Loss of Dab1 Alters Expression Patterns of Endocytic and Signaling Molecules During Embryonic Lung Development in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Megalin Expression
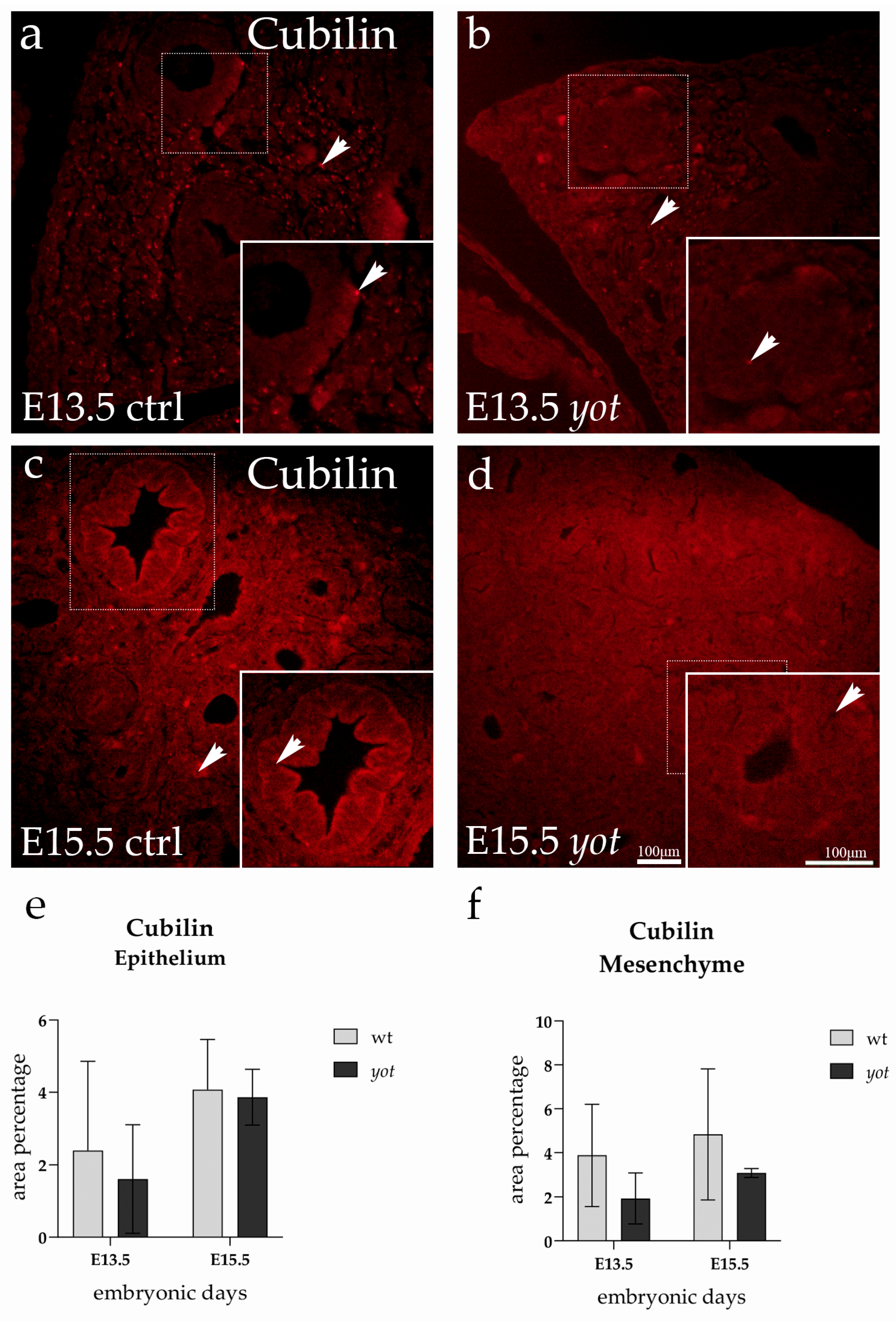
3.2. Cubilin Expression
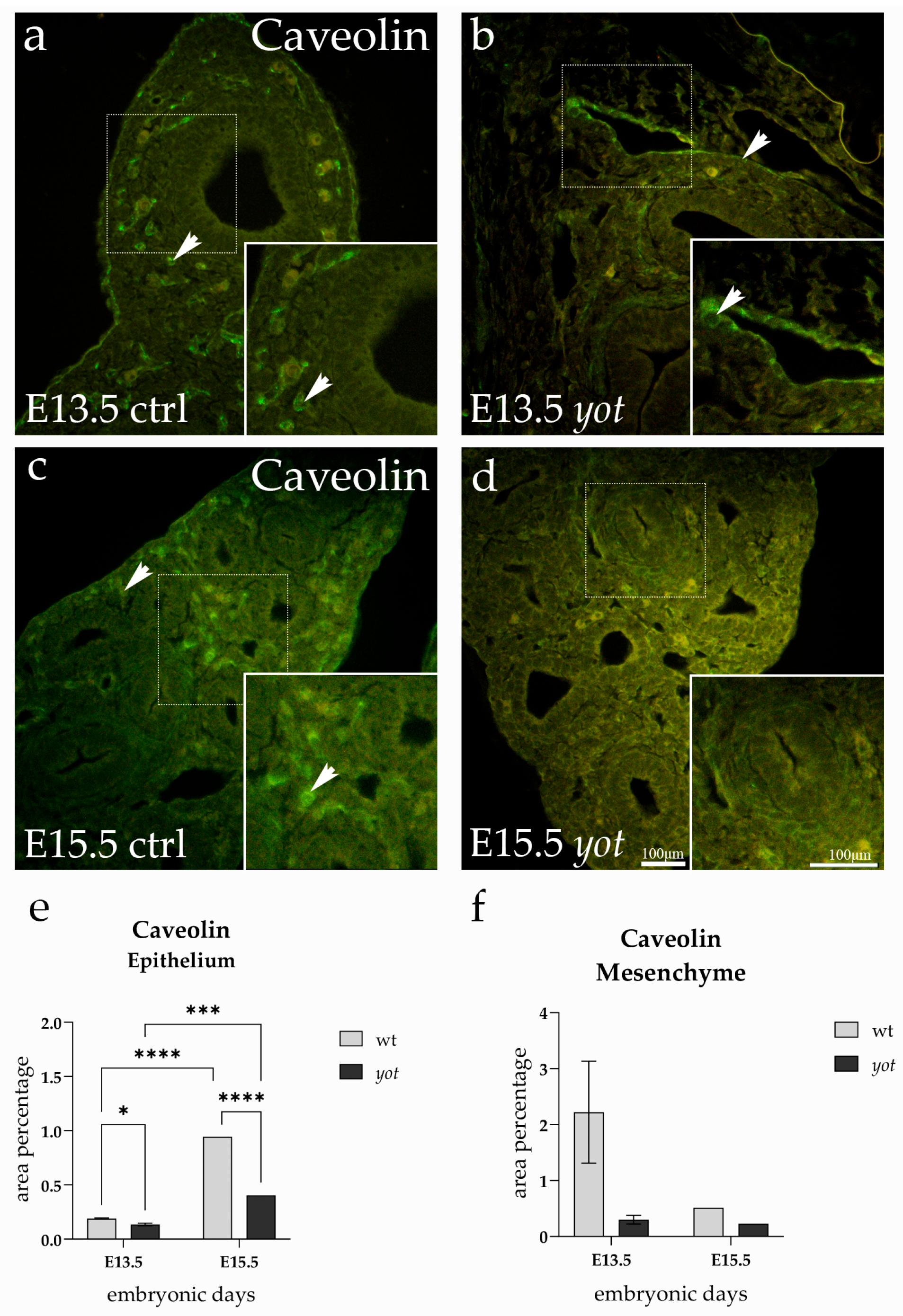
3.3. Caveolin Expression
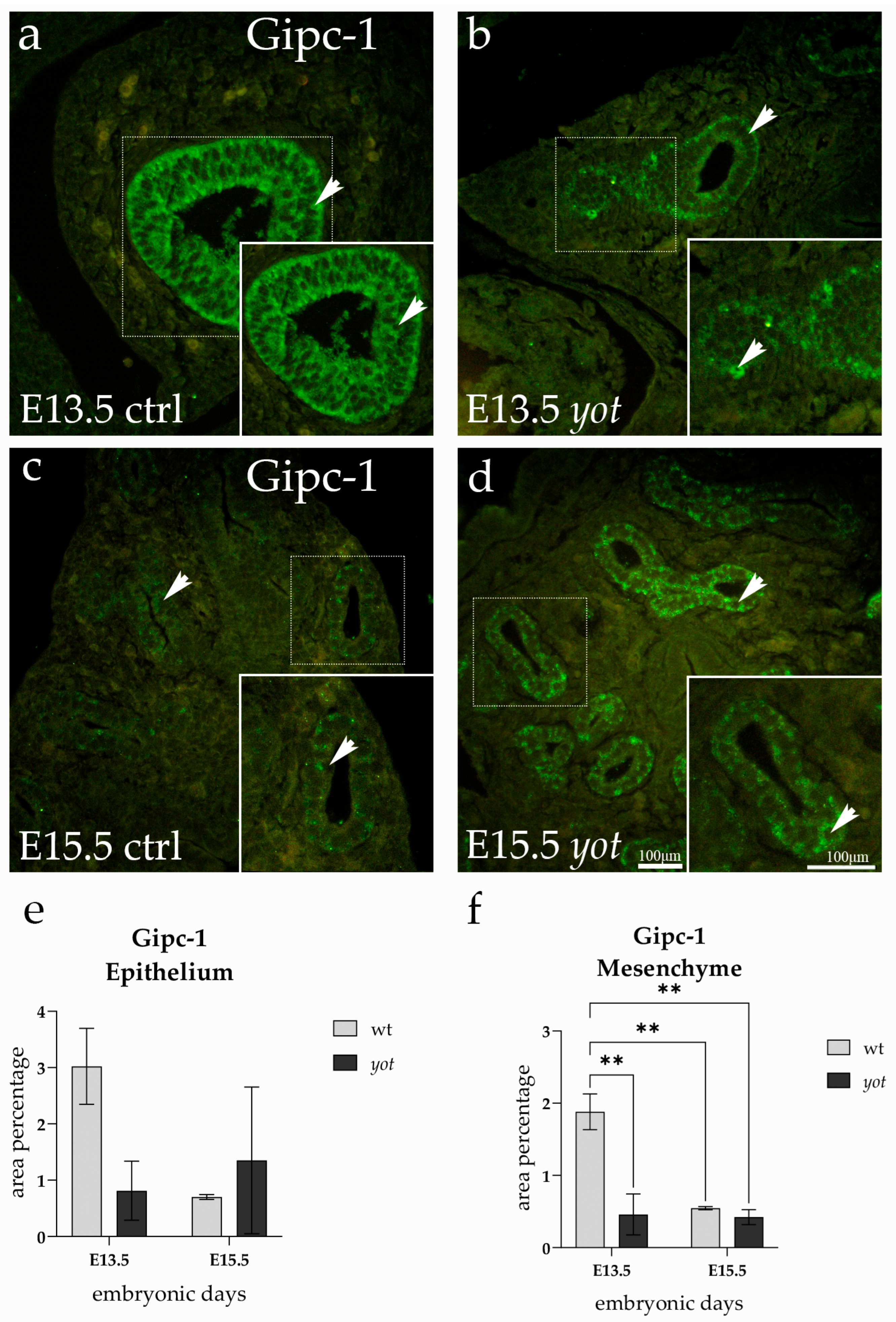
3.4. GIPC1 Expression
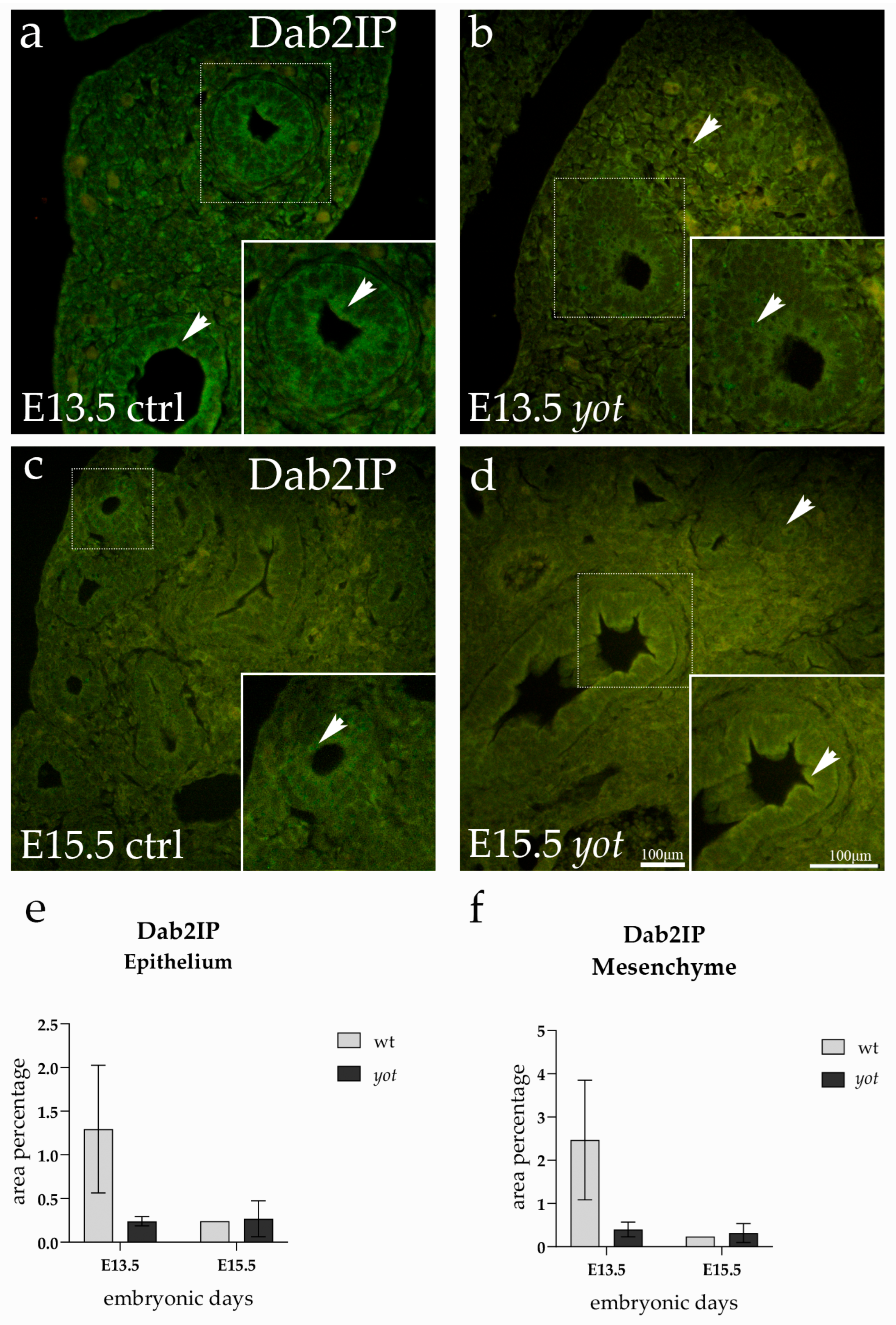
3.5. Dab2IP Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herriges, M.; Morrisey, E.E. Lung development: Orchestrating the generation and regeneration of a complex organ. Development 2014, 141, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.; El-Hashash, A.; Carraro, G.; Tiozzo, C.; Sala, F.; Rogers, O.; De Langhe, S.; Kemp, P.J.; Riccardi, D.; Torday, J.; et al. Lung organogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2010, 90, 73–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokel, C.; Brand, M. Endocytosis and signaling during development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a017020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, B.; Suzanne, M. The Morphogenetic Role of Apoptosis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 114, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauler, M.; Bazan, I.S.; Lee, P.J. Cell Death in the Lung: The Apoptosis-Necroptosis Axis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartis, D.; Mise, N.; Mahida, R.Y.; Eickelberg, O.; Thickett, D.R. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung development and disease: Does it exist and is it important? Thorax 2014, 69, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, Y.; Setsu, T.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kikkawa, S.; Terashima, T.; Maeda, K. Cortical layer V neurons in the auditory and visual cortices of normal, reeler, and yotari mice. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2010, 56, E50–E59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoneshima, H.; Nagata, E.; Matsumoto, M.; Yamada, M.; Nakajima, K.; Miyata, T.; Ogawa, M.; Mikoshiba, K. A novel neurological mutant mouse, yotari, which exhibits reeler-like phenotype but expresses CR-50 antigen/reelin. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 29, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglica, M.; Kelam, N.; Haque, E.; Perutina, I.; Racetin, A.; Filipovic, N.; Katsuyama, Y.; Vukojevic, K. Immunoexpression Pattern of Autophagy Markers in Developing and Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1(−/−)(yotari) Mice. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racetin, A.; Juric, M.; Filipovic, N.; Solic, I.; Kosovic, I.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Kunac, N.; Zekic Tomas, S.; Saraga, M.; Soljic, V.; et al. Expression and localization of DAB1 and Reelin during normal human kidney development. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.; Kelam, N.; Racetin, A.; Filipovic, N.; Pogorelic, Z.; Prusac, I.K.; Vukojevic, K. Expression Profiles of ITGA8 and VANGL2 Are Altered in Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT). Molecules 2024, 29, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizikalo, A.; Maglica, M.; Kelam, N.; Perutina, I.; Ogorevc, M.; Racetin, A.; Filipovic, N.; Katsuyama, Y.; Zovko, Z.; Miskovic, J.; et al. Unraveling the Impact of Dab1 Gene Silencing on the Expression of Autophagy Markers in Lung Development. Life 2024, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.E.; Howie, S.E. The role of megalin (LRP-2/Gp330) during development. Dev. Biol. 2006, 296, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchackert, Y.; Rummel, S.; Vohwinkel, C.U.; Gabrielli, N.M.; Grzesik, B.A.; Mayer, K.; Herold, S.; Morty, R.E.; Seeger, W.; Vadasz, I. Megalin mediates transepithelial albumin clearance from the alveolar space of intact rabbit lungs. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 5167–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Christensen, E.I.; Birn, H. Megalin and cubilin in proximal tubule protein reabsorption: From experimental models to human disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarci, S.; Al-Gazali, L.; Hill, R.S.; Donnai, D.; Black, G.C.; Bieth, E.; Chassaing, N.; Lacombe, D.; Devriendt, K.; Teebi, A.; et al. Mutations in LRP2, which encodes the multiligand receptor megalin, cause Donnai-Barrow and facio-oculo-acoustico-renal syndromes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniatis, N.A.; Chernaya, O.; Shinin, V.; Minshall, R.D. Caveolins and lung function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 729, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Saux, O.; Teeters, K.; Miyasato, S.; Choi, J.; Nakamatsu, G.; Richardson, J.A.; Starcher, B.; Davis, E.C.; Tam, E.K.; Jourdan-Le Saux, C. The role of caveolin-1 in pulmonary matrix remodeling and mechanical properties. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L1007–L1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Huang, F.; Nong, W.; Lao, D.; Gong, Z.; Huang, W. N-methyl-D-aspartic acid increases tight junction protein destruction in brain endothelial cell via caveolin-1-associated ERK1/2 signaling. Toxicology 2022, 470, 153139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zheng, S.; Wang, M.; Yuan, X. The critical roles of caveolin-1 in lung diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1417834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Shen, W.J.; Azhar, S.; Qu, Y.F.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z. The adaptor protein GIPC1 stabilizes the scavenger receptor SR-B1 and increases its cholesterol uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhong, W.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.I.