New Characterization of Lipedema Stages: Focus on Pain, Water, Fat and Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Chart Review
2.2. Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS)
2.3. Hypothermia
2.4. Skeletal Muscle Mass Index (SMMI)
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic of Lipedema Stages
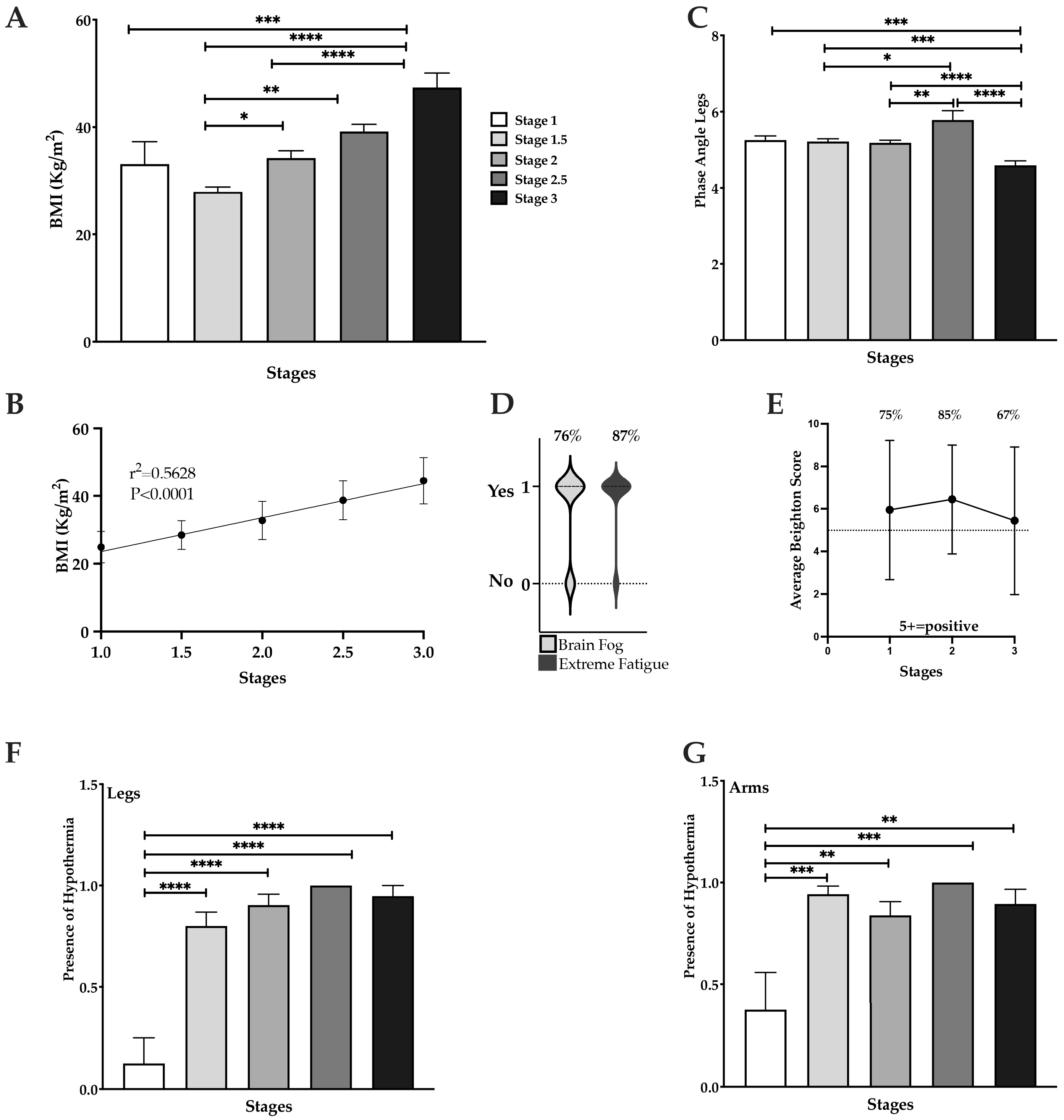
3.2. BMI Significantly Increases in Stages 2 and 3
3.3. High Prevalence of Fatigue, Brain Fog, Hypermobility, and Hypothermia in Lipedema
3.4. Pain, Swelling and Heaviness in Lipedema
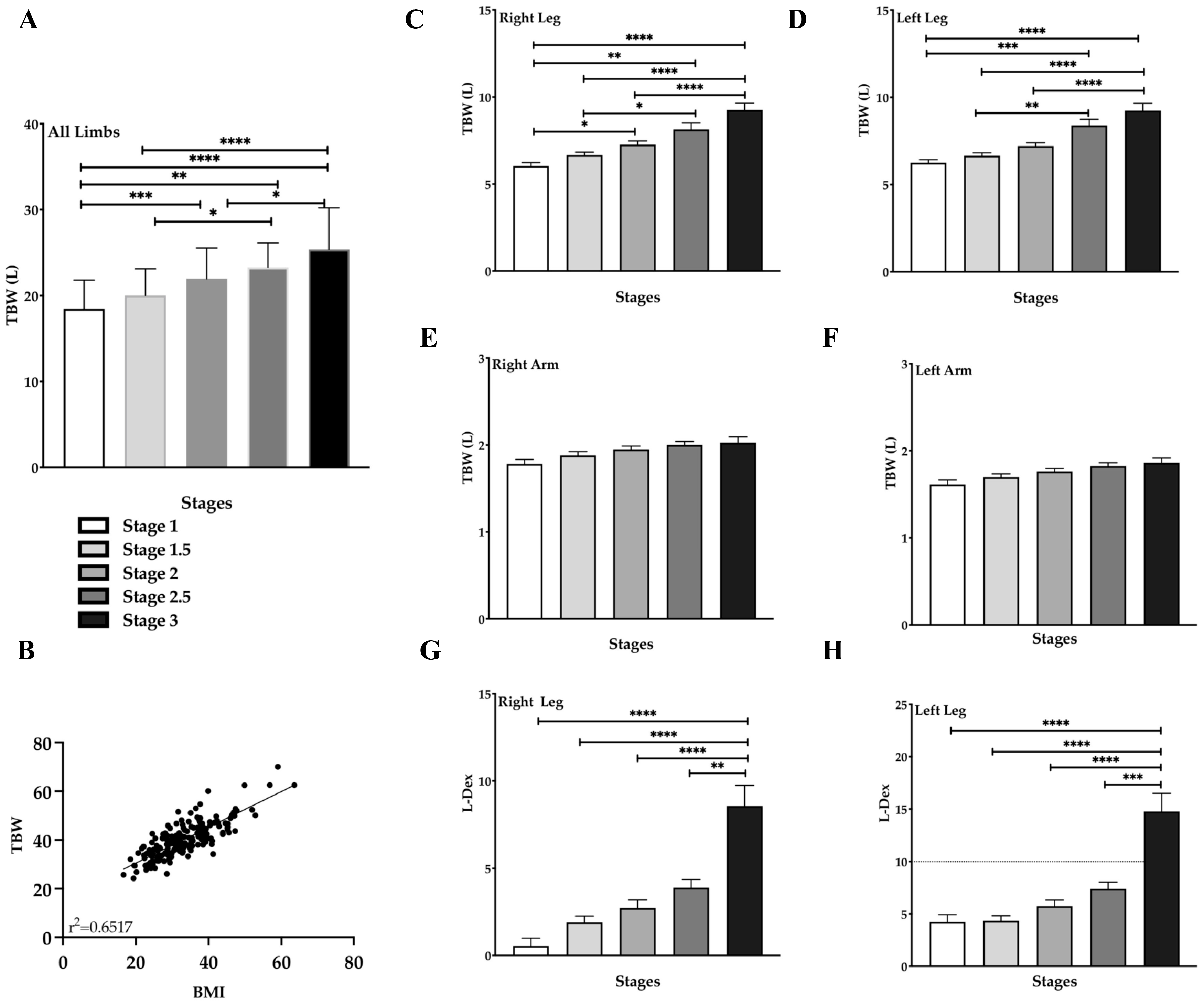
3.5. Leg Fat Increases with Advancing Stages of Lipedema
3.6. Total Body Water (TBW) Increases with Stage in Lipedema Tissue
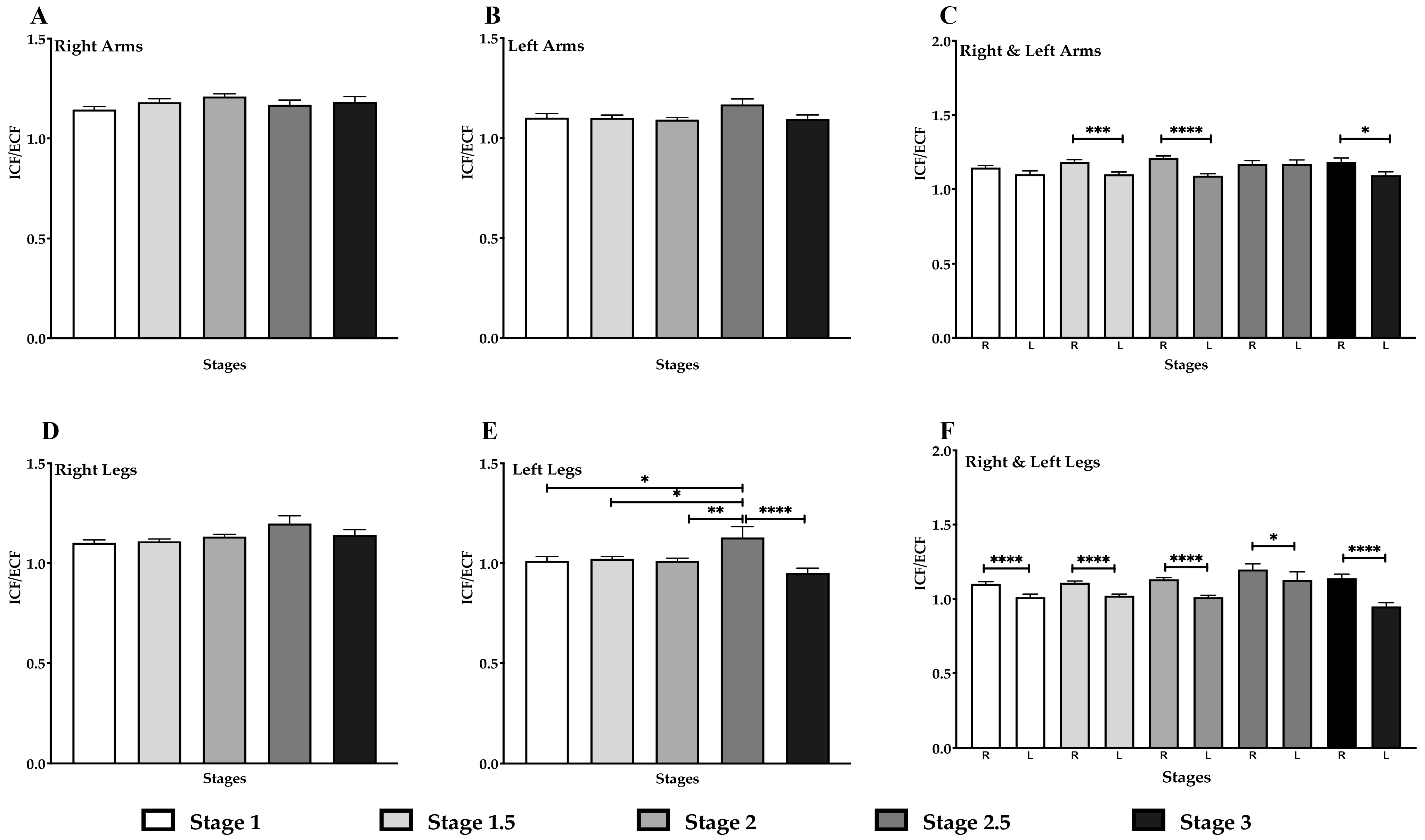
3.7. Decrease in ICF/ECF in the Left Arm & Legs in Lipedema Stage
3.8. Skeletal Muscle Mass (SMM) Increases with Fat Mass in Lipedema Stage 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herbst, K.L.; Kahn, L.A.; Iker, E.; Ehrlich, C.; Wright, T.; McHutchison, L.; Schwartz, J.; Sleigh, M.; MC Donahue, P.; Lisson, K.H.; et al. Standard of Care for lipedema in the United States. Phlebology 2021, 36, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, G.; Paoli, A.; Manzi, V.; Camajani, E.; Laterza, F.; Verde, L.; Capó, X.; Padua, E.; Bianco, A.; Carraro, A.; et al. The Role of Physical Exercise as a Therapeutic Tool to Improve Lipedema: A Consensus Statement from the Italian Society of Motor and Sports Sciences (Società Italiana di Scienze Motorie e Sportive, SISMeS) and the Italian Society of Phlebology (Società Italiana di Flebologia, SIF). Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhon, B.H.; Phan, T.T.; Taylor, S.L.; Crescenzi, R.L.; Rutkowski, J.M. Current Mechanistic Understandings of Lymphedema and Lipedema: Tales of Fluid, Fat, and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poojari, A.; Dev, K.; Rabiee, A. Lipedema: Insights into Morphology, Pathophysiology, and Challenges. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruppa, P.; Georgiou, I.; Biermann, N.; Prantl, L.; Klein-Weigel, P.; Ghods, M. Lipedema-Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Crescenzi, R.; Usman, T.A.; Reyna, A.J.; Garza, M.E.; Al-Ghadban, S.; Herbst, K.L.