Transient Overexpression of the Pepper WRKY2 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana Markedly Delays the Systemic Necrosis Caused by Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants and Virus Inoculations
2.2. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis by RT-PCR
2.3. Analysis of Gene Expression Using Quantitative Real-Time RT-qPCR
2.4. The Construction of Gateway Vectors Carrying the CaWRKY2 Gene
2.5. Agroinfiltration of N. benthamiana Leaves
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
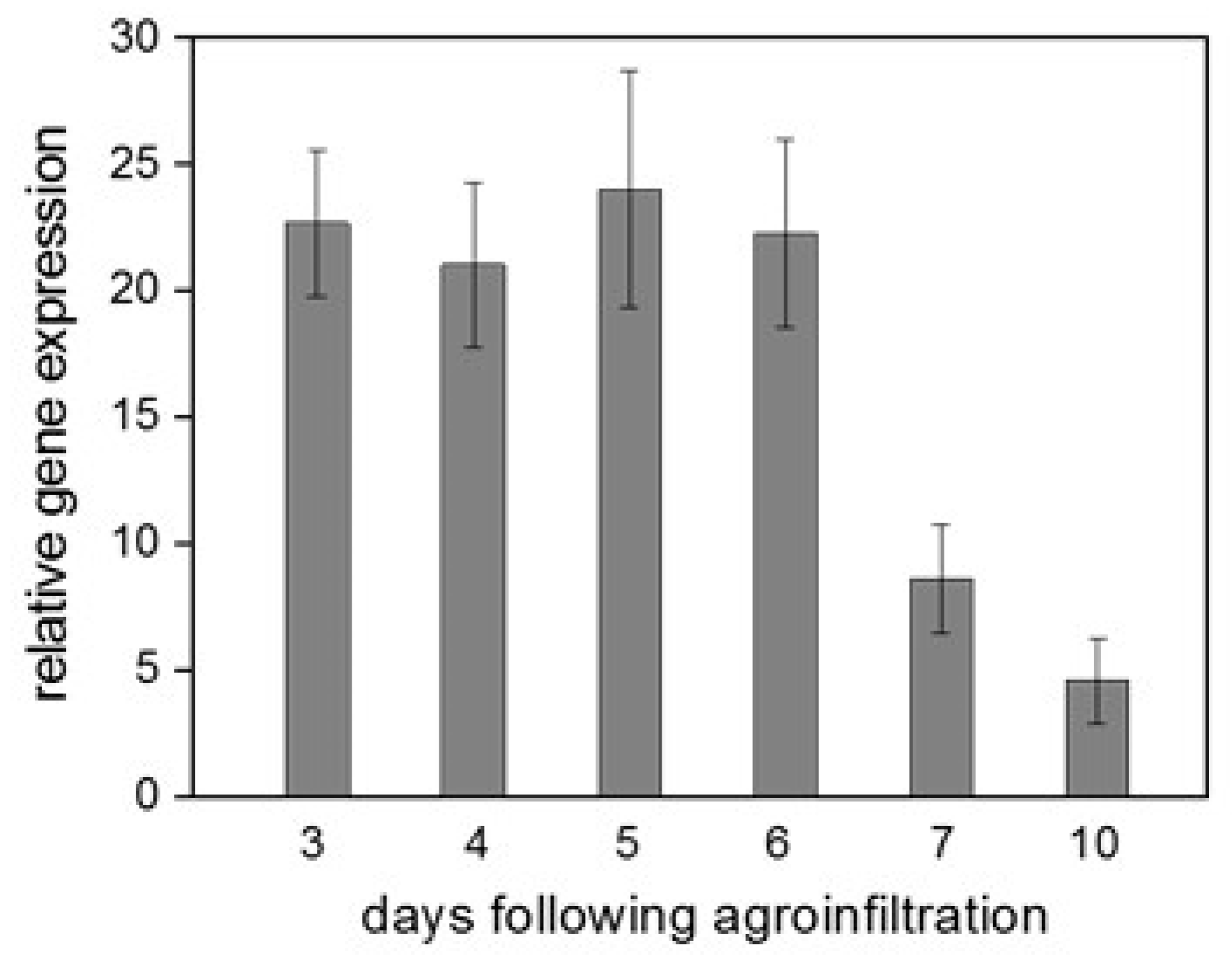
3.1. The Effects of ObPV and PMMoV on the Expression of CaWRKY2 in Infected Pepper Leaves
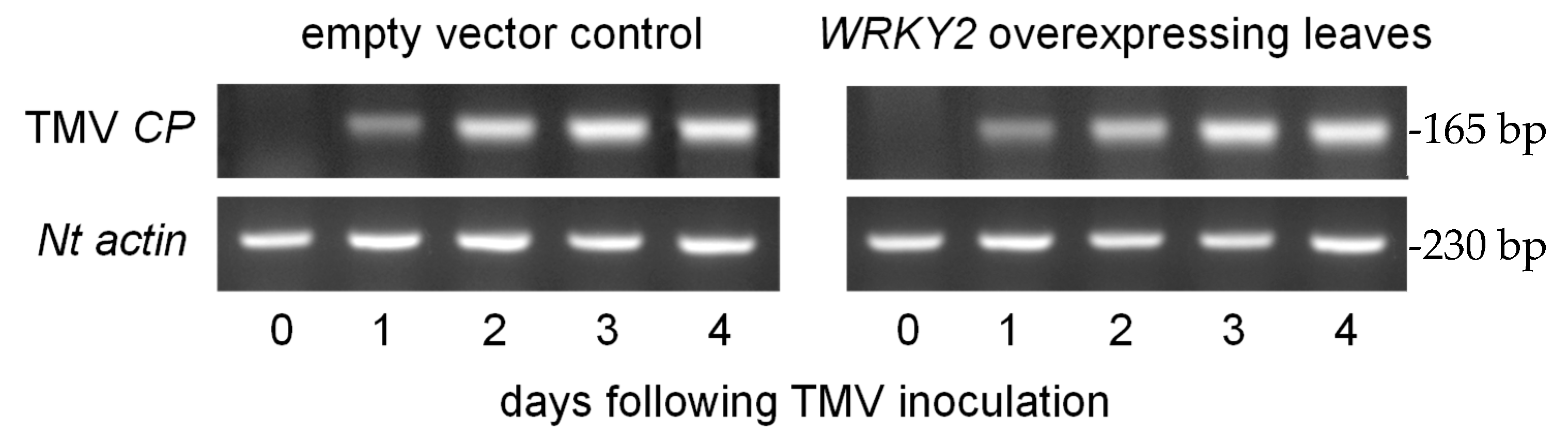