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Lv, H.; Wang, S.; Yan, J.; et al. GIPC1 promotes tumor growth and migration in gastric cancer via activating PDGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncol. Res. 2023, 32, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Ortega, J.; Chhangawala, Z.; Hunt, S.; Narvaez, C.; Menendez-Gonzalez, J.; Gay, C.M.; Zygmunt, T.; Li, X.; Torres-Vazquez, J. GIPC proteins negatively modulate Plexind1 signaling during vascular development. eLife 2019, 8, e30454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Functional proteomics, human genetics and cancer biology of GIPC family members. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Gore, C.; Zhou, J.; Pong, R.C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Vessella, R.L.; Min, W.; Hsieh, J.T. DAB2IP coordinates both PI3K-Akt and ASK1 pathways for cell survival and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19878–19883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Perurena, N.; Gardner, A.; Hinoue, T.; Loi, P.; Laird, P.W.; Cichowski, K. DAB2IP Is a Bifunctional Tumor Suppressor That Regulates Wild-Type RAS and Inflammatory Cascades in KRAS Mutant Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; North, B.J.; Inuzuka, H. Negative regulation of DAB2IP by Akt and SCFFbw7 pathways. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, G.; Arcoleo, G.; Bucchieri, F.; Montalbano, A.M.; Marchese, R.; Albano, G.D.; Di Sano, C.; Moscato, M.; Gagliardo, R.; Ricciardolo, F.L.M.; et al. Cigarette smoke affects the onco-suppressor DAB2IP expression in bronchial epithelial cells of COPD patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, S.; Kim, S.H.; Heck, D.; Goldowitz, D.; LeDoux, M.S.; Homayouni, R. Dab2IP GTPase activating protein regulates dendrite development and synapse number in cerebellum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayouni, R.; Magdaleno, S.; Keshvara, L.; Rice, D.S.; Curran, T. Interaction