Immunonutritional Markers and the Protective Role of Sternal Irrigation and Antibiotic-Impregnated Membranes in Sternal Wound Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
- Age ≥ 18 years.
- Undergoing isolated off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (OPCABG) via median sternotomy.
- Availability of complete laboratory data at all four predefined time points (preoperative, postoperative day 1, day 3, and day 7).
- Regular postoperative outpatient follow-up attendance.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
- Patients with incomplete laboratory or clinical data, including those who died or were lost to follow-up within the first postoperative week, or who failed to attend scheduled outpatient follow-up visits after discharge.
- Patients in whom cardiopulmonary bypass was used during the procedure.
- Minimally invasive coronary artery bypass techniques.
- Acute myocardial infarction within the preceding 30 days.
- Emergent surgical indication or the need for intra-aortic balloon pump support.
- Redo coronary artery bypass procedures.
- Dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease.
- Clinically diagnosed hematological, immunological, or autoimmune disorders.
- The use of chemotherapy or immunosuppressive medication.
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CAR | C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| OPCABG | Off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PNI | Prognostic nutritional index |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| Δ | Delta |
References
- Pignatti, M.; Dolci, G.; Zamagni, E.; Pascale, R.; Piccin, O.; Ammar, A.; Zeneli, F.; Miralles, M.E.L.; Mancuso, K.; Cipriani, R.; et al. Multidisciplinary Management of Sternal Osteomyelitis Due to Klebsiella aerogenes after Open Heart Surgery in a Patient with Multiple Myeloma: A Case Report and Discussion of the Literature. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancari, F.; Santoro, G.; Provenzano, F.; Savarese, L.; Iorio, F.; Giordano, S.; Zebele, C.; Speziale, G. Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy for Prevention of Sternal Wound Infection after Adult Cardiac Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Yu, H.; Shen, C. Review on Risk Factors, Classification, and Treatment of Sternal Wound Infection. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alebrahim, K.; Al-Ebrahim, E. Prevention, Classification and Management Review of Deep Sternal Wound Infection. Heart Surg. Forum 2020, 23, E652–E657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashkhusha, A.; Butt, S.; Abdelghaffar, M.; Wang, W.; Rajananthanan, A.; Roy, S.; Khurshid, B.N.; Zeinah, M.; Harky, A. Sternal Wound Reconstruction Following Deep Sternal Wound Infection: Past, Present and Future: A Literature Review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalpey, Z.; Kumar, U.A.; Hitscherich, P.; Khalpey, Z.; Phillips, T.; Chnari, E.; Long, M. Implementation of Aseptically Processed Human Placental Membrane Allografts Within a Comprehensive Sternal Wound Closure Strategy: A Three-Phase Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett-Guerrero, E.; Ferguson, T.B., Jr.; Lin, M.; Garg, J.; Mark, D.B.; Scavo, V.A., Jr.; Kouchoukos, N.; Richardson, J.B., Jr.; Pridgen, R.L.; Corey, G.R.; et al. Effect of an Implantable Gentamicin-Collagen Sponge on Sternal Wound Infections Following Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized Trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.; Bratu, A.G.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Collagen-Based Wound Dressings: Innovations, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewski, M.; Pawliszak, W.; Zaborowska, K.; Navarese, E.P.; Szwed, K.A.; Kowalkowska, M.E.; Kowalewski, J.; Borkowska, A.; Anisimowicz, L. Gentamicin-Collagen Sponge Reduces the Risk of Sternal Wound Infections After Heart Surgery: Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 1631–1640.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, Y.; Fukunaga, N.; Abe, T.; Nakamura, K.; Usui, A.; Koyama, T. Efficacy of New Multimodal Preventive Measures for Post-Operative Deep Sternal Wound Infection. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 67, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, T. Sternal Wound Infections. In Cardiac Surgery; Raja, S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauley, R.P.; Slatnick, B.L.; Truche, P.; Barron, S.; Kang, C.; Morris, D.; Chu, L. Development of a Risk Score to Predict Occurrence of Deep Sternal Dehiscence Requiring Operative Debridement. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2024, 167, 757–764.