The Role of Maternal Gut Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in Shaping Fetal Development and Neonatal Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anthropometric Evaluation
2.2. Biochemical Samples
2.3. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.4. Fetal Ultrasound
2.5. Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Maternal Anthropometric, Biochemical, and Microbiota Changes During Pregnancy
3.2. Fetal and Newborn Variables
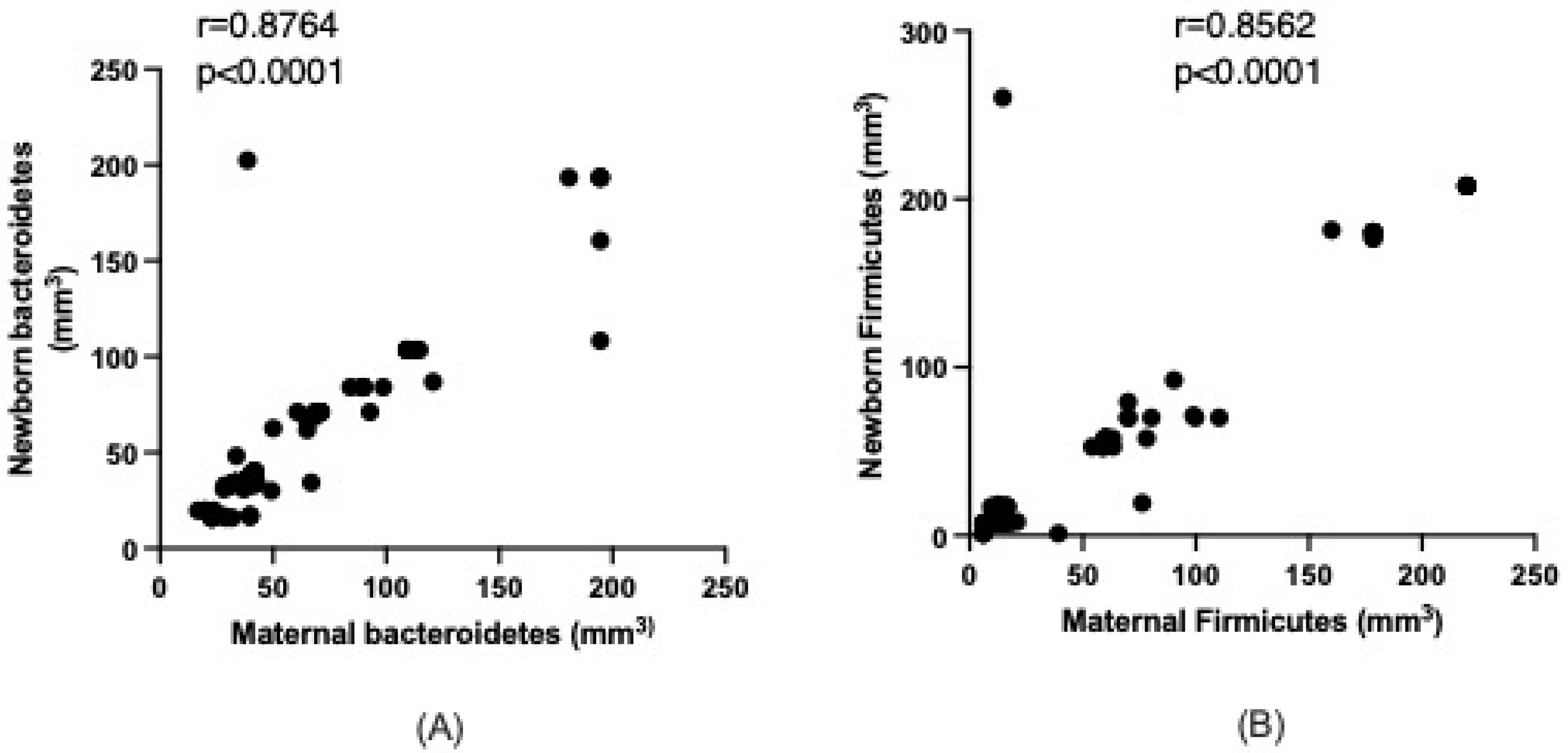
3.3. Maternal–Newborn Microbiota Relations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| cHDL | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
References
- Tejada, P.; Cohen, A.; Font, I.; Bermúdez, J.; Schulitemaker, J. Modificaciones fisiológicas del embarazo e implicaciones farmacológicas: Maternas, fetales y neonatales. Rev. Obstet. Ginecol. Venez. 2007, 67, 246–267. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.M.; Cunningham, S.A.; Dunlop, A.L.; Corwin, E.J. The Maternal Gut Microbiome During Pregnancy. MCN Am. J. Matern. Child Nurs. 2017, 42, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas Aguilera, A. El bajo peso al nacer un reto en la provincia de Holguín. Rev. Infodir. 2012, 11, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Ladino, M.L.; Moreno-Torres, R.; Campoy, F.C. Infant adiposity is influenced by maternal nutrition. Rev. Salud Bosque 2014, 4, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Qin, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, T.; Chen, G.; Sun, X.; Lu, T.; White, R.A., III; et al. Gestational diabetes mellitus is associated with the neonatal gut microbiota and metabolome. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussar, S.; Griffin, N.W.; Bezy, O.; Fujisaka, S.; Vienberg, S.; Softic, S.; Deng, L.; Bry, L.; Gordon, J.I.; Kahn, C.R. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet modulate the predisposition to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, A.M.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361, k2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.L.; Heaver, S.L.; Walters, W.A.; Ley, R.E. Microbiome and metabolic disease: Revisiting the bacterial phylum Bacteroidetes. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Gavalko, Y.; Dorofeyev, A.; Romanenko, M.; Tkach, S.; et al. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, I.; Muller, C.E.; Walter, J. Long-term temporal analysis of the human fecal microbiota revealed a stable core of dominant bacterial species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiulio, D.B.; Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Costello, E.K.; Lyell, D.J.; Robaczewska, A.; Sun, C.L.; Goltsman, D.S.A.; Wong, R.J.; Shaw, G.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Variation of the Human Microbiota during Pregnancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11060–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Liang, X.; Bao, H.; Ma, G.; Tang, X.; Luo, H.; Xiao, X. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Associations between Altered Gut Microbiota, Metabolites, and Cytokines during Pregnancy. mSystems 2024, 9, e0125223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Liang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wei, S.; Li, W.; et al. Longitudinal Change and Causal Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno del Castillo, J.; Valladares-García, J.; Halabe-Cherem, J. Microbiota humano. Rev. Fac. Med. UNAM 2018, 61, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.A.; Harris, P.R. Desarrollo del microbioma intestinal en niños. Impacto en salud y enfermedad. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2016, 87, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdella, R.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Moustafa, M.I. Sonographic evaluation of fetal abdominal circumference and cerebroplacental Doppler indices for the prediction of fetal macrosomia in full term pregnant women: A cohort study. Middle East Fertil. Soc. J. 2014, 19, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Egan, M.; Ryan, C.A.; Boyaval, P.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. A good start in life is important—Perinatal factors dictate early microbiota development and longer-term maturation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serdan Ruiz, D.L.; Vasquez Bone, K.K.; Yupa Pallchisaca, A.E. Physiological and anatomical changes in a woman’s body during pregnancy. Univ. Cienc. Tecnol. 2023, 27, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez Ibarra, A.A.; Mariscal Ramírez, B.E.; González Ponce, A.M.; Valbuena Gregorio, E. Cambios en la microbiota durante el embarazo: Revisión narrativa. Ginecol. Obstet. Mex. 2023, 91, 499–515. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Time 1 | Time 2 | Time 3 | Time 4 | Time 5 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (m) Median (Q1–Q3) | 1.60 (1.58–1.63) | |||||
| Weight, kg Median (Q1–Q3) * | 68.6 (60.0–81.0) a | 71.0 (61.0–83.0) b | 73.0 (64.0–85.5) c | 77.0 (67.4–88.0) d | 82.0 (73.0–91.5) e | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 26.5 (24.1–30.1) a | 27.8( 24.8–30.9) b | 28.9 (25.5–31.7) c | 29.8 (27.2–32.7) d | 30.9 (28.9–33.9) e | <0.0001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) Mediana (Q1–Q3) * | 83.0 (76.0–93.0) a | 87.0 (78.0–95.0) b | 86.0 (78.0–94.5) b | 88.0 (80.0–98.5) c | 90.0 (84.0–100.0) c | <0.0001 |
| TC (mg/dL) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 138.0 (108.5–167.0) a | 140.0 (111.0–162.5) a | 140.0 (114.0–163.0) b | 140.0 (115.0–160.0) b | 140.0 (116.0–180.0) b | <0.0001 |
| TG (mg/dL) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 103.0 (90.0–128.0) a | 110.0 (90.0–125.0) a | 110.0 (91.0–118.0) b,a | 110 (91.0–129.0) a | 110 (95.0–133.0) a | <0.0001 |
| cHLD (mg/dL) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 31.0 (26.5–39.0) a | 29.0 (25.0–37.0) a | 30.0 (25.0–38.5) a | 30.0 (21.5–37.5) a | 30.0 (20.0–36.0) a | <0.0001 |
| Systolic pressure (mmHg) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 118.0 (115.0–120.0) a | 118.0 (110.0–119.5) a | 115.0 (110.0–121.5) a | 115.0 (110.0–120.0) a | 119.0 (110.0–124.0) a | >0.9999 |
| Diastolic pressure (mmHg) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 78.0 (75.0–80.0) a | 77.0 (70.0–78.0) a | 76.0 (71.0–78.0) a | 77.0 (73.0–80.0) a | 77.0 (70.0–80.0) a | 0.1638 |
| Bacteroidetes (mm3) Mediana (Q1–Q3) ** | 39.7 (32.1–72.6) | 39.8 (33.0–69.8) | 0.2720 | |||
