Pilin Processing Follows a Different Temporal Route than That of Archaellins in Methanococcus maripaludis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
| Description and/or genotype | Source or reference | |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| E. coli K113 | BL21(DE3)/pLysS; expression host, CmR | Novagen |
| Methanococcus maripaludis Mm900 | Δhpt | [7] |
| M. maripaludis ∆flaK | Mm900∆flaK | [35] |
| M. maripaludis ∆eppA | Mm900∆eppA | [11] |
| M. maripaludis ∆flaK ∆eppA | Mm900∆flaK ∆eppA | [11] |
| M. maripaludis ∆aglB | Mm900∆aglB | [34] |
| M. maripaludis ∆flaK ∆aglB | Mm900∆flaK ∆aglB | This study |
| M. maripaludis ∆eppA ∆aglB | Mm900∆eppA ∆aglB | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pKJ574 | pCRPrtNeo with inframe deletion of aglB | [34] |
| pKJ697 | pCRPrtNeo with inframe deletion of eppA | [11] |
| pET23a+ | T7 promoter-based expression vector, Ampr | Novagen |
| pKJ900 | pET23a+ with epdE Nde1-Xho1 fragment C-terminal histagged | This study |
| pWLG40 | hmv promoter-lacZ fusion plus Purr cassette; Ampr | [30] |
| pKJ880 | pWLG40 with epdE complement | [12] |
| pKJ1072 | pWLG40 with epdE C-terminal histagged complement | This study |
| pKJ1079 | pWLG40 with epdE (+3 Gly) C-terminal histagged complement | This study |
| pKJ1107 | pWLG40 with epdE C-terminal FLAG complement | This study |
| pKJ1108 | pWLG40 with epdE (+3 Gly) C-terminal FLAG complement | This study |
| pHW40 | nif promoter-lacZ fusion plus Purr cassette; Ampr | [30] |
| pKJ1169 | pHW40 with epdD C-terminal FLAG complement | This study |
| pKJ1226 | pHW40 with epdE C-terminal FLAG complement | This study |
| pKJ1216 | pHW40 with +1 Ala +3 Gly epdE C-terminal FLAG complement | This study |
| pKJ711 | pHW40 with epdE | [13] |
2.2. M. maripaludis Mutant Generation
| Primers | Primer Sequence 5’ to 3’ | Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| 1685+3_sdm_For Nsi1 | CCAATGCATGAAATTTTTAGAAAAACTAACATCAAAAAAAGGTC AAATAGGAATGGAACTCGG * | Nsi1 |
| 1685+1+3_sdm_For Nsi1 | CCAATGCATGAAATTTTTAGAAAAACTAACATCAAAAAAAGGTG CAATAGGAATGGAACTCGG * | Nsi1 |
| 1685_Mlu_Rev | AGCACGCGTTTAATCCGTAATATTTGACATTTGTGAGG | Mlu1 |
| 1685_Nsi1_For | CCAATGCATGAAATTTTTAGAAAAACTAACATC | Nsi1 |
| 1685_histag_Mlu_Rev | CGCGACGCGTTTAGTGATGGTGGTGATGGTGATCCGTAATA TTTGACATTTGTGAGG | Mlu1 |
| 1685_FLAG_Mlu_Rev | CGACGCGTTTATTTGTCATCGTCATCTTTGTAATCATCCGTA ATATTTGACATTTGTGAG | Mlu1 |
