Efficacy and Safety of Selexipag Treatment in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CTD-PAH | connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| ILD | interstitial lung disease |
| PH | pulmonary hypertension |
| CTD | connective tissue disease |
| RHC | right heart catheterization |
| 6MWD | six-minute walk distance |
| eRVSP | estimated right ventricular systolic pressure |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide |
| PFTs | pulmonary function tests |
| PH-ILD | pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PAH | pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PH-LHD | pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease |
| PH-LD | pulmonary hypertension due lung disease |
| CTEPH | chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| HP | hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| NSIP | nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |
| mPAP | mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| PCWP | pulmonary capillary wedge pressure |
| WU | wood units |
| DLCO | diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide |
| FEV1 | forced expiratory volume in one second |
| FVC | forced vital capacity |
| FDA | food and drug administration |
| MCTD | mixed connective tissue disease |
| PDE-5-I | phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor |
| ERA | endothelin receptor antagonist |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
References
- Coghlan, J.G.; Picken, C.; Clapp, L.H. Selexipag in the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension: An update. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2019, 11, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte, T.J.; Keir, G.J.; Dimopoulos, K.; Howard, L.; Corris, P.A.; Parfitt, L.; Foley, C.; Yanez-Lopez, M.; Babalis, D.; Marino, P. Bosentan in pulmonary hypertension associated with fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Price, L.C.; Valenzuela, C. The unmet medical need of pulmonary hypertension in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2018, 51, 1702596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.-L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Behr Brown, K.K., Jr.; du Bois, R.M.; Lancaster, L.; de Andrade, J.A.; Stahler, G.; Leconte, I.; Roux, S.; Raghu, G. BUILD-1: A randomized placebo-controlled trial of bosentan in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King Jr, T.E.; Brown, K.K.; Raghu, G.; Du Bois, R.M.; Lynch, D.A.; Martinez, F.; Valeyre, D.; Leconte, I.; Morganti, A.; Roux, S. BUILD-3: A randomized, controlled trial of bosentan in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, M.; Blair, C.; Takahashi, T.; Langley, J.; Coghlan, J.G. Initial combination therapy of ambrisentan and tadalafil in connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (CTD-PAH) in the modified intention-to-treat population of the AMBITION study: Post hoc analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, C.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Browning, R.F.; Barnett, S.D.; Ahmad, S.; Shorr, A.F. The distance-saturation product predicts mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K.; Ernst, R.; Hess, P.; Studer, R.; Clozel, M. Selexipag: A selective prostacyclin receptor agonist that does not affect rat gastric function. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadrous, H.F.; Pellikka, P.A.; Krowka, M.J.; Swanson, K.L.; Chaowalit, N.; Decker, P.A.; Ryu, J.H. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2005, 128, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, S.D.; Behr, J.; Collard, H.R.; Cottin, V.; Hoeper, M.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Corte, T.J.; Keogh, A.M.; Leuchte, H.; Mogulkoc, N. Riociguat for idiopathic interstitial pneumonia-associated pulmonary hypertension (RISE-IIP): A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Na, J.O.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Chang, H.-J. 2020 KSC/KATRD guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: Executive summary. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2022, 85, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Egan, J.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Nathan, S.D.; Wells, A.U.; Collard, H.R. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with ambrisentan: A parallel, randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Million-Rousseau, R.; Morganti, A.; Perchenet, L.; Behr, J.; Group, M.S. Macitentan for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The randomised controlled MUSIC trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, L.J.; Badesch, D.B.; Barst, R.J.; Galie, N.; Black, C.M.; Keogh, A.; Pulido, T.; Frost, A.; Roux, S.; Leconte, I. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, W.; Adir, Y.; Barberà, J.A.; Champion, H.; Coghlan, J.G.; Cottin, V.; De Marco, T.; Galiè, N.; Ghio, S.; Gibbs, S. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung diseases. Turk Kardiyoloji Dernegi Arsivi 2014, 42, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlobin, O.A.; Brown, A.W.; Nathan, S.D. Pulmonary hypertension in diffuse parenchymal lung diseases. Chest 2017, 151, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Channick, R.; Chin, K.M.; Frey, A.; Gaine, S.; Galiè, N.; Ghofrani, H.-A.; Hoeper, M.M.; Lang, I.M.; Preiss, R. Selexipag for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, A.; Restrepo-Jaramillo, R.; Thenappan, T.; Ravichandran, A.; Engel, P.; Bajwa, A.; Allen, R.; Feldman, J.; Argula, R.; Smith, P. Inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, R.; Nishiyama, O.; Yoshikawa, K.; Tohda, Y.; Matsumoto, H. Outcome of patients who were incidentally diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: How early in the disease should we identify patients? Respir. Med. 2022, 201, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Nishiyama, O.; Yamazaki, R.; Kunita, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Sano, A.; Matsumoto, H. Selexipag for patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with lung disease: A preliminary study. Respir. Investig. 2024, 62, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, E.; Polito, P.; Famoso, G.; Larosa, M.; De Zorzi, E.; Scarpieri, E.; Cozzi, F.; Doria, A. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in connective tissue disorders: Pathophysiology and treatment. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 55 | 62 | 49 | 48 | 51 | 59 | 52 | 51 |
| Gender | M | F | F | F | F | M | F | M |
| CTD type | MCTD | MCTD | Scleroderma | Scleroderma | Scleroderma | MCTD | Scleroderma | MCTD |
| CTD duration | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| PAH treatment | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA | PDE-5-I + ERA |
| Cardiopulmonary hospitalizations | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| DLCO (%) | 38 | 46 | 40 | 28 | 50 | 46 | 31 | 32 |
| ILD | ||||||||
| Type | NSIP | NSIP | Fibrotic NSIP | Fibrotic NSIP | Fibrotic NSIP | Fibrotic NSIP | Fibrotic NSIP | Fibrotic NSIP |