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, B.M.M.; Mejia, O.A.V.; Sorio, J.L.; Silva, P.d.B.e.; Oliveira, M.A.P.; Nakazone, M.A.; Tiveron, M.G.; Campagnucci, V.P.; Lisboa, L.A.F.; Zubelli, J.; et al. Performance of a Novel Risk Model for Deep Sternal Wound Infection After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abanoz, M.; Engin, M. The Effect of the Relationship Between Post-Cardiotomy Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet Counts on Early Major Adverse Events After Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Turk. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 29, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurbuz, O.; Kumtepe, G.; Ozkan, H.; Karal, I.H.; Velioglu, Y.; Ercan, A.; Yüksel, A.; Ener, S. Predictive Value of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Long-Term Cardiovascular Event Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 35, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parla, K.; Tatli, A.B.; Pala, A.A.; Goncu, M.T. The Importance of Inflammatory Parameters in Predicting Deep Sternal Wound Infections After Open Heart Surgery. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2022, 68, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akam, E.A.; Pelekhaty, S.L.; Knisley, C.P.; Ley, M.G.; Loran, N.V.; Ley, E.J. Nutritional Support for Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Patients: From ICU to Outpatient Care. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, M.I.; Shim, J.K.; Lee, H.S.; Jeon, S.; Kwak, Y.L. Predictive Value of Postoperative Prognostic Nutritional Index Trajectory for Mortality Outcomes After Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1530651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Cai, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, C.; Ni, X. Prognostic Nutritional Index and Prognosis of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1114053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkaya, Ö.; Arslan, Ü. Sex-Specific Impact of Inflammation and Nutritional Indices on AVF Blood Flow and Maturation: A Retrospective Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greberski, K.; Batko, J.; Bugajski, P.; Łuczak, M.; Brzeziński, M.; Bartuś, K. Predictive Value of Preoperative Morphology Parameters in Patients Undergoing On-Pump and Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jęczmyk, A.; Krych, S.; Jekiełek, M.; Jurkiewicz, M.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kramkowski, K.; Hrapkowicz, T. Wound Healing Complications After Sternotomy—Causes, Prevention, and Treatment—A New Look at an Old Problem. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivert, T.; Berge, A.; Bratt, S.; Dalén, M. Incidence and Healing Times of Postoperative Sternal Wound Infections: A Retrospective Observational Single-Centre Study. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2024, 58, 2330349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenitsky, S.A.; Calic, D.; Arora, R.C.; Grocott, H.P.; Lakowski, T.M.; Lillico, R.; Ariano, R.E. Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: Intraoperative Cefazolin Concentrations and Sternal Wound Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01360-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, H.L.; Salm, T.V.; Engelman, R.; Orgill, D.; Gordon, S. Prevention and Management of Sternal Wound Infections. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 152, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgand, G.; Radu, C.; Alkhoder, S.; Al Attar, N.; Raffoul, R.; Dilly, M.P.; Nataf, P.; Lucet, J.C. Does a Gentamicin-Impregnated Collagen Sponge Reduce Sternal Wound Infections in High-Risk Cardiac Surgery Patients? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 16, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Anderson, E.; Harper, J.G. Overview and Management of Sternal Wound Infection. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2011, 25, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perezgrovas-Olaria, R.; Audisio, K.; Cancelli, G.; Rahouma, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Soletti, G.J.; Chadow, D.; Demetres, M.; Girardi, L.N.; Gaudino, M. Deep Sternal Wound Infection and Mortality in Cardiac Surgery: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 115, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoon, P.H.Y.; Hwang, N.C. Deep Sternal Wound Infection: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesthesia 2020, 34, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creanor, S.; Barton, A.; Marchbank, A. Effectiveness of a Gentamicin Impregnated Collagen Sponge on Reducing Sternal Wound Infections Following Cardiac Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2012, 94, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegranzi, B.; Bischoff, P.; de Jonge, S.; Kubilay, N.Z.; Zayed, B.; Gomes, S.M.; Abbas, M.; Atema, J.J.; Gans, S.; van Rijen, M.; et al. New WHO Recommendations on Preoperative Measures for Surgical Site Infection Prevention: An Evidence-Based Global Perspective. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e276–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegranzi, B.; Zayed, B.; Bischoff, P.; Kubilay, N.Z.; de Jonge, S.; de Vries, F.; Gomes, S.M.; Gans, S.; Wallert, E.D.; Wu, X.; et al. New WHO Recommendations on Intraoperative and Postoperative Measures for Surgical Site Infection Prevention: An Evidence-Based Global Perspective. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e288–e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Oakley, R.M.; Wright, J.E. Postoperative Mediastinitis: Classification and Management. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1996, 61, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajja, L.R. Strategies to Reduce Deep Sternal Wound Infection after Bilateral Internal Mammary Artery Grafting. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 16, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabay, O.; Fermanci, E.; Silistreli, E.; Aykut, K.; Yurekli, I.; Catalyurek, H.; Acikel, U. Intracutaneous versus Transcutaneous Suture Techniques: Comparison of Sternal Wound Infection Rates in Open-Heart Surgery Patients. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2005, 32, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Risnes, I.; Abdelnoor, M.; Baksaas, S.T.; Lundblad, R.; Svennevig, J.L. Sternal Wound Infections in Patients Undergoing Open Heart Surgery: Randomized Study Comparing Intracutaneous and Transcutaneous Suture Techniques. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 72, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, H.; Takahashi, A. Sternal Suturing Technique and Chest Wound Complication. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, N.J.; Juvany, M.; Guillaumes, S.; Hoyuela, C.; Vidal, O.; Pera, M. Effect of Topical Gentamicin in Preventing Surgical Site Infection in Elective Incisional Hernia Repair in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 80112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wistrand, C.; Söderquist, B.; Sundqvist, A.S. Time-Dependent Bacterial Air Contamination of Sterile Fields in a Controlled Operating Room Environment: An Experimental Intervention Study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 110, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammelin, A.; Domicel, P.; Hambraeus, A.; Ståhle, E. Dispersal of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis by Staff in an Operating Suite for Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: Relation to Skin Carriage and Clothing. J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 44, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, S.S.; Bicer, Y.; Yapici, N.; Kalaca, S.; Aydin, O.O.; Camur, G.; Kocak, F.; Aykac, Z. Analysis of Risk Factors for Sternal Surgical Site Infection Emphasizing the Appropriate Ventilation of the Operating Theaters. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2006, 27, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühme, T.; Isaksson, B.; Dahlin, L.G. Wound Contamination in Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Quantitative and Qualitative Study of the Bacterial Growth in Sternal Wounds in Cardiac Surgery Patients. APMIS 2007, 115, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berríos-Torres, S.I.; Umscheid, C.A.; Bratzler, D.W.; Leas, B.; Stone, E.C.; Kelz, R.R.; Reinke, C.E.; Morgan, S.; Solomkin, J.S.; Mazuski, J.E.; et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Cano, M.; Kraft, M.; Curell, A.; Puig-Asensio, M.; Balibrea, J.; Armengol-Carrasco, M.; García-Alamino, J.M. Use of Topical Antibiotics before Primary Incision Closure to Prevent Surgical Site Infection: A Meta-Analysis. Surg. Infect. 2019, 20, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, O.; Svedjeholm, R.; Söderquist, B.; Granfeldt, H.; Vikerfors, T.; Källman, J. Local Gentamicin Reduces Sternal Wound Infections after Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 79, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, H.L.; Ejiofor, J.I.; McGurk, S.; Tsuyoshi, K.; Shekar, P.; Body, S.C. Vancomycin Paste Does Not Reduce the Incidence of Deep Sternal Wound Infection After Cardiac Operations. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.L.; Diaconescu, A.C.; Horvath, K.A. Routine Use of Topical Bacitracin to Prevent Sternal Wound Infections After Cardiac Surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ling, M.L.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Abbas, A.; Morikane, K.; Lee, K.Y.; Warrier, A.; Yamada, K. APSIC Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infections. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Surgical Site Infections: Prevention and Treatment; NICE Guideline No. 125; NICE: London, UK, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542473/ (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Kowalewski, M.; Pasierski, M.; Makhoul, M.; Comanici, M.; Dąbrowski, E.J.; Matteucci, M.; Litwinowicz, R.; Kowalówka, A.; Wańha, W.; Jiritano, F.; et al. Topical Vancomycin for Sternal Wound Infection Prophylaxis. A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis of over 40,000 Cardiac Surgery Patients. Surgery 2023, 174, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, T.J.; Sino, S.; Paraforos, A.; Leick, J.; Friedrich, I. Topical Vancomycin Reduces the Incidence of Deep Sternal Wound Complications after Sternotomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 114, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, H.L. The Use of Vancomycin Paste to Reduce Sternal Wound Infections after Cardiac Surgery—Why Is This Still a “Sticky” Subject. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 1324–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, M.V.; Braile, D.M.; Joaquim, M.R.; Suzuki, F.A.; Alves, R.H. The Use of the Vancomycin Paste for Sternal Hemostasis and Mediastinitis Prophylaxis. Rev. Bras. Cir. Cardiovasc. 2008, 23, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servito, M.; Khani-Hanjani, A.; Smith, K.M.; Tsuyuki, R.T.; Mullen, J.C. Topical Vancomycin and Risk of Sternal Wound Infections: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 114, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewski, M.; Kołodziejczak, M.M.; Urbanowicz, T.; De Piero, M.E.; Mariani, S.; Pasierski, M.; Makhoul, M.; Comanici, M.; Dąbrowski, E.J.; Matteucci, M.; et al. Regional Antibiotic Delivery for Sternal Wound Infection Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LifeNet Health Foundation. ReadiGraft Fascia Lata. Available online: https://www.lifenethealth.org/general-orthopedics/soft-tissue/readigraftr-fascia-lata?fr=NTU= (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Friberg, O.; Jones, I.; Sjöberg, L.; Söderquist, B.; Vikerfors, T.; Källman, J. Antibiotic Concentrations in Serum and Wound Fluid after Local Gentamicin or Intravenous Dicloxacillin Prophylaxis in Cardiac Surgery. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 35, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassen, M.B.; Hanberg, P.; Stilling, M.; Petersen, K.K.; Søballe, K.; Krag, L.B.; Højskov, C.S.; Bue, M. Local Concentrations of Gentamicin Obtained by Microdialysis after a Controlled Application of a GentaColl Sponge in a Porcine Model. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Omar, Y.; Kocher, G.J.; Bosco, P.; Barbero, C.; Waller, D.; Gudbjartsson, T.; Sousa-Uva, M.; Licht, P.B.; Dunning, J.; Schmid, R.A.; et al. European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery Expert Consensus Statement on the Prevention and Management of Mediastinitis. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2017, 51, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, O.; Dahlin, L.G.; Källman, J.; Kihlström, E.; Söderquist, B.; Svedjeholm, R. Collagen-Gentamicin Implant for Prevention of Sternal Wound Infection; Long-Term Follow-Up of Effectiveness. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 9, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rai, V.K.; Narang, R.K.; Markandeywar, T.S. Collagen-Based Formulations for Wound Healing: A Literature Review. Life Sci. 2022, 290, 120096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozioł, M.; Targońska, S.; Stążka, J.; Kozioł-Montewka, M. Gentamicin-Impregnated Collagen Sponge for Preventing Sternal Wound Infection after Cardiac Surgery. Pol. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2014, 11, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, O. Local Collagen-Gentamicin for Prevention of Sternal Wound Infections: The LOGIP Trial. APMIS 2007, 115, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, H.; Yoshii, S.; Abraham, S.J.; Okamoto, Y.; Hosaka, S.; Fukuda, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nakajima, M.; Honda, Y.; Takizawa, K. Topical Spraying of Cefazolin and Gentamicin Reduces Deep Sternal Wound Infections after Heart Surgery: A Multicenter, Large Volume, Retrospective Study. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirahara, N.; Miyata, H.; Motomura, N.; Kohsaka, S.; Nishimura, T.; Takamoto, S. Procedure- and Hospital-Level Variation of Deep Sternal Wound Infection from All-Japan Registry. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 109, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, M.; Modrow, M.; Thompson-Brazill, K.A.; Ledford, J.E.; Harr, C.D.; Williams, J.B. Eliminating Sternal Wound Infections: Why Every Cardiac Surgery Program Needs an I Hate Infections Team. JTCVS Tech. 2023, 19, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, D.T.; Adams, D.H.; Byrne, J.G.; Aranki, S.F.; Collins, J.J., Jr.; Couper, G.S.; Allred, E.N.; Cohn, L.H.; Rizzo, R.J. Impact of Body Mass Index and Albumin on Morbidity and Mortality after Cardiac Surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1999, 118, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madjarov, J.M.; Katz, M.G.; Hadas, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Freage-Kahn, L.; Madzharov, S.; Vincek, A.; Madjarova, S.J.; Seidman, P.; Shtraizent, N.; et al. Chronic Thoracic Pain after Cardiac Surgery: Role of Inflammation and Biomechanical Sternal Stability. Front. Pain Res. 2023, 4, 1180969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoz, G.; Aytacoglu, B.N.; Sucu, N.; Tamer, L.; Bayindir, I.; Kose, N.; Kaya, A.; Dikmengil, M. Comparison and Evaluation of Experimental Mediastinitis Models: Precolonized Foreign Body Implants and Bacterial Suspension Inoculation Seems Promising. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jennings, J.A.; Carpenter, D.P.; Troxel, K.S.; Beenken, K.E.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Courtney, H.S.; Haggard, W.O. Novel Antibiotic-Loaded Point-of-Care Implant Coating Inhibits Biofilm. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 2270–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, L.R.; Awais, R.; Beenken, K.E.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Haggard, W.O.; Jessica, A.J. Local Delivery of Amikacin and Vancomycin from Chitosan Sponges Prevent Polymicrobial Implant-Associated Biofilm. Mil. Med. 2018, 183 (Suppl. S1), 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götz, F. Staphylococcus and Biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risnes, I.; Ueland, T.; Aukrust, P.; Lundblad, R.; Baksaas, S.T.; Mollnes, T.E.; Svennevig, J.L. Complement Activation and Cytokine and Chemokine Release during Mediastinitis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 75, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, R.J.; van Putte, B.P.; de Mol, B.A.J.M.; Hoogewerf, M.; Mandigers, T.J.; Kloppenburg, G.T.L. Application of Local Gentamicin in the Treatment of Deep Sternal Wound Infection: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2022, 61, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, M.; Wong, C.H.M.; Harky, A. Sternal Wound Infections, Risk Factors and Management—How Far Are We? A Literature Review. Hear. Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, U.; Bibo, L.; Pierre, M.; Bayfield, N.; Raichel, L.; Merry, C.; Larbalestier, R. Deep Sternal Wound Infections after Cardiac Surgery: A New Australian Tertiary Centre Experience. Hear. Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Raz, A.; Leibovici, L.; Madar, H.; Holinger, R.; Rubinovitch, B. Sternal Wound Infection after Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: Validation of Existing Risk Scores. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 133, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bota, O.; Pablik, J.; Taqatqeh, F.; Mülhausen, M.; Matschke, K.; Dragu, A.; Rasche, S.; Bienger, K. Pathological Study of Sternal Osteomyelitis after Median Thoracotomy—A Prospective Cohort Study. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2023, 408, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Oen, K.Q.X.; Lim, G.R.S.; Hartono, J.L.; Muthiah, M.; Huang, D.Q.; Teo, F.S.W.; Li, A.Y.; Mak, A.; Chandran, N.S.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Development of Immune-Related Adverse Events and Outcomes from Immune Checkpoint Blockade: A Case-Control Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargın, M.; Taşdemir Mete, M.; Bayer Erdoğan, S.; Kuplay, H.; Baştopçu, M.; Bayraktar, F.; Acarel, M.; Aykut Aka, S. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Early Renal Failure under Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support for Postcardiotomy Shock. Turk. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 27, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zang, F. Clinical Risk Factors for Postoperative Infection in Adult Cardiac Surgery with Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Retrospective Study. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2025, 7, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonocito, C.; Sanfilippo, F.; De Locker, I.; Chiarenza, F.; Giacomo, C.; Njimi, H.; George, S.; Astuto, M.; Vincent, J.L. C-Reactive Protein Kinetics after Cardiac Surgery: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2022, 25, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosmarakis, E.S.; Prapas, S.N.; Rellos, K.; Michalopoulos, A.; Samonis, G.; Falagas, M.E. Nosocomial Infections after Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: Frequency, Characteristics, and Risk Factors. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 6, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudino, M.; Nasso, G.; Andreotti, F.; Minniti, G.; Iacoviello, L.; Donati, M.; Schiavello, R.; Possati, G. Preoperative C-Reactive Protein Level and Outcome Following Coronary Surgery. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2002, 22, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foldyna, B.; Mueller, M.; Etz, C.D.; Luecke, C.; Haunschild, J.; Hoffmann, I.; Gutberlet, M.; Lehmkuhl, L. Computed Tomography Improves the Differentiation of Infectious Mediastinitis from Normal Postoperative Changes after Sternotomy in Cardiac Surgery. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2949–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, D. The Early Diagnostic Value of C-Reactive Protein (CRP) in Deep Sternal Wound Infection after Cardiac Surgery. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, A.R.; Kwon, J.H.; Park, J.; Min, J.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, S.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, W.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Preoperative C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio and Mortality of Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Graft. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1354816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, F.G.; Szalai, A.J. C-Reactive Protein Gene Polymorphisms, C-Reactive Protein Blood Levels, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, R.G.; Toori, K.U. Correlation between Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and C-Reactive Protein in Diverse Disease States in Hospitalized Patients. Pak. J. Med Sci. 2024, 40, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Cheng, N.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Risk Factors for Sternal Wound Infection after Median Sternotomy: A Nested Case-Control Study and Time-to-Event Analysis. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, C.; Feng, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y. Risk Factors for Sternal Wound Infection after Open-Heart Operations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, H.L. A Review of the AATS Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Sternal Wound Infections. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 34 (Suppl. S3), 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooh, E.; Griesbach, C.; Rösch, J.; Weyand, M.; Harig, F. Development of a New Sternal Dehiscence Prediction Scale for Decision Making in Sternal Closure Techniques after Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrisi, C.; Loreni, F.; Nenna, A.; Giacinto, O.; Lusini, M.; Chello, M. Bioengineering Approaches and Novel Biomaterials to Enhance Sternal Wound Healing after Cardiac Surgery: A Crosstalk between Innovation and Surgical Practice. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speir, A.M.; Kasirajan, V.; Barnett, S.D.; Fonner, E., Jr. Additive Costs of Postoperative Complications for Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Patients in Virginia. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 88, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, D.; Aytac, J.; Aydinli, A.; Bayer, A. Mortality Rate, Length of Stay and Extra Cost of Sternal Surgical Site Infections Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in a Private Medical Centre in Turkey. J. Hosp. Infect. 2005, 60, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, O.; Dahlin, L.G.; Levin, L.A.; Magnusson, A.; Granfeldt, H.; Källman, J.; Svedjeholm, R. Cost Effectiveness of Local Collagen-Gentamicin as Prophylaxis for Sternal Wound Infections in Different Risk Groups. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2006, 40, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, V.; Vaja, R.; Richens, D. Cost Analysis of Gentamicin-Impregnated Collagen Sponges in Preventing Sternal Wound Infection Post Cardiac Surgery. J. Wound Care 2016, 25, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosav, E.M.; Tanase, D.M.; Ouatu, A.; Buliga-Finis, O.N.; Popescu, D.; Dascalu, C.G.; Dima, N.; Badescu, M.C.; Rezus, C. The Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Atrial Fibrillation and Its Comorbidities. Life 2025, 15, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
