Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Healthcare: Environmental and Clinical Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
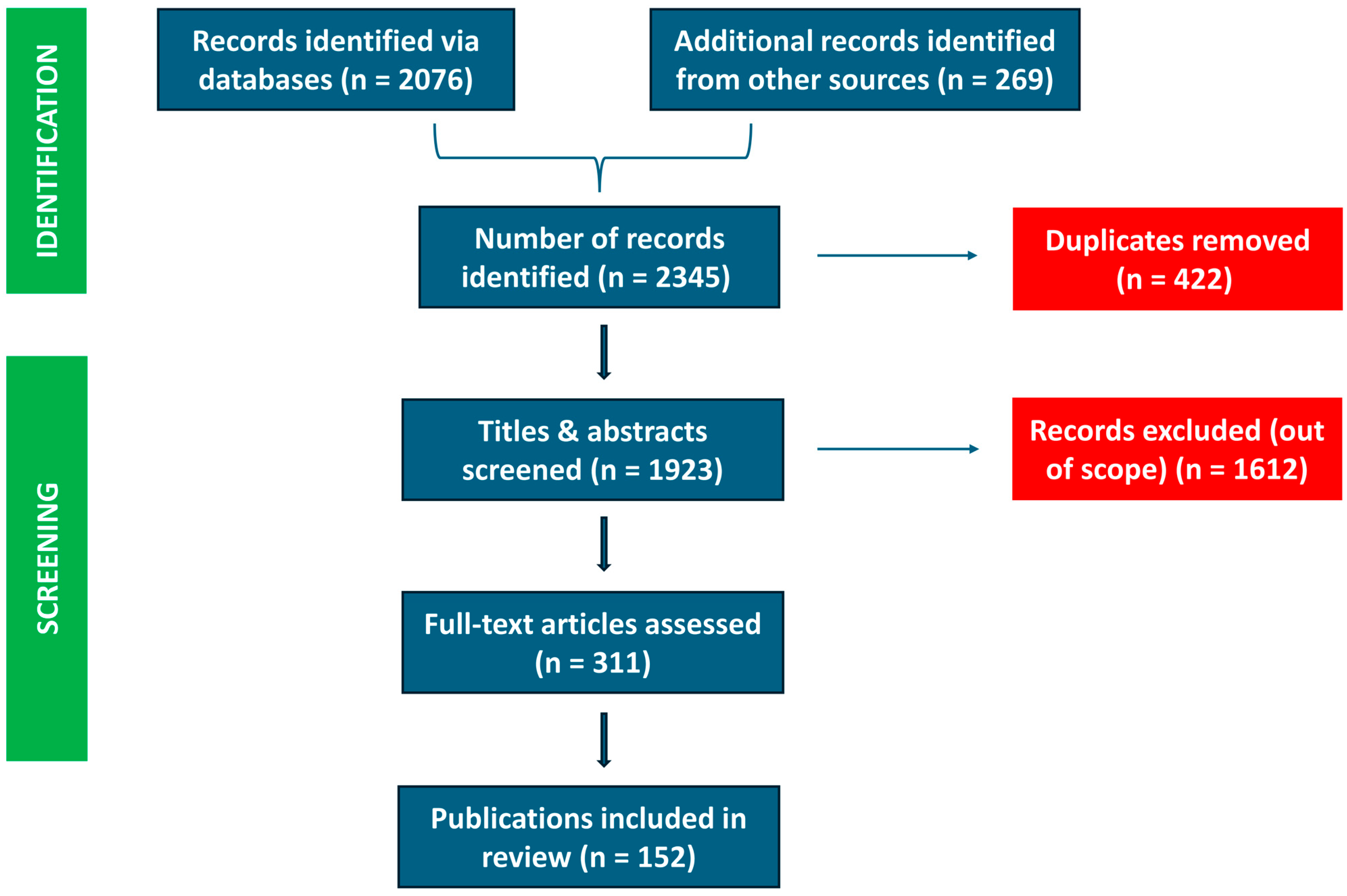
2.2.1. Screening Process
2.2.2. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- The presence or use of PFASs in clinical settings and medical devices;
- (2)
- Environmental PFASs contamination in residential or community settings affecting pediatric populations;
- (3)
- Health effects of PFASs exposure, particularly in children;
- (4)
- Regulatory frameworks or mitigation strategies.