| Treatment | Mycophenolate mofetil Hydroxychloroquine | Mycophenolate mofetil Hydroxychloroquine | Hydroxychloroquine | Hydroxychloroquine | Mycophenolate mofetil | Mycophenolate mofetil Prednisone | Hydroxychloroquine | Hydroxychloroquine |
| Patient | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHC | ||||||||
| mPAP | 45 | 33 | 41 | 52 | 35 | 39 | 50 | 29 |
| PCWP | 10 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 5 | 14 | 14 | 7 |
| CO | 5 | 3.9 | 5.2 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 5.3 |
| PVR | 7 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 13.4 | 7.3 | 12.4 | 12.4 | 4.2 |
| Patient | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6MWD | ||||||||
| Baseline | 287 | 390 | 332 | 150 | 340 | 380 | 166 | 400 |
| 16 weeks | 350 | 500 | 503 | 299 | 392 | 452 | 288 | 475 |
| NT-proBNP | ||||||||
| Baseline | 1100 | 743 | 1039 | 4203 | 922 | 522 | 6922 | 320 |
| 16 weeks | 532 | 402 | 829 | 937 | 642 | 482 | 1825 | 187 |
| eRSVP | ||||||||
| Baseline | 77 | 60 | 71 | 90 | 55 | 65 | 88 | 60 |
| 16 weeks | 58 | 43 | 44 | 67 | 44 | 47 | 52 | 41 |
| O2 therapy | ||||||||
| Baseline | 2 L | RA | 2 L | 4 L | 2 L | RA | 4 L | 2 L |
| 16 weeks | RA | RA | RA | 2 L | 2 L | RA | 4 L | RA |
| Absolute FVC | ||||||||
| Baseline | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 2.1 |
| 16 weeks | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 2 | 2.2 |
| Predicted FVC | ||||||||
| Baseline | 63 | 59 | 67 | 49 | 62 | 54 | 68 | 62 |
| 16 weeks | 61 | 54 | 63 | 47 | 65 | 62 | 62 | 57 |
| Predicted FEV1 | ||||||||
| Baseline | 65 | 60 | 65 | 50 | 60 | 58 | 65 | 61 |
| 16 weeks | 65 | 61 | 64 | 51 | 59 | 60 | 65 | 63 |
| Absolute FEV1 | ||||||||
| Baseline | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| 16 weeks | 1.9 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 2.2 |
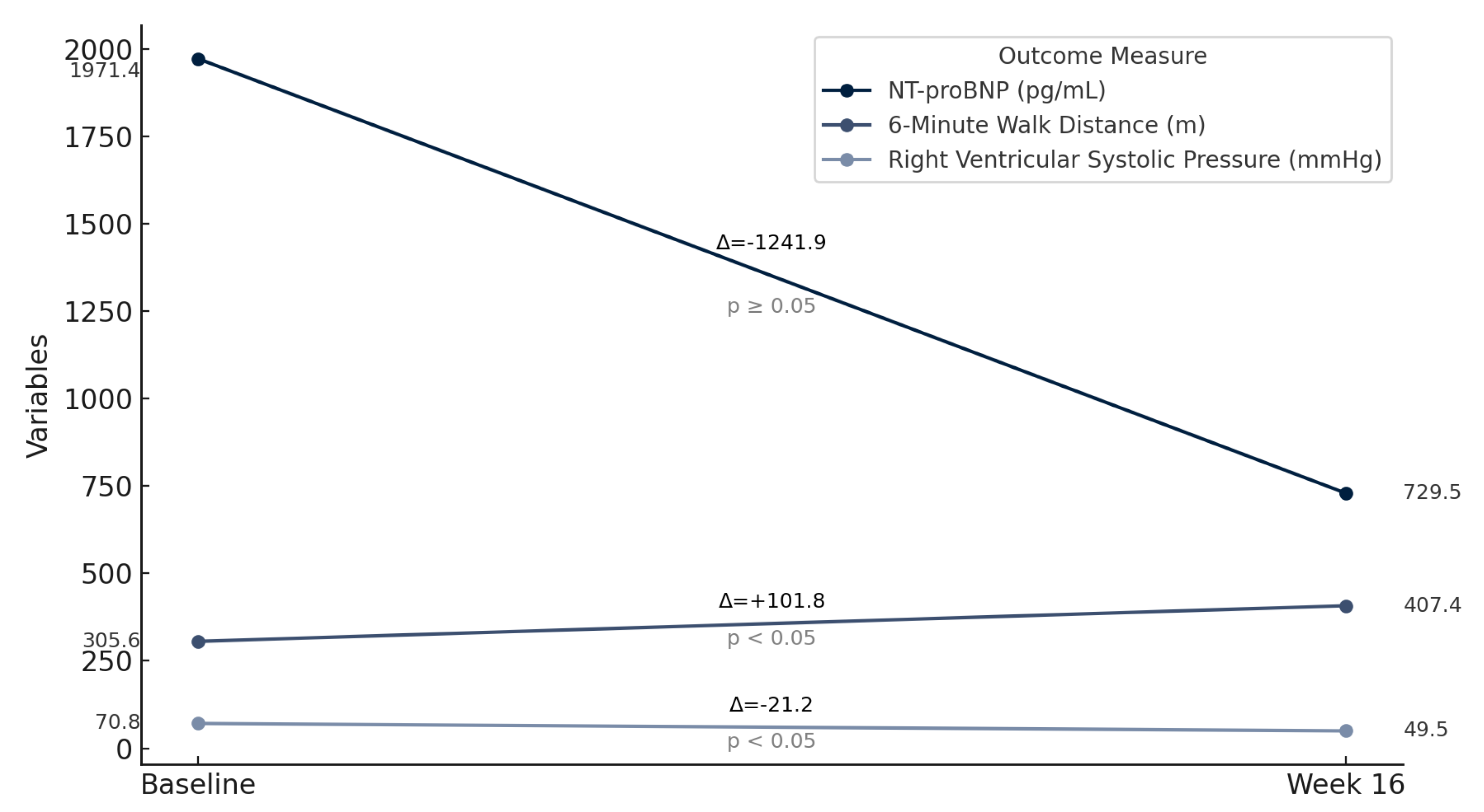
| Baseline Average | Average After 16 Weeks of Therapy | Difference | T-Score | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6MWD | 305.62 | 407.37 | 101.75 | −6.66 | 0.00029 |
| NT-proBNP | 1971.37 | 729.5 | −1241.87 | 1.86 | 0.1048 |
| eRSVP | 70.75 | 49.5 | −21.25 | 7.98 | 0.000093 |
| Supplemental O2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2.65 | 0.033 |
| Absolute FVC | 2.01 | 1.89 | −0.12 | 1.39 | 0.208 |
| Predicted FVC | 60.5 | 58.87 | −1.62 | 0.96 | 0.371 |
| Absolute FEV1 | 2 | 2.06 | +0.06 | −1.93 | 0.095 |
| Predicted FEV1 | 60.5 | 61 | +0.5 | 1.17 | 0.280 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dagher, C.; Akiki, M.; Swanson, K.; Carollo, B.; Farber, H.W.; Parikh, R. Efficacy and Safety of Selexipag Treatment in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease. Life 2025, 15, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060974
Dagher C, Akiki M, Swanson K, Carollo B, Farber HW, Parikh R. Efficacy and Safety of Selexipag Treatment in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease. Life. 2025; 15(6):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060974
Chicago/Turabian StyleDagher, Chebly, Maria Akiki, Kristen Swanson, Brett Carollo, Harrison W. Farber, and Raj Parikh. 2025. "Efficacy and Safety of Selexipag Treatment in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease" Life 15, no. 6: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060974
APA StyleDagher, C., Akiki, M., Swanson, K., Carollo, B., Farber, H. W., & Parikh, R. (2025). Efficacy and Safety of Selexipag Treatment in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease. Life, 15(6), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060974