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Rutkowski, J.M. Indications of Peripheral Pain, Dermal Hypersensitivity, and Neurogenic Inflammation in Patients with Lipedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, A.A.W.; Kappos, E. Lipedema: Diagnostic and management challenges. Int. J. Women’s Heal. 2016, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okhovat, J.P.; Alavi, A. Lipedema: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2015, 14, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R. Lipedema: A common though often unrecognized condition. Chin. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 6, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buso, G.; Depairon, M.; Tomson, D.; Raffoul, W.; Vettor, R.; Mazzolai, L. Lipedema: A Call to Action! Obesity 2019, 27, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.C.; Aldrich, M.B.; Fife, C.E.; Herbst, K.L.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M. Lymphatic function and anatomy in early stages of lipedema. Obesity 2022, 30, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, J.; Kelly-Hope, L. Comparison of Staging Systems to Assess Lymphedema Caused by Cancer Therapies, Lymphatic Filariasis, and Podoconiosis. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2019, 17, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzová, M.; Lagová, E.; Keith, L. Mental and physical health burden and quality of life in Czech women with lipedema. Front. Glob. Women’s Heal. 2025, 6, 1629077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Gabriel, M. Quality of life, its factors, and sociodemographic characteristics of Polish women with lipedema. BMC Women’s Health 2021, 21, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, T.F.; Herbst, K.L. A Young Woman with Excessive Fat in Lower Extremities Develops Disordered Eating and Is Subsequently Diagnosed with Anorexia Nervosa, Lipedema, and Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e930840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.; Schwartz, M.; Herbst, K.L. Interstitial Fluid in Lipedema and Control Skin. Women’s Heal. Rep. 2020, 1, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Donahue, P.M.; Petersen, K.J.; Garza, M.; Patel, N.; Lee, C.; Beckman, J.A.; Donahue, M.J. Upper and Lower Extremity Measurement of Tissue Sodium and Fat Content in Patients with Lipedema. Obesity 2020, 28, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L.; Zelaya, C.; Sommerville, M.; Zimmerman, T.; McHutchison, L. An Advanced Pneumatic Compression Therapy System Improves Leg Volume and Fluid, Adipose