The Genes—Candidates for Prognostic Markers of Metastasis by Expression Level in Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vuyyala, S.; Gandhi, S.; Kuechle, J.B.; George, S. Complete Remission of Bone Metastases in Renal Cell Carcinoma with Nivolumab. Cureus 2019, 11, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, B.; Hwang, E.C.; Hong, S.-H.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Byun, S.S.; Chung, J. Retrospective Multicenter Long-Term Follow-up Analysis of Prognostic Risk Factors for Recurrence-Free, Metastasis-Free, Cancer-Specific, and Overall Survival After Curative Nephrectomy in Non-metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frees, S.K.; Kamal, M.M.; Nestler, S.; Levien, P.M.; Bidnur, S.; Brenner, W.; Thomas, C.; Jaeger, W.; Thüroff, J.W.; Roos, F.C. Risk-adjusted proposal for >60 months follow up after surgical treatment of organ-confined renal cell carcinoma according to life expectancy. Int. J. Urol. 2018, 26, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Porta, C.; Schmidinger, M.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Bex, A.; Khoo, V.; Grünwald, V.; Gillessen, S.; Horwich, A.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, L.; Dabestani, S.; Lam, T.B.; Hofmann, F.; Stewart, F.; Norrie, J.; Bex, A.; Bensalah, K.; Canfield, S.E.; Hora, M.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy of Percutaneous Renal Tumour Biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, S.; Gu, W.; Wan, F.; Zhang, H.; Shi, G.; Qu, Y.; Ye, D. Construction and Validation of a 9-Gene Signature for Predicting Prognosis in Stage III Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Giles, R.H.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Lam, T. EAU Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Assoc. Urol. 2010, 58, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, V.; Di Nunno, V.; Gatto, L.; Santoni, M.; Scarpelli, M.; Cimadamore, A.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cheng, L.; Battelli, N.; Montironi, R.; et al. Resistance to Systemic Agents in Renal Cell Carcinoma Predict and Overcome Genomic Strategies Adopted by Tumor. Cancers 2019, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorban’, N.A.; Popov, A.M.; Karyakin, O.B. Prognostic value of the expression of carbonic anhydrase 9 in combination with other markers in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Urol. 2016, 12, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huo, P.; Hu, G.; Wei, B.; Kong, D.; Li, H. Identification of gene markers associated with metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4755–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Lv, Y.