Exploring the Role of Diabetes in ALS: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Measures
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Features
3.2. Genetics and Phenotypes
3.3. Comorbidities and Interventions
3.4. Impact of Diabetes, Comorbidities, and Clinical Features on Disease Progression
3.5. Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Treatments for ALS
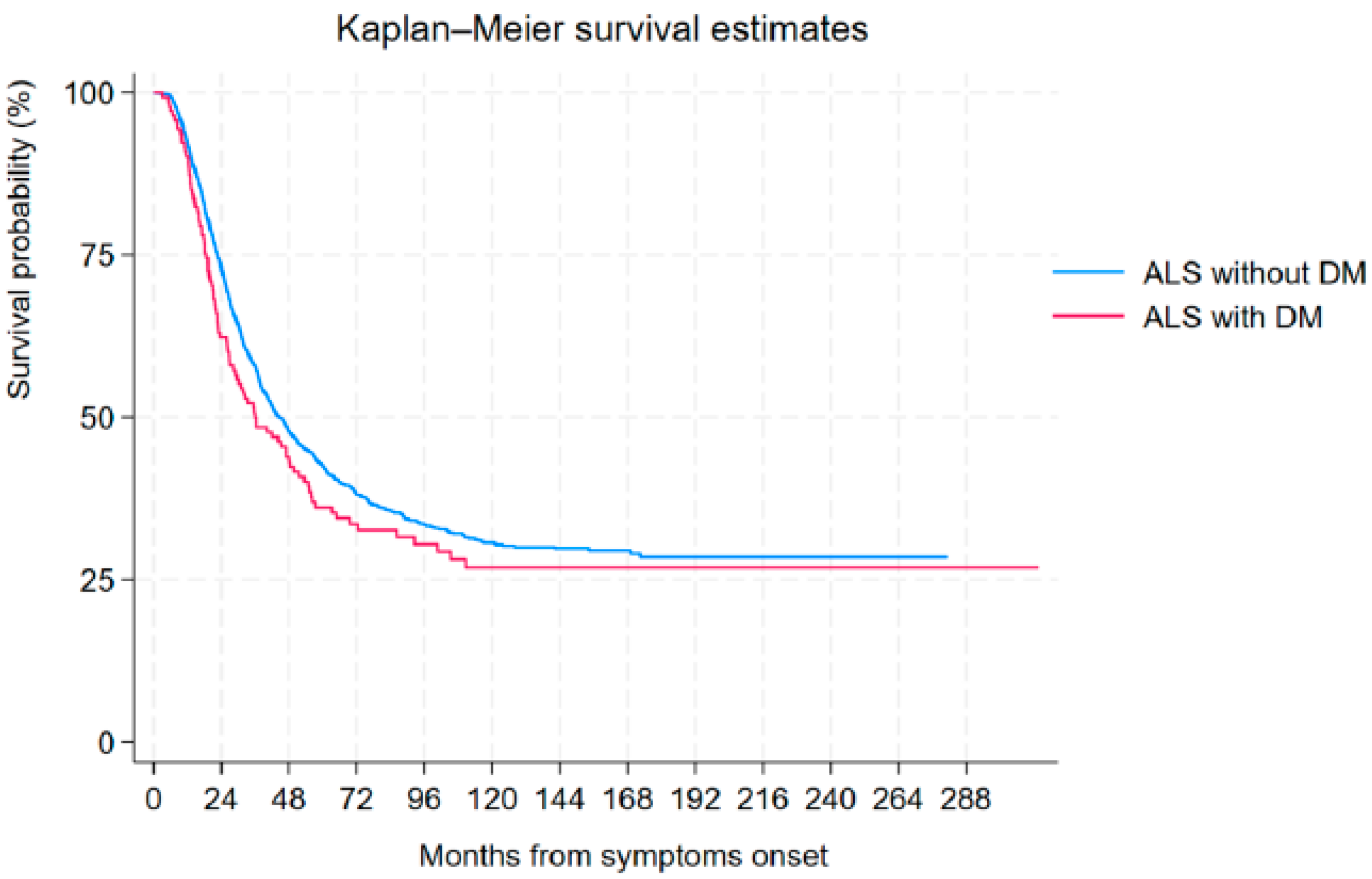
3.6. Tracheostomy-Free Survival Analysis
3.7. Influence of Diabetes on Respiratory Function
3.7.1. Diabetes and Other Clinical Variables and Non-Invasive Ventilation
3.7.2. Impact of Diabetes and Other Clinical Variables on Invasive Ventilation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Members of ERRALS Group
- Project coordinator: Prof. J. Mandrioli
- Collaborating centers:
- Department of Neurosciences, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria di Modena and Department of Biomedical, Metabolic and Neural Sciences, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena, Italy (Jessica Mandrioli, Nicola Fini, Ilaria Martinelli, Elisabetta Zucchi, Giulia Gianferrari, Cecilia Simonini, Annalisa Gessani, Andrea Ghezzi, and Marco Vinceti);
- Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche e Neuromotorie, University of Bologna, and IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, Bellaria Hospital, Bologna, Italy (Veria Vacchiano, Luigi Bonan, Silvia De Pasqua and Rocco Liguori);
- IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, Department of Neurology and Stroke Center, Maggiore Hospital, Bologna, Italy (Anna Maria Borghi and Andrea Zini);
- IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, UOC Interaziendale Clinica Neurologica Metropolitana (NeuroMet), Bologna, Italy (Rita Rinaldi and Maria Guarino);
- Department of Neurosciences and Rehabilitation, UOC Neurologia Provinciale, St Anna Hospital, Ferrara, Italy (Elisabetta Sette, Riccardo De Gennaro and Daniela Gragnaniello);
- Department of Neuroscience and Rehabilitation, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy (Maura Pugliatti);
- Department of Neurology, IRCCS Arcispedale Santa Maria Nuova, Reggio Emilia, Italy (Elena Canali, Luca Codeluppi, and Franco Valzania);
- Department of General and Specialized Medicine, University Hospital of Parma, Parma, Italy (Lucia Zinno, Filippo Stragliati, Pietro Anceschi, Andi Nuredini, Sonia Romano, Alessandro D’Orsi, Giorgia Libelli);
- Department of Neurology, Fidenza Hospital, Parma, Italy (Doriana Medici and Giovanna Pilurzi);
- Department of Neurology, G. Da Saliceto Hospital, Piacenza, Italy (Emilio Terlizzi and Paolo Immovilli);
- Department of Neurology, Carpi Hospital, Modena, Italy (Mario Santangelo);
- Department of Neurology, Imola Hospital, Bologna, Italy (Patrizia De Massis);
- Department of Neurology, Faenza and Ravenna Hospital, Ravenna, Italy (Matteo Gizzi, Marco Currò Dossi, Pietro Querzani and Maria Grazia Piscaglia);
- Department of Neurology, Bufalini Hospital, Cesena, Italy (Simonetta Morresi, Maria Vitiello, and Marco Longoni);
- Department of Neurology, Forlì Hospital, Forlì, Italy (Alberto Patuelli, Susanna Malagù, Francesca Bianchi, and Marco Longoni);
- Department of Neurology, Infermi Hospital, Rimini, Italy (Cristiana Ganino, Tommaso Baldini and Claudio Callegarini);
- Department of Hospital Services, Emilia Romagna Regional Health Authority, Bologna, Italy (Salvatore Ferro).
References
- Feldman, E.L.; Goutman, S.A.; Petri, S.; Mazzini, L.; Savelieff, M.G.; Shaw, P.J.; Sobue, G. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Lancet 2022, 400, 1363–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couratier, P.; Lautrette, G.; Luna, J.A.; Corcia, P. Phenotypic Variability in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinnen, B.; Robberecht, W. The Phenotypic Variability of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R. Understanding the Cause of Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. IJMS 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.K.