Tissue Thickness, Symptoms, and Quality of Life and Reduces Risk of Lymphedema in Women with Lipedema. Life 2025, 15, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmer, M.; Schingale, F.J. Intracellular and Extracellular Water Balance in Patients with Lipedema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2023, 21, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, L.E.; Hines, E.A., Jr.; Allen, E.V. Lipedema of the legs; a syndrome characterized by fat legs and edema. Ann. Intern. Med. 1951, 34, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beighton, P.; Grahame, R.; Bird, H. Assessment of Hypermobility. In Hypermobility of Joints; Beighton, P., Grahame, R., Bird, H., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rio, C.J.; Gehling, G.M.; Blumhorst, C.; Ross, A.; Saligan, L.N. Defining fatigue from the experiences of patients living with chronic fatigue. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1429275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Stewart, J.M.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Kolaitis, G. Brain “fog,” inflammation and obesity: Key aspects of neuropsychiatric disorders improved by luteolin. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Donahue, P.M.; Weakley, S.; Garza, M.; Donahue, M.J.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema and Dercum’s Disease: A New Application of Bioimpedance. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2019, 17, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.R.; Orsso, C.E.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Sicchieri, J.M.F.; Mialich, M.S.; Jordao, A.A.; Prado, C.M. Phase angle and cellular health: Inflammation and oxidative damage. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felmerer, G.; Stylianaki, A.; Hägerling, R.; Wang, A.; Ströbel, P.; Hollmén, M.; Lindenblatt, N.; Gousopoulos, E. Adipose Tissue Hypertrophy, An Aberrant Biochemical Profile and Distinct Gene Expression in Lipedema. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 253, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, E.V.; Hines, E.A.J. Lipedema of the legs: A syndrome characterised by fat legs and orthostatic edema. Proc. Staff Meet. Mayo Clin. 1940, 15, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Moncorps, C.; Brinkhaus, G.; Herteld, F. Experimentelle untersuchungen zur frage akrozyanotischer zustandsbilder. Arch. Derm. Syph. 1940, 186, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Deuel, J.W.; Hollmén, M.; Felmerer, G.; Kim, B.