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Z. Identification of key genes involved in the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Differential expressions of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 between primary and metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moein, S.; Javanmard, S.H.; Abedi, M.; Izadpanahi, M.H.; Gheisari, Y. Identification of Appropriate Housekeeping Genes for Gene Expression Analysis in Long-term Hypoxia-treated Kidney Cells. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Poudel, B.; Pandeya, D.R.; Gupta, S.P.; Sathian, B.; Yadav, S.K. Serum amyloid a as an independent prognostic factor for renal cell carcinoma—A hospital based study from the Western region of Nepal. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2253–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuizaka, M.; Naganuma, S.; Kagawa, S.; Ohashi, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Subramanian, H.; Chang, S.; Nakagawa, K.L.; Ji, X.; Liebhaber, S.A. Hypoxia induces IGFBP3 in esophageal squamous cancer cells through HIF-1alpha-mediated mRNA transcription and continuous protein synthesis. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2620–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatovicova, M.; Jelenska, L.; Hulikova, A.; Csaderova, L.; Ditte, Z.; Ditte, P.; Goliasova, T.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S. Carbonic anhydrase IX as an anticancer therapy target: Preclinical evaluation of internalizing monoclonal antibody directed to catalytic domain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3255–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, E.; Ovenberger, M.; Borg, K.; Påhlman, S. Transcriptional adaptation ofneuroblastoma cells to hypoxia. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescador, N.; Cuevas, Y.; Naranjo, S.; Alcaide, M.; Villar, D.; Landázuri, M.O.; Del Peso, L. Identification of a functional hypoxia-responsive element that regulates the expression of the egl nine homologue 3 (egln3/phd3) gene. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanimoto, K.; Nishiyama, M.; Honda, H.; Kato, Y. Identification of Functional Hypoxia Response Elements in the Promoter Region of the DEC1 and DEC2 Genes. J. Boil. Chem. 2002, 277, 47014–47021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengler, V.L.; Galbraith, M.; Espinosa, J.M. Transcriptional Regulation by Hypoxia Inducible Factors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pio, R.; Corrales, L.; Lambris, J.D. The role of complement in tumor growth. Single Mol. Single Cell Seq. 2014, 772, 229–262. [Google Scholar]
