Abstract
Background: The association between blood pressure (BP) dipping profiles and kidney function among chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients has been well established within the literature, but studies conducted on kidney transplant (KT) patients remain limited. Individual KT studies have small sample sizes and conflicting results. Meta-analysis overcomes these limitations by pooling data to increase statistical power and provide robust clinical guidance. This meta-analysis systematically assesses the impact of BP patterns on KT and CKD populations, aiming to highlight improved BP management strategies in these populations. Materials and methods: A comprehensive search was conducted up to September 9th, 2024, using multiple electronic databases. Results: The current study included 7 studies with a total of 788 patients. KT recipients showed a higher prevalence of non-dipper blood pressure profile than CKD patients. Also, those with a dipper profile had a significantly higher estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) compared to non-dippers and reverse dippers, implying better graft function. No significant differences were observed in acute rejection risk, proteinuria, renal resistive index, cholesterol, or triglycerides across blood pressure profiles. Conclusions: These findings reveal a high prevalence of non-dipping blood pressure profiles in KT and CKD patients, linked to worse renal and cardiovascular outcomes, while also highlighting the need for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and tailored BP management strategies in these high-risk populations to potentially improve outcomes. However, the observational nature of available studies limits causal inference, and further prospective research is required to establish definitive therapeutic recommendations.
1. Introduction
Hypertension (HTN) is a major concern in both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney transplant (KT) patients due to it being an independent risk factor for progression of CKD, the development of cardiovascular disease, all-cause mortality, and graft function loss in these populations [1,2,3].
Although the conventional management strategy of HTN in CKD and KT recipients revolved around the measurement of blood pressure (BP) in a clinical setting, office BP lacks the ability to give insights on circadian BP variation and short-term BP variability, which is associated with aggravated cardiovascular and renal outcomes [4].
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) has thus paved its way as the gold standard clinical tool for the evaluation and management of hypertension, as it allows serial BP monitoring at specific time intervals throughout a 24 h period, capturing intra- and inter-individual variability [5,6]. In essence, ABPM provides accurate insights into the dipping phenomenon and nocturnal HTN while allowing the diagnosis of particular forms of HTN, such as white-coat and masked HTN [7].
Normally, a healthy individual exhibits a 10% nocturnal decrement in BP values and is classified as a dipper. The non-dipping BP pattern corresponds to the failure of BP to decline during nighttime sleep by 10%. The pathophysiology behind the non-dipping BP phenomenon is dependent on myriads of mechanisms:
- a.
- Disruption of the autonomic nervous system;
- b.
- Disruption of the circadian rhythm;
- c.
- Water and sodium dysregulation;
- d.
- Endocrine disorders (e.g., thyroid) [8,9].
Typically, the expected dipping pattern occurs due to decreased cardiac output and heart rate at night, while systematic vascular resistance may remain slightly elevated. The non-dipping pattern arises from a lesser decline in nocturnal cardiac output or an exaggerated rise in vascular resistance [8,9,10].
The circadian rhythm, regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus, influences BP values via hormonal controls like melatonin and the autonomic nervous system. Disruptions in the sleep–wake cycle, such as obstructive sleep apnea and autonomic dysfunction, contribute to a non-dipping BP pattern [11].
High salt intake, particularly in salt-sensitive individuals, affects sodium excretion and endothelial dysfunction, further aggravating the non-dipping variability [8,10].
Hypertension is an independent risk factor for allograft dysfunction and failure in KT patients [3]. Hence, the high cardiovascular risk inherent to the KT population makes identification and management of abnormal BP patterns critically important for long-term patient survival.
The aim of the present meta-analysis is to evaluate the impact of different blood pressure profiles on kidney graft and renal function in KT recipients compared to CKD patients by investigating the variations in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), acute rejection risk, renal resistive index (RRI), proteinuria, and lipid levels and potentially improve the management of BP control in these populations.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted in alignment with the Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020 guidelines) [12]. The study is registered with PROSPERO.
2.1. Literature Search
An extensive literature search was performed to determine studies focusing on the variability of blood pressure measurements in patients with KT and CKD up to the 9 September 2024.
The literature search was conducted in electronic databases (PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, and Ovid MEDLINE) through the following terms:
- ‘Nocturnal hypertension’;
- ‘Reverse dipping’;
- ‘Non-dipping’;
- ‘Kidney transplantation’;
- ‘Renal transplantation’;
- ‘Renal outcome’;
- ‘Decline in kidney function’;
- ‘Kidney allograft failure/loss’;
- ‘Cardiovascular event’;
- ‘All-cause mortality’.
In addition to the initial database search, a manual search was conducted to detect unidentified articles. All the studies gathered from both electronic and manual searches were transferred into Covidence for a more comprehensive assessment. All articles were evaluated by two authors and reviewed by a third reviewer in case of a conflict.
The search strategy and keyword combinations are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Quality assessment of included studies using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale for cohort studies.
2.2. Study Selection Process
The primary database search included 965 studies from electronic databases and 40 studies that were identified through the manual search. After the removal of duplicates, 868 studies were screened for meta-analysis.
The inclusion criteria in this meta-analysis were as follows:
- Studies comprising adult patients age ≥18;
- Studies published in English;
- Studies reporting ABPM outcomes in CKD and KT patients;
- Randomized controlled trials and prospective and retrospective cohort studies.
The exclusion criteria were as follows:
- Studies involving pediatric populations or animals;
- Literature reviews;
- Case reports;
- Non-comparable observational studies.
2.3. Outcome Measures
The outcome measures were as follows:
- eGFR;
- BP profiles (dipping, non-dipping, and reverse dipping) recorded by ABPM in CKD and KT patients;
- Acute rejection episodes;
- RRI;
- 24 h proteinuria;
- Serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The random-effects meta-analysis model was utilized for data synthesis. For categorical outcomes, odds ratios (ORs) were calculated, and for continuous outcomes, standardized mean differences (SMDs) were utilized. Both outcome types were reported with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Statistical significance was defined as a p-value < 0.05. For the heterogeneity assessment, I2 statistics were used, with values of 25%, 50%, and 75% indicating low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively. All statistical analyses were conducted using STATA V16.0.
The quality of the relevant studies was assessed with the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS), which evaluates studies based on the parameters of selection, comparability, and outcome ascertainment on a scale of 0 to 8.
After a detailed evaluation, 7 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Table 2 demonstrates the details of these studies, including baseline characteristics of the participants, study design, outcome measures, and results (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Characteristics of the included studies.