2.3. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. PFAS in Medical Applications
3.1. Essential Roles in Medical Devices
3.2. PFAS in In Vitro Diagnostics and Analytical Instruments
3.3. Types and Classes of PFASs Used in Medical Technologies
- (i)
- In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Reagents and Instruments
- (ii)
- Medical Devices
- (iii)
- Specialty Fluorinated Lubricants and Suture Materials
3.4. Concerns About PFASs Leaching and Exposure
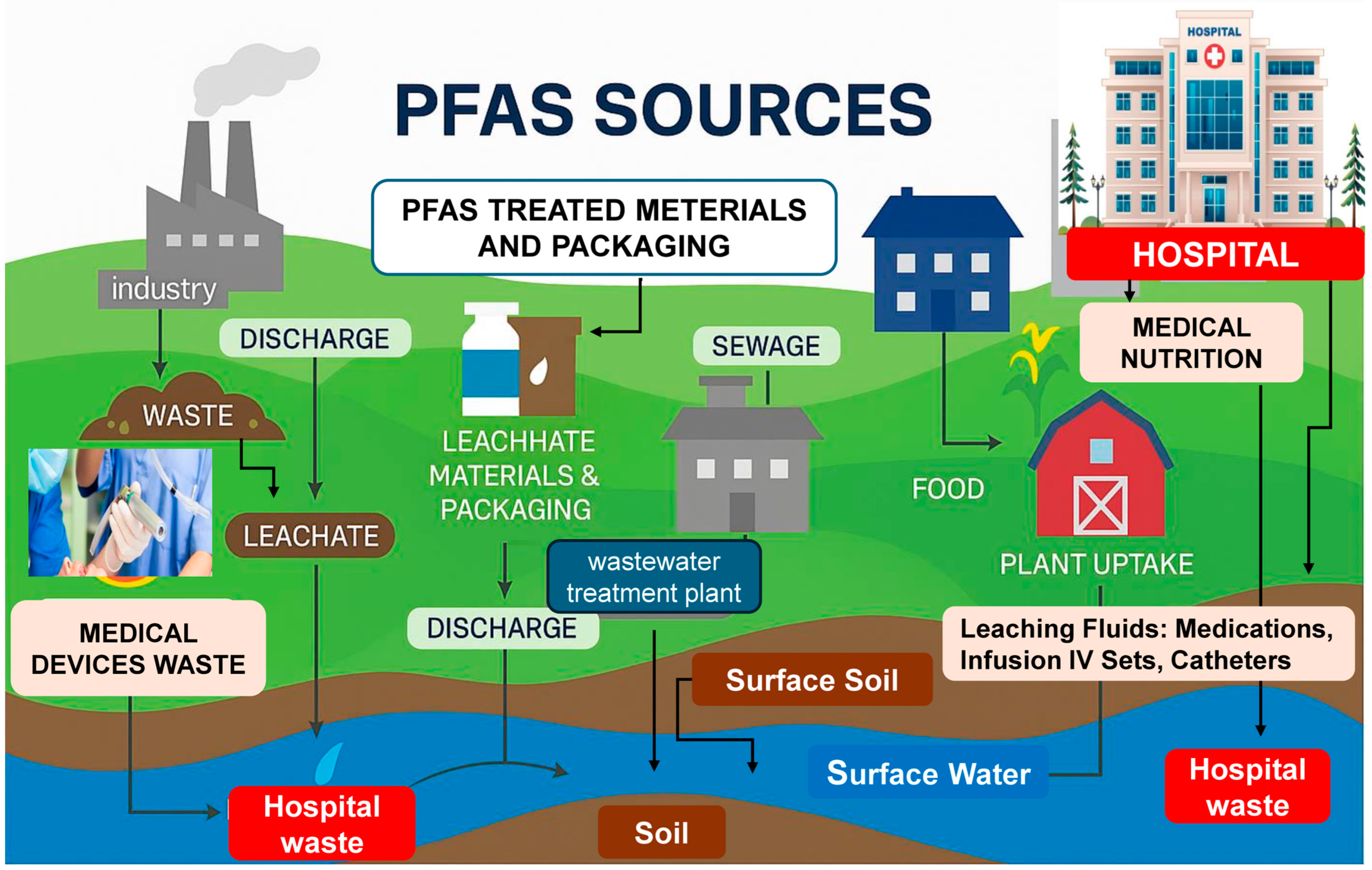
4. Environmental Contamination and Residential Exposure
4.1. Environmental Sources and Pathways of Exposure
4.2. PFASs in European Residential Areas
4.3. Vulnerability in Pediatric Populations
4.4. Importance of Surveillance and Remediation
5. Toxicological Effects of PFAS Exposure
5.1. Hematological and Cardiovascular Effects
5.2. Liver and Metabolic Disruption
5.3. Immune System Impairment
5.4. Endocrine Disruption
5.5. Neurodevelopmental and Mental Health Effects
5.6. Carcinogenicity
5.7. Multi-Organ Metabolic Disruption
5.8. Early-Life and Dietary Exposure
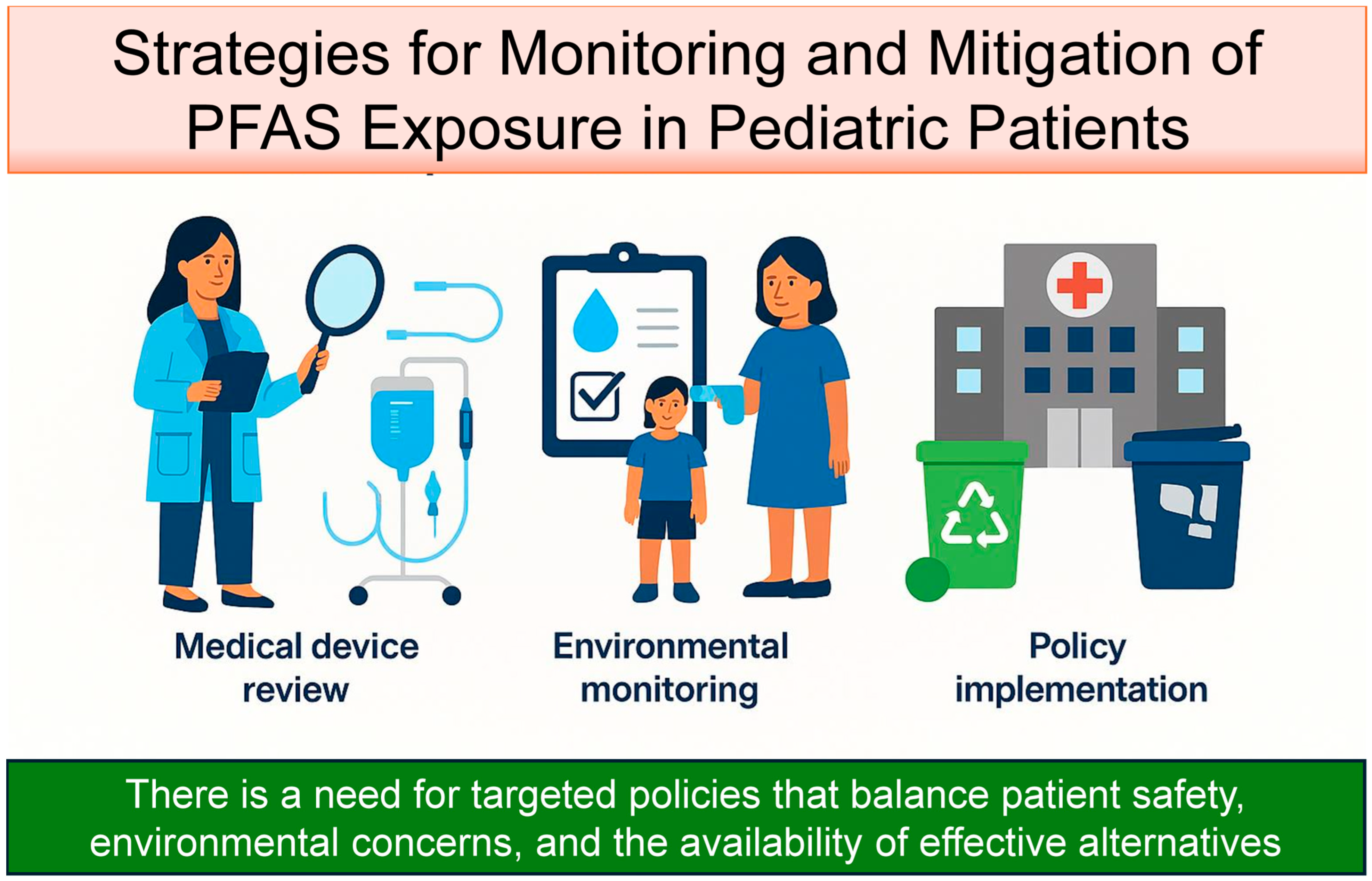
6. Strategies for Monitoring and Mitigation of PFAS Exposure in Pediatric Patients
6.1. Medical Device Review
6.2. Environmental Monitoring and Patient Screening
6.3. Policy Implementation and Circular Economy Integration
7. Regulatory Measures and Guidelines
7.1. European Union Initiatives
7.2. United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Actions
7.3. Gaps in Medical Device Regulation
7.4. Suggestions for Pediatric Care Environments
7.5. Advancing a Circular Economy in Pediatric Healthcare
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFASs | Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| ICU | Intensive care units |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| IVD | In vitro diagnostic |
| HFP | Hexafluoro-2-propanol |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| FEP | Fluorinated ethylene propylene |
| PCTFE | Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene) |
| ETFE | Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene |
| FKM/FPM | Fluoroelastomers |
| FFKM/FFPM | Perfluoroelastomers |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PVDF-HFP | Poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) |
| C6–C14 | Perfluorinated acrylates |
| AFFFs | Aqueous film-forming foams |
| MAFLD | Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| EU | European Union |
| ECHA | European Chemicals Agency |
| REACH | Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| CERCLA | Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act |
| MCLs | Maximum contaminant levels |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| PFOA | Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| TSCA | Toxic Substances Control Act |
| MDR | Medical device regulation |
| MDD | Medical device directive |
| NIS | Na+/I- symporter |
| EtFOSAA | N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamido acetic acid |
| PPAR-α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| ADHD | Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder |
| SHBG | Sex hormone binding globulin |
| OWO | Obesity and overweight |
| PBPK | Physiologically based pharmacokinetic |
| MAFLD | Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| AAC | Aortic calcification |
| AFFF | Aqueous film-forming foams |
| MeSH | Medical subject headings |
References
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: Terminology, Classification, and Origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An Overview of the Uses of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global Distribution of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, M.-Y.; Oh, J.-E. Perfluorinated Compounds in Serum and Urine Samples from Children Aged 5-13 Years in South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Andersen, E.W.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Nielsen, F.; Mølbak, K.; Weihe, P.; Heilmann, C. Serum Vaccine Antibody Concentrations in Children Exposed to Perfluorinated Compounds. JAMA 2012, 307, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, B.E.; Fenton, S.E. Early Life Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Latent Health Outcomes: A Review Including the Placenta as a Target Tissue and Possible Driver of Peri- and Postnatal Effects. Toxicology 2020, 443, 152565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Fletcher, T.; Savitz, D.A. Epidemiologic Evidence on the Health Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A Review of the Pathways of Human Exposure to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Present Understanding of Health Effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuis, S.J.; Birkholz, D.; Rodushkin, I.; Beesoon, S. Blood, Urine, and Sweat (BUS) Study: Monitoring and Elimination of Bioaccumulated Toxic Elements. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 61, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örnhem Gal, A.O.; Åström, M.E.; Filipsson, M.E.M. A Review of Selected Alternative Remediation Methods for PFAS Contamination. Remediat. J. 2025, 35, e70007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, C.F.; Andrews, D.Q.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Bruton, T.A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Maffini, M.V.; Miller, M.F.; Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; et al. Scientific Basis for Managing PFAS as a Chemical Class. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsch, T. Determination of PFAS in Water According to EU 2020/2184 and DIN 38407-42 Using Online SPE–LC–MS/MS. MJH Life Sci. 2022, 18, 8–14. Available online: https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/determination-of-pfas-in-water-according-to-eu-2020-2184-and-din-38407-42-using-online-spe-lc-ms-ms (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Nie, Q.; Liu, T. Large Language Models: Tools for New Environmental Decision-Making. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EurEau Publications. Available online: https://www.eureau.org/resources/publications/eureau-s-publications (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Ren, X.