-S.; Vasella, M.; Grünherz, L.; Giovanoli, P.; Lindenblatt, N.; Gousopoulos, E. A Distinct Cytokine Profile and Stromal Vascular Fraction Metabolic Status without Significant Changes in the Lipid Composition Characterizes Lipedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, T.; Kempa, S.; Buechler, C. Lipedema: A Disease Triggered by M2 Polarized Macrophages? Biomedicines 2025, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, L.G.; Funcke, J.-B.; Joffin, N.; Joung, C.; Al-Ghadban, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Kruglikov, I.L.; Zhu, Y.; Langlais, P.R.; et al. Defining lipedema’s molecular hallmarks by multi-omics approach for disease prediction in women. Metabolism 2025, 168, 156191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, H.; Araki, J.; Aoi, N.; Kato, H.; Higashino, T.; Yoshimura, K. Adipose tissue remodeling in lipedema: Adipocyte death and concurrent regeneration. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2009, 36, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Cromer, W.; Allen, M.; Ussery, C.; Badowski, M.; Harris, D.; Herbst, K.L. Dilated Blood and Lymphatic Microvessels, Angiogenesis, Increased Macrophages, and Adipocyte Hypertrophy in Lipedema Thigh Skin and Fat Tissue. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 8747461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruppa, P.; Gohlke, S.; Łapiński, K.; Garcia-Carrizo, F.; Soultoukis, G.A.; Infanger, M.; Schulz, T.J.; Ghods, M. Lipedema stage affects adipocyte hypertrophy, subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammation and interstitial fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1223264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Rannikko, J.H.; Virtakoivu, R.; Cinelli, P.; Felmerer, G.; Burger, A.; Giovanoli, P.; Detmar, M.; Lindenblatt, N.; Hollmén, M.; et al. A distinct M2 macrophage infiltrate and transcriptomic profile decisively influence adipocyte differentiation in lipedema. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1004609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelini, S.; Greco, S.; Vaia, N.; Puleo, V.; Pellegrino, P.