3. Results
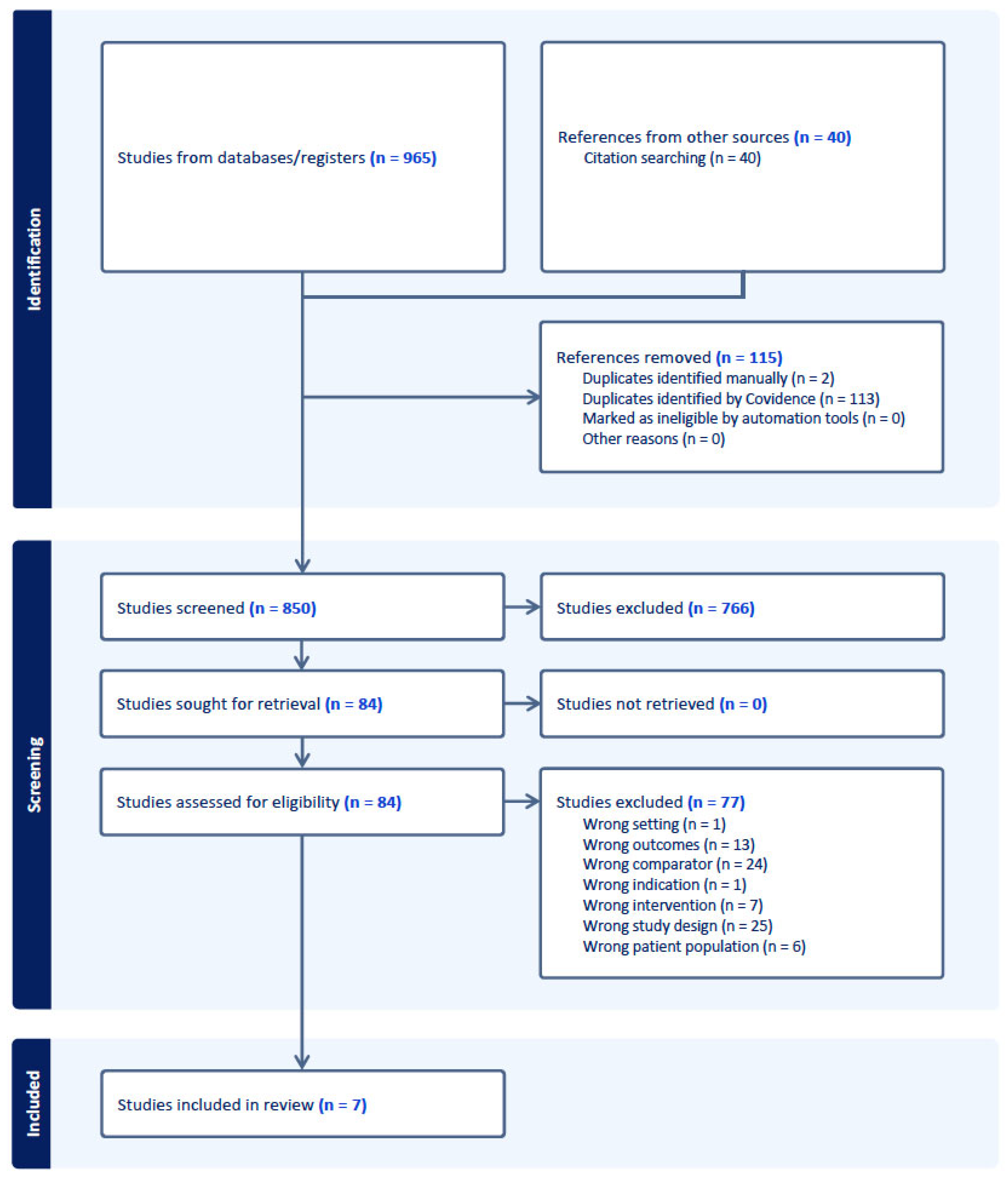
The initial extensive search contained 965 studies; following the comprehensive search and post-screening procedure, 34 studies were included in the full-text review, of which 7 studies met all inclusion criteria and were included in the final meta-analysis (see Figure 1) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19].
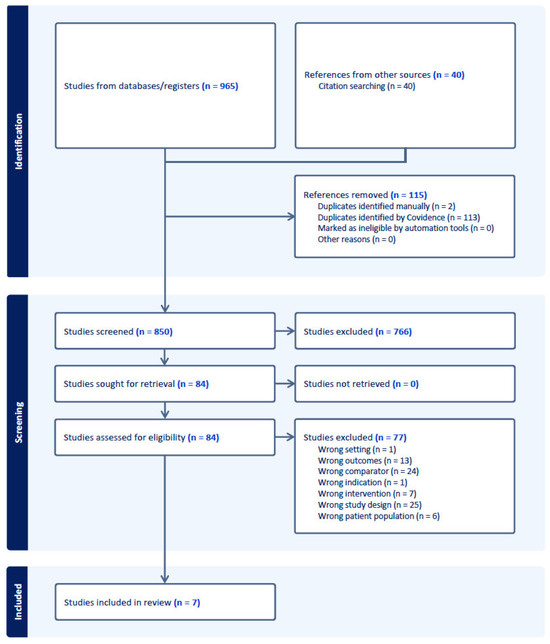
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of study selection process.
Azancot et al. conducted the largest study, an observational cohort with 189 participants, consisting of 97 CKD and 92 KT patients [13]. In contrast, the study with the fewest participants was by Wajdlich et al., who included 55 participants, consisting of 41 CKD and 14 KT patients, in their prospective observational study [14]. Ibernon et al., in their prospective cohort study, had 126 patients, while Wadei et al. analyzed 119 participants in a retrospective cohort study design [15,16]. Similarly, Jaques et al. conducted a retrospective analysis with 123 patients, and Paoletti et al. included 95 KT recipients in their observational cohort [17,18]. Finally, Sezer et al. reported on 82 KT patients in their cross-sectional study [19].
