Cerebral Hemodynamics as a Diagnostic Bridge Between Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late-Life Depression: A Multimodal Approach Using Transcranial Doppler and MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Clinical and Demographic Assessment
2.3. Neuropsychological Assessment
2.4. Assessment of Depressive Symptoms
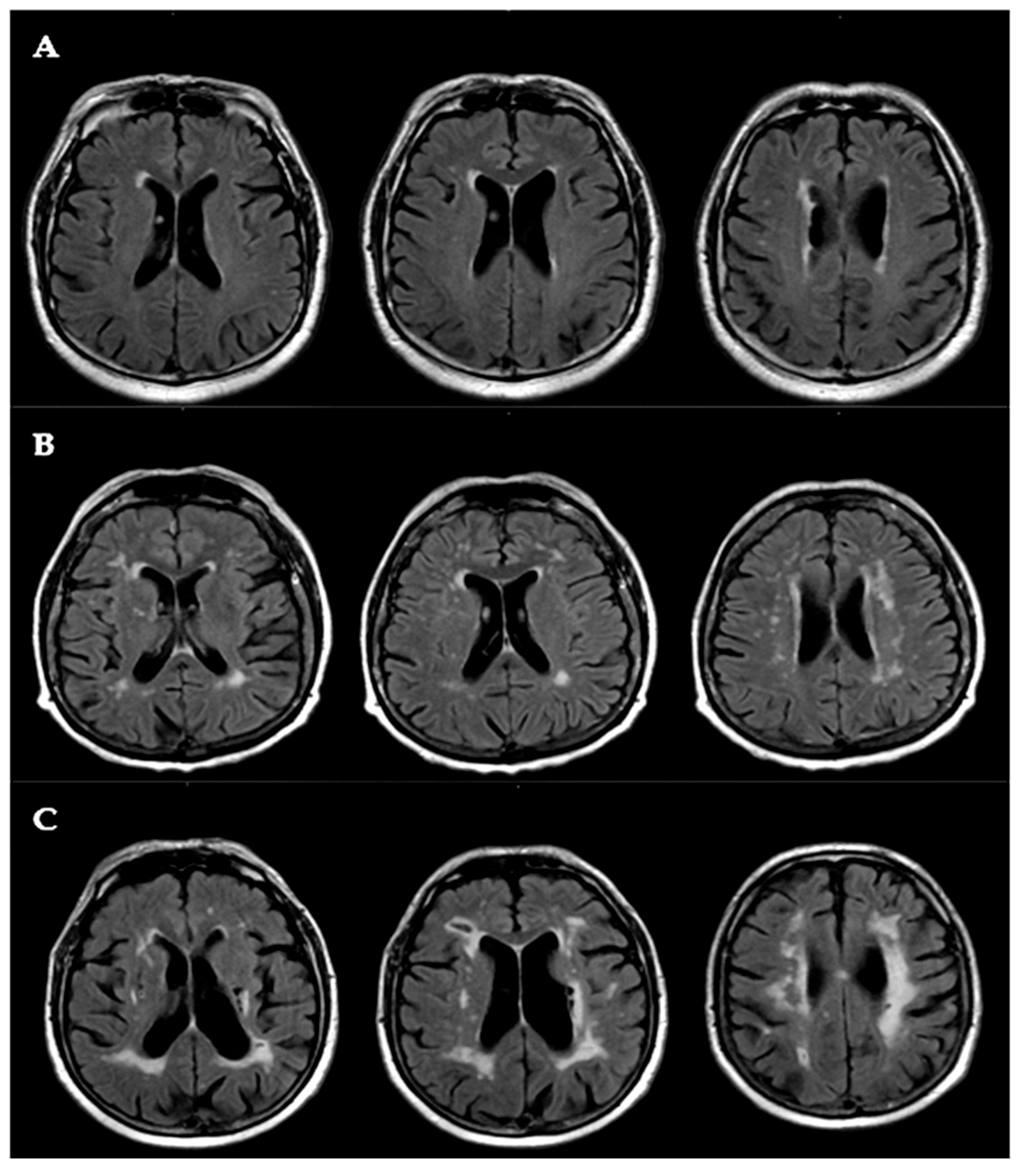
2.5. White Matter Lesion (WML) Assessment
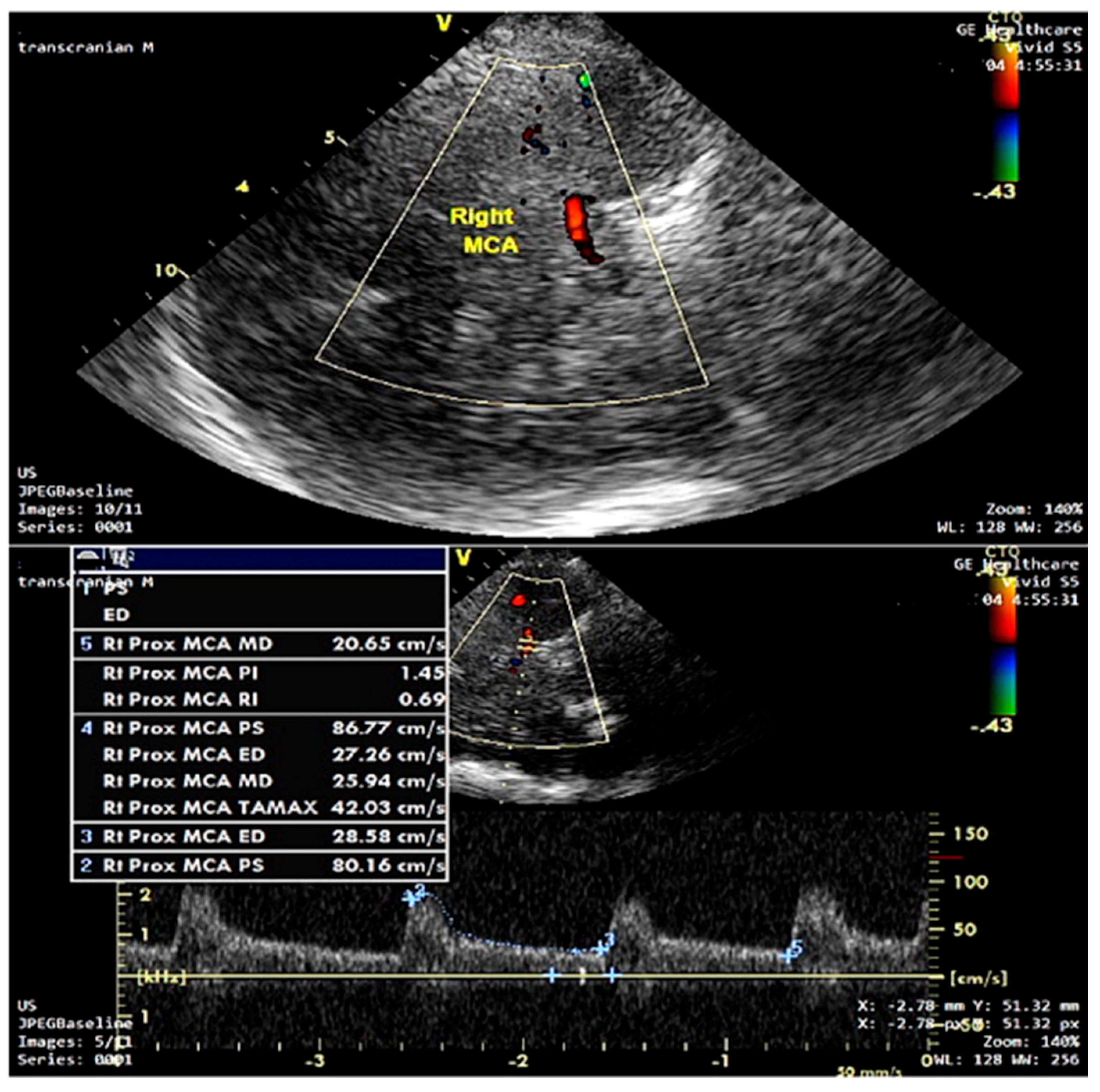
2.6. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) Protocol
2.7. Ethics
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Neuropsychological and Neuroradiological Features
3.3. Transcranial Doppler Hemodynamics
3.4. Predictors of Mild Cognitive Impairment
3.4.1. Univariate Logistic Regression
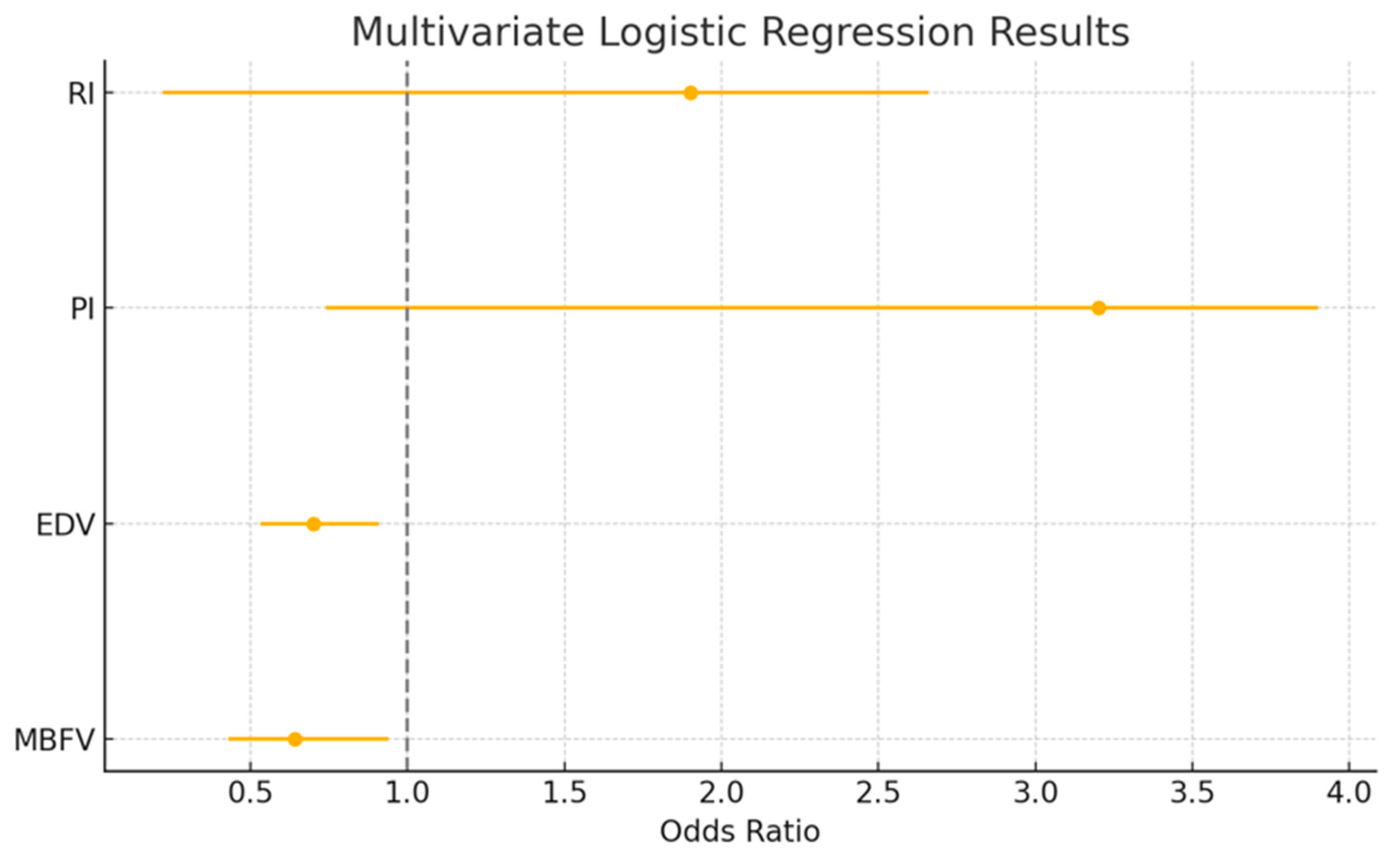
3.4.2. Multivariate Logistic Regression
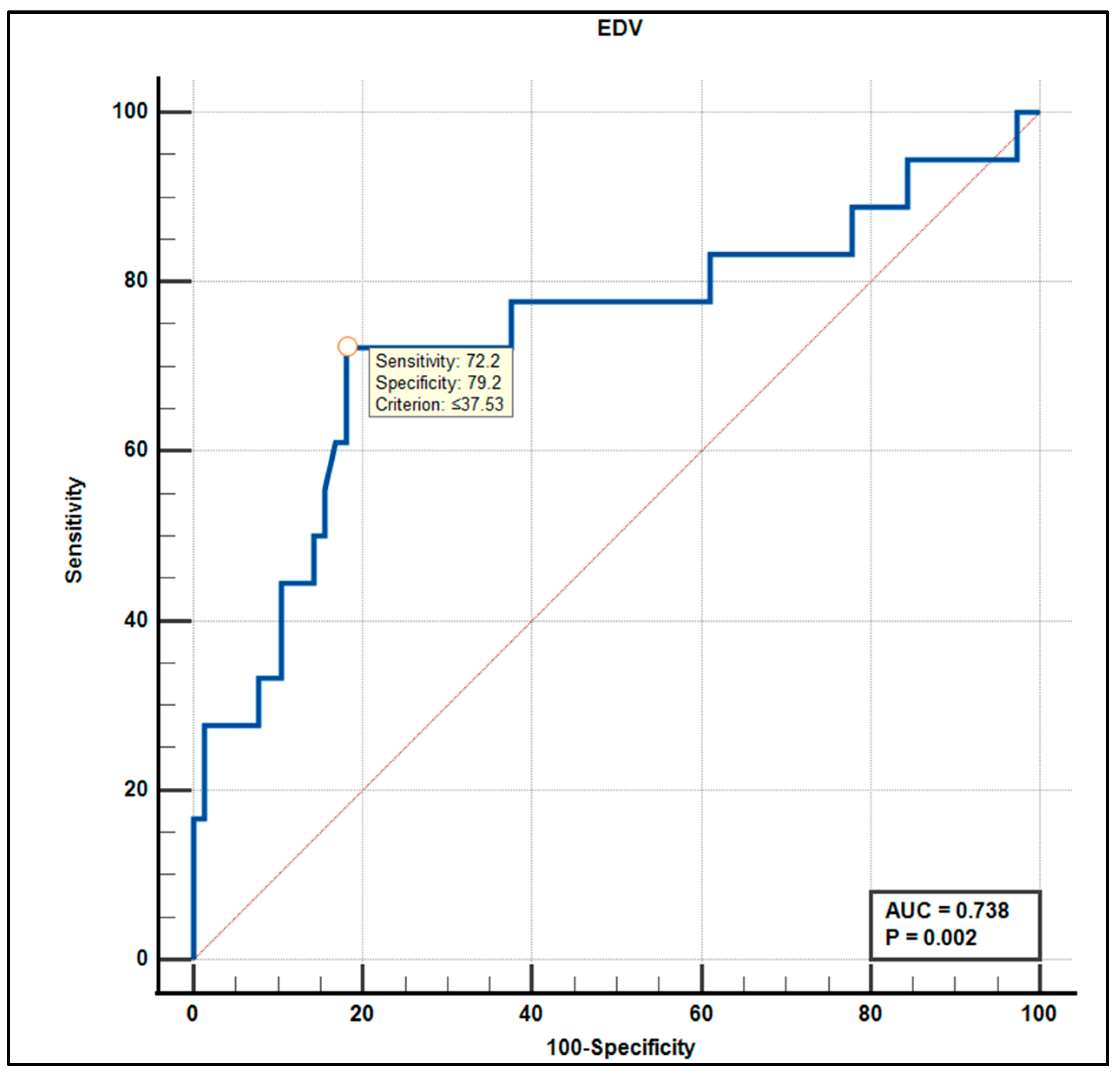
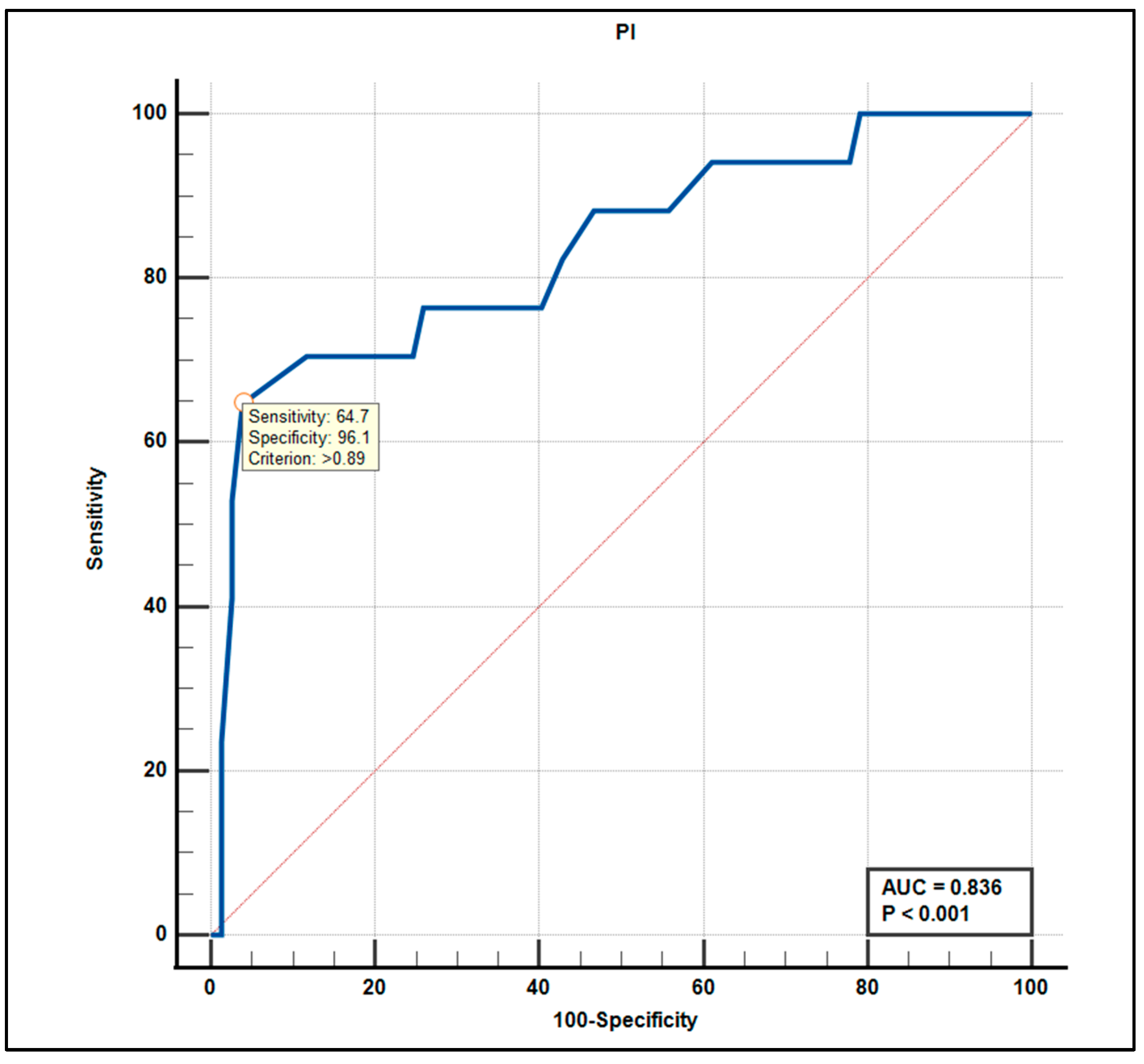
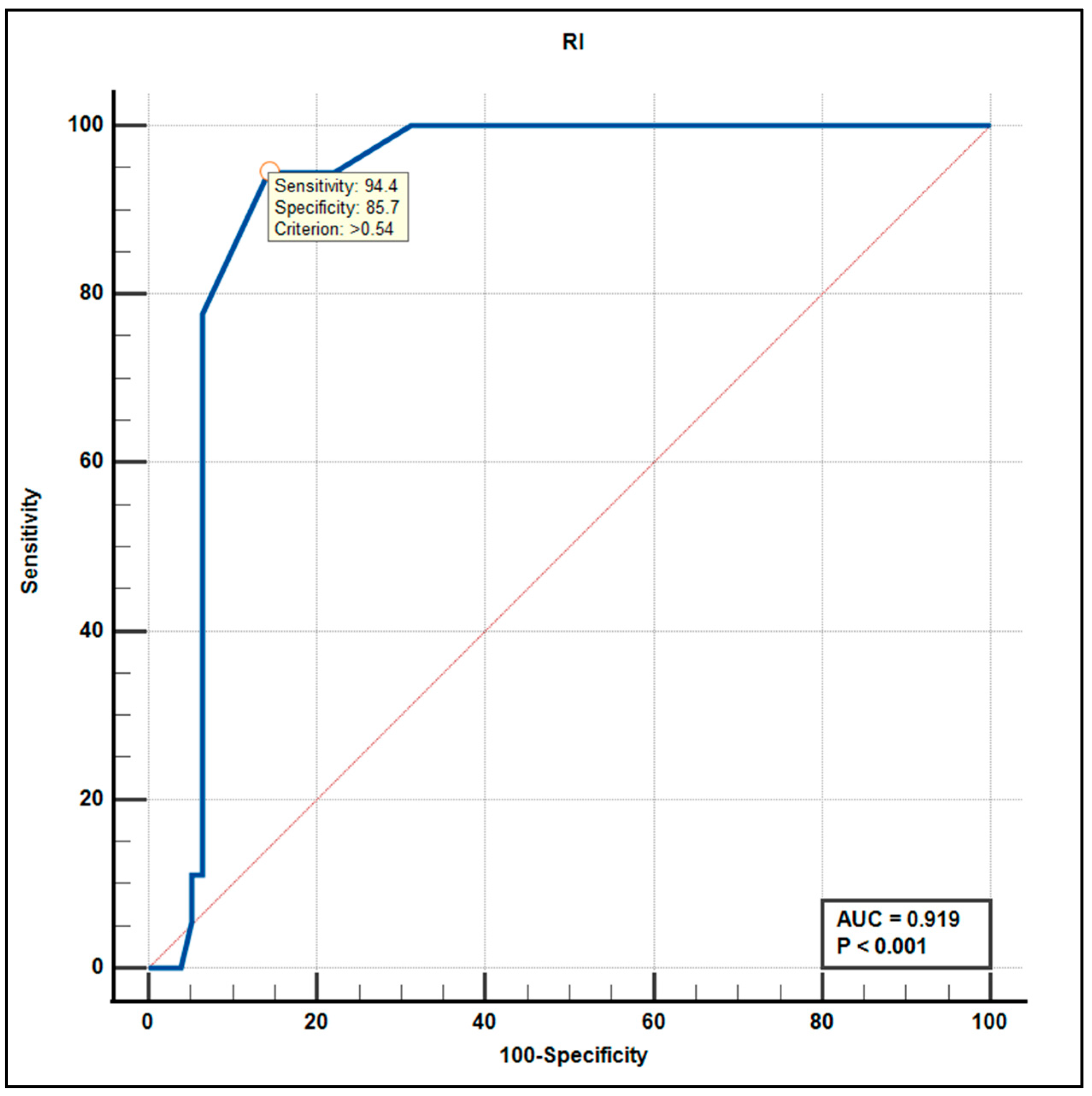
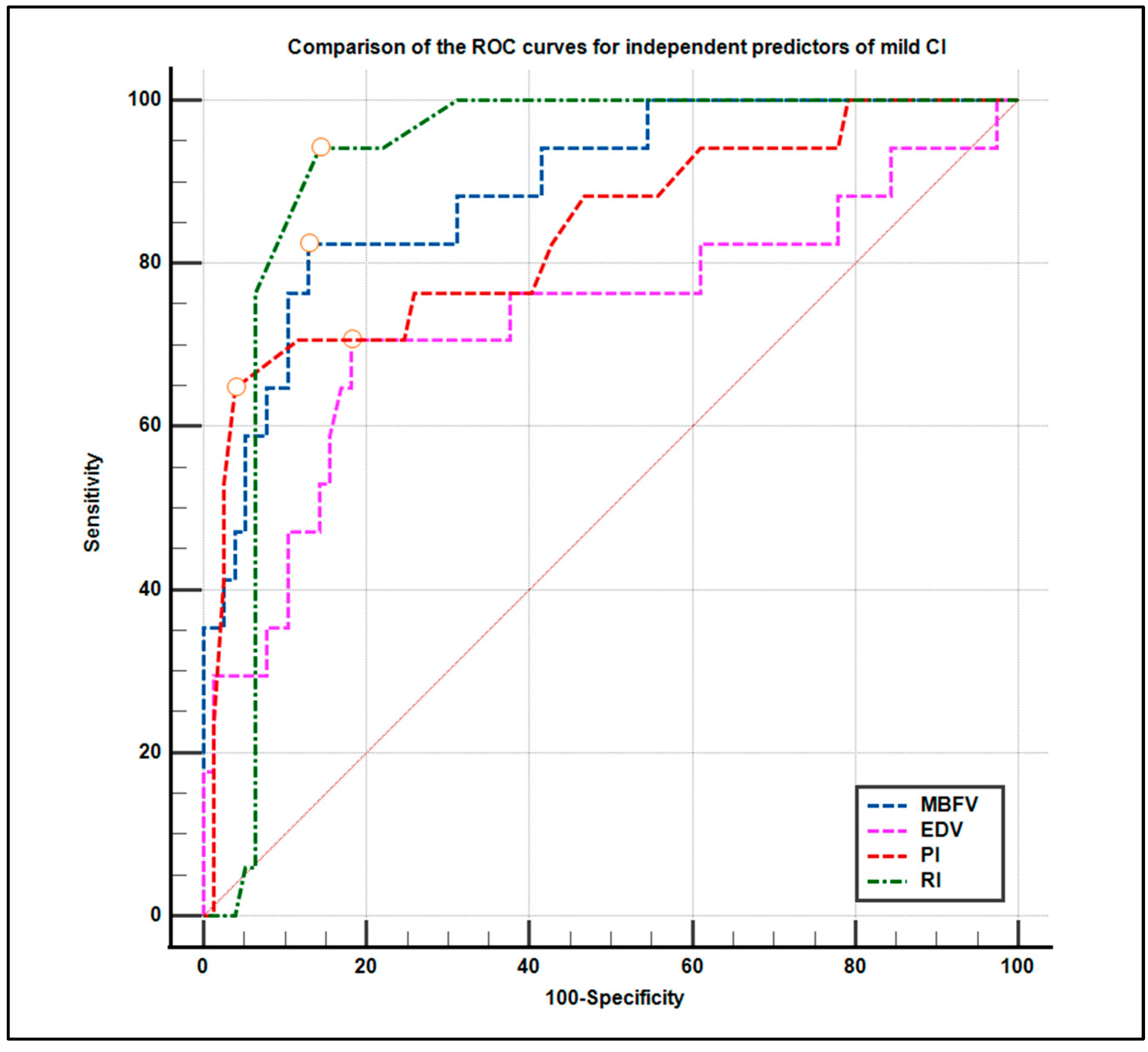
3.5. Diagnostic Accuracy: ROC Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byers, A.L.; Yaffe, K. Depression and risk of developing dementia. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ownby, R.L.; Crocco, E.; Acevedo, A.; John, V.; Loewenstein, D. Depression and risk for Alzheimer disease: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, G.S. Vascular disease, depression, and dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 1178–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, J.C.; de Leeuw, F.E.; Oudkerk, M.; Hofman, A.; Jolles, J.; Breteler, M.M. Cerebral white matter lesions and depressive symptoms in elderly adults. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffens, D.C.; Helms, M.J.; Krishnan, K.R.; Burke, G.L. Cerebrovascular disease and depression symptoms in the cardiovascular health study. Stroke 1999, 30, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelick, P.B.; Scuteri, A.; Black, S.E.; Decarli, C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Iadecola, C.; Launer, L.J.; Laurent, S.; Lopez, O.L.; Nyenhuis, D.; et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2011, 42, 2672–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrobot, O.A.; Black, S.E.; Chen, C.; DeCarli, C.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Ford, G.A.; Kalaria, R.N.; O’Brien, J.; Pantoni, L.; Pasquier, F.; et al. Progress toward standardized diagnosis of vascular cognitive impairment: Guidelines from the VASCOG statement. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, P.S.; Lipnicki, D.M.; Crawford, J.D.; Brodaty, H. The Vascular Behavioral and Cognitive Disorders criteria for vascu-lar cognitive disorders: A validation study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Joseph, M. Transcranial Doppler: An Overview of its Clinical Applications. ISRN Neurol. 2000, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, H.S. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound. Br. Med. Bull. 2000, 56, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicenzini, E.; Ricciardi, M.C.; Altieri, M.; Puccinelli, F.; Bonaffini, N.; Di Piero, V.; Lenzi, G.L. Cerebrovascular reactivity in degenerative and vascular dementia: A transcranial Doppler study. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 58, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; White, T.; Messer, M.A. Mini-Mental State Examination, 2nd Edition (MMSE-2): User’s Manual; Psychological Assessment Resources: Lutz, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehea, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Simões, M.R.; Alves, L.; Santana, I. Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA): Normative study for the Portuguese population. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2011, 33, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Smailagic, N.; Figuls, M.R.; Ciapponi, A.; Sanchez-Perez, E.; Giannakou, A.; Pedraza, O.L.; Bonfill Cosp, X.; Cullum, S. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD010783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist 1969, 9, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, J.I.; Yesavage, J.A. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clin. Gerontol. 1986, 5, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Brink, T.L.; Rose, T.L.; Lum, O.; Huang, V.; Adey, M.; Leirer, V.O. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, R.G.; King, D.H. Arterial assessment by Doppler-shift ultrasound. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1974, 67, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Sloan, M.A.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Sloan, M.A.; Wong, L.K.S.; Douville, C.; Razumovsky, A.Y.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Kaps, M.; Tegeler, C.H. Practice standards for transcranial Doppler ultrasound: Part I–Test performance. J. Neuroimaging 2007, 17, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Fabiani, D.; Cante, L.; Caputo, A.; Sabatella, F.; Riegler, L.; Alfano, G.; Russo, V. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound: Clinical applications from neurological to cardiological setting. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2022, 50, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, V.; Ding, D.; Fu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Chu, W.W.C.; Wang, D.; Abrigo, J.M.; Yang, J.; Wong, A.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound for screening cerebral small vessel disease: A community study. Stroke 2012, 43, 2791–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wan, W.; Xiang, M.; Guan, Y. Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography as a diagnostic tool for cerebrovascular disorders. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 841809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MedCalc® Statistical Software, version 23.1.6; MedCalc Software Ltd.: Ostend, Belgium, 2025. Available online: https://www.medcalc.org (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabayan, B.; van der Grond, J.; Westendorp, R.G.; de Craen, A.J.; van Buchem, M.A.; Mooijaart, S.P. Total cerebral blood flow and mortality in old age: A 9-year follow-up study. Neurology 2012, 79, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabayan, B.; van der Grond, J.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Jukema, J.W.; Ford, I.; Buckley, B.M.; Sattar, N.; van Osch, M.J.P.; van Buchem, M.A.; de Craen, A.J.M. Total cerebral blood flow and the risk of dementia: A population-based study. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.D.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Alexopoulos, G.S. The vascular depression hypothesis: Mechanisms linking vascular disease with depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.Y.; Yang, D.W.; Cho, A.H.; Shim, Y.S.; Seo, S.W. Cerebrovascular hemodynamics on transcranial Doppler ultrasonography and cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 65, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejza, J.; Mariak, Z.; Melhem, E.R.; Bert, R.J. A guide to identification of major cerebral arteries with transcranial color Doppler sonography. AJR 2012, 174, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantone, M.; Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Ferri, R.; Fisicaro, F.; Cappellani, F.; David, E.; Nicosia, V.; Cortese, K.; Pennisi, G.; et al. Transcranial Doppler sonography follow-up study in mild vascular cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2025, 24, e0317888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debette, S.; Markus, H.S. The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 341, c3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.R.; Mungas, D.M.; Kramer, J.H.; Ellis, W.G.; Vinters, H.V.; Zarow, C.; Jagust, W.J.; Chui, H.C. Profiles of neuropsychological impairment in autopsy-defined Alzheimer’s disease and cerebrovascular disease. Brain 2004, 127, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, C.S.; el-Saden, S.; Livshits, Z.; Martin, N.A.; Glenn, T.C.; Saver, J.L. Transcranial Doppler pulsatility indices as a measure of diffuse small-vessel disease. J. Neuroimaging 2001, 11, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, S.E.; Prins, N.D.; den Heijer, T.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M. Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Yaffe, K.; Biller, J.; Bratzke, L.C.; Faraci, F.M.; Gorelick, P.B.; Gulati, M.; Kamel, H.; Knopman, D.S.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Impact of hypertension on cognitive function: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2016, 68, e67–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.T.; Thomas, A. Vascular dementia. Lancet 2015, 386, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, G.S.; Meyers, B.S.; Young, R.C.; Campbell, S.; Silbersweig, D.; Charlson, M. ‘Vascular depression’ hypothesis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, M.; Karim, H.T.; Becker, J.T.; Lopez, O.L.; Anderson, S.J.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Zmuda, M.D.; Butters, M.A. Late-life depression and increased risk of dementia: A longitudinal cohort study. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Group I (No Cognitive Impairment) n = 78 | Group II (Mild Cognitive Impairment) n = 18 | All Patients n = 96 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical characteristics | ||||
| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 68.8 ± 5.8 | 72.5 ± 5.2 | 71.8 ± 5.5 | 0.01 |
| Male sex n (%) | 39 (50) | 10 (55) | 49 (51) | 0.70 |
| Educational level, mean ± SD (years) | 8.0 ± 3.4 | 6.8 ± 3.9 | 8.0 ±3.5 | 0.24 |
| Smokers n (%) | 18 (23) | 5 (25) | 23 (23.9) | 0.85 |
| Hypertension n (%) | 63 (81) | 15 (83) | 78 (81.2) | 0.84 |
| Hypercholesterolemia n (%) | 27 (34) | 6 (35) | 33 (34) | 0.93 |
| Diabetes n (%) | 17 (21) | 4 (22) | 21 (21.8) | 0.92 |
| Coronaropathy n (%) | 11 (14) | 3 (15) | 14 (14.5) | 0.91 |
| Atrial fibrillation n (%) | 11 (14) | 3 (15) | 14 (14.5) | 0.91 |
| Neuropsychological and imaging data | ||||
