Complex Transfemoral Access During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Narrative Review of Management, Complexity Scores, and Alternative Access
Abstract
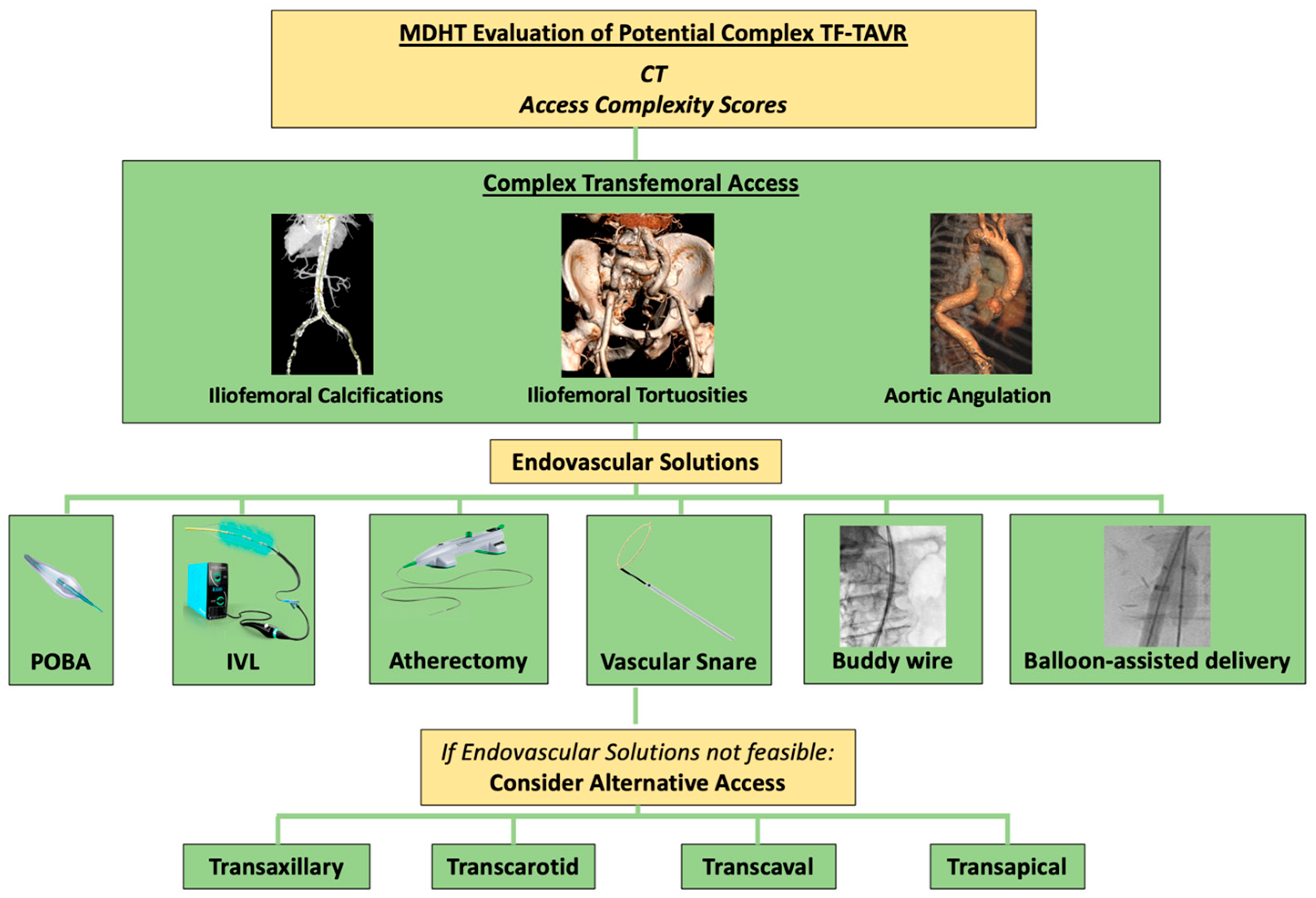
1. Introduction
2. Hostile Vascular Access
- Narrow Vessel Diameter:
- o
- Any segment of the arterial tree with a diameter less than 5.0 mm.