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Hao, X.; Lv, J.; Ma, N.; Li, W. Surface Modification and Endothelialization of Biomaterials as Potential Scaffolds for Vascular Tissue Engineering Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5680–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-H.; Yang, X.; Zheng, C.-G.; Cui, Y. Recent Advances in the Design of Cardiovascular Materials for Biomedical Applications. Regen. Med. 2020, 15, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B.D.; Bryant, S.J. Biomaterials: Where We Have Been and Where We Are Going. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthy, S.; Kannaiah, K.P.; Narayanasamy, D. Polyfluoroalkyl-Substances Detection in Junk Food Packing Materials Using Various Analytical Methods: A Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e70301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G.; Westby, M.J.; Rithalia, A.D.; Stubbs, N.; Soares, M.O.; Dumville, J.C. Dressings and Topical Agents for Treating Venous Leg Ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD012583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Jia, C.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, M. Research Progress in Preparation, Properties, and Applications of Medical Protective Fiber Materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 32, 101792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuti, F.; Fernández, F.R.; Severi, M.; Traversi, R.; Fanos, V.; Street, M.E.; Palanza, P.; Rovero, P.; Papini, A.M. Study of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Infant Formulas and Baby Bottles: Data from the European LIFE-MILCH PROJECT. Molecules 2024, 29, 5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, A.; McLean, A.; Sterner, M.; Robbins, C.; Cunningham, M.; Walters, M.; Doddapaneni, K.; Keitel, I.; Gallagher, C. Slippery Liquid Infused Fluoropolymer Coating for Central Lines to Reduce Catheter Associated Clotting and Infections. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunadian, V.; Gitto, M.; Vogel, B.; Sartori, S.; Angiolillo, D.J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Chehab, B.M.; Feng, Y.; de la Torre Hernandez, J.M.; Krucoff, M.W.; et al. 1-Month or 3-Month DAPT in Women and Men at High Bleeding Risk Undergoing PCI. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2025, 18, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, V.; Prontera, G.; Carlino, R.; Di Trani, H.; Carlettini, I.; Pittiruti, M.; Vento, G. Optical Detection of Infiltration during Peripheral Intravenous Infusion in Neonates. J. Vasc. Access 2024, 25, 1780–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbuehler, K. Hazard Assessment of Fluorinated Alternatives to Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) and Their Precursors: Status Quo, Ongoing Challenges and Possible Solutions. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, R.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Glüge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Miller, M.F.; Ng, C.A.; Patton, S.; et al. Are Fluoropolymers Really of Low Concern for Human and Environmental Health and Separate from Other PFAS? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12820–12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delatour, T.; Theurillat, X.; Eriksen, B.; Mujahid, C.; Mottier, P. Inadequate Definition of the Limit of Quantification Used for the Analysis of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Food by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry May Compromise the Reliability of the Data Requested by the European Regulation. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Analytical Results of Testing Food for PFAS from Environmental Contamination. 2025. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/environmental-contaminants-food/analytical-results-testing-food-pfas-environmental-contamination (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Smeltz, M.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Wetmore, B.A. Plasma Protein Binding Evaluations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances for Category-Based Toxicokinetic Assessment. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 36, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantan, H.; Albuainain, A.; Otaif, W.; Alfawaz, A.M.; Abusayf, M.M.; AlBloushi, A.F. Scleral Melting Following Scleral Sutured Intraocular Lens Using a Polytetrafluoroethylene (Gore-Tex®) Suture. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025, 25, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Thomson, J.A.; Turng, L.-S.; Guan, G. Surface Modification of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with a Heparin-Immobilized Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Coating for Small-Diameter Vascular Grafts Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 128, 112301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagogiorgas, C.; Otto, M. Semifluorinated Alkanes as New Drug Carriers-An Overview of Potential Medical and Clinical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Xie, C.; Dietrich, K.N.; Braun, J.M.; Webster, G.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A. Childhood Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Neurobehavioral Domains in Children at Age 8 Years. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2021, 88, 107022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman Grunfeld, D.; Gilbert, D.; Hou, J.; Jones, A.M.; Lee, M.J.; Kibbey, T.C.G.; O’Carroll, D.M. Underestimated Burden of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Global Surface Waters and Groundwaters. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PFAS Pollution in European Waters. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/publications/pfas-pollution-in-european-waters (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) in Agricultural Plants: A Review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, J.A. PFAS on Atmospheric Aerosol Particles: A Review. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2023, 25, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, U.M.; Elnakar, H.; Khan, M.F. Sources, Fate, and Detection of Dust-Associated Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleman, T.D.; Higgins, C.P.; Quiñones, O.; Vanderford, B.J.; Kolstad, C.; Zeigler-Holady, J.C.; Dickenson, E.R.V. Treatment of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances in U.S. Full-Scale Water Treatment Systems. Water Res. 2014, 51, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Jenkins, T.M.; Washington, J.W. A North American and Global Survey of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Surface Soils: Distribution Patterns and Mode of Occurrence. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Shan, X.-Q.; Zhang, S. Field Study on the Uptake and Translocation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) by Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Grown in Biosolids-Amended Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.J.; Webster, T.F.; Watkins, D.J.; Nelson, J.W.; Stapleton, H.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Kato, K.; Shoeib, M.; Vieira, V.M.; McClean, M.D. Polyfluorinated Compounds in Serum Linked to Indoor Air in Office Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Wilford, B.H.; Jones, K.C.; Zhu, J. Perfluorinated Sulfonamides in Indoor and Outdoor Air and Indoor Dust: Occurrence, Partitioning, and Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6599–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Mair, D.C.; Lange, C.C.; Harrington, L.M.; Church, T.R.; Goldberg, C.L.; Herron, R.M.; Hanna, H.; Nobiletti, J.B.; Rios, J.A.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in American Red Cross Adult Blood Donors, 2000–2015. Environ. Res 2017, 157, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadasi, R.; Mumberg, T.; Wanner, P. Spatial Prediction of Concentrations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in European Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Our Current Understanding of the Human Health and Environmental Risks of PFAS. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pfas/our-current-understanding-human-health-and-environmental-risks-pfas (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Zhang, M.; Yu, C.H.; Wang, G.; Buckley, J.P.; Hong, X.; Pearson, C.; Adams, W.G.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Longitudinal Trajectories and Determinants of Plasma Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Levels from Birth to Early Childhood and Metabolomic Associations: A Pilot Study in the Boston Birth Cohort. Precis. Nutr. 2022, 1, e00004. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, A.B.; Plasse, K.M.; Kirk, K.C.; Martin, C.F.; Ozsoy, G. Predicting Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) among US Infants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Paul, K.C.; Walker, D.I.; Jones, D.P.; Wang, X.; Ritz, B.R.; Heck, J.E. Neonatal Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure in Relation to Retinoblastoma. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdam, J.; Bell, E.M. Determinants of Maternal and Neonatal PFAS Concentrations: A Review. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beijsterveldt, I.A.L.P.; van Zelst, B.D.; de Fluiter, K.S.; van den Berg, S.A.A.; van der Steen, M.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S. Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure through Infant Feeding in Early Life. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, A.J.; Norén, E.; Haug, L.S.; Lindh, C.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Pineda, D.; Jakobsson, K.; Nielsen, C. Estimated Transfer of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Maternal Serum to Breast Milk in Women Highly Exposed from Contaminated Drinking Water: A Study in the Ronneby Mother-Child Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Goodrich, J.A.; Costello, E.; Walker, D.I.; Cardenas-Iniguez, C.; Chen, J.C.; Alderete, T.L.; Valvi, D.; Rock, S.; Eckel, S.P.; et al. Examining Disparities in PFAS Plasma Concentrations: Impact of Drinking Water Contamination, Food Access, Proximity to Industrial Facilities and Superfund Sites. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaKind, J.S.; Naiman, J.; Verner, M.-A.; Lévêque, L.; Fenton, S. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Breast Milk and Infant Formula: A Global Issue. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, M.; Blomberg, A.J.; Bolmsjö, B.B.; Jöud, A.S.; Jensen, T.K.; Nielsen, C. Common Infections in Children Aged 6 Months to 7 Years after High Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Contaminated Drinking Water in Ronneby, Sweden. Environ. Res. 2025, 268, 120787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Shao, L.-X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S.-W.; Wang, X.; Lu, G.-L.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.-H. Target Analysis and Suspect Screening of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Paired Samples of Maternal Serum, Umbilical Cord Serum, and Placenta near Fluorochemical Plants in Fuxin, China. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.L.; Hollister, J.; Fisher, J.M.; Beitel, S.C.; Ramadan, F.; O’Leary, S.; Fan, Z.T.; Lutrick, K.; Burgess, J.L.; Ellingson, K.D. Differences in Serum Concentrations of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances by Occupation among Firefighters, Other First Responders, Healthcare Workers, and Other Essential Workers in Arizona, 2020–2023. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 35, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, M.; ter Laak, T.L.; Cornelissen, E.R.; van Wezel, A.P. Exploring Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Presence and Potential Leaching from Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Implications for Drinking Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15799–15806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minucci, J.M.; DeLuca, N.M.; Durant, J.T.; Goodwin, B.; Kowalski, P.; Scruton, K.; Thomas, K.; Cohen Hubal, E.A. Linking Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in House Dust and Biomonitoring Data in Eight Impacted Communities. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Shin, H.-M.; Kannan, K.; Calafat, A.M.; Schmidt, R.J.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Bennett, D.H. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Serum of 2 to 5 Year-Old Children: Temporal Trends, Determinants, and Correlations with Maternal PFAS Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forthun, I.H.; Roelants, M.; Haug, L.S.; Knutsen, H.K.; Schell, L.M.; Jugessur, A.; Bjerknes, R.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Bruserud, I.S.; Juliusson, P.B. Levels of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Norwegian Children Stratified by Age and Sex—Data from the Bergen Growth Study 2. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 252, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratier, A.; Casas, M.; Grazuleviciene, R.; Slama, R.; Småstuen Haug, L.; Thomsen, C.; Vafeiadi, M.; Wright, J.; Zeman, F.A.; Vrijheid, M.; et al. Estimating the Dynamic Early Life Exposure to PFOA and PFOS of the HELIX Children: Emerging Profiles via Prenatal Exposure, Breastfeeding, and Diet. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, U.B.; Grandjean, P.; Nielsen, F.; Weihe, P.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E. Breastfeeding as an Exposure Pathway for Perfluorinated Alkylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10466–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, E.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Namork, E.; Nygaard, U.C.; Granum, B.; Haug, L.S. Exposure of Norwegian Toddlers to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): The Association with Breastfeeding and Maternal PFAS Concentrations. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hong, H. Unraveling the Link between Heavy Metals, Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Depression: Insights from Epidemiological and Bioinformatics Strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Eliot, M.N.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Kelsey, K.T.; Fore, R.; Langevin, S.; Buckley, J.; Chen, A.; Lanphear, B.P.; Cecil, K.M.; et al. Gestational Perfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure and DNA Methylation at Birth and 12 Years of Age: A Longitudinal Epigenome-Wide Association Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 37005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice; Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology; Committee on the Guidance on PFAS Testing and Health Outcomes. Guidance on PFAS Exposure, Testing, and Clinical Follow-Up; The National Academies Collection: Reports Funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-0-309-48244-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bredel, T.T.; Adamsen, J.; Helmer, T. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Primary Packaging and the Proposed Ban in the European Union. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2025, 79, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Cawdrey, R.W.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.C.; Wilkin, R. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water and Wastewater: A Critical Review of Their Global Occurrence and Distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panieri, E.; Baralic, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Buha Djordjevic, A.; Saso, L. PFAS Molecules: A Major Concern for the Human Health and the Environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguzzi, A.; Fava, C.; Castelli, M.; Minuz, P. Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Chemicals and Cardiovascular Disease: Experimental and Epidemiological Evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, W.; Ma, C.; Awais, M.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, S.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, S.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Interact with Platelet Glycoprotein Ibα and Exacerbate Thrombosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Xu, X.; Dong, X.-X.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Du, Z.; Pan, C.-W.; Liang, G.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zheng, Y.-J.; et al. Integration of Animal, Population, and Toxicogenomic Evidence on the Hematotoxic and Immunosuppressive Effects of Environmental Exposure to PFAS Mixtures in Adolescents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 10841–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Tan, Z.; Li, L.; Xiao, F.; An, Z.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Association of Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Risk of the Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Case-Control Study in Shijiazhuang Hebei Province. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, K.; Wāng, Y. Associations between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals and Abdominal Aortic Calcification in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 70, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, F.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Y. Associations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: NHANES 2017–2018. Cancer Causes Control 2024, 35, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.A.; Walker, D.I.; He, J.; Lin, X.; Baumert, B.O.; Hu, X.; Alderete, T.L.; Chen, Z.; Valvi, D.; Fuentes, Z.C.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Youth Exposure to Mixtures of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Multi-Cohort Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 27005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Young, A.S.; Keil, A.; Mullins, C.E.; Liang, D.; Zhao, S.; Jones, D.P.; Hu, X.; Walker, D.I.; White, A.J. Novel and Legacy Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Humans: Long-Term Temporal Variability and Metabolic Perturbations. Environ. Int. 2025, 201, 109590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Hong, X.; Wang, G.; Choi, G.; Nadeau, K.C.; Buckley, J.P.; Wang, X. Cord Plasma Metabolomic Signatures of Prenatal Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Exposures in the Boston Birth Cohort. Environ. Int. 2024, 194, 109144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Braun, J.M.; Hong, X.; Choi, G.; O’Leary, S.P.; Yu, C.H.; Pearson, C.; Adams, W.G.; Fan, Z.T.; et al. Associations of Early Life Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure with Body Mass Index and Risk of Overweight or Obesity at Age 2-18 Years: Mixture Analysis in the Prospective Boston Birth Cohort. Environ. Int. 2025, 195, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Shih, Y.-H.; Jørgensen, L.H.; Nielsen, F.; Weihe, P.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E. Estimated Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances during Infancy and Serum-Adipokine Concentrations in Later Childhood. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Wan, H.T.; Cheng, Z.; Chan, W.Y.; Lam, T.K.Y.; Lai, K.P.