3.1. Prevalence of Blood Pressure Patterns in CKD and KT Patients
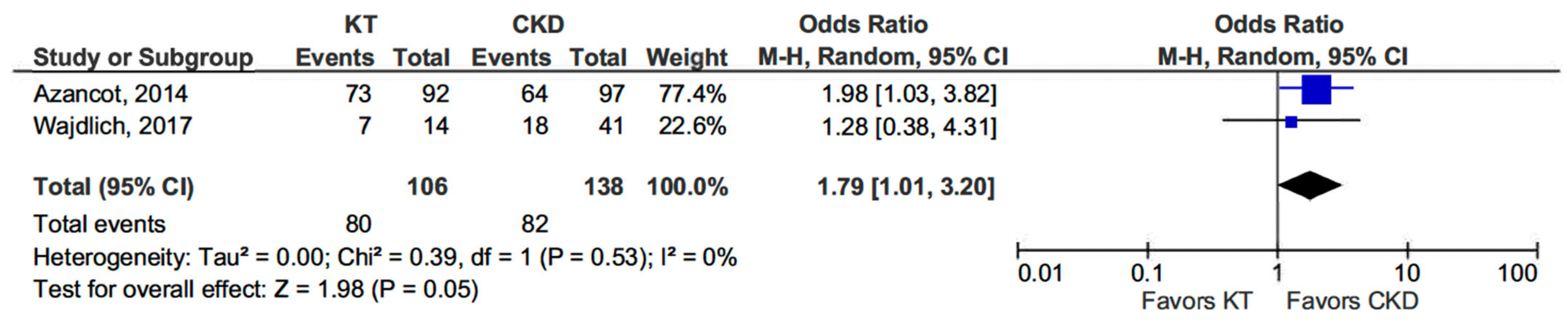
Two studies provided comparative data on blood pressure profiles in CKD patients and KT recipients. KT patients exhibited a higher prevalence of the non-dipper profile compared to those in the CKD group (OR 1.79, 95% CI, 1.01–3.20; p = 0.05) (see Figure 2) [13,14].
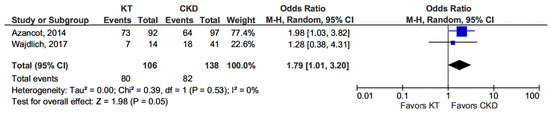
Figure 2.
Forest plot of non-dipper profile in kidney transplant (KT) vs. chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
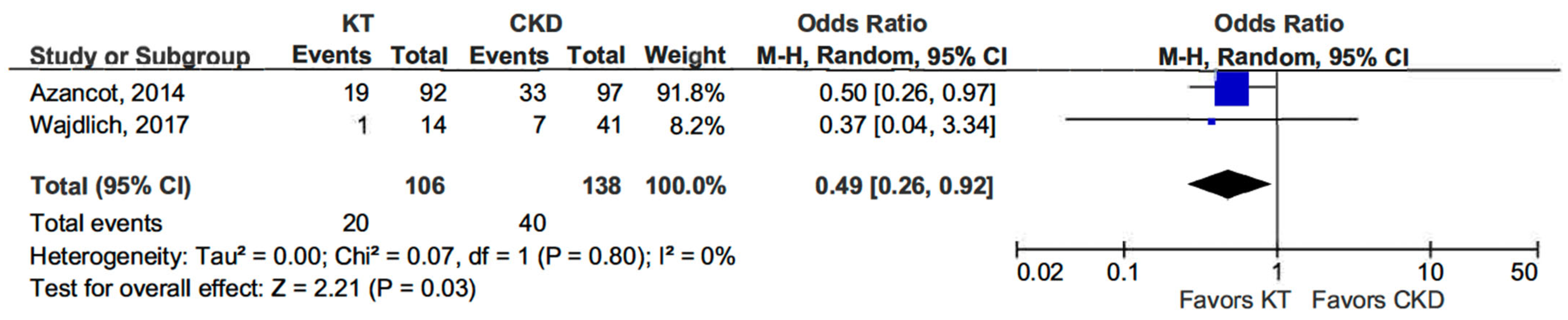
Additionally, the dipper profile was significantly less common in KT patients than in the CKD group (OR 0.49, 95% CI, 0.26–0.92; p = 0.03) (see Figure 3) [13,14].
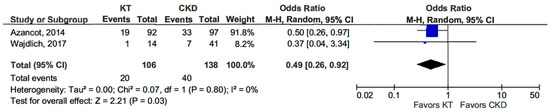
Figure 3.
Forest plot of dipper profile in kidney transplant (KT) vs. chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
3.2. Blood Pressure Profiles and Rejection Risk in KT Patients
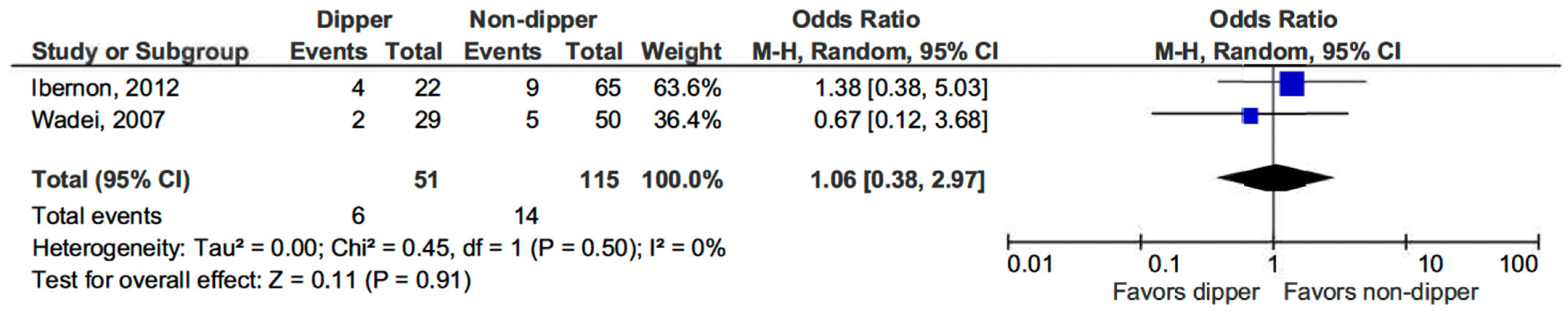
Regarding the risk of acute rejection in KT patients, no significant difference was observed between those with a dipping BP profile and non-dippers (OR 1.06, 95% CI, 0.38–2.97; p = 0.91) (see Figure 4) [15,16].
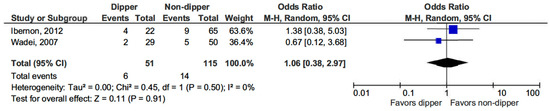
Figure 4.
