Association Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Overall and Site-Specific Cancers (Pancreatic, Liver, Thyroid, Lung): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Registration Information
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
- (1)
- Duplicate literature.
- (2)
- Review articles or meta-analyses.
- (3)
- Protocols or guidelines.
- (4)
- Conference abstracts or letters.
- (5)
- Animal studies.
- (6)
- Mechanism studies.
- (7)
- Irrelevant studies.
- (8)
- Abstract only, full text not available.
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Quality Assessment
2.7. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Compliance with the Registered Protocol
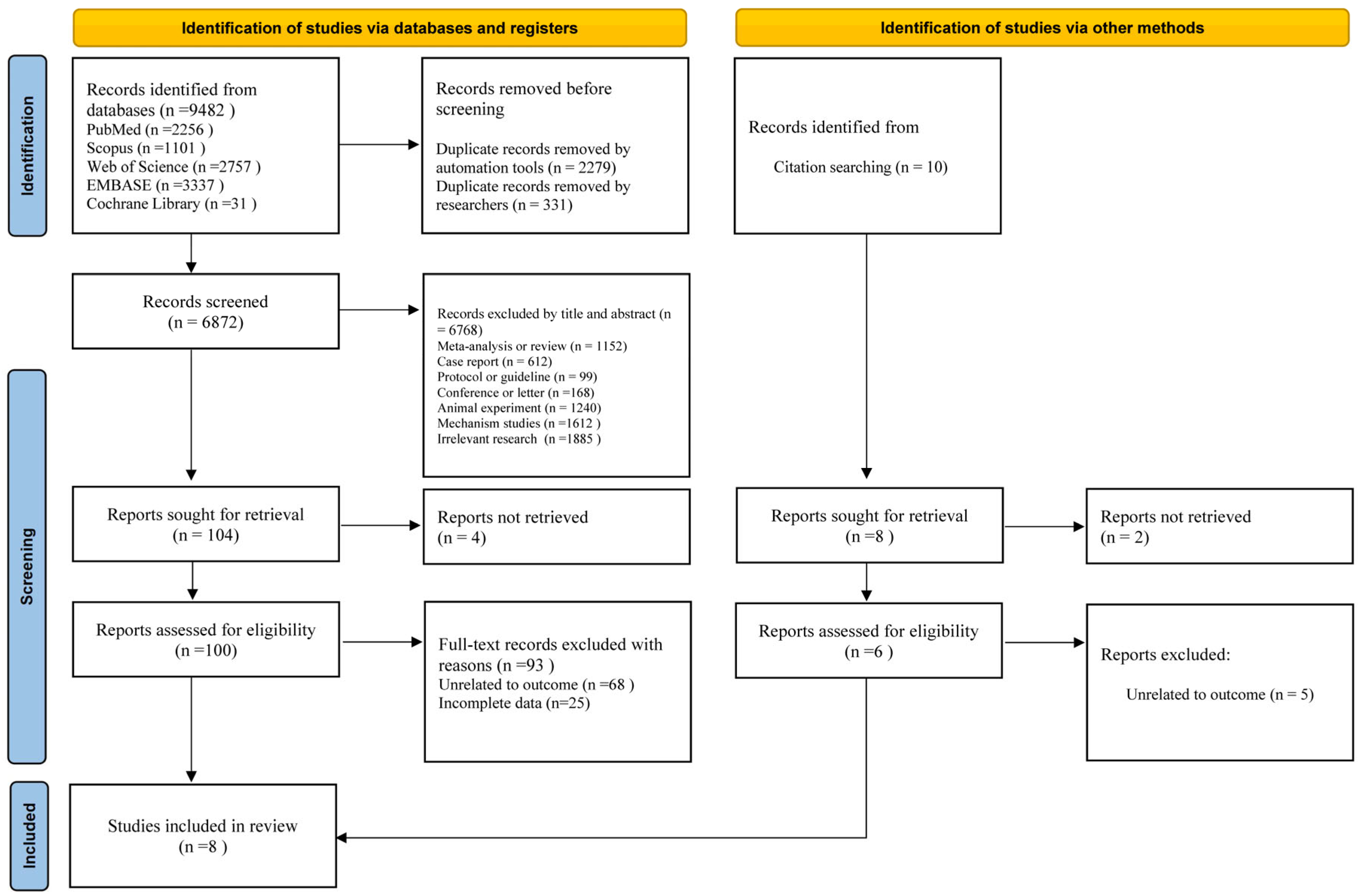
3.2. Study Selection
3.3. Study Characteristics