of Disabled-1 and the GTPase activating protein Dab2IP in mouse brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 115, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.K.; Hwang, D.Y. Use of C57BL/6N mice on the variety of immunological researches. Lab. Anim. Res. 2017, 33, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Shoji, H.; Ogata, M.; Kagawa, Y.; Owada, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Sakimura, K.; Terashima, T.; Katsuyama, Y. Dorsal Forebrain-Specific Deficiency of Reelin-Dab1 Signal Causes Behavioral Abnormalities Related to Psychiatric Disorders. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 3485–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavic, B.; Ogorevc, M.; Boric, K.; Vukovic, D.; Saraga-Babic, M.; Mardesic, S. Connexin 37, 40, 43 and Pannexin 1 Expression in the Gastric Mucosa of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisey, E.E.; Hogan, B.L. Preparing for the first breath: Genetic and cellular mechanisms in lung development. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.H.; May, P. Canonical and Non-canonical Reelin Signaling. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, E.I.; Birn, H. Megalin and cubilin: Multifunctional endocytic receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohwinkel, C.U.; Buchackert, Y.; Al-Tamari, H.M.; Mazzocchi, L.C.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Mayer, K.; Morty, R.E.; Herold, S.; Seeger, W.; Pullamsetti, S.S.; et al. Restoration of Megalin-Mediated Clearance of Alveolar Protein as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yammani, R.R.; Seetharam, S.; Seetharam, B. Cubilin and megalin expression and their interaction in the rat intestine: Effect of thyroidectomy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E900–E907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.R.; Robinson, J.Y.; Sanchez, N.S.; Townsend, T.A.; Arrieta, J.A.; Merryman, W.D.; Trykall, D.Z.; Olivey, H.E.; Hong, C.C.; Barnett, J.V. Common pathways regulate Type III TGFbeta receptor-dependent cell invasion in epicardial and endocardial cells. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, C.; Hsieh, J.T.; Gong, J.; Xie, D. DAB2IP in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3766–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drab, M.; Verkade, P.; Elger, M.; Kasper, M.; Lohn, M.; Lauterbach, B.; Menne, J.; Lindschau, C.; Mende, F.; Luft, F.C.; et al. Loss of caveolae, vascular dysfunction, and pulmonary defects in caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice. Science 2001, 293, 2449–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parton, R.G.; del Pozo, M.A. Caveolae as plasma membrane sensors, protectors and organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shihata, W.A.; Putra, M.R.A.; Chin-Dusting, J.P.F. Is There a Potential Therapeutic Role for Caveolin-1 in Fibrosis? Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, H.P.; Zhou, Z.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Liu, F.; Ifedigbo, E.; Xu, X.; Oury, T.D.; Kaminski, N.; et al. Caveolin-1: A critical regulator of lung fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2895–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibodies | Host | Dilution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Anti-Lrp2/Megalin antibody | Rabbit | 1:250 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| Human/Mouse/Rat Cubilin Antibody (#AF3700) | Sheep | 1:50 | R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA | |
| Caveolin-1 (D46G3) XP® Rabbit mAb (#3267S) | Rabbit | 1:300 | Cell Signaling Technology (CST), Danvers, MA, USA | |
| Gipc1 Polyclonal antibody (14822-1-AP) | Rabbit | 1:100 | Proteintech Group, Inc., Rosemont, IL, USA | |