Forest plot of acute rejection episodes in dipper vs. non-dipper profile in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
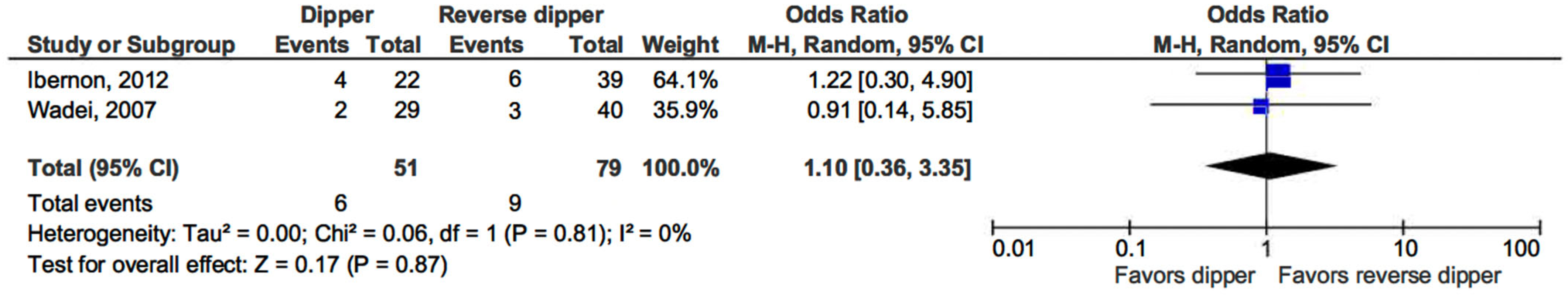
Similarly, the risk of acute rejection did not differ between patients with a dipping profile and reverse dippers (OR 1.10, 95% CI, 0.36–3.35; p = 0.87) (see Figure 5) [15,16].
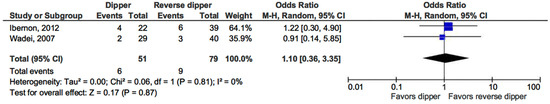
Figure 5.
Forest plot of acute rejection episodes in dipper vs. reverse-dipper profile in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
3.3. Blood Pressure Profiles and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in KT Patients
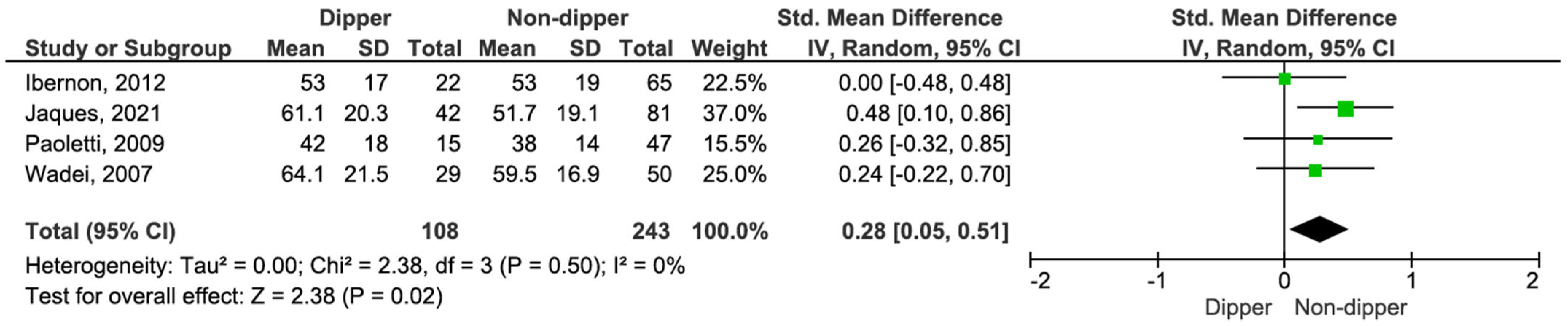
KT patients with a dipping profile exhibited a significantly higher eGFR compared to non-dippers (SMD 0.28, 95% CI, 0.05–0.51; p = 0.02) (see Figure 6) [15,16,17,18].
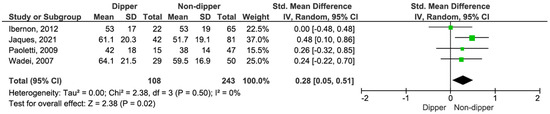
Figure 6.
Forest plot of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in dipper vs. non-dipper profile in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
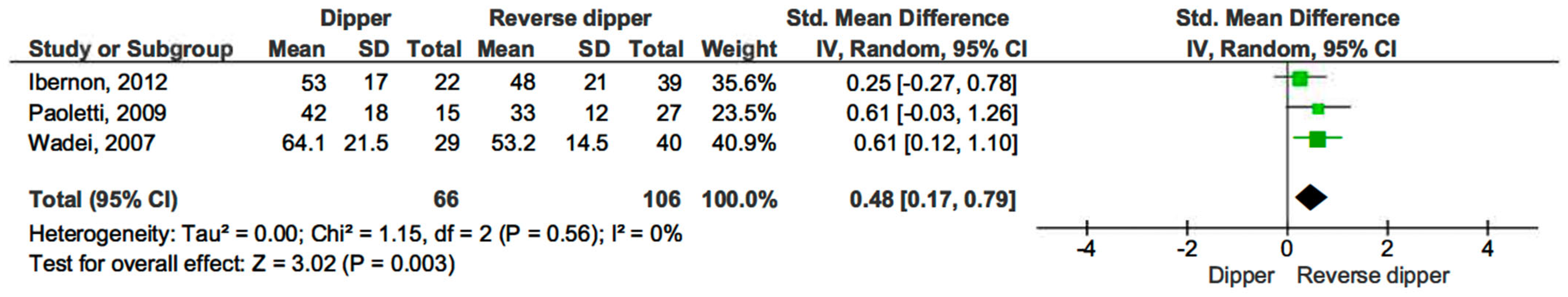
Additionally, dippers had improved eGFR values compared to those with a reverse-dipper profile (SMD 0.48, 95% CI, 0.17–0.79; p = 0.003) (see Figure 7) [15,16,17].
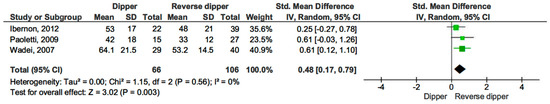
Figure 7.