| 1685_For_exp | GGAATTCCATATGATGAAATTTTTAGAAAAACTAACATC | NdeI |
| 1685-Rev_exp | CCGCTCGAGATCCGTAATATTTGACATTTGTGAG | XhoI |
| 1283_Nsi1_For | CCAATGCATGTCTGTTGCTTTAAAGAAGTTTTTTTCGAAACG | Nsi1 |
| 1283_FLAG_Mlu_Rev | GCTACGCGTTTATTTGTCATCGTCATCTTTGTAATCACTAACTT CACTTAAAGCATCTAT | Mlu1 |
| FlaK_seq_For | AATATCTGGCGGATACAGG | - |
| FlaK_seq_Rev | TTCAAAGCCAATAGATACTGC | - |
| EppA_seq_For | CTGGAGCTGTATGAAATGCAAC | - |
| EppA_seq_Rev | GGATGACCTGGGATAATGCAGG | - |
| AglB_seq_For | CATAACCATATTTGTAATTAAC | - |
| AglB_seq_Rev | CTCAATAGCCATAAAATCACC | - |
2.3. Complementation Experiments
2.4. Expression of Epitope-Tagged Versions of EpdD and EpdE in Various M. maripaludis Strains
2.5. Overexpression and Purification of His-Tagged EpdE
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The +3 Position Alone Does Not Distinguish Archaellins from Pilins as FlaK Substrates
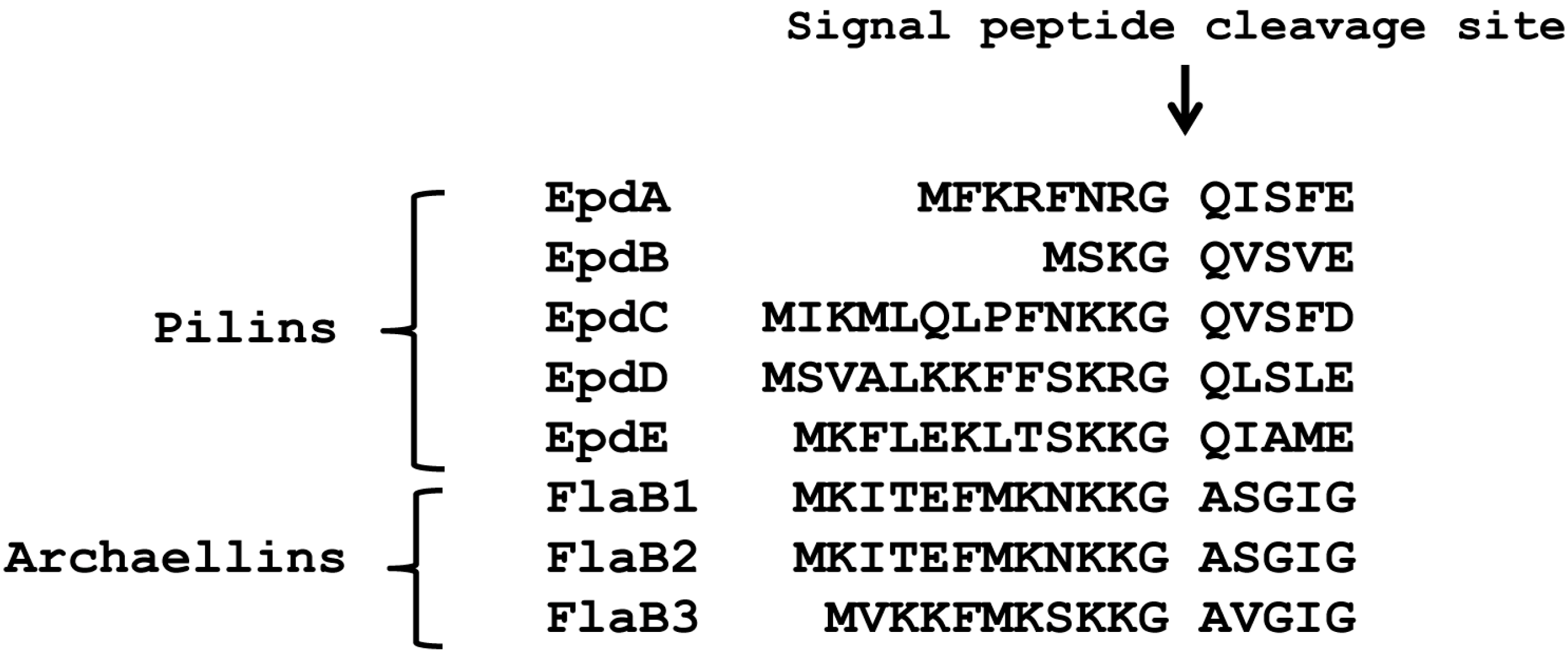
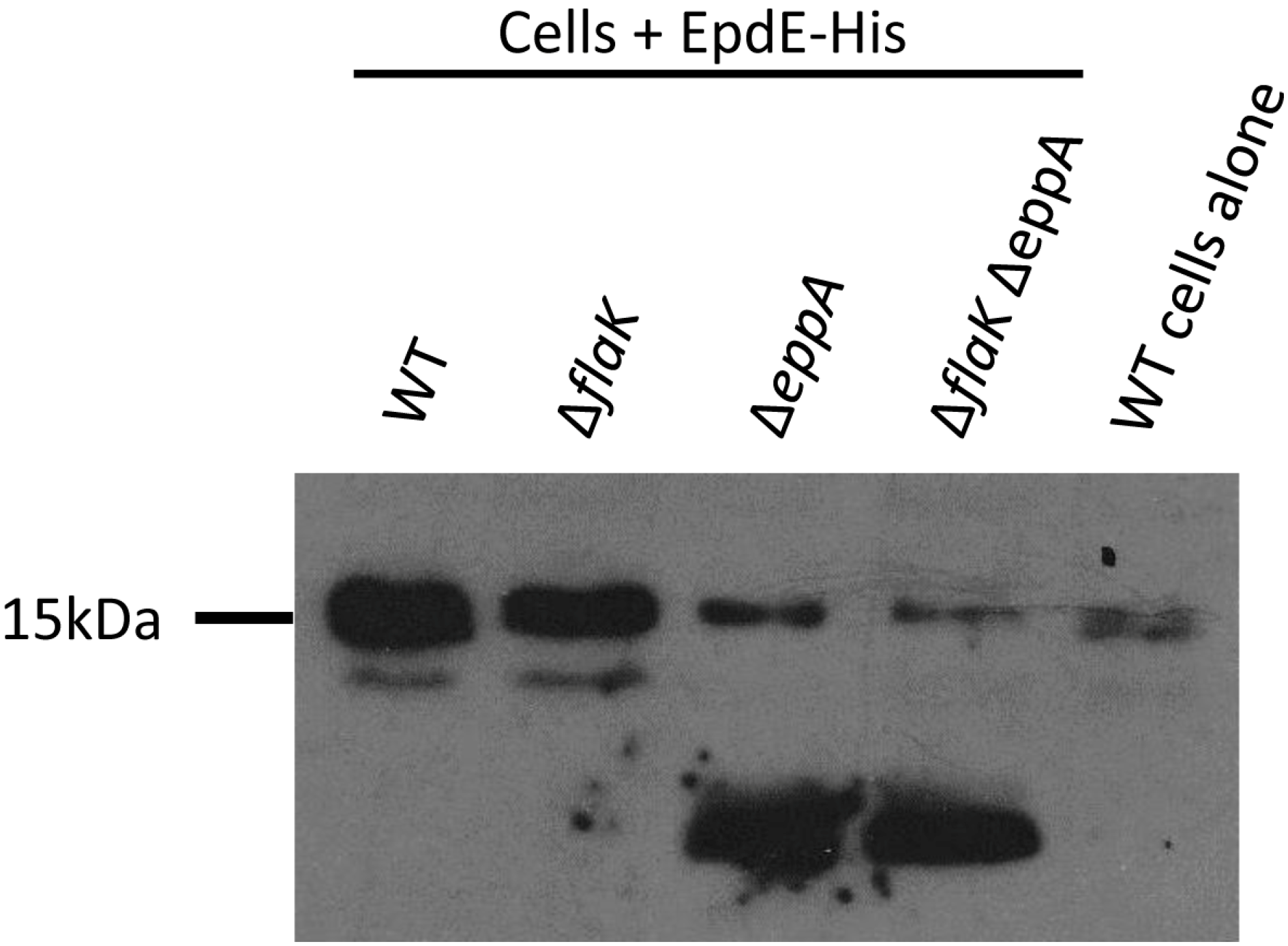
3.2. Posttranslational Modifications of Native EpdE in Various Mutant Strains
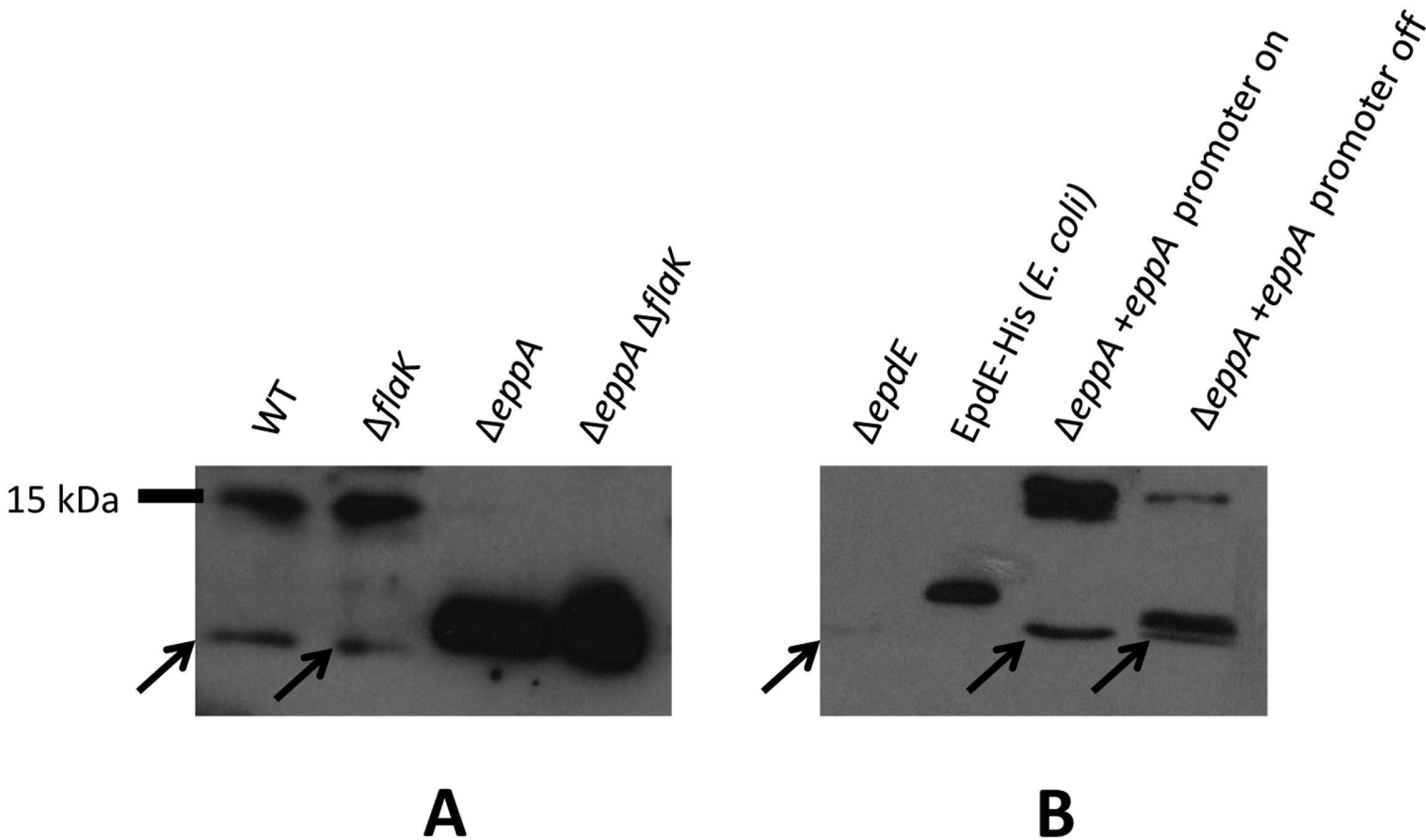
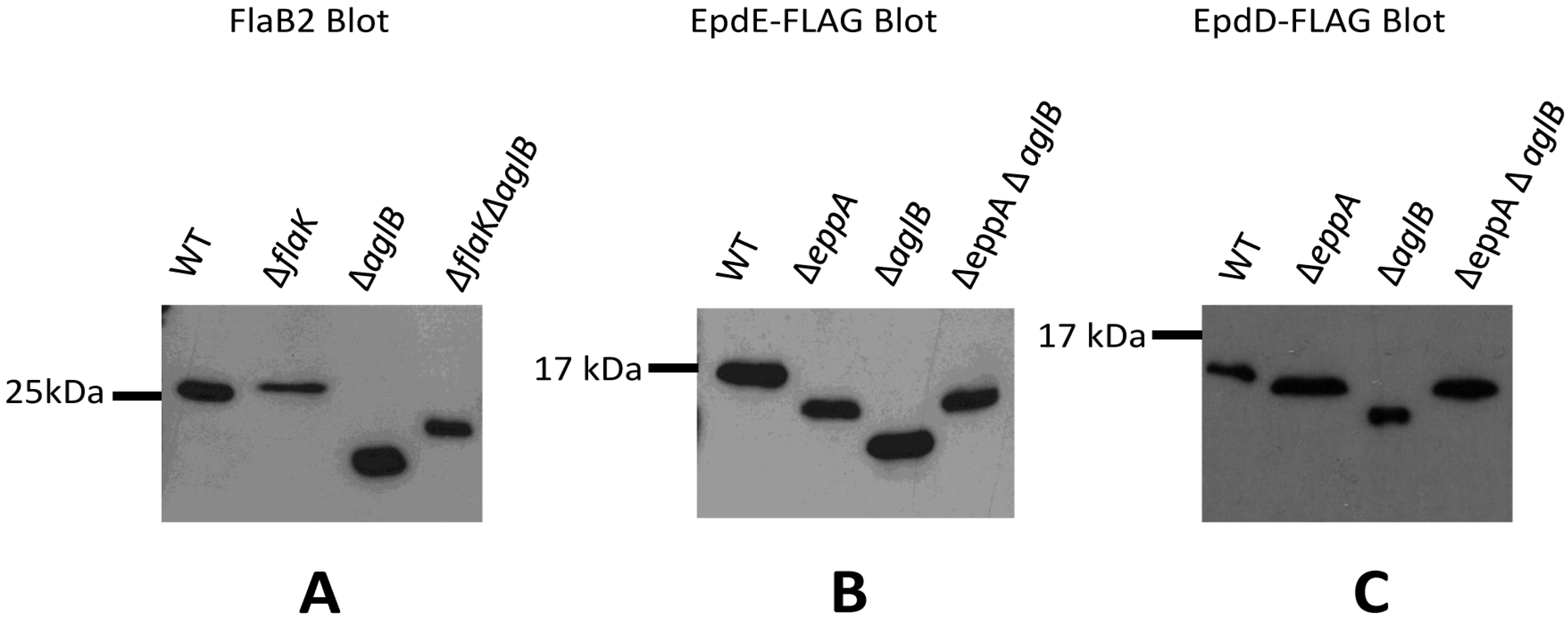
3.3. Signal Peptide Removal Is a Prerequisite for N-glycosylation of Pilins but Not Archaellins
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarrell, K.F.; Ding, Y.; Meyer, B.H.; Albers, S.V.; Kaminski, L.; Eichler, J. N-linked glycosylation in Archaea: A structural, functional, and genetic analysis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 304–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, K.F.; Ding, Y.; Nair, D.B.; Siu, S. Surface appendages of Archaea: Structure, function, genetics and assembly. Life 2013, 3, 86–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, K.F. The Archaeal Flagellum: A Novel Prokaryotic Motility Structure and the Role of Posttranslational Modifications in Its Assembly and Function. In Archaea: Structure, Habitats and Ecological Significance; Kata, S.Y., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell, K.F.; VanDyke, D.J.; Wu, J. Archaeal Flagella and Pili. In Pili and Flagella: Current Research and Future Trends; Jarrell, K.F., Ed.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Tumbula, D.L.; Whitman, W.B. Genetics of Methanococcus: Possibilities for functional genomics in Archaea. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumbula, D.L.; Makula, R.A.; Whitman, W.B. Transformation of Methanococcus maripaludis and identification of a Pst I-like restriction system. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 121, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.C.; Leigh, J.A. Markerless mutagenesis in Methanococcus maripaludis demonstrates roles for alanine dehydrogenase, alanine racemase, and alanine permease. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, E.L.; Kaul, R.; Zhou, Y.; Bovee, D.; Chapman, P.; Chung, J.; Conway de Macario, E.; Dodsworth, J.A.; Gillett, W.; Graham, D.E.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the genetically tractable hydrogenotrophic methanogen Methanococcus maripaludis. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 6956–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.A.; Albers, S.V.; Atomi, H.; Allers, T. Model organisms for genetics in the domain Archaea: Methanogens, halophiles, Thermococcales and Sulfolobales. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 577–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, K.F.; Albers, S.V. The archaellum: An old motility structure with a new name. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, K.F.; Stark, M.; Nair, D.B.; Chong, J.P.J. Flagella and pili are both necessary for efficient attachment of Methanococcus maripaludis to surfaces. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 319, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.Y.M.; Wu, J.; Nair, D.B.; Logan, S.M.; Robotham, A.; Tessier, L.; Kelly, J.F.; Uchida, K.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Genetic and mass spectrometry analysis of the unusual type IV-like pili of the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.B.; Uchida, K.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Genetic analysis of a type IV pili-like locus in the archaeon Methanococcus mariplaudis. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.B.; Chung, D.K.C.; Schneider, J.; Uchida, K.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of an additional minor pilin essential for piliation in the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassak, K.; Ghosh, A.; Albers, S.V. Diversity, assembly and regulation of archaeal type IV pili-like and non-type-IV pili-like surface structures. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, L.L. Weapons of mass retraction. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.Y.; Chaban, B.; VanDyke, D.J.; Jarrell, K.F. Archaeal signal peptidases. Microbiology 2007, 153, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardy, S.L.; Jarrell, K.F. FlaK of the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis possesses preflagellin peptidase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 208, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardy, S.L.; Jarrell, K.F. Cleavage of preflagellins by an aspartic acid signal peptidase is essential for flagellation in the archaeon Methanococcus voltae. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, S.V.; Szabo, Z.; Driessen, A.J.M. Archaeal homolog of bacterial type IV prepilin signal peptidases with broad substrate specificity. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3918–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, Z.; Stahl, A.O.; Albers, S.V.; Kissinger, J.C.; Driessen, A.J.M.; Pohlschroder, M. Identification of diverse archaeal proteins with class III signal peptides cleaved by distinct archaeal prepilin peptidases. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripepi, M.; Imam, S.; Pohlschroder, M. Haloferax volcanii flagella are required for motility but are not involved in PibD-dependent surface adhesion. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquivel, R.N.; Xu, R.; Pohlschroder, M. Novel archaeal adhesion pilins with a conserved N terminus. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 17, 3808–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henche, A.L.; van Wolferen, M.; Ghosh, A.; Albers, S.V. Dissection of key determinants of cleavage activity in signal peptidase III (SPaseIII) PibD. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patenge, N.; Berendes, A.; Engelhardt, H.; Schuster, S.C.; Oesterhelt, D. The fla gene cluster is involved in the biogenesis of flagella in Halobacterium salinarum. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.A.; Mueller, S.; Klein, A.; Jarrell, K.F. Mutants in flaI and flaJ of the archaeon Methanococcus voltae are deficient in flagellum assembly. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Albers, S.V. Assembly and function of the archaeal flagellum. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassak, K.; Neiner, T.; Ghosh, A.; Klingl, A.; Wirth, R.; Albers, S.V. Molecular analysis of the crenarchaeal flagellum. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, S.V.; Pohlschroder, M. Diversity of archaeal type IV pilin-like structures. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaban, B.; Ng, S.Y.; Kanbe, M.; Saltzman, I.; Nimmo, G.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Systematic deletion analyses of the fla genes in the flagella operon identify several genes essential for proper assembly and function of flagella in the archaeon, Methanococcus maripaludis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Hartung, S.; van der Does, C.; Tainer, J.A.; Albers, S.V. Archaeal flagellar ATPase motor shows ATP-dependent hexameric assembly and activity stimulation by specific lipid binding. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Ghosh, A.; Mills, D.J.; Kahnt, J.; Vonck, J.; Albers, S.V. FlaX, a unique component of the crenarchaeal archaellum, forms oligomeric ring-shaped structures and interacts with the motor ATPase FlaI. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43322–43330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.; Logan, S.M.; Jarrell, K.F.; Vandyke, D.J.; Vinogradov, E. A novel N-linked flagellar glycan from Methanococcus maripaludis. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandyke, D.J.; Wu, J.; Logan, S.M.; Kelly, J.F.; Mizuno, S.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of genes involved in the assembly and attachment of a novel flagellin N-linked tetrasaccharide important for motility in the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 72, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.Y.; VanDyke, D.J.; Chaban, B.; Wu, J.; Nosaka, Y.; Aizawa, S.; Jarrell, K.F. Different minimal signal peptide lengths recognized by the archaeal prepilin-like peptidases FlaK and PibD. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6732–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDyke, D.J.; Wu, J.; Ng, S.Y.; Kanbe, M.; Chaban, B.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of putative acetyltransferase gene, MMP0350, which affects proper assembly of both flagella and pili in the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 5300–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Jones, G.M.; Uchida, K.; Aizawa, S.I.; Robotham, A.; Logan, S.M.; Kelly, J.