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus, Fasting Blood Glucose Concentration, and Risk of Vascular Disease: A Collaborative Meta-Analysis of 102 Prospective Studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bao, M.; He, B. Exploring the Causal Relationships between Type 2 Diabetes and Neurological Disorders Using a Mendelian Randomization Strategy. Medicine 2024, 103, e40412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellary, S.; Kyrou, I.; Brown, J.E.; Bailey, C.J. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults: Clinical Considerations and Management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, A.; Salamone, A.R.; Strutt, A.M.; Murthy, S.B.; Wheaton, M.; McDowell, E.J.; Simpson, E.; Appel, S.H.; York, M.K.; Schulz, P.E. ALS Disease Onset May Occur Later in Patients with Pre-morbid Diabetes Mellitus. Euro J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, L.; Corcia, P.; Fergani, A.; Gonzalez De Aguilar, J.-L.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Bittar, R.; Seilhean, D.; Hauw, J.-J.; Lacomblez, L.; Loeffler, J.-P.; et al. Dyslipidemia Is a Protective Factor in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurology 2008, 70, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, Q.; Cao, B.; Zeng, Y.; Shang, H. The Serum Lipid Profiles of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients: A Study from South-West China and a Meta-Analysis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioumourtzoglou, M.-A.; Rotem, R.S.; Seals, R.M.; Gredal, O.; Hansen, J.; Weisskopf, M.G. Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity, and Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Population-Based Study. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, É.J.; Wang, H.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Fitzgerald, K.C.; Falcone, G.; McCullough, M.L.; Thun, M.; Park, Y.; Kolonel, L.N.; Ascherio, A. Premorbid Body Mass Index and Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2013, 14, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.; Wark, P.A.; Jenab, M.; Pearce, N.; Brayne, C.; Vermeulen, R.; Andersen, P.M.; Hallmans, G.; Kyrozis, A.; Vanacore, N.; et al. Prediagnostic Body Fat and Risk of Death from Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: The EPIC Cohort. Neurology 2013, 80, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, J.; Peter, R.S.; Nagel, G.; Rothenbacher, D.; Rosenbohm, A.; Ludolph, A.C.; Dorst, J.; ALS Registry Swabia Study Group. Statins, Diabetes Mellitus and Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Data from 501 Patients of a Population-Based Registry in Southwest Germany. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, J.; Bottman, L.; Arra, E.J.; Selkirk, S.M.; Kozlowski, F. Nutrition Management Methods Effective in Increasing Weight, Survival Time and Functional Status in ALS Patients: A Systematic Review. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2018, 19, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardiotis, E.; Siokas, V.; Sokratous, M.; Tsouris, Z.; Aloizou, A.-M.; Florou, D.; Dastamani, M.; Mentis, A.-F.A.; Brotis, A.G. Body Mass Index and Survival from Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis. Neur. Clin. Pract. 2018, 8, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta, R.; D’Ovidio, F.; Logroscino, G.; Chiò, A. The Links between Diabetes Mellitus and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.; Oliveira Santos, M.; Gromicho, M.; Swash, M.; de Carvalho, M. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on the Respiratory Function of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, R.M.; Mayer, B.; Kuncl, R.W.; Check, D.P.; Cahoon, E.K.; Rivera, D.R.; Freedman, D.M. Identifying Potential Targets for Prevention and Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Based on a Screen of Medicare Prescription Drugs. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2020, 21, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A. Thiazolidinediones as Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Atherogenic Agents. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2008, 24, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, T.; Guo, S.; Bardhi, O.; Ryskamp, D.A.; Li, J.; Khoramian Tusi, S.; Engelbrecht, A.; Klippel, K.; Chakrabarty, P.; Nguyen, L.; et al. Metformin Inhibits RAN Translation through PKR Pathway and Mitigates Disease in C9orf72 ALS/FTD Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18591–18599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, L.; Ajdinaj, P.; Rispoli, M.G.; Carrarini, C.; Barbone, F.; D’Ardes, D.; Capasso, M.; Muzio, A.D.; Cipollone, F.; Onofrj, M.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lange, D.J.; Voustianiouk, A.; MacGrogan, D.; Ho, L.; Suh, J.; Humala, N.; Thiyagarajan, M.; Wang, J.; Pasinetti, G.M. A Ketogenic Diet as a Potential Novel Therapeutic Intervention in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, S.; Saito, K.; Yachi, Y.; Asumi, M.; Sugawara, A.; Totsuka, K.; Saito, A.; Sone, H. Association between Serum Uric Acid and Development of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Park, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Jun, J.-B.; Park, S.; Kang, D.R.; Choi, H. Prevalence of Motor Neuron Diseases in Gout Patients: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, N.; Hoshiyama, E.; Ouchi, M.; Takekawa, H.; Suzuki, K. Uric Acid and Neurological Disease: A Narrative Review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1164756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.-H.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Zhang, J.-N.; Gu, L.; Yang, H.-M.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Xia, N.; Zhang, H. Urate Inhibits Microglia Activation to Protect Neurons in an LPS-Induced Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L.; World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial Revisited: Revised Criteria for the Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, J.; Biguzzi, S.; Guidi, C.; Venturini, E.; Sette, E.; Terlizzi, E.; Ravasio, A.; Casmiro, M.; Salvi, F.; Liguori, R.; et al. Epidemiology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Emilia Romagna Region (Italy): A Population Based Study. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2014, 15, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee Report on the Role of the A1C Assay in the Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghri, F.; Brunn, F.; Dadu, A.; PARALS consortium; ERRALS consortium; Zucchi, E.; Martinelli, I.; Mazzini, L.; Vasta, R.; Canosa, A.; et al. Identifying and Predicting Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Clinical Subgroups: A Population-Based Machine-Learning Study. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e359–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, M.J.; Abrahams, S.; Goldstein, L.H.; Woolley, S.; Mclaughlin, P.; Snowden, J.; Mioshi, E.; Roberts-South, A.; Benatar, M.; HortobáGyi, T.; et al. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis—Frontotemporal Spectrum Disorder (ALS-FTSD): Revised Diagnostic Criteria. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2017, 18, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianferrari, G.; Martinelli, I.; Zucchi, E.; Simonini, C.; Fini, N.; Vinceti, M.; Ferro, S.; Gessani, A.; Canali, E.; Valzania, F.; et al. Epidemiological, Clinical and Genetic Features of ALS in the Last Decade: A Prospective Population-Based Study in the Emilia Romagna Region of Italy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, J.; Ferri, L.; Fasano, A.; Zucchi, E.; Fini, N.; Moglia, C.; Lunetta, C.; Marinou, K.; Ticozzi, N.; Drago Ferrante, G.; et al. Cardiovascular Diseases May Play a Negative Role in the Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, J.; Biguzzi, S.; Guidi, C.; Sette, E.; Terlizzi, E.; Ravasio, A.; Casmiro, M.; Salvi, F.; Liguori, R.; Rizzi, R.; et al. Heterogeneity in ALSFRS-R Decline and Survival: A Population-Based Study in Italy. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianferrari, G.; Martinelli, I.; Simonini, C.; Zucchi, E.; Fini, N.; Caputo, M.; Ghezzi, A.; Gessani, A.; Canali, E.; Casmiro, M.; et al. Insight into Elderly ALS Patients in the Emilia Romagna Region: Epidemiological and Clinical Features of Late-Onset ALS in a Prospective, Population-Based Study. Life 2023, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiò, A.; Moglia, C.; Canosa, A.; Manera, U.; D’Ovidio, F.; Vasta, R.; Grassano, M.; Brunetti, M.; Barberis, M.; Corrado, L.; et al. ALS Phenotype Is Influenced by Age, Sex, and Genetics: A Population-Based Study. Neurology 2020, 94, e802–e810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupillo, E.; Messina, P.; Logroscino, G.; Beghi, E.; SLALOM Group. Long-Term Survival in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Population-Based Study. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, E.; Rafiq, M.K. Prognostic Factors for Survival in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Analysis of a Multi-Centre Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 32, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westeneng, H.-J.; Debray, T.P.A.; Visser, A.E.; van Eijk, R.P.A.; Rooney, J.P.K.; Calvo, A.; Martin, S.; McDermott, C.J.; Thompson, A.G.; Pinto, S.; et al. Prognosis for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Development and Validation of a Personalised Prediction Model. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltenberger-Miltenyi, G.; Conceição, V.A.; Gromicho, M.; Pronto-Laborinho, A.C.; Pinto, S.; Andersen, P.M.; de Carvalho, M. C9orf72 Expansion Is Associated with Accelerated Decline of Respiratory Function and Decreased Survival in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, A.; Calvo, A.; Moglia, C.; Mazzini, L.; Mora, G.; PARALS Study group. Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Population Based Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, T.S.; Kumar, V.; Fung, J.N.; Woodruff, T.M.; Lee, J.D. Glucose Clearance and Uptake Is Increased in the SOD1G93A Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis through an Insulin-Independent Mechanism. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamiuc, L.; Schlagowski, A.; Ngo, S.T.; Vernay, A.; Dirrig-Grosch, S.; Henriques, A.; Boutillier, A.-L.; Zoll, J.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Loeffler, J.-P.; et al. A Metabolic Switch toward Lipid Use in Glycolytic Muscle Is an Early Pathologic Event in a Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 526–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moțățăianu, A.; Mănescu, I.B.; Șerban, G.; Bărcuțean, L.; Ion, V.; Bălașa, R.; Andone, S. Exploring the Role of Metabolic Hormones in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Song, Y.; Fu, K.; Gao, Z.; Liu, D.; He, W.; Yang, L.-L. Energy Metabolism in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglia, C.; Calvo, A.; Canosa, A.; Bertuzzo, D.; Cugnasco, P.; Solero, L.; Grassano, M.; Bersano, E.; Cammarosano, S.; Manera, U.; et al. Influence of Arterial Hypertension, Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Factors on ALS Outcome: A Population-Based Study. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2017, 18, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Fan, D. The Protective Role of Pre-Morbid Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Center-Based Survey in China. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2020, 21, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.S.; Egede, L.E. The Association Between Multimorbidity and Quality of Life, Health Status and Functional Disability. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 352, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Deng, H.; Hu, Z. Plasma Progranulin Concentrations Are Increased in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity and Correlated with Insulin Resistance. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 360190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, A.S.; Van Hoecke, A.; De Muynck, L.; Timmers, M.