A Cross-Sectional Study on the Biomechanical Effects of Squat Depth and Movement Speed on Dynamic Postural Stability in Tai Chi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
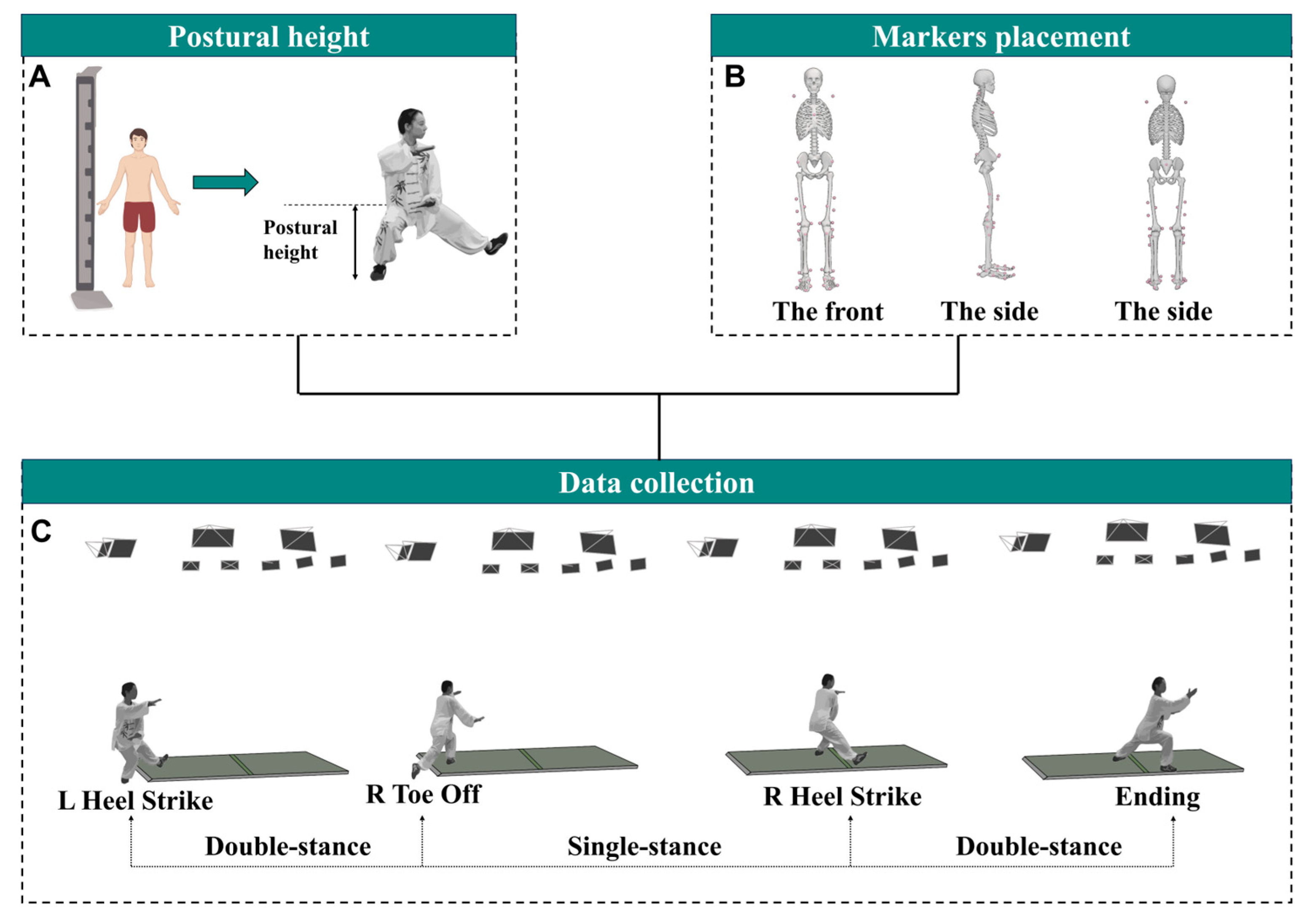
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
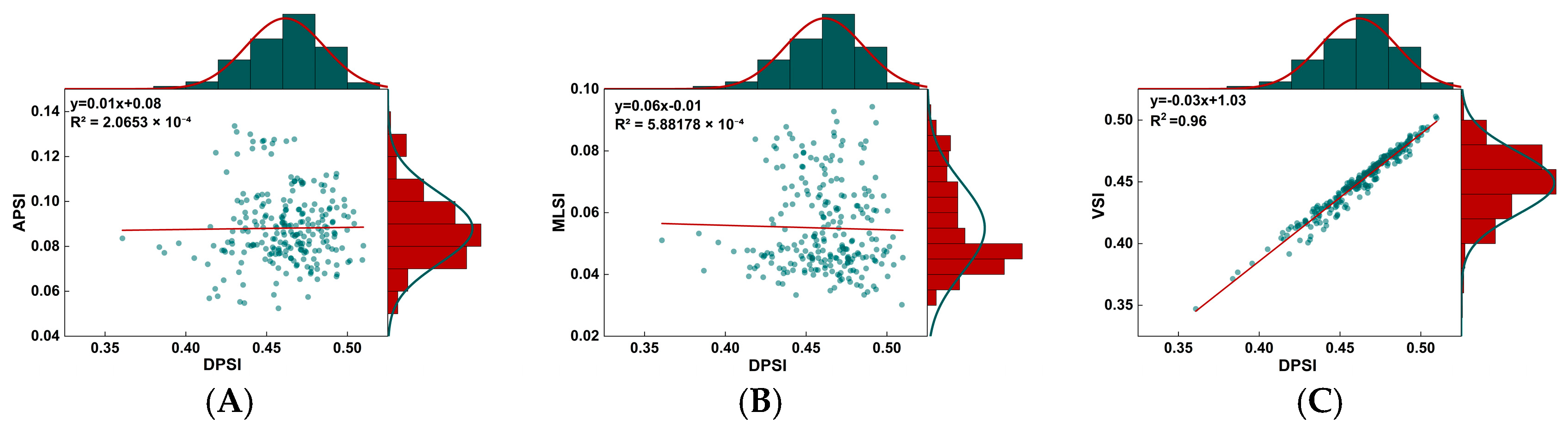
3.1. Dynamic Postural Steadiness Index
3.2. Center of Pressure
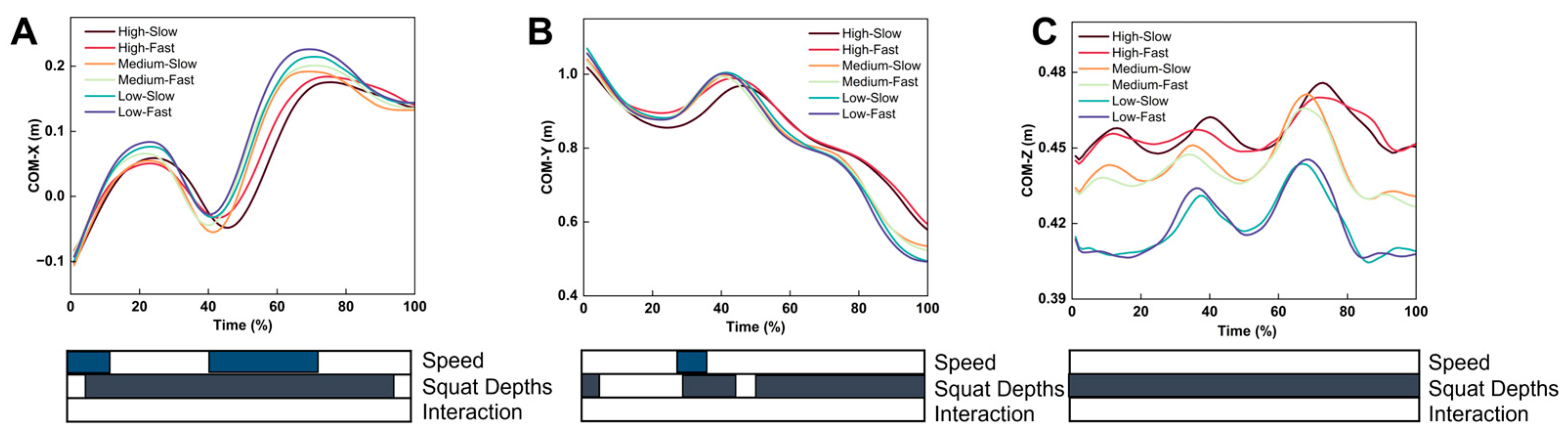
3.3. Center of Mass
3.4. CoM-CoP Separation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWHM | Part the Wild Horse’s Mane |
| HS | High squat |
| MS | Middle squat |
| LS | Low squat |
| CoM | Center of mass |
| CoP | Center of pressure |
| GRF | Ground reaction forces |
| DPSI | Dynamic postural stability index |
| MLSI | Mediolateral stability index |
| APSI | Anteroposterior stability index |
| VSI | Vertical stability index |
| BOS | Base of support |
| ML | Mediolateral |
| AP | Anteroposterior |
| LHS | Left heel strike |
| RTO | Right toe off |
| RHS | Right heel strike |
| LTO | Left toe off |
| SnPM | Statistical nonparametric mapping |
| COG | Center of gravity |
References
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. S2), ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldhof, E.; Cardon, G.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Danneels, L.; Coorevits, P.; Vanderstraeten, G.; De Clercq, D. Static and dynamic standing balance: Test-retest reliability and reference values in 9 to 10 year old children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2006, 165, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, S.; Myers, J.; Sell, T.; Tsai, Y.; Bradley, J. Golf injury prevention: An orthopedic approach through physical testing, biomechanics, and training. In Proceedings of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–18 February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.K.; Chen, C.H.; Shiang, T.Y.; Jan, M.H.; Lin, K.H. Risk-factor analysis of high school basketball-player ankle injuries: A prospective controlled cohort study evaluating postural sway, ankle strength, and flexibility. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, M.; Ashayeri, H.; Salavati, M.; Sarafzadeh, J.; Taghipoor, K.D.; Saeedi, A.; Salehi, R. Reliability of center of pressure measures of postural stability in healthy older adults: Effects of postural task difficulty and cognitive load. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijoux, F.; Nicolaï, A.; Chairi, I.; Bargiotas, I.; Ricard, D.; Yelnik, A.; Oudre, L.; Bertin-Hugault, F.; Vidal, P.P.; Vayatis, N.; et al. A review of center of pressure (COP) variables to quantify standing balance in elderly people: Algorithms and open-access code. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Han, S.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, F.; Yue, J. A study on the balance ability and plantar pressure of sarcopenia patients in different standing postures. Gait Posture 2025, 118, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendell, C.; Lemaire, E.D.; Dudek, N.L.; Kofman, J. Indicators of dynamic stability in transtibial prosthesis users. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.L.; Peters, D.M.; Robinson, P.D.; Watt, T.N.; Hollands, M.A. Older adults who have previously fallen due to a trip walk differently than those who have fallen due to a slip. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.E.; Chou, L.-S. Age-related reduction in sagittal plane center of mass motion during obstacle crossing. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, T.C. An examination, correlation, and comparison of static and dynamic measures of postural stability in healthy, physically active adults. Phys. Ther. Sport 2012, 13, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikstrom, E.A.; Tillman, M.D.; Smith, A.N.; Borsa, P.A. A new force-plate technology measure of dynamic postural stability: The dynamic postural stability index. J. Athl. Train. 2005, 40, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, P.S.; Lee, D.; Hosmer, E. The dynamic postural steadiness and stabilization time between older adults with and without recurrent low back pain. Gait Posture 2023, 100, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, D.C.; Curry, S.J.; Owens, D.K.; Barry, M.J.; Caughey, A.B.; Davidson, K.W.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W., Jr.; Kemper, A.R.; Krist, A.H.; et al. Interventions to Prevent Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promsri, A.; Pitiwattanakulchai, P.; Saodan, S.; Thiwan, S. Age-Related Changes in Postural Stability in Response to Varying Surface Instability in Young and Middle-Aged Adults. Sensors 2024, 24, 6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Keegan, T.H.M.; Sternfeld, B.; Sidney, S.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Kelsey, J.L. Outdoor falls among middle-aged and older adults: A neglected public health problem. Am. J. Public Health 2006, 96, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Harmer, P.; Fitzgerald, K.; Eckstrom, E.; Stock, R.; Galver, J.; Maddalozzo, G.; Batya, S.S. Tai chi and postural stability in patients with Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Qiu, P.; Liu, T. Tai Ji Quan: An overview of its history, health benefits, and cultural value. J. Sport Health Sci. 2014, 3, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Transforming traditional Tai Ji Quan techniques into integrative movement therapy-Tai Ji Quan: Moving for Better Balance. J. Sport Health Sci. 2014, 3, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; István, B.; Xuan, R.; Wei, S.; Zhong, G.; Gu, Y. Current Evidence on Traditional Chinese Exercises for Quality of Life in Patients With Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 627518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sun, D.; István, B.; Thirupathi, A.; Liang, M.; Teo, E.C.; Gu, Y. Current Evidence on Traditional Chinese Exercise for Cancers: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, I.W.; Sung, W.H.; Lin, C.H.; Chuang, E.; Chuang, T.Y.; Lin, P.H. Effects of individualized Tai-Chi on balance and lower-limb strength in