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of genes involved in the biosynthesis of the third and fourth sugars of the Methanococcus maripaludis archaellin N-linked tetrasaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 4094–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.M.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Uchida, K.; Aizawa, S.; Robotham, A.; Logan, S.M.; Kelly, J.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of genes involved in the acetamidino group modification of the flagellin N-linked glycan of Methanococcus maripaludis. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.A.; Chao, E.D.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of amino acids in the leader peptide of Methanococcus voltae preflagellin that are important in posttranslational processing. Arch. Microbiol. 2001, 175, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balch, W.E.; Fox, G.E.; Magrum, L.J.; Woese, C.R.; Wolfe, R.S. Methanogens: Reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol. Rev. 1979, 43, 260–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gardner, W.L.; Whitman, W.B. Expression vectors for Methanococcus maripaludis: Overexpression of acetohydroxyacid synthase and beta-galactosidase. Genetics 1999, 152, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lie, T.J.; Wood, G.E.; Leigh, J.A. Regulation of nif expression in Methanococcus maripaludis: Roles of the euryarchaeal repressor NrpR, 2-oxoglutarate, and two operators. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5236–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, S.; Speicher, D.W. Detection of proteins on blot membranes. Curr. Protocol. Prot. Sci. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardy, S.L.; Ng, S.Y.; Jarrell, K.F. Recent advances in the structure and assembly of the archaeal flagellum. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 7, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.A.; Bardy, S.L.; Jarrell, K.F. The archaeal flagellum: A different kind of prokaryotic motility structure. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaban, B.; Voisin, S.; Kelly, J.; Logan, S.M.; Jarrell, K.F. Identification of genes involved in the biosynthesis and attachment of Methanococcus voltae N-linked glycans: Insight into N-linked glycosylation pathways in Archaea. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horzempa, J.; Comer, J.E.; Davis, S.A.; Castric, P. Glycosylation substrate specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1244 pilin. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voisin, S.; Houliston, R.S.; Kelly, J.; Brisson, J.R.; Watson, D.; Bardy, S.L.; Jarrell, K.F.; Logan, S.M. Identification and characterization of the unique N-linked glycan common to the flagellins and S-layer glycoprotein of Methanococcus voltae. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16586–16593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, L.; Naparstek, S.; Kandiba, L.; Cohen-Rosenzweig, C.; Arbiv, A.; Konrad, Z.; Eichler, J. Add salt, add sugar: N-glycosylation in Haloferax volcanii. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripepi, M.; You, J.; Temel, S.; Önder, Ö.; Brisson, D.; Pohlschröder, M. N-glycosylation of Haloferax volcanii flagellins requires known Agl proteins and is essential for biosynthesis of stable flagella. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4876–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, J.; Sumper, M. The primary structure of a procaryotic glycoprotein. Cloning and sequencing of the cell surface glycoprotein gene of halobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9724–9729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieland, F. Structure and biosynthesis of prokaryotic glycoproteins. Biochimie 1988, 70, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, F.; Paul, G.; Sumper, M. Halobacterial flagellins are sulfated glycoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 15180–15185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sumper, M. Halobacterial glycoprotein biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 906, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, J.; Sumper, M. Structure and biosynthesis of prokaryotic glycoproteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1989, 58, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, L.; Guan, Z.; Yurist-Doutsch, S.; Eichler, J. Two distinct N-glycosylation pathways process the Haloferax volcanii S-layer glycoprotein upon changes in environmental salinity. mBio 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, G.; Köhler, R.; Larquet, E.; Giroux, S.; Prévost, M.C.; Roux, P.; Pugsley, A.P. Type IV-like pili formed by the type II secreton: Specificity, composition, bundling, polar localization, and surface presentation of peptides. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3416–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; McCarter, L.L. Cross-regulation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Compensatory activation of polar flagellar genes by the lateral flagellar regulator LafK. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 4014–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, P.; Habash, M.; Burrows, L.L. Disparate subcellular localization patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type IV pilus ATPases involved in twitching motility. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keilberg, D.; Søgaard-Andersen, L. Regulation of bacterial cell polarity by small GTPases. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, J. Localizing the subunit pool for the temporally regulated polar pili of Caulobacter crescentus. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, A.J.; Larson, D.E.; Smith, C.S.; Brun, Y.V. The Caulobacter crescentus polar organelle development protein PodJ is differentially localized and is required for polar targeting of the PleC development regulator. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardy, S.L.; Maddock, J.R. Polar explorations. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, M. Shape, polarity, and multicellular morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nair, D.B.; Jarrell, K.F. Pilin Processing Follows a Different Temporal Route than That of Archaellins in Methanococcus maripaludis. Life 2015, 5, 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010085
Nair DB, Jarrell KF. Pilin Processing Follows a Different Temporal Route than That of Archaellins in Methanococcus maripaludis. Life. 2015; 5(1):85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleNair, Divya B., and Ken F. Jarrell. 2015. "Pilin Processing Follows a Different Temporal Route than That of Archaellins in Methanococcus maripaludis" Life 5, no. 1: 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010085
APA StyleNair, D. B., & Jarrell, K. F. (2015). Pilin Processing Follows a Different Temporal Route than That of Archaellins in Methanococcus maripaludis. Life, 5(1), 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010085