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Van Damme, P.; Robberecht, W. Progranulin Is Neurotrophic In Vivo and Protects against a Mutant TDP-43 Induced Axonopathy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, L.; Huang, T.; Fan, D. Association between Type 2 Diabetes and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariosa, D.; Kamel, F.; Bellocco, R.; Ye, W.; Fang, F. Association between Diabetes and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in S Weden. Euro J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Araki, A.; Honda, D.; Izumoto, T.; Hashizume, A.; Hijikata, Y.; Yamada, S.; Iguchi, Y.; Hara, A.; Ikumi, K.; et al. TDP-43 Regulates Early-Phase Insulin Secretion via CaV1.2-Mediated Exocytosis in Islets. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3578–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings, N.R.; Puttaparthi, K.; Dowling, K.J.; Luther, C.M.; Burns, D.K.; Davis, K.; Elliott, J.L. TDP-43, an ALS Linked Protein, Regulates Fat Deposition and Glucose Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korner, S.; Kammeyer, J.; Zapf, A.; Kuzma-Kozakiewicz, M.; Piotrkiewicz, M.; Kuraszkiewicz, B.; Goszczynska, H.; Gromicho, M.; Grosskreutz, J.; Andersen, P.M.; et al. Influence of Environment and Lifestyle on Incidence and Progress of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in A German ALS Population. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganoni, S.; Hyman, T.; Shui, A.; Allred, P.; Harms, M.; Liu, J.; Maragakis, N.; Schoenfeld, D.; Yu, H.; Atassi, N.; et al. Pre-Morbid Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Is Not a Prognostic Factor in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglia, C.; Calvo, A.; Grassano, M.; Canosa, A.; Manera, U.; D’Ovidio, F.; Bombaci, A.; Bersano, E.; Mazzini, L.; Mora, G.; et al. Early Weight Loss in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Outcome Relevance and Clinical Correlates in a Population-Based Cohort. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccolella, S.; Beghi, E.; Palagano, G.; Fraddosio, A.; Guerra, V.; Samarelli, V.; Lepore, V.; Simone, I.L.; Lamberti, P.; Serlenga, L.; et al. Analysis of Survival and Prognostic Factors in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Population Based Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millul, A.; Beghi, E.; Logroscino, G.; Micheli, A.; Vitelli, E.; Zardi, A. Survival of Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in a Population-Based Registry. Neuroepidemiology 2005, 25, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollewe, K.; Mauss, U.; Krampfl, K.; Petri, S.; Dengler, R.; Mohammadi, B. ALSFRS-R Score and Its Ratio: A Useful Predictor for ALS-Progression. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 275, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. C9orf72-Dependent Lysosomal Functions Regulate Epigenetic Control of Autophagy and Lipid Metabolism. Autophagy 2019, 15, 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Ji, Y.J.; Johnson, K.; Liu, H.; Johnson, K.; Bailey, S.; Suk, Y.; Lu, Y.-N.; Liu, M.; et al. A C9orf72–CARM1 Axis Regulates Lipid Metabolism under Glucose Starvation-Induced Nutrient Stress. Genes. Dev. 2018, 32, 1380–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.D.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Schootman, M. Epidemiology of Diabetes and Diabetes-Related Complications. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatelli, M.; Conforti, F.L.; Zollino, M.; Mora, G.; Monsurrò, M.R.; Volanti, P.; Marinou, K.; Salvi, F.; Corbo, M.; Giannini, F.; et al. C9ORF72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansions in the Italian Sporadic ALS Population. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1848.e15–1848.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJesus-Hernandez, M.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Boxer, A.L.; Baker, M.; Rutherford, N.J.; Nicholson, A.M.; Finch, N.A.; Flynn, H.; Adamson, J.; et al. Expanded GGGGCC Hexanucleotide Repeat in Noncoding Region of C9ORF72 Causes Chromosome 9p-Linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 2011, 72, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.; Elamin, M.; Bede, P.; Shatunov, A.; Walsh, C.; Corr, B.; Heverin, M.; Jordan, N.; Kenna, K.; Lynch, C.; et al. Cognitive and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Carrying a C9orf72 Repeat Expansion: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta, R.; Chia, R.; Traynor, B.J.; Chiò, A. Unraveling the Complex Interplay between Genes, Environment, and Climate in ALS. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J. The Burden and Risks of Emerging Complications of Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, H.; Senkevich, K.; Patel, R.K.; Bestwick, J.P.; Jacobs, B.M.; Bandres Ciga, S.; Gan-Or, Z.; Noyce, A.J. Type 2 Diabetes as a Determinant of Parkinson’s Disease Risk and Progression. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athauda, D.; Evans, J.; Wernick, A.; Virdi, G.; Choi, M.L.; Lawton, M.; Vijiaratnam, N.; Girges, C.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Ismail, K.; et al. The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, C.; Brunaud-Danel, V.; Dallongeville, J.; Duhamel, A.; Laurier-Grymonprez, L.; de Reuck, J.; Wiart, A.C.; Perez, T.; Richard, F.; Amouyel, P.; et al. Modifying Effect of Arterial Hypertension on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2012, 13, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaManna, J.C.; Chavez, J.C.; Pichiule, P. Structural and Functional Adaptation to Hypoxia in the Rat Brain. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, S.M. Complications and Consequences of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2000, 6, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, R.; Tonelli, R.; Castaniere, I.; Tabbì, L.; Pellegrino, M.R.; Cerri, S.; Livrieri, F.; Giaroni, F.; Monelli, M.; Ruggieri, V.; et al. Serial Ultrasound Assessment of Diaphragmatic Function and Clinical Outcome in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, P.M.; Mollar, E.; Melissari, L.; Buscema, M.; Bagnoli, E.; Cabona, C.; Gemelli, C.; Vignolo, M.; Maranzana, C.; Marogna, M.; et al. Longitudinal Respiratory Trajectories in Motor Neuron Disease Phenotypes: Multiparametric Characterization and Clinical Management. Respir. Med. 2025, 239, 108003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, K.S.; Mitchem, M.R.; Hogg, M.C.; Prehn, J.H.M. “Preconditioning” with Latrepirdine, an Adenosine 5′-Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Activator, Delays Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Progression in SOD1G93A Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbohm, A.; Nagel, G.; Peter, R.S.; Brehme, T.; Koenig, W.; Dupuis, L.; Rothenbacher, D.; Ludolph, A.C. ALS Registry Study Group Association of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Concentration With Risk for and Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable |
ndALS (n = 1611), n (%), Mean [SD] |
diALS (n = 145), n (%), Mean [SD] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male | 878 (54.50) | 96 (66.21) | 0.007 |
| Age at onset, y | 65.76 [11.61] | 71.56 [8.36] | <0.001 |
| Age at diagnosis, y | 66.82 [11.59] | 72.89 [8.54] | <0.001 |
| Diagnostic delay, m | 13.81 [14.17] | 15.93 [21.48] | 0.101 |
| BMI at diagnosis, kg/m2 | 24.23 [3.89] | 25.63 [4.63] | <0.001 |
| Weight change (%) * | −5.44 [8.12] | −6.87 [7.05] | 0.070 |
| FVC (%) | 87.88 [24.21] | 74.87 [26.48] | <0.001 |
| Progression rate (from onset to diagnosis), points/month | 0.96 [1.24] | 1.23 [1.39] | 0.022 |
| Time to PEG, m | 27.13 [18.46] | 25.28 [18.22] | 0.567 |
| Time to NIV, m | 28.03 [23.70] | 23.66 [21.01] | 0.141 |
| Time to IV, m | 31.25 [23.31] | 25.26 [18.97] | 0.224 |
| ALSFRS-R at diagnosis | 38.85 [7.17] | 36.70 [7.63] | 0.001 |
| Site of onset | |||
| Bulbar | 535 (33.21) | 48 (33.10) | 0.979 |
| Respiratory | 42 (2.61) | 9 (6.21) | 0.013 |
| UULL distal | 428 (26.57) | 24 (16.55) | 0.008 |
| UULL proximal | 205 (12.73) | 11 (7.59) | 0.071 |
| LLLL distal | 496 (30.79) | 52 (35.86) | 0.207 |
| LLLL proximal | 291 (18.06) | 31 (21.38) | 0.323 |
| Death ** | 914 (57.77) | 93 (65.03) | 0.092 |
| Type of ALS Onset | ndALS (n = 1611), n (%) | diALS (n = 145), n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasciculations | 289 (17.94) | 17 (11.72) | 0.059 |
| Cramps | 235 (14.59) | 13 (8.97) | 0.063 |
