Can Bisphenols Alter the Inflammation Process?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bisphenols

2.1. Bisphenol A
2.2. Bisphenol S
2.3. Bisphenol F
2.4. Bisphenol AF
2.5. Bisphenol B
3. Elementary Process of Inflammation
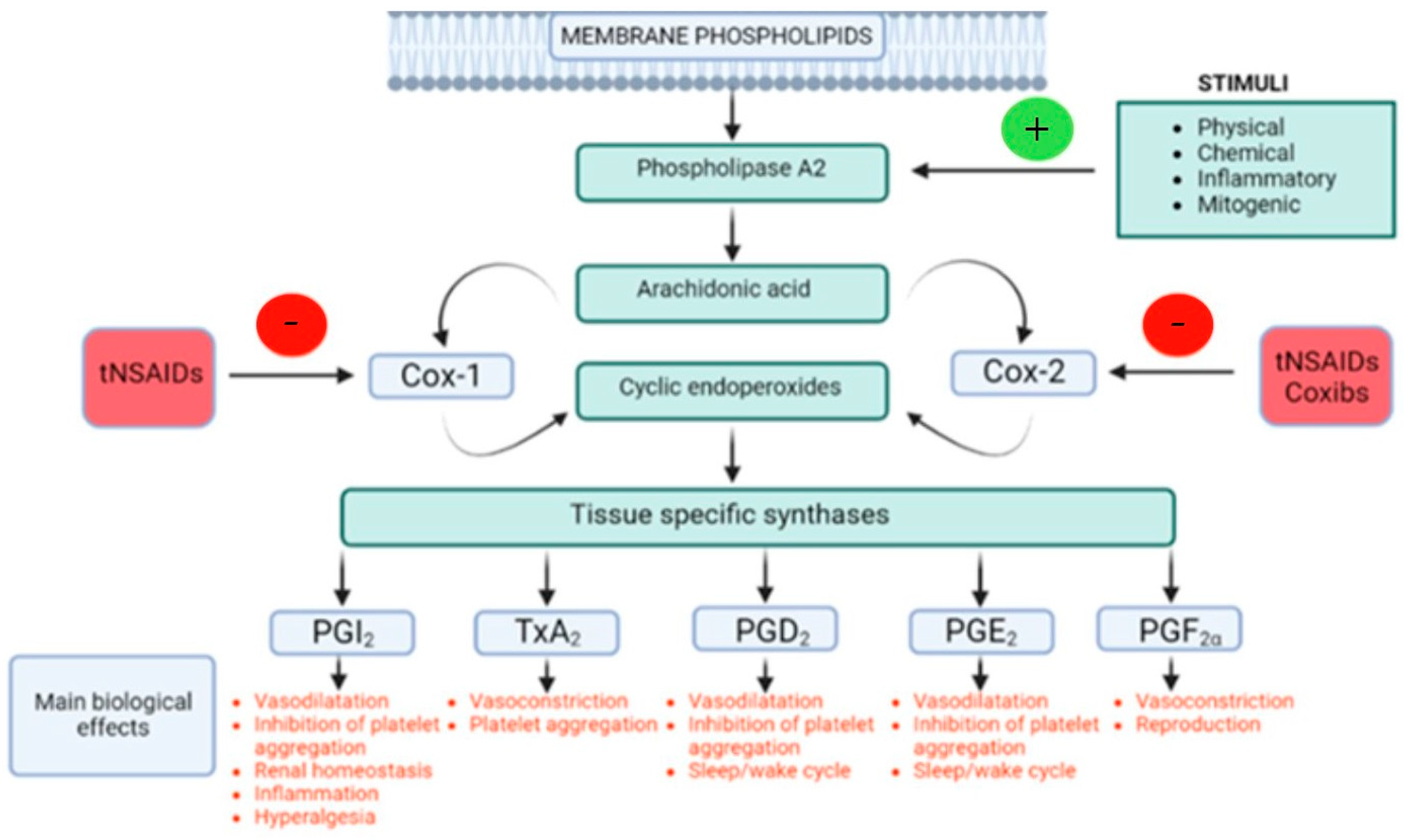
3.1. Arachidonic Acid
3.2. Phospholipase A2
3.3. COX-1 and COX-2 Pathways
3.3.1. COX-1
3.3.2. COX-2
3.3.3. Lipoxygenases
4. Inflammation Mediators
- Vasoactive amines (mainly histamine and serotonin)—primary local vasodilation and vasoconstriction
- Lipid mediators (eicosanoids)—derived from arachidonic acid metabolism
- Products of the complement system—inactive parts of the complement that can be activated by immunocomplexes
- Cytokines involved in inflammatory responses
- The kinin–kallikrein system and vasoactive peptides (bradykinin and lysyl-bradkinin)
- Chemokines (chemotactic cytokines and chemotactic factors)
- The hemocoagulation system and involved proteolytic enzymes
4.1. Vasoactive Amines
4.2. Lipid Mediators (Eicosanoids)
4.2.1. Prostanoids (Prostaglandins and Thromboxanes)
Prostaglandin D2
Prostaglandin I2
Prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin F2α
Thromboxane A2
4.2.2. Leukotrienes
4.2.3. Lipoxins
4.3. Cytokines Involved in Inflammatory Response
5. Effect of Bisphenols on Alteration of Inflammation Markers
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wautier, J.-L.; Wautier, M.-P. Endothelial Cell Participation in Inflammatory Reaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.U. An Overview of Inflammation: Mechanism and Consequences. Front. Biol. 2011, 6, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Miliani, L.; Nielsen, O.H.; Andersen, P.S.; Girardin, S.E. Chronic Inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in Interleukin-1beta Generation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannoodee, S.; Nasuruddin, D.N. Acute Inflammatory Response. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, K. An Inflammation Classification System Using Cytokine Parameters. Scand. J. Immunol. 2021, 93, e12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, T.; Greifova, H.; Kovacik, A.; Kovacikova, E.; Tvrda, E.; Forgacs, Z.; Massanyi, P.; Lukac, N. Parallel Effect of 4-Octylphenol and Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP) Alters Steroidogenesis, Cell Viability and ROS Production in Mice Leydig Cells. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Lee, D.-H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Low-Dose Effects and Nonmonotonic Dose Responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human Exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrello, J.; Matozzo, V. Bisphenol Analogs in Aquatic Environments and Their Effects on Marine Species—A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, H.M.; Abd Elkader, H.-T.A.E.; El-Gendy, A.H.; Eweda, S.M. Neurotoxicity and Neuroinflammatory Effects of Bisphenol A in Male Rats: The Neuroprotective Role of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9257–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambor, T.; Kovacikova, E.; Greifova, H.; Kovacik, A.; Libova, L.; Lukac, N. Assessment of the Effective Impact of Bisphenols on Mitochondrial Activity and Steroidogenesis in a Dose-Dependency in Mice TM3 Leydig Cells. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacova, J.; Jambor, T.; Knazicka, Z.; Tvrda, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Lukac, N. Dose- and Time-Dependent Effects of Bisphenol A on Bovine Spermatozoa in Vitro. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol Analogues Other Than BPA: Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Toxicity—A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, T.; Knizatova, N.; Greifova, H.; Kovacik, A.; Lukac, N. Toxicity of Bisphenol A and Its Replacements in the Mice Leydig Cells In Vitro. Physiol. Res. 2023, 72, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercog, K.; Maisanaba, S.; Filipič, M.; Sollner-Dolenc, M.; Kač, L.; Žegura, B. Genotoxic Activity of Bisphenol A and Its Analogues Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F and Bisphenol AF and Their Mixtures in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, J.; Kristofco, L.A.; Steele, W.B.; Yates, B.S.; Breed, C.S.; Williams, E.S.; Brooks, B.W. Global Assessment of Bisphenol A in the Environment: Review and Analysis of Its Occurrence and Bioaccumulation. Dose-Response 2015, 13, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, I.T.; Staples, C.A.; Klečka, G.M.; Mackay, D. A Multimedia Assessment of the Environmental Fate of Bisphenol A. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2002, 8, 1107–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsania, P.; Singhal, K.; Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G. Food Grade Plastics and Bisphenol A: Associated Risks, Toxicity, and Bioremediation Approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, R.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Smułek, W.; Grześkowiak, T. Removal of Bisphenol A and Its Potential Substitutes by Biodegradation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 191, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomza-Marciniak, A.; Stępkowska, P.; Kuba, J.; Pilarczyk, B. Effect of Bisphenol A on Reproductive Processes: A Review of in Vitro, in Vivo and Epidemiological Studies. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 51–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhamad, M.S.; Salim, M.R.; Lau, W.J.; Yusop, Z. A Review on Bisphenol A Occurrences, Health Effects and Treatment Process via Membrane Technology for Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 11549–11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.-T. Human Health Risk on Environmental Exposure to Bisphenol-A: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2006, 24, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food Exposure and Impact on Human Health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, A.; Sirohi, R.; Balakumaran, P.A.; Reshmy, R.; Madhavan, A.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Kumar, Y.; Kumar, D.; Sim, S.J. The Hazardous Threat of Bisphenol A: Toxicity, Detection and Remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.I.; Moon, J.; Kim, D.; Cui, R.; An, Y.-J. Determination of the Soil Hazardous Concentrations of Bisphenol A Using the Species Sensitivity Approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P.W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The Adverse Health Effects of Bisphenol A and Related Toxicity Mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, C.; Totaro, M.; Parisi, A.; D’Andrea, S.; Lucente, L.; Cordeschi, G.; Francavilla, S.; Francavilla, F.; Barbonetti, A. Bisphenol A and Male Fertility: Myths and Realities. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 540459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Aerts, D.; Berthot, C.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Goeyens, L.; Lecomte, P.; Maghuin-Rogister, G.; Pironnet, A.-M.; Pussemier, L.; Scippo, M.-L.; et al. A Review of Dietary and Non-Dietary Exposure to Bisphenol-A. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3725–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Maffini, M.V.; Sonnenschein, C.; Rubin, B.S.; Soto, A.M. Bisphenol-A and the Great Divide: A Review of Controversies in the Field of Endocrine Disruption. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.; Sinclair, R.; Watson, D. Chemical Migration and Food Contact Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-1-84569-209-4. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes and Processing Aids (CEP); Lambré, C.; Barat Baviera, J.M.; Bolognesi, C.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; Lampi, E.; et al. Re-Evaluation of the Risks to Public Health Related to the Presence of Bisphenol A (BPA) in Foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e06857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortenkamp, A. Ten Years of Mixing Cocktails: A Review of Combination Effects of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franko, N.; Kodila, A.; Sollner Dolenc, M. Adverse Outcomes of the Newly Emerging Bisphenol A Substitutes. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Hong, Y.-C. Bisphenol A, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Epidemiological, Laboratory, and Clinical Trial Evidence. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2016, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, Ó.; Aquilino, M.; Sánchez-Argüello, P.; Planelló, R. The BPA-Substitute Bisphenol S Alters the Transcription of Genes Related to Endocrine, Stress Response and Biotransformation Pathways in the Aquatic Midge Chironomus Riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-H.; Zhang, X.-M.; Wang, F.; Gao, C.-J.; Chen, D.; Palumbo, J.R.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Occurrence of Bisphenol S in the Environment and Implications for Human Exposure: A Short Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaimal, A.; Al Mansi, M.H.; Dagher, J.B.; Pope, C.; Varghese, M.G.; Rudi, T.B.; Almond, A.E.; Cagle, L.A.; Beyene, H.K.; Bradford, W.T.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Bisphenols Affects Pregnancy Outcomes and Offspring Development in Rats. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héliès-Toussaint, C.; Peyre, L.; Costanzo, C.; Chagnon, M.-C.; Rahmani, R. Is Bisphenol S a Safe Substitute for Bisphenol A in Terms of Metabolic Function? An in Vitro Study. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 280, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R.; Bolden, A.L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoene, M.; Dzika, E.; Gonkowski, S.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Bisphenol S in Food Causes Hormonal and Obesogenic Effects Comparable to or Worse than Bisphenol A: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Alomirah, H.; Loi, V.D.; Mohd, M.A.; Moon, H.-B.; Nakata, H.; Kannan, K. Bisphenol S in Urine from the United States and Seven Asian Countries: Occurrence and Human Exposures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6860–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes, Flavourings and Processing Aids (CEF). Scientific Opinion on the Risks to Public Health Related to the Presence of Bisphenol A (BPA) in Foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yu, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Yu, Y. Estimation of Intake and Uptake of Bisphenols and Triclosan from Personal Care Products by Dermal Contact. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Pirzada, M.; Afsar, T.; Razak, S.; Almajwal, A.; Jahan, S. Effect of Bisphenol F, an Analog of Bisphenol A, on the Reproductive Functions of Male Rats. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaton, N.; Chagnon, M.-C.; Lhuguenot, J.-C.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Zalko, D. Disposition and Metabolic Profiling of Bisphenol F in Pregnant and Nonpregnant Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10307–10314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabaton, N.; Zalko, D.; Rathahao, E.; Canlet, C.; Delous, G.; Chagnon, M.-C.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Perdu, E. Biotransformation of Bisphenol F by Human and Rat Liver Subcellular Fractions. Toxicol. In Vitro 2008, 22, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeirssen, E.L.M.; Dietschweiler, C.; Werner, I.; Burkhardt, M. Corrosion Protection Products as a Source of Bisphenol A and Toxicity to the Aquatic Environment. Water Res. 2017, 123, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qi, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L.; Qian, L.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; et al. Environmental Level of Bisphenol F Induced Reproductive Toxicity toward Zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 149992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; An, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Noh, H.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Song, K.S.; Chae, C.; Ryu, H.Y. Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity Evaluation Following Oral Exposure to Bisphenol F. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1711–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Ikhlas, S.; Ahmad, M. Occurrence, Toxicity and Endocrine Disrupting Potential of Bisphenol-B and Bisphenol-F: A Mini-Review. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 312, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B.; Wu, Y. Determination of Bisphenol AF (BPAF) in Tissues, Serum, Urine and Feces of Orally Dosed Rats by Ultra-High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 901, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFleur, A.D.; Schug, K.A. A Review of Separation Methods for the Determination of Estrogens and Plastics-Derived Estrogen Mimics from Aqueous Systems. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 696, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, A.; Liu, X.; Okada, H.; Shimohigashi, M.; Shimohigashi, Y. Bisphenol AF Is a Full Agonist for the Estrogen Receptor ERα but a Highly Specific Antagonist for ERβ. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Direct Interactions in the Recognition between the Environmental Estrogen Bisphenol AF and Human Serum Albumin. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wu, L.-H.; Wang, F.; Gao, C.-J.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y. Several Environmental Endocrine Disruptors in Beverages from South China: Occurrence and Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5873–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Lv, L.; Li, X.; Qin, Z. Effects of Low-Dose Bisphenol AF on Mammal Testis Development via Complex Mechanisms: Alterations Are Detectable in Both Infancy and Adulthood. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 3373–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.-V.; Liu, J.-H.; Liao, C.-S. Aerobic Degradation of Bisphenol-A and Its Derivatives in River Sediment. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Ike, M.; Fujita, M. Acute Toxicity, Mutagenicity, and Estrogenicity of Bisphenol-A and Other Bisphenols. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Ahmad, M. From BPA to Its Analogues: Is It a Safe Journey? Chemosphere 2016, 158, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Córcoles, M.T.; Cipa, M.; Rodríguez-Gómez, R.; Rivas, A.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Vílchez, J.L.; Zafra-Gómez, A. Determination of Bisphenols with Estrogenic Activity in Plastic Packaged Baby Food Samples Using Solid-Liquid Extraction and Clean-up with Dispersive Sorbents Followed by Gas Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Talanta 2018, 178, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, T.; Knížatová, N.; Lukáč, N. Men’s Reproductive Alterations Caused by Bisphenol A and Its Analogues: A Review. Physiol. Res. 2021, 70, S643–S656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, M.L.; Mogildea, M.; Moreno, I.; Lopes, A. Acute Inflammation and Metabolism. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punchard, N.A.; Whelan, C.J.; Adcock, I. The Journal of Inflammation. J. Inflamm. 2004, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Feuerstein, G.Z.; Ruffolo, R.R.; Coughlin, C.; Wang, J.; Miller, D. Inflammation. In Encyclopedia of Stress, 2nd ed.; Fink, G., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 530–535. ISBN 978-0-12-373947-6. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein, G.W. Analysis of Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 93–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fu, X.; Chen, Q.; Patra, J.K.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Gai, Z. Arachidonic Acid Metabolism and Kidney Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, C.A.; Wright, T.M. Cytokines in Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 1997, 2, d12–d26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Wang, C.; Xu, X. The Associations between Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Markers of Inflammation and Immune Responses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, F.M.; Iribarne-Durán, L.M.; Artacho-Cordón, F. Human Exposure to Bisphenols, Parabens, and Benzophenones, and Its Relationship with the Inflammatory Response: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J. Bisphenol S Exposure Induces Intestinal Inflammation: An Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Study. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yan, J.; Jiang, H. Association of Urinary Bisphenols with Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers and Their Role in Obesity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lim, S.-R.; Jung, D.-H.; Kim, E.-J.; Sung, J.; Kim, S.C.; Choi, C.-H.; Kang, J.-W.; Lee, S.-J. Grifola Frondosa Extract Containing Bioactive Components Blocks Skin Fibroblastic Inflammation and Cytotoxicity Caused by Endocrine Disrupting Chemical, Bisphenol A. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantengco, O.A.G.; Vidal, M.S., Jr.; Bento, G.F.C.; Menon, R. Impact of Bisphenol A on Cell Viability and Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Human Cervical Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2023, 90, e13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Kai, L.; Han, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Equipotent Bisphenol S and Bisphenol F with Widely Differing Modes of Action Exhibit Additive Effects in Immunotoxicity: Insights Based on Intrinsic Immunity, Apoptosis and Regeneration, and Oxidative Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 977, 179405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, P.F. Leukocyte lipid bodies—Structure and function as “Eicosasomes”. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2016, 127, 328–340. [Google Scholar]
- Brash, A.R. Arachidonic Acid as a Bioactive Molecule. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnweber, T.; Pizzini, A.; Nairz, M.; Weiss, G.; Tancevski, I. Arachidonic Acid Metabolites in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchlis, V.D.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 Catalysis and Lipid Mediator Lipidomics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaydin, C.; Bilge, S.S. Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs at the Molecular Level. Eurasian J. Med. 2018, 50, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.; Norris, P.C. Eicosanoid Storm in Infection and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Abellán, V.; Sepulcre, M.P. The Role of Prostaglandins in the Regulation of Fish Immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 69, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hla, T.; Bishop-Bailey, D.; Liu, C.H.; Schaefers, H.J.; Trifan, O.C. Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 Isoenzymes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazanfari, N.; van Waarde, A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Doorduin, J.; de Vries, E.F.J. Is Cyclooxygenase-1 Involved in Neuroinflammation? J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 2976–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.G.; Scilimati, A.; Simone, L.; Vitale, P. Selective COX-1 Inhibition: A Therapeutic Target to Be Reconsidered. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 3769–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannunzio, A.; Coluccia, M. Cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-1 Inhibitors in Cancer: A Review of Oncology and Medicinal Chemistry Literature. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, K.; Patrignani, P. New Insights into the Use of Currently Available Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierse, J.K.; Koboldt, C.M. Cyclooxygenase Assays. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2001, 1, 3-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisastra, R.; Dekker, F.J. Inflammation, Cancer and Oxidative Lipoxygenase Activity Are Intimately Linked. Cancers 2014, 6, 1500–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caterina, R.; Zampolli, A. From Asthma to Atherosclerosis—5-Lipoxygenase, Leukotrienes, and Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, I.; Sugimoto, M.A.; Vago, J.P.; Machado, M.G.; Sousa, L.P. Mediators of Inflammation. In Immunopharmacology and Inflammation; Riccardi, C., Levi-Schaffer, F., Tiligada, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–32. ISBN 978-3-319-77658-3. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, M.; Siebenhaar, F.; Maurer, M. Mast Cell Functions in the Innate Skin Immune System. Immunobiology 2008, 213, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, L.; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Regulation of the Immune Response and Inflammation by Histamine and Histamine Receptors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, M.D.; Tekin, I.; Vrana, K.E.; Mawe, G.M. Review Article: The Many Potential Roles of Intestinal Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) Signalling in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shajib, M.S.; Khan, W.I. The Role of Serotonin and Its Receptors in Activation of Immune Responses and Inflammation. Acta Physiol. 2015, 213, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; DuBois, R.N. Eicosanoids and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Eicosanoids. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.G.; Padilla, J.; Koumas, L.; Ray, D.; Phipps, R.P. Prostaglandins as Modulators of Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and Inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.B. Prostaglandins in Health and Disease: An Overview. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 36, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittchen, S.; Heinemann, A. Therapeutic Potential of Hematopoietic Prostaglandin D2 Synthase in Allergic Inflammation. Cells 2019, 8, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, K.; Guo, C.; Gao, H.; Yao, Y.; Lin, D. Expression and Purification of Cysteine Mutation Isoforms of Rat Lipocalin-Type Prostaglandin D Synthase for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yu, Y. Prostaglandin D2 Signaling and Cardiovascular Homeostasis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 167, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Eguchi, N.; Oda, H.; Seiki, K.; Kijima, Y.; Matsu-ura, Y.; Urade, Y.; Hayaishi, O. Expression of Lipocalin-Type Prostaglandin D Synthase (β-Trace) in Human Heart and Its Accumulation in the Coronary Circulation of Angina Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14689–14694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urade, Y.; Ujihara, M.; Horiguchi, Y.; Ikai, K.; Hayaishi, O. The Major Source of Endogenous Prostaglandin D2 Production Is Likely Antigen-Presenting Cells. Localization of Glutathione-Requiring Prostaglandin D Synthetase in Histiocytes, Dendritic, and Kupffer Cells in Various Rat Tissues. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 2982–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.N.; Breyer, R.M. Pharmacology and Signaling of Prostaglandin Receptors: Multiple Roles in Inflammation and Immune Modulation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 103, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostenis, E.; Ulven, T. Emerging Roles of DP and CRTH2 in Allergic Inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santus, P.; Radovanovic, D. Prostaglandin D2 Receptor Antagonists in Early Development as Potential Therapeutic Options for Asthma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maehara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Maeda, S.; Aritake, K.; Nakamura, M.; Murata, T. Epithelial Cell–Derived Prostaglandin D2 Inhibits Chronic Allergic Lung Inflammation in Mice. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8202–8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.E.; Lui, F. Physiology, Prostaglandin I2. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dorris, S.L.; Peebles, R.S. PGI2 as a Regulator of Inflammatory Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 926968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Goleniewska, K.; Dulek, D.E.; Toki, S.; Newcomb, D.C.; Cephus, J.Y.; Collins, R.D.; Wu, P.; Boothby, M.R.; et al. Prostaglandin I2 Suppresses Proinflammatory Chemokine Expression, CD4 T Cell Activation, and STAT6-Independent Allergic Lung Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wen, D.; Yu, F.; Yang, S.; Jia, X.; Cong, B.; Ma, C. Prostaglandin I2-IP Signalling Regulates Human Th17 and Treg Cell Differentiation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2013, 89, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumiya, S. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Prostanoid Receptors. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2007, 83, 296–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, R.P.; Stein, S.H.; Roper, R.L. A New View of Prostaglandin E Regulation of the Immune Response. Immunol. Today 1991, 12, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinski, P. Regulation of Immune Responses by Prostaglandin E2. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, S.; Willmes, D.M.; Nassiri, M.; Babina, M.; Worm, M. PGE2 Deficiency Predisposes to Anaphylaxis by Causing Mast Cell Hyperresponsiveness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1387–1396.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, F.; Boccatonda, A.; Davì, G.; Cipollone, F. The Coxib Case: Are EP Receptors Really Guilty? Atherosclerosis 2016, 249, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Long, A.; Fang, X.; Wood, S.L.; Slater, D.M.; Ni, X.; Olson, D.M. Effects of PGF2α on the Expression of Uterine Activation Proteins in Pregnant Human Myometrial Cells From Upper and Lower Segment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, M.; Nakajima, T.; Yasuda, K.; Kanzaki, H.; Sasaguri, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ito, S. Close Kinship of Human 20α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Gene with Three Aldo-Keto Reductase Genes. Genes Cells 2000, 5, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Yamamoto, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Fukui, M.; Okuda-Ashitaka, E.; Nakajima, T.; Ito, S.; Watanabe, K. cDNA Cloning, Expression and Characterization of Human Prostaglandin F synthase11The Amino Acid Sequence of Human PGFS and the Amplified Genomic DNA with PGFS-F4 and R5 Were Registered in the DDBJ under Accession No. AB018580 and No. AB028065, Respectively. FEBS Lett. 1999, 462, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, S.A.; Jabbour, H.N. Prostaglandin (PG) F2α Receptor Expression and Signaling in Human Endometrium: Role of PGF2α in Epithelial Cell Proliferation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonczyk, A.W.; Piotrowska-Tomala, K.K.; Skarzynski, D.J. Effects of Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) on Cell-Death Pathways in the Bovine Corpus Luteum (CL). BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnould, T.; Thibaut-Vercruyssen, R.; Bouaziz, N.; Dieu, M.; Remacle, J.; Michiels, C. PGF2α, a Prostanoid Released by Endothelial Cells Activated by Hypoxia, Is a Chemoattractant Candidate for Neutrophil Recruitment. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, D.; Dhamoon, A.S. Physiology, Thromboxane A2. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Szczuko, M.; Kozioł, I.; Kotlęga, D.; Brodowski, J.; Drozd, A. The Role of Thromboxane in the Course and Treatment of Ischemic Stroke: Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, A.W.; Zhang, Y.; Cazzolli, R.; Honn, K.V. The Role and Regulation of Thromboxane A2 Signaling in Cancer-Trojan Horses and Misdirection. Molecules 2022, 27, 6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, A.; Yokoyama, C.; Ihara, H.; Bandoh, S.; Takeda, O.; Takahashi, E.; Tanabe, T. Characterization of the Human Gene (TBXAS1) Encoding Thromboxane Synthase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 224, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Jiang, X.; Kim, D.; Guan, T.; Nicolls, M.R.; Rockson, S.G. Leukotrienes in Tumor-Associated Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo-Watanabe, A.; Okuno, T.; Yokomizo, T. The Role of Leukotrienes as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Allergic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, M.; Powell, W.S.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Drazen, J.M.; Evans, J.F.; Serhan, C.N.; Shimizu, T.; Yokomizo, T.; Rovati, G.E. Update on Leukotriene, Lipoxin and Oxoeicosanoid Receptors: IUPHAR Review 7. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3551–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, M.; Ito, N.; Hoshino, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Yokomizo, T.; Nakamura, M.; Shimizu, T.; Yamada, Y. Role of Leukotriene B4 (LTB4)-LTB4 Receptor 1 Signaling in Post-Incisional Nociceptive Sensitization and Local Inflammation in Mice. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokomizo, T.; Nakamura, M.; Shimizu, T. Leukotriene Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2691–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Sasaki, F.; Saeki, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Okuno, T.; Ohba, M.; Ichiki, T.; Iwamoto, S.; Uzawa, H.; Kitajima, K.; et al. Expression of Leukotriene B4 Receptor 1 Defines Functionally Distinct DCs That Control Allergic Skin Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Gupta, S.; Dastidar, S.; Ray, A. Cysteinyl Leukotrienes and Their Receptors: Molecular and Functional Characteristics. Pharmacology 2010, 85, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, J.A.; Sharma-Walia, N. Lipoxins: Nature’s Way to Resolve Inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 8, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Sheppard, K.A. Lipoxin Formation during Human Neutrophil-Platelet Interactions. Evidence for the Transformation of Leukotriene A4 by Platelet 12-Lipoxygenase in Vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Hamberg, M.; Samuelsson, B. Lipoxins: Novel Series of Biologically Active Compounds Formed from Arachidonic Acid in Human Leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5335–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clària, J.; Serhan, C.N. Aspirin Triggers Previously Undescribed Bioactive Eicosanoids by Human Endothelial Cell-Leukocyte Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9475–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation and Pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory Cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, A.H.; Khalil, R.A. Inflammatory Cytokines in Vascular Dysfunction and Vascular Disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshtam, M.; Asgary, S.; Kouhpayeh, S.; Shariati, L.; Khanahmad, H. Aptamers Against Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines: A Review. Inflammation 2017, 40, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Park, S.B.; Park, J.W.; Oh, S.R.; Han, M. Bisphenol A Modulates Inflammation and Proliferation Pathway in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells by Inducing Oxidative Stress. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 81, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, R.; D’Esposito, V.; Passaretti, F.; Liotti, A.; Cabaro, S.; Longo, M.; Perruolo, G.; Oriente, F.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P. Bisphenol-A Impairs Insulin Action and Up-Regulates Inflammatory Pathways in Human Subcutaneous Adipocytes and 3T3-L1 Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.; Brittebo, E. Proangiogenic Effects of Environmentally Relevant Levels of Bisphenol A in Human Primary Endothelial Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, I.; Oriente, F.; D’Esposito, V.; Liguoro, D.; Liguoro, P.; Ambrosio, M.; Cabaro, S.; D’Andrea, F.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; et al. Low Dose Bisphenol-A Regulates Inflammatory Cytokines through GPR30 in Mammary Adipose Cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-W.; Ha, S.K.; Kim, Y. Bisphenol A Disrupts Inflammatory Responses via Nod-like Receptor Protein 3 Pathway in Macrophages. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Ge, M.; Jin, J.; Xu, H.; Mao, L.; Geng, S.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, C. Mechanism Investigation on Bisphenol S-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Murine RAW264.7 Cells: The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome, TLR4, Nrf2 and MAPK. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mei, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Lin, J.; Xu, M. Modulation of Cytokine Expression in Human Macrophages by Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Bisphenol-A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elswefy, S.E.-S.; Abdallah, F.R.; Atteia, H.H.; Wahba, A.S.; Hasan, R.A. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Cascade Implications in Bisphenol A-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Male Rats. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 97, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Sun, J.; Ding, L.; Lv, X.; Ma, Q.; Bi, Y.; Liu, R.; et al. Bisphenol A Promotes Adiposity and Inflammation in a Nonmonotonic Dose-Response Way in 5-Week-Old Male and Female C57BL/6J Mice Fed a Low-Calorie Diet. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2333–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bazany, D.; Greifova, H.; Zuscikova, L.; Tokarova, K.; Jambor, T.; Kovacik, A.; Lukac, N. Can Bisphenols Alter the Inflammation Process? Life 2025, 15, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050782
Bazany D, Greifova H, Zuscikova L, Tokarova K, Jambor T, Kovacik A, Lukac N. Can Bisphenols Alter the Inflammation Process? Life. 2025; 15(5):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050782
Chicago/Turabian StyleBazany, Denis, Hana Greifova, Lucia Zuscikova, Katarina Tokarova, Tomas Jambor, Anton Kovacik, and Norbert Lukac. 2025. "Can Bisphenols Alter the Inflammation Process?" Life 15, no. 5: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050782
APA StyleBazany, D., Greifova, H., Zuscikova, L., Tokarova, K., Jambor, T., Kovacik, A., & Lukac, N. (2025). Can Bisphenols Alter the Inflammation Process? Life, 15(5), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050782