older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Harmer, P.; Fitzgerald, K.; Eckstrom, E.; Akers, L.; Chou, L.S.; Pidgeon, D.; Voit, J.; Winters-Stone, K. Effectiveness of a Therapeutic Tai Ji Quan Intervention vs a Multimodal Exercise Intervention to Prevent Falls Among Older Adults at High Risk of Falling: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, C.; Blank, C.; Arvandi, M.; Wehner, C.; Schobersberger, W. Effect of Tai Chi on muscle strength, physical endurance, postural balance and flexibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Mao, D. Long-term Tai Chi practitioners have superior body stability under dual task condition during stair ascent. Gait Posture 2018, 66, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.P.; Kuo, C.C.; Lu, S.H.; Chen, S.C.; Ho, T.J.; Lu, T.W. Synergistic multi-joint kinematic strategies to reduce tripping risks during obstacle-crossing in older long-term Tai-Chi Chuan practitioners. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 961515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ren, X. Speed effect of selected Tai Chi Chuan movement on leg muscle activity in young and old practitioners. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Hitt, J.; Millon, D. Spatial, temporal and muscle action patterns of Tai Chi gait. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2004, 14, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, M.; Quan, W.; Liang, M.; Baker, J.S.; Liu, Y. Biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in Tai Chi Novices with d ifferent squatting depths: A pilot study. Mol. Cell. Biomech. 2024, 21, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, H.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Cen, H.; Fan, Y. Biomechanical effects of typical lower limb movements of Chen-style Tai Chi on knee joint. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2023, 61, 3087–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Jian, W.; Fei, W.; Xiaomei, L. Determination and Control of Three Postures of Taijiquan. Chin. Sport. Sci. Technol. 2005, 41, 103–104+143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yu, P.; Shim, V.; Wang, A.; Fernandez, J. Integrating an LSTM framework for predicting ankle joint biomechanics during gait using inertial sensors. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Mei, Q.; Wang, A.; Shim, V.; Fernandez, J.; Gu, Y. Evaluating function in the hallux valgus foot following a 12-week minimalist footwear intervention: A pilot computational analysis. J. Biomech. 2022, 132, 110941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Cen, X.; Mei, Q.; Wang, A.; Gu, Y.; Fernandez, J. Differences in intra-foot movement strategies during locomotive tasks among chronic ankle instability, copers and healthy individuals. J. Biomech. 2024, 162, 111865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Deng, K.; Gao, Z.; Shim, V.; Wang, A.; Fernandez, J. Integrating personalized shape prediction, biomechanical modeling, and wearables for bone stress prediction in runners. npj Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Xiang, L.; Ying, S.; Li, J.; Fernandez, J.; Gu, Y. Effects of different cushioned insoles on ankle and knee joints biomechanics during load carriage running. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2023, 43, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L. A comparison of the EEG of the exercisers who exercised Taijiquan at different speeds. J. Phys. Educ. 2014, 21, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Mao, M.; Song, Q.; Zhang, C.; Fong, D.T.P.; Sun, W. Muscle co-contraction and pre-activation in knee and ankle joint during a typical Tai Chi brush-knee twist-step. Res. Sports Med. 2023, 31, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, A. Research on Knee Joint Load and Influencing Factors of Typical Tai Chi Movements. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2022, 2022, 6774980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Wang, K.; Chang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Niu, W. Tai Chi Is Safe and Effective for the Hip Joint: A Biomechanical Perspective. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2020, 28, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmenhoven, J.; Harrison, A.; Robinson, M.A.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Bargary, N.; Smith, R.; Cobley, S.; Draper, C.; Donnelly, C.; Pataky, T. A force profile analysis comparison between functional data analysis, statistical parametric mapping and statistical non-parametric mapping in on-water single sculling. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2018, 21, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Nomura, Y.; Kamide, K. Relationship between static balance and gait parameters in preschool children. Gait Posture 2022, 96, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, L.Z. Falls in older people: Epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for prevention. Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. S2), ii37–ii41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsue, B.J.; Su, F.C. Effects of age and gender on dynamic stability during stair descent. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lewis, C.L.; Gill, S.V. Effects of obesity and foot arch height on gait mechanics: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lewis, C.L.; Silverman, A.K.; Gill, S.V. Changes in dynamic balance control in adults with obesity across walking speeds. J. Biomech. 2022, 144, 111308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, O.; Simoneau, M.; Marcotte, J.; Berrigan, F.; Doré, J.; Marceau, P.; Marceau, S.; Tremblay, A.; Teasdale, N. Body weight is a strong predictor of postural stability. Gait Posture 2007, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, S.; Cheng, R.; Tsai, T.Y.; Wang, H. Sarcopenia in older adults is associated with static postural control, fear of falling and fall risk: A study of Romberg test. Gait Posture 2024, 112, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikstrom, E.A.; Arrigenna, M.A.; Tillman, M.D.; Borsa, P.A. Dynamic postural stability in subjects with braced, functionally unstable ankles. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert-Losier, K.; Murray, L. Reliability of centre of pressure, plantar pressure, and plantar-flexion isometric strength measures: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2020, 75, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.W.; Li, J.X.; Hong, Y. The duration and plantar pressure distribution during one-leg stance in Tai Chi exercise. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, S.C.; Bazett-Jones, D.M.; Joshi, M.N.; Earl-Boehm, J.E.; James, C.R. The relationship among foot posture, core and lower extremity muscle function, and postural stability. J. Athl. Train. 2014, 49, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuchi, C.A.; Fukuchi, R.K.; Duarte, M. Effects of walking speed on gait biomechanics in healthy participants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, S.A.; Granata, K.P. The influence of gait speed on local dynamic stability of walking. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Squat Depth | Slow | Fast | Squat Depth | Speed | Squat Depth × Speed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | η2 | p | η2 | p | η2 | ||||
| APSI (BW) | High | 0.075 ± 0.013 | 0.081 ± 0.010 | 0.001 a | 0.442 | 0.179 | 0.008 | 0.106 | 0.020 |
| Medium | 0.088 ± 0.010 | 0.088 ± 0.010 | |||||||
| Low | 0.100 ± 0.017 | 0.100 ± 0.018 | |||||||
| MLSI (BW) | High | 0.050 ± 0.010 | 0.052 ± 0.010 | 0.001 a | 0.114 | 0.357 | 0.004 | 0.409 | 0.008 |
| Medium | 0.054 ± 0.014 | 0.053 ± 0.011 | |||||||
| Low | 0.060 ± 0.017 | 0.061 ± 0.020 | |||||||
| VSI (BW) | High | 0.440 ± 0.029 | 0.442 ± 0.027 | 0.001 a | 0.077 | 0.024 b | 0.023 | 0.708 | 0.003 |
| Medium | 0.452 ± 0.023 | 0.461 ± 0.016 | |||||||
| Low | 0.447 ± 0.025 | 0.452 ± 0.026 | |||||||
| DPSI (BW) | High | 0.449 ± 0.029 | 0.453 ± 0.026 | 0.001 a | 0.108 | 0.013 b | 0.027 | 0.764 | 0.002 |
| Medium | 0.464 ± 0.021 | 0.473 ± 0.016 | |||||||
| Low | 0.463 ± 0.022 | 0.468 ± 0.022 | |||||||
| Squat Depth | Slow | Fast | Squat Depth | Speed | Squat Depth × Speed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | η2 | p | η2 | p | η2 | ||||
| Path length (mm) | High | 849.205 ± 112.985 | 764.129 ± 90.451 | 0.001 a | 0.378 | 0.001 b | 0.160 | 0.082 | 0.032 |
| Medium | 905.681 ± 110.559 | 823.961 ± 93.739 | |||||||
| Low | 944.438 ± 87.953 | 910.002 ± 105.934 | |||||||
| CoP D-x (mm) | High | 152.992 ± 16.090 | 145.555 ± 9.839 | - | - | - | - | 0.026 c | 0.047 |
| Medium | 155.005 ± 12.084 | 151.309 ± 16.150 | |||||||
| Low | 158.295 ± 11.434 | 162.020 ± 14.505 | |||||||
| CoP D-y (mm) | High | 136.522 ± 22.458 | 125.836 ± 25.430 | 0.001 a | 0.113 | 0.322 | 0.013 | 0.055 | 0.037 |
| Medium | 131.903 ± 19.963 | 129.912 ± 22.673 | |||||||
| Low | 140.053 ± 19.686 | 140.985 ± 17.846 | |||||||
| 95% area (mm2) | High | 985.045 ± 264.557 | 906.513 ± 226.123 | 0.001 a | 0.284 | 0.402 | 0.009 | 0.400 | 0.012 |
| Medium | 1094.852 ± 292.342 | 1036.017 ± 317.222 | |||||||
| Low | 1225.087 ± 297.009 | 1242.360 ± 291.745 | |||||||