| Motor deficit | 1411 (87.59) | 138 (95.17) | 0.007 |
| Spasticity | 102 (6.33) | 3 (2.07) | 0.038 |
| (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Genes * | ndALS (n = 1611), n (%) | diALS (n = 145), n (%) | p-Value |
| Genes | |||
| C9ORF72 | 46 (7.64) | 0 | 0.039 |
| SOD1 | 24 (3.85) | 2 (3.92) | 0.980 |
| FUS | 8 (1.30) | 1 (2.00) | 0.678 |
| TARDBP | 8 (1.29) | 0 | 0.423 |
| OPTN | 1 (0.16) | 0 | 0.773 |
| FIG4 | 6 (0.94) | 0 | 0.479 |
| CHMP2B | 2 (0.31) | 0 | 0.683 |
| VAPB | 1 (0.16) | 0 | 0.773 |
| DCTN1 | 3 (0.47) | 0 | 0.617 |
| KIF5A | 3 (0.47) | 0 | 0.617 |
| MAPT | 4 (0.62) | 0 | 0.564 |
| SQSTM1 | 3 (0.47) | 0 | 0.615 |
| (b) | |||
| Phenotypes ** | ndALS (n = 1611), n (%) | diALS (n = 145), n (%) | p-Value |
| Phenotypes | 0.138 | ||
| Bulbar | 456 (34.89) | 42 (35.59) | 1.000 |
| Classic | 612 (46.82) | 57 (48.31) | 0.924 |
| Flail Arm | 72 (5.51) | 4 (3.39) | 0.328 |
| Flail Leg | 69 (5.28) | 7 (5.93) | 0.831 |
| UMN-predominant | 79 (6.04) | 5 (4.24) | 0.543 |
| Respiratory | 19 (1.45) | 5 (4.24) | 0.045 |
| Age Classes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <55 Years | 55–64 Years | 65–74 Years | 75–84 Years | ≥85 Years | p-Value | ||
| C9ORF72 Expansion, n (%) | diALS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| ndALS | 15 (32.61) | 20 (43.48) | 11 (23.91) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.010 | |
| Respiratory onset, n (%) | diALS | 1 (11.11) | 1 (11.11) | 4 (44.44) | 3 (33.33) | 0 (0) | 0.773 |
| ndALS | 1 (2.38) | 9 (21.43) | 21 (50.00) | 10 (23.81) | 1 (2.38) | 0.086 | |
| FVC (%), mean [SD] | diALS | 96.77 [27.92] | 69.20 [18.89] | 79.28 [27.17] | 71.61 [27.77] | 55.00 [7.07] | 0.537 |
| ndALS | 94.00 [22.44] | 91.98 [22.84] | 86.06 [23.54] | 80.17 [26.33] | 77.32 [26.44] | 0.329 | |
| Progression rate, mean [SD] | diALS | 1.64 [0.89] | 0.88 [0.92] | 1.21 [1.25] | 1.33 [1.77] | 1.18 [0.58] | 0.002 |
| ndALS | 0.75 [0.82] | 0.74 [0.85] | 0.94 [1.15] | 1.38 [1.81] | 1.28 [1.16] | <0.001 | |
| Total, n (%) | diALS | 6 (4.14) | 17 (11.72) | 59 (40.69) | 54 (37.24) | 9 (6.21) | <0.001 |
| ndALS | 260 (16.18) | 382 (23.77) | 563 (35.03) | 348 (21.66) | 54 (3.36) | ||
| Comorbidities |
ndALS (n = 1611), n (%) |
diALS (n = 145), n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontotemporal dementia | 151 (9.37) | 11 (7.59) | 0.476 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | 1 (0.06) | 0 (0.00) | 0.764 |
| Vascular dementia | 1 (0.06) | 1 (0.69) | 0.032 |
| Other dementias | 4 (0.25) | 1 (0.69) | 0.339 |
| Parkinson’s disease | 29 (1.80) | 7 (4.83) | 0.014 |
| Bradykinesia | 23 (1.43) | 5 (3.45) | 0.063 |
| Tremor | 23 (1.43) | 1 (0.69) | 0.463 |
| Rigidity | 21 (1.30) | 3 (2.07) | 0.447 |
| Respiratory diseases | 192 (11.92) | 22 (15.17) | 0.379 |
| COPD | 116 (7.20) | 18 (12.41) | 0.024 |
| Thyroid disorder | 174 (10.80) | 21 (14.48) | 0.419 |
| Autoimmune diseases | 116 (7.20) | 4 (2.76) | 0.537 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 249 (15.46) | 50 (30.48) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 74 (4.59) | 9 (6.21) | 0.381 |
| Heart conduction disorders | 27 (1.68) | 4 (2.76) | 0.343 |
| Coronary artery disease | 41 (2.55) | 16 (11.03) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction | 23 (1.43) | 6 (4.14) | 0.014 |
| Hypertensive heart disease | 30 (1.86) | 10 (6.90) | <0.001 |
| Valvular heart disease | 20 (1.24) | 2 (1.38) | 0.886 |
| Congestive heart failure | 2 (0.12) | 1 (0.69) | 0.114 |
| Other diseases | 31 (1.92) | 2 (1.38) | 0.643 |
| Hypertension | 673 (41.78) | 103 (71.03) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 133 (8.04) | 12 (11.76) | 0.184 |
| Neoplasms | 293 (18.20) | 39 (26.90) | 0.337 |
| Psychiatric diseases | 132 (8.19) | 8 (5.52) | 0.254 |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | 228 (14.15) | 18 (12.41) | 0.563 |
| Independent Variables | Regression Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.45 (0.14–0.75) | 0.004 |
| Age at onset, years | 0.01 (0.00–0.02) | 0.007 |
| Weight loss at diagnosis, kg | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | <0.001 |
