck, G.; Hemminki, K.; Kumar, R. Mutations in TERT promoter and FGFR3 and telomere length in bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 24 Chou, R.; Gore, J.L.; Buckley, D.; Fu, R.; Gustafson, K.; Griffin, J.C.; Grusing, S.; Selph, S. Urinary Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Descotes, F.; Kara, N.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Piaton, E.; Geiguer, F.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C.; Terrier, J.E.; Lopez, J.; Ruffion, A. Non-invasive prediction of recurrence in bladder cancer by detecting somatic TERT promoter mutations in urine. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.; Vinagre, J.; Prazeres, H.; Sampaio, C.; Peralta, P.; Conceição, P.; Sismeiro, A.; Leão, R.; Gomes, A.; Furriel, F.; et al. Validation of a Novel, Sensitive, and Specific Urine-Based Test for Recurrence Surveillance of Patients with Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Comprehensive Multicenter Study. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, R.; Selph, S.; Buckley, D.I.; Fu, R.; Griffin, J.C.; Grusing, S.; Gore, J.L. Comparative Effectiveness of Fluorescent Versus White Light Cystoscopy for Initial Diagnosis or Surveillance of Bladder Cancer on Clinical Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, S.; Algaba, F.; Babjuk, M.; Bryan, R.T.; Sun, Y.-H.; Valiquette, L.; den Rosette, J. The Clinical Research Office of the Endourological Society (CROES) Multicentre Randomised Trial of Narrow Band Imaging-Assisted Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumour (TURBT) Versus Conventional White Light Imaging-Assisted TURBT in Primary Non-Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Patients: Trial Protocol and 1-year Results. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, M.; Grossman, H.B.; Droller, M.; Schmidbauer, J.; Hermann, G.; Dragoescu, O.; Ray, E.; Fradet, Y.; Karl, A.; Burgués, J.P.; et al. Photodynamic diagnosis of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer with hexaminolevulinate cystoscopy: A meta-analysis of detection and recurrence based on raw data. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.; Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Sullivan, R.; Witjes, J.A. Economic Burden of Bladder Cancer across the European Union. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavalieris, L.; O’Sullivan, P.; Frampton, C.; Guilford, P.; Darling, D.; Jacobson, E.; Suttie, J.; Raman, J.D.; Shariat, S.F.; Lotan, Y. Performance Characteristics of a Multigene Urine Biomarker Test for Monitoring for Recurrent Urothelial Carcinoma in a Multicenter Study. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Morote, J.; Cornel, E.B.; Gakis, G.; Valenberg, F.J.P.v.; Lozano, F.; Sternberg, I.A.; Willemsen, E.; Hegemann, M.L.; Paitan, Y.; et al. Performance of the Bladder EpiCheckTM Methylation Test for Patients Under Surveillance for Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: Results of a Multicenter, Prospective, Blinded Clinical Trial. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 1, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Valenberg, F.J.P.; Hiar, A.M.; Wallace, E.; Bridge, J.A.; Mayne, D.J.; Beqaj, S.; Sexton, W.J.; Lotan, Y.; Weizer, A.Z.; Jansz, G.K.; et al. Prospective Validation of an mRNA-based Urine Test for Surveillance of Patients with Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VandenBussche, C.J.; Rosenthal, D.L.; Olson, M.T. Adequacy in voided urine cytology specimens: The role of volume and a repeat void upon predictive values for high-grade urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Non Bladder Cancer (n = 20) | NMIBC Recurrence (n = 29) | NMIBC Nonrecurrence (n = 48) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Median (min–max) | 71 (22–82) | 68 (50–85) | 72.5 (49–93) |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 8 (40%) | 9 (31%) | 12 (25%) |
| Male | 12 (60%) | 20 (69%) | 36 (75%) |
| Smoking | |||
| No | 1 (5%) | 4 (13.8%) | 6 (12.5%) |
| Yes, former | 2 (10%) | 19 (65.5%) | 35 (7.9%) |