| MMSE-2, median (IQR) | 27.0 (26.0–29.0) | 23.0 (22–24) | 27.0 (25.2–29.0) | <0.001 |
| MoCA (I–III quartile) | 26.0 (24.0–28.0) | 21.0 (20–24) | 23.0 (21.0–25.0) | <0.001 |
| GDS-15 median (I–III quartile) | 7.8 (6.8–8.7) | 8.8 (7.6–9.9) | 7.9 (6.9–8.8) | 0.02 |
| MRI Fazekas visual scale | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 3.0 (2.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 0.03 |
| Grade 1 n (%) | 27 (35) | 3 (17 | 30 (31) | 0.14 |
| Grade 2 n (%) | 30 (38) | 5 (28) | 35 (37 | 0.42 |
| Grade 3 n (%) | 21 (27) | 10 (55) | 31 (32) | 0.02 |
| TCD parameters | ||||
| Mean BFV | 56.3 (53.6–62.5) | 51.6 (50.8–52.6) | 56.3 (53.6–62.5) | <0.001 |
| PI (%) median (I–III quartile) | 0.73 (0.66–0.81) | 0.94 (0.91–0.96) | 0.73 (0.66–0.81) | <0.001 |
| RI (%) median (I–III quartile) | 0.51 (0.45–0.54) | 0.58 (0.55–0.65) | 0.51 (0.45–0.54) | 0.002 |
| PSV (cm/s) median (I–III quartile) | 84.95 (83.82–85.89) | 86.4 (84.9–88.6) | 84.9 (84.02–86.32) | 0.15 |
| EDV (cm/s) median (I–III quartile) | 40.65 (38.07–42.82) | 36.3 (33.4–39.3) | 39.9 (36.91–42.67) | 0.04 |
| Univariate Logistic Regression | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.88 | 0.79–0.97 | 0.01 |
| GDS-15 | 1.66 | 1.04–2.66 | 0.03 |
| MRI Fazekas visual scale | 2.17 | 1.07–1.41 | 0.03 |
| MBFV (cm/s) | 0.64 | 0.49–0.84 | <0.01 |
| PSV (cm/s) | 1.32 | 1.03–1.69 | 0.02 |
| EDV (cm/s) | 0.78 | 0.66–0.91 | <0.01 |
| PI (%) | 0.79 | 0.63–1.00 | 0.04 |
| RI (%) | 3.4 | 2.97–3.88 | 0.02 |
| Multivariate Logistic Regression | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
| MBFV (cm/s) | 0.64 | 0.43–0.94 | 0.02 |
| EDV (cm/s) | 0.70 | 0.53–0.91 | 0.03 |
| PI (%) | 3.2 | 0.74–3.9 | <0.01 |
| RI (%) | 1.9 | 0.22–2.66 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arnautu, S.-F.; Arnautu, D.-A.; Andor, M.; Vacarescu, C.; Cozma, D.; Bernad, B.-C.; Juratu, C.; Tutelca, A.; Jianu, C.-D. Cerebral Hemodynamics as a Diagnostic Bridge Between Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late-Life Depression: A Multimodal Approach Using Transcranial Doppler and MRI. Life 2025, 15, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081246
Arnautu S-F, Arnautu D-A, Andor M, Vacarescu C, Cozma D, Bernad B-C, Juratu C, Tutelca A, Jianu C-D. Cerebral Hemodynamics as a Diagnostic Bridge Between Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late-Life Depression: A Multimodal Approach Using Transcranial Doppler and MRI. Life. 2025; 15(8):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081246
Chicago/Turabian StyleArnautu, Sergiu-Florin, Diana-Aurora Arnautu, Minodora Andor, Cristina Vacarescu, Dragos Cozma, Brenda-Cristina Bernad, Catalin Juratu, Adrian Tutelca, and Catalin-Dragos Jianu. 2025. "Cerebral Hemodynamics as a Diagnostic Bridge Between Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late-Life Depression: A Multimodal Approach Using Transcranial Doppler and MRI" Life 15, no. 8: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081246
APA StyleArnautu, S.-F., Arnautu, D.-A., Andor, M., Vacarescu, C., Cozma, D., Bernad, B.-C., Juratu, C., Tutelca, A., & Jianu, C.-D. (2025). Cerebral Hemodynamics as a Diagnostic Bridge Between Mild Cognitive Impairment and Late-Life Depression: A Multimodal Approach Using Transcranial Doppler and MRI. Life, 15(8), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081246








