Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Nutritional Powerhouse with Multifaceted Pharmacological and Functional Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Botanical Identity, Taxonomy, and Cultivation
3.1. Botanical Description
3.2. Taxonomy
3.3. Cultivation and Agronomical Practices
3.3.1. Growing Conditions
3.3.2. Cultivation
- Planting density is usually tailored to the production objective. For example, for intensive leaf production: spacing is 10–20 cm, with harvest every 35–45 days, and requires irrigation and fertilization; for semi-intensive systems: spacing is approximately 50 × 100 cm, with harvest every 50–60 days and moderate inputs; for agroforestry systems: 2–4 m between rows, designed for low-input integration into wider farming systems.
- Yields vary widely depending on genotype, climate, and spacing, with intensive plantations producing between 40 and 580 metric tons of fresh biomass per hectare per year [23]. Shoots are typically harvested at 0.5–1 m height to stimulate regrowth, while harvesting individual leaves—although faster—may reduce vigor over time.
4. Nutritional Profile
5. Phytochemical Composition and Associated Bioactivities
6. Therapeutic Potential of M. oleifera Lam.
6.1. Antioxidant Activity
6.1.1. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
6.1.2. Cellular and In Vivo Evidence for Antioxidant Activity
6.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
6.3. Antimicrobial (Antibacterial, Antifungal) Activity
| Type | Part of the Plant | Dose | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial effects | |||
| S. typhi | Leaves (ethanolic extract) | 800 mg/mL | [83] |
| S. aureus, E. faecalis, B. subtilis, S. typhi, E. coli | Leaves (petroleum ether extract) | 62.5, 125, 250, 10,000 μg | [59] |
| S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa | Seeds (aqueous and methanolic extracts) | EC 5, 10, 20, 40% | [83] |
| S. aureus, V. parahaemolyticus, E. faecalis, A. caviae | Leaves (aqueous and ethanolic extracts) | 400 μL (20 g/180 mL) | [85] |
| Salmonella sp., E. coli, S. aureus | Seed (powder) | 0.017 g/mL | [87] |
| E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, S. pneumoniae, S. aureus. | Seeds (methanolic extract) | 2, 4, 6 mg/mL | [84] |
| S. aureus, S. epidermidis, B. subtilis | Isothiocyanates isolated from seeds | 1, 10 mg/mL | [88] |
| S. aureus | Leaves (aqueous and saline extracts) | 100, 200 μg/mL | [86] |
| K. pneumoniae, E. coli, S. aureus. | Leaves (ethanolic extract) | 1000–3906 mg/mL | [89] |
| L. monocytogenes | Moringin, isolated from seeds | 0.124 mg/mL | [104] |
| E. coli, S. sciuri, S. aureus, S. typhi, S. enterica, P. aeruginosa | Leaves (ethanolic extract, aqueous extract) | 0.04–0.42 mg/mL 0.03–0.33 mg/mL | [91] |
| S. aureus, S. mutans | Seeds, roots, leaves (ethanolic, acetate, ethyl-acetate extracts) | 400 mg/mL | [92] |
| E. coli, S. typhi, S. aureus, Enterococcus sp., P. aeruginosa | Leaves (aqueous and methanolic extracts) | 30 mg/mL | [93] |
| Antifungal effects | |||
| Yeasts (Candida species, etc.) | |||
| C. albicans | Leaves (ethanolic and aqueous extracts) | 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 µg/mL | [96] |
| C. albicans, C. dulblinesis, C. glabarata, C. kefyr, C. krusei, C. lusitania. | Seeds (oil) | 1.0% | [98] |
| C. albicans, C. parapsilosis, C. krusei, C. tropicalis. | Seeds (purified protein, Mo-CBP2) | 0.32 mg/g | [102] |
| Dermatophytes | |||
| T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, E. xoccosum, M. canis | Leaves (crude essential oil) (ethanolic extract) Seed extract | 0.2. 0.4, 0.6, 1.6 mg/mL 2.5 mg/mL 2.5 mg/mL | [97] |
| E. floccosum and T. rubrum | Isothiocyanates isolated from seed extract | 1, 10 mg/mL | [88] |
| Phytopathogenic fungi | |||
| Fusarium solani, F. oxysporum, C. musae and C. gloesporioides | Protein Mo-CBP3 isolated from seeds | 0.05 mg/mL | [100,101] |
| T. mentagrophytes | Protein Mo-CBP4 isolated from seeds | 5, 10, 20 mg/g | [103] |
6.4. Antiviral Activity
| Virus Type | Plant Part (Extract Type) | Dose/EC50/EC90 | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza Virus (H1N1) | Seeds (ethanolic) | EC50 = 1.27 µM; EC90 = 5.30 µM | [105] |
| Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) | Leaves | 300 mg/kg (in vivo) | [106] |
| Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) | Leaves (aqueous) | 30, 45, and 60 µg/mL | [105] |
| Foot and Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) | Leaves (ethanolic) | 1.6, 6.12, 25, 50, 100, 200 µg/mL | [110] |
| Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) | Leaves (methanolic) | 200 mg/kg (in vivo) | [111] |
6.5. Anticancer Effects
6.5.1. In Vitro and Mechanistic Evidence
6.5.2. In Vivo Studies and Cancer Chemopreventive Potential
6.6. Hepatoprotective Effects
6.7. Antidiabetic Effects
6.8. Cardiovascular Effects
6.9. Neuroprotective Effects
6.10. Gastrointestinal Protective Effects
6.11. Anti-Obesity Effects
6.12. Effects on Fertility
6.12.1. Fertility-Enhancing Effects
6.12.2. Antifertility and Abortifacient Effects
6.13. Effects on Bones
7. Toxicity Studies
7.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
- Methanolic leaf extract applied to HBF4 cells for 24 h caused noticeable changes at doses ≥1000 μg/mL, including increased cell size. The concentration affecting viability was ≥700 μg/mL [186].
- Aqueous leaf extract showed cytotoxic effects on A549 lung cancer cells, with 30% and 15% cell death at 400 μg/mL and 500 μg/mL, respectively [187].
- Essential oil from seeds tested on HeLa, HepG2, MCF-7, Caco-2, and L929 cell lines (0.15–1 mg/mL) showed the highest cytotoxicity in HeLa, HepG2, and MCF-7 cells, suggesting a dose- and cell type-specific toxicity [170].
7.2. In Vivo Toxicity in Animal Models
7.3. Safety Considerations for Human Use
8. Moringa oleifera and Its Application in Dietary Supplements
8.1. Commercial Use in Dietary Supplements
8.2. Applications in Functional Foods and Nutritional Enrichment
9. Cosmetic Applications
10. Preparation of Moringa Formulations
11. Existing Patents on Compositions with Extracts from Different Parts of M. oleifera
12. Interactions Between M. oleifera and Pharmaceutical Drugs
12.1. Synergistic Effects
12.2. Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions
- Antimalarial drugs. An experimental study demonstrated that co-administration of M. oleifera leaf extract with chloroquine resulted in antagonistic effects, potentially due to the inhibition of chloroquine absorption. This interaction may reduce the drug efficacy in treating malaria, highlighting the need for caution when combining Moringa with certain antimalarial drugs [212].
- Cytochrome P450 enzyme inhibition. In vitro studies have shown that M. oleifera extracts can inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, which are involved in the metabolism of many drugs. The degree of inhibition varied depending on the extract type and concentration, with methanolic leaf extracts showing more potent effects [213].
- Antihypertensive drugs. Compared to standard antihypertensive drugs, M. oleifera leaf extract administered alone to spontaneously hypertensive rats reduced blood pressure. However, when combined with these drugs, no synergistic effects were observed. This suggests that the concurrent use of Moringa with antihypertensive medications may not enhance therapeutic outcomes [214].
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| GSH | reduced glutathione |
| GSSG | oxidized glutathione |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| GGT | gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| BSS | β-sitosterol |
| MO | Moringa oleifera |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| iNOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| MOL | M. oleifera leaf |
| Mo-CBP | Moringa oleifera-Chitin-binding proteins |
| NDV | Newcastle disease virus |
| HSV-1 | Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| p.os | orally |
| STZ | streptozotocin |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| HFD | follicle-stimulating hormone |
| mRNA | Messenger Ribonucleic acid |
References
- Fuglie, L.J. Producing Food Without Pesticides: Local Solutions to Crop Pest Control in West Africa; Church World Service: Dakar, Senegal, 1998; pp. 1–158. [Google Scholar]
