rESWT in Shoulder Periarthritis: Does the Protocol Intensity Matter?—A Quasi-Experimental Non-Randomized Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction:
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Data Collection
- -
- -
- Shoulder function and disability were measured using the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI), a validated self-administered questionnaire composed of 13 items: 5 assessing pain and 8 assessing disability. SPADI scores are expressed as percentages and interpreted as follows: 0–20%—mild shoulder pain and disability; 21–40%—moderate; 41–60%—severe; 61–80%—very severe; 81–100%—extremely severe. The numerical version was used, with total scores expressed as percentages and higher values indicating more severe impairment. Its test–retest reliability is high (ICC = 0.89–0.93) [44,45].
- -
2.4. Participants
2.5. Eligibility Criteria
2.6. Intervention and Exposure
2.7. Outcome Measures and Data Sources
- -
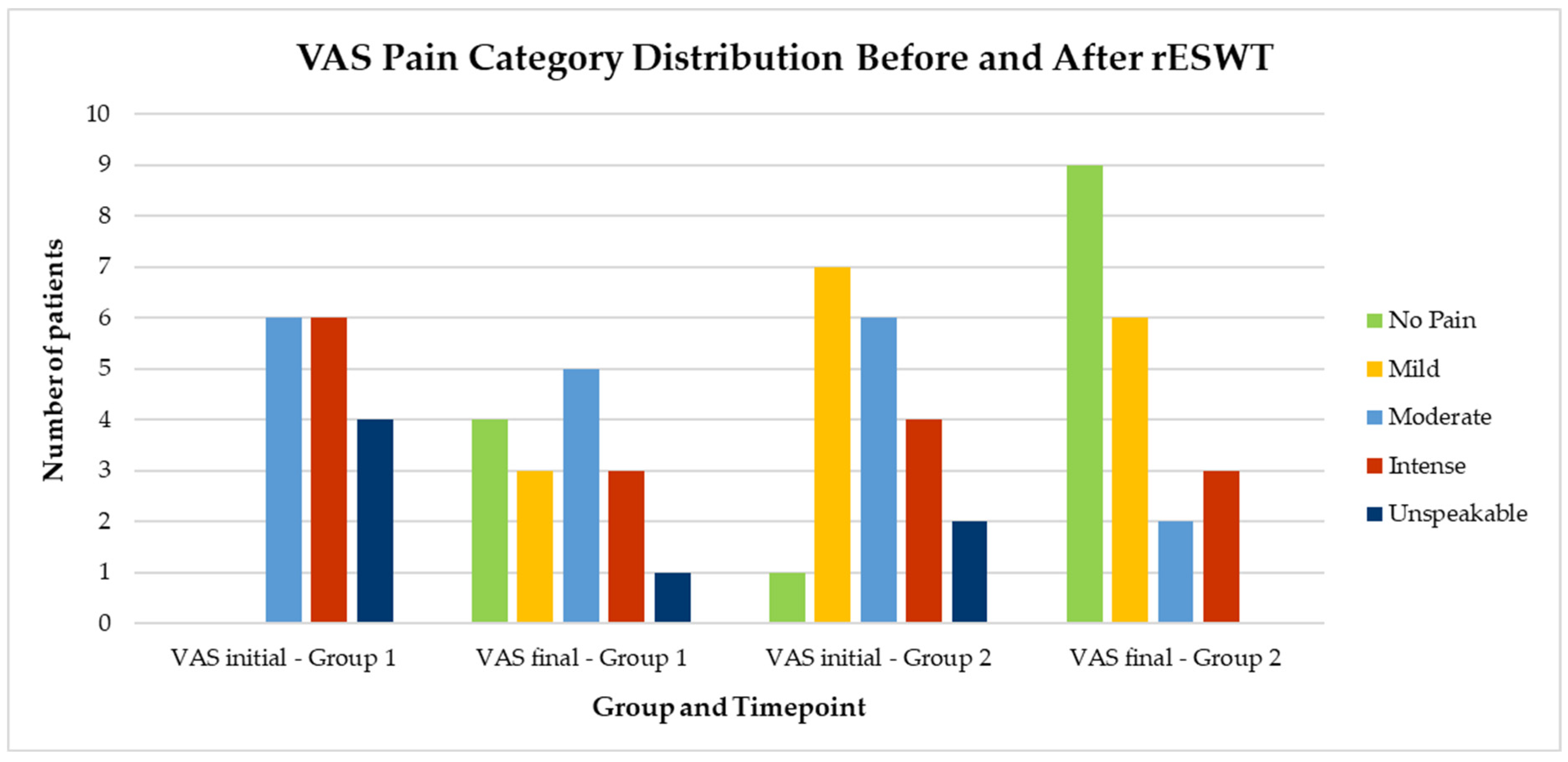
- Pain intensity (VAS, 0–10 scale);
- -
- Function/disability (SPADI, numerical format, 0–100%);
- -
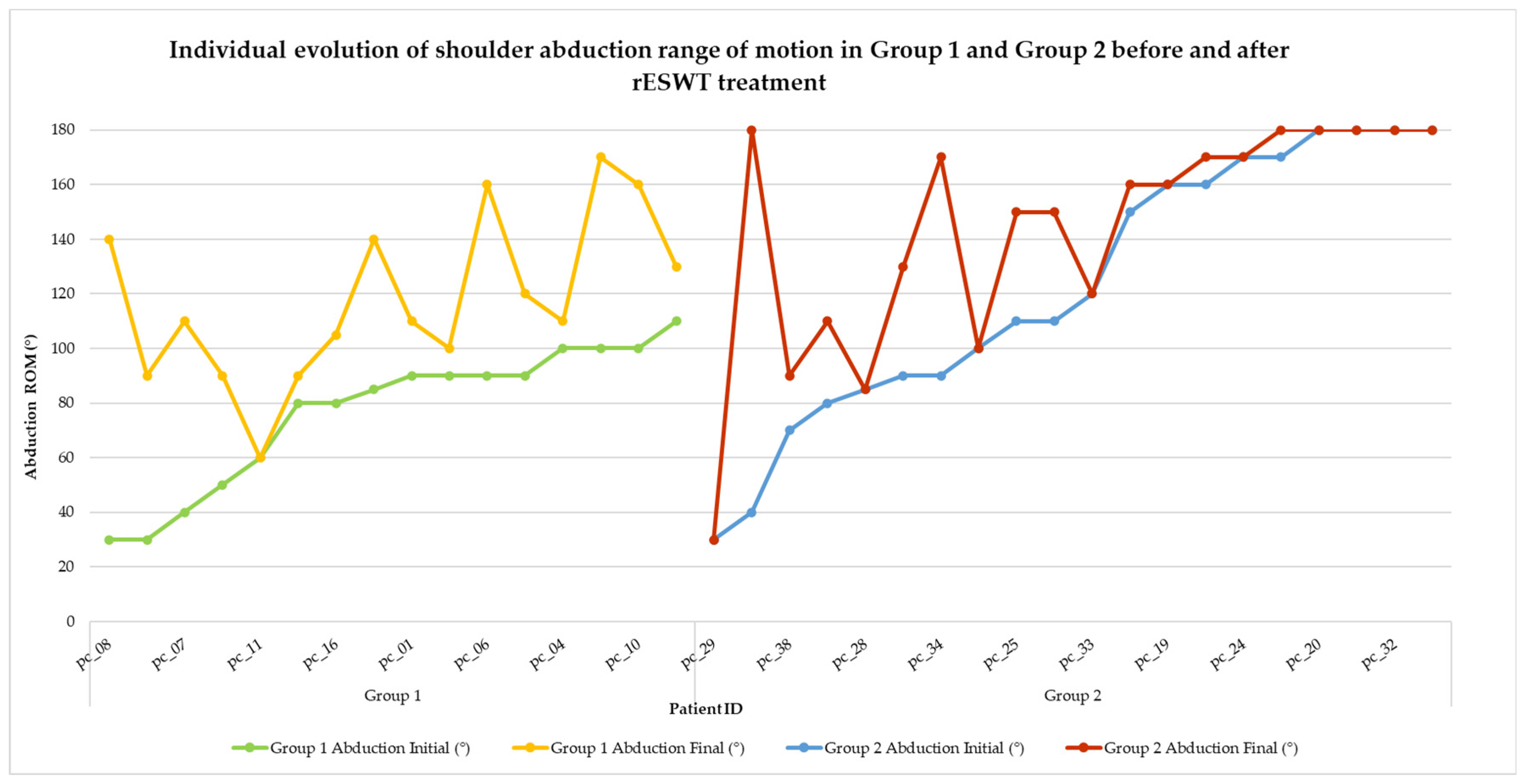
- Shoulder ROM—goniometric assessment of flexion, extension, abduction, and internal and external rotation.
2.8. Bias Control
2.9. Sample Size Considerations
2.10. Handling of Variables
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
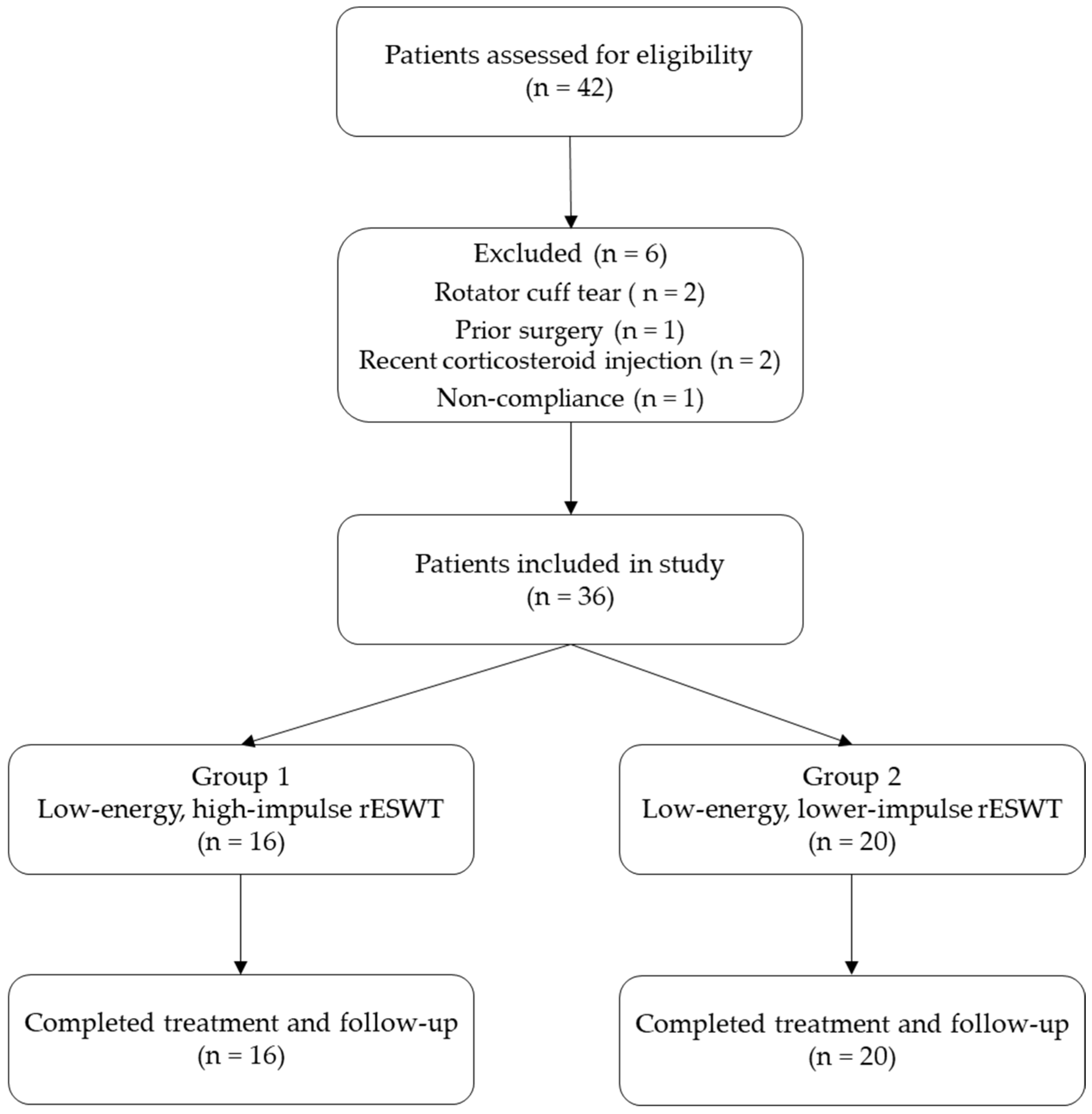
3.1. Participants
- -
- Group 1: 16 patients received low-energy, high-impulse rESWT.
- -
- Group 2: 20 patients received high-energy, lower-impulse rESWT.
- -
- Two patients presented with a rotator cuff tear confirmed by ultrasound examination;
- -
- One patient had a history of shoulder surgery;
- -
- Two patients had received a corticosteroid injection in the affected shoulder within the previous six months;
- -
- One patient was excluded due to non-compliance with the prescribed home exercise protocol.
3.2. Descriptive Data
3.3. Outcome Data
- -
- Pain intensity (VAS);
- -
- Function/disability (SPADI);
- -
- Shoulder ROM—flexion, extension, abduction, and external and internal rotation.
3.4. Main Results
3.5. Absolute Risk Translation
3.6. Other Analyses
4. Discussion
- -
- Flexion—103.75° vs. 160.00°, p = 0.031, r = 0.365;
- -
- Abduction—87.50° vs. 122.75°, p = 0.006, r = 0.468;
- -
- External rotation—51.88° vs. 80.00°, p = 0.002, r = 0.520.
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
- Pain relief, as measured by the VAS scale, was strongly associated with functional improvements (SPADI), reinforcing the critical role of effective pain management in the success of rehabilitation protocols.
- The recovery of shoulder mobility—particularly in flexion, abduction, and internal rotation—was closely linked to improved functional performance, highlighting the importance of incorporating movement-specific goals into therapy plans.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ioppolo, F.; Rompe, J.D.; Furia, J.P.; Cacchio, A. Clinical Application of Shock Wave Therapy (SWT) in Musculoskeletal Disorders. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 50, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ioppolo, F.; Tattoli, M.; Di Sante, L.; Attanasi, C.; Venditto, T.; Servidio, M.; Cacchio, A.; Santilli, V. Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy for Supraspinatus Calcifying Tendinitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Two Different Energy Levels. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussy, C.; Brendel, W.; Schmiedt, E. Extracorporeally Induced Destruction of Kidney Stones by Shock Waves. Lancet 1980, 2, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedes, V.; Stergioulas, A.; Kipreos, G.; Dede, A.M.; Mitseas, A.; Panoutsopoulos, G.I. Effectiveness and Safety of Shockwave Therapy in Tendinopathies. Mater. Sociomed. 2018, 30, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.; Wiley, J.P. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy: A Review. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furia, J.P.; Rompe, J.D.; Cacchio, A.; Maffulli, N. Shock Wave Therapy as a Treatment of Nonunions, Avascular Necrosis, and Delayed Healing of Stress Fractures. Foot Ankle Clin. 2010, 15, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Wang, F.S.; Yang, K.D.; Weng, L.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Huang, C.S.; Yang, L.C. Shock Wave Therapy Induces Neovascularization at the Tendon–Bone Junction. A Study in Rabbits. J. Orthop. Res. 2003, 21, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, S.; de Prati, A.; Cavalieri, E.; Amelio, E.; Marlinghaus, E.; Suzuki, H. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Inflammatory Diseases: Molecular Mechanism That Triggers Anti-Inflammatory Action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, I.H.W.; Cheing, G.L.Y. Comparison of Different Energy Densities of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for the Management of Chronic Heel Pain. Clin. Rehabil. 2007, 21, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofer, M.D.; Hinrichs, F.; Peterlein, C.D.; Arendt, M.; Schmitt, J. High-versus Low-Energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Prospective, Randomised, Controlled Study. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2009, 75, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, C.; Császár, N.B.M.; Milz, S.; Schieker, M.; Maffulli, N.; Rompe, J.-D.; Furia, J.P. Efficacy and Safety of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Orthopedic Conditions: A Systematic Review on Studies Listed in the PEDro Database. Br. Med. Bull. 2015, 116, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durst, H.B.; Blatter, G.; Kuster, M.S. Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head after Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Lithotripsy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. B 2002, 84, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Luboldt, W.; Schwarz, W.; Jacobi, V.; Herzog, C.; Vogl, T.J. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder. Skelet. Radiol. 2004, 33, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, M.; Böddeker, I.; Decker, T.; Buch, A.; Vogel, M.; Labek, G.; Maier, M.; Loew, M.; Maier-Boerries, O.; Fischer, J.; et al. Side-Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) in the Treatment of Tennis Elbow. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2002, 122, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrer, H.; Nauck, T.; Dorn-Lange, N.V.; Schöll, J.; Vester, J.C. Comparison of Radial Versus Focused Extracorporeal Shock Waves in Plantar Fasciitis Using Functional Measures. Foot Ankle Int. 2010, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Worp, H.; Zwerver, J.; Hamstra, M.; van den Akker-Scheek, I.; Diercks, R.L. No Difference in Effectiveness between Focused and Radial Shockwave Therapy for Treating Patellar Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.V.; Lee, S.J.; Nazarian, A.; Rodriguez, E.K. Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder: Review of Pathophysiology and Current Clinical Treatments. Shoulder Elb. 2017, 9, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, H.S.; Evans, J.P.; Smith, C. Frozen Shoulder: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Options. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.; van Doorn, P.; Hegedus, E.; Lewis, J.; van der Windt, D. A Systematic Review of the Global Prevalence and Incidence of Shoulder Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmick, S.; Hayter, C.; Linklater, J. Acute Calcific Periarthritis—A Commonly Misdiagnosed Pathology. Skeletal Radiol. 2022, 51, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, G.; Baker, C.L. Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 34, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merolla, G.; Bhat, M.G.; Paladini, P.; Porcellini, G. Complications of Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder: A Concise Review. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2015, 16, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merolla, G.; Singh, S.; Paladini, P.; Porcellini, G. Calcific Tendinitis of the Rotator Cuff: State of the Art in Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2015, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijpers, T.; Van Der Windt, D.A.W.M.; Van Der Heijden, G.J.M.G.; Bouter, L.M. Systematic Review of Prognostic Cohort Studies on Shoulder Disorders. Pain 2004, 109, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolathuru, S.; Khanna, M.; Jayaraman, M. Management of Periarthritis Shoulder—Current Concept Review. IP Int. J. Orthop. Rheumatol. 2023, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotzman, S.B. Handbook of Orthopaedic Rehabilitation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, C.; Robinson, K.; Mccreesh, K. Understanding Shoulder Pain: A Qualitative Evidence Synthesis Exploring the Patient Experience. Phys. Ther. 2021, 101, pzaa229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, C.; Császár, N.B.M.; Rompe, J.D.; Chaves, H.; Furia, J.P. Treatment of Chronic Plantar Fasciopathy with Extracorporeal Shock Waves (Review). J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2013, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchio, A.; Paoloni, M.; Barile, A.; Don, R.; De Paulis, F.; Calvisi, V.; Ranavolo, A.; Frascarelli, M.; Santilli, V.; Spacca, G. Effectiveness of Radial Shock-Wave Therapy for Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder: Single-Blind, Randomized Clinical Study. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Jiang, B.; Li, Z. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Is Effective in Treating Chronic Plantar Fasciitis. Medicine 2017, 96, e6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoboni, F.; Balducci, S.; D’Errico, V.; Haxhi, J.; Vetrano, M.; Piccinini, G.; Ferretti, A.; Pugliese, G.; Vulpiani, M.C. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Improves Functional Outcomes of Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder in Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, e12–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, A.; Ahmad, A.; Gilani, S.A.; Darain, H.; Kazmi, S.; Hanif, K. Effects of High-Energy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Pain, Functional Disability, Quality of Life, and Ultrasonographic Changes in Patients with Calcified Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1230857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Song, Q.; Yang, X.; Kuati, A.; Fu, H.; Cui, G. Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, D.; Rashid, M.; Rowinski, S.; Al-Qahtani, S.; Bernáldez Domínguez, P.; Gómez, D.; Dallo, I. Therapeutic Options in Rotator Cuff Calcific Tendinopathy. SICOT-J 2025, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Wu, K.T.; Yang, Y.J.; Cheng, J.H.; Wang, S.W. Comparative Outcomes of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Shoulder Tendinitis or Partial Tears of the Rotator Cuff in Athletes and Non-Athletes: Retrospective Study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 51, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duymaz, T.; Sındel, D. Comparison of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and Traditional Physiotherapy in Rotator Cuff Calcific Tendinitis Treatment. Arch. Rheumatol. 2019, 34, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuspahić, S.; Bojičić, S.; Katana, B.; Mačak-Hadžiomerović, A.; Jušić, M. Effectiveness of Shock Wave Therapy Versus Standard Physical Therapy Modalities in Patients with Shoulder Pain. Knowl. Int. J. 2023, 59, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bably, S.; Ganeb, S.; El-Shambaky, A.; Hassan, W. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy versus Local Corticosteroid Injection and Platelet-Rich Plasma in The Treatment of Supraspinatus Tendinopathy. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2023, 92, 5900–5906. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, R.; Di Iorio, A.; Brindisino, F.; Paolucci, T.; Moretti, A.; Iolascon, G. Effectiveness of Combined Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy and Hyaluronic Acid Injections for Patients with Shoulder Pain Due to Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Person-Centered Approach with a Focus on Gender Differences to Treatment Response. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjithkumar, N.; Paul, J.; Alagesan, J.; Viswanathan, R. Comparative Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Short Wave Therapy, Low-Level Laser Therapy, and Ultrasound in the Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2025, 18, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, C.W.; Haotian, B.; Lee, G.W.; Noh, K.C. Comparison of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and Ultrasound-Guided Shoulder Injection Therapy in Patients with Supraspinatus Tendinitis. CiOS Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huskisson, E.C. Measurement of Pain. Lancet 1974, 304, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijur, P.E.; Silver, W.; Gallagher, E.J. Reliability of the Visual Analog Scale for Measurement of Acute Pain. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, K.E.; Budiman-Mak, E.; Songsiridej, N.; Lertratanakul, Y. Development of a Shoulder Pain and Disability Index. Arthritis Care Res. Off. J. Arthritis Health Prof. Association 1991, 4, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDermid, J.C.; Solomon, P.; Prkachin, K. The Shoulder Pain and Disability Index Demonstrates Factor, Construct and Longitudinal Validity. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2006, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.; Walton, J.R.; Szomor, Z.L.; Murrell, G.A. Reliability of Five Methods for Assessing Shoulder Range of Motion. Aust. J. Physiother. 2001, 47, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; Bobocea, L.; David, I.; Burcea, C.-C.; Sporea, C. The Role of the Six-Minute Walk Test in the Functional Evaluation of the Efficacy of Rehabilitation Programs After COVID-19. Life 2024, 14, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAteer, J.A.; Evan, A.P. The Acute and Long-Term Adverse Effects of Shock Wave Lithotripsy. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, G.; Vescio, A.; Perez, S.; Consoli, A.; Costarella, L.; Sessa, G.; Pavone, V. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Treatment in Upper Limb Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilek, F.; Karakaya, M.G.; Karakaya, I.Ç. Immediate Effects of TENS and HVPS on Pain and Range of Motion in Subacromial Pain Syndrome: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2021, 34, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcea, C.-C.; Oancea, M.-D.-A.; Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; Georgescu, L.; Neagoe, I.-C.; Sporea, C. The Benefits of a Rehabilitation Program Following Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction. Life 2024, 14, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.G.T.; Dailey, D.L.; Chimenti, R.L.; Van Gorp, B.J.; Crofford, L.J.; Sluka, K.A. Using TENS for Pain Control: Update on the State of the Evidence. Medicina 2022, 58, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; Trăistaru, M.R. The Effectiveness of High Intensity Laser in Improving Motor Deficits in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation. Life 2024, 14, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, U.G.; Risi Ambrogioni, L.; Berton, A.; Candela, V.; Carnevale, A.; Schena, E.; Gugliemelli, E.; Denaro, V. Physical Therapy and Precision Rehabilitation in Shoulder Rotator Cuff Disease. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burcea, C.-C.; Bobu, V.; Ferechide, D.; Neagoe, I.C.; Lupușoru, G.E.; Sporea, C.; Ovidiu, M.; Lupușoru, D. New Methodological Aspects in Rehabilitation after Proximal Humerus Fracture. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2023, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, L.; Lewis, J.; Kuppens, K.; Jochems, J.; Bruijstens, T.; Joossens, L.; Struyf, F. An Update of Systematic Reviews Examining the Effectiveness of Conservative Physical Therapy Interventions for Subacromial Shoulder Pain. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2020, 50, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganotti, P.; Amelio, E.; Guerra, C. Shock Wave over Hand Muscles: A Neurophysiological Study on Peripheral Conduction Nerves in Normal Subjects. Muscles. Ligaments Tendons J. 2012, 2, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Notarnicola, A.; Moretti, B. The Biological Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (Eswt) on Tendon Tissue. Muscles. Ligaments Tendons J. 2012, 2, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Rompe, J.D.; Hopf, C.; Nafe, B.; Bürger, R. Low-Energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Painful Heel: A Prospective Controlled Single-Blind Study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 1996, 115, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BTL Industries, Ltd. BTL-6000 SWT Top Line User’s Manual. Available online: http://www.frankshospitalworkshop.com/equipment/documents/physiotherapy/user_manuals/BTL%206000%20Topline%20-%20User%20manual.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; Tache-Codreanu, A. Acting and Dancing during the COVID-19 Pandemic as Art Therapy for the Rehabilitation of Children with Behavioural Disorders Living in Socially Disadvantaged Environments. Children 2024, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS; Open University Press: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Crevenna, R.; Mickel, M.; Schuhfried, O.; Gesslbauer, C.; Zdravkovic, A.; Keilani, M. Focused Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2021, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, D.; Angelcheva, M.; Bogdanova, S. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and Interferential Electrotherapy in Periarthritis Humeroscapularis. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Congress “Applied Sports Sciences”, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2–3 December 2022; Volume 2, pp. 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvarani, G.; Paul, J.; Manoj Abraham, M.; Harikrishnan, N. A Study to Analyse the Prevalence of Periarthritis among Shoulder Pain Subjects—A Cross Sectional Study. Biomedicine 2021, 41, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cristofaro, L.; Brindisino, F.; Venturin, D.; Andriesse, A.; Pellicciari, L.; Poser, A. Prognostic Factors of Nonsurgical Intervention Outcomes for Patients with Frozen Shoulder: A Retrospective Study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2024, 47, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.Q.; Wylie, J.D.; Greis, P.E.; Burks, R.T.; Tashjian, R.Z. Psychological Distress Negatively Affects Self-Assessment of Shoulder Function in Patients with Rotator Cuff Tears. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 3926–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostol, O.A.; Morcov, M.V.; Sporea, C.; Morcov, M.; Morcov, C.G.; Cioca, I.E. Findings Regarding the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Sociodemographic Parameters in Families Having Children with Cerebral Palsy. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2023, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challoumas, D.; Biddle, M.; McLean, M.; Millar, N.L. Comparison of Treatments for Frozen Shoulder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2029581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elerian, A.E.; Rodriguez-Sanz, D.; Elsherif, A.A.; Dorgham, H.A.; Al-Hamaky, D.M.A.; El Fakharany, M.S.; Ewidea, M. Effectiveness of Shock Wave Therapy versus Intra-Articular Corticosteroid Injection in Diabetic Frozen Shoulder Patients’ Management: Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwerens, J.K.G.; Sierevelt, I.N.; Kramer, E.T.; Boonstra, R.; van den Bekerom, M.P.J.; van Royen, B.J.; Eygendaal, D.; van Noort, A. Comparing Ultrasound-Guided Needling Combined with a Subacromial Corticosteroid Injection Versus High-Energy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Calcific Tendinitis of the Rotator Cuff: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2020, 36, 1823–1833.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.N.; Tenforde, A.S.; Jelsing, E.J. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in the Management of Sports Medicine Injuries. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2021, 20, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, A.S.; Borgstrom, H.E.; DeLuca, S.; McCormack, M.; Singh, M.; Hoo, J.S.; Yun, P.H. Best Practices for Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Medicine: Clinical Application and Training Consideration. Pm&R 2022, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Lew, H.L.; Özçakar, L.; Wu, C.H. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Spasticity: Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraelen, F.; Schotanus, M.; Klemann-Harings, S.; Lambers Heerspink, O.; Jansen, E. Comparison of Clinical and Radiological Outcomes after Three Different Surgical Treatments for Resistant Calcifying Tendinitis of the Shoulder: A Short-Term Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catapano, M.; Robinson, D.M.; Schowalter, S.; McInnis, K.C. Clinical Evaluation and Management of Calcific Tendinopathy: An Evidence-Based Review. J. Osteopath. Med. 2022, 122, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szajkowski, S.; Pasek, J.; Cieślar, G. Dose Escalation Can Enhance the Therapeutic Potential of Radial Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in Runners. Medicina 2024, 60, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axente, M.; Sporea, C.; Mirea, A.; Burcea, C.C.; Ion, D.A. Time-Efficacy in SMA Type 1 and 2 Cases Treated with Nusinersen. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2023, 14, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Lee, S.; Bae, S.; Jung, S.; Shinkai, Y.; Chiba, I.; Shimada, H. Pain Characteristics and Incidence of Functional Disability among Community-Dwelling Older Adults. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ligero, M.; Moral-Munoz, J.A.; Salazar, A.; Failde, I. MHealth Intervention for Improving Pain, Quality of Life, and Functional Disability in Patients with Chronic Pain: Systematic Review. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2023, 11, e40844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.S.; Cenzer, I.S.; Yelin, E.; Covinsky, K.E. Pain as a Risk Factor for Disability or Death. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; David, I.; Popp, C.G.; Bobocea, L.; Trăistaru, M.R. Successfully Physical Therapy Program for Functional Respiratory Rehabilitation after Lung Transplant Surgery—Case Report. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2024, 65, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, S.; Alghadir, A.H.; Al-Eisa, E.S.; Iqbal, Z.A. The Relationships between Shoulder Pain, Range of Motion, and Disability in Patients with Shoulder Dysfunction. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2018, 31, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporea, C.; Morcov, M.V.; Morcov, M.; Mirea, A. Effectiveness of Passive Movement Training in Patients with Cerebral Palsy: A Comparative Analysis of Robot-Assisted Therapy and Electrical Stimulation in Hand Rehabilitation. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2023, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.; Neto, M.G.; Sales, S.d.S.R.; Cavalcante, B.d.S.; Torrierri, P.; Roever, L.; de Araújo, R.P.C. Effect of Mobilization with Movement on Pain, Disability, and Range of Motion in Patients with Shoulder Pain and Movement Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Hur, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Park, J. Shoulder Range of Motion Rehabilitation Robot Incorporating Scapulohumeral Rhythm for Frozen Shoulder. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.10163. [Google Scholar]
- Rangan, A.; Brealey, S.D.; Keding, A.; Corbacho, B.; Northgraves, M.; Kottam, L.; Goodchild, L.; Srikesavan, C.; Rex, S.; Charalambous, C.P.; et al. Management of Adults with Primary Frozen Shoulder in Secondary Care (UK FROST): A Multicentre, Pragmatic, Three-Arm, Superiority Randomised Clinical Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | Group 1 (n = 16) | Group 2 (n = 20) | p-Value | Effect Size (r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.00 (59.25 to 65.00) | 64.00 (47.00 to 73.00) | 0.388 | 0.146 |
| VAS Initial | 7.56 ± 1.71 | 5.50 ± 2.14 | 0.004 | 1.051 (Cohen’s d) |
| SPADI Initial | 78.38 ± 15.33 | 66.15 (27.10 to 75.80) | 0.010 | 0.436 |
| Flexion Initial (°) | 103.75 ± 39.22 | 160.00 (95.00 to 170.00) | 0.031 | 0.365 |
| Extension Initial (°) | 36.88 ± 13.65 | 45.00 (30.00 to 57.50) | 0.334 | 0.163 |
| Abduction Initial (°) | 87.50 (52.50 to 97.50) | 122.75 ± 48.98 | 0.006 | 0.468 |
| External Rotation Initial (°) | 51.88 ± 22.87 | 80.00 (70.00 to 90.00) | 0.002 | 0.303 |
| Internal Rotation Initial (°) | 42.50 ± 26.20 | 42.00 ± 24.46 | 0.953 | 0.02 (Cohen’s d) |
| Group | Variable | Baseline (Mean ± SD/Median, IQR) | Final (Mean ± SD/Median, IQR) | Difference (Mean ± SD/Median, IQR) | p-Value | Effect Size (r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | ||||||
| VAS | 7.56 ± 1.71 | 4.69 ± 2.58 | −2.87 ± 2.06 | <0.001 | 1.31 (Cohen’s d) | |
| SPADI | 78.38 ± 15.33 | 33.10 (25.00 to 70.98) | −31.90 (−46.90 to 16.17) | <0.001 | 0.622 | |
| Flexion (°) | 103.75 ± 39.22 | 136.56 ± 31.82 | 32.81 ± 33.21 | 0.001 | 0.918 (Cohen’s d) | |
| Extension (°) | 36.88 ± 13.65 | 50.00 (45.00 to 60.00) | 10.00 (1.25 to 20.00) | 0.002 | 0.546 | |
| Abduction (°) | 87.50 (52.50 to 97.50) | 117.81 ± 30.28 | 35.00 (12.50 to 67.50) | 0.001 | 0.604 | |
| External Rotation (°) | 51.88 ± 22.87 | 80.00 (60.00 to 90.00) | 15.00 (10.00 to 27.50) | 0.001 | 0.606 | |
| Internal Rotation (°) | 42.50 ± 26.20 | 75.00 (38.75 to 88.75) | 20.00 (10.00 to 28.75) | 0.001 | 0.585 | |
| Group 2 | ||||||
| VAS | 5.50 ± 2.14 | 3.25 ± 2.40 | −2.25 ± 1.59 | <0.001 | 0.988 (Cohen’s d) | |
| SPADI | 66.15 (27.10 to 75.80) | 31.85 ± 22.77 | −20.62 (−36.92 to −13.05) | <0.001 | 0.620 | |
| Flexion (°) | 160.00 (95.00 to 170.00) | 170 (120.00 to 178.75) | 0.00 (0.00 to 10.00) | 0.007 | 0.486 | |
| Extension (°) | 45.00 (30.00 to 57.50) | 60.00 (45.00 to 60.00) | 5.00 (0.00 to 15.00) | 0.002 | 0.446 | |
| Abduction (°) | 122.75 ± 48.98 | 160.00 (112.50 to 180.00) | 5.00 (0.00 to 37.50) | 0.005 | 0.488 | |
| External Rotation (°) | 80.00 (70.00 to 90.00) | 90.00 (81.25 to 90.00) | 5.00 (0.00 to 13.75) | 0.002 | 0.429 | |
| Internal Rotation (°) | 42.00 ± 24.46 | 58.50 ± 21.59 | 16.50 ± 16.71 | <0.001 | 0.715 (Cohen’s d) |
| Variable | Δ Group 1 (Mean ± SD/Median, IQR) | Group 2 (Mean ± SD/Median, IQR) | p-Value | Effect Size (r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | −2.87 ± 2.06 | −2.25 ± 1.59 | 0.153 | 0.345 (Cohen’s d) |
| SPADI | −31.90 (−46.90 to 16.17) | −20.62 (−36.92 to −13.05) | 0.072 | 0.304 |
| Flexion (°) | 32.81 ± 33.21 | 0.00 (0.00 to 10.00) | 0.005 | 0.476 |
| Extension (°) | 10.00 (1.25 to 20.00) | 5.00 (0.00 to 15.00) | 0.328 | 0.165 |
| Abduction (°) | 35.00 (12.50 to 67.50) | 5.00 (0.00 to 37.50) | 0.011 | 0.430 |
| External Rotation (°) | 15.00 (10.00 to 27.50) | 5.00 (0.00 to 13.75) | 0.004 | 0.492 |
| Internal Rotation (°) | 20.00 (10.00 to 28.75) | 16.50 ± 16.71 | 0.39 | 0.145 |
| VAS Initial | VAS Final | SPADI Initial | SPADI Final | Flexion Gain | Extension Gain | ABD Gain | ER Gain | IR Gain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS Initial | 1 | 0.602 * p = 0.014 | 0.625 ** p = 0.010 | 0.456 p = 0.076 | −0.024 p = 0.930 | 0.123 p = 0.649 | −0.008 p = 0.977 | 0.409 p = 0.115 | −0.207 p = 0.442 |
| VAS Final | 1 | 0.271 p = 0.310 | 0.777 ** p < 0.001 | −0.036 p = 0.895 | 0.130 p = 0.630 | −0.113 p = 0.676 | 0.486 p = 0.056 | −0.022 p = 0.934 | |
| SPADI Initial | 1 | 0.581 * p = 0.018 | 0.111 p = 0.682 | −0.166 p = 0.538 | 0.272 p = 0.309 | 0.386 p = 0.139 | −0.062 p = 0.819 | ||
| SPADI Final | 1 | −0.029 p = 0.917 | −0.187 p = 0.488 | 0.019 p = 0.943 | 0.390 p = 0.135 | −0.093 p = 0.731 | |||
| Flexion Gain | 1 | 0.389 p = 0.136 | 0.385 p = 0.141 | 0.019 p = 0.944 | 0.608 * p = 0.012 | ||||
| Extension Gain | 1 | −0.295 p = 0.268 | −0.129 p = 0.634 | 0.230 p = 0.391 | |||||
| Abduction Gain | 1 | 0.413 p = 0.112 | 0.280 p = 0.294 | ||||||
| External Rotation Gain | 1 | 0.278 p = 0.298 | |||||||
| Internal Rotation Gain | 1 |
| VAS Initial | VAS Final | SPADI Initial | SPADI Final | Flexion Gain | Extension Gain | ABD Gain | ER Gain | IR Gain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS Initial | 1 | 0.762 ** p < 0.001 | 0.802 ** p < 0.001 | 0.478 * p = 0.033 | 0.334 p = 0.150 | 0.356 p = 0.123 | 0.405 p = 0.077 | −0.021 p = 0.929 | 0.037 p = 0.878 |
| VAS Final | 1 | 0.749 ** p < 0.001 | 0.624 ** p = 0.003 | 0.430 p = 0.059 | 0.289 p = 0.217 | 0.339 p = 0.144 | 0.351 p = 0.129 | 0.075 p = 0.752 | |
| SPADI Initial | 1 | 0.810 ** p < 0.001 | 0.294 p = 0.208 | 0.218 p = 0.357 | 0.319 p = 0.170 | 0.159 p = 0.504 | 0.139 p = 0.559 | ||
| SPADI Final | 1 | 0.093 p = 0.697 | 0.023 p = 0.924 | 0.045 p = 0.851 | 0.368 p = 0.111 | −0.117 p = 0.622 | |||
| Flexion Gain | 1 | 0.803 ** p < 0.001 | 0.822 ** p < 0.001 | 0.145 p = 0.542 | 0.364 p = 0.114 | ||||
| Extension Gain | 1 | 0.809 ** p < 0.001 | 0.080 p = 0.737 | 0.213 p = 0.368 | |||||
| Abduction Gain | 1 | 0.070 p = 0.770 | 0.409 p = 0.074 | ||||||
| External Rotation Gain | 1 | 0.085 p = 0.723 | |||||||
| Internal Rotation Gain | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; David, I.; Tache-Codreanu, A.-M.; Sporea, C.; Burcea, C.-C.; Blendea, D.C.; Morcov, M.-V.; Cioca, I.E. rESWT in Shoulder Periarthritis: Does the Protocol Intensity Matter?—A Quasi-Experimental Non-Randomized Comparative Study. Life 2025, 15, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060922
Tache-Codreanu D-L, David I, Tache-Codreanu A-M, Sporea C, Burcea C-C, Blendea DC, Morcov M-V, Cioca IE. rESWT in Shoulder Periarthritis: Does the Protocol Intensity Matter?—A Quasi-Experimental Non-Randomized Comparative Study. Life. 2025; 15(6):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060922
Chicago/Turabian StyleTache-Codreanu, Diana-Lidia, Iuliana David, Ana-Maria Tache-Codreanu, Corina Sporea, Claudia-Camelia Burcea, Dan Corneliu Blendea, Maria-Veronica Morcov, and Ioana Elena Cioca. 2025. "rESWT in Shoulder Periarthritis: Does the Protocol Intensity Matter?—A Quasi-Experimental Non-Randomized Comparative Study" Life 15, no. 6: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060922
APA StyleTache-Codreanu, D.-L., David, I., Tache-Codreanu, A.-M., Sporea, C., Burcea, C.-C., Blendea, D. C., Morcov, M.-V., & Cioca, I. E. (2025). rESWT in Shoulder Periarthritis: Does the Protocol Intensity Matter?—A Quasi-Experimental Non-Randomized Comparative Study. Life, 15(6), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060922