| Squat Depth | Slow | Fast | Squat Depth | Speed | Squat Depth × Speed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | η2 | p | η2 | p | η2 | ||||
| Path length (m) | High | 1.035 ± 0.080 | 0.968 ± 0.065 | 0.001 a | 0.846 | 0.001 b | 0.146 | 0.212 | 0.041 |
| Medium | 1.121 ± 0.112 | 1.077 ± 0.063 | |||||||
| Low | 1.220 ± 0.072 | 1.184 ± 0.065 | |||||||
| CoM D-x (m) | High | 0.286 ± 0.043 | 0.275 ± 0.043 | 0.001 a | 0.289 | 0.003 b | 0.039 | 0.202 | 0.014 |
| Medium | 0.303 ± 0.053 | 0.292 ± 0.044 | |||||||
| Low | 0.321 ± 0.058 | 0.324 ± 0.062 | |||||||
| CoM D-y (m) | High | 0.448 ± 0.053 | 0.452 ± 0.041 | 0.001 a | 0.772 | 0.354 | 0.004 | 0.342 | 0.010 |
| Medium | 0.512 ± 0.048 | 0.514 ± 0.048 | |||||||
| Low | 0.580 ± 0.034 | 0.568 ± 0.039 | |||||||
| CoM D-z (m) | High | 0.058 ± 0.013 | 0.054 ± 0.015 | 0.001 a | 0.248 | 0.001 b | 0.045 | 0.773 | 0.002 |
| Medium | 0.070 ± 0.019 | 0.063 ± 0.020 | |||||||
| Low | 0.076 ± 0.017 | 0.070 ± 0.017 | |||||||
| Squat Depth | Slow | Fast | Squat Depth | Speed | Squat Depth × Speed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | η2 | p | η2 | p | η2 | ||||
| AP CoM-CoP separation (m) | High | −0.543 ± 0.073 | −0.543 ± 0.050 | 0.032 a | 0.030 | 0.955 | 0.001 | 0.458 | 0.007 |
| Medium | −0.567 ± 0.072 | −0.556 ± 0.076 | |||||||
| Low | −0.547 ± 0.054 | −0.548 ± 0.062 | |||||||
| Peak AP CoM-CoP separation (m) | High | 0.820 ± 0.102 | 0.821 ± 0.072 | 0.001 a | 0.298 | 0.524 | 0.002 | 0.502 | 0.006 |
| Medium | 0.874 ± 0.093 | 0.867 ± 0.085 | |||||||
| Low | 0.897 ± 0.070 | 0.896 ± 0.068 | |||||||
| ML CoM-CoP separation (m) | High | −0.203 ± 0.029 | −0.204 ± 0.027 | 0.001 a | 0.329 | 0.399 | 0.003 | 0.209 | 0.014 |
| Medium | −0.220 ± 0.039 | −0.217 ± 0.049 | |||||||
| Low | −0.241 ± 0.044 | −0.251 ± 0.060 | |||||||
| Peak ML CoM-CoP separation (m) | High | 0.301 ± 0.048 | 0.300 ± 0.043 | 0.001 a | 0.298 | 0.872 | 0.001 | 0.266 | 0.012 |
| Medium | 0.323 ± 0.061 | 0.326 ± 0.061 | |||||||
| Low | 0.353 ± 0.071 | 0.364 ± 0.086 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Liang, M.; Xiang, L.; Radak, Z.; Gu, Y. A Cross-Sectional Study on the Biomechanical Effects of Squat Depth and Movement Speed on Dynamic Postural Stability in Tai Chi. Life 2025, 15, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060977
Li W, Liang M, Xiang L, Radak Z, Gu Y. A Cross-Sectional Study on the Biomechanical Effects of Squat Depth and Movement Speed on Dynamic Postural Stability in Tai Chi. Life. 2025; 15(6):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060977
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenlong, Minjun Liang, Liangliang Xiang, Zsolt Radak, and Yaodong Gu. 2025. "A Cross-Sectional Study on the Biomechanical Effects of Squat Depth and Movement Speed on Dynamic Postural Stability in Tai Chi" Life 15, no. 6: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060977
APA StyleLi, W., Liang, M., Xiang, L., Radak, Z., & Gu, Y. (2025). A Cross-Sectional Study on the Biomechanical Effects of Squat Depth and Movement Speed on Dynamic Postural Stability in Tai Chi. Life, 15(6), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060977