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Michelini, S.; Herbst, K.L.; Goteri, G.; Luca, T.; et al. Endothelial cell alterations in capillaries of adipose tissue from patients affected by lipedema. Obesity 2025, 33, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aday, A.W.; MC Donahue, P.; Garza, M.; Crain, V.N.; Patel, N.J.; Beasley, J.A.; Herbst, K.L.; Beckman, J.A.; Taylor, S.L.; Pridmore, M.; et al. National survey of patient symptoms and therapies among 707 women with a lipedema phenotype in the United States. Vasc. Med. 2024, 29, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luta, X.; Buso, G.; Porceddu, E.; Psychogyiou, R.; Keller, S.; Mazzolai, L.; Kezele, T.G. Clinical characteristics, comorbidities, and correlation with advanced lipedema stages: A retrospective study from a Swiss referral centre. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319099. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, T.; Babula, M.A.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, C.B.; Danesh, N.B.; Herbst, K. Lipedema Reduction Surgery Improves Pain, Mobility, Physical Function, and Quality of Life: Case Series Report. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e5436. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, P.M.; Crescenzi, R.; Petersen, K.J.; Garza, M.; Patel, N.; Lee, C.; Chen, S.-C.; Donahue, M.J. Physical Therapy in Women with Early Stage Lipedema: Potential Impact of Multimodal Manual Therapy, Compression, Exercise, and Education Interventions. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2022, 20, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faerber, G.; Cornely, M.; Daubert, C.; Erbacher, G.; Fink, J.; Hirsch, T.; Mendoza, E.; Miller, A.; Rabe, E.; Rapprich, S.; et al. S2k guideline lipedema. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2024, 22, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.; Mirkovskaya, L.; Bharhagava, A.; Chava, Y. Lipedema Fat and Signs and Symptoms of Illness, Increase with Advancing Stage. Arch. Med. 2015, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Lee, K.H.; Ko, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, K.S.; Seo, J.; Kim, M. Neurologic symptoms as a hallmark of glymphatic alteration in recovered patients with COVID-19. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-T.; An, X.-B.; Chen, M.-J.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.-Q.; Yang, J.