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.; Wong, C.K.C. Impact of PFOS Exposure on Murine Fetal Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Associated with Intrauterine Metabolic Perturbation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5496–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, J.C.; Blossom, S.J.; Schaider, L.A. Exposure to Per-Fluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Leads to Immunotoxicity: Epidemiological and Toxicological Evidence. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Timmermann, C.A.G.; Kruse, M.; Nielsen, F.; Vinholt, P.J.; Boding, L.; Heilmann, C.; Mølbak, K. Severity of COVID-19 at Elevated Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkylates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, E.E.; Dekant, W. Childhood PFAS Exposure and Immunotoxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Studies. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait Bamai, Y.; Goudarzi, H.; Araki, A.; Okada, E.; Kashino, I.; Miyashita, C.; Kishi, R. Effect of Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances on Childhood Allergies and Common Infectious Diseases in Children up to Age 7 Years: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taibl, K.R.; Liang, D.; Dunlop, A.L.; Barr, D.B.; Smith, M.R.; Steenland, K.; Tan, Y.; Ryan, P.B.; Panuwet, P.; Everson, T.; et al. Pregnancy-Related Hemodynamic Biomarkers in Relation to Trimester-Specific Maternal per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposures and Adverse Birth Outcomes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Larebeke, N.; Cox, B.; Remy, S.; Voorspoels, S.; Den Hond, E.; Colles, A.; Leermakers, M.; Schoeters, G.; Verheyen, V. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Thyroid Hormones, Sexual Hormones and Pubertal Development in Adolescents Residing in the Neighborhood of a 3M Factory. Environ. Health 2025, 24, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajana, R.; Rachoń, D.; Gałęzowska, G. Reproductive Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 117, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, S.L.; Walker, D.I.; Calafat, A.M.; Chen, A.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Xu, Y.; Jones, D.P.; Lanphear, B.P.; Pennell, K.D.; Braun, J.M. Metabolomics of Childhood Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances: A Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, J.L.; Sharma, V.; Lyall, K. Effects of Early-Life PFAS Exposure on Child Neurodevelopment: A Review of the Evidence and Research Gaps. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2025, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogheim, T.S.; Weyde, K.V.F.; Aase, H.; Engel, S.M.; Surén, P.; Øie, M.G.; Biele, G.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Haug, L.S.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Associations with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yan, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ren, S. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Perfluorinated and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances with Childhood Neurodevelopment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, S.M.; Ortlund, K.E.; Barr, D.B.; Dunlop, A.L.; Liang, D.; Corwin, E.J.; Ryan, P.B.; Friedman, S.; Buhr, M.; Panuwet, P.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Persistent Organic Pollutants and Associations with Child Behavior Problems at 1-5 Years. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Grahl, E.; Hilz, E.N.; Gore, A.C. Regrettable Substitutes and the Brain: What Animal Models and Human Studies Tell Us about the Neurodevelopmental Effects of Bisphenol, Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, and Phthalate Replacements. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.V.; Till, C.; Green, R.; El-Sabbagh, J.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Hornung, R.; Lanphear, B.; Seguin, J.R.; Booij, L.; Fisher, M.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Legacy PFAS and Neurodevelopment in Preschool-Aged Canadian Children: The MIREC Cohort. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2023, 98, 107181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Ding, J.; Guo, J.; Qi, X.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Z. Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, Fetal Thyroid Function, and Intelligence Quotient at 7 Years of Age: Findings from the Sheyang Mini Birth Cohort Study. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PFOA, PFOS, and Related PFAS Chemicals. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/chemicals/teflon-and-perfluorooctanoic-acid-pfoa.html (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- IARC Working Group on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS); IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2025; ISBN 978-92-832-4532-2. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK614282/ (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Zahm, S.; Bonde, J.P.; Chiu, W.A.; Hoppin, J.; Kanno, J.; Abdallah, M.; Blystone, C.R.; Calkins, M.M.; Dong, G.-H.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. Carcinogenicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winquist, A.; Hodge, J.M.; Diver, W.R.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Troeschel, A.N.; Daniel, J.; Teras, L.R. Case-Cohort Study of the Association between PFAS and Selected Cancers among Participants in the American Cancer Society’s Cancer Prevention Study II LifeLink Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binczewski, N.R.; Morimoto, L.M.; Wiemels, J.L.; Ma, X.; Metayer, C.; Vieira, V.M. Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Contaminated Water and Risk of Childhood Cancer in California, 2000–2015. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 9, e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metayer, C.; Morimoto, L.M.; Vieira, V.M.; Godri Pollitt, K.J.; Bartell, S.M.; Wong, L.; Young, T.M. Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Residential Settled Dust and Risk of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Cancer 2025, 157, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.R.; Madrigal, J.M.; Troisi, R.; Surcel, H.