Effects of Betulinic Acid and Ursolic Acid on IL-17-Induced CCL20 Release in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cells and Cell Culture
2.3. WST-8 Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Semi-Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Immunofluorescence–Immunocytochemistry (IF-IC)
2.7. Immunoblot Analyses
2.8. HPLC Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Declarations of Generative AI in Scientific Writing
3. Results
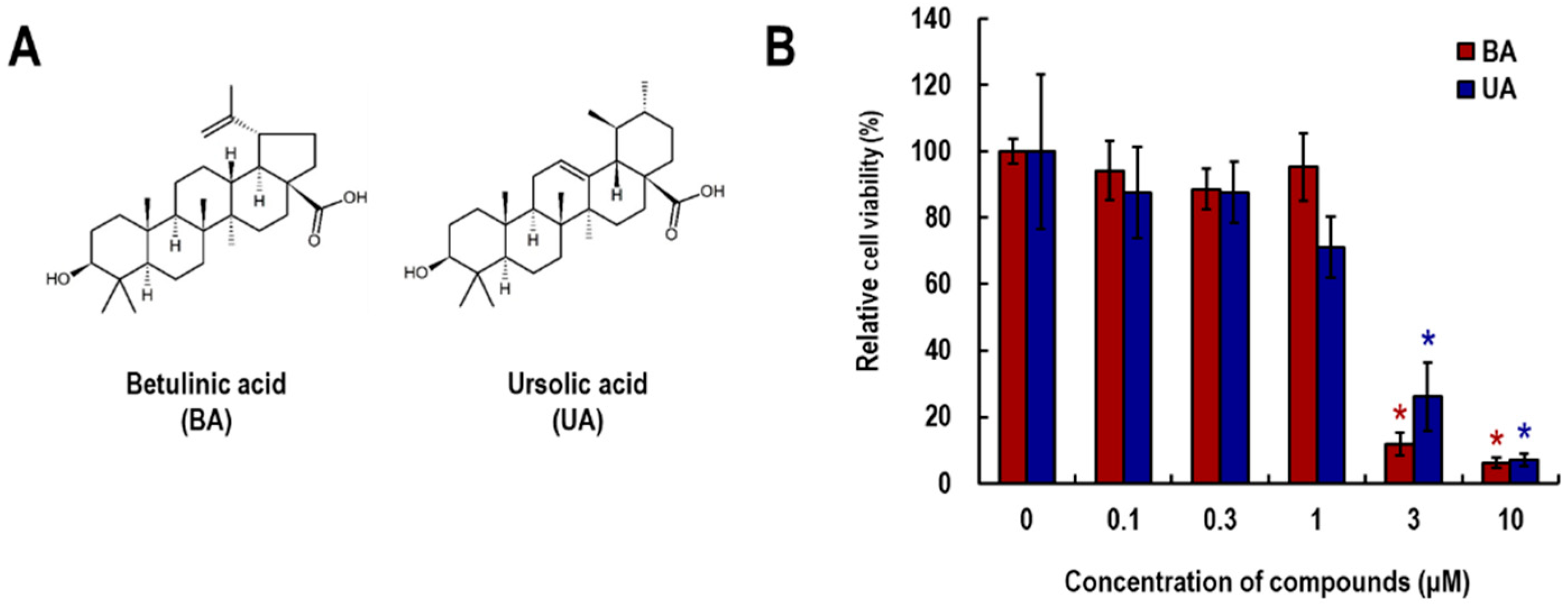
3.1. Effects of Betulinic Acid (BA) and Ursolic Acid (UA) on Viability of NHEK Cells
3.2. Effects of BA and UA on IL-17-Induced CCL20 Expression and Release
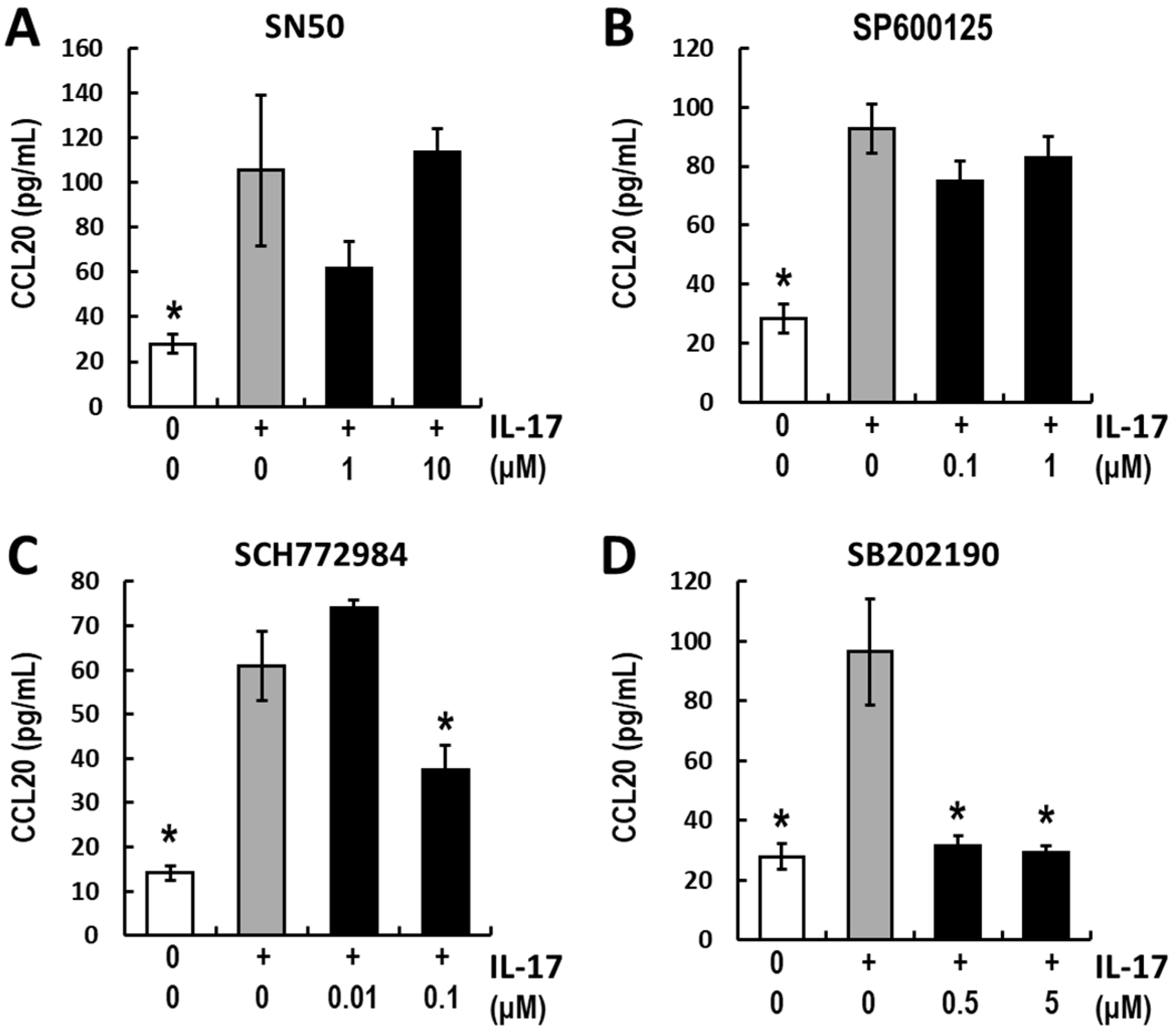
3.3. Analyses of the Intracellular Signaling of IL-17-Induced CCL20 Expression
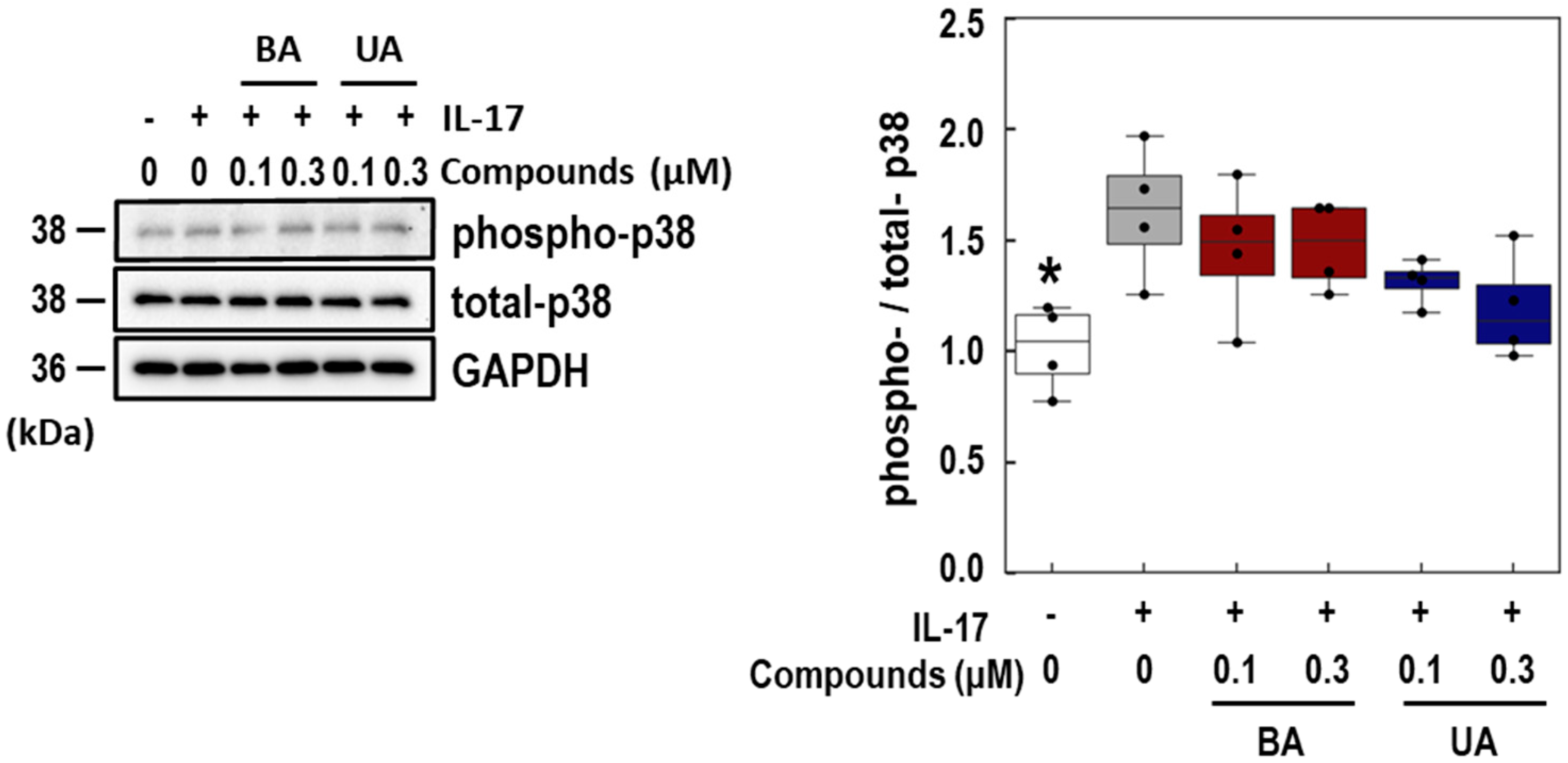
3.4. Effects of BA and UA on IL-17-Induced p38 Phosphorylation
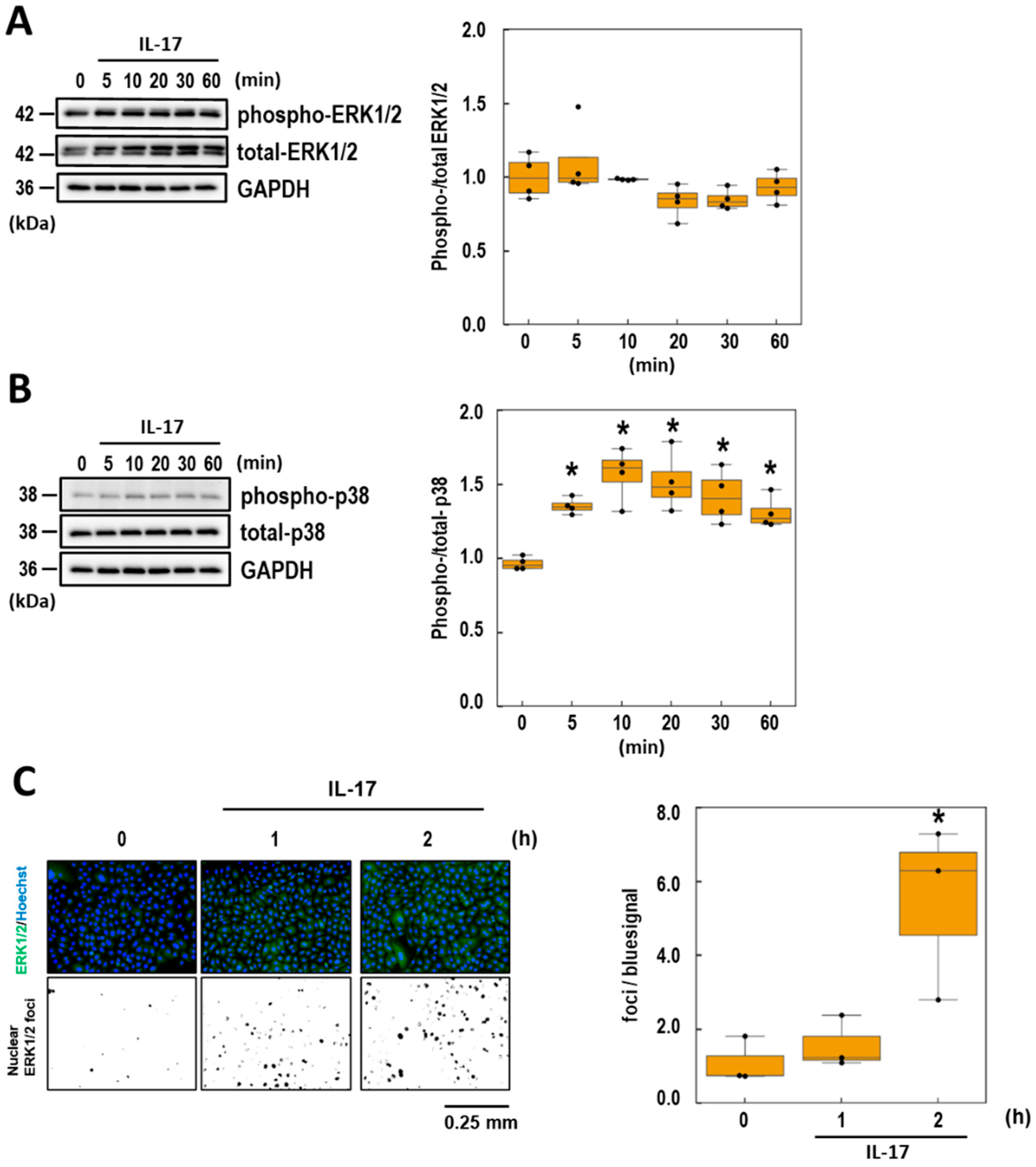
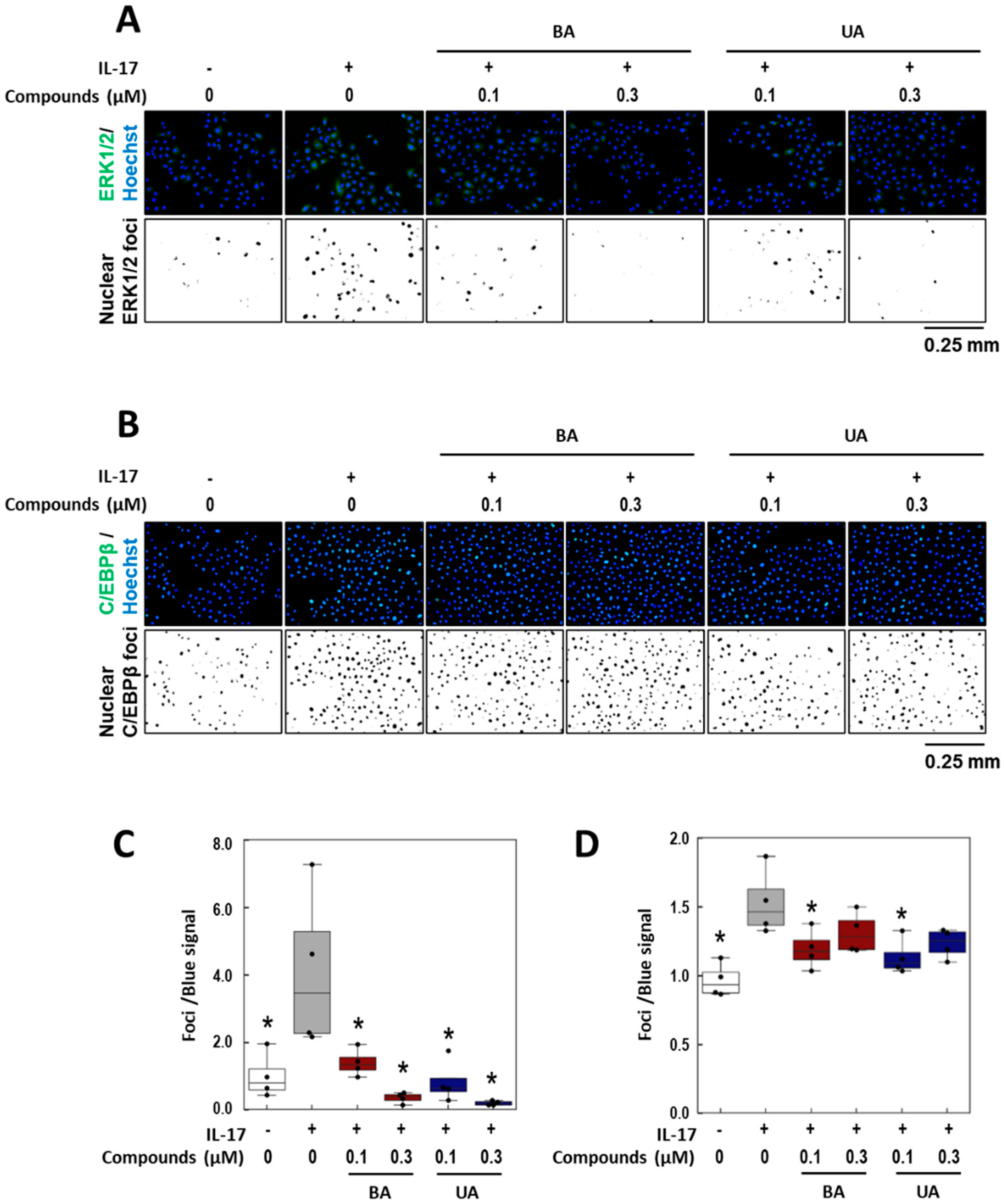
3.5. Effects of BA and UA on IL-17-Induced ERK1/2 Nuclear Localization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, C. Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: From keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratton, Z.; Giovannini, I.; Zabotti, A.; Errichetti, E. Skin and nail predictors of psoriatic arthritis development: A holistic overview integrating epidemiological and physiopathological data. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nograles, K.E.; Zaba, L.C.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Cardinale, I.; Khatcherian, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Pierson, K.C.; White, T.R. Th17 cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and keratinocyte-response pathways. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, N.; Garg, A.V.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 signaling: The yin and the yang. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Akiyama, T. The vicious cycle of itch and anxiety. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 87, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewski, B.; Alexis, A.F.; Lebwohl, M.; Stein Gold, L.; Pariser, D.; Del Rosso, J.; Yosipovitch, G. Itch: An under-recognized problem in psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Verma, P.; Tripathi, S.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Shukla, M.; Suvirya, S. Association of pruritus with sleep in patients with psoriasis and chronic spontaneous urticaria: A cross-sectional study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2023, 12, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstone, N.D.; Mosca, M.; Hadeler, E.; Liao, W.; Bhutani, T.; Koo, J. Biologic treatments of psoriasis: An update for the clinician. Biologics 2021, 15, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; An, K.-W.; Lee, M.-J.; Park, D.-H. Usage of natural volatile organic compounds as biological modulators of disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.-H.; Vederas, J.C. Drug discovery and natural products: End of an era or an endless frontier? Science 2009, 325, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, T.; Usui, M.; Sato, E.; Abe, H.; Kamiya, T.; Abe, T.; Tanuma, S. Morus alba extract suppresses IL-17-induced abnormal proliferation in 3D-reconstructed epidermis. Phytomed Plus 2023, 3, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Song, W.; Li, M.; Hua, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Xue, Z. Natural products of pentacyclic triterpenoids: From discovery to heterologous biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 1303–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.-C.; Phui-Yan, L.Y.E.; Siu-Kuin, W. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical trials of Morus alba. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Kadota, S.; Terashima, S.; Shimizu, M.; Namba, T. Two new 2-arylbenzofuran derivatives from hypoglycemic activity-bearing fractions of Morus insignis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, A.; Itokawa, H. Triterpenoids of Paeonia japonica callus tissue. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 2813–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-G.; Matsuzaki, K.; Takamatsu, S.; Kitanaka, S. Inhibitory effects of constituents from Morus alba var. multicaulis on differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 6010–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullally, M.; Mimeault, C.; Otárola Rojas, M.; Sanchez Vindas, P.; Garcia, M.; Poveda Alvarez, L.; Moon, T.W.; Gilmour, K.M.; Trudeau, V.L.; Arnason, J.T. A botanical extract of Souroubea sympetala and its active principle, betulinic acid, attenuate the cortisol response to a stressor in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, J.; Lingaraju, M.C.; Mathesh, K.; Kumar, D.; Parida, S.; Singh, T.U.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, D.; Tandan, S.K. Betulinic acid alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and visceral pain in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viji, V.; Helen, A.; Luxmi, V.R. Betulinic acid inhibits endotoxin-stimulated phosphorylation cascade and pro-inflammatory prostaglandin E(2) production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, O.B.; Giniyatullina, G.V.; Yamansarov, E.Y.; Tolstikov, G.A. Betulin and ursolic acid synthetic derivatives as inhibitors of Papilloma virus. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4088–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N. Clinically useful anticancer, antitumor, and antiwrinkle agent, ursolic acid and related derivatives as medicinally important natural product. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2011, 26, 616–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, W.R.; de Matos, G.X.; Souza, M.G.M.; Tozatti, M.G.; e Silva, M.L.A.; Martins, C.H.G.; da Silva, R.; Filho, A.A.D.S. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of the methylene chloride extract of Miconia ligustroides, isolated triterpene acids, and ursolic acid derivatives. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-R.; Jin, J.-L.; Li, C.-H.; Piao, X.-X.; Jin, N.-G. Ursolic acid enhances mouse liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Ong, T.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Lun, C.K.; Ho, P.C.; Wong, P.T.; Hui, K.M.; Sethi, G. Ursolic acid inhibits the initiation, progression of prostate cancer and prolongs the survival of TRAMP mice by modulating pro-inflammatory pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossiez, F.; Djossou, O.; Chomarat, P.; Flores-Romo, L.; Ait-Yahia, S.; Maat, C.; Pin, J.-J.; Garrone, P.; Garcia, E.; Saeland, S. T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awane, M.; Andres, P.G.; Li, D.J.; Reinecker, H.C. NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sønder, S.U.; Saret, S.; Tang, W.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Porcella, S.F.; Siebenlist, U. IL-17-induced NF-κB activation via CIKS/Act1: Physiologic significance and signaling mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12881–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Fanslow, W.C.; Seldin, M.F.; Rousseau, A.-M.; Painter, S.L.; Comeau, M.R.; Cohen, J.I.; Spriggs, M.K. Herpesvirus Saimiri encodes a new cytokine, IL-17, which binds to a novel cytokine receptor. Immunity 1995, 3, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.N.; King, C.A.; Bailey, S.R.; Holt, J.W.; Venkatachalam, K.; Agrawal, A.; Valente, A.J.; Chandrasekar, B. Interleukin-17 stimulates C-reactive protein expression in hepatocytes and smooth muscle cells via p38 MAPK and ERK1/2-dependent NF-κB and C/EBPβ activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27229–27238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, D.M.; Feldman, M.D.; Mummidi, S.; Valente, A.J.; Steffensen, B.; Vincenti, M.; Barnes, J.L.; Chandrasekar, B. IL-17 stimulates MMP-1 expression in primary human cardiac fibroblasts via p38 MAPK- and ERK1/2-dependent C/EBP-β, NF-κB, and AP-1 activation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H3356–H3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, L.; Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S. The IL-17 family in diseases: From bench to bedside. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jin, J.; Chang, M.; Nakaya, M.; Hu, H.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Brittain, G.C.; Cheng, X.; Sun, S.-C. TPL2 mediates autoimmune inflammation through activation of the TAK1 axis of IL-17 signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantke, T.; Sriskantharajah, S.; Ley, S.C. Regulation and function of TPL-2, an IκB kinase-regulated MAP kinase kinase kinase. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, Y.; Vogel, P.; Chi, H. Control of IL-17 receptor signaling and tissue inflammation by the p38α–MKP-1 signaling axis in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Sci. Signal 2015, 8, ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Syrovets, T.; Simmet, T. The serine protease plasmin triggers expression of the CC-chemokine ligand 20 in dendritic cells via Akt/NF-κB-dependent pathways. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 186710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xia, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, F. Transcriptional regulation of CCL20 expression. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, T.; Ołdak, M.; Walch-Rückheim, B.; Wickenhauser, C.; Doorbar, J.; Pfister, H.; Malejczyk, M.; Majewski, S.; Keates, A.C.; Smola, S. Human papillomavirus type 8 interferes with a novel C/EBPβ-mediated mechanism of keratinocyte CCL20 chemokine expression and Langerhans cell migration. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-A.; Suh, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, J.L.; Woo, S.-Y. IL-17 and IL-22 enhance skin inflammation by stimulating the secretion of IL-1β by keratinocytes via the ROS-NLRP3-caspase-1 pathway. Int. Immunol. 2012, 24, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-H.; Kao, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Yuliani, F.S.; Lin, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, B.-C. Amphiregulin induces CCN2 and fibronectin expression by TGF-β through EGFR-dependent pathway in lung epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, T.D.; Khabusheva, E.R.; Mareeva, S.R.; Ivanenko, K.A.; Morozov, A.V.; Spirin, P.V.; Rubtsov, P.M.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Sorokin, M.I. Identification of cell type–specific correlations between ERK activity and cell viability upon treatment with ERK1/2 inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.B.; Robson, C.N.; Neal, D.E.; Leung, H.Y. Keratinocyte growth factor activates p38 MAPK to induce stress fibre formation in human prostate DU145 cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5359–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taralkar, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, S. A HPLC Method for Determination of Ursolic Acid and Betulinic Acids from their Methanolic Extracts of Vitex Negundo Linn. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2012, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ruiz Villalba, A.; Hellemans, J.; Untergasser, A.; van den Hoff, M.J.B. Removal of between-run variation in a multi-plate qPCR experiment. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2015, 5, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Thygesen, H.H.; Schoneveld, O.J.; Das, A.T.; Berkhout, B.; Lamers, W.H. Factor correction as a tool to eliminate between-session variation in replicate experiments: Application to molecular biology and retrovirology. Retrovirology 2006, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, E.; Zubrzycka, N.; Marzec, K.; Maksylewicz, A.; Sochalska, M.; Kulawik-Pióro, A.; Lasoń, E.; Śliwa, K.; Malinowska, M.; Sikora, E. Ursolic acid formulations effectively induce apoptosis and limit inflammation in the psoriasis models In Vitro. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meares, G.P.; Ma, X.; Qin, H.; Benveniste, E.N. Regulation of CCL20 expression in astrocytes by IL-6 and IL-17. Glia 2012, 60, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoanaivo, P.; Wright, C.W.; Willcox, M.L.; Gilbert, B. Whole plant extracts versus single compounds for the treatment of malaria: Synergy and positive interactions. Malar. J. 2011, 10, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Estanqueiro, M.; Oliveira, M.B.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Main benefits and applicability of plant extracts in skin care products. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, J.B. Efficacy, safety, quality control, marketing and regulatory guidelines for herbal medicines (phytotherapeutic agents). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-Z.; Xie, P.; Chan, K. Quality control of herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Taelmol Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 812, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.-G.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, W.-B.; Liao, D.-F. Designing multi-targeted agents: An emerging anticancer drug discovery paradigm. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.-P.; Ji, S.-K.; Fu, M.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Hou, W.-Q.; Dai, X.-J.; Liu, H.