| Dab2IP Polyclonal antibody (23582-1-AP) | Rabbit | 1:50 | Proteintech Group, Inc., Rosemont, IL, USA | |
| Secondary | Alexa Fluor® 488 AffiniPureTM Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) (711-545-152) | Donkey | 1:300 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc., West Groove, PA, USA |
| Rhodamine RedTM-X (RRX) AffiniPureTM Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) (711-295-152) | Donkey | 1:300 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc., West Groove, PA, USA | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todorović, P.; Maglica, M.; Kelam, N.; Filipović, N.; Rizikalo, A.; Perutina, I.; Mišković, J.; Katsuyama, Y.; Vukojević, K. Loss of Dab1 Alters Expression Patterns of Endocytic and Signaling Molecules During Embryonic Lung Development in Mice. Life 2025, 15, 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091395
Todorović P, Maglica M, Kelam N, Filipović N, Rizikalo A, Perutina I, Mišković J, Katsuyama Y, Vukojević K. Loss of Dab1 Alters Expression Patterns of Endocytic and Signaling Molecules During Embryonic Lung Development in Mice. Life. 2025; 15(9):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091395
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodorović, Petar, Mirko Maglica, Nela Kelam, Natalija Filipović, Azer Rizikalo, Ilija Perutina, Josip Mišković, Yu Katsuyama, and Katarina Vukojević. 2025. "Loss of Dab1 Alters Expression Patterns of Endocytic and Signaling Molecules During Embryonic Lung Development in Mice" Life 15, no. 9: 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091395
APA StyleTodorović, P., Maglica, M., Kelam, N., Filipović, N., Rizikalo, A., Perutina, I., Mišković, J., Katsuyama, Y., & Vukojević, K. (2025). Loss of Dab1 Alters Expression Patterns of Endocytic and Signaling Molecules During Embryonic Lung Development in Mice. Life, 15(9), 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091395








