Involvement of Gonolabis distincta in the Control of Root Maggots in Garlic Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Morphological Identification
2.3. DNA Barcode Identification
2.3.1. Extraction of the Sample for Genomic DNA
2.3.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Sequence Determination
2.3.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Predation Behavior of Domiant Earwig Species on Dominant Root Maggot Species
2.4.1. Determination of Predation Preferences of Larvae and Pupae by Nymph and Adults of Dominant Earwig Species
2.4.2. Preference of Different States of Dominant Earwig Species on Dominant Root Maggot Species
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analyses
3.1. Observation Point Setting and Garlic Root Maggot Sampling
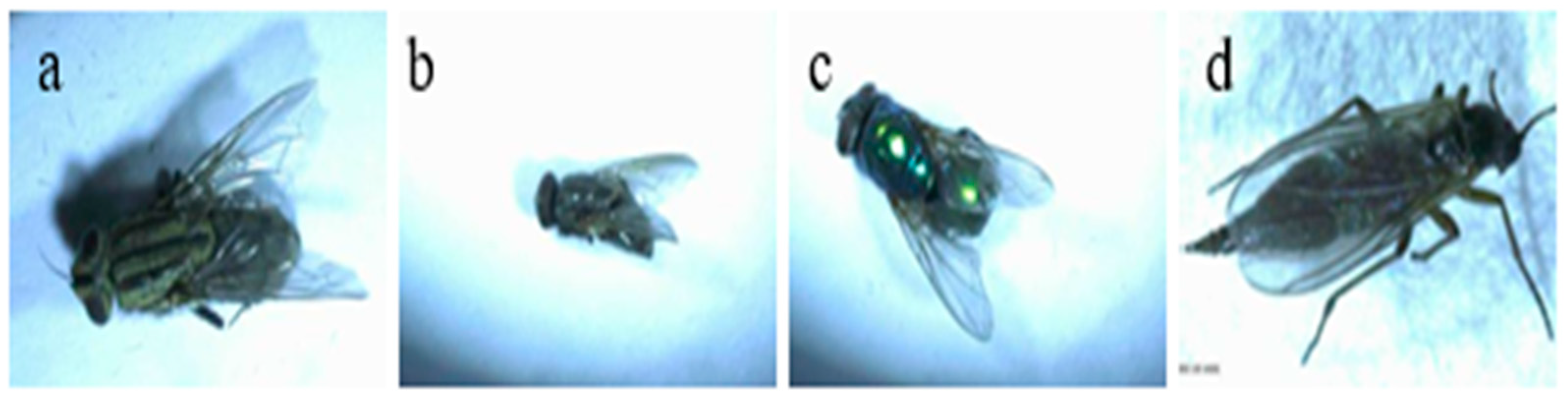
3.2. Identification of Root Maggots and Earwigs Collected from Garlic Field
3.2.1. Species Compositions, Morphological Descriptions, and Life Cycle Observations
3.2.2. Subculture Rearing of D. platura
3.3. Predation Behavior, Predation Capacity, and Predation Preference
3.3.1. Predation Behavior of G. marginalis
3.3.2. Predation Ability of G. distincta Against Larvae and Pupae of D. platura
3.3.3. Predatory Preference of Fifth Instar Nymphs and Male and Female Adults of G. distincta Against Different Developmental Stages of D. platura
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Saber, B.G.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Wasef, L.G.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Al-Sagan, A.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Taha, A.E.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Devkota, H.P. Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Garlic (Allium sativum L.): A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, X. Analysis on the High-quality Development Path of Rural Characteristic Advantageous Industries-Taking Garlic in Qixian County of Henan Province as an Example. Rural. Areas Agric. Farmers 2024, 19, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Testen, A.L.; Mamiro, D.P.; Meulia, T.; Subedi, N.; Islam, M.; Baysal-Gurel, F.; Miller, S.A. First Report of Leek yellow stripe virus in Garlic in Ohio. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Wu, Y.H.; Liu, X.H.; Du, Z.Z.; Qiu, Y.; Song, J.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, X.X. Resistance and clonal selection among Allium sativum L. germplasm resources to Delia antiqua M. and its correlation with allicin content. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2830–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, G.P.; Huang, J.R.; Yin, X.M.; Feng, H.Q. Biological characteristics of riparian earwig Labidura riparia and its predatory capacity against fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Ebach, M.C.; Holdrege, C. DNA barcoding is no substitute for taxonomy. Nature 2005, 434, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindel, D.E.; Miller, S.E. DNA barcoding: A useful tool for taxonomists. Nature 2005, 435, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.H.; Feng, H.Q.; Yang, L.R.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.P.; Huang, J.R.; Feng, H.Y. An Adult Garlic Root Maggot Trap. Patent No. ZL 2024 2 1222735.4, 14 January 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bastin, S.; Percy, D.M.; Siverio, F. Establishing reliable DNA barcoding primers for jumping plant lice (Psylloidea, Hemiptera). BMC Res. Notes 2023, 16, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Bioinform. Methods Protoc. 