- Tohgi, H.; Utsugisawa, K.; Nagane, Y. Hypoxia-induced expression of C1q, a subcomponent of the complement system, in cultured rat PC12 cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 291, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Pednekar, L.; Reid, K.B.; Kishore, U. Complement and non-complement activating functions of C1q: A prototypical innate immune molecule. Innate Immun. 2012, 18, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.; Sze, C.-I.; Lin, S.-R.; Lee, M.-H.; He, R.-Y.; Schultz, L.; Chang, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Boackle, R.J.; Hsu, L.-J.; et al. Complement C1q Activates Tumor Suppressor WWOX to Induce Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanek, D.M.; Ghouse, S.M.; Karbowniczek, M.M.; Markiewski, M.M. Complementing Cancer Metastasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immonen, K.; Finne, P.; Hakala, M.; Kautiainen, H.; Pettersson, T.; Groenhagen-Riska, C. No improvement in survival of patients with amyloidosis associated with inflammatory rheumatic diseases data from Finish National registry for kidney diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sung, B.; Gupta, S.C. The Role of Inflammation in Kidney Cancer; Chapter 9 Inflammation and Cancer; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; p. 816. [Google Scholar]
- Paret, C.; Schön, Z.; Szponar, A.; Kovacs, G. Inflammatory Protein Serum Amyloid A1 Marks a Subset of Conventional Renal Cell Carcinomas with Fatal Outcome. Eur. Urol. 2010, 57, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sato, F.; Bhawal, U.K.; Kawamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Noshiro, M.; Morohashi, S.; Kato, Y.; Kijima, H. Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors DEC1 and DEC2 regulate the paclitaxel-induced apoptotic pathway of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 491–495. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Jia, Y.-F.; Ma, X.-L.; Zheng, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, S.; Chen, Z.-T.; Wang, Y.-S. DEC2 suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis by regulating ERK/NF-κB pathway in gastric cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1741–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Bigot, P.; Colli, L.M.; Machiela, M.J.; Jessop, L.; Myers, T.A.; Carrouget, J.; Wagner, S.; Roberson, D.; Eymerit, C.; Henrion, D.; et al. Functional characterization of the 12p12.1 renal cancer-susceptibility locus implicates BHLHE41. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Cui, X.; Lu, J. Overexpression of BHLHE41, correlated with DNA hypomethylation in 3′UTR region, promotes the growth of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2137–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagner, M.; Enzo, E.; Forcato, M.; Zanconato, F.; Parenti, A.; Rampazzo, E.; Basso, G.; Leo, G.; Rosato, A.; Bicciato, S.; et al. SHARP1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis by promoting degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors. Nature 2012, 487, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sato, F.; Kawamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Morohashi, S.; Akasaka, H.; Kondo, J.; Wu, Y.; Noshiro, M.; Kato, Y.; et al. Anti-apoptotic effect of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor DEC2 in human breast cancer cells. Genes Cells 2010, 15, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; Kim, H.T.; Bissonnette, R.P.; Lamph, W.W.; Yan, B.; Brown, P.H. The rexinoid bexarotene represses cyclin D1 transcription by inducing the DEC2 transcriptional repressor. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 128, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, F.; Kawamura, H.; Wu, Y.; Sato, H.; Jin, D.; Bhawal, U.K.; Kawamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Noshiro, M.; Seino, H.; et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor DEC2 inhibits TGF-beta-induced tumor progression in human pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanoma, K.; Liu, G.; Yamane, T.; Miyanari, Y.; Takao, T.; Yagi, H.; Ohgami, T.; Ichinoe, A.; Sonoda, K.; Wake, N.; et al. Regulation Mechanism of TWIST1 Transcription by BHLHE40 and BHLHE41 in Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 4096–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, D.; Balsa, E.; Acosta-Iborra, B.; Fuertes-Yebra, E.; Elorza, A.; Ordoñez, A.; Corral-Escariz, M.; Soro, I.; López-Bernardo, E.; Perales-Clemente, E.; et al. Induction of the Mitochondrial NDUFA4L2 Protein by HIF-1α Decreases Oxygen Consumption by Inhibiting Complex I Activity. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apanovich, N.V.; Poyarkov, S.V.; Peters, M.V.; Korotaeva, A.A.; Markova, A.S.; Kamolov, B.S.; Pronina, I.V.; Braga, E.A.; Matveev, V.B.; Karpukhin, A.V. The differential gene expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and biomarker development. Eur. J. Hum.Gen. 2015, 23, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Apanovich, N.V.; Peters, M.V.; Korotaeva, A.A.; Apanovich, P.V.; Markova, A.S.; Kamolov, B.S.; Matveev, V.B.; Karpukhin, A.V. Molecular genetic diagnostics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Urol. 2016, 12, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minton, D.R.; Fu, L.; Mongan, N.P.; Shevchuk, M.M.; Nanus, D.M.; Gudas, L.J. Role of NADH Dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex 4-like 2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2791–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Lan, G.; Peng, L.; Xie, X.; Peng, F.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X. NDUFA4L2 expression predicts poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yang, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, M. Mitochondrial NDUFA4L2 protein promotes the vitality of lung cancer cells by repressing oxidative stress. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Hu, H.; Chang, R.; Zhong, J.; Knabel, M.; O’Meally, R.; Cole, R.N.; Pandey, A.; Semenza, G.L. Pyruvate Kinase M2 is a PHD3-stimulated Coactivator for Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1. Cell 2011, 145, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaravinos, A.; Pieri, M.; Mourmouras, N.; Anastasiadou, N.; Zouvani, I.; Delakas, D.; Deltas, C. Altered metabolic pathways in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis and validation study focused on the deregulated genes and their associated networks. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zodro, E.; Jaroszewski, M.; Ida, A.; Wrzesińki, T.; Kwias, Z.; Bluyssen, H.; Wesoly, J. C227: FUT11 as a potential biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression based on meta-analysis of gene expression data. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2014, 13, e1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogie-Brahim, S.; Feldman, D.; Oh, Y. Unraveling insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 actions in human disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braczkowski, R.; Białożyt, M.; Plato, M.; Mazurek, U.; Braczkowska, B. Expression of insulin-like growth factor family genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Współczesna Onkologia 2016, 20, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.-T.; Patton, K.T.; Schafernak, K.T.; Papavero, V.; Lin, F.; Baxter, R.C.; Teh, B.T.; Yang, X.J. Over Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, S.; Grote, V.A.; Becker, S.; Rinaldi, S.; Tjønneland, A.; Roswall, N.; Grønbæk, H.; Overvad, K.