| Firmicutes (mm3) Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 13.1 (8.8–61.6) | 15.4 (10.4–66.7) | <0.0001 | |||
| Ratio F/B Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 0.38 (0.24–0.58) | 0.44 (0.27–0.67) | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | Time 1 | Time 2 | Time 3 | Time 4 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crown-rump length (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 19.0 (11.0–24.0) a | 76.3 (70.0–90.4) b | <0.0001 | ||
| DBP (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 27.0 (25.2–33.8) a | 59.1 (53.9–62.3) b | 86.4 (80.1–88.8) c | <0.0001 | |
| Nuchal translucency (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) | 2.10 (1.47–2.34) | ||||
| Head circumference (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 94.1 (87.0–101.7) a | 210.2 (207.1–229.3) b | 298.0 (288.2–316.2) c | <0.0001 | |
| Abdominal circumference (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 81.2 (75.7–119.7) a | 192.0 (184.1–203.9) b | 290.0 (273.6–311.6) c | <0.0001 | |
| Femur length (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 13.0 (10.6–19.8) a | 43.1 (39.0–45.2) b | 63.1 (59.8–67.0) c | <0.0001 | |
| Fetal heart rate (lpm) Median (Q1–Q3) ** | 149.0 (145.5–158.0) a,b | 156.0 (145.5–163.0) b,b | 153 (140–165) a,b | 0.013 | |
| Venous duct (mm) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 1.03 (0.97–1.90) a | 0.78 (0.58–0.90) b | <0.0001 | ||
| Estimated weight (g) Median (Q1–Q3) * | 483 (380–674) a | 2115 (1875–2507) b | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | Median (Q1–Q3) |
|---|---|
| Birth weight (g) | 3200 (3090–3580) |
| Birth size (cm) | 50.5 (49.6–51.4) |
| Head circumference (cm) | 34.3 (33.5–35.4) |
| Microbiota | Median (Q1–Q3) |
| Bacteroidetes (mm3) | 36.3 (32.8–71.2) |
| Firmicutes (mm3) | 12.8 (7.5–57.8) |
| Ratio F/B | 0.43 (0.21–0.65) |
| Parameter | Maternal Median (Q1–Q3) | Newborn Median (Q1–Q3) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteroidetes (mm3) | 39.8 (33.0–69.8) | 36.3 (32.8–71.2) | 0.2820 |
| Firmicutes (mm3) | 15.4 (10.4–66.7) | 12.8 (7.5–57.8) | 0.1652 |
| Ratio F/B | 0.44 (0.27–0.67) | 0.43 (0.21–0.65) | 0.3145 |
| Weight | BMI | Glucose | Total Cholesterol | Triglycerides | c-HDL | Systolic Pressure | Diastolic Pressure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteroidetes | r = −0.1758 p = 0.0994 | r = −0.1639 p = 0.9869 | r = 0.08854 p = 0.4093 | r = 0.1436 p = 0.1794 | r = −0.1568 p = 0.1424 | r = −0.1402 p = 0.1899 | r = 0.0017 p = 0.9869 | r = 0.07828 p = 0.4659 |
| Firmicutes | r = −0.1666 p = 0.1188 | r = −0.1070 p = 0.3182 | r = 0.07897 p = 0.4620 | r = 0.3676 p = 0.0004 | r = 0.1374 p = 0.1993 | r = −0.3302 p = 0.0016 | r = 0.1320 p = 0.2174 | r = 0.2598 p = 0.0140 |
| Ratio F/B | r = −0.1735 p = 0.1040 | r = −0.0755 p = 0.4814 | r = 0.07341 p = 0.4942 | r = 0.3490 p = 0.0008 | r = 0.2137 p = 0.0444 | r = −0.3014 p = 0.0041 | r = 0.2597 p = 0.0140 | r = 0.2999 p = 0.0043 |
| Bacteroidetes Correlation | Firmicutes Correlation | Ratio F/B | Bacteroidetes Correlation | Firmicutes Correlation | Ratio F/B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal Variable Evaluated | Fetal Variable Evaluated | ||||||