2000, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.L.; Liu, D.; Guo, L.J.; Li, Y. Rapid and accurate identification of Tenuipalpus hornotinus based on morphology and DNA barcode technology. Environ. Entomol. 2025, 47, 630–640. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.J.; Wang, K.; Hu, J.X.; Gao, B.; Li, H.Y.; Gu, H.L.; Zhang, L.S. Application of DNA barcoding in identification of parasitoids on Myzus persicae. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2024, 65, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.; Zhao, C.Y.; Li, F.; Chen, S.M.; Jia, J.; Liu, F.X.; Wu, S.Y. Application of DNA barcoding in rapid identification of Contarinia maculipennis Felt infesting Dendrobium nobile. J. Trop. Biol. 2024, 15, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, K.M. Bidirectional Predation Between Larvae of the Hoverfly Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae) and the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosdall, L.M.; Clayton, G.W.; Harker, K.N.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Stevenson, F.C. Effects of fall and spring seeding date and other agronomic factors on infestations of root maggots, Delia spp. (Diptera: Anthomyiidae), in canola. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlinger, E.I.; Vandenbosch, R.; Dietrick, E.J. Biological Notes on the Predaceous Earwig Labidura riparia (Pallas), a Recent Immigrant to California [Dermaptera: Labiduridae]. J. Econ. Entomol. 1959, 52, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F.; Shepard, M. Calosoma sayi and Labidura riparia Predation on Noctuid Prey in Soybeans and Locomotor Activity. Environ. Entomol. 1978, 7, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orpet, R.J.; Goldberger, J.R.; Crowder, D.W.; Jones, V.P. Field evidence and grower perceptions on the roles of an omnivore, European earwig, in apple orchards. Biol. Control. 2019, 132, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, A.E.; Mattingly, T.M.; Toro, A.A.; Donald, L.J.; Holliday, N.J. Age and sex-related variation in defensive secretions of adult Chlaenius cordicollis and evidence for their role in sexual communication. Chemoecology 2016, 26, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rork, A.M.; Renner, T. Carabidae semiochemistry: Current and future directions. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.H.; Errabeli, R.; Will, K.; Arias, E.; Attygalle, A.B. 3-Methyl-1-(methylthio)-2-butene: A component in the foul-smelling defensive secretion of two ceroglossus species (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Chemoecology 2019, 29, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.H.; Cao, H.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, X.G.; Cai, C.T.; Li, G.P.; Huang, J.R.; Feng, H.Q. Behavioral and Functional Responses of Labidura riparia Pallas Preying on Spodoptera frugiperda. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2021, 37, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Li, G.P.; Huang, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.S.; Feng, H.Y.; Yin, X.M.; Feng, H.Q. Predation capacity of Labidura riparia Pallas against helicoverpa armiagera (Hübner). Plant Prot. 2023, 49, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.H.; Huang, J.R.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, G.P.; Hao, X.Z.; Wang, L.; Yin, X.M.; Feng, H.Q. Can the Generalist Predator Calosoma chinense Kirby Be Effectively Employed in the Biological Control of Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith)? Insects 2025, 16, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.Q.; Zhu, W.J.; Jin, Q.A.; Wen, H.B.; Peng, Z.Q.; Du, Y.Z. Biology of Chelisoches morio as an enemy of Brontispa longissima. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 49, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X. A new pest of maize-Ladiidae sp. Plant Prot. Technol. Ext. 1996, 2, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.L.; Shi, J.L. Research on the Occurrence and Harm of the Earwig Pest on Eustoma grandiflorum. Yunnan Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.Q.; Qiu, J.Z. Occurrence and Prevention of the Earwig Pest on Bagged Apples. Northwest Hortic. (Fruit Trees Spec. Issue) 2008, 8, 50. [Google Scholar]




| Root Maggots and Earwig Samples Collected from the Same Garlic Field | GenBank/BOLD Number | Gene Fragment Length/bp | Name of Insect Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NC_085745.1 | 681 | D. platura |
| 2 | NC_061662.1 | 688 | B. odoriphaga |
| 3 | NC_028226.1 | 684 | D. antiqua |
| 4 | NC_034805.1 | 680 | M. angustifrons |
| 5 | NW_023995419.1 | 686 | L. sericata |
| 6 | LC767867.1 | 658 | G. marginalis |
| D. platura | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G. distincta | 1st Instar Larvae | 2nd Instar Larvae | 3rd Instar Larvae | Pupae |
| 1st instar nymph | (1.85 ± 0.13) Da | (1.75 ± 0.20) Ca | (1.0 ± 0.16) Db | (0.95 ± 0.09) Db |
| 2nd instar nymph | (2.05 ± 0.15) Da | (1.95 ± 0.15) Ca | (1.35 ± 0.17) Db | (1.30 ± 0.18) Dd |
| 3rd instar nymph | (2.45 ± 0.18) Da | (2.15 ± 0.24) Ca | (1.60 ± 0.13) Db | (1.45 ± 0.18) Db |
| 4th instar nymph | (24.00 ± 0.57) Ca | (21.05 ± 0.43) Bb | (20.65 ± 0.31) Cc | (17.30 ± 0.51) Cc |
| 5th instar nymph | (36.00 ± 0.57) Ba | (28.85 ± 0.29) Bb | (24.80 ± 0.21) Cc | (14.25 ± 0.55) Cd |
| Female adults | (71.25 ± 0.66) Aa | (67.60 ± 0.38) Aa | (57.70 ± 0.54) Ab | (31.40 ± 0.48) ABd |
| Male adults | (63.85 ± 0.41) ABa | (53.45 ± 0.26) Ab | (42.75 ± 0.41) ABc | (41.40 ± 0.18) Ac |
| G. distincta | D. platura | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Instar Larvae | 2nd Instar Larvae | 3rd Instar Larvae | Pupae | |||||
| 5th instar nymph | PN | Ci | PN | Ci | PN | Ci | PN | Ci |
| (27.75 ± 0.27) Aa | 0.097 Bb | (22.75 ± 0.48) Ab | 0.14 Aa | (22.50 ± 0.3) Bb | 0.13 ABa | (18.40 ± 0.2) Cc | −0.11 Bb | |
| Female adults | (28.80 ± 2.24) Aa | 0.24 Ba | (28.40 ± 0.75) Aa | 0.37 Aa | (27.45 ± 2.14) Aa | 0.35 Ab | (21.35 ± 1.14) Ab | 0.09 Ca |
| Male adults | (28.6 ± 0.34) Aa | 0.06 Cb | (27.7 ± 0.15) Aa | 0.38 Ab | (27.3 ± 0.16) Aa | 0.18 Bb | (19.9 ± 0.37) Bb | −0.14 Da |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Yin, X.; Yang, L.; Feng, H. Involvement of Gonolabis distincta in the Control of Root Maggots in Garlic Fields. Life 2025, 15, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081192
Tian C, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Gao X, Yin X, Yang L, Feng H. Involvement of Gonolabis distincta in the Control of Root Maggots in Garlic Fields. Life. 2025; 15(8):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081192
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Caihong, Junpeng Li, Yan Zhang, Junyi Zhang, Xinju Gao, Xinming Yin, Lirong Yang, and Hongqiang Feng. 2025. "Involvement of Gonolabis distincta in the Control of Root Maggots in Garlic Fields" Life 15, no. 8: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081192
APA StyleTian, C., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Gao, X., Yin, X., Yang, L., & Feng, H. (2025). Involvement of Gonolabis distincta in the Control of Root Maggots in Garlic Fields. Life, 15(8), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081192