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. Concentrations of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and pancreatic cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schairer, C.; Mccarty, C.A.; Isaacs, C.; Sue, L.Y.; Pollak, M.N.; Berg, C.D.; Ziegler, R.G. Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I and IGF Binding Protein (IGFBP)-3 Levels and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Risk in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial (PLCO) Cohort. Horm. Cancer 2010, 1, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.W.; Vesey, D.A.; Nicol, D.L.; Johnson, D.W.; Cheung, D.A.V.C.W. The roles of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in the regulation of proximal tubule, and renal cell carcinoma cell proliferation. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosendahl, A.H.; Forsberg, G. IGF-I and IGFBP-3 augment transforming growth factor-b actions in human renal carcinoma cells. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Beasley, N.J.; Watson, P.H.; Turner, K.J.; Pastorek, J.; Sibtain, A.; Wilson, G.D.; Turley, H.; Talks, K.L.; Maxwell, P.H.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible expression of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 7075–7083. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, M.H.; Seligson, D.; Han, K.R. Carbonic anhydrase IX is an independent predictor of survival in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma: Implications for prognosis and therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 802–811. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Liao, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Fernando, S. Prognostic Value of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Immunohistochemical Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of the Literature. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, C.V. Molecular and cellular biology of von Willebrand factor. Int. J. Hematol. 2002, 75, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Chen, X.; Zeng, S.; Guan, B.; Hu, B.; Meng, Y.; Liu, F.; Wong, T.; Lu, Y.; Yun, C.; et al. Bioinformatic identification of key genes and analysis of prognostic values in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.H.; Serie, D.J.; Parasramka, M.; Cheville, J.C.; Bot, B.M.; Tan, W.; Wang, L.; Joseph, R.W.; Hilton, T.; Leibovich, B.C.; et al. Differential gene expression profiling of matched primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases reveals upregulation of extracellular matrix genes. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 604–610. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.I.; Czarnecka, A.M.; Lewicki, S.; Helbrecht, I.; Brodaczewska, K.; Koch, I.; Zdanowski, R.; Król, M.; Szczylik, C. Comparative Gene Expression Profiling of Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Stem Cell-Like Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
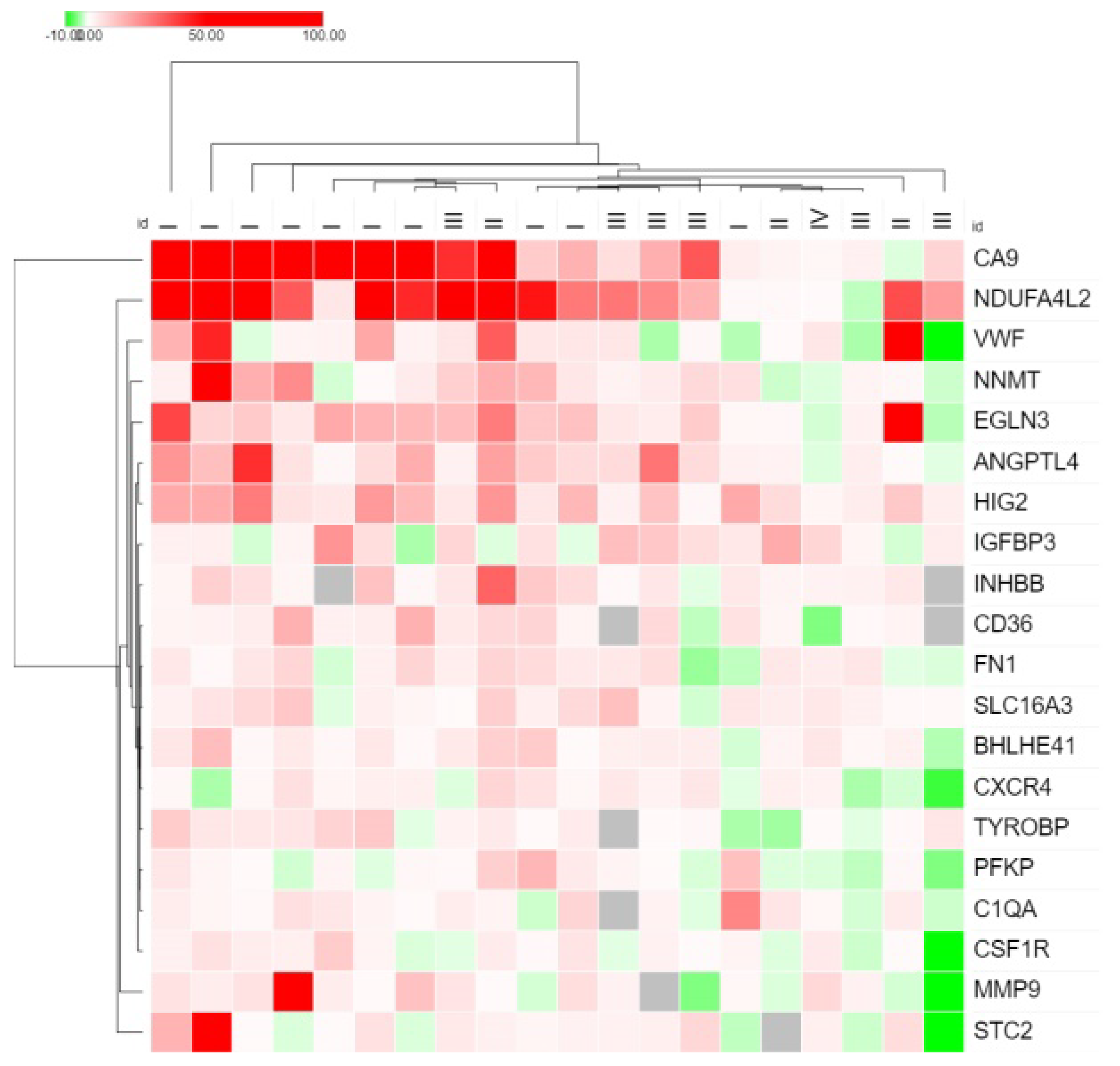
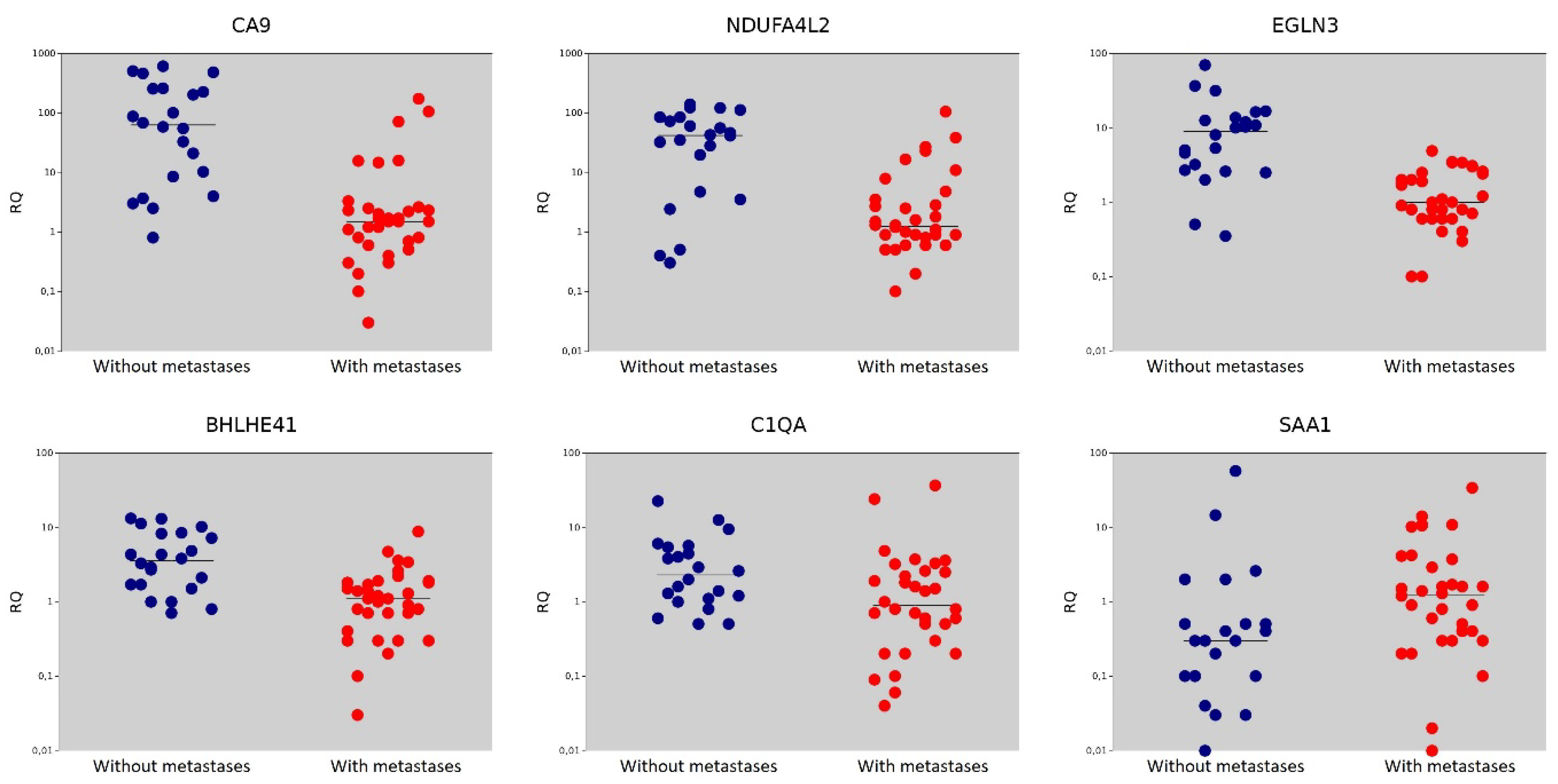
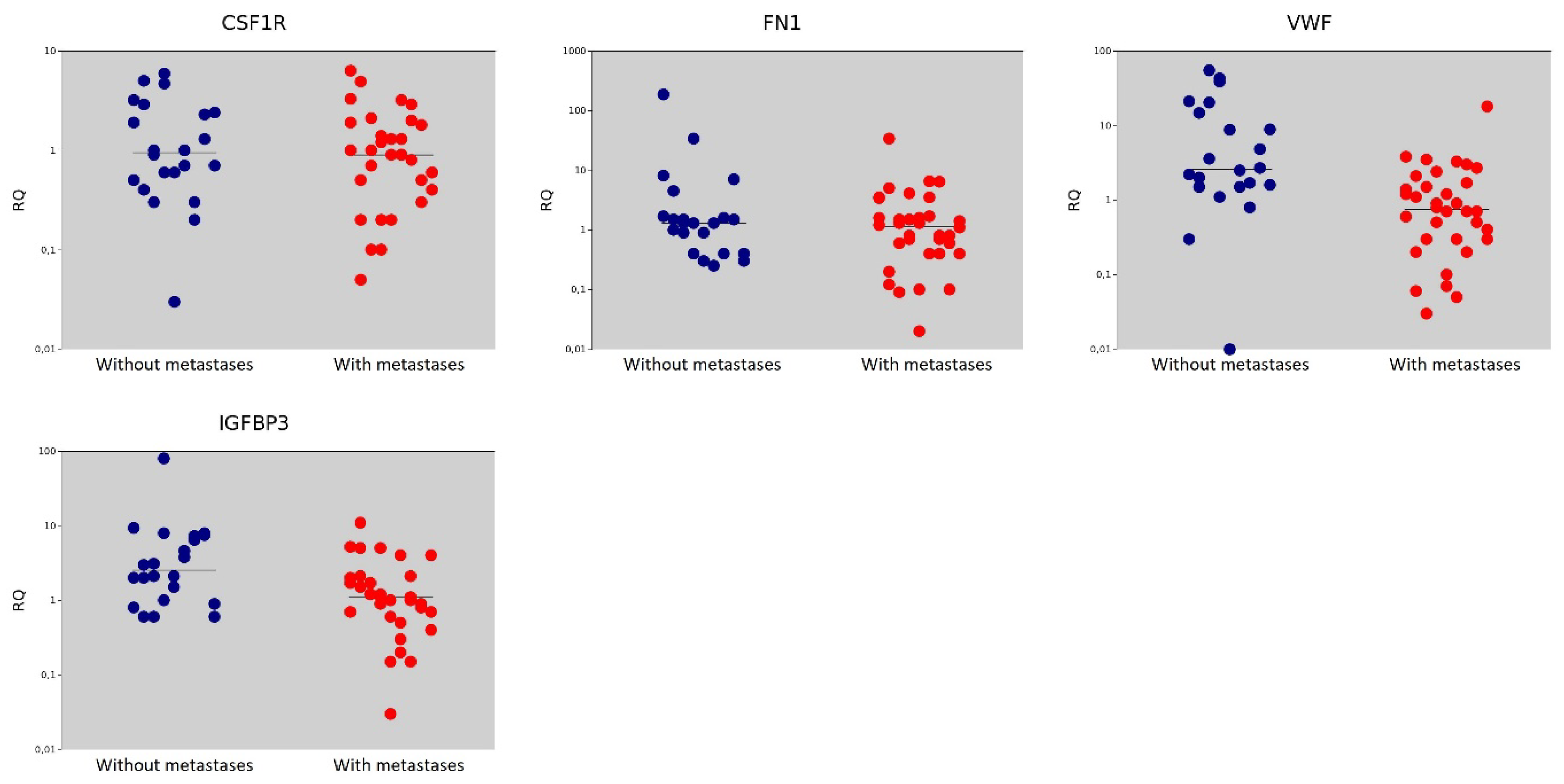
| Gene | Gene Name | The Median Value in the Non-Metastasis Group | The Median Value in the Metastasis Group | p = (Mann–Whitney U-test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA9 | Carbonic Anhydrase 9 | 63.15 | 1.50 | <0.001 |
| NDUFA4L2 | NADH Dehydrogenase [Ubiquinone] 1 Alpha Subcomplex Subunit 4-Like 2 | 42.00 | 1.25 | <0.001 |
| EGLN3 | Egl Nine Homolog 3 | 9.00 | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| BHLHE41 | Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Family Member E41 | 3.55 | 1.10 | <0.001 |
| C1QA | Complement C1q Subcomponent Subunit A | 2.30 | 0.90 | 0.016 |
| SAA1 | Serum Amyloid A1 | 0.30 | 1.25 | 0.018 |
| CSF1R | Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.562 |
| FN1 | Fibronectin | 1.30 | 1.15 | 0.396 |
| VWF | Von Willebrand Factor | 2.60 | 0.75 | <0.001 |
| IGFBP3 | Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein | 2.55 | 1.10 | 0.007 |
| Gene | Area under ROC Curve (AUC) | 95% CI | Cutoff Value | Significance Level p (Area = 0.5) | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA9 | 0.891 | 0.804–0.978 | ≤2.6 | <0.001 | 79.41 | 90.91 |
| NDUFA4L2 | 0.811 | 0.672–0.951 | ≤27 | <0.001 | 94.12 | 68.18 |
| VWF | 0.788 | 0.659–0.917 | ≤1.4 | <0.001 | 70.59 | 81.82 |
| BHLHE41 | 0.808 | 0.691–0.925 | ≤2.6 | <0.001 | 88.24 | 63.64 |
| EGLN3 | 0.873 | 0.760–0.986 | ≤3.5 | <0.001 | 97.06 | 68.18 |
| IGFBP3 | 0.714 | 0.572–0.856 | ≤1.7 | 0.003 | 73.53 | 68.18 |
| SAA1 | 0.689 | 0.537–0.841 | >0.5 | 0.015 | 64.71 | 77.27 |
| CSF1R | 0.547 | 0.389–0.705 | ≤2.1 | 0.562 | - | - |
| C1QA | 0.693 | 0.552–0.833 | ≤3.7 | 0.007 | 91.18 | 40.91 |
| FN1 | 0.568 | 0.412–0.724 | ≤0.8 | 0.198 | - | - |