Forest plot of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in dipper vs. reverse-dipper profile in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
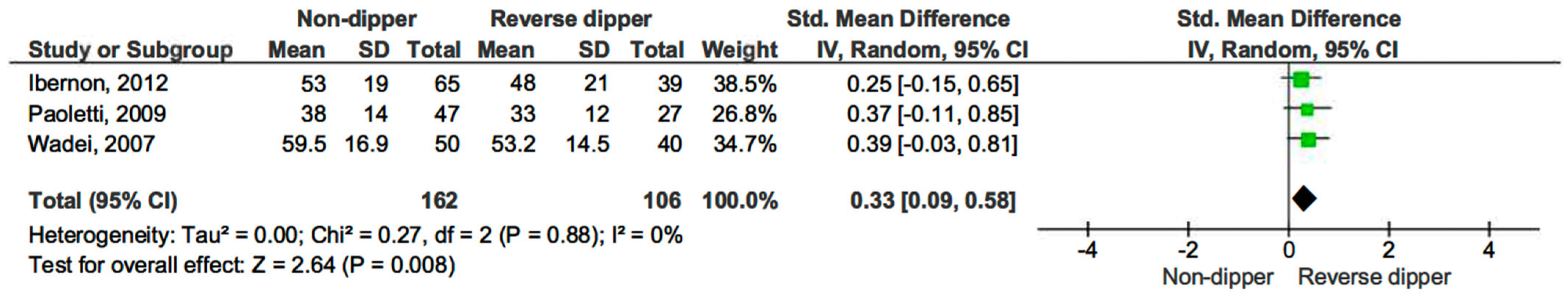
Non-dippers also displayed higher eGFR levels than reverse dippers (SMD 0.33, 95% CI, 0.09–0.58; p = 0.008) (see Figure 8) [15,16,17].
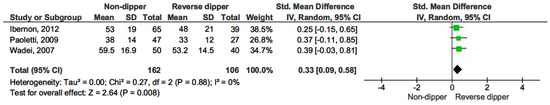
Figure 8.
Forest plot of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of non-dipper vs. reverse-dipper profile in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
3.4. Blood Pressure Profiles and Proteinuria
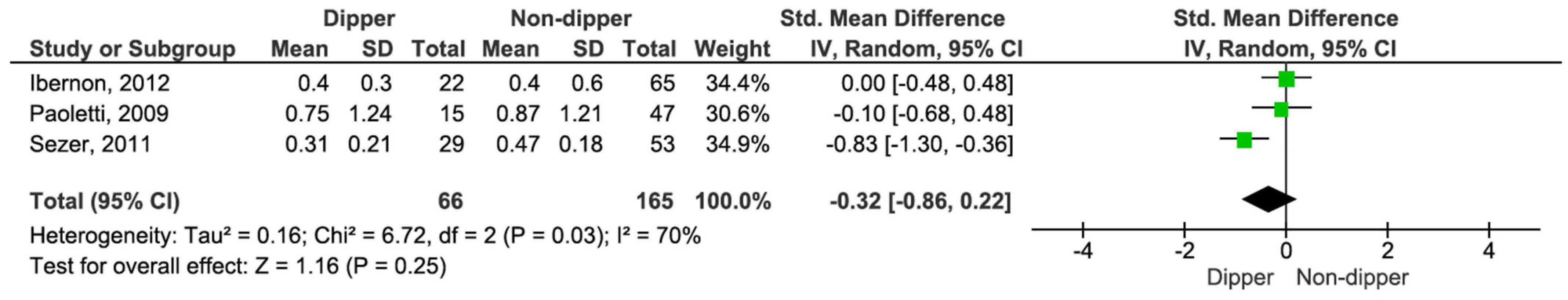
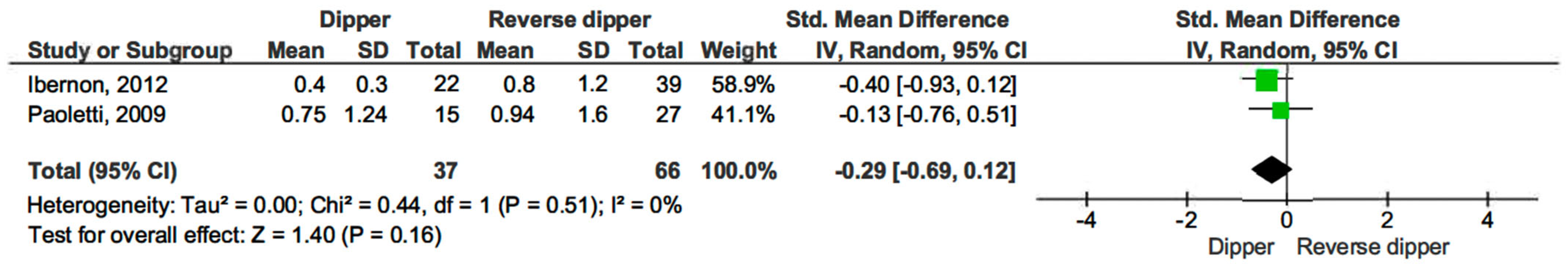
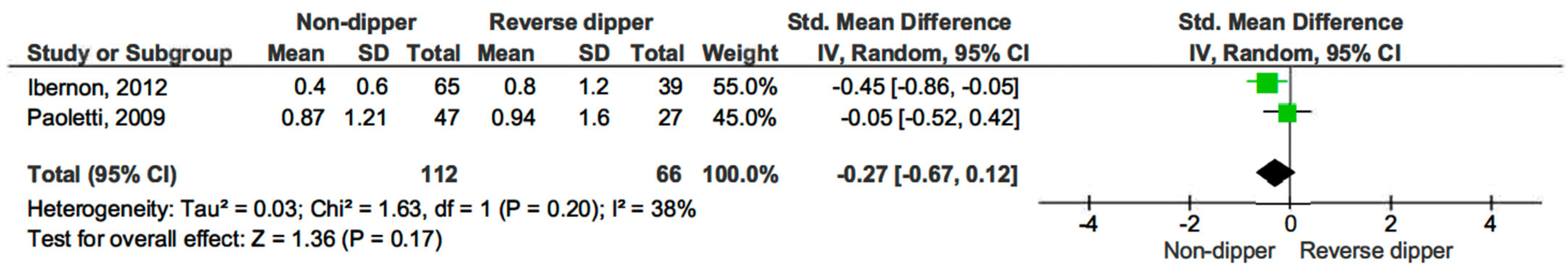
Additionally, we compared 24 h proteinuria across different blood pressure profiles. Proteinuria levels were similar across all comparisons: dippers versus non-dippers (SMD −0.32, 95% CI, −0.86 to 0.22; p = 0.25) (see Figure 9) [15,17,19], dippers versus reverse dippers (SMD −0.29, 95% CI, −0.69 to 0.12; p = 0.16) (see Figure 10) [15,17], and non-dippers versus reverse dippers (SMD −0.27, 95% CI, −0.67 to 0.12; p = 0.17) (see Figure 11) [15,17].
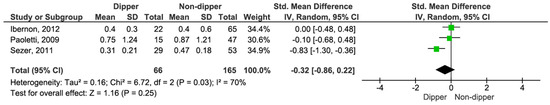
Figure 9.
Forest plot of 24 h proteinuria in dipper vs. non-dipper in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
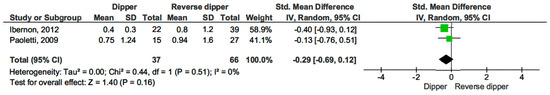
Figure 10.
Forest plot of 24 h proteinuria in dipper vs. reverse dipper in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
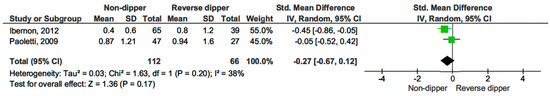
Figure 11.
Forest plot of 24 h proteinuria in non-dipper vs. reverse dipper in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
3.5. Blood Pressure Profiles and Renal Resistive Index
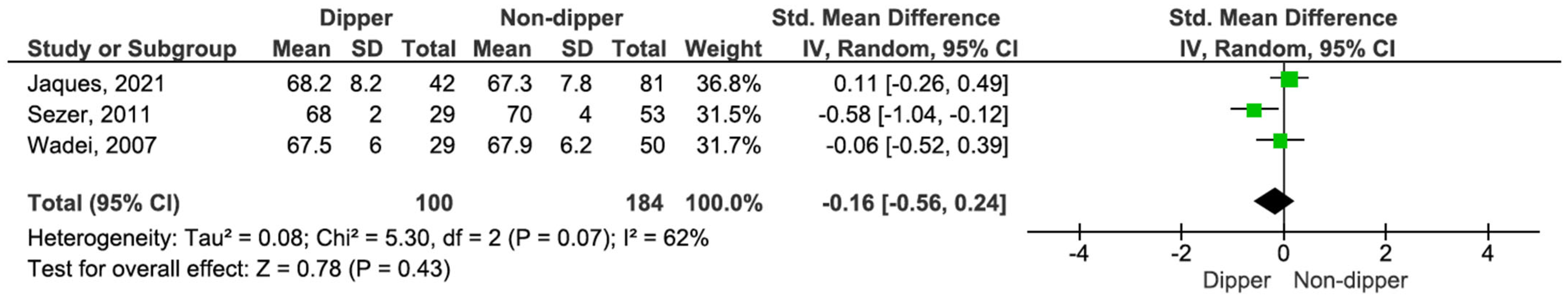
Three studies provided comparative data on RRI between dipping and non-dipping profiles. RRI was similar across both blood pressure groups, with an SMD of −0.16 (95% CI, −0.56 to 0.24; p = 0.43) (see Figure 12) [16,18,19].
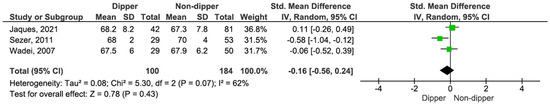
Figure 12.
Forest plot of RRI in dipper vs. non-dipper in kidney transplantation (KT) patients.
4. Discussion
This meta-analysis provides key insights into the prevalence and clinical impact of BP variability among KT recipients and CKD patients, reinforcing the critical role of ABPM in the identification of nocturnal hypertension patterns of dipping, non-dipping, and reverse-dipping BP variability in specifically KT and CKD patient populations. To reiterate our findings, KT patients had a higher prevalence of non-dipper BP profiles compared to CKD patients, highlighting the need to tailor BP management strategies in this category. The inverse association between kidney function and non-dipping status among CKD patients has been well established in multiple clinical trials, whereas studies conducted on kidney transplant recipients are scarce [20,21,22].
A meta-analysis evaluating a total of 4115 kidney transplant recipients from 42 clinical studies illustrated high rates of uncontrolled HTN (56%) according to ABPM and non-dipping status (54%, 95% CI: 45–63%) [2].
The study at hand also displayed that KT patients with a dipping profile had significantly higher eGFR values compared to their non-dipper and reverse-dipper counterparts, highlighting that maintenance of the circadian rhythm in BP may preserve graft function and viability. An analysis of 1.061 patients during 4.759 person-years of follow-up period illustrated that every 10% increase in nighttime systolic BP is linked to a 1.21-fold increase in CKD progression, defined as at least a 50% decline in eGFR or initiation of kidney replacement therapies [6].
This study has also provided the first strong evidence of a similar pattern of association between CKD progression and non-dipping blood pressure status. Another large-scale clinical trial conducted on over 906 patients with CKD stages 1 to 3 identified absence of nocturnal dipping as a risk factor for CKD progression, as patients without a nighttime dipping pattern are at higher risk for CKD progression even if they maintain 24 h ambulatory BP goals (HR 1.82, 95% CI: 1.17–2.82) [23].
Similarly, multiple other clinical trials have identified a non-dipping BP pattern as a risk factor for CKD progression among normotensive individuals [24,25,26]. It is also considered a cardiovascular mortality predictor and is associated with worse outcomes in hemodialysis patients [27].
In short, these findings suggest that non-dipping and reverse-dipper profiles are associated with poorer kidney graft function compared to dippers. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first large-scale clinical data revealing higher rates of non-dipping status among KT recipients compared to the CKD population with low heterogeneity. Such an outcome indicates the presence of potentially irreversible pathophysiological events leading to non-dipping status and nocturnal HTN among CKD patients, which persist even in the post-transplant period despite improvements in kidney function.
Nevertheless, our meta-analysis lacks such analysis, highlighting a major limitation of our study. Our analysis revealed no significant difference in acute rejection rates between dipping and non-dipping profiles, implying that BP variability may impact graft function through chronic hemodynamic alterations rather than via immunologic rejection events. In addition, no notable differences were observed in proteinuria, RRI, or lipid levels across BP profiles, suggesting that the primary impact of a non-dipping profile is likely related to graft hemodynamics rather than acute renal damage or metabolic disturbances.
The exact underlying mechanism of non-dipping status among either CKD patients or KT recipients is unclear, though multiple hypotheses have been postulated. The following factors appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of a non-dipping BP pattern among CKD patients: disruption of circadian rhythm regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus mediated via upregulation of angiotensin-1 or uremic state; impaired sleeping pattern, including later onset, shorter duration, and increased fragmentation of sleep cycle; over-activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, leading to salt retention and vasoconstriction; and multiple comorbidities, including obstructive sleep apnea, diabetes mellitus, and obesity [28,29,30,31,32].