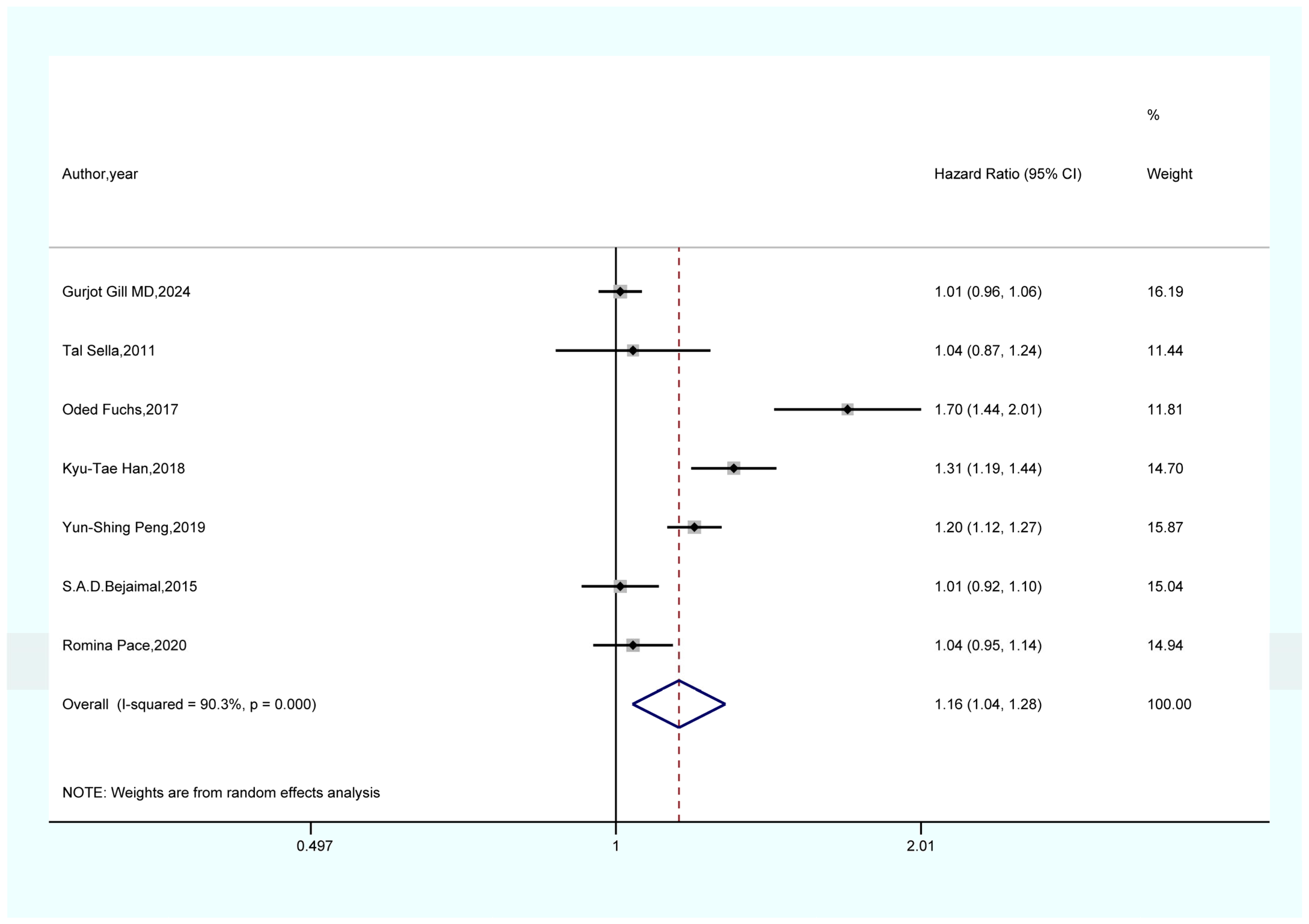
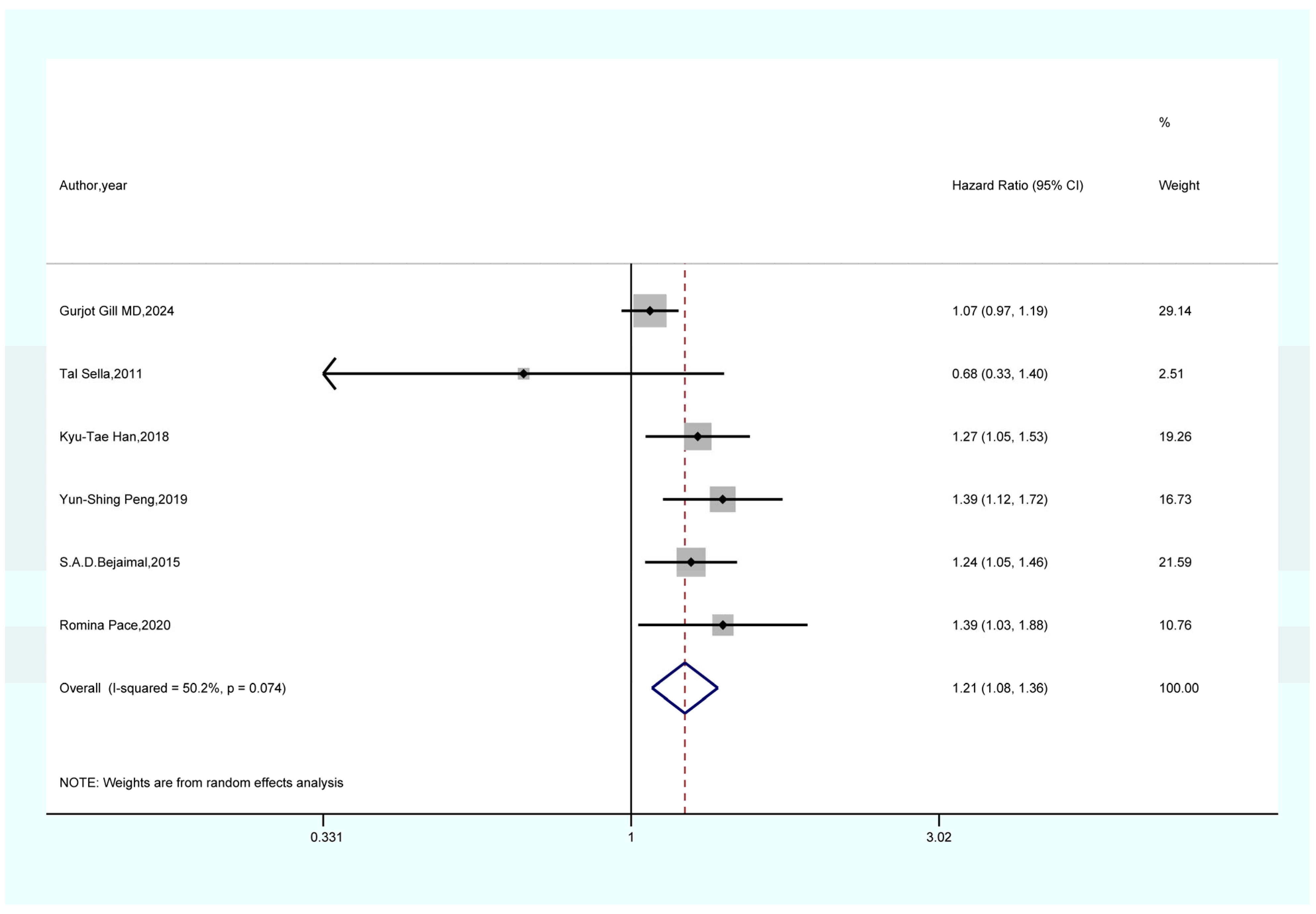
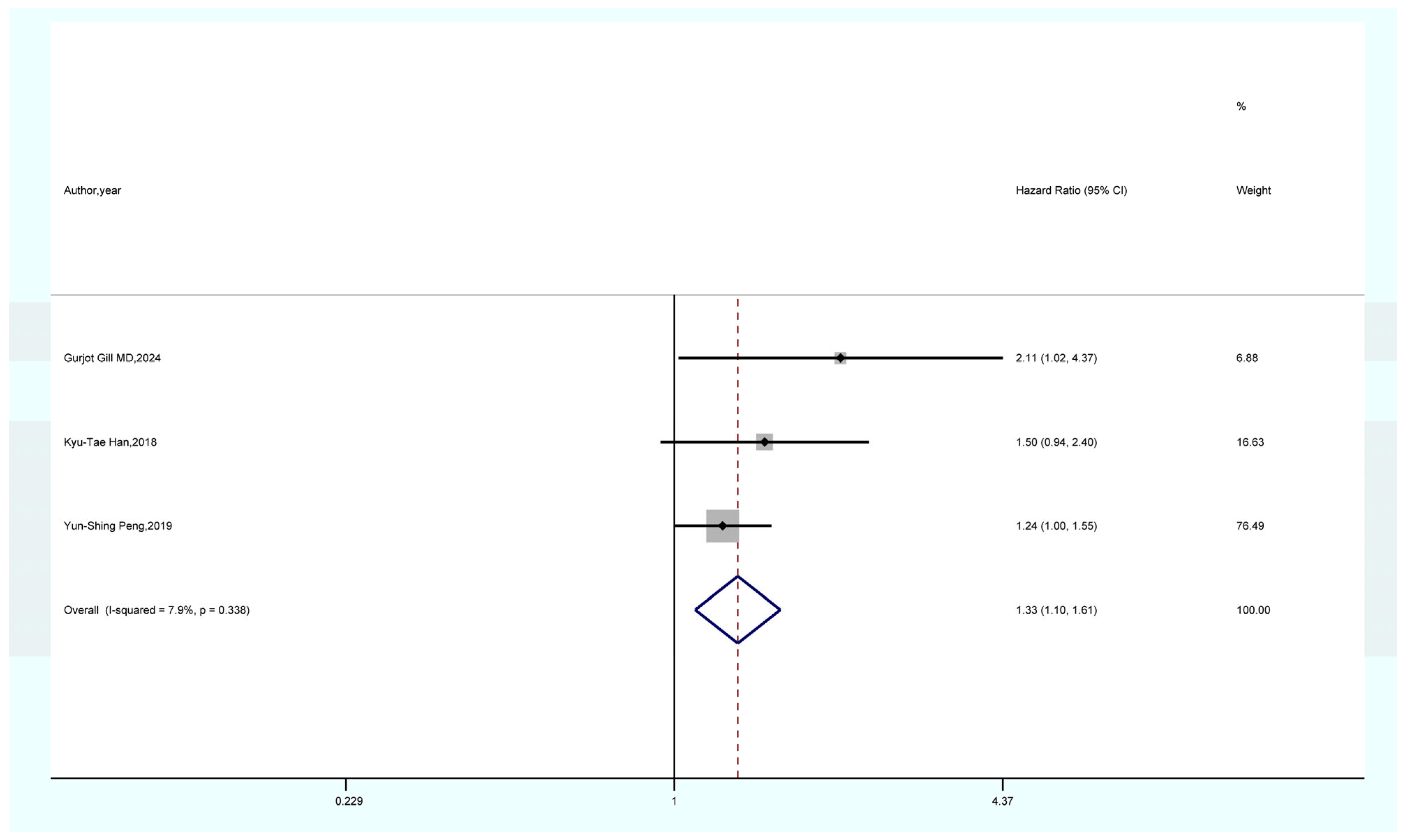
3.4. Outcomes of the Meta-Analysis
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3.6. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Mechanisms of GDM and Cancer
4.1.1. GDM and Overall Cancer
4.1.2. GDM and Pancreatic Cancer
4.1.3. GDM and Thyroid Cancer
4.1.4. GDM and Liver Cancer
4.2. Comparison with the Published Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
4.3. Limitations and Strengths
- (1)
- Most of the included studies were observational, which may be subject to confounding factors and biases.
- (2)
- Variations in the definitions and diagnosis codes of GDM and cancer across different studies could potentially affect the accuracy of the results.
- (3)
- The limited number of studies meeting the criteria and included in the analysis hindered the possibility of conducting subgroup analyses based on study characteristics such as age, region, and follow-up time, thereby impeding the exploration of sources of heterogeneity.
- (4)
- The included studies differed in terms of the types and numbers of cancers investigated, with some covering multiple cancers and others focusing on a single type. Due to the limited number of studies, sensitivity analysis and publication bias testing could not be performed for liver and lung cancer data, requiring caution in interpreting the results. Future studies with larger sample sizes are needed for further validation.
- (1)
- The results of the sensitivity analysis demonstrate the robustness and reliability of our primary findings, including the associations between GDM and overall cancer, pancreatic cancer, and thyroid cancer. Both Begg’s and Egger’s tests did not indicate any publication bias.
- (2)
- This study represents the first meta-analysis to investigate the relationship between GDM and the risk of overall cancer, providing valuable guidance for clinical practice.
- (3)
- Furthermore, this study explores the potential underlying mechanisms between GDM and cancer, offering a stronger theoretical foundation to support the research conclusions.
4.4. Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Buchanan, T.A.; Catalano, P.A.; Damm, P.; Dyer, A.R.; Leiva, A.; Hod, M.; Kitzmiler, J.L.; et al. International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.; Kjos, S.L.; Watanabe, R. What is gestational diabetes? Diabetes Care 2007, 30 (Suppl. S2), S105–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eades, C.E.; Cameron, D.M.; Evans, J.M.M. Prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus in Europe: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 129, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM). Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/data-by-indicator/hyperglycaemia-in-pregnancy-hip-20-49-y/prevalence-of-gestational-diabetes-mellitus-gdm/ (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Preston, E.V.; Eberle, C.; Brown, F.M.; James-Todd, T. Climate factors and gestational diabetes mellitus risk—A systematic review. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Levi, A.; Barabash, A.; Valerio, J.; García de la Torre, N.; Mendizabal, L.; Zulueta, M.; de Miguel, M.P.; Diaz, A.; Duran, A.; Familiar, C.; et al. Genetic variants for prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus and modulation of susceptibility by a nutritional intervention based on a Mediterranean diet. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1036088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustianowski, P.; Malinowski, D.; Czerewaty, M.; Safranow, K.; Tarnowski, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Pawlik, A. THADA, SDHAF4, and MACF1 Gene Polymorphisms and Placental Expression in Women with Gestational Diabetes. Genes 2022, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Aqel, Y.; Alnesf, A.; Aigha, I.I.; Islam, Z.; Kolatkar, P.R.; Teo, A.; Abdelalim, E.M. Glucokinase (GCK) in diabetes: From molecular mechanisms to disease pathogenesis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitzgebel, V.M.; Blouin, J.L.; Dehos, B.; Köhler-Ballan, B.; Puder, J.J.; Rieubland, C.; Triantafyllidou, M.; Zanchi, A.; Abramowicz, M.; Nouspikel, T. Enhancing fetal outcomes in GCK-MODY pregnancies: A precision medicine approach via non-invasive prenatal GCK mutation detection. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1347290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.P.; Hauguel-De Mouzon, S.; Lepercq, J.; Challier, J.C.; Huston-Presley, L.; Friedman, J.E.; Kalhan, S.C.; Catalano, P.M. TNF-alpha is a predictor of insulin resistance in human pregnancy. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, L.A. New concepts in insulin resistance of pregnancy and gestational diabetes: Long-term implications for mother and offspring. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2003, 23, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, C. Insulin secretion and insulin resistance in pregnancy and GDM: Implications for diagnosis and management. Diabetes 1991, 40 (Suppl. S2), 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.H.; Vinter, C.A.; Olesen, T.B.; Petersen, M.H.; Nohr, E.A.; Rubin, K.H.; Andersen, M.S.; Jensen, D.M. Breast cancer in women with previous gestational diabetes: A nationwide register-based cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2024, 26, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, T.O.; Chhetri, G.; Yeh, H.; Dong, H.H. Beta-cell compensation and gestational diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Subsequent Risks of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases: The Life Course Perspective and Implications of Racial Disparities. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2024, 24, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biete, M.; Vasudevan, S. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Impacts on fetal neurodevelopment, gut dysbiosis, and the promise of precision medicine. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1420664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Li, H.Z.; Gong, W.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhong, J.M.; Du, L.B. Cancer incidence and mortality in Zhejiang Province, Southeast China, 2016: A population-based study. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra da Costa, A.; Hernandes, I.C.P.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fregnani, J. Cancer Statistics over Time in Northwestern São Paulo State, Brazil: Incidence and Mortality. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2022, 31, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.M.; Wang, W.; Wu, F.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Ma, L.L.; Feng, J. Comorbidity in Older Patients Hospitalized with Cancer in Northeast China based on Hospital Discharge Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, O.; Sheiner, E.; Meirovitz, M.; Davidson, E.; Sergienko, R.; Kessous, R. The association between a history of gestational diabetes mellitus and future risk for female malignancies. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 295, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.T.; Cho, G.J.; Kim, E.H. Evaluation of the Association between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus at First Pregnancy and Cancer within 10 Years Postpartum Using National Health Insurance Data in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.S.; Lin, J.R.; Cheng, B.H.; Ho, C.; Lin, Y.H.; Shen, C.H.; Tsai, M.H. Incidence and relative risk for developing cancers in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, G.; Giannakeas, V.; Read, S.; Lega, I.C.; Shah, B.R.; Lipscombe, L.L. Risk of Breast Cancer After Diabetes in Pregnancy: A Population-based Cohort Study. Can. J. Diabetes 2024, 48, 171–178.e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.; Rahme, E.; Dasgupta, K. Gestational diabetes mellitus and risk of incident primary cancer: A population-based retrospective cohort study. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45 Pt A, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsopoulos, N.A.; Evangelou, E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Sensitivity of between-study heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Proposed metrics and empirical evaluation. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 37, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaimal, S.A.; Wu, C.F.; Lowe, J.; Feig, D.S.; Shah, B.R.; Lipscombe, L.L. Short-term risk of cancer among women with previous gestational diabetes: A population-based study. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, M.C.; Terry, M.B.; Kleinhaus, K.; Deutsch, L.; Yanetz, R.; Tiram, E.; Calderon, R.; Friedlander, Y.; Paltiel, O.; Harlap, S. Gestational diabetes as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer: A prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2007, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sella, T.; Chodick, G.; Barchana, M.; Heymann, A.D.; Porath, A.; Kokia, E.; Shalev, V. Gestational diabetes and risk of incident primary cancer: A large historical cohort study in Israel. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhu, X.; Beeraka, N.M.; Zhao, R.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Mahesh, P.A.; Nikolenko, V.N.; Fan, R.; Liu, J. Projected epidemiological trends and burden of liver cancer by 2040 based on GBD, CI5plus, and WHO data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slouha, E.; Gates, K.M.; Al-Geizi, H.; Baah, E.; Clunes, L.A.; Kollias, T.F. The Relationship Between Gestational Diabetes and the Risk of Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e53328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qin, Y.; Kong, L.; Long, J.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Qin, J. Clinical and pathological characteristics of gestational diabetes mellitus with different insulin resistance. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2024, 38, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Wu, N.; Bai, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, L. circMAP3K4 regulates insulin resistance in trophoblast cells during gestational diabetes mellitus by modulating the miR-6795-5p/PTPN1 axis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakadia, J.H.; Khalid, M.U.; Heinemann, I.U.; Han, V.K. AMPK-mTORC1 pathway mediates hepatic IGFBP-1 phosphorylation in glucose deprivation: A potential molecular mechanism of hypoglycemia-induced impaired fetal growth. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2024, 72, e230137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, M.; Izutsu, A.; Hara, A.; Shimizu, M. Evaluation of binding capacity of circulating insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1b in salmonids using a ligand immunofunctional assay. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 284, 111488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, E.; Liguori, F.; Merigliano, C.; Schiano, L.; Gnocchini, E.; Pilesi, E.; Volonté, C.; Di Salvo, M.L.; Contestabile, R.; Tramonti, A.; et al. Vitamin B6 rescues insulin resistance and glucose-induced DNA damage caused by reduced activity of Drosophila PI3K. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 3578–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Murmu, N.; Mondal, T.; Saha, I.; Chatterjee, S.; Manna, R.; Haldar, S.; Dash, S.K.; Sarkar, T.R.; Giri, B. Multifaceted entrancing role of glucose and its analogue, 2-deoxy-D-glucose in cancer cell proliferation, inflammation, and virus infection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Z. Diabetes and cancer: Epidemiological and biological links. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.; Al Qarni, A.; Bakillah, A. The Interlinking Metabolic Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Insights. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarek, W.; Koper, M.; Lewicki, S.; Szczylik, C.; Czarnecka, A.M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factors act as renal cell cancer intratumoral regulators. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 13, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, R.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Bhosale, P.R.; Wang, X.; Fogelman, D.R.; Shroff, R.T.; Overman, M.J.; Wolff, R.A.; Javle, M. Randomized, phase I/II study of gemcitabine plus IGF-1R antagonist (MK-0646) versus gemcitabine plus erlotinib with and without MK-0646 for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.L.; Kim, J.; Kwak, S.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Huh, J.; Park, J.W. The polyol pathway and nuclear ketohexokinase A signaling drive hyperglycemia-induced metastasis of gastric cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Z.; Choi, Y.H.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Piao, H.; et al. Imperatorin alleviates ROS-mediated airway remodeling by targeting the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supabphol, S.; Seubwai, W.; Wongkham, S.; Saengboonmee, C. High glucose: An emerging association between diabetes mellitus and cancer progression. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1175–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garufi, A.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Cirone, M.; D’Orazi, G. ZnCl2 sustains the adriamycin-induced cell death inhibited by high glucose. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, B.U. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Recent insights with implications for early diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 37, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Xia, Y.H.; Lin, J.S.H.; Chu, K.H.; Wang, W.C.K.; Ruiter, T.J.J.; Yang, J.C.C.; Chen, N.; Chhuor, J.; Patil, S.; et al. Hyperinsulinemia acts via acinar insulin receptors to initiate pancreatic cancer by increasing digestive enzyme production and inflammation. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 2119–2135.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Cai, L.; Chen, H. The protective effect of phloretin in osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, H.J.; Oh, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Eom, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.N.; Chung, K.S.; Jang, H.J. Effects of salmon DNA fraction in vitro and in a monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis rat model. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Xiao, J.; Feng, N.; Zhou, M. Inhibition of advanced glycation endproducts formation by lotus seedpod oligomeric procyanidins through RAGE-MAPK signaling and NF-κB activation in high-AGEs-diet mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 156, 112481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legiawati, L. The Role of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Advanced Glycation End Product in Skin Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 18, e200921196637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Kang, J.; Deng, T.; Yang, X.; Chen, M. Exposure to DBP and High Iodine Aggravates Autoimmune Thyroid Disease Through Increasing the Levels of IL-17 and Thyroid-Binding Globulin in Wistar Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, K.S.; Kaschek, L.; Knörck, A.; Cappello, S.; Lünsmann, N.; Küchler, N.; Hoxha, C.; Schäfer, G.; Iden, S.; Bogeski, I.; et al. Interdependence of sequential cytotoxic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell cytotoxicity against melanoma cells. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 5027–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Jung, H.; Kim, T.D.; Lee, H.G.; Choi, I.; Yoon, S.R. Prostaglandin E2 Secreted by Thyroid Cancer Cells Contributes to Immune Escape Through the Suppression of Natural Killer (NK) Cell Cytotoxicity and NK Cell Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Jiao, Q.; Shen, C.T.; Song, H.J.; Zhang, H.Z.; Qiu, Z.L.; Luo, Q.Y. Interleukin 6 regulates the expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 in thyroid cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jin, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z. Appraising the effectiveness of immune cells on thyroid cancer: A Mendelian randomization study. Endocrine 2024, 86, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Hu, J. Application and mechanism of Chinese herb medicine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1499602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Y.; Meng, L.; Deng, G.; Qin, Y. The Role of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Related Risk Factors and Drugs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2024, 11, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Tan, L.; Lv, Z.; Chen, W.; Wu, J. Pharmacology of bioactive compounds from plant extracts for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through endoplasmic reticulum stress modulation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Murata, M.; Suwa, K.; Tsuneyama, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Naganuma, M. Smad3 Phospho-Isoform Signaling in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Qin, C.; Yin, L. ROS-scavenging nanomedicine for “multiple crosstalk” modulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 3709–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, D.; Ling, J.; Yu, P.; Shen, Y. O-GlycNacylation Remission Retards the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | Country | Study Design | Age (GDM/Non-GDM) | Sample Size | Main Outcome | Follow-Up Time (Years) | Quality (Scores) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancers | RR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |||||||
| Gurjot Gill MD, 2024 [24] | Canada | Cohort study | 33(IQR 33–37) | 297,771 | Overall Cancer; Pancreatic Cancer; Liver Cancer; Thyroid Cancer; Lung Cancer | 1.01 (0.96, 1.06); 2.04 (1.21, 3.43); 2.11 (1.02, 4.38); 1.07 (0.97, 1.19); 0.98 (0.71, 1.34) | 8 (IQR 4–13) | High (7) | |
| Romina Pace, 2020 [25] | Canada | Cohort study | 44.9% ≤ 30; 55.1% > 30 | 68,588 | Overall Cancer; Thyroid Cancer; Lung Cancer | 1.04 (0.95, 1.14); 1.39 (1.03, 1.89); 1.20 (0.73, 1.99) | 13.1 (SD 5.2) | High (7) | |
| Yun-Shing Peng, 2019 [23] | Taiwan, China | Cohort study | 31.61 (SD 4.54)/28.83 (SD 4.89) | 990,572 | Overall Cancer; Pancreatic Cancer; Liver Cancer; Thyroid Cancer; Lung Cancer | 1.197 (1.125, 1.274); 1.072 (0.655, 1.755); 1.242 (0.998, 1.545); 1.389 (1.121, 1.721); 1.372 (1.044, 1.803) | 6.84 (SD 3.05) | High (7) | |
| Kyu-Tae Han, 2018 [22] | South Korea | Cohort study | 28.25 (SD 3.28)/27.28 (SD 3.02) | 102,900 | Overall Cancer; Liver Cancer; Thyroid Cancer | 1.31 (1.192, 1.449); 1.5 (0.939, 2.397); 1.27 (1.054, 1.532) | 10 | High (8) | |
| Oded Fuchs, 2017 [21] | Israel | Cohort study | 31.8 (SD 5.9)/28.1 (SD 5.9) | 104,715 | Overall Cancer | 1.7 (1.5, 2.1) | 11.2 (Average) | High (7) | |
| S.A.D. Bejaimal, 2015 [32] | Canada | Cohort study | 32 (IQR 28–35) | 149,049 | Overall Cancer; Thyroid Cancer | 1.01 (0.93, 1.11); 1.24 (1.05, 1.46) | 8 (IQR 5–12) | High (7) | |
| Tal Sella, 2011 [34] | Israel | Cohort study | 32.74 (SD 5.51)/30.59 (SD 5.51) | 185,315 | Overall Cancer; Pancreatic Cancer; Thyroid Cancer | 1.04 (0.87, 1.24); 7.06 (1.69, 29.45); 0.68 (0.33, 1.39) | 5.19(SD 3.9) | High (8) | |
| MC Perrin, 2007 [33] | Israel | Cohort study | >35 | 37,926 | Pancreatic Cancer | 7.1 (2.8, 18.0) | 38.0 (Average) | High (7) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, L.; Wen, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; Fan, J. Association Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Overall and Site-Specific Cancers (Pancreatic, Liver, Thyroid, Lung): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050808
Tian L, Wen Y, Liu C, Li T, Fan J. Association Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Overall and Site-Specific Cancers (Pancreatic, Liver, Thyroid, Lung): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life. 2025; 15(5):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050808
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Lv, Yixuan Wen, Chuanwang Liu, Tao Li, and Jun Fan. 2025. "Association Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Overall and Site-Specific Cancers (Pancreatic, Liver, Thyroid, Lung): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Life 15, no. 5: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050808
APA StyleTian, L., Wen, Y., Liu, C., Li, T., & Fan, J. (2025). Association Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Overall and Site-Specific Cancers (Pancreatic, Liver, Thyroid, Lung): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life, 15(5), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050808