- Moderate Narrowing with Severe Calcification or Tortuosity:
- o
- Vessel diameter less than 5.5 mm, combined with:
- Severe calcification (270–360° circumferential calcification),
- Severe tortuosity (greatest angle of tortuosity <90°).
- Combination of Severe Calcification and Severe Tortuosity:
- o
- The coexistence of both severe calcification and severe tortuosity along the arterial pathway, regardless of vessel diameter.
3. Access Complexity Scores
3.1. Hostile Score
3.2. Passage–Puncture Score
4. Severely Calcified Peripheral Artery Disease Preparation
4.1. Intravascular Lithotripsy
4.2. Orbital Atherectomy
5. Severe Tortuosity Management
5.1. Aortic Angulation
5.2. Iliofemoral Tortuosity
6. Management of Aortic Wall Pathology (Aneurysm–Thrombus)
7. Complex Puncture Site Management
8. Alternative Access Sites for TAVR
8.1. Subclavian/Transaxillary Access (TAx)
8.2. Transcarotid Access
8.3. Transcaval Access
8.4. Rare Access (Transapical Access–Transaortic)
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| IVL | Intravascular Lithotripsy |
| MAE | Major Adverse Event |
| OA | Orbital Atherectomy |
| PAD | Peripheral Artery Disease |
| POBA | Plain Old Balloon Angioplasty |
| SAVR | Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement |
| TAVR | Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement |
| TAX | Transaxillary |
| TF-TAVR | Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement |
References
- Windecker, S.; Okuno, T.; Unbehaun, A.; Mack, M.; Kapadia, S.; Falk, V. Which patients with aortic stenosis should be referred to surgery rather than transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2729–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavaria, J.E.; Tommaso, C.L.; Brindis, R.G.; Carroll, J.D.; Deeb, G.M.; Feldman, T.E.; Gleason, T.G.; Horlick, E.M.; Kavinsky, C.J.; Kumbhani, D.J.; et al. 2018 AATS/ACC/SCAI/STS Expert Consensus Systems of Care Document: Operator and Institutional Recommendations and Requirements for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Joint Report of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Cardiology, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 340–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reinöhl, J.; Kaier, K.; Reinecke, H.; Schmoor, C.; Frankenstein, L.; Vach, W.; Cribier, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Bode, C.; Zehender, M. Effect of Availability of Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement on Clinical Practice. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbash, I.M.; Sharon, A. In the Garden of Forking Paths: Choosing Between Alternative Access for TAVR. Cardiovasc. Revasc Med. 2022, 40, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribier, A.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Bash, A.; Borenstein, N.; Tron, C.; Bauer, F.; Derumeaux, G.; Anselme, F.; Laborde, F.; Leon, M.B.; et al. Percutaneous Transcatheter Implantation of an Aortic Valve Prosthesis for Calcific Aortic Stenosis. Circulation 2002, 106, 3006–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the Management of Valvular Heart Disease: Developed by the Task Force for the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, R.R.; Thourani, V.H.; Mack, M.J.; Kodali, S.K.; Kapadia, S.; Webb, J.G.; Yoon, S.-H.; Trento, A.; Svensson, L.G.; Herrmann, H.C.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of Transcatheter or Surgical Aortic-Valve Replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, K.; Asturias, K.M.; Garg, J.; Poudyal, A.; Lantz, G.; Golwala, H.; Doberne, J.; Politano, A.; Song, H.K.; Zahr, F. Alternative Access for TAVR: Choosing the Right Pathway. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniloae, C.S.; Jilaihawi, H.; Amoroso, N.S.; Ibrahim, H.; Hisamoto, K.; Sin, D.N.; Williams, M.R. Systematic Transfemoral Transarterial Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Hostile Vascular Access. Structural Heart 2019, 3, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmerini, T.; Saia, F.; Kim, W.K.; Renker, M.; Iadanza, A.; Fineschi, M.; Bruno, A.G.; Ghetti, G.; Vanhaverbeke, M.; Søndergaard, L.; et al. Vascular Access in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease Undergoing TAVR: The Hostile Registry. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2023, 16, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garot, P.; Morice, M.C.; Angiolillo, D.J.; Cabau, J.R.; Park, D.W.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Collet, J.P.; Leon, M.B.; Sengottuvelu, G.; Neylon, A.; et al. Defining high bleeding risk in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A VARC-HBR consensus document. EuroIntervention 2024, 20, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmerini, T. The Hostile Score: A New Anatomical Tool to Predict Vascular Complications in Patients Undergoing TAVR. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2024, 17, 2364–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, M.; Tomii, D.; Samim, D.; Gräni, C.; Praz, F.; Lanz, J.; Stortecky, S.; Reineke, D.; Windecker, S.; Pilgrim, T. Impact of Severity and Extent of Iliofemoral Atherosclerosis on Clinical Outcomes in Patients Undergoing TAVR. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2024, 17, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Michel, J.; Stähli, B.E.; Templin, C.; Jakob, P.; Gilhofer, T.S.; Tanner, F.C.; Kasel, A.M. A Novel Risk Score Facilitates Femoral Artery Access in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Passage-Puncture Score. Struct. Heart 2024, 8, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VARC-3 Writing Committee; Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Alu, M.C.; Nazif, T.; Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Bax, J.J.; Leipsic, J.A.; Blanke, P.; et al. Valve Academic Research Consortium 3: Updated Endpoint Definitions for Aortic Valve Clinical Research. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1825–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, G.; De Backer, O.; Saia, F.; Søndergaard, L.; Ristalli, F.; Meucci, F.; Stolcova, M.; Mattesini, A.; Demola, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Peripheral intravascular lithotripsy for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A multicentre observational study. EuroIntervention 2022, 17, e1397–e1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyens, P.; Wong, I.; Vanhaverbeke, M.; Wang, X.; Bieliauskas, G.; Sondergaard, L.; De Backer, O. Intravascular Lithotripsy-Assisted Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 181, e63556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, F.J.; Bajoras, V.; Vanhaverbeke, M.; Wang, C.; Bieliauskas, G.; Søndergaard, L.; De Backer, O. Intravascular Lithotripsy-Assisted Transfemoral TAVI: The Copenhagen Experience and Literature Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 739750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sole, P.A.; Lunardi, M.; Andreaggi, S.; Fezzi, S.; Pesarini, G.; Scarsini, R.; Ribichini, F. Intravascular lithotripsy-assisted transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation after failed balloon angioplasty in patients with severe calcified peripheral artery disease. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2024, 36, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.; Grundmann, D.; Kellner, C.; Demal, T.; Waldschmidt, L.; Bhadra, O.; Ludwig, S.; Voigtländer, L.; von der Heide, I.; Nebel, N.; et al. Intravascular Lithotripsy-Assisted Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Patients with Severe Iliofemoral Calcifications: Expanding Transfemoral Indications. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Has, P.; Kassis, N.; Shippey, E.; Elkaryoni, A.; Gordon, P.C.; Sharaf, B.L.; Soukas, P.A.; Hyder, O.N.; Sellke, F.; et al. Characteristics, Trends, and Outcomes of Intravascular Lithotripsy-Assisted Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in United States. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2024, 17, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachutzik, F.; Meier, S.; Weissner, M.; Schlattner, S.; Gori, T.; Ullrich, H.; Gaede, L.; Achenbach, S.; Möllmann, H.; Chitic, B.; et al. Coronary intravascular lithotripsy and rotational atherectomy for severely calcified stenosis: Results from the ROTA.shock trial. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2023, 102, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaluski, E.; Khan, S.U.; Singh, M.; Reitknecht, F.; Sattur, S.; Rogers, G.; Sporn, D. Iliofemoral peripheral orbital atherectomy for optimizing TAVR access: An innovative strategy in the absence of alternative access options. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2018, 19, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliana, A.; Montarello, N.J.; Vanhaverbeke, M.; Willemen, Y.; Campens, L.; Sondergaard, L.; De Backer, O. Orbital atherectomy to facilitate transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with calcified iliofemoral arteries: A case series. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2023, 7, ytad310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauler-Wittwer, S.; Arcens, M.; Noble, S. Severe angulation of the descending aorta with a kink: Buddy wire is key for a successful transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Cardiol. J. 2024, 31, 778–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza Rueda, M.A.; Muratalla González, R.; García García, J.F.; Morales Portano, J.D.; Alcántara Meléndez, M.A.; Jiménez Valverde, A.S.; Rivas Gálvez, R.E.; Campos Delgadillo, J.L.; González, C.L.; Gayosso Ortiz, J.R.; et al. Description of the Step-by-Step Technique with Snare Catheter for TAVR in Horizontal Aorta. JACC Case Rep. 2021, 3, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesario, V.; De Biase, C.; Tchetche, D. Available online: https://www.pcronline.com/Cases-resources-images/Tools-and-Practice/My-Toolkit/2024/How-to-deal-with-ilio-femoral-tortuosity-during-TAVI-procedure-the-buddy-wire-technique-to-straighten-the-pathway (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Kadoya, Y.; Zen, K.; Kuwabara, K.; Ito, N.; Nakamura, T.; Matoba, S. Balloon-assisted sheath insertion technique for transfemoral aortic valve replacement through an aortoiliac endograft. Cardiovasc. Interv. Ther. 2019, 34, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Lazkani, M.; Moualla, S.; Orazio, A.; Tasset, M.; Morris, M.; Fang, K.; Pershad, A. Impact of aortic aneurysms in trans-catheter aortic valve replacement: A single center experience. Indian. Heart J. 2018, 70 (Suppl. S3), S303–S308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.; Al-Taweel, O.; Fakhra, S.; Nadeem-Tariq, A.; Hawwass, D.; Ahsan, C. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients with a concomitant aortic aneurysm. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, ehac544-1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.; Maxo, L.; Lohse, T.; Mangin, L.; Courand, P.Y.; Ricard, C.; Bouali, A.; Boussel, L.; Aktaa, S.; Ali, N.; et al. Association Between Aortic Wall Thrombus and Thromboembolic Events After Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2024, 17, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, S.; Nnaoma, C.B.; Retcho, D.E.; Girgis, K.; Wats, A.; Tayal, R.; Wasty, N. High Common Femoral Artery Bifurcation in Patients Being Evaluated for TAVR. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2024, 83 (Suppl. S13), 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Dumpies, O.; Shibata, M.; Hartung, P.; Obradovic, D.; Boekstegers, P.; Vorpahl, M.; Rotta Detto Loria, J.; Kiefer, P.; Desch, S.; et al. Femoral Arterial Calcification and Plug- vs. Suture-Based Closure Device Strategies Post-Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Insights from CHOICE-CLOSURE. Struct. Heart. 2023, 8, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.; Lahr, B.D.; Greason, K.L.; Arghami, A.; Gulati, R.; Eleid, M.F.; Crestanello, J.A. Obesity and vascular complication in percutaneous transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve insertion. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2023, 101, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Li, W.; Safiriyu, I.; Kharawala, A.; Nagraj, S.; Tahir, A.; Doundoulakis, I.; Koliastasis, L.; Rios, S.; Palaiodimos, L.; et al. A Meta-Analysis on the Impact of High BMI in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagrosso, M.; Cavallo, E.; Bracale, U.M.; Peluso, A.; Silvestri, O.; Intrieri, F.; Molinari, V.; Esposito, A.; Trimarchi, S.; Settembrini, A.M.; et al. Collagen-Based Vascular Closure Device Multicenter Italian Experience in Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair Compared with Suture-Mediated Closure Vascular Device. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2024, 1177, 15266028241275804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosseel, L.; Mylotte, D.; Cosyns, B.; Vanhaverbeke, M.; Zweiker, D.; Teles, R.C.; Angerås, O.; Neylon, A.; Rudolph, T.K.; Wykrzykowska, J.J.; et al. Contemporary European practice in transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Results from the 2022 European TAVI Pathway Registry. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1227217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Saadat, S.; Soin, A.; Kawabori, M.; Chen, F.Y. A meta-analysis comparing transaxillary and transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 5140–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wely, M.; van Nieuwkerk, A.C.; Rooijakkers, M.; van der Wulp, K.; Gehlmann, H.; Verkroost, M.; van Garsse, L.; Geuzebroek, G.; Baz, J.A.; Tchétché, D.; et al. Transaxillary versus transfemoral access as default access in TAVI: A propensity matched analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 394, 131353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.S.; Rawasia, W.F.; Siddiqi, T.J.; Mujeeb, F.A.; Nadeem, S.; Alkhouli, M. Meta-analysis evaluating