- Pareek, A.; Pant, M.; Gupta, M.M.; Kashania, P.; Ratan, Y.; Jain, V.; Pareek, A.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Moringa oleifera: An Updated Comprehensive Review of Its Pharmacological Activities, Ethnomedicinal, Phytopharmaceutical Formulation, Clinical, Phytochemical, and Toxicological Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharsallah, K.; Rezig, L.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Ali, M.A.; Chew, S.C. Moringa oleifera: Processing, Phytochemical Composition, and Industrial Applications. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y. Moringa oleifera: A Systematic Review of Its Botany, Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Toxicity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 296–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, E.; Blundell, R. A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemicals, Health Benefits, Pharmacological Safety and Medicinal Prospects of Moringa oleifera. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Bendre, S.; Patil, S. Overview of Pharmacognostical and Pharmacological Properties of Moringa oleifera. Asian J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 12, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Li, B.; Olayanju, J.B.; Drake, J.M.; Chen, N. Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients 2018, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malage, A.; Jadhav, S.; Yogekar, T.; Sharma, S. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Characteristics of Moringa oleifera: A Review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2020, 13, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Ashraf, M.; Bhanger, M.I. Interprovenance Variation in the Composition of Moringa oleifera Oilseeds from Pakistan. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2005, 82, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Kuipers, S. The Antibacterial Action of Moringa oleifera: A Systematic Review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiș, A.; Noubissi, P.A.; Pop, O.-L.; Mureșan, C.I.; Tagne, M.A.F.; Kamgang, R.; Fodor, A.; Sitar-Tăut, A.-V.; Cozma, A.; Orășan, O.H.; et al. Bioactive Compounds in Moringa oleifera: Mechanisms of Action, Focus on Their Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Plants 2024, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Szczykutowicz, M.; Gaweł-Bęben, K.; Rutka, A.; Blicharska, E.; Tatarczak-Michalewska, M.; Kulik-Siarek, K.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Malinowska, M.A.; Szopa, A. Moringa oleifera (Drumstick Tree)—Nutraceutical, Cosmetological and Medicinal Importance: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1288382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwanis, F.M.; Abdelaty, H.S.; Saleh, S.A. Exploring the Multifaceted Uses of Moringa oleifera: Nutritional, Industrial and Agricultural Innovations in Egypt. Discov. Food 2024, 4, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsadek, N.A.; Aboukhadr, M.A.; Kamel, F.R.; Mostafa, H.M.; El-Kimary, G.I. Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Promotes the Healing of Critical Sized Bone Defects in the Mandibles of Rabbits. BDJ Open 2024, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Gautam, D.N.S.; Sourav, S.; Sharma, R. Role of Moringa oleifera Lam. in Cancer: Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Insights. Food Front. 2023, 4, 164–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzano, A.; Ammar, M.; Papaianni, M.; Grauso, L.; Sabbah, M.; Capparelli, R.; Lanzotti, V. Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Overview. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Fahey, J.W. Moringa oleifera: Un árbol multiusos para las zonas tropicales secas. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2011, 82, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J. Tree Seed Handbook of Kenya; GTZ Forestry Seed Center: Nairobi, Kenya, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ambasta, S.P. The Useful Plants of India; Publications & Information Directorate, CSIR: New Delhi, India, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Nadkarni, K.M. Indian Materia Medica, 3rd ed.; Popular Prakashan: Bombay, India, 2000; p. 811. [Google Scholar]
- Paikra, B.K.; Dhongade, H.K.J.; Gidwani, B. Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Pharmacopunct. 2017, 20, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Mallenakuppe, R.; Homabalegowda, H.; Gouri, M.D.; Basavaraju, P.S.; Chandrashekharaiah, U.B. History, Taxonomy and Propagation of Moringa oleifera: A Review. Int. J. Life Sci. 2019, 5, 2322–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Zavala, M.; Peón-Escalante, I.E.; Zepeda-Bautista, R.; Jiménez-Arellanes, M.A. Moringa oleifera Lam.: Potential Uses in Agriculture, Industry and Medicine. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Hortic. 2016, 22, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Spada, A.; Battezzati, A.; Schiraldi, A.; Aristil, J.; Bertoli, S. Cultivation, Genetic, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Moringa oleifera Leaves: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12791–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatia, A.; Virk, A.K.; Kumari, C.; Ali, A.; Garg, P.; Thakur, P.; Attri, C.; Ulshrestha, S. Moringa oleifera—A Never Die Tree: An Overview. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoun, K.; Alsagan, A.; Altahir, O.; Suliman, G.; Al-Haidary, A.; Alsaiady, M. Cultivation and Uses of Moringa oleifera as Non-Conventional Feedstuff in Livestock Production: A Review. Life 2023, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.T.; Mugal, T.; Haq, I.U. Moringa oleifera: A Natural Gift—A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 775–781. [Google Scholar]
- Eke, M.O.; Elechi, J.O.G.; Bello, F. Effect of Fortification of Defatted Moringa oleifera Seed Flour on Consumers’ Acceptability and Nutritional Characteristics of Wheat Bread. Eur. Food Sci. Eng. 2022, 3, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.V.; Mohite, B.V.; Marathe, K.R.; Salunkhe, N.S.; Marathe, V.; Patil, V.S. Moringa Tree, Gift of Nature: A Review on Nutritional and Industrial Potential. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 8, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milla, P.G.; Peñalver, R.; Nieto, G. Health Benefits of Uses and Applications of Moringa oleifera in Bakery Products. Plants 2021, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaofe, O.; Adeyeye, E.I.; Ojugbo, S. Comparative Study of Proximate, Amino Acids and Fatty Acids of Moringa oleifera Tree. Elixir Appl. Chem. 2013, 54, 12543–12554. [Google Scholar]
- Hedhili, A.; Lubbers, S.; Bou-Maroun, E.; Griffon, F.; Akinyemi, B.E.; Husson, F.; Valentin, D. Moringa oleifera-Supplemented Biscuits: Nutritional Values and Consumer Segmentation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 138, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.; Scotti-Campos, P.; Pais, I.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Viegas, D.; Reboredo, F. Elemental Composition, Total Fatty Acids, Soluble Sugar Content and Essential Oils of Flowers and Leaves of Moringa oleifera Cultivated in Southern Portugal. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, C.; Castelló, M.L.; Ortolá, M.D.; García-Mares, F.J.; Soriano, M.D. Moringa oleifera: An Unknown Crop in Developed Countries with Great Potential for Industry and Adapted to Climate Change. Foods 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesse, A.; Goshu, D.; Gelaw, F.; Ademe, A. Food and Nutrition Security Impacts of Moringa: Evidence from Southern Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1733330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglie, L.J. The Miracle Tree: Moringa oleifera: Natural Nutrition for the Tropics; Church World Service: Dakar, Senegal, 1999; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, P.; Kumar, S.; Riar, C.S.; Jindal, N.; Baniwal, P.; Guiné, R.P.F.; Correia, P.M.R.; Mehra, R.; Kumar, H. Recent Advances in Drumstick (Moringa oleifera) Leaves Bioactive Compounds: Composition, Health Benefits, Bioaccessibility, and Dietary Applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceci, R.; Maldini, M.; La Rosa, P.; Sireno, L.; Antinozzi, C.; Olson, M.E.; Dimauro, I.; Duranti, G. The Effect of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract on C2C12 Myoblast Proliferation and Redox Status Under Oxidative Insult. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluhackova, H.; Weichtova, L.; Lojkova, L.; Nemec, P.; Svoboda, Z.; Bosko, R.; Pernica, M.; Benesova, K. The Content of Bioactive Compounds in Moringa oleifera and Moringa stenopetala Species Grown in Ethiopia. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 155, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaknis, J.; Lalas, S.; Gergis, V.; Dourtoglou, V.; Spiliotis, V. Characterization of Moringa oleifera Variety Mbololo Seed Oil of Kenya. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4495–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalas, S.; Tsaknis, J. Characterization of Moringa oleifera Seed Oil Variety “Periyakulam 1”. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Bhanger, M.I. Analytical Characterization of Moringa oleifera Seed Oil Grown in Temperate Regions of Pakistan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6558–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.A.; Owon, M.A.; Osman, M.F.; Esmail, A.I.; Matthäus, B. Characterization of Egyptian Moringa oleifera Lipids (Whole Seeds and Kernels). J. Food Dairy Sci. Mansoura Univ. 2018, 9, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, M.M.; Ghafoor, K.; Al Juhaimi, F.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Babiker, E.E. Effect of Cold-Press and Soxhlet Extraction on Fatty Acids, Tocopherols and Sterol Contents of the Moringa Seed Oils. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, R.C.; Maurya, S.D.; Pooniya, B.K.; Bairwa, N.; Gupta, M.; Sanwarmal. Moringa: The Herbal Gold to Combat Malnutrition. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, C.; Sastri, B.R.; Balasubramanian, S. Nutritive Value of Indian Foods; National Institute of Nutrition, Indian Council of Medical Research: Hyderabad, India, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, S.M.R.; Hossen, F.; Mahtab-Ul-Islam, K.; Hasan, M.R.; Karim, R. Moringa oleifera Is a Prominent Source of Nutrients with Potential Health Benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 6627265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Tao, L.; Shi, C.; Yang, S.; Li, D.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y. Fermentation Improves Calcium Bioavailability in Moringa oleifera Leaves and Prevents Bone Loss in Calcium-Deficient Rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3692–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivapragasam, G.; Devi, T.G.; Ragavan, N.D.; Suryadevara, N.; Sridewi, N.; Al Obaid, S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Arulselvan, P. A Comparative Phytochemical Characterization of Moringa oleifera Plant Parts by Different Solvent Extraction. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2024, 58, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.; Wan, H.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J.; Hao, S.; Jin, K.; Yao, Y. Photoperiod and Shading Regulate Coloration and Anthocyanin Accumulation in the Leaves of Malus Crabapples. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2015, 121, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, B.; Masika, P.J.; Hugo, A.; Muchenje, V. Nutritional Characterization of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12925–12933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Gui, J.; Liu, D. Subcritical Ethanol Extraction of Flavonoids from Moringa oleifera Leaf and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijarotimi, O.S.; Adeoti, O.A.; Ariyo, O. Comparative Study on Nutrient Composition, Phytochemical, and Functional Characteristics of Raw, Germinated, and Fermented Moringa oleifera Seed Flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Jimenez, M.; Almatrafi, M.M.; Fernandez, M.L. Bioactive Components in Moringa oleifera Leaves Protect Against Chronic Disease. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Xu, T.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ali, F.A.Z.; Yang, X.; Lu, B. Health Benefits and Phenolic Compounds of Moringa oleifera Leaves: A Comprehensive Review. Phytomedicine 2021, 93, 153771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-B.; Chen, G.-L.; Guo, M.-Q. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Crude Extracts of Moringa oleifera from Kenya and Their Correlations with Flavonoids. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakade, V.; Cukrowska, E.; Chimuka, L. Comparison of Antioxidant Activity of Moringa oleifera and Selected Vegetables in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2013, 109, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Martínez, M.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; González-Domínguez, J.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Aguilar, C.N.; Morlett-Chávez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R. Location and Tissue Effects on Phytochemical Composition and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Moringa oleifera. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, M.; Dhanarajan, M.S.; Rajalakshmi, A.; Jayachitra, A.; Mathi, P.; Bhogireddy, N. Analysis of Phytochemicals, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaf Extract—An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2014, 6, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Herman-Lara, E.; Rodríguez-Miranda, J.; Ávila-Manrique, S.; Dorado-López, C.; Villalva, M.; Jaime, L.; Santoyo, S.; Martínez-Sánchez, C.E. In Vitro Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Bioaccessibility of Ethanolic Extracts from Mexican Moringa oleifera Leaf. Foods 2024, 13, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.-C.; Chang, C.-M.; Kang, S.-M.; Tsai, M.-L. Effect of Different Parts (Leaf, Stem and Stalk) and Seasons (Summer and Winter) on the Chemical Compositions and Antioxidant Activity of Moringa oleifera. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6077–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiorgou, I.; Grigorakis, S.; Lalas, S.; Makris, D. Polyphenolic Burden and In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Moringa oleifera Root Extracts. J. Herbmed Pharmacol. 2015, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Luqman, S.; Srivastava, S.; Kumar, R.; Maurya, A.K.; Chanda, D. Experimental Assessment of Moringa oleifera Leaf and Fruit for Its Antistress, Antioxidant, and Scavenging Potential Using In Vitro and In Vivo Assays. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 519084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuigbe, C.A.; Okeri, H.A.; Erharuyi, O.; Oghenero, E.E.; Obamedo, D.A. Phytochemical and Antioxidant Evaluation of Moringa oleifera (Moringaceae) Leaf and Seed. J. Pharm. Bioall. Resour. 2014, 11, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver, R.; Martínez-Zamora, L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Ros, G.; Nieto, G. Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of Moringa oleifera Leaves in Functional Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, O.J.; Ra, S.W. Quercetin Prevents LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Modulating NOX2/ROS/NF-κB in Lung Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudjema, K.; Chouala, K.; Khelef, Y.; Chenna, H.; Badraoui, R.; Boumendjel, M.; Boumendjel, A.; Messarah, M. Antioxidant Effects of Moringa oleifera Against Abamectin-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Brain and Erythrocytes of Rats. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 22, e202402709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.C.; Lai, M.H.; Hsu, K.P.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Li, C.-X.; Yin, X.J.; Jeyashoke, N.; Chao, L.K.P. Identification of β-Sitosterol as in Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Constituent in Moringa oleifera. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10748–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.S.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Fakurazi, S. Moringa oleifera Flower Extract Suppresses the Activation of Inflammatory Mediators in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages via NF-κB Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 720171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailaja, B.S.; Hassan, S.; Cohen, E.; Tmenova, I.; Farias-Pereira, R.; Verzi, M.P.; Raskin, I. Moringa Isothiocyanate-1 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation in Mouse Myoblasts and Skeletal Muscle. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miękus, N.; Marszałek, K.; Podlacha, M.; Iqbal, A.; Puchalski, C.; Świergiel, A.H. Health Benefits of Plant-Derived Sulfur Compounds, Glucosinolates, and Organosulfur Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheenpracha, S.; Park, E.-J.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Barit, C.; Wall, M.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Chang, L.C. Potential Anti-Inflammatory Phenolic Glycosides from the Medicinal Plant Moringa oleifera Fruits. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6598–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar-Núñez, M.L.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Berhow, M.; Gonzalez De Mejia, E. Glucosinolate-Rich Hydrolyzed Extract from Moringa oleifera Leaves Decreased the Production of TNF-α and IL-1β Cytokines and Induced ROS and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, K.; Robinson, K.; Suh, N.; Michniak-Kohn, B.; Goedken, M.; Polunas, M.; Raskin, I. Isothiocyanate-Rich Moringa Seed Extract Reduces Skin Inflammation in Mouse Ear Edema Model. Phytomed. Plus 2023, 3, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeamuzie, I.C.; Ambakederemo, A.W.; Shode, F.O.; Ekwebelem, S.C. Antiinflammatory Effects of Moringa oleifera Root Extract. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 1996, 34, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, S.; Singh, V.J. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Moringa oleifera Leaf and Pod Extracts against Carrageenan Induced Paw Edema in Albino Mice. J. Pharm. Sci. Innov. 2011, 1, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Oguntibeju, O.O.; Aboua, G.Y.; Omodanisi, E.I. Effects of Moringa oleifera on Oxidative Stress, Apoptotic and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Animal Model. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Chhipa, A.S.; Gupta, M.; Lalotra, S.; Sisodia, S.S.; Baksi, R.; Nivsarkar, M. Phytochemical Analysis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Methanolic Leaf Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. in Ovalbumin Induced Allergic Asthma. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 130, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhare, M.; Sivakumar, T. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activity of Stem Bark of Moringa oleifera. Pharmacologyonline 2011, 3, 641–650. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhye, K.P.; Rangari, V.D.; Mathur, V.B. Antimigraine Activity Study of Moringa oleifera Leaf Juice. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2012, 6, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeneye, A. Herbal Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension. Phytother. Manag. Diabetes Hypertens. 2016, 2, 3–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, L.; M., T.; S., A.S.; Nayabaniya, A. Phytochemical Screening and In Vitro Evaluation of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of Moringa oleifera Linn Leaf Extract. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 16, 4512–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadabi, A.M.; Zaid, I.E.A. An In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Moringa oleifera L. Seed Extracts Against Different Groups of Microorganisms. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Akintelu, S.A.; Folorunso, A.S.; Oyebamiji, A.K. Phytochemical and Antibacterial Investigation of Moringa oleifera Seed: Experimental and Computational Approaches. Eclética Química 2021, 46, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.R.O.; Silva, G.C.; Costa, R.A.; de Sousa Fontenelle, J.R.; Vieira, G.H.F.; Filho, A.A.F.; Vieira, R.H.S.F. In Vitro Antibacterial Effect of Aqueous and Ethanolic Moringa Leaf Extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.M.; Da Silva Férnandes, M.; De Abreu Filho, B.A.; Gomes, R.G.; Bergamasco, R. Inhibition and Removal of Staphylococcal Biofilms Using Moringa oleifera Lam. Aqueous and Saline Extracts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboagye, G.; Navele, M.; Essuman, E. Protocols for Assessing Antibacterial and Water Coagulation Potential of Moringa oleifera Seed Powder. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padla, E.P.; Solis, L.T.; Levida, R.M.; Shen, C.C.; Ragasa, C.Y. Antimicrobial Isothiocyanates from the Seeds of Moringa oleifera Lam. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2012, 67, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, Q.; Aqib, A.I.; Majeed, H.; Haq, S.U.; Nisar, M.F.; Usman, M.; Muneer, A.; Batool, S.; Ataya, F.S. Effective Synergism of Moringa oleifera with Antibiotics, Body Growth, and Decoction Replacement. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 175, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashikala, B.S.; Ashwini, K.R.; Lavanya, D.R.; Jessica, Y.; Ushasri, P.; Sunitha, D.V.; Shobha, G.; Dsouza, P.P.P.; Naidu, K.C.B. Moringa oleifera Leaf-Based Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Antibacterial Investigations. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 170, 113355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Marrez, D.A.; Abdelmoeen, N.M.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Ali, M.A.S.; Decsi, K.; Tóth, Z. Proximate Analysis of Moringa oleifera Leaves and the Antimicrobial Activities of Successive Leaf Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts Compared with Green Chemically Synthesized Ag-NPs and Crude Aqueous Extract against Some Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgamily, H.; Moussa, A.; Elboraey, A.; El-Sayed, H.; Al-Moghazy, M.; Abdalla, A. Microbiological Assessment of Moringa oleifera Extracts and Its Incorporation in Novel Dental Remedies against Some Oral Pathogens+. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluduro, A.O. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Properties and Nutritional Potentials of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaf in South-Western Nigeria. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2012, 8, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.; Singh, A. Clinical Efficacy of Moringa oleifera Lam. Stems Bark in Urinary Tract Infections. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Patel, N.; Dhara, P.; Desai, S.; Meshram, D. Phytochemical Analysis and Antifungal Activity of Moringa oleifera. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.; Atiyah, M. Anti-Fungal Activities of Aqueous and Alcoholic Leaf Extracts of Moringa oleifera Lam. on Candida albicans Isolated from Diabetic Foot Infections. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2414, 020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, P.; Lee, C.; Chou, J.; Murugan, M.; Shieh, B.; Chen, H. Anti-Fungal Activity of Crude Extracts and Essential Oil of Moringa oleifera Lam. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nessma, E.; Metwally, M.A.; Samah, H. Assessment of Oil and Seed Extracts of Moringa oleifera for Promising Anticandidal Activity in Autistic Children. Egypt. J. Bot. 2022, 62, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mohamedy, R.S.R.; Abdalla, A.M. Evaluation of Antifungal Activity of Moringa oleifera Extracts as Natural Fungicide against Some Plant Pathogenic Fungi In-Vitro. J. Agric. Technol. 2014, 10, 963–982. [Google Scholar]
- Gifoni, J.M.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Oliveira, H.D.; Batista, A.B.; Pereira, M.L.; Gomes, A.S.; Oliveira, H.P.; Grangeiro, T.B.; Vasconcelos, I.M. A Novel Chitin-Binding Protein from Moringa oleifera Seed with Potential for Plant Disease Control. Pept. Sci. 2012, 98, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.B.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Gifoni, J.M.; Pereira, M.L.; Almeida, M.G.G.; Gomes, V.M.; Da Cunha, M.; Ribeiro, S.F.F.; Dias, G.B.; Beltramini, L.M.; et al. New Insights into the Structure and Mode of Action of Mo-CBP3, an Antifungal Chitin-Binding Protein of Moringa oleifera Seeds. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.X.S.; Pereira, M.L.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Rocha-Bezerra, L.C.B.; Lopes, T.D.P.; Costa, H.P.S.; Sousa, D.O.B.; Rocha, B.A.M.; Grangeiro, T.B.; Freire, J.E.C.; et al. A Chitin-Binding Protein Purified from Moringa oleifera Seeds Presents Anticandidal Activity by Increasing Cell Membrane Permeability and Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.D.P.; Souza, P.F.N.; da Costa, H.P.S.; Pereira, M.L.; da Silva Neto, J.X.; de Paula, P.C.; Brilhante, R.S.N.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Sousa, D.O.B. Mo-CBP4, a Purified Chitin-Binding Protein from Moringa oleifera Seeds, Is a Potent Antidermatophytic Protein: In Vitro Mechanisms of Action, in Vivo Effect against Infection, and Clinical Application as a Hydrogel for Skin Infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Su, R.; Yang, M.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y. Multi-Target Antibacterial Mechanism of Moringin from Moringa oleifera Seeds Against Listeria monocytogenes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 925291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feustel, S.; Ayón-Pérez, F.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Rodríguez-Echevarría, R.; Contreras-Salinas, H.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V. Protective Effects of Moringa oleifera on HBV Genotypes C and H Transiently Transfected Huh7 Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 6063850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, M.; Wadhwani, A.; Kai, H.; Hidaka, M.; Yoshida, H.; Sugita, C.; Watanabe, W.; Matsuno, K.; Hagiwara, A. Activation of Cellular Immunity in Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1-Infected Mice by the Oral Administration of Aqueous Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, H.C.A.; Souza, M.D.A.; Sousa, C.S.; Viana, E.K.A.; Alves, S.K.S.; Marques, A.O.; Ribeiro, A.S.N.; de Sousa do Vale, V.; Islam, M.T.; de Miranda, J.A.L.; et al. Molecular Docking and ADME-TOX Profiling of Moringa oleifera Constituents against SARS-CoV-2. Adv. Respir. Med. 2023, 91, 464–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathpal, S.; Sharma, P.; Joshi, T.; Joshi, T.; Pande, V.; Chandra, S. Screening of Potential Bio-Molecules from Moringa oleifera against SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Using Computational Approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 9885–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, D.; Bhaumik, S.; Debnath, P.; Debnath, S. Potentiality of Moringa oleifera against SARS-CoV-2: Identified by a Rational Computer Aided Drug Design Method. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 7517–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, I.; Altaf, I.; Ashraf, M.; Javeed, A.; Munir, N.; Bashir, R. In Vitro Evaluation of Antiviral Activity of Leaf Extracts of Azadirachta indica, Moringa oleifera, and Morus alba against the Foot and Mouth Disease Virus on BHK-21 Cell Line. Sci. Asia 2016, 42, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, D.C.; Okwor, E.C.; Okoye, J.O.A.; Onah, D.N. Immunologic Effects of Moringa oleifera Methanolic Leaf Extract in Chickens Infected with Newcastle Disease Virus (Kudu 113) Strain. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadumane, V.; Nair, S. Anticancer, Cytotoxic Potential of Moringa oleifera Extracts on HeLa Cell Line. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2011, 2, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafalla, M.M.; Abdellatef, E.; Dafalla, H.M.; Nassrallah, A.A.; Aboul-Enein, K.M.; Lightfoot, D.A.; El-Deeb, F.E.; El-Shemy, H.A. Active Principle from Moringa oleifera Lam Leaves Effective against Two Leukemias and a Hepatocarcinoma. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8467–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, F.; Borjac, J.; Fakhouri, R.; Usta, J. Cytotoxic Effect of Moringa oleifera on Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1158, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.L. Soluble Extract from Moringa oleifera Leaves with a New Anticancer Activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Albalawi, S.M.; Athar, M.T.; Khan, A.Q.; Al-Shahrani, H.; Islam, M. Moringa oleifera as an Anti-Cancer Agent against Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, B.H.; Hoang, N.S.; Nguyen, T.P.T.; Ho, N.Q.C.; Le, T.L.; Doan, C.C. Phenolic Extraction of Moringa oleifera Leaves Induces Caspase-Dependent and Caspase-Independent Apoptosis through the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and the Activation of Intrinsic Mitochondrial Pathway in Human Melanoma Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Peng, L.; Yang, M.; Jiang, W.; Mao, J.; Shi, C.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Alkaloid Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Exerts Antitumor Activity in Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer via Modulation of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5591687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Pandey, P.; Ahmad, V.; Upadhyay, T.K. Moringa oleifera Methanolic Leaves Extract Induces Apoptosis and G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest via Downregulation of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Human Prostate PC-3 Cancer Cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovich, L.; Earon, G.; Ron, I.; Rimmon, A.; Vexler, A.; Lev-Ari, S. Moringa oleifera Aqueous Leaf Extract Down-Regulates Nuclear Factor-kappaB and Increases Cytotoxic Effect of Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, R.; Ahmed, A.; Wei, L.; Saeed, H.; Islam, M.; Ishaq, M. The Anticancer Potential of Chemical Constituents of Moringa oleifera Targeting CDK-2 Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Using in-Silico and in Vitro Approaches. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelatha, S.; Padma, P. Modulatory Effects of Moringa oleifera Extracts against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Damage. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, R.; Sargsyan, D.; Zheng, M.; Li, S.; Yin, R.; Su, S.; Raskin, I.; Kong, A.-N. CpG Methyl-Seq and RNA-Seq Epigenomic and Transcriptomic Studies on the Preventive Effects of Moringa Isothiocyanate in Mouse Epidermal JB6 Cells Induced by the Tumor Promoter TPA. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 68, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiphet, S.; Butryee, C.; Rungsipipat, A.; Budda, S.; Rattanapinyopituk, K. Apoptosis Induced by Moringa oleifera Lam. Pod in Mouse Colon Carcinoma Model. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 27, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriota, L.L.D.S.; Ramos, D.D.B.M.; Dos Santos, A.C.L.A.; Silva, Y.A.; Gama, E.; Silva, M.; Torres, D.J.L.; Procópio, T.F.; De Oliveira, A.M.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Moringa oleifera (Drumstick Tree) Flower Trypsin Inhibitor (MoFTI) in Sarcoma 180-Bearing Mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laftah, A.H.; Alhelfi, N.; Al Salait, S.K.; Altemimi, A.B.; Tabandeh, M.R.; Tsakali, E.; Van Impe, J.F.M.; Abd El-Maksoud, A.A.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G. Mitigation of Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice Breast Cancer Model by Green Tea and Moringa oleifera Combination: Targeting Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 124, 106626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunica, E.R.M.; Yang, S.; Coulter, A.; White, C.; Kirwan, J.P.; Gilmore, L.A. Moringa oleifera Seed Extract Concomitantly Supplemented with Chemotherapy Worsens Tumor Progression in Mice with Triple Negative Breast Cancer and Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toson, E.; Elbakry, K.; Serag, M.; Aboser, M. Hepatoprotective Effect of Moringa oleifera Leaves Extract against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Damage in Rats. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 5, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, K.; Kumar, A. Hepatoprotective Studies on Aerial Parts of Moringa oleifera Lam. on Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Liver Cell Damage in Albino Rats. Ann. Biol. Res. 2010, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Toppo, R.; Roy, B.K.; Gora, R.H.; Baxla, S.L.; Kumar, P. Hepatoprotective Activity of Moringa oleifera against Cadmium Toxicity in Rats. Vet. World 2015, 8, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotio, A.L.; Nguepi, M.S.D.; Tonfack, L.B.; Temdie, R.J.G.; Nguelefack, T.B. Acetaminophen Induces Liver Injury and Depletes Glutathione in Mice Brain: Prevention by Moringa oleifera Extract. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elnaby, Y.A.; El Sayed, I.E.; AbdEldaim, M.A.; Badr, E.A.; Abdelhafez, M.M.; Elmadbouh, I. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effect of Moringa oleifera against Bisphenol-A-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Egypt. Liver J. 2022, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fiky, S.A.; Hassan, N.A. Protective Role of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract as a Natural Antioxidant against Toxic Effect of Paracetamol on Male Mice. World J. Pharm. 2018, 7, 115–135. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Fattah, M.E.; Sobhy, H.M.; Reda, A.; Abdelrazek, H.M.A. Hepatoprotective Effect of Moringa oleifera Leaves Aquatic Extract against Lead Acetate-Induced Liver Injury in Male Wistar Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 43028–43043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, A.S.; Hegazy, A.M. Ameliorative Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract on Levofloxacin-Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 43, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, F.S.; Dada, O.; Cyrus, J.W.; Adedoyin, O.O.; Adunlin, G. The Effects of Moringa oleifera on Blood Glucose Levels: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 50, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, D.; Rai, P.K.; Mehta, S.; Chatterji, S.; Shukla, S.; Rai, D.K.; Sharma, G.; Sharma, B.; Khair, S.; Watal, G. Role of Moringa oleifera in Regulation of Diabetes-Induced Oxidative Stress. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-L.; Xu, Y.-B.; Wu, J.-L.; Li, N.; Guo, M.-Q. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaves and Their Functional Chemical Constituents. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, U.; Das, A.K.; Ghosh, S.; Sil, P.C. An Overview on the Role of Bioactive α-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Ameliorating Diabetic Complications. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongrung, R.; Pannangpetch, P.; Senggunprai, L.; Sangkhamanon, S.; Boonloh, K.; Tangsucharit, P. Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Ameliorates Early Stages of Diabetic Nephropathy in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljazzaf, B.; Regeai, S.; Elghmasi, S.; Alghazir, N.; Balgasim, A.; Hdud Ismail, I.M.; Eskandrani, A.A.; Shamlan, G.; Alansari, W.S.; Al-Farga, A.; et al. Evaluation of Antidiabetic Effect of Combined Leaf and Seed Extracts of Moringa oleifera (Moringaceae) on Alloxan-Induced Diabetes in Mice: A Biochemical and Histological Study. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 9136217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tang, J.; Gao, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, W.; Peng, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y. Exploring the Protection on Islet β-Cells and Hypoglycemic Effect of Moringa oleifera Stem Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 122, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, S.; Chawla, P.; Kochhar, A. Effect of Supplementation of Drumstick (Moringa oleifera) and Amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor) Leaves Powder on Antioxidant Profile and Oxidative Status among Postmenopausal Women. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 3464–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Martínez, S.; Díaz-Prieto, L.; Castro, I.; Jurado, C.; Iturmendi, N.; Martín-Ridaura, M.; Calle, N.; Dueñas, M.; Picón, M.; Marcos, A.; et al. Moringa oleifera Leaf Supplementation as a Glycemic Control Strategy in Subjects with Prediabetes. Nutrients 2021, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.P.; Mandapaka, R.T. Effect of Moringa oleifera on Blood Glucose, LDL Levels in Type II Diabetic Obese People. Innov. J. Med. Health Sci. 2013, 3, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Randriamboavonjy, J.I.; Loirand, G.; Vaillant, N.; Lauzier, B.; Derbré, S.; Michalet, S.; Pacaud, P.; Tesse, A. Cardiac Protective Effects of Moringa oleifera Seeds in Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2016, 29, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Ji, Q.-Q.; Wang, Z.; Shen, L.-H.; He, B. Moringa oleifera Seeds Mitigate Myocardial Injury and Prevent Ventricular Failure Induced by Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandave, M.; Ojha, S.K.; Joshi, S.; Kumari, S.; Arya, D.S. Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Prevents Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Damage in Rats: Evidence for an Antioxidant, Antiperoxidative, and Cardioprotective Intervention. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oseni, O.; Ogunmoyole, T.; Idowu, K. Lipid Profile and Cardioprotective Effects of Aqueous Extract of Moringa oleifera (Lam) Leaf on Bromate-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Albino Rats. Eur. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Life Sci. 2015, 3, 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- Odii, E.; Okoro, J.; Okorie, N.; Chukwuka, C.; Okoye, C.; Okeke, E.; Ejere, V.; Eyo, J. Antihypertensive Effect of Moringa oleifera (Moringaceae) Methanolic Leaf Extract (MoMLE) on Cricetomys gambianus (Muridae). Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 6, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Subedi, L.; Acharya, N.; Gaire, B.P. Moringa oleifera: A Tree of Life as a Promising Medicinal Plant for Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14358–14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Burgos, E.; Ureña-Vacas, I.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Nutritional Value of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaf Powder Extracts and Their Neuroprotective Effects via Antioxidative and Mitochondrial Regulation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, J.F.; Vichitphan, S.; Boonsiri, P.; Vichitphan, K. Neuroprotective Assessment of Moringa oleifera Leaves Extract against Oxidative-Stress-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Plants 2021, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirisattayakul, W.; Wattanathorn, J.; Tong-Un, T.; Muchimapura, S.; Wannanon, P.; Jittiwat, J. Cerebroprotective Effect of Moringa oleifera against Focal Ischemic Stroke Induced by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 951415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutalangka, C.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Thukham-mee, W. Moringa oleifera Mitigates Memory Impairment and Neurodegeneration in Animal Model of Age-Related Dementia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 695936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idoga, E.; Ambali, S.; Ayo, J. Assessment of Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Activities of Methanol Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves in Subchronic Chlorpyrifos-Intoxicated Rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 27, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, C.; Mohsin, S.; Faheem, M.; Hanif, U.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Shaik, M.R.; Riaz, H.A.; Anjum, R.; Jurrat, H.; Khan, M. In Vivo Study of Moringa oleifera Seed Extracts as Potential Sources of Neuroprotection against Rotenone-Induced Neurotoxicity. Plants 2024, 13, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsayed, E.M.; Medhat, D.; Mandour, Y.M.; Hanafi, R.S.; Motaal, A.A. Niazimicin: A Thiocarbamate Glycoside from Moringa oleifera Lam. Seeds with a Novel Neuroprotective Activity. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Huang, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Bao, J.; Salissou, M.T.M.; Ke, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; et al. Moringa oleifera Alleviates Homocysteine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Cognitive Impairments. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Feng, J.; Huang, F.; Salissou, M.T.M.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X. Moringa oleifera Alleviates Aβ Burden and Improves Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Impairments in APP/PS1 Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onasanwo, S.A.; Adamaigbo, V.O.; Adebayo, O.G.; Eleazer, S.E. Moringa oleifera-Supplemented Diet Protect against Cortico-Hippocampal Neuronal Degeneration in Scopolamine-Induced Spatial Memory Deficit in Mice: Role of Oxido-Inflammatory and Cholinergic Neurotransmission Pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambuno, N.T.; Putra, A.G.A.; Louisa, M.; Wuyung, P.E.; Timan, I.S.; Silaen, O.S.M.; Sukria, H.A.; Supali, T. Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Improves Cognitive Function in Rat Offspring Born to Protein-Deficient Mothers. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Elsoud, R.A.E.A.; Abdelaziz, S.A.M.; Eldaim, M.A.A.; Hazzaa, S.M. Moringa oleifera Alcoholic Extract Protected Stomach from Bisphenol A–Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rats via Its Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 68830–68841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedi, B.F.L.; Garba, K.; Shuai’bu, A.B.; Basheer, A.Z.; Chedi, B. Evaluation of the Antiulcer Activity of Aqueous Seed Extract of Moringa oleifera Lamarck (Moringaceae). Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 2, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed Husien, H.; Peng, W.; Su, H.; Zhou, R.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, M.; Bo, R.; Li, J. Moringa oleifera Leaf Polysaccharide Alleviates Experimental Colitis by Inhibiting Inflammation and Maintaining Intestinal Barrier. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1055791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeyohannes, M.G.; Eshete, G.T.; Abiye, A.A.; Hailu, A.E.; Huluka, S.A.; Tadesse, W.T. Antidiarrheal and Antisecretory Effect of 80% Hydromethanolic Leaf Extract of Moringa stenopetala Baker f. in Mice. Biochem. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5768805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adji, A.S.; Atika, N.; Kusbijantoro, Y.B.; Billah, A.; Putri, A.; Handajani, F. A Review of Leaves and Seeds Moringa oleifera Extract: The Potential Moringa oleifera as Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory, Antidiarrhoeal, and Antiulcer Approaches to Bacterial Gastroenteritis. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 10, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouki, L.; Rjeibi, I.; Taleb, J.; Zourgui, L. Cardiac Ameliorative Effect of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rat Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6583603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, H.; Kim, B.; Park, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.-H.; Sim, H.-C.; Do, H.-J.; Hyun, C.-K.; Do, M.-S. Fermented Moringa oleifera Decreases Hepatic Adiposity and Ameliorates Glucose Intolerance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alia, F.; Syamsunarno, M.; Sumirat, V.; Ghozali, M.; Atik, N. The Haematological Profiles of High Fat Diet Mice Model with Moringa oleifera Leaves Ethanol Extract Treatment. BioMed Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Metwally, F.; Rashad, H.; Zaazaa, A.; Ezzat, S.; Salama, M. Moringa oleifera Offers a Multi-Mechanistic Approach for Management of Obesity in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 29, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, S.M.; El Bishbishy, M.H.; Aborehab, N.M.; Salama, M.M.; Hasheesh, A.; Motaal, A.A.; Rashad, H.; Metwally, F.M. Upregulation of MC4R and PPAR-α Expression Mediates the Anti-Obesity Activity of Moringa oleifera Lam. in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrafi, M.M.; Vergara-Jimenez, M.; Murillo, A.G.; Norris, G.H.; Blesso, C.N.; Fernandez, M.L. Moringa Leaves Prevent Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Guinea Pigs by Reducing the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Khan, I.; Almutairi, N.S.; Almutairi, A.H.; Khan, B.; Mehboob, N. Effect of Moringa Leaves Powder on Body Weight, Glycemic Status, Lipid Profile, and Blood Pressure in Overweight Individuals with Hyperlipidemia. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2025, 37, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.F.; Arisha, A.H.; Al-Gamal, M.; Yahia, R.; Elsayed, A.A.; Saad, S.; El-Bohi, K.M. Moringa oleifera Leaves Extract Ameliorates Melamine-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Rats. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2020, 8, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekayev, M.; Bostancieri, N.; Saadat, K.A.S.M.; Turker, M.; Yuncu, M.; Ulusal, H.; Cicek, H.; Arman, K. Effects of Moringa oleifera Lam Extract (MOLE) in the Heat Shock Protein 70 Expression and Germ Cell Apoptosis on Experimentally Induced Cryptorchid Testes of Rats. Gene 2019, 688, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Ibrahim, K.G.; Ndhlala, A.R.; Erlwanger, K.H. Moringa oleifera Lam. Prevents the Development of High Fructose Diet-Induced Fatty Liver. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attah, A.F.; Akindele, O.O.; Nnamani, P.O.; Jonah, U.J.; Sonibare, M.A.; Moody, J.O. Moringa oleifera Seed at the Interface of Food and Medicine: Effect of Extracts on Some Reproductive Parameters, Hepatic and Renal Histology. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 816498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, N.; Nath, D.; Shukla, S.C.; Dyal, R. Abortifacient Activity of a Medicinal Plant Moringa oleifera. Anc. Sci. Life 1988, 7, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hajar, A.; Abdelmounaim, B.; Hamid, K.; Jaouad, L.; Abdelfattah, A.B.; Majda, B.; Loubna, E.Y.; Mohammed, L.; Rachida, A.; Abderrahman, C. Developmental Toxicity of Moringa oleifera and Its Effect on Postpartum Depression, Maternal Behavior and Lactation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 171, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.S.; Vishal, D.; Sumeet, G.; Shekhar, C.; Ashish, N.; Parul, D.; Ankita, S.; Prakash, A.; Prakash, T.; Kumar, P.; et al. Antifertility Activity of Ethanol Leaf Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam in Female Wistar Rats. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 80, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuogu, P.K.; Mgbere, O.O.; Bila, D.S.; McFarlane, J.R. Hormonal Changes, Semen Quality and Variance in Reproductive Activity Outcomes of Post Pubertal Rabbits Fed Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaf Powder. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 233, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-H.; Yang, X.-Y.; Lian, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Tao, S.-Y.; Liu, N.-N.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G.-J. Moringa oleifera Leaf Attenuate Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Rats by Modulating Gut Microbiota Composition and MAPK Signaling Pathway. BioMed Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, D.; Dai, J.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y. Exploration of Anti-Osteoporotic Peptides from Moringa oleifera Leaf Proteins by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics and Cellular Assay Analyses. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 116, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Siddiqui, S.; Barkat, M.d.A.; Alhodieb, F.S.; Ashfaq, F.; Barkat, H.A.; Alanezi, A.A.; Arshad, M. Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Induces Osteogenic-like Differentiation of Human Osteosarcoma SaOS2 Cells. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2022, 12, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, G.M.; Alluqmani, A.J.; Elsehemy, I.A.; Kalaba, M.H. Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Cytotoxicity, and Phytochemical Screening of Moringa oleifera Leaves. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Agrawal, D.; Sahu, P.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, S.; Patnaik, S. Analgesic Effect of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Moringa oleifera on Albino Mice. Indian J. Pain 2014, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hettiarachchy, S.N.; Horax, R.; Kannan, A.; Praisoody, M.D.A.; Muhundan, A.; Mallangi, C.R. Phytochemicals, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Hibiscus sabdariffa, Centella asiatica, Moringa oleifera and Murraya koenigii Leaves. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 6672–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedapo, A.A.; Mogbojuri, O.M.; Emikpe, B.O. Safety Evaluations of the Aqueous Extract of the Leaves of Moringa oleifera in Rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Awodele, O.; Oreagba, I.A.; Odoma, S.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Osunkalu, V.O. Toxicological Evaluation of the Aqueous Leaf Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. (Moringaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu-Gyekye, I.J.; Frimpong-Manso, S.; Awortwe, C.; Antwi, D.A.; Nyarko, A.K. Micro- and Macroelemental Composition and Safety Evaluation of the Nutraceutical Moringa oleifera Leaves. J. Toxicol. 2014, 2014, 786979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibade, T.O.; Arowolo, R.; Olayemi, F.O. Phytochemical Screening and Toxicity Studies on the Methanol Extract of the Seeds of Moringa oleifera. J. Combin. Theory Med. 2013, 10, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Aguilar, C.; Dominguez-Pacheco, A.; Valderrama-Bravo, C.; Cruz-Orea, A.; Ortiz, E.M.; Ivanov, R.; Ordonez-Miranda, J. Photoacoustic characterization of wheat bread mixed with Moringa oleifera. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuberti, G.; Bresciani, A.; Cervini, M.; Frustace, A.; Marti, A. Moringa oleifera L. leaf powder as ingredient in gluten-free biscuits: Nutritional and physicochemical characteristics. Eur. Food Res. Technology 2021, 247, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, R.D.; Landázuri, A.C.; Vernaza, M.G. Development of a cereal-based product using residual Moringa oleifera Lam. seed powder biomass and pseudo-plastic behavior of the dough mixtures. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 51, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira Nair, D.; James, T.J.; Sreelatha, S.L.; Kariyil, B.J.; Nair, S.N. Moringa oleifera (Lam.): A natural remedy for ageing? Nat. Product Res. 2020, 35, 6216–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumalaningsih, S.; Arwani, M. Nutritious pure herbal whitening suxcream processed from seed and leaf of Moringa oleifera fortified with Red Rice. Pharmacogn. J. 2018, 10, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://florafarma.com/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Available online: https://us.nuxe.com/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Available online: https://www.thebodyshop.bg/moringa (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Available online: https://makeup.bg/product/531425/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Available online: https://incidecoder.com/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Available online: https://thebalm.com/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Althomali, A.; Daghestani, M.H.; Almukaynizi, F.B.; Al-Zahrani, S.A.; Awad, M.A.; Merghani, N.M.; Bukhari, W.I.; Ibrahim, E.M.; Alzahrani, S.M.; Altowair, N.; et al. Anti-Colon Cancer Activities of Green-Synthesized Moringa Oleifera–AgNPs against Human Colon Cancer Cells. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.K.; Jarald, E.E.; Showkat, A.; Daud, A. In Vitro Evaluation of Moringa Oleifera Gum for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Moringaceae Tablet and Its Producing Method. CN 1935165, 22 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, R. Dietary Supplement Composition. WO2011098819, 18 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gokaraju, G.R. Synergistic Phytochemical Composition for the Treatment of Obesity. US 8541383 B2, 24 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vankwani, S.; Ansari, A.; Azhar, A.; Galani, S. Synergistic evaluation of Moringa oleifera extract and ß-lactam antibiotic to restore the susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hussien, S.H.; Nasry, A.R.; Samy, Z.; El-Sayed, S.M.; Bakry, A.; Ebeed, N.; Elhariry, H.; ElNoby, T. Synergistic Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Mixture of Moringa Oleifera, Cinnamomum Verum and Nigella Sativa against Staphylococcus Aureus Using L-Optimal Mixture Design. AMB Express 2025, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Invally, M.; Sanzagiri, R.; Buttar, H.S. Evaluation of the Antidepressant Activity of Moringa Oleifera Alone and in Combination with Fluoxetine. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2015, 6, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawoye, O.S.; Adeagbo, B.A.; Bolaji, O.O. Moringa Oleifera Leaf Powder Alters the Pharmacokinetics of Amodiaquine in Healthy Human Volunteers. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 43, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoukh, O.I.; Albadry, M.A.; Parveen, A.; Hawwal, M.F.; Majrashi, T.; Ali, Z.; Khan, S.I.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Khan, I.A. Isolation, Synthesis, and Drug Interaction Potential of Secondary Metabolites Derived from the Leaves of Miracle Tree (Moringa Oleifera) against CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 Isozymes. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 153010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumolosasi, E.; Cheong, M.L.C.; Ahmad Salwanizam, N.A.; Muhammad Esham, N.S.A.; Ayob, Q.A.; Ramasamy, R.; Govindan, H.; Md Redzuan, A.; Jasamai, M. Drug-Herb Interactions: Selected Antihypertensive Drugs with Moringa Oleifera Leaves Extract. Jimmy Swaggart Minist. 2022, 51, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