-M.; Öhman, H.; Kivelä, J.; Kiviranta, H.; Rantakokko, P.; Koponen, J.; Medgyesi, D.N.; et al. Maternal Serum Concentrations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2024, 116, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeny, S.; Jarrell, Z.R.; Krigbaum, N.Y.; Cirillo, P.M.; Go, Y.-M.; Cohn, B.A.; Jones, D.P. Environmental Basis for Early Onset Breast Cancer. Reprod. Toxicol. 2025, 133, 108866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Li, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, Z.; Liu, Z.; Mi, Y.; Geng, H.; Xin, S. Integrative in Silico Analysis of Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS)-Associated Molecular Alterations in Human Cancers: A Multi-Cancer Framework for Predicting Toxicogenomic Disruption. Int. J. Surg. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Decoding Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multi-Omics and Computational Toxicology Approach. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, D.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Du, Z.; Hong, Y. Analyzing the Potential Targets and Mechanism of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) on Breast Cancer by Integrating Network Toxicology, Single-Cell Sequencing, Spatial Transcriptomics, and Molecular Simulation. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2025, 25, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Baumert, B.O.; Stratakis, N.; Goodrich, J.A.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, H.; Beglarian, E.; Bartell, S.M.; Eckel, S.P.; et al. Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Alterations in Plasma microRNA Profiles in Children. Environ. Res. 2024, 259, 119496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.-Y.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-W.; Huang, G.-L.; Zeng, E.Y. Use of Glioma to Assess the Distribution Patterns of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Human Brain. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Yan, W.; Gao, S.; Li, X. The Effect of PFAS Exposure on Glucolipid Metabolism in Children and Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1261008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Furnary, T.; Vasiliou, V.; Yan, Q.; Nyhan, K.; Jones, D.P.; Johnson, C.H.; Liew, Z. Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Associations with per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure in Humans: A Scoping Review. Environ. Int. 2022, 162, 107159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Du, K.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, H.; Pan, T.; Wu, T.; Zhao, L.; Du, W.; Zheng, S.-S.; et al. PFOS and Its Commercial Alternative, 6:2 Cl-PFESA, Induce Multidrug Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 22027–22038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Qin, S.; Zeng, H.; Chou, W.; Oudin, A.; Kanninen, K.M.; Jalava, P.; Dong, G.; Zeng, X. Adverse Outcome Pathway for the Neurotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Systematic Review. Eco Environ. Health 2024, 3, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, T.S.; Abington, L.M.; van ’t Erve, T.J.; Wang, L.; McDonald, J.M.; Wasilevich, E.A.; Gray, J.S.; Karrer, T.A.; Smith, K.; Bailey, J.M. Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Affect Thyroid Hormones for People with a History of Exposure from Drinking Water. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.E.; Yu, J.; Shin, H.-M. Exploring the Neurodegenerative Potential of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances through an Adverse Outcome Pathway Network. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 969, 178972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, H.E.; Costello, E.; Walker, D.I.; Wang, H.; Baumert, B.O.; Valvi, D.; Rock, S.; Jones, D.P.; Goran, M.I.; Gilliland, F.D.; et al. Associations of Dietary Intake and Longitudinal Measures of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Predominantly Hispanic Young Adults: A Multicohort Study. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, S.M.; Sehgal, N.; Salamova, A.; Fiedler, N.; Hood, R.B.; Yakimavets, V.; Promkam, N.; Prapamontol, T.; Suttiwan, P.; Sittiwang, S.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Paired Serum and Breastmilk Samples among Pregnant Farmworkers in Thailand. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2025, 264, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, G.; Howe, C.G.; Gallagher, L.G.; Gilbert-Diamond, D.; Calafat, A.M.; Botelho, J.C.; Karagas, M.R.; Romano, M.E. Prenatal Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Mixtures and Weight for Length from Birth to 12 Months: The New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 980, 179446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, E.; Ding, L.; Liu, Y. Associations between in Utero Exposure of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Mixture and Anthropometry Measures at Birth. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-N.; Wu, K.-J.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.-J.; Liang, H.-R.; Jiang, Z.-X.; Li, Z.-L.; Hu, C.-Y. Association Between Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Birth Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 855348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Oliva, P.; Zhang, L.; Goodrich, J.A.; McConnell, R.; Conti, D.V.; Chatzi, L.; Aung, M. Associations between per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and county-level cancer incidence between 2016 and 2021 and incident cancer burden attributable to PFAS in drinking water in the United States. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 35, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dui, W.; Smith, M.P.; Bartock, S.H. Development, Validation, and Clinical Assessment of a Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Serum Assay for per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Recommended by the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 6333–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisacq, P.; De Keuster, M.; Prinsen, E.; Jeong, Y.; Bervoets, L.; Eens, M.; Covaci, A.; Willems, T.; Groffen, T. Assessment of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Commercially Available Drinking Straws Using Targeted and Suspect Screening Approaches. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2023, 40, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)—ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/hot-topics/perfluoroalkyl-chemicals-pfas (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Drinking Water—European Commission. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/water/drinking-water_en (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- EPA Places Limits on 4 Types of Toxic “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water. Available online: https://www.verywellhealth.com/epa-pfas-limits-drinking-water-5496696 (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Levelut, V. Impact of PFAS Regulations on Medical Devices; NAMSA: Chasse-sur-Rhône, France, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Taliantzis, K.; Ellinas, K. Green Hydrophobic and Superhydrophobic Coatings and Surfaces for Water Related Applications: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 343, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Chen, H.; Song, D.; Fang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, H. Nontarget Screening and Occurrence of Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Municipal and Semiconductor Industrial Wastewater: A Large-Scale Survey in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 11829–11841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. FDA Issues Comprehensive Draft Guidance for Developers of Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Medical Devices. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-issues-comprehensive-draft-guidance-developers-artificial-intelligence-enabled-medical-devices (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Kisielinski, K.; Hockertz, S.; Hirsch, O.; Korupp, S.; Klosterhalfen, B.; Schnepf, A.; Dyker, G. Wearing Face Masks as a Potential Source for Inhalation and Oral Uptake of Inanimate Toxins—A Scoping Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 115858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Song, H.; Wang, F.; Su, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J. Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Surfaces: From Nature to Application. Materials 2025, 18, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, J. Recent Advances in Microbial and Bioelectrochemical Strategies for Degradation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Mechanisms, Limitations, and Research Opportunities. Biotechnol. Lett. 2025, 47, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fluoropolymers | Fluoroelastomers | Fluorinated Surfactants/Solvents |
|---|---|---|
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Fluoroelastomers (FKM/FPM) | Hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFP) |
| Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) | Perfluoroelastomers (FFKM/FFPM) | Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) |
| PFAS Category | Compound/Class | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorinated Polymers and Copolymers | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Catheters, sutures, vascular grafts, and implant coatings |
| Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) | Tubing, filter membranes, and drug delivery systems | |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) | Tubing, membranes, and infusion systems | |
| PVDF-Hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) | Multilayer films, drug packaging, and infusion bags | |
| Perfluoropolyethers (PFPEs) | Lubricated device components (e.g., moving joints, seals) | |
| Perfluorinated acrylates (C6–C14) | Hydrophobic coatings and anti-fouling surface treatments | |
| Surface Modifications | Proprietary fluoropolymer coatings | Biocompatibility enhancement and reduced microbial adhesion on medical device surfaces |
| PFAS Type | Compound/Class | Medical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Fluoroelastomers | FKM/FPM fluoroelastomers | Seals, O-rings, and flexible components in surgical and diagnostic instruments |
| FFKM/FFPM perfluoroelastomers | High-performance sealing systems in sterilizable and chemically resistant environments | |
| Suture and Graft Materials | PTFE-based sutures and vascular grafts | Soft tissue suturing, vascular repair, low reactivity, and improved knot security |
| PVDF-based sutures | Durable suturing, enhanced mechanical strength and biocompatibility | |
| Semi-fluorinated Alkanes | 1-(Perfluorohexyl)octane; 1-(Perfluorobutyl)pentane | Ophthalmic surgery (e.g., retinal procedures) and biocompatible surgical lubricants |
| Exposure Route | Pathway | Magnitude of Exposure * | Confidence Level * | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental–Drinking water | Ingestion of contaminated tap or bottled water | High | High | Children consume more water per kg than adults, increasing exposure risk [53,54] |
| Environmental–Dust/Soil | Ingestion during hand-to-mouth activity | Moderate | High | Dust exposures are significant due to behavioral factors [47] |
| Breastfeeding | Transfer of PFASs through human milk | High (infancy) | High | Exclusive breastfeeding can increase serum PFAS by ~30%/month [53,55] |
| Prenatal (gestational transfer) | Maternal–fetal transfer via placenta | Moderate | Moderate | Contributes significantly to exposure at birth [53,56,57] |
| Medical devices | PFAS-containing bottles, tubing, catheters, and ECMO lines | Low–Moderate | Low | Not well quantified, but clinically relevant [22,27,58,59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Briassoulis, G.; Ilia, S.; Briassouli, E. Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Healthcare: Environmental and Clinical Insights. Life 2025, 15, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071057
Briassoulis G, Ilia S, Briassouli E. Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Healthcare: Environmental and Clinical Insights. Life. 2025; 15(7):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071057
Chicago/Turabian StyleBriassoulis, George, Stavroula Ilia, and Efrossini Briassouli. 2025. "Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Healthcare: Environmental and Clinical Insights" Life 15, no. 7: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071057
APA StyleBriassoulis, G., Ilia, S., & Briassouli, E. (2025). Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Healthcare: Environmental and Clinical Insights. Life, 15(7), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071057