the safety and efficacy of transcarotid transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 124, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.; Sous, M.; Sedhom, R.; Megaly, M.; Roman, S.; Sweeney, J.; Alkhouli, M.; Pollak, P.; El Sabbagh, A.; Garcia, S.; et al. Meta-analysis on transcarotid versus transfemoral and other alternate accesses for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 192, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirker, E.B.; Hodson, R.W.; Spinelli, K.J.; Korngold, E.C. The carotid artery as a preferred alternative access route for transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, F.; Akodad, M.; Macia, J.C.; Gandet, T.; Lattuca, B.; Schmutz, L.; Gervasoni, R.; Nogue, E.; Nagot, N.; Levy, G.; et al. Vascular Complications and Bleeding After Transfemoral Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Performed Through Open Surgical Access. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, A.B.; Babaliaros, V.C.; Chen, M.Y.; Stine, A.M.; Rogers, T.; O’Neill, W.W.; Paone, G.; Thourani, V.H.; Muhammad, K.I.; Leonardi, R.A.; et al. Transcaval Access and Closure for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Prospective Investigation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbash, I.M.; Segev, A.; Berkovitch, A.; Fefer, P.; Maor, E.; Elian, D.; Regev, E.; Guetta, V. Clinical outcome and safety of transcaval access for transcatheter aortic valve replacement as compared to other alternative approaches. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 731639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, R.J.; Babaliaros, V.C.; Lisko, J.C.; Rogers, T.; Mahoney, P.; Foerst, J.R.; Depta, J.P.; Muhammad, K.I.; McCabe, J.M.; Pop, A.; et al. Transcaval versus transaxillary TAVR in contemporary practice: A propensity-weighted analysis. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 15, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochos, P.; Kirsch, M.; Monney, P.; Tzimas, G.; Meier, D.; Fournier, S.; Ferlay, C.; Nowacka, A.; Rancati, V.; Abellan, C.; et al. Transcaval versus supra-aortic vascular accesses for transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thourani, V.H.; Jensen, H.A.; Babaliaros, V.; Suri, R.; Vemulapalli, S.; Dai, D.; Brennan, J.M.; Rumsfeld, J.; Edwards, F.; Tuzcu, E.M.; et al. Transapical and transaortic transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the United States. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 1718–1726; discussion 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofler, M.; Reinstadler, S.J.; Stastny, L.; Dumfarth, J.; Reindl, M.; Wachter, K.; Rustenbach, C.J.; Müller, S.; Feuchtner, G.; Friedrich, G.; et al. EuroSCORE II and the STS score are more accurate in transapical than in transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 26, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, A.; Tessari, C.; Tarantini, G.; Cibin, G.; Lorenzoni, G.; Pesce, R.; Fraccaro, C.; Napodano, M.; Gregori, D.; Gerosa, G. Transapical TAVI: Survival, Hemodynamics, Devices and Machine Learning. Lessons Learned After 10-Year Experience. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Score | Variable | Description | Points/Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hostile Score | Number of segments with significant disease | Each affected segment | 1 point per segment |
| Presence of obstruction | 100% stenosis in any segment | 2 points | |
| Iliac disease involving the aortic bifurcation | Atherosclerotic disease at aortic bifurcation | 0.5 points | |
| Lesion in tortuous segment (tortuosity > 90°) | Significant disease in tortuous segments | 1 point per segment | |
| ≥180° arc calcified lesion | Significant calcified lesion with an arch ≥ 180° | 1 point per lesion | |
| Lesion length ≤ 100 mm | Short-segment calcification | 1 point | |
| Lesion length 101–200 mm | Intermediate-length lesion | 2 points | |
| Lesion length > 200 mm | Long lesion segment | 3 points | |
| Minimal lumen diameter 3.1–5.0 mm | Mild narrowing | 0.5 points | |
| Minimal lumen diameter 0.1–3.0 mm | Severe narrowing | 1 point | |
| Passage Score | Minimal lumen diameter | Narrowest point of the access artery | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) |
| Calcification length | Length of calcified segments along the artery | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) | |
| Maximal calcification thickness | Thickness of the most severe calcified plaque | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) | |
| Vessel tortuosity | Presence of double iliac sign or high tortuosity index (with calcification) | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) | |