-N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, L.; et al. A Gene Cluster of Mitochondrial Complexes Contributes to the Cognitive Decline of COVID-19 Infection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 6869–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankam, P.A.N.; Cornely, M.; Klöting, N.; Blüher, M. Is subcutaneous adipose tissue expansion in people living with lipedema healthier and reflected by circulating parameters? Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1000094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, Y.S.; Wadeea, R.; Rosas, V.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: Friend and foe. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 33, 20170076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Marton, A.; Donahue, P.M.; Mahany, H.B.; Lants, S.K.; Wang, P.; Beckman, J.A.; Donahue, M.J.; Titze, J. Tissue Sodium Content is Elevated in the Skin and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Women with Lipedema. Obesity 2018, 26, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.M.; Valenti, E.; Hock, K.; Leffler, J.; Compston, A.; Abraham, W.T. The clinical characteristics of lower extremity lymphedema in 440 patients. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2020, 8, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W. Reference values for the timed up and go test: A descriptive meta-analysis. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2006, 29, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundanes, J.; Nes, V.F.; Aakervik, O.; Ryan, L.; Hansson, P.; Rokstad, A.M.; Martins, C.; Nymo, S. Changes in Cytokines and Fibrotic Growth Factors after Low-Carbohydrate or Low-Fat Low-Energy Diets in Females with Lipedema. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2025, 9, 104571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, L.; Ricolfi, L.; Bortolon, M.; Gabriele, G.; Zolesio, P.; Cione, E.; Cannataro, R. Observational Study on a Large Italian Population with Lipedema: Biochemical and Hormonal Profile, Anatomical and Clinical Evaluation, Self-Reported History. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiose, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Takahashi, H. Effect of regional muscle damage and inflammation following eccentric exercise on electrical resistance and the body composition assessment using bioimpedance spectroscopy. J. Physiol. Sci. 2019, 69, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, A.; Choi, D.; Uzun, S.; Maitland, A.; Riley, B. Association of mast-cell-related conditions with hypermobile syndromes: A review of the literature. Immunol. Res. 2022, 70, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