| Gene | Frequency of Expression Higher/Lower from the Cut-Off Value in the Non-Metastasis Group | Frequency of Expression Higher/Lower from the Cut-Off Value in the Metastasis Group | Odds Ratio/95% CI | Relative Risk/95%CI | Fisher Exact Two-Tailed, p = | Logistic Regression, p = |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA9 | 20/2 | 7/27 | 38.57/7.23–205.82 | 8.74/2.30–33.11 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| NDUFA4L2 | 15/7 | 2/32 | 34.29/6.35–185.24 | 2.96/1.60–5.48 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| VWF | 18/4 | 10/24 | 10.80/2.91–40.06 | 3.88 1.56–9.67 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| BHLHE41 | 14/8 | 4/30 | 13.13/3.38–51.01 | 2.43/1.38–4.27 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| EGLN3 | 15/7 | 1/33 | 70.71/7.97–627.07 | 3.05/1.65–5.64 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| IGFBP3 | 15/7 | 9/25 | 5.95/1.83–19.31 | 2.31/1.21–4.40 | 0.003 * | 0.005 * |
| SAA1 | 5/17 | 22/12 | 6.23/ 1.84–21.12 | 2.85/1.27–6.40 | 0.003 * | 0.967 |
| CSF1R | 7/15 (31.8) | 5/29 (14.7) | 2.71/0.73–10.00 | 1.25/0.91–1.72 | 0.184 | 0.421 |
| C1QA | 9/13 (40.9) | 3/31 (8.8) | 7.16/1.66–30.75 | 1.54/1.07–2.21 | 0.007 * | 0.540 |
| FN1 | 16/6 (72.7) | 18/16 (52.9) | 2.37/0.75–7.52 | 1.73/0.80–3.73 | 0.169 | 0.153 |
| Gene Group | Sensitivity/Specificity | Odds Ratio/95% CI | Relative Risk/95%CI | Negative Predictive Value %/95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two genes of CA9 BHLHE41 EGLN3 NDUFA4L2 | 100.00%/68.18% | 142.60/7.66–2656.78 | 3.14/1.70–5.79 | 100.00 |
| Three genes of CA9 BHLHE41 EGLN3 NDUFA4L2 | 88.24%/72.73% | 20.00/4.92–81.36 | 3.24/1.62–6.47 | 80.00/60.61–91.23 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apanovich, N.; Peters, M.; Apanovich, P.; Mansorunov, D.; Markova, A.; Matveev, V.; Karpukhin, A. The Genes—Candidates for Prognostic Markers of Metastasis by Expression Level in Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010030
Apanovich N, Peters M, Apanovich P, Mansorunov D, Markova A, Matveev V, Karpukhin A. The Genes—Candidates for Prognostic Markers of Metastasis by Expression Level in Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleApanovich, Natalya, Maria Peters, Pavel Apanovich, Danzan Mansorunov, Anna Markova, Vsevolod Matveev, and Alexander Karpukhin. 2020. "The Genes—Candidates for Prognostic Markers of Metastasis by Expression Level in Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer" Diagnostics 10, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010030
APA StyleApanovich, N., Peters, M., Apanovich, P., Mansorunov, D., Markova, A., Matveev, V., & Karpukhin, A. (2020). The Genes—Candidates for Prognostic Markers of Metastasis by Expression Level in Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer. Diagnostics, 10(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10010030