| Puncture Score | Bifurcation height | Position of femoral bifurcation relative to puncture site | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) |
| Calcification orientation | Circumferential location and severity of calcifications | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) | |
| Calcification-free vessel length | Distance from puncture site to nearest calcium | 0 (favorable), 1 (challenging), 2 (unfavorable) |
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Plain Old Balloon Angioplasty (POBA) | High immediate technical success | High rates of flow-limiting dissections |
| Easy to use | Vascular recoil and residual stenosis | |
| Efficacious for lesions < 100 mm | High restenosis rate | |
| Vessel tortuosity | Presence of double iliac sign or high tortuosity index (with calcification) 2 | |
| Atherectomy | Useful for vessel preparation before balloon or drug-covered balloon angioplasty | Risk of distal embolization |
| Less operator familiarity | ||
| Reduces inflation pressures and risk of dissections | High procedural cost | |
| Not widely available | ||
| Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) | Useful for vessel preparation before balloon or drug-covered balloon angioplasty | Each affected segment |
| Reduces inflation pressures and risk of dissections | Requires more technical expertise | |
| Less operator familiarity |
| Parameter | Measurement/Condition | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Minimal Luminal Diameter (MLD) | Reported at site of most critical stenosis | Determines feasibility of IVL |
| Maximal Luminal Diameter | Measured perpendicular to the vessel axis | Helps calculate mean lumen diameter |
| Mean Luminal Diameter | (Maximal diameter + minimal diameter)/2 | Provides overall vessel dimension |
| Vessel Area | Measured at stenotic site | Assesses severity of narrowing |
| Vessel Tortuosity | Evaluated along the iliofemoral course | High tortuosity may increase procedural complexity |
| Calcification Arc | 360° or 270° (horseshoe-shaped) | Affects vessel expandability for sheath insertion |
| Calcification Length | Localized (<20 mm) vs. diffuse (>20 mm) | Influences MLD requirements for IVL eligibility |
| Calcium Blooming Artifacts | Can lead to overestimation of calcification severity | Requires windowing correction for accuracy |
| Femoral Artery Puncture Site | Presence of an anterior calcium-free window | Crucial for vascular closure and sheath insertion |
| Calcification Pattern | Minimal Luminal Diameter Requirement | Suitability for IVL-Assisted TF-TAVR |
| Localized Calcification (<20 mm length) | ||
| −360° Circumferential | ≥4.0 mm | Suitable |
| −270° Horseshoe-Shaped | ≥3.0 mm | Suitable |
| Diffuse Calcification (>20 mm length) | ||
| −360° Circumferential | ≥4.5 mm | Suitable |
| −270° Horseshoe-Shaped | ≥3.5 mm | Suitable |
| Severe Calcification with MLD < 3.0 mm | <3.0 mm | Not suitable for IVL, consider alternative access |
| Irregular or Extensive Eccentric Calcification | Severe asymmetric calcium distribution | Not optimal, higher procedural risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skalidis, I.; Sayah, N.; Unterseeh, T.; Hovasse, T.; Sanguineti, F.; Garot, P.; Lounes, Y.; Neylon, A.; Akodad, M. Complex Transfemoral Access During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Narrative Review of Management, Complexity Scores, and Alternative Access. Life 2025, 15, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050810
Skalidis I, Sayah N, Unterseeh T, Hovasse T, Sanguineti F, Garot P, Lounes Y, Neylon A, Akodad M. Complex Transfemoral Access During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Narrative Review of Management, Complexity Scores, and Alternative Access. Life. 2025; 15(5):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050810
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkalidis, Ioannis, Neila Sayah, Thierry Unterseeh, Thomas Hovasse, Francesca Sanguineti, Philippe Garot, Youcef Lounes, Antoinette Neylon, and Mariama Akodad. 2025. "Complex Transfemoral Access During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Narrative Review of Management, Complexity Scores, and Alternative Access" Life 15, no. 5: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050810
APA StyleSkalidis, I., Sayah, N., Unterseeh, T., Hovasse, T., Sanguineti, F., Garot, P., Lounes, Y., Neylon, A., & Akodad, M. (2025). Complex Transfemoral Access During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Narrative Review of Management, Complexity Scores, and Alternative Access. Life, 15(5), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050810