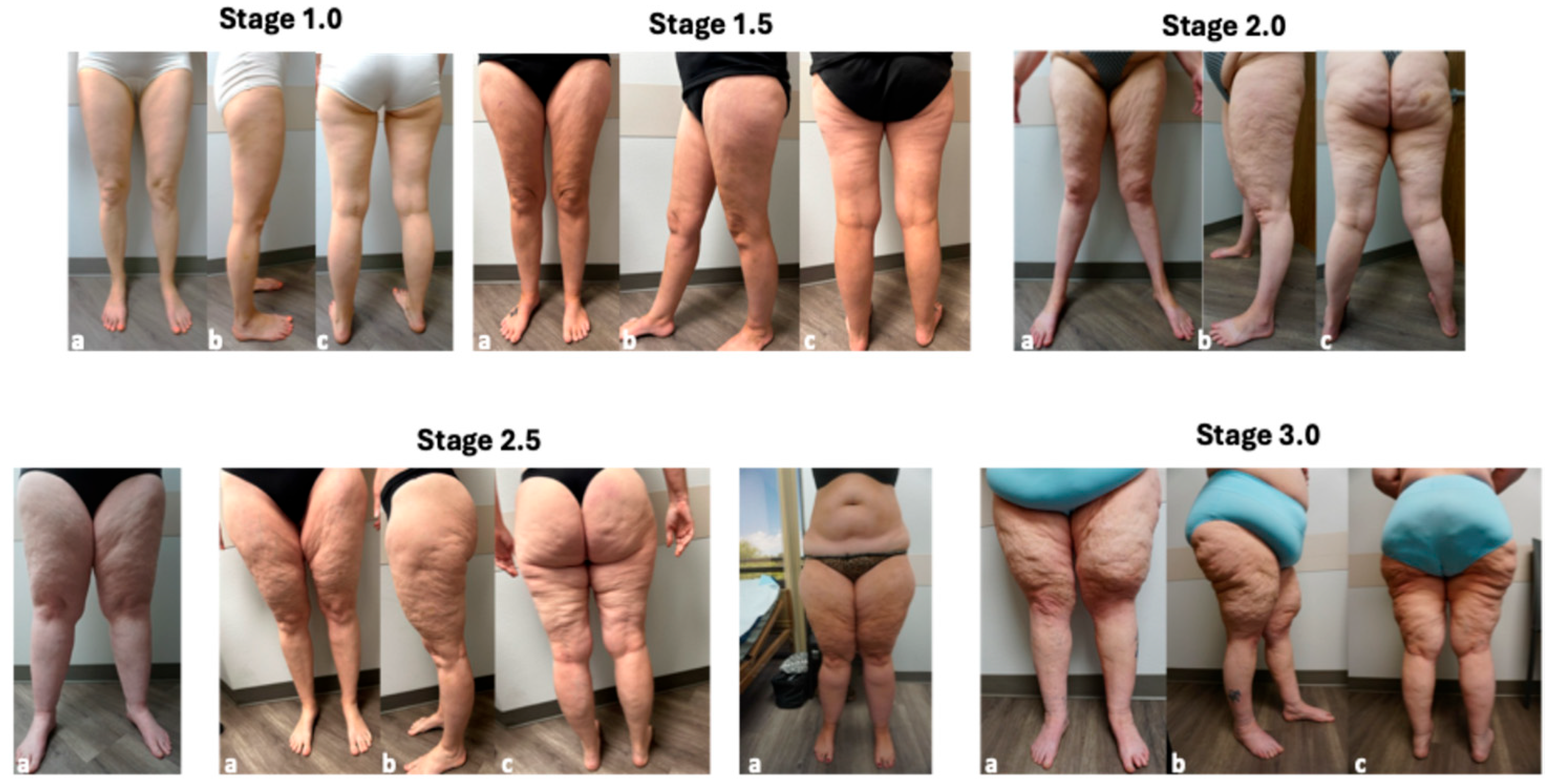



| Lipedema Stages | N | Age | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | 8 | 44.1 ± 3.9 | 33.1 ± 11.0 |
| Stage 1.5 | 35 | 51.2 ± 10 | 28 ± 5.1 |
| Stage 2 | 32 | 51.2 ± 11.1 | 34.3 ± 7.4 |
| Stage 2.5 | 8 | 44.1 ± 3.9 | 39.2 ± 3.8 |
| Stage 3 | 19 | 59.1 ± 11.2 | 47.4 ± 11.8 |
| Stage | Tissue | |
|---|---|---|
| Skin | Hypodermis | |
| 1 | Smooth | Grainy to pearl-sized nodules |
| 1.5 | Indentations in the skin that affect the upper ½ or lower ½ of the leg anterior, lateral and posterior | Grainy to pearl-sized nodules |
| 2 | Indentations in the skin of the entire thigh, anterior, lateral and posterior | Grainy to pearl-to-walnut-sized nodules |
| 2.5 | Beginning of lobules in the tissue especially at the hip and around the knee; indentations in the skin of the entire thigh, anterior, lateral and posterior | Grainy, pearl-to-walnut-sized and larger nodules; lobules around the hips and knees; overhang over the elbow often present |
| 3 | Skin folds on the upper arms, abdomen, hips and knees; indentations in the skin of the entire thigh, anterior, lateral and posterior | Grainy, pearl-to-walnut-sized, and larger deformations; multiple lobules on upper arms, over elbows, on the abdomen, hips, thighs, knees and ankles |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Ghadban, S.; Evancio, J.V.; Alfiscar, P.E.F.; Herbst, K.L. New Characterization of Lipedema Stages: Focus on Pain, Water, Fat and Skeletal Muscle. Life 2025, 15, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091397
Al-Ghadban S, Evancio JV, Alfiscar PEF, Herbst KL. New Characterization of Lipedema Stages: Focus on Pain, Water, Fat and Skeletal Muscle. Life. 2025; 15(9):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091397
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Ghadban, Sara, Jane V. Evancio, Paula E. F. Alfiscar, and Karen L. Herbst. 2025. "New Characterization of Lipedema Stages: Focus on Pain, Water, Fat and Skeletal Muscle" Life 15, no. 9: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091397
APA StyleAl-Ghadban, S., Evancio, J. V., Alfiscar, P. E. F., & Herbst, K. L. (2025). New Characterization of Lipedema Stages: Focus on Pain, Water, Fat and Skeletal Muscle. Life, 15(9), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091397