In-Line Monitoring of Milk Lactose for Evaluating Metabolic and Physiological Status in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Animal Housing Conditions
2.2. Parameter Registration
2.3. Milk Parameters
2.4. Blood Parameters
2.5. Monitoring of Cow Behavior and Physiological Parameters
2.6. Group Creation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Examined Characteristics Based on the Lactose Group
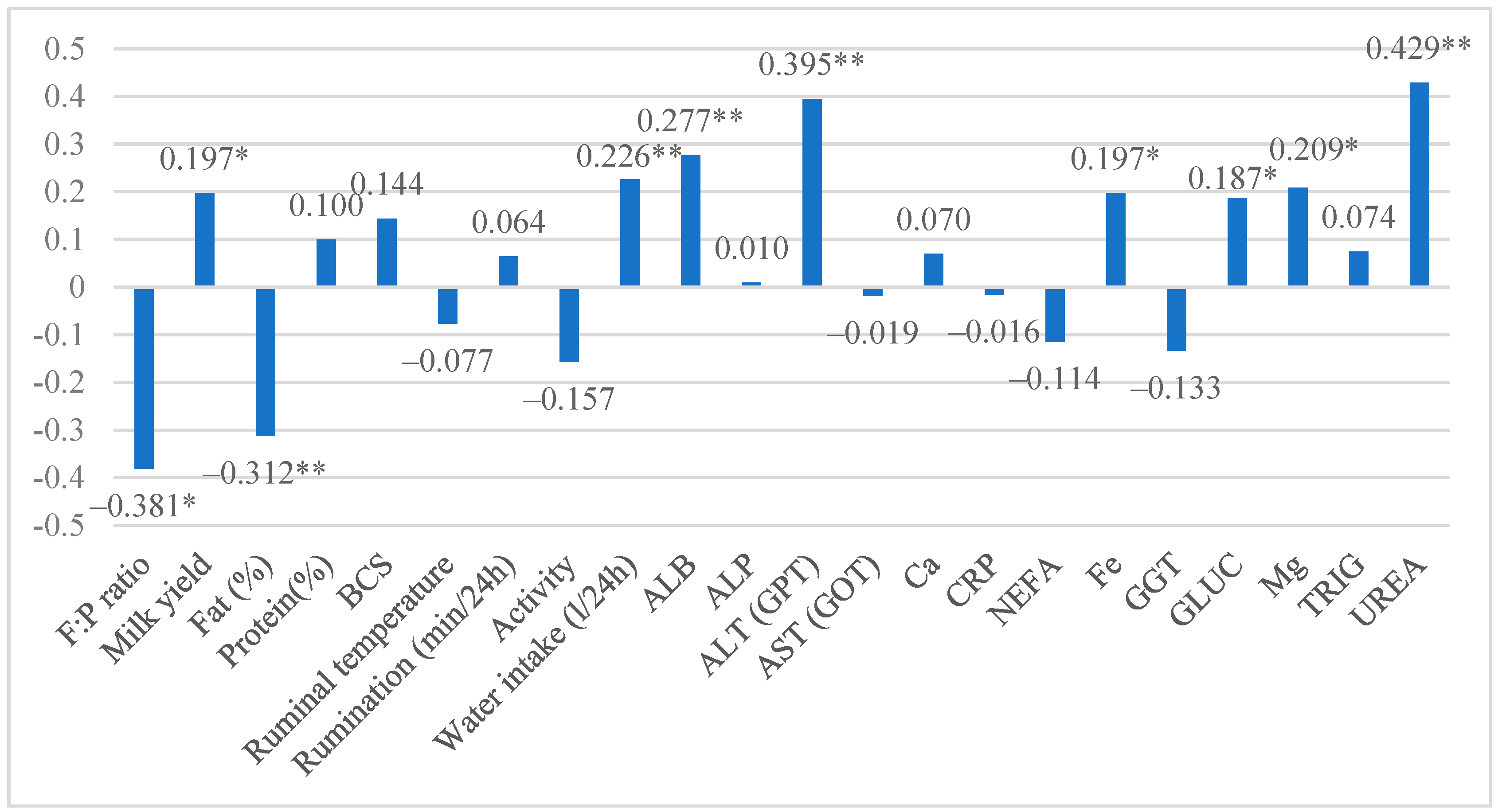
3.2. Correlation Between Behavioral, Milk, and Blood Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djoković, R.; Cincović, M.; Ilić, Z.; Kurčubić, V.; Andjelić, B.; Petrović, M.; Lalic, N.; Jasovic, B. Estimation metabolic status in high yielding dairy cows during transition period and full lactation. Acta Sci. Vet. 2019, 47, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, G.; Licitra, F.; Stamilla, A.; Amore, S.; Dipasquale, M.; Salonia, R.; Antoci, F.; Zecconi, A. Subclinical ketosis in dairy herds: Impact of early diagnosis and treatment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 895468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.J.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Review: Metabolic challenges in lactating dairy cows and their assessment via established and novel indicators in milk. Animal 2019, 13 (Suppl. S1), s75–s81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.; Ranaweera, K.; Weerasinghe, W.; Mahipala, M. Serum metabolic profile based assessment of nutritional status of temperate crossbred, stall-fed, lactating dairy cows: A case study of a medium scale mid-country cattle farm. Trop. Agric. Res. 2018, 29, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geßner, D.; Sandrock, L.; Most, E.; Koch, C.; Ringseis, R.; Eder, K. Performance and metabolic, inflammatory, and oxidative stress-related parameters in early lactating dairy cows with high and low hepatic FGF21 expression. Animals 2022, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan, A.; Piñeiro, J.; Schuenemann, G.; Rajala-Schultz, P.; Sanders, D.; Lakritz, J.; Bas, S. Assessment of daily activity patterns and biomarkers of pain, inflammation, and stress in lactating dairy cows diagnosed with clinical metritis. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8248–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Meng, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, H.; Kan, C.; Wang, T.; Wei, W.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; et al. A novel signaling transduction pathway of melatonin on lactose synthesis in cows via melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and prolactin receptor (PRLR). PeerJ 2023, 11, e15932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Televičius, M.; Juozaitienė, V.; Malašauskienė, D.; Antanaitis, R.; Rutkauskas, A.; Urbutis, M.; Baumgartner, W. Inline milk lactose concentration as biomarker of the health status and reproductive success in dairy cows. Agriculture 2021, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanaitis, R.; Juozaitienė, V.; Jonikė, V.; Baumgartner, W.; Paulauskas, A. Milk lactose as a biomarker of subclinical mastitis in dairy cows. Animals 2021, 11, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, H.; Okuyucu, İ. Changes in udder surface temperature and milk quality characteristics in cows during the hot season. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 10, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Egger-Danner, C.; Mészáros, G.; Fuerst, C.; Penasa, M.; Sölkner, J.; Fuerst-Waltl, B. Genetic associations of lactose and its ratios to other milk solids with health traits in Austrian Fleckvieh cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4238–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antanaitis, R.; Džermeikaitė, K.; Krištolaitytė, J.; Girdauskaitė, A.; Arlauskaitė, S.; Tolkačiovaitė, K.; Baumgartner, W. The relation between milk lactose concentration and the rumination, feeding, and locomotion behavior of early-lactation dairy cows. Animals 2024, 14, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heins, B.; Pereira, G.; Sharpe, K. Precision technologies to improve dairy grazing systems. JDS Commun. 2023, 4, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinard-Flament, J.; Gallard, Y.; Larroque, H. Lactose in blood plasma and the ability of dairy cows to tolerate once-daily milking in terms of milk loss and milk recovery. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3446–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, M.M. Genetic Evaluation of Lactose Percentage and Its Relationship with Fertility and Milk Yield in Irish Dairy Cattle. Master’s Thesis, University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 2019. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/etd/7135 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Costa, A.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Sneddon, N.W.; Shalloo, L.; Franzoi, M.; De Marchi, M.; Penasa, M. Invited review: Milk lactose—Current status and future challenges in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5883–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannuzzi, D.; Piccioli-Cappelli, F.; Pegolo, S.; Bisutti, V.; Schiavon, S.; Gallo, L.; Toscano, A.; Marsan, P.A.; Cattaneo, L.; Trevisi, E.; et al. Observational study on the associations between milk yield, composition, and coagulation properties with blood biomarkers of health in Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaghi, A.; Vakili, A.; Khorrami, B.; Ghaffari, M.; Rico, D. Effect of dietary supplementation or cessation of magnesium-based alkalizers on milk fat output in dairy cows under milk fat depression conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreck, A.L.; Silva, P.R.B.; Collao-Saenz, E.A.; Felix, T.L.; Weiss, W.P. Effects of dietary crude protein concentration and rumen-protected amino acids on production, nitrogen utilization, and energy metabolism in dairy cows. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1498357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.H.; Mayakrishnan, V.; Lee, H.J.; Ki, K.S.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, Y. A comparative study on milk composition of Jersey and Holstein dairy cows during the early lactation. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timkovičová Lacková, P.; Maskaľová, I.; Vajda, V. Effect of parity and days in milk on milk urea concentration and milk components in Holstein dairy cows. Folia Vet. 2022, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TMR Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Corn silage | 31% |
| Alfalfa grass hay | 4% |
| Grass silage | 10% |
| Grain concentrate mash | 49% |
| Mineral mix | 6% |
| TMR Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Dry Matter (DM) | 50.7% |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber (NDF) | 28.3% of DM |
| Acid Detergent Fiber (ADF) | 19.8% of DM |
| Non-Fiber Carbohydrates (NFC) | 38.7% of DM |
| Crude Protein (CP) | 15.8% of DM |
| Net Lactation Energy | 1.6 Mcal/kg |
| Investigated Trait | Lactose Group | (M ± SEM) |
|---|---|---|
| Milk yield, kg | 1 | 33.54 ± 1.340 * |
| 2 | 37.82 ± 1.011 | |
| Fat % | 1 | 4.42 ± 0.098 *** |
| 2 | 4.03 ± 0.052 | |
| Protein % | 1 | 3.33 ± 0.062 |
| 2 | 3.39 ± 0.021 | |
| Body condition score (BCS) | 1 | 3.33 ± 0.064 |
| 2 | 3.44 ± 0.032 | |
| Ruminal temperature | 1 | 38.63 ± 0.060 |
| 2 | 38.58 ± 0.028 | |
| Rumination (min/24 h) | 1 | 506.22 ± 10.535 |
| 2 | 514.44 ± 5.528 | |
| Activity | 1 | 5.96 ± 0.290 |
| 2 | 5.34 ± 0.176 | |
| Water intake | 1 | 112.81 ± 6.593 ** |
| 2 | 130.23 ± 3.141 | |
| Albumin (ALB) | 1 | 34.34 ± 0.538 |
| 2 | 36.27 ± 0.294 | |
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | 1 | 49.27 ± 2.576 |
| 2 | 49.64 ± 1.800 | |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 1 | 22.21 ± 0.879 *** |
| 2 | 27.31 ± 0.537 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | 1 | 86.82 ± 3.329 |
| 2 | 85.96 ± 2.103 | |
| Calcium (Ca) | 1 | 2.46 ± 0.036 |
| 2 | 2.48 ± 0.017 | |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | 1 | 10.49 ± 0.804 |
| 2 | 10.30 ± 0.555 | |
| Non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA) | 1 | 0.30 ± 0.035 |
| 2 | 0.25 ± 0.016 | |
| Iron (Fe) | 1 | 17.75 ± 0.934 * |
| 2 | 20.13 ± 0.526 | |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) | 1 | 29.99 ± 1.194 |
| 2 | 28.01 ± 0.643 | |
| Glucose (GLUC) | 1 | 3.37 ± 0.065 * |
| 2 | 3.53 ± 0.038 | |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 1 | 0.97 ± 0.032 * |
| 2 | 1.05 ± 0.017 | |
| Triglycerides (TRIG) | 1 | 0.09 ± 0.004 |
| 2 | 0.10 ± 0.011 | |
| UREA | 1 | 3.56 ± 0.101 *** |
| 2 | 4.33 ± 0.078 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Girdauskaitė, A.; Arlauskaitė, S.; Rutkauskas, A.; Džermeikaitė, K.; Krištolaitytė, J.; Televičius, M.; Malašauskienė, D.; Anskienė, L.; Japertas, S.; Antanaitis, R. In-Line Monitoring of Milk Lactose for Evaluating Metabolic and Physiological Status in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows. Life 2025, 15, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081204
Girdauskaitė A, Arlauskaitė S, Rutkauskas A, Džermeikaitė K, Krištolaitytė J, Televičius M, Malašauskienė D, Anskienė L, Japertas S, Antanaitis R. In-Line Monitoring of Milk Lactose for Evaluating Metabolic and Physiological Status in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows. Life. 2025; 15(8):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081204
Chicago/Turabian StyleGirdauskaitė, Akvilė, Samanta Arlauskaitė, Arūnas Rutkauskas, Karina Džermeikaitė, Justina Krištolaitytė, Mindaugas Televičius, Dovilė Malašauskienė, Lina Anskienė, Sigitas Japertas, and Ramūnas Antanaitis. 2025. "In-Line Monitoring of Milk Lactose for Evaluating Metabolic and Physiological Status in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows" Life 15, no. 8: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081204
APA StyleGirdauskaitė, A., Arlauskaitė, S., Rutkauskas, A., Džermeikaitė, K., Krištolaitytė, J., Televičius, M., Malašauskienė, D., Anskienė, L., Japertas, S., & Antanaitis, R. (2025). In-Line Monitoring of Milk Lactose for Evaluating Metabolic and Physiological Status in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows. Life, 15(8), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081204