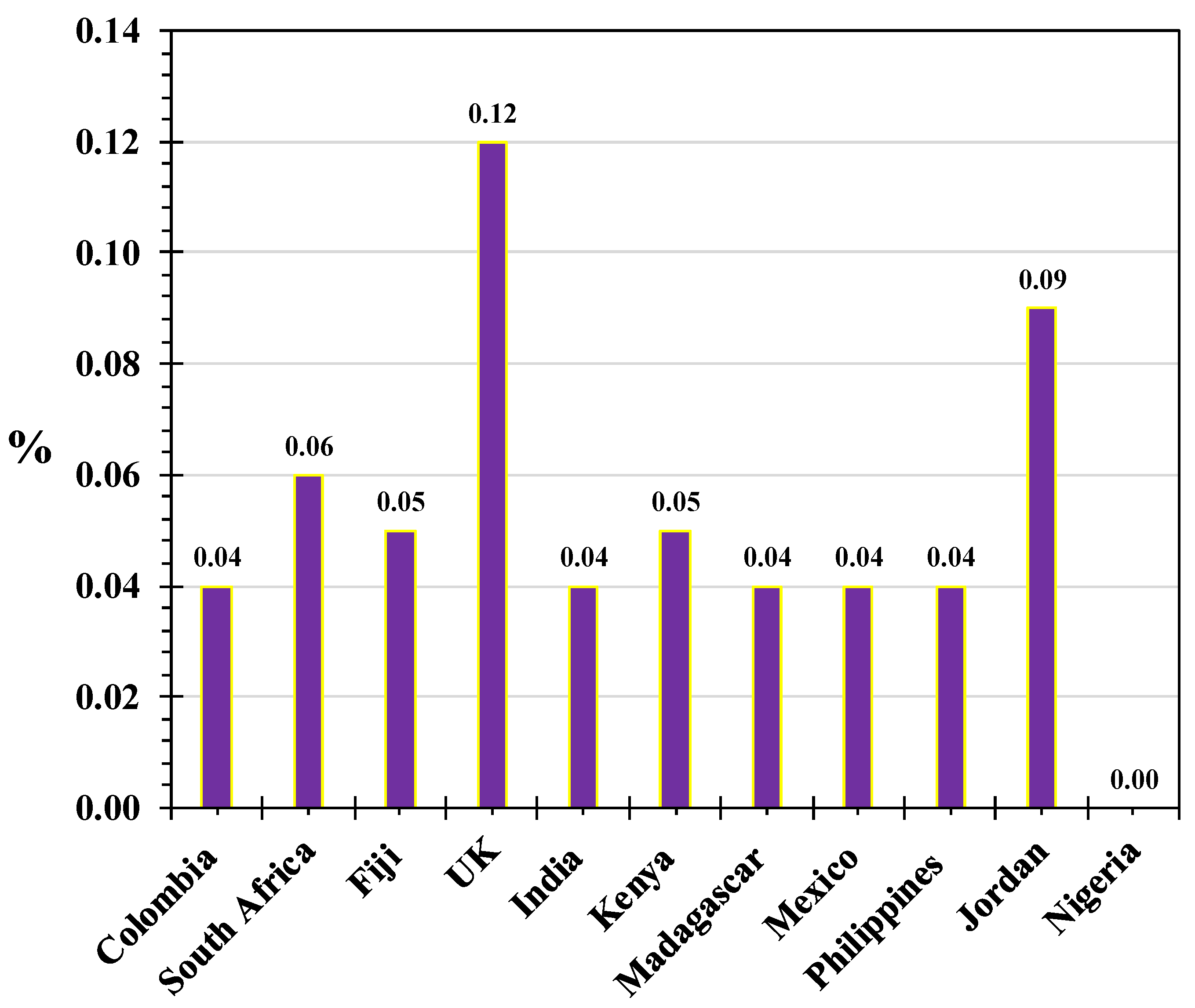

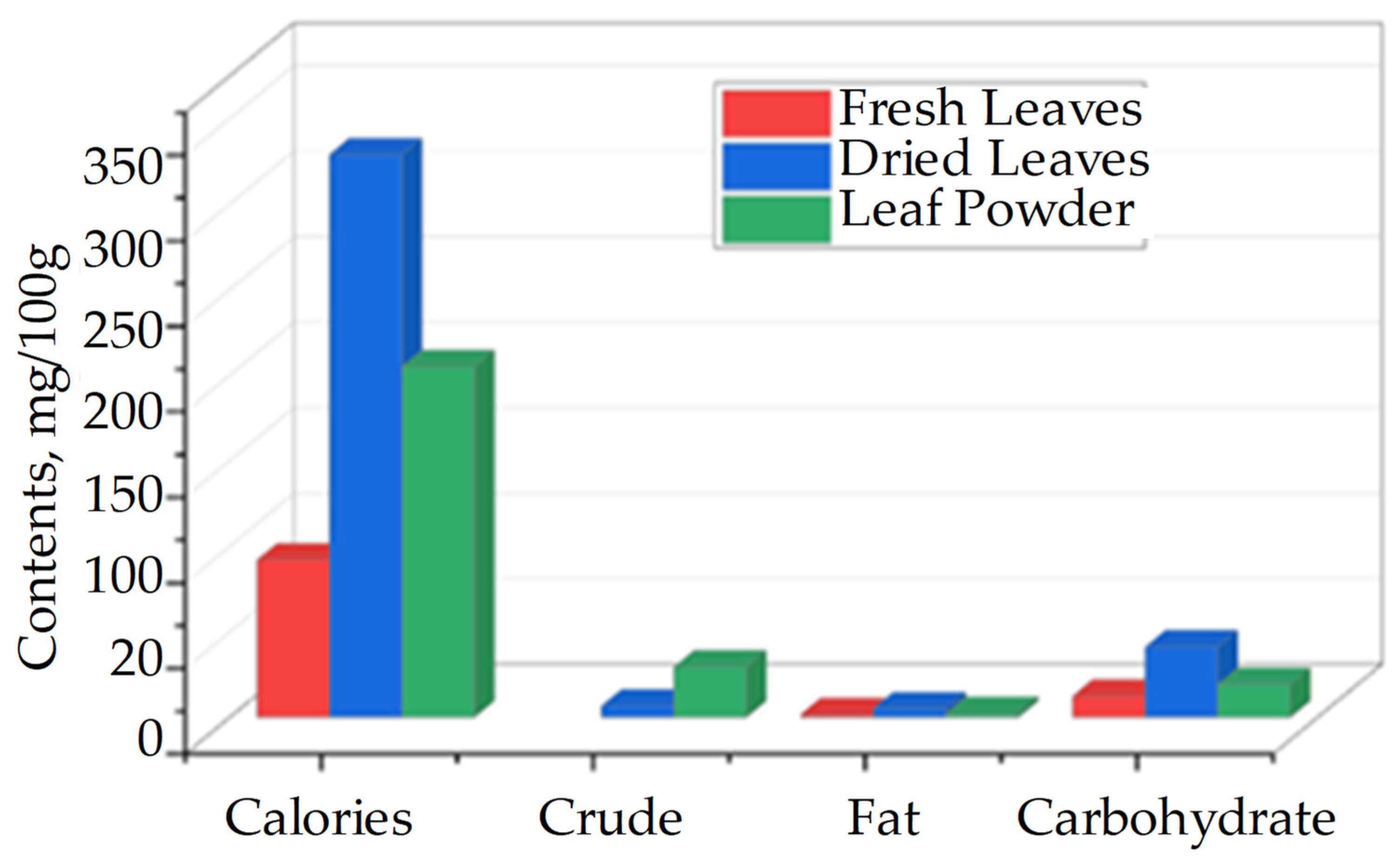
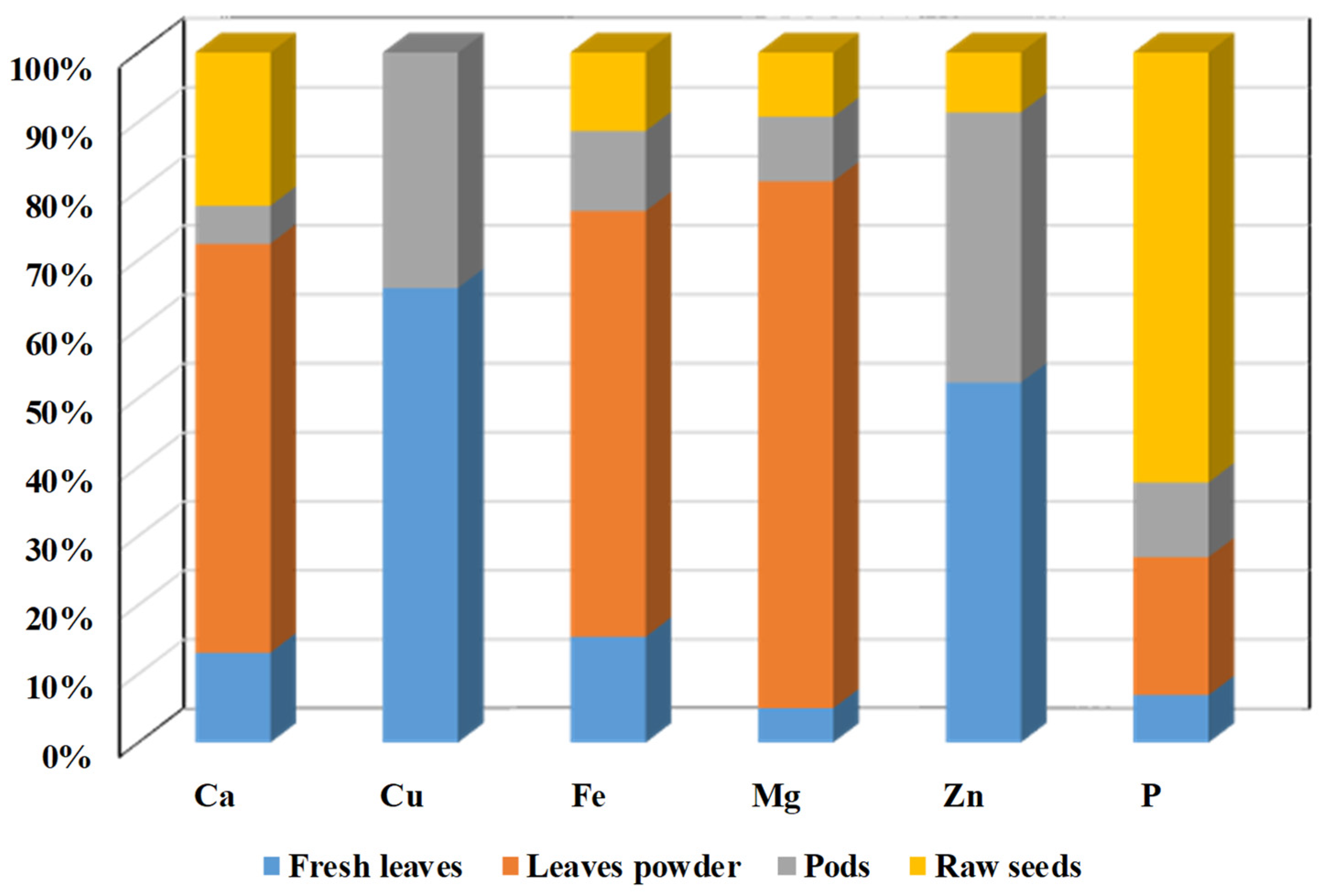
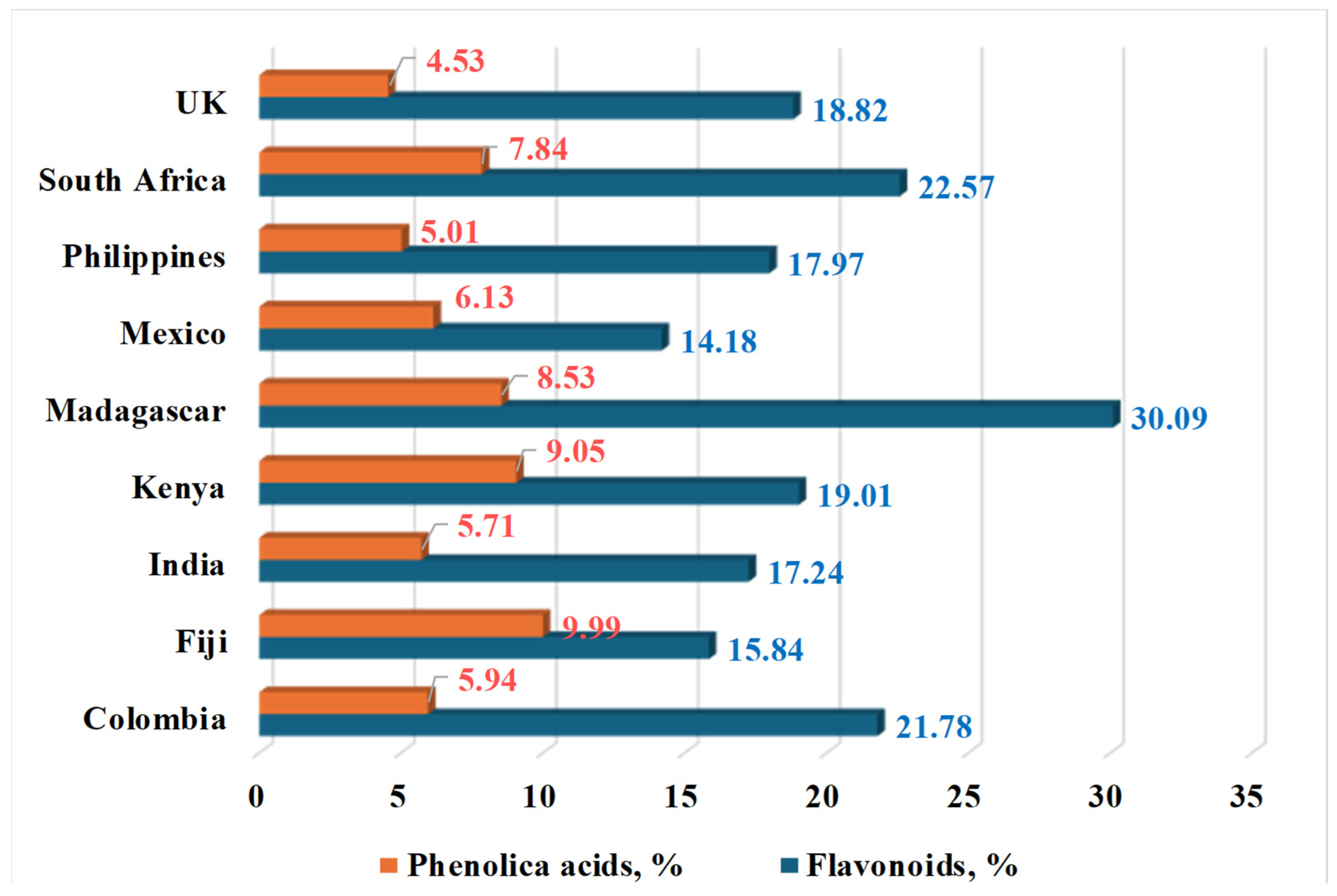
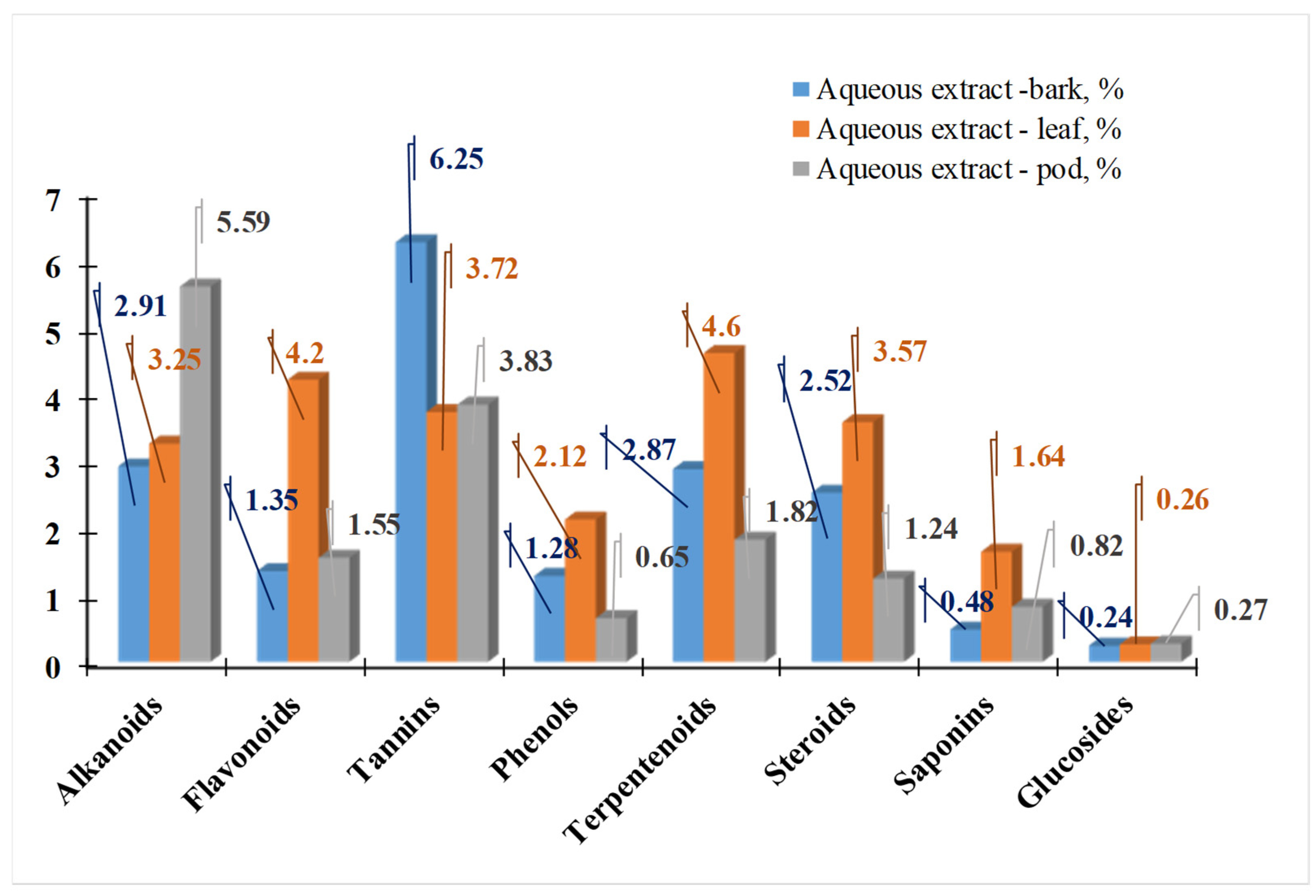

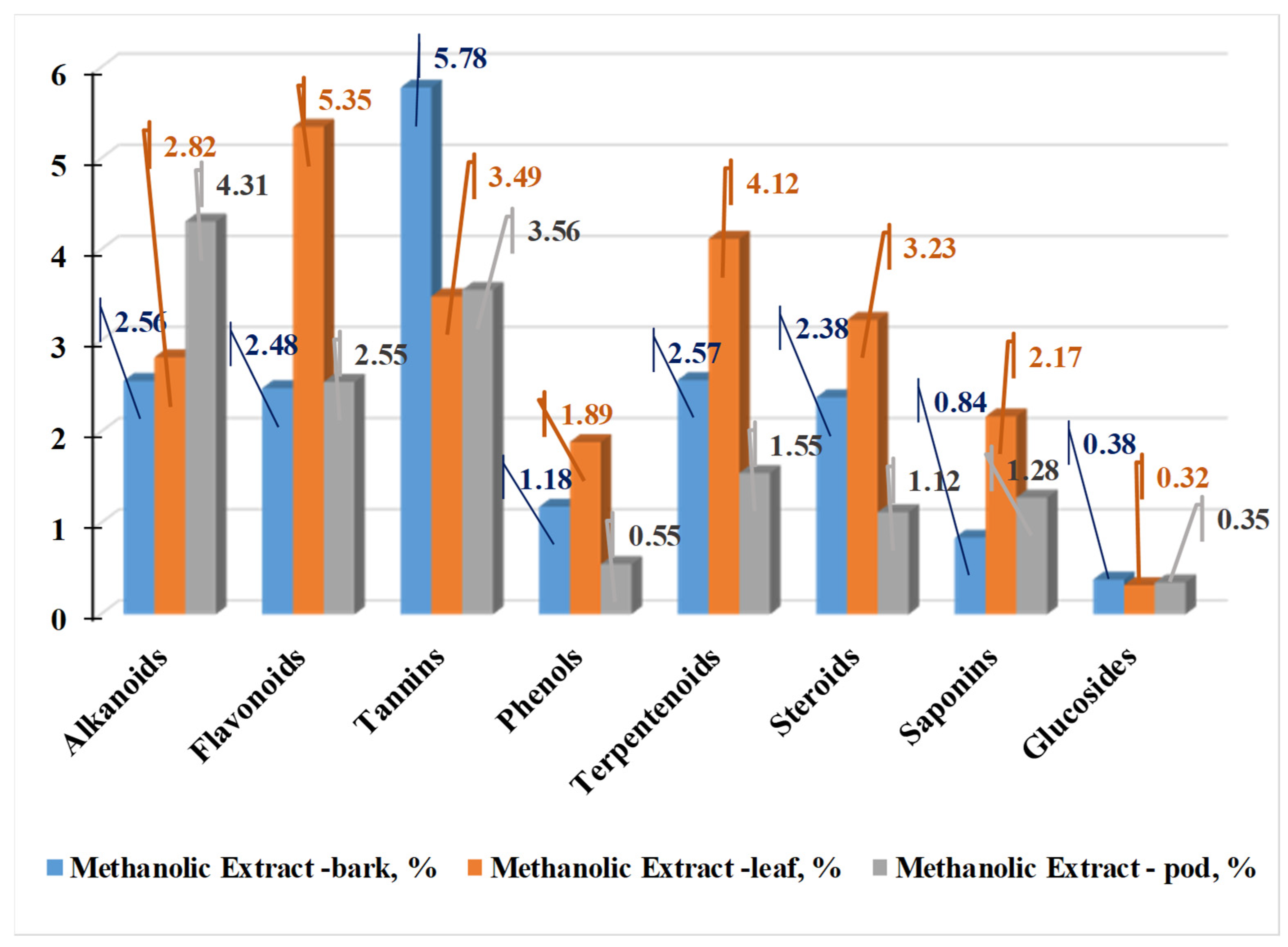
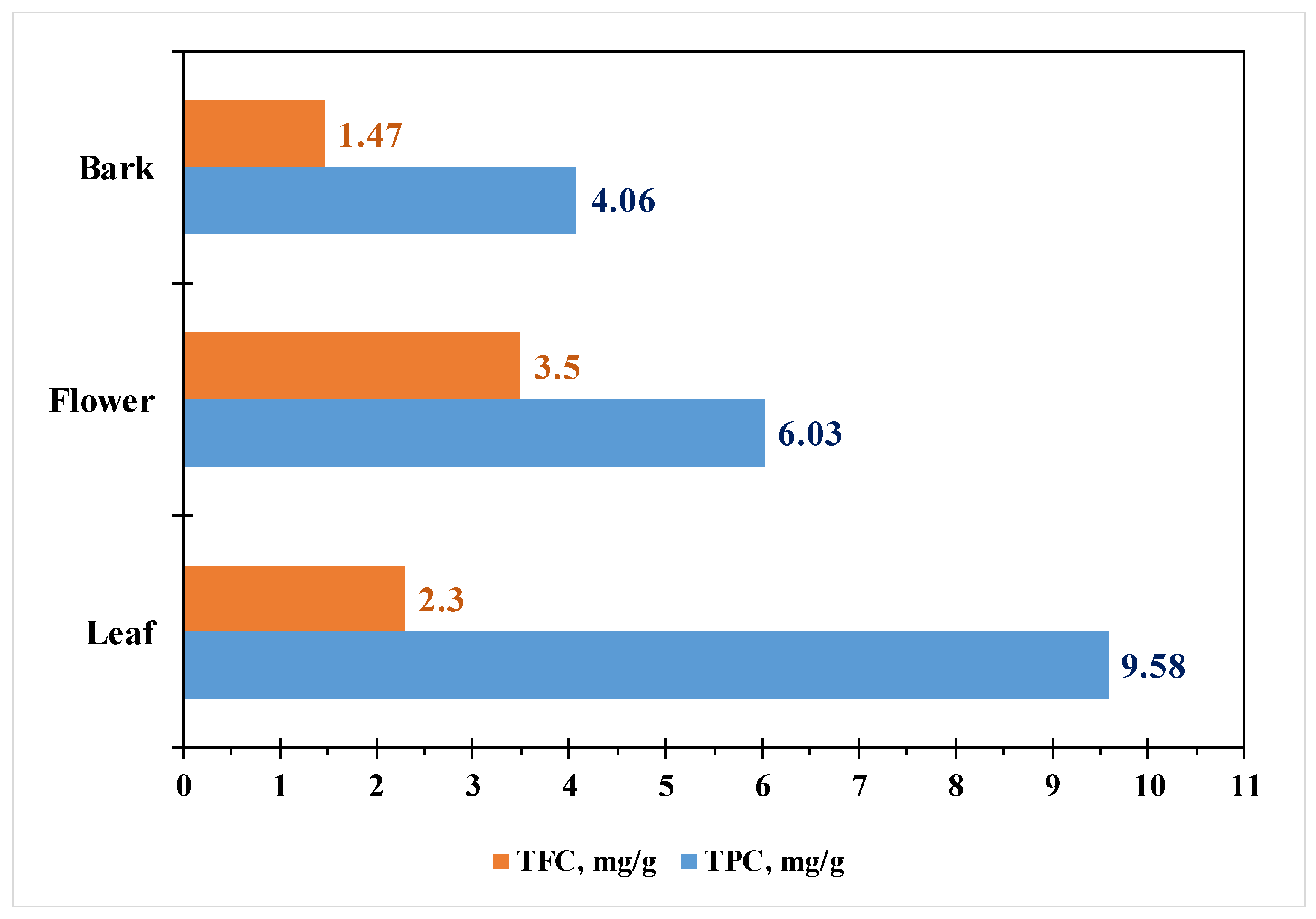

| Country | Language | Common Name(s) |
| Arab countries | Arabic | rawag |
| Bangladesh/India | Bengali | sujina, sohjna, sajina |
| East Africa | Swahili | mronge, mzunze, mlonge, mrongo |
| Ethiopia | Amharic | shiferaw |
| France | French | acacia blanc, neverdie, moringa ailé, ben ailé, pois quenique |
| Germany | German | pferderettichbaum, meerrettichbaum |
| Haiti/Martinique | Creole | patois |
| Hong Kong | Cantonese | nuge |
| India | Hindi | sanjna, suhujna, sondna, sohanjna, shajna, munga ara, sainjna, mungna |
| Laos | Lao | ‘ii h’um |
| Latin America | Spanish | paraíso blanco, paraíso francés, reseda |
| Malaysia | Malay | sajina, merunggai |
| Myanmar | Burmese | dan-da-lun, dandalonbin |
| Nepal | Nepali | shobhanjan, sohijan |
| Nigeria | Yoruba | ewe-igbale |
| Pakistan | Urdu | sahjnao |
| Thailand | Thai | makhonkom, ma-rum, phakihum |
| USA/UK/Other | English | moringa tree, ben-oil tree, cabbage tree, clarifier |
| Vietnam | Vietnamese | chùm ngây |
| Taxonomic Rank | Classification |
|---|---|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Subkingdom: | Tracheobionta |
| Superdivision: | Spermatophyta |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass: | Dilleniidae |
| Order: | Capparales |
| Family: | Moringaceae |
| Genus: | Moringa |
| Species: | Oleifera |
| Vitamins | mg/100 g | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Leaves | Dried Leaves | Leaf Powder | |
| A | 1.28 | 3.63 | 16.30 |
| B1 | 0.06 | 2.02 | 2.64 |
| B2 | 0.05 | 21.30 | 20.50 |
| C | 220.00 | 15.80 | 17.30 |
| E | 448.00 | 10.80 | 113.00 |
| Minerals | mg/100 g | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Leaves | Dried Leaves | Leaf Powder | |
| Calcium | 440.00 | 2185.00 | 2003.00 |
| Potassium | 259.00 | 1236.00 | 1324.00 |
| Magnesium | 42.00 | 448.00 | 368.00 |
| Phosphorus | 70.00 | 252.00 | 204.00 |
| Iron | 0.85 | 25.60 | 28.20 |
| Class Compounds | Plant Part | Phytoconstituent |
|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | Leaves | Apigenin, Apigenin-O-8-glucoside, Apigenin-7-C-glucoside, Astragalin, Daidzein, Genistein, Isoquercitrin, Isorhamnetin, Isorhamnetin 3-O-(6″-malonylglucoside), Kaempferide-3-O-(2″-O-galloyl rhamnoside), Kaempferol, Kaempferol-3-O-β-D-(6″-O-malonyl)-glucoside, Luteolin, Myricetin, Quercetin, Quercetin-3-acetylglucoside, Quercetin-O-3-glucoside, Quercetin-O-3,7-diglucoside, Rutin |
| Flowers | Rhamnetin, Isoquercitrin, Kaempferitrin | |
| Carbamates | Leaves | Niazinin A, Niazinin B, Niazimicin, Niazimimin A, Niazimimins B, Marumoside A, Marumoside B, Pterygospermin |
| Pods | Niazicin A, Niazidin, Niazinin A, S-Methyl-N-thiocarbamate, Pterygospermin | |
| Seeds | O-n-Butyl-4-[(α-l-rhamnopyranosyloxy)benzyl]thiocarbamate, O-Ethyl-4-[(α-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxybenzyl]thiocarbamate, N-[4-(β-l-Rhamnopyranosyl)benzyl]-1-O-α-d-glucopyranosyl-thiocarboxamide | |
| Roots | 1,3-Dibenzyl urea | |
| Phenolics | Leaves | Sinapic acid, Gentistic acid, Syringic acid, Chlorogenic acid, Cryptochlorogenic acid, 4-O-caffeoyl quinic acid, 5-O-caffeoyl quinic acid, Epicatechin, |
| Seeds | Gallic acid, p-Coumaric acid, Ferulic acid, Caffeic acid, Protocatechuic acid, Vanillin, Ellagic acid, Catechin, Moringyne | |
| Stems | 4-Hydroxymellein, p-Hydroxybenzoic acid, p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, trans-Ferulic acid, Lasiodiplodin | |
| Rootbark | p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, De-O-methyllasiodiplodin | |
| Glucosinolates | Leaves | Niazirin, Niazirinin |
| Pods | Sulforaphane, Methyl-1-aminopentasulfide-5-sulfinate | |
| Seeds | Niazirin, Glucomoringin, Glucosinalbin, Glucoraphanin, Glucoiberin, Glucobarbarin | |
| Roots | 4-O-(α-l-Acetylrhamnopyranosyloxy)-benzyl glucosinolate |
| Plant Part | Solvent Type | Assay | IC50 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Petroleum ether | DPPH | 42.56 μg/mL | [64] |
| Ethyl acetate | DPPH | 5.72 μg/mL | [64] | |
| Ethanol | DPPH | 1.87 mg/mL | [56] | |
| Ethanol | ABTS | 1.36 mg/mL | [56] | |
| Methanol | DPPH | 387.00 µg/mL | [61] | |
| Crude methanol | DPPH | 35.42 μg/L | [64] | |
| Dry leaves | Methanol | FRAP | 396.43 μmol TE/g | [65] |
| Dry leaves | Methanol | ORAC | 3197.24 μmol TE/g | [65] |
| Stems | Methanol | DPPH | 1116.00 µg/mL | [61] |
| Roots | Ethanol | DPPH | 3.31 mg/mL | [56] |
| Roots | Ethanol | ABTS | 1.24 mg/mL | [56] |
| Seeds | Ethanol | ABTS | 40.35 mg/mL | [56] |
| Crude methanol | DPPH | 91.13 μg/mL | [64] |
| Extract Type | Animal Model/Dose | Observed Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous leaf extract | 200 mg/kg (rat paw edema) | Inhibition of inflammation comparable to ibuprofen (40 mg/kg) using egg albumin-induced edema model | [48] |
| Aqueous leaf extract | 424 mg/kg (rat paw edema) | Similar anti-inflammatory effect to ibuprofen; egg albumin-induced model | [81] |
| 95% Ethanolic leaf extract | 1000 mg/kg (rat paw edema) | Reduced carrageenan-induced paw edema by 79% after 5 h, comparable to diclofenac | [76] |
| Methanolic leaf extract | 250 and 500 mg/kg (guinea pig model) | Anti-asthmatic effect; bronchodilation, ↓ WBC count and histamine in lungs (ovalbumin-sensitized) | [78] |
| Product | Manufacturer | Plant Part/Extract | Reported Purpose(s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swanson M. oleifera | Swanson Health Products, USA | Leaf extract | Antioxidant, supports immune function | [47] |
| Yango M. oleifera | Yango, Poland | Leaf extract | Anticancer and neuroprotective effects | [47] |
| Vitama Nature M. oleifera | Vitamin Nature, Germany | Leaf extract | Hematoprotective, antioxidant | [193] |
| Jiva Botanicals M. oleifera | Jiva Botanicals, USA | Leaf extract | Supports metabolic function | [47] |
| Natgrown M. oleifera leaf | Natgrown, USA | Leaf extract | Regulates blood sugar, antibacterial activity | [193] |
| M. oleifera bark extract capsules | Herbal Hills, India | Bark extract | Hepatoprotective, anticancer effects | [193] |
| Nature’s Way M. oleifera seed | Nature’s Way, Bulgaria | Seed extract | Antidiabetic effects | [193] |
| Organic M. oleifera root extract | Kuli Kuli, Canada | Root extract | Anti-inflammatory properties, immune stimulant | [193] |
| M. oleifera fruit powder | Grenera Nutrients, India | Fruit extract | Supports cardiovascular health | [194] |
| Product Description | Plant Part Used | Manufacturer Country | Reported Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wrinkle serum | Seeds | Italy | Anti-wrinkle, smoothing effect | [198] |
| Natural moringa oil | Seeds | Bulgaria | Hydrates, reduces wrinkles and scars | [199] |
| Micellar water | Seeds | France | Makeup removal, hydration, soothing | [200] |
| Moringa body yogurt | Seeds | United Kingdom | Skin hydration and softness | [201] |
| Facial cleansing foam | Seeds | Bulgaria | Skin purification, pollution removal | [202] |
| Oil body lotion | Seeds | India | Moisturizing and nourishing | [203] |
| Facial cleansing foam | Leaves | USA | Gentle cleansing, hydration support | [204] |
| Anti-aging facial therapy | Leaves | Italy | Hydration, firming, and wrinkle reduction | [198] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panova, N.; Gerasimova, A.; Gentscheva, G.; Nikolova, S.; Makedonski, L.; Velikova, M.; Beraich, A.; Talhaoui, A.; Petkova, N.; Batovska, D.; et al. Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Nutritional Powerhouse with Multifaceted Pharmacological and Functional Applications. Life 2025, 15, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060881
Panova N, Gerasimova A, Gentscheva G, Nikolova S, Makedonski L, Velikova M, Beraich A, Talhaoui A, Petkova N, Batovska D, et al. Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Nutritional Powerhouse with Multifaceted Pharmacological and Functional Applications. Life. 2025; 15(6):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060881
Chicago/Turabian StylePanova, Natalina, Anelia Gerasimova, Galia Gentscheva, Stoyanka Nikolova, Lubomir Makedonski, Margarita Velikova, Abdessamad Beraich, Abdelmonaem Talhaoui, Nadezhda Petkova, Daniela Batovska, and et al. 2025. "Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Nutritional Powerhouse with Multifaceted Pharmacological and Functional Applications" Life 15, no. 6: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060881
APA StylePanova, N., Gerasimova, A., Gentscheva, G., Nikolova, S., Makedonski, L., Velikova, M., Beraich, A., Talhaoui, A., Petkova, N., Batovska, D., & Nikolova, K. (2025). Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Nutritional Powerhouse with Multifaceted Pharmacological and Functional Applications. Life, 15(6), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060881