Post-transplant graft function and immunosuppressive regimens may be potential additional contributors to 24 h ABPM among KT recipients, though further pre-clinical and clinical studies are required for a better understanding of underlying molecular mechanisms [29].
This hypothesis was also brought into question by Mendoza-Romo-Ramírez et al. Their study found a higher frequency of non-dipping BP profiles in KT patients compared to the general population and proposed it to be a consequence of immunosuppressive therapy (cyclosporine-induced arterial hypertension), along with changes in homocysteine and alterations in the autonomic nervous system encountered in chronic renal patients [33]. Similar findings were previously presented by Lipkin et al. when comparing cyclosporin- and non-cyclosporin-treated renal transplant recipients [34].
Along with the recipients, living kidney donors should also be evaluated with ABPM, as shown by Yazawa et al. Although they are expected to have an increase in BP of around 5–10 mmHg, in their study, they did not show any significant increase in values. However, around 40% displayed non-dipping BP profiles following nephrectomy [35].
In CKD patients, the prevalence of resistant hypertension and abnormal BP profiles is also higher and requires investigation through 24 h ABPM and targeted pathophysiological treatment, i.e., optimizing diuretic regimens in volume excess assessment, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockade in hyperactive states, or beta-/alpha-blockade in the presence of clues of sympathetic nervous system mediation [36].
Apart from the BP profile, ABPM can aid in identifying several specific forms of HTN, such as white-coat or sustained HTN. These are significant in renal patients, since they are also associated with histopathological alterations in kidney biopsies [37].
On the other hand, BP values vary significantly in CKD patients depending on the stages, and since consistency is poor, several publications are against using single 24 h ABPM measurements for properly assessing BP profile [38].
Our meta-analysis has provided insights into the association between 24 h ABPM and multiple clinical outcomes among kidney transplant recipients, though our study is not without major limitations. First, our meta-analysis includes data from only a few observational studies, potentially limiting the generalizability of our outcomes and potential alterations in outcomes with the publication of future studies. The observational design carries a risk of residual confounding despite statistical adjustments. Second, while statistical heterogeneity across the included studies appears low, the small number of studies (n = 7) and limited sample sizes for several comparisons restrict the statistical power and limit the robustness of pooled estimates. Third, we were unable to perform separate analysis on normotensive individuals with non-dipping status, which may provide valuable information regarding whether our clinical outcomes may solely be attributable to dipping pattern. Lastly, our meta-analysis lacks data on potential confounding factors on post-transplant blood pressure readings, including maintenance immunosuppression regimens, anti-hypertensive therapies, and comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Due to the limited number of studies available, meaningful subgroup analyses to address these potential confounders were not feasible. Despite these limitations, the consistency of findings across diverse populations and study designs strengthens confidence in the observed association.
Although several studies have addressed the association between blood pressure variability and outcomes in either CKD or KT patients, the study at hand is the first comprehensive analysis to include both populations.
This meta-analysis at hand not only captures the high prevalence of non-dipping profiles among KT and CKD patients but also provides evidence on its significant implications for graft function and renal outcomes. Non-dipping and reverse-dipping profiles are linked to lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and potentially poorer graft function, while dipping profiles are correlated with better renal outcomes (see Table 3).

Table 3.
What is known and unknown regarding the dipping status of blood pressure among kidney transplant recipients.
5. Conclusions
These findings emphasize the need for ABPM use in CKD patients and KT recipients to monitor nocturnal BP patterns. For reverse and non-dipper populations, personalized BP management strategies, such as sodium restriction, timely antihypertensive therapy, and lifestyle modifications, should be considered. The observational nature of the included studies limits causal inference, but the strength and consistency of associations across diverse populations support clinical relevance. These findings provide the best currently available evidence to inform clinical practice while recognizing the need for additional high-quality research, including prospective studies with standardized blood pressure monitoring protocols. Hence, more effective management of BP variability could enhance the quality of life and survival of these vulnerable groups.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. (Mehmet Kanbay), S.O., and C.G.; methodology, M.K. (Mehmet Kanbay), S.O., and C.G.; software, A.B. and C.B.; validation, A.D.C., I.I.C.E., and A.S.C.; formal analysis, A.D.C., I.I.C.E., and A.S.C.; investigation, P.S. and M.K. (Masanari Kuwabara); data curation, A.B. and C.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K. (Mehmet Kanbay), C.B., O.A., and B.Z.B.; writing—review and editing, M.K. (Mehmet Kanbay), A.B., P.S., M.K. (Masanari Kuwabara), and A.C.; visualization, A.D.C., I.I.C.E., and A.S.C.; supervision, M.K. (Mehmet Kanbay) and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ABPM | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CrCl | Creatinine clearance |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| KT | Kidney transplant |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| RRI | Renal resistive index |
| SMD | Standardized mean differences |
References
- Johansen, K.L.; Chertow, G.M.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Herzog, C.A.; Ishani, A.; Israni, A.K.; Ku, E.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; et al. US Renal Data System 2021 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, A8–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Jhee, J.H.; Chun, K.H.; Seo, J.; Lee, C.J.; Park, S.H.; Hwang, J.T.; Han, S.H.; Kang, S.W.; Park, S.; et al. Nocturnal systolic blood pressure dipping and progression of chronic kidney disease. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.W.; Joo, Y.S.; Ryu, J.; Jung, H.Y.; Jeong, K.H.; Kim, M.G.; Ju, M.K.; Han, S.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Impact of Blood Pressure on Allograft Function and Survival in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, M.T.; Beddhu, S.; Nobakht, E.; Rahman, M.; Raj, D.S. Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease: Ready for Prime Time. Kidney Int. Rep. 2016, 1, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Chia, Y.C.; Buranakitjaroen, P.; Siddique, S.; Shin, J.; Turana, Y.; Park, S.; Tsoi, K.; Chen, C.H.; et al. Guidance on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: A statement from the HOPE Asia Network. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, A.; Mallamaci, F.; D’Arrigo, G.; Bolignano, D.; Wuerzner, G.; Ortiz, A.; Burnier, M.; Kanaan, N.; Sarafidis, P.; Persu, A.; et al. Assessment of hypertension in kidney transplantation by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Turkmen, K.; Ecder, T.; Covic, A. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: From old concepts to novel insights. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2012, 44, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huart, J.; Persu, A.; Lengelé, J.P.; Krzesinski, J.M.; Jouret, F.; Stergiou, G.S. Pathophysiology of the Nondipping Blood Pressure Pattern. Hypertension 2023, 80, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanbay, M.; Turgut, F.; Karakurt, F.; Isik, B.; Alkan, R.; Akcay, A.; Yigitoglu, R.; Covic, A. Relation between serum thyroid hormone and ‘nondipper’ circadian blood pressure variability. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2007, 30, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbian, F.; Smolensky, M.H.; Tiseo, R.; Pala, M.; Manfredini, R.; Portaluppi, F. Dipper and non-dipper blood pressure 24-hour patterns: Circadian rhythm-dependent physiologic and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Chronobiol. Int. 2013, 30, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, M.; Dulková, K.; Bada, V.; Herichová, I. Plasma melatonin concentrations in hypertensive patients with the dipping and non-dipping blood pressure profile. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azancot, M.A.; Ramos, N.; Moreso, F.J.; Ibernon, M.; Espinel, E.; Torres, I.B.; Fort, J.; Seron, D. Hypertension in chronic kidney disease: The influence of renal transplantation. Transplantation 2014, 98, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajdlich, M.B.F. Evaluation of the relationship between circadian blood pressure profile and natriuresis in patients with chronic kidney disease and renal transplant recipients. Arter. Hypertens. 2017, 21, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ibernon, M.; Moreso, F.; Sarrias, X.; Sarrias, M.; Grinyó, J.M.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Ricart, W.; Serón, D. Reverse dipper pattern of blood pressure at 3 months is associated with inflammation and outcome after renal transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadei, H.M.; Amer, H.; Taler, S.J.; Cosio, F.G.; Griffin, M.D.; Grande, J.P.; Larson, T.S.; Schwab, T.R.; Stegall, M.D.; Textor, S.C. Diurnal blood pressure changes one year after kidney transplantation: Relationship to allograft function, histology, and resistive index. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, E.; Gherzi, M.; Amidone, M.; Massarino, F.; Cannella, G. Association of arterial hypertension with renal target organ damage in kidney transplant recipients: The predictive role of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Transplantation 2009, 87, 1864–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, D.A.; Saudan, P.; Martinez, C.; Andres, A.; Martin, P.Y.; Pechere-Bertschi, A.; Ponte, B. Relationship between renal function and blood pressure dipping status in renal transplant recipients: A longitudinal study. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, S.; Karakan, S.; Çolak, T.; Haberal, M. Nocturnal nondipping hypertension is related to dyslipidemia and increased renal resistivity index in renal transplant patients. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, C.K.; Goldsmith, D.J.; Cox, J.; Dallyn, P.; Kingswood, J.C.; Sharpstone, P. An investigation of the effect of advancing uraemia, renal replacement therapy and renal transplantation on blood pressure diurnal variability. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pogue, V.; Rahman, M.; Lipkowitz, M.; Toto, R.; Miller, E.; Faulkner, M.; Rostand, S.; Hiremath, L.; Sika, M.; Kendrick, C.; et al. Disparate estimates of hypertension control from ambulatory and clinic blood pressure measurements in hypertensive kidney disease. Hypertension 2009, 53, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojón, A.; Ayala, D.E.; Piñeiro, L.; Otero, A.; Crespo, J.J.; Moyá, A.; Bóveda, J.; de Lis, J.P.; Fernández, J.R.; Hermida, R.C. Comparison of ambulatory blood pressure parameters of hypertensive patients with and without chronic kidney disease. Chronobiol. Int. 2013, 30, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, S.; Garofalo, C.; Gabbai, F.B.; Chiodini, P.; Signoriello, S.; Paoletti, E.; Ravera, M.; Bussalino, E.; Bellizzi, V.; Liberti, M.E.; et al. Dipping Status, Ambulatory Blood Pressure Control, Cardiovascular Disease, and Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Cohort Study of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 81, 15–24.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiky, B.; Kovács, T.; Wágner, L.; Vass, T.; Nagy, J. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and progression in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Timio, M.; Lolli, S.; Verdura, C.; Monarca, C.; Merante, F.; Guerrini, E. Circadian blood pressure changes in patients with chronic renal insufficiency: A prospective study. Ren. Fail. 1993, 15, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.B.; Hix, J.K.; Vidt, D.G.; Brotman, D.J. Association of impaired diurnal blood pressure variation with a subsequent decline in glomerular filtration rate. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Takahashi, H.; Morita, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Mizuno, M.; Yuzawa, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Toriyama, T.; Kawahara, H.; Matsuo, S. Non-dipping is a potent predictor of cardiovascular mortality and is associated with autonomic dysfunction in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.M.; McLachlan, E.; Piggins, H.D. Angiotensin II regulates the activity of mouse suprachiasmatic nuclei neurons. Neuroscience 2008, 154, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, R.; Douma, L.G.; Scindia, Y.; Gumz, M.L. Circadian rhythms and renal pathophysiology. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e148277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Light, R.P. Sleep and activity in chronic kidney disease: A longitudinal study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.D.; Agarwal, R. The complex relationship between CKD and ambulatory blood pressure patterns. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015, 22, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Borne, P.; Tielemans, C.; Collart, F.; Vanherweghem, J.L.; Degaute, J.P. Twenty-four-hour blood pressure and heart rate patterns in chronic hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1993, 22, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Romo-Ramírez, M.A.; García-Hernández, J.A.; Rodríguez-Quilantán, F.J.; Ávila-Infante, A.; Bartolo-Sánchez, F.D.; Silva-Ortiz, J.A.; Valdés-Méndez, J.A. Non-dipper effect in hypertense patients after renal transplantation by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Cirugía Y Cir. 2021, 89, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, G.W.; Tucker, B.; Giles, M.; Raine, A.E. Ambulatory blood pressure and left ventricular mass in cyclosporin- and non-cyclosporin-treated renal transplant recipients. J. Hypertens. 1993, 11, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazawa, M.; Kido, R.; Shibagaki, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Nakazawa, R.; Sasaki, H.; Sato, Y.; Chikaraishi, T.; Kimura, K. Kidney function, albuminuria and cardiovascular risk factors in post-operative living kidney donors: A single-center, cross-sectional study. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, Y.R.; Bomback, A.S. Definition, identification and treatment of resistant hypertension in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, E.; Uslu, A.; Tasli, F.; Karatas, M. Relationship between diurnal blood pressure and renal histopathological changes in white coat hypertension. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elung-Jensen, T.; Strandgaard, S.; Kamper, A.L. Longitudinal observations on circadian blood pressure variation in chronic kidney disease stages 3–5. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2873–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).