| Yes, current | 0 (0%) | 5 (17.2%) | 7 (14.6%) |
| Unknown | 17 (85%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) |
| Most recent intravesical treatment | |||
| Chemotherapy | N.A. | 13 (44.8%) | 21 (43.8%) |
| BCG | N.A. | 5 (17.2%) | 11 (22.9%) |
| Synergo | N.A. | 8 (27.6%) | 13 (27.1%) |
| Other | N.A. | 1 (3.4%) | 1 (2.1%) |
| None | N.A. | 2 (6.9%) | 2 (4.2%) |
| Time since last treatment (in months) | |||
| Mean (min–max) | N.A. | 10.81 (1–56) | 5.20 (0–28) |
| Stage initial tumor | |||
| PUNLMP | N.A. | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0%) |
| pTa | N.A. | 17 (58.6%) | 27 (56.3%) |
| pT1 | N.A. | 3 (10.3%) | 8 (16.7%) |
| CIS | N.A. | 7 (24.1%) | 13 (27.1%) |
| Grade initial tumor | |||
| Low-grade | N.A. | 13 (44.8%) | 19 (39.6%) |
| High-grade | N.A. | 16 (55.2%) | 29 (60.4%) |
| Stage last recurrence | |||
| pTa | N.A. | 6 (20.7%) | N.A. |
| pT1 | N.A. | 2 (6.9%) | N.A. |
| CIS | N.A. | 5 (17.2%) | N.A. |
| MIBC | N.A. | 1 (3.5%) | N.A. |
| Not available | N.A. | 15 (51.7%) | N.A. |
| Grade last recurrence | |||
| Low-grade | N.A. | 2 (6.9%) | N.A. |
| High-grade | N.A. | 12 (41.4%) | N.A. |
| Not available | N.A. | 15 (51.7%) | N.A. |
| Cytology at enrollment cystoscopy | |||
| TPS2 | N.A. | 13 (44.8%) | 28 (58.3%) |
| TPS3 | N.A. | 1 (3.4%) | 2 (4.2%) |
| TPS4 | N.A. | 3 (10.3%) | 2 (4.2%) |
| TPS5 | N.A. | 2 (6.9%) | 1 (2.1%) |
| Not available | N.A. | 10 (34.5%) | 15 (31.3%) |
| Test Result | Recurrence-Positive | Recurrence-Negative | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmed by Histology | Confirmed by Cytology/Cystoscopy | Non-Recurrent NMIBC | Non-BCa | ||
| Positive | 14 | 13 | 7 | 2 | 36 |
| Negative | 0 | 2 | 41 | 18 | 61 |
| Total | 14 | 15 | 48 | 20 | 97 |
| Patients | Parameter | n/N | Results, % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uromonitor-V2® NMIBC patients | Sensitivity | 27/29 | 93.1 (75.8–98.8) |
| Specificity | 41/48 | 85.4 (75.8–93.4) | |
| PPV | 27/34 | 79.4 (57.5–87.3) | |
| NPV | 41/43 | 95.3 (87.6–99.4) | |
| Uromonitor-V2® All patients | Sensitivity | 27/29 | 93.1 (75.8–98.8) |
| Specificity | 59/68 | 86.8 (71.6–93.5) | |
| PPV | 27/36 | 75.0 (61.6–90.7) | |
| NPV | 59/61 | 96.7 (82.9–99.2) | |
| Cytology | Sensitivity | 5/19 | 26.3 (10.1–51.4) |
| Specificity | 30/33 | 90.9 (74.5–97.6) | |
| PPV | 5/8 | 62.5 (25.9–89.8) | |
| NPV | 30/44 | 68.2 (52.3–80.9) |
| Cytology | Uromonitor-V2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Sensitivity | 48% [10] | 93% |
| Overall Specificity | 86% [10] | 85% |
| Type of sample required | Urine | Urine |
| Amount of sample recommended | >30 mL [34] | 10 mL |
| Technical time required from sample to result | Couple of days | 6 h |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sieverink, C.A.; Batista, R.P.M.; Prazeres, H.J.M.; Vinagre, J.; Sampaio, C.; Leão, R.R.; Máximo, V.; Witjes, J.A.; Soares, P. Clinical Validation of a Urine Test (Uromonitor-V2®) for the Surveillance of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100745
Sieverink CA, Batista RPM, Prazeres HJM, Vinagre J, Sampaio C, Leão RR, Máximo V, Witjes JA, Soares P. Clinical Validation of a Urine Test (Uromonitor-V2®) for the Surveillance of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(10):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100745
Chicago/Turabian StyleSieverink, Caroline A., Rui P. M. Batista, Hugo J. M. Prazeres, João Vinagre, Cristina Sampaio, Ricardo R. Leão, Valdemar Máximo, J. Alfred Witjes, and Paula Soares. 2020. "Clinical Validation of a Urine Test (Uromonitor-V2®) for the Surveillance of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients" Diagnostics 10, no. 10: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100745
APA StyleSieverink, C. A., Batista, R. P. M., Prazeres, H. J. M., Vinagre, J., Sampaio, C., Leão, R. R., Máximo, V., Witjes, J. A., & Soares, P. (2020). Clinical Validation of a Urine Test (Uromonitor-V2®) for the Surveillance of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients. Diagnostics, 10(10), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100745