| LCC 1 | r = 0.4005 p = 0.0001 | r = 0.2715 p = 0.0101 | r = 0.2003 p = 0.0598 | FL 2 | r = 0.1606 p = 0.1328 | r = 0.2546 p = 0.0161 | r = 0.1694 p = 0.1126 |
| LCC 2 | r = 0.3055 p = 0.0036 | r = 0.0964 p = 0.3686 | r = −0.0209 p = 0.8452 | FL 3 | r = 0.3417 p = 0.0010 | r = 0.2701 p = 0.0105 | r = 0.1016 p = 0.3433 |
| DBP 2 | r = 0.1683 p = 0.1148 | r = 0.1557 p = 0.1450 | r = 0.0658 p = 0.5400 | FL 4 | r = −0.2310 p = 0.0294 | r = −0.4132 p < 0.0001 | r = −03658 p = 0.0004 |
| DBP 3 | r = 0.1880 p = 0.0776 | r = 0.0916 p = 0.3929 | r = −0.1057 p = 0.3244 | FCF 2 | r = 0.0466 p = 0.6643 | r = 0.0770 p = 0.4733 | r = −0.0414 p = 0.6995 |
| DBP 4 | r = 0.1020 p = 0.3414 | r = −0.1321 p = 0.2170 | r = −0.2288 p = 0.0311 | FCF 3 | r = −0.04302 p = 0.6890 | r = −0.0497 p = 0.6432 | r = −0.0755 p = 0.4819 |
| CC 2 | r = 0.0818 p = 0.4457 | r = −0.0117 p = 0.9130 | r = −0.0440 p = 0.6817 | FCF 4 | r = 0.07917 p = 0.4608 | r = 0.04365 p = 0.6846 | r = −0.0308 p = 0.7742 |
| CC 3 | r = 0.1735 p = 0.1039 | r = 0.2278 p = 0.0318 | r = 0.1023 p = 0.3402 | DV 2 | r = 0.2033 p = 0.0560 | r = 0.2328 p = 0.0281 | r = 0.0827 p = 0.4408 |
| CC 4 | r = 0.0070 p = 0.9479 | r = −0.0920 p = 0.3907 | r = −0.2100 p = 0.0482 | DV 3 | r = 0.2008 p = 0.0592 | r = 0.2754 p = 0.0090 | r = 0.2272 p = 0.0323 |
| AC 2 | r = 0.1443 p = 0.1772 | r = 0.2623 p = 0.0130 | r = 0.1721 p = 0.1068 | PE 3 | r = 0.4921 p < 0.0001 | r = 0.4653 p < 0.0001 | r = 0.2344 p = 0.0271 |
| AC 3 | r = 0.2854 p = 0.0067 | r = 0.4029 p < 0.0001 | r = 0.2345 p = 0.0270 | PE 3 | r = −0.1108 p = 0.3014 | r = −0.2890 p = 0.0060 | r = −0.3635 p = 0.0005 |
| AC 4 | r = −0.121 p = 0.2545 | r = −0.3630 p = 0.0005 | r = −0.3752 p = 0.0003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omaña-Covarrubias, A.; González-Olivares, L.G.; López Póntigo, L.; Nez-Castro, A.T.; Cruz-Martínez, R.; Hernández-Ortega, M. The Role of Maternal Gut Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in Shaping Fetal Development and Neonatal Microbial Communities. Life 2025, 15, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15070990
Omaña-Covarrubias A, González-Olivares LG, López Póntigo L, Nez-Castro AT, Cruz-Martínez R, Hernández-Ortega M. The Role of Maternal Gut Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in Shaping Fetal Development and Neonatal Microbial Communities. Life. 2025; 15(7):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15070990
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmaña-Covarrubias, Arianna, Luis Guillermo González-Olivares, Lydia López Póntigo, Ana Teresa Nez-Castro, Rogelio Cruz-Martínez, and Marcela Hernández-Ortega. 2025. "The Role of Maternal Gut Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in Shaping Fetal Development and Neonatal Microbial Communities" Life 15, no. 7: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15070990
APA StyleOmaña-Covarrubias, A., González-Olivares, L. G., López Póntigo, L., Nez-Castro, A. T., Cruz-Martínez, R., & Hernández-Ortega, M. (2025). The Role of Maternal Gut Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in Shaping Fetal Development and Neonatal Microbial Communities. Life, 15(7), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15070990