| C9ORF72 expansion | 0.42 (0.12–0.73) | 0.006 |
| Independent Variables | Regression Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.72 (0.98–3.02) | 0.057 |
| Age at onset, years | 0.98 (0.97–1.00) | 0.013 |
| Respiratory onset | 5.1 (1.67–15.58) | 0.004 |
| BMI at diagnosis, kg/m2 | 1.04 (1.00–1.08) | 0.041 |
| FVC | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.007 |
| Independent Variables | Multivariable Cox Regression Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age of onset, years | 1.02 (1.00–1.03) | <0.001 |
| Definite ALS according to EEC-R criteria | 1.22 (1.03–1.44) | 0.019 |
| Possible ALS according to EEC-R criteria | 0.78 (0.64–0.95) | 0.018 |
| Diagnostic delay, months | 0.96 (0.95–0.97) | <0.001 |
| Presence of FTD | 1.38 (1.11–1.73) | 0.003 |
| Progression rate from onset to diagnosis points/month | 1.19 (1.10–1.29) | <0.001 |
| Weight loss, kg | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 |
| ALSFRS-R total score at diagnosis | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 0.013 |
| Independent Variables | Multivariable Cox Regression Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Definite ALS according to EEC-R criteria EC-R criteria | 2.24 (1.38–3.83) | 0.023 |
| Diagnostic delay, m | 0.97 (0.95–0.99) | 0.013 |
| Presence of FTD | 2.24 (1.05–4.78) | 0.037 |
| Progression rate (from onset to diagnosis) | 1.23 (1.03–1.48) | 0.024 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.94 (0.89–0.99) | 0.026 |
| Respiratory onset | 2.53 (1.07–5.99) | 0.034 |
| Variables for Time to NIV | Multivariable Cox Regression Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Diagnostic delay, months | 0.9 (0.93–0.96) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory onset | 2.89 (1.46–5.63) | 0.002 |
| Hypertension | 1.37 (1.04–1.79) | 0.023 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 1.52 (1.09–2.13) | 0.014 |
| Progression rate (from onset to diagnosis) | 2.10 (1.77–2.49) | <0.001 |
| Weight loss, kg | 1.05 (1.03–1.08) | <0.001 |
| FVC | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 |
| Phenotypes (bulbar as reference) | 0.81 (0.72–0.93) | 0.002 |
| T2DM | 1.71 (1.07–2.74) | 0.024 |
| Variables for Time to IV | Multivariable Cox Regression Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age at onset | 1.07 (1.05–1.10) | <0.001 |
| Diagnostic delay | 0.94 (0.91–0.97) | <0.001 |
| Progression rate (from onset to diagnosis) | 1.45 (1.20–1.75) | <0.001 |
| Phenotype (bulbar as reference) | 0.83 (0.71–0.96) | 0.012 |
| C9ORF72 expansion | 2.66 (1.43–4.92) | 0.002 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 2.74 (1.49–5.03) | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinelli, I.; Gianferrari, G.; Santarelli, R.; Zucchi, E.; Simonini, C.; Fini, N.; Ghezzi, A.; Gessani, A.; Ferri, L.; Smolik, K.; et al. Exploring the Role of Diabetes in ALS: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Life 2025, 15, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060936
Martinelli I, Gianferrari G, Santarelli R, Zucchi E, Simonini C, Fini N, Ghezzi A, Gessani A, Ferri L, Smolik K, et al. Exploring the Role of Diabetes in ALS: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Life. 2025; 15(6):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060936
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinelli, Ilaria, Giulia Gianferrari, Rebecca Santarelli, Elisabetta Zucchi, Cecilia Simonini, Nicola Fini, Andrea Ghezzi, Annalisa Gessani, Laura Ferri, Krzysztof Smolik, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Role of Diabetes in ALS: A Population-Based Cohort Study" Life 15, no. 6: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060936
APA StyleMartinelli, I., Gianferrari, G., Santarelli, R., Zucchi, E., Simonini, C., Fini, N., Ghezzi, A., Gessani, A., Ferri, L., Smolik, K., Ferraro, D., Bedin, R., Gizzi, M., Sette, E., Vacchiano, V., Bonan, L., Zinno, L., De Massis, P., Canali, E., ... Mandrioli, J. (2025). Exploring the Role of Diabetes in ALS: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Life, 15(6), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060936