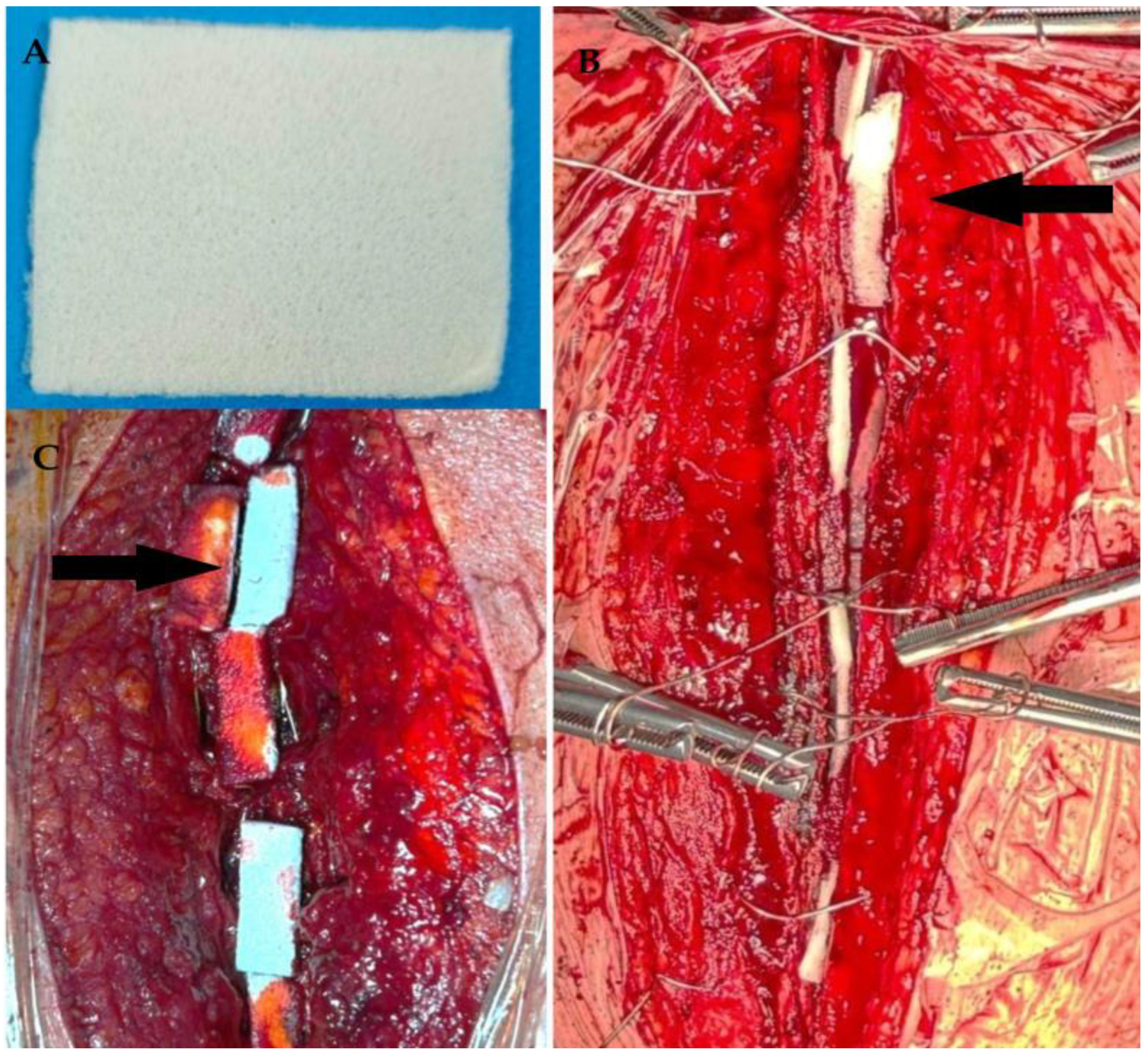
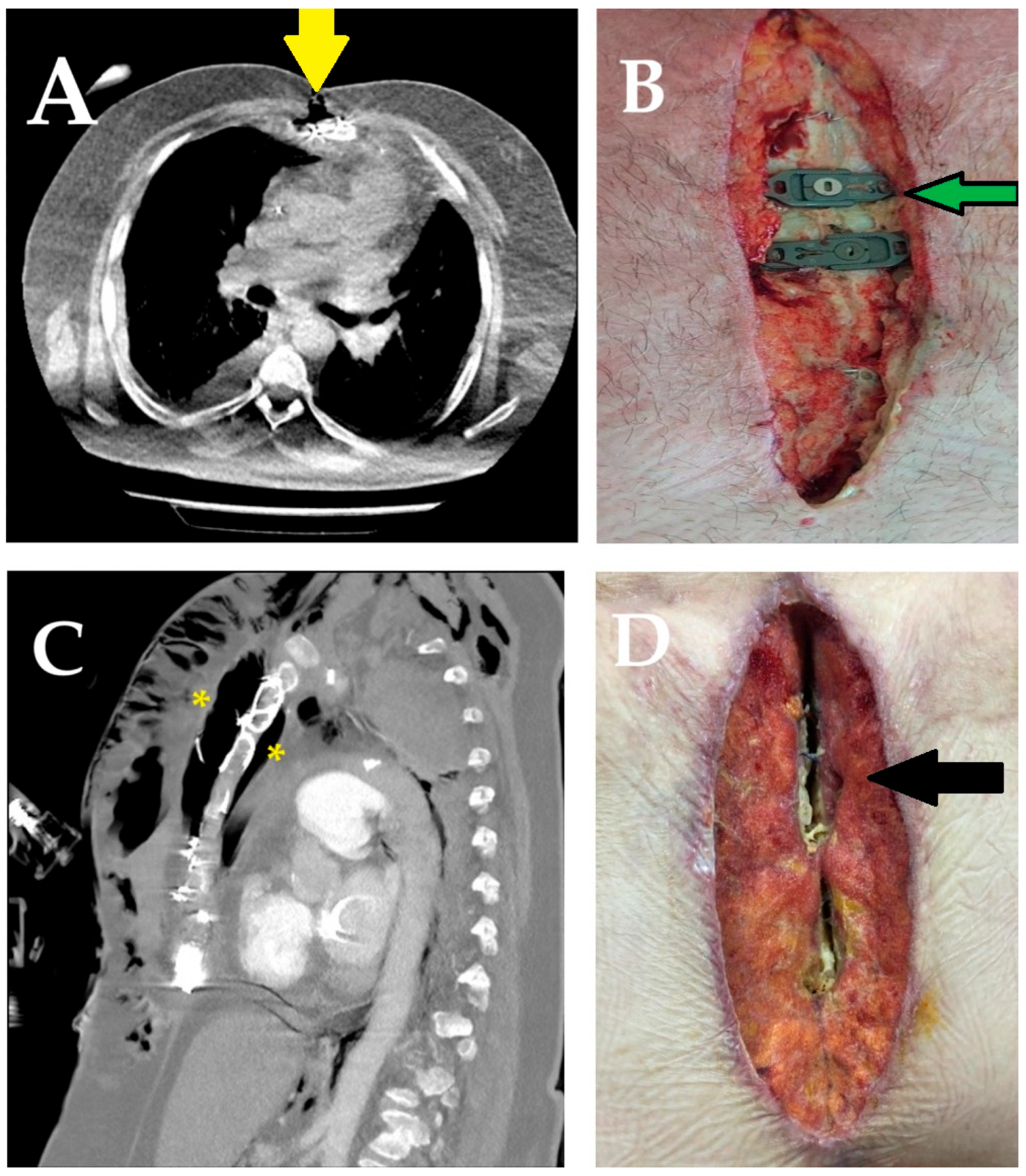
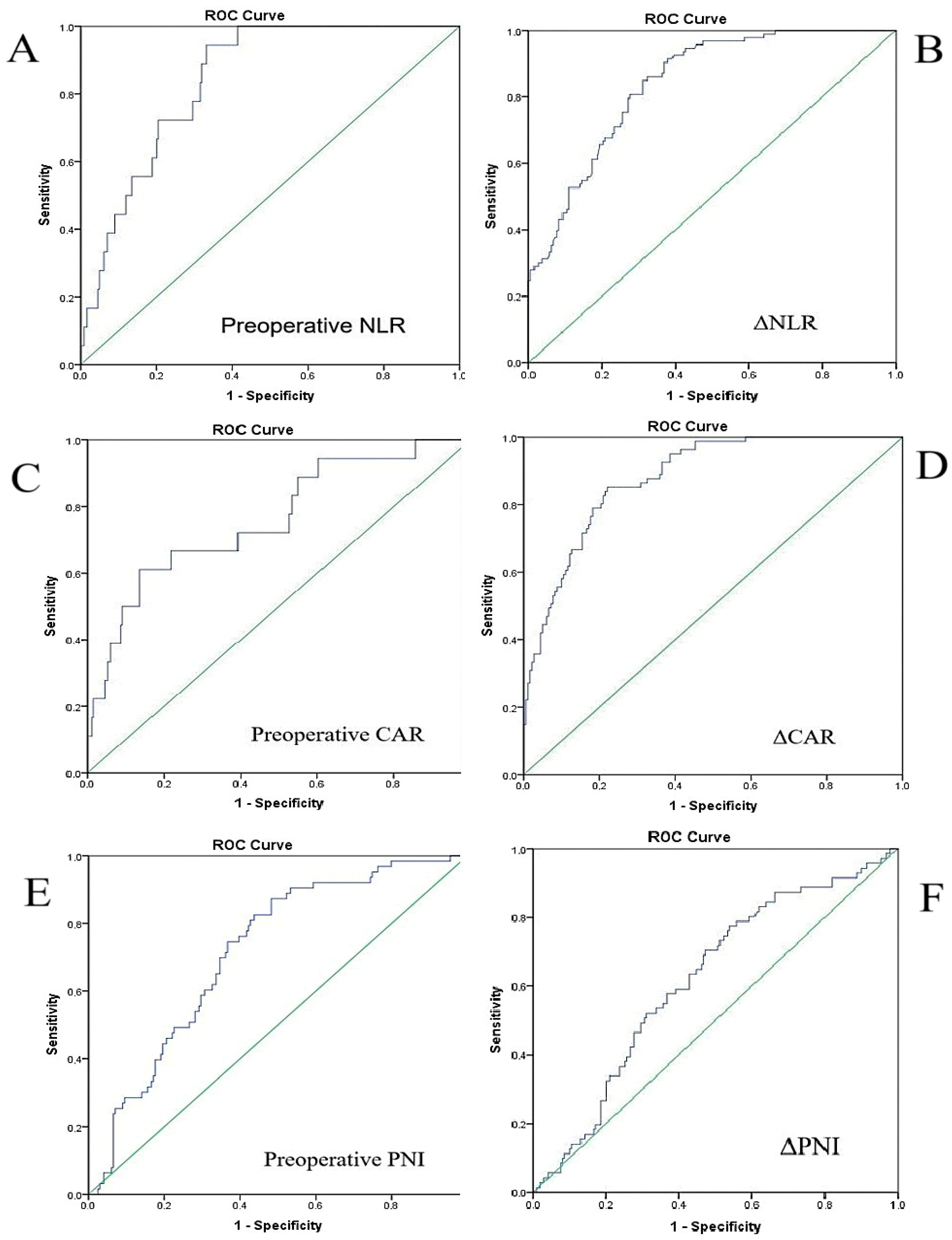
| Index/Parameter | Calculation Method |
|---|---|
| Body mass index (kg/m2) (BMI) | Weight (kg)/Height (m2) |
| C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR) | CRP (mg/L)/Albumin (g/dL) |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) | Neutrophil count/Lymphocyte count |
| Prognostic nutritional index (PNI) | [10 × serum Albumin (g/dL)] + [0.005 × Lymphocyte count] |
| Delta value (Δ) | Postoperative day 3 minus preoperative measurements |
| Patient Demographics | Control Group (n = 250) | Sternal Intervention Group * (n = 230) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female/male | 54/196 | 69/161 | 0.065 |
| Age (years) | 61.5 ± 8.5 | 62.4 ± 7.9 | 0.438 |
| Body mass index, (kg/m2) | 28.1 ± 3.0 | 27.7 ± 3.0 | 0.124 |
| EuroSCORE | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 0.107 |
| Ejection fraction, % | 51.0 ± 6.0 | 51.2 ± 6.9 | 0.312 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 105 (42) | 103 (44.7) | 0.539 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 113 (45.2) | 106 (46.0) | 0.845 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), n (%) | 63 (25.2) | 55 (24.0) | 0.744 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 104 (41.6) | 82 (35.6) | 0.181 |
| Cerebrovascular event, n (%) | 14 (5.6) | 12 (5.2) | 0.853 |
| Peripheral artery disease, n (%) | 20 (8.0) | 27 (11.7) | 0.169 |
| COPD, n (%) | 51 (20.4) | 55 (23.9) | 0.354 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 157 ± 61 | 156 ± 64 | 0.866 |
| Cr, mg/dL | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.142 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.8 ± 1.3 | 14.8 ± 1.4 | 0.701 |
| a Neutrophil count, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 6.1 (4.9–7.1) | 5.9 (4.8–6.6) | 0.410 |
| a Lymphocyte count, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 2.0 (1.5–2.3) | 2.1 (1.5–2.4) | 0.334 |
| a Monocyte count, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 0.63 (0.53–0.78) | 0.65 (0.55–0.79) | 0.403 |
| Platelet count, 103/μL | 253 ± 60 | 257 ± 50 | 0.155 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 115 ± 30 | 110 ± 27 | 0.744 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 159 ± 62 | 150 ± 48 | 0.370 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 0.040 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 7.2 ± 2.3 | 6.9 ± 1.9 | 0.337 |
| HbA1c, % | 6.7 ± 1.9 | 6.5 ± 1.8 | 0.203 |
| b NLR; median (Q1–Q3) | 2.9 (2.3–4.1) | 2.8 (2.3–3.6) | 0.575 |
| b CAR, median (Q1–Q3) | 1.7 (1.4–2) | 1.6 (1.3–1.9) | 0.241 |
| b PNI, median (Q1–Q3) | 42 (39.6–43.5) | 43 (40.8–44.2) | 0.020 |
| Parameters | Control Group (n = 250) | Sternal Intervention Group * (n = 230) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | Postoperative Day 3 | Postoperative Week 1 | Preoperative | Postoperative Day 3 | Postoperative Week 1 | p * | |
| CAR, median (Q1–Q3) | 1.7 (1.4–2) | 32 (25–40) | 4.2 (2.5–7.7) | 1.6 (1.3–1.9) | 25 (21–32) | 3.3 (2.4–5.1) | <0.001 |
| NLR; median (Q1–Q3) | 2.9 (2.3–4.1) | 11 (8.6—14.6) | 7.2 (5.0–11.2) | 2.8 (2.3–3.6) | 7.8 (5.9–10.7) | 4.2 (3.3–5.8) | <0.001 |
| PNI, median (Q1–Q3) | 42 (39.6–43.5) | 38 (33.0–40.2) | 39 (36.6–41.7) | 43 (40.8–44.2) | 40 (36.9–41.4) | 41.4 (39.0–42.5) | <0.001 |
| Albumin, g/dL, median (Q1–Q3) | 4.2 (4.0–4.3) | 3.8 (3.3–4.0) | 3.9 (3.7–4.2) | 4.3 (4.0–4.5) | 4.0 (3.7–4.2) | 4.2 (3.9–4.3) | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/L median (Q1–Q3) | 7.1 (5.7–8.1) | 120 (96–141) | 16.2 (10.9–28.3) | 6.8 (5.5–8.1) | 101 (83–120) | 12.8 (9.6–19.0) | <0.001 |
| Nc, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 6.1 (4.9–7.1) | 12.8 (11.2–14.5) | 8.8 (7.7–10.5) | 5.9 (4.8–6.6) | 11.1 (9.5–13.0) | 7.6 (6.8–8.6) | <0.001 |
| Lc, 103/μL median (Q1–Q3) | 2.0 (1.5–2.3) | 1.1 (0.9–1.4) | 1.2 (0.9–1.6) | 2.1 (1.5–2.4) | 1.4 (1.1–1.9) | 1.9 (1.4–2.3) | <0.001 |
| Patient Demographics | Superficial SWIs (n = 75) | Deep SWIs (n = 18) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female/male | 22/53 | 10/8 | 0.012 | |
| Age (years) | 62.9 ± 8.0 | 64.8 ± 7.6 | 0.369 | |
| Body mass index, (kg/m2) | 28.8 ± 2.8 | 33.4 ± 3.9 | <0.001 | |
| EuroSCORE | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | 0.023 | |