3.2. Overexpression of CaWRKY2 in Transformed N. benthamiana Leaves
3.3. TMV Inoculation of N. benthamiana Leaves Expressing CaWRKY2
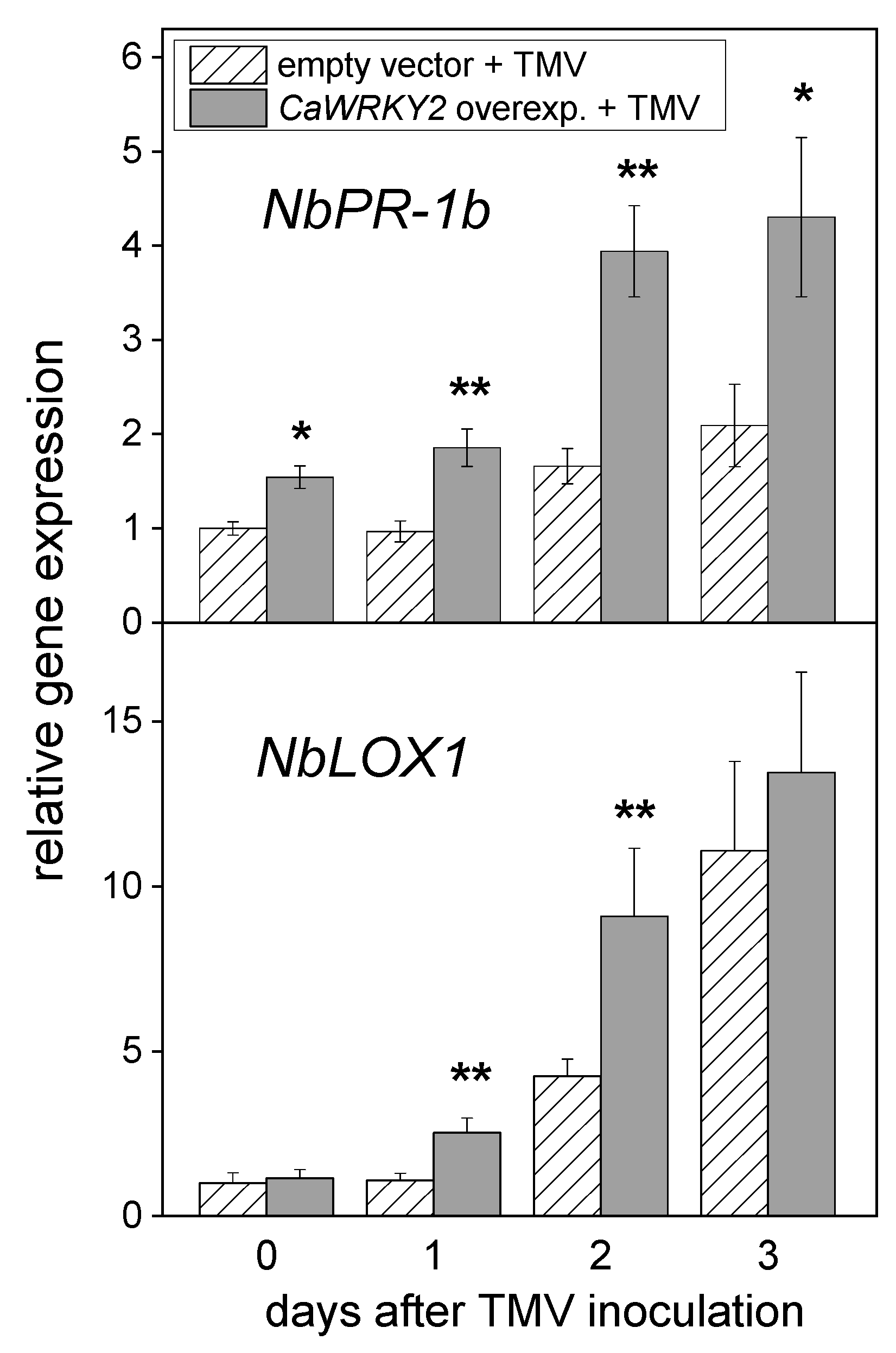
3.4. Induction of Defense Genes in N. benthamiana Leaves by TMV Inoculation
3.5. Effect of Overexpression of CaWRKY2 on TMV-Induced Systemic Necrosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teixeira, R.M.; Ferreira, M.A.; Raimundo, G.A.S.; Loriato, V.A.P.; Reis, P.A.B.; Fontes, E.P.B. Virus perception at the cell surface: Revisiting the roles of receptor-like kinases as viral pattern recognition receptors. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, P.; Chandra-Shekara, A.C.; Klessig, D.F. Plant signal transduction and defense against viral pathogens. Adv. Virus Res. 2006, 66, 161–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardo, L.; Souza, G.; Alves, M. Transcriptomics of plant–virus interactions: A review. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2019, 31, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, R.; García-Marcos, A.; Manzano, A.; de Lacoba, M.G.; Camañes, G.; García-Agustín, P.; Díaz-Ruíz, J.R.; Tenllado, F. Comparative analysis of transcriptomic and hormonal responses to compatible and incompatible plant-virus interactions that lead to cell death. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. MPMI 2012, 25, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapos, B.; Juhász, C.; