Neurobehavioral Protection by Prebiotic Formulations in a Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impaired Zebrafish Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant-Based Materials
2.2. Zebrafish Husbandry and Experimental Design
2.3. Behavioral Testing Procedure
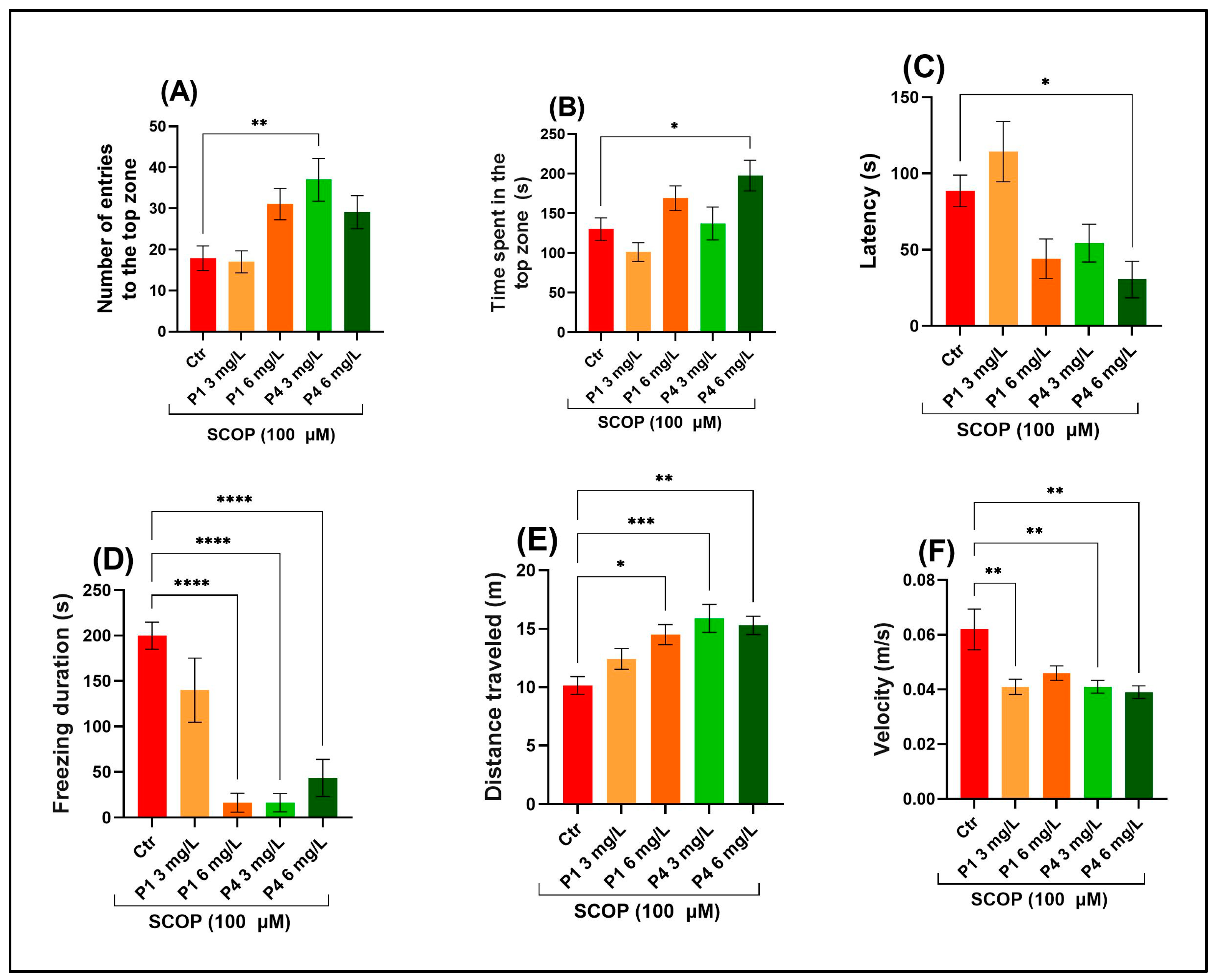
2.3.1. Novel Tank Diving Test
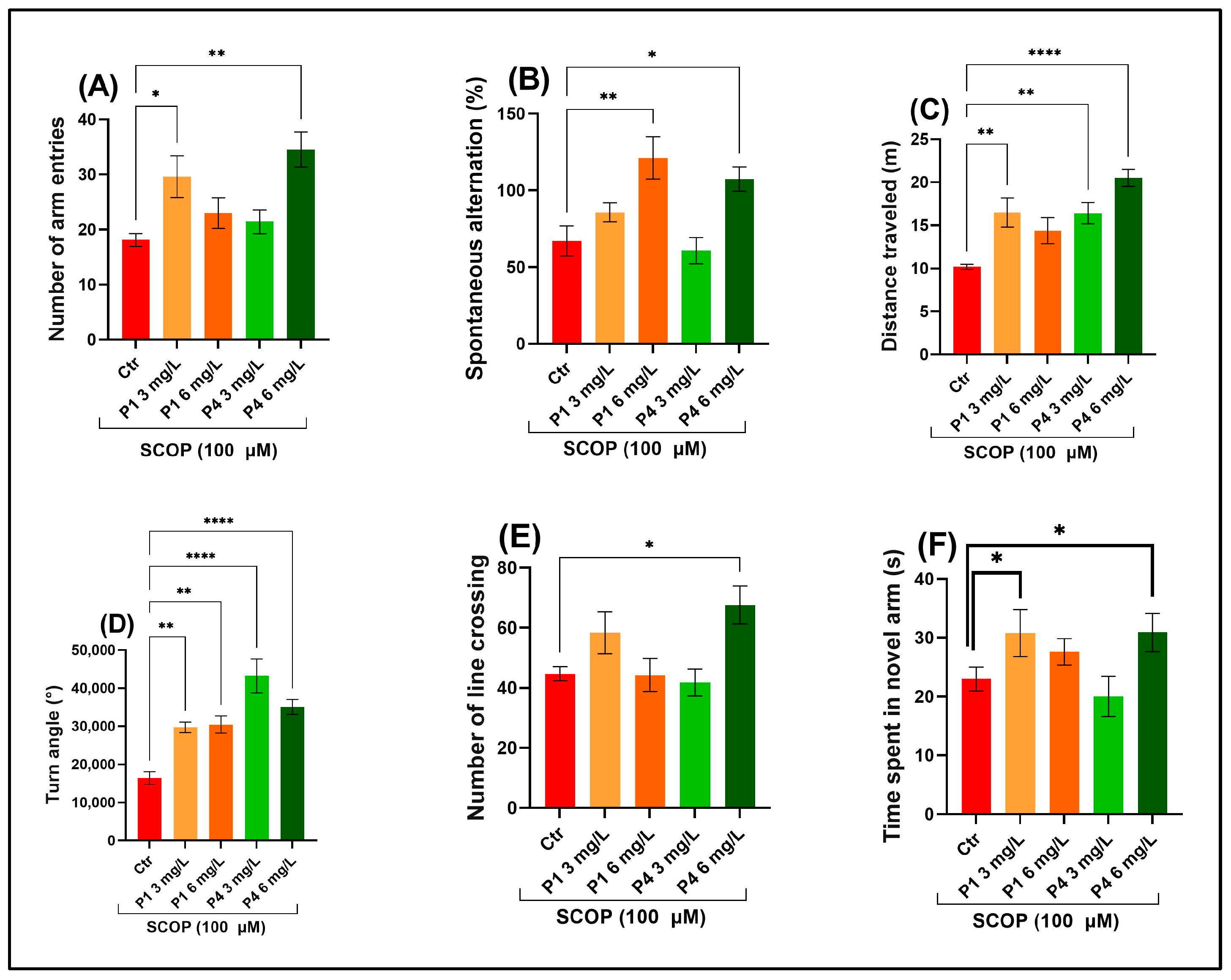
2.3.2. Y-Maze Test
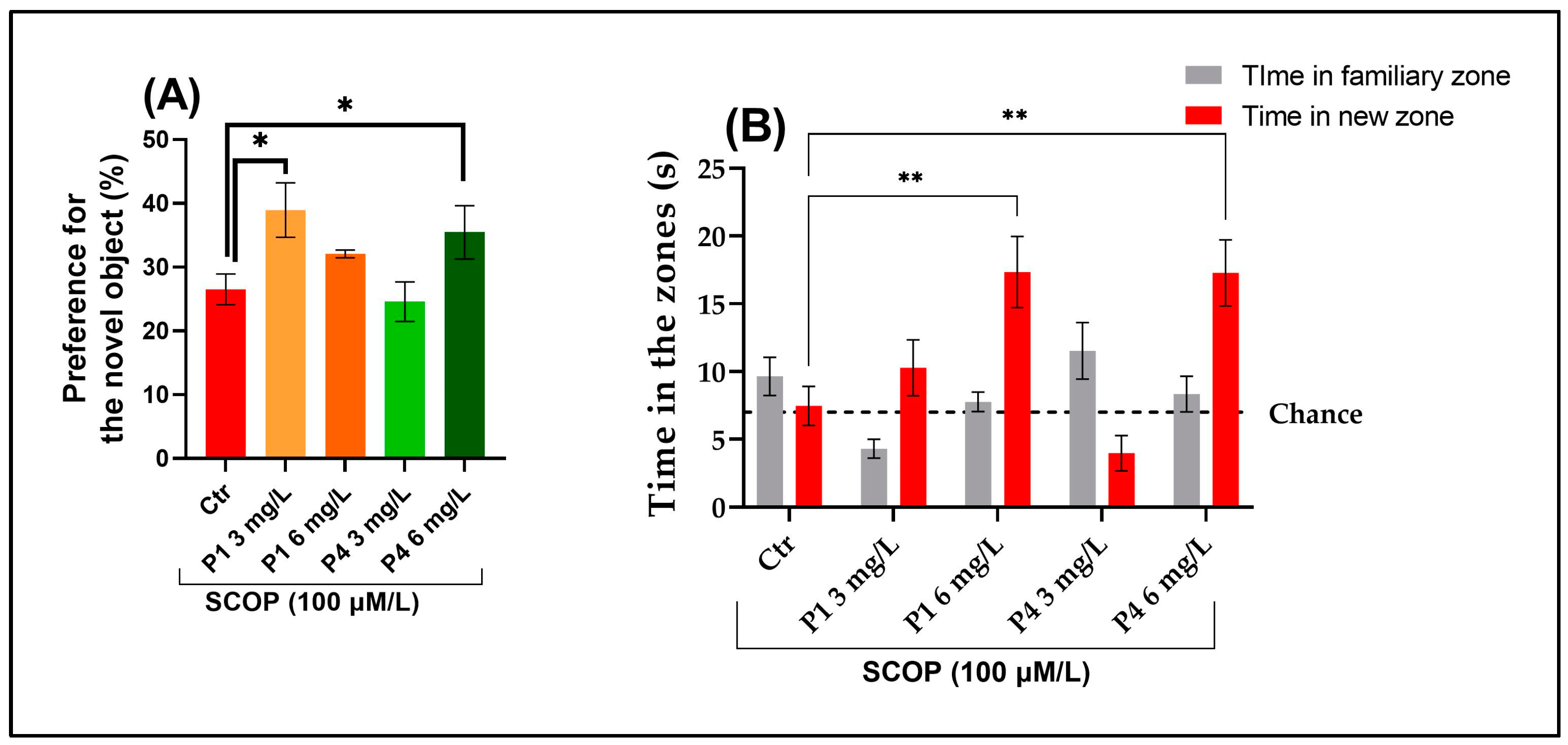
2.3.3. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.4. Assessment of Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. P1 and P4 Reduced Anxiety-Like Responses Induced by Scopolamine in the Novel Diving Test
3.2. P1 and P4 Reversed Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits in Y-Maze and Novel Object Recognition Tests
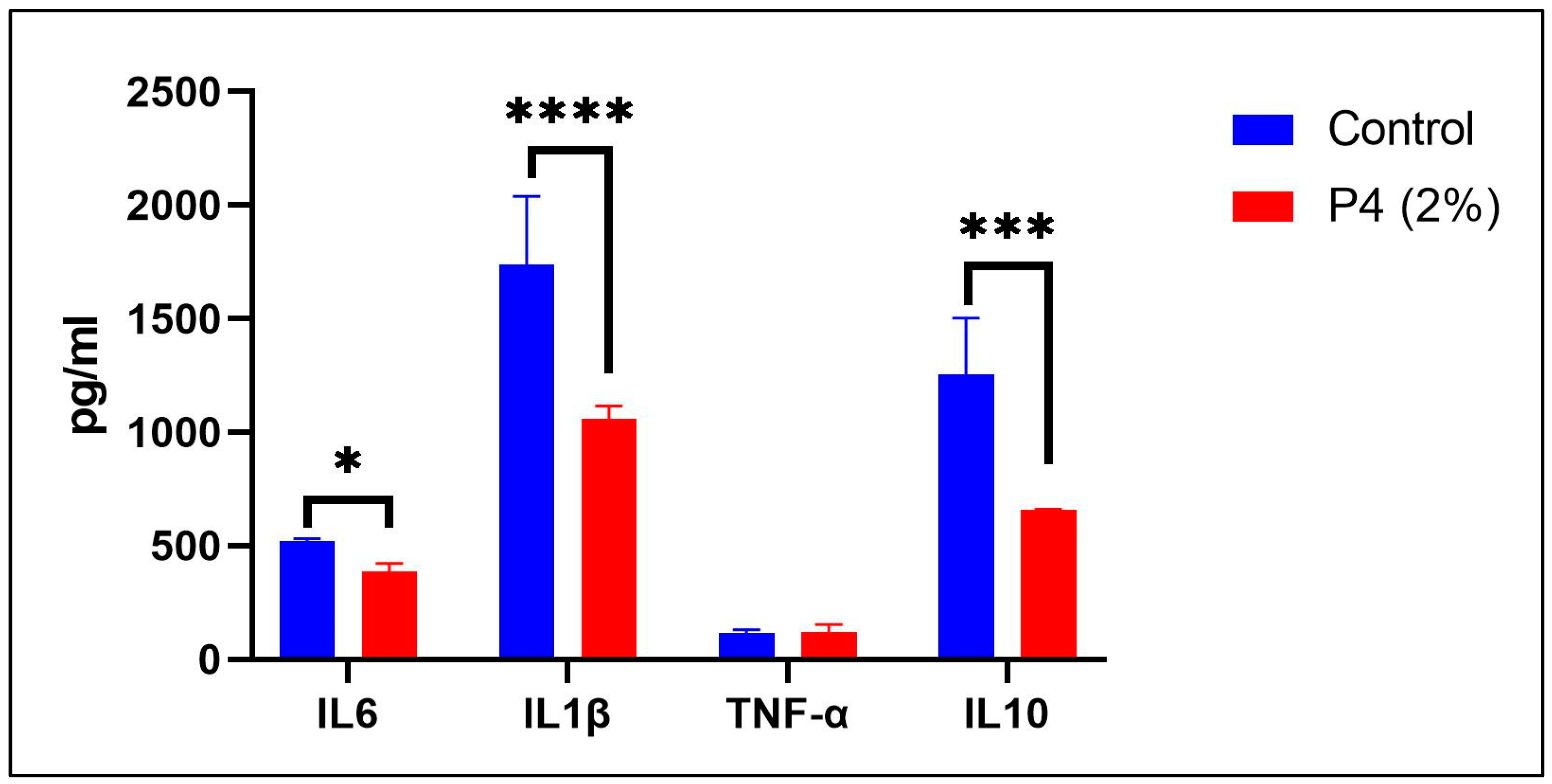
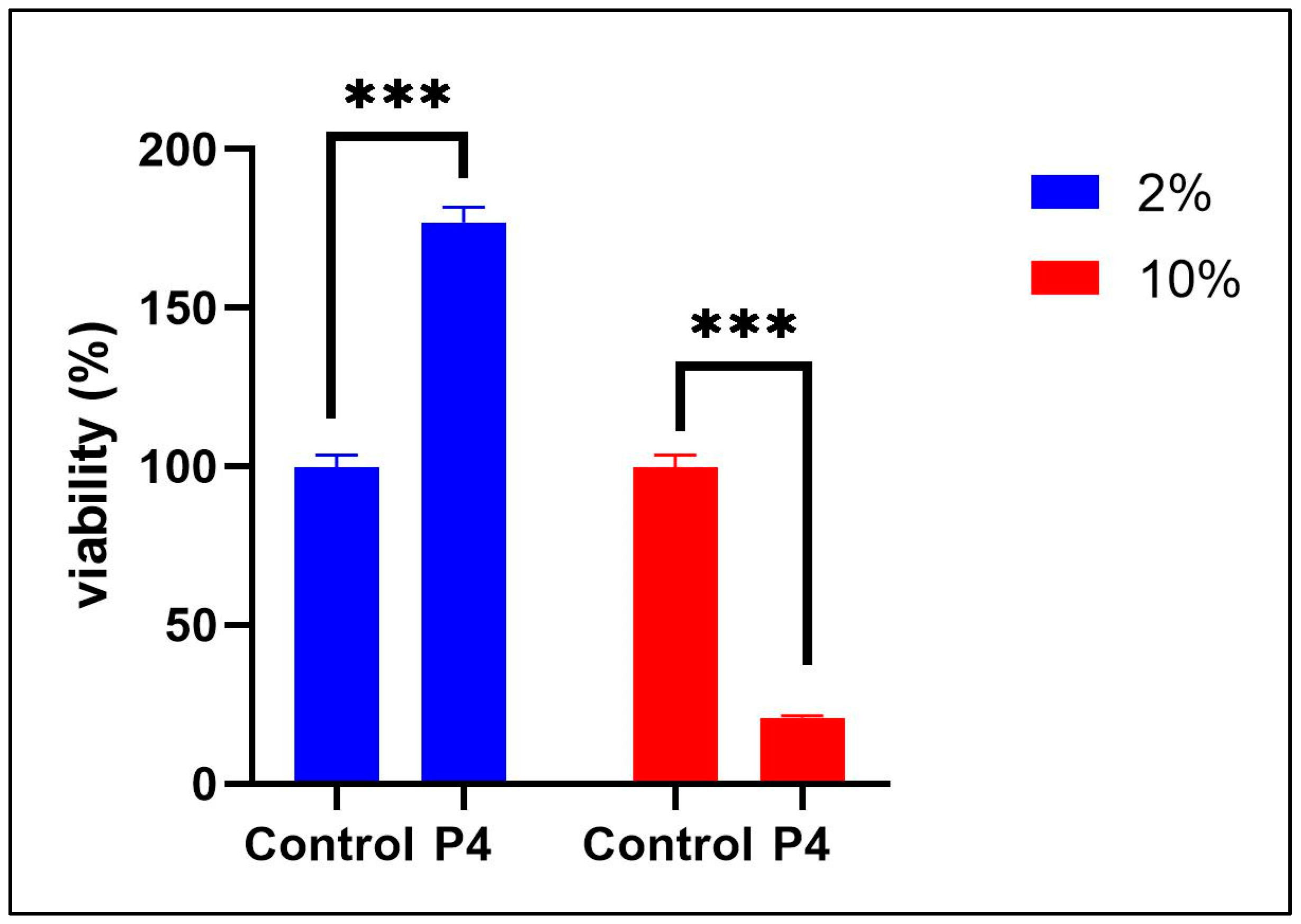
3.3. Prebiotic Treatment on Cytokine Responses: Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Novel Prebiotic Formulations (P4)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gautam, M.K.; Panda, P.K.; Dubey, A.; Kumari, M.; Ghosh, N.S. Zebrafish as a Fascinating Animal Model: A Robust Platform for in Vivo Screening for Biomedical Research. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2024, 14, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Braubach, O.; Spitsbergen, J.; Gerlai, R.; Kalueff, A.V. Zebrafish Models for Translational Neuroscience Research: From Tank to Bedside. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teame, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Xie, M.; Gao, C.; Ye, Y.; Duan, M.; et al. The Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as Biomedical Models. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The Zebrafish Reference Genome Sequence and Its Relationship to the Human Genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Syed, Y.A.; Khan, M.R. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Brain Development and Its Association with Neurodevelopmental Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 880544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, S.; Abe, R.; Fujimoto, H.; Higashi, K.; Zang, L.; Nakayama, H.; Matsuoka, I.; Shimada, Y. Paraburkholderia sabiae Administration Alters Zebrafish Anxiety-like Behavior via Gut Microbial Taurine Metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1079187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; Yin, X.; Man, J.; Yang, L.; Lu, M. Global, Regional and National Burden of Anxiety Disorders from 1990 to 2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2021, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Buccafusco, J.J. Multi-Functional Drugs for Various CNS Targets in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Dey, S.; Kumar, Y.; Malviya, R.; Prajapati, B.G.; Chaiyasut, C. Probiotics as Modulators of Gut-Brain Axis for Cognitive Development. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1348297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Brummer, R.J.M.; Rastall, R.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faas, M.; Eggersdorfer, M. The Role of the Microbiome for Human Health: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnechère, B.; Amin, N.; van Duijn, C. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Neuropsychiatric Diseases—Creation of an Atlas-Based on Quantified Evidence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 831666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, T.J.; Morrill, A.; Lucas, K.; Gallup, J.; Harris, M.; Healey, M.; Pitman, T.; Schalomon, M.; Digweed, S.; Tresguerres, M. Establishing Zebrafish as a Model to Study the Anxiolytic Effects of Scopolamine. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongrong, S.; Promsrisuk, T.; Sriraksa, N.; Surapinit, S.; Jittiwat, J.; Kongsui, R. Alleviative Effect of Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit via Enhancing Antioxidant and Cholinergic Function in Rats by Pinostrobin from Boesenbergia rotunda (L.). Biomed. Rep. 2024, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, H.; Hu, X.; Ren, T.; Dong, R.; Aadil, R.M.; Zou, L.; Sharif, M.K.; Li, L. Characterization and Exploration of the Neuroprotective Potential of Oat-Protein-Derived Peptides in PC12 Cells and Scopolamine-Treated Zebrafish. Nutrients 2024, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinza, I.; Guliev, C.; Oresanya, I.O.; Gok, H.N.; Orhan, I.E.; Hritcu, L. Solanum macrocarpon L. Ethanolic Leaf Extract Exhibits Neuroprotective and Anxiolytic Effects in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesic Zebrafish Model. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinza, I.; Boiangiu, R.S.; Honceriu, I.; Abd-Alkhalek, A.M.; Osman, S.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Todirascu-Ciornea, E.; Dumitru, G.; Hritcu, L. Neuroprotective Potential of Origanum majorana L. Essential Oil Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits and Oxidative Stress in a Zebrafish Model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, Y.P. Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, I.; Pelinescu, D.; Gatea, F.; Ionescu, R.; Barcan, A.; Rosca, R.; Zanfirescu, A.; Vamanu, E. Boletus Edulis Extract—A New Modulator of Dysbiotic Microbiota. Life 2023, 13, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinza, I.; Stache, B.A.; Mihasan, M.; Gorgan, D.L.; El Raey, M.A.; El-Kashak, W.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Hritcu, L. Sweroside Modulates Oxidative Stress and Neuroplasticity-Related Gene Expression in Scopolamine-Treated Zebrafish. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2025, 24, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, S.T.; Clark, R.A. The Design and Statistical Analysis of Animal Experiments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781139344319. [Google Scholar]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L 276, 33–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Hart, P.C.; Elegante, M.F.; Beeson, E.C.; Laffoon, A.L.; Haymore, W.A.M.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Video-Aided Analysis of Zebrafish Locomotion and Anxiety-Related Behavioral Responses. In Zebrafish Neurobehavioral Protocols; Kalueff, A., Cachat, J., Eds.; Neuromethods; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 51, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiangiu, R.S.; Bagci, E.; Dumitru, G.; Hritcu, L.; Todirascu-Ciornea, E. Angelica purpurascens (Avé-Lall.) Gilli. Essential Oil Improved Brain Function via Cholinergic Modulation and Antioxidant Effects in the Scopolamine-Induced Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model. Plants 2022, 11, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capatina, L.; Napoli, E.M.; Ruberto, G.; Hritcu, L. Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (Lamiaceae) Essential Oil Prevents Behavioral and Oxidative Stress Changes in the Scopolamine Zebrafish Model. Molecules 2021, 26, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cell Growth and Survival: Modifications to the Tetrazolium Dye Procedure Giving Improved Sensitivity and Reliability. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyum, A. Isolation of Mononuclear Cells and Granulocytes from Human Blood. Isolation of Monuclear Cells by One Centrifugation, and of Granulocytes by Combining Centrifugation and Sedimentation at 1 g. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1968, 21, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Erridge, C.; Bennett-Guerrero, E.; Poxton, I.R. Structure and Function of Lipopolysaccharides. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, J.R. The ELISA Guidebook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vamanu, E.; Avram, I.; Pelinescu, D.R.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Hritcu, L.; Brinza, I.; Dinu, L.-D.; Boiangiu, R.S. Neurobehavioral Protection by Prebiotic Formulations in a Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impaired Zebrafish Model. Life 2025, 15, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081268
Vamanu E, Avram I, Pelinescu DR, El-Seedi HR, Hritcu L, Brinza I, Dinu L-D, Boiangiu RS. Neurobehavioral Protection by Prebiotic Formulations in a Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impaired Zebrafish Model. Life. 2025; 15(8):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081268
Chicago/Turabian StyleVamanu, Emanuel, Ionela Avram, Diana Roxana Pelinescu, Hesham R. El-Seedi, Lucian Hritcu, Ion Brinza, Laura-Dorina Dinu, and Razvan Stefan Boiangiu. 2025. "Neurobehavioral Protection by Prebiotic Formulations in a Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impaired Zebrafish Model" Life 15, no. 8: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081268
APA StyleVamanu, E., Avram, I., Pelinescu, D. R., El-Seedi, H. R., Hritcu, L., Brinza, I., Dinu, L.-D., & Boiangiu, R. S. (2025). Neurobehavioral Protection by Prebiotic Formulations in a Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impaired Zebrafish Model. Life, 15(8), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081268