| Ejection fraction, % | 49.0 ± 5.9 | 49.2 ± 5.6 | 0.925 | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 55 (73) | 16 (89) | 0.137 | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 42 (56) | 12 (66) | 0.410 | |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), n (%) | 30 (40) | 15 (83) | 0.001 | |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 49 (65) | 7 (39) | 0.040 | |
| Cerebrovascular event, n (%) | 3 (4) | 4 (22) | 0.024 | |
| Peripheral artery disease, n (%) | 12 (16) | 2 (11) | 0.461 | |
| COPD, n (%) | 21 (28) | 10 (55) | 0.026 | |
| Nc, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 6.5 (5.4–7.3) | 8.0 (7.4–8.8) | <0.001 | |
| Lc, 103/μL median (Q1–Q3) | 1.8 (1.3–2.1) | 1.5 (1.0–2.0) | 0.150 | |
| LDL, mg/dL | 120 ± 30 | 142 ± 26 | 0.010 | |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 170 ± 56 | 195 ± 58 | 0.112 | |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 0.001 | |
| CRP, mg/L median (Q1–Q3) | 7.6 (6.0–8.5) | 8.3 (6.7–9.5) | 0.016 | |
| HbA1c, % | 7.6 ± 1.9 | 10.2 ± 2.7 | 0.001 | |
| NLR; median (Q1-Q3) | 3.5 (2.9–5.2) | 4.7 (4.0–7.2) | 0.005 | |
| CAR, median (Q1–Q3) | 1.8 (1.5–2.1) | 2.2 (1.6–2.6) | 0.075 | |
| PNI, median (Q1–Q3) | 40.9 (38.6–42.2) | 38.6 (32.6–40.6) | 0.002 | |
| ΔNLR ** median (Q1–Q3) | 6.9 (4.9–9.7) | 11.5 (8.2–15.8) | 0.003 | |
| ΔCAR ** median (Q1–Q3) | 34.5 (30.4–41.1) | 61.6 (52.2–76.0) | <0.001 | |
| ΔPNI ** median (Q1–Q3) | −4.8 (−8.5–−3.0) | −5.5 (−6.8–−2.9) | 0.985 | |
| Distal anastomoses (mean ± SD) | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 3.0 ± 0.8 | 0.077 | |
| Graft types, n (%) | LIMA | 75 (100) | 18 (100) | 1.000 |
| Radial artery | 26 (35%) | 7 (39) | 0.787 | |
| Saphenous vein | 70 (93%) | 16 (89) | 0.617 | |
| Operative time, minutes | 100 ± 25 | 135 ± 30 | <0.001 | |
| Red blood cell transfusion, units | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 0.095 | |
| Predictor | Superficial SWIs | Deep SWIs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Sternal intervention * | 0.89 (0.5–1.3) | 0.061 | 0.55 (0.15–0.87) | 0.001 |
| Prolonged operative time (>108 min) | 1.1 (0.91–1.9) | 0.095 | 2.1 (1.2–3.1) | 0.012 |
| Female | 2.9 (1.2–7.9) | 0.027 | 3.8 (1.7–10.2) | 0.003 |
| Age, years | 1.1 (1.01–1.5) | 0.039 | 1.3 (1.1–3.4) | 0.012 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2.8 (1.3–8.8) | <0.001 | 3.9 (1.6–9.8) | <0.001 |
| Current smoking | 2.1 (1.5–8.7) | 0.004 | 3.8 (1.3–9.9) | <0.001 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 1.3 (0.6–5.2) | 0.328 | 1.9 (0.76–7.1) | 0.122 |
| HbA1c (≥7%) | 1.5 (1.1–2.0) | 0.011 | 3.1 (1.6–5.9) | <0.001 |
| C-reactive protein | 1.4 (0.71–3.3) | 0.076 | 2.2 (1.4–2.9) | 0.007 |
| Albumin (≥3.8 g/dL) | 0.9 (0.15–0.81) | 0.004 | 0.53 (0.2–0.93) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 1.5 (1.2–2.4) | 0.002 | 2.2 (1.3–4.8) | 0.001 |
| * Delta neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 1.06 (0.9–1.1) | 0.253 | 1.2 (1.1–3.9) | 0.003 |
| C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio | 1.2 (0.71–3.0) | 0.751 | 2.9 (0.68–5.6) | 0.220 |
| * Delta C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio | 1.1 (1.0–1.2) | 0.034 | 2.4 (1.3–5.6) | <0.001 |
| Prognostic nutritional index | 0.72 (0.4–0.95) | 0.001 | 0.52 (0.31–0.90) | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sönmez, E.; Jalalzai, İ.; Arslan, Ü.; Yıldız, A.; Çelik, F.; Çetin, M. Immunonutritional Markers and the Protective Role of Sternal Irrigation and Antibiotic-Impregnated Membranes in Sternal Wound Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Life 2025, 15, 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081163
Sönmez E, Jalalzai İ, Arslan Ü, Yıldız A, Çelik F, Çetin M. Immunonutritional Markers and the Protective Role of Sternal Irrigation and Antibiotic-Impregnated Membranes in Sternal Wound Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Life. 2025; 15(8):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081163
Chicago/Turabian StyleSönmez, Ebubekir, İzatullah Jalalzai, Ümit Arslan, Alperen Yıldız, Furkan Çelik, and Merve Çetin. 2025. "Immunonutritional Markers and the Protective Role of Sternal Irrigation and Antibiotic-Impregnated Membranes in Sternal Wound Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Life 15, no. 8: 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081163
APA StyleSönmez, E., Jalalzai, İ., Arslan, Ü., Yıldız, A., Çelik, F., & Çetin, M. (2025). Immunonutritional Markers and the Protective Role of Sternal Irrigation and Antibiotic-Impregnated Membranes in Sternal Wound Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Life, 15(8), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081163