-M. Combination Therapy and Dual-Target Inhibitors Based on LSD1: New Emerging Tools in Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 922–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anighoro, A.; Bajorath, J.; Rastelli, G. Polypharmacology: Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Discovery: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Guo, J.; Sun, X.; Gou, W.; Ning, H.; Fang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Hou, W.; Li, Y. Discovery and radiosensitization research of ursolic acid derivatives as SENP1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 227, 113918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arai, A.; Oyama, T.; Nakajima, T.; Usui, M.; Sato, E.; Kamiya, T.; Oyama, M.; Tanikawa, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Abe, T.; et al. Effects of Betulinic Acid and Ursolic Acid on IL-17-Induced CCL20 Release in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Life 2025, 15, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071073
Arai A, Oyama T, Nakajima T, Usui M, Sato E, Kamiya T, Oyama M, Tanikawa T, Takeuchi T, Abe T, et al. Effects of Betulinic Acid and Ursolic Acid on IL-17-Induced CCL20 Release in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Life. 2025; 15(7):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071073
Chicago/Turabian StyleArai, Anna, Takahiro Oyama, Toyoaki Nakajima, Michiru Usui, Ena Sato, Takanori Kamiya, Midori Oyama, Takashi Tanikawa, Tomoharu Takeuchi, Takehiko Abe, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Betulinic Acid and Ursolic Acid on IL-17-Induced CCL20 Release in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes" Life 15, no. 7: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071073
APA StyleArai, A., Oyama, T., Nakajima, T., Usui, M., Sato, E., Kamiya, T., Oyama, M., Tanikawa, T., Takeuchi, T., Abe, T., & Hatanaka, T. (2025). Effects of Betulinic Acid and Ursolic Acid on IL-17-Induced CCL20 Release in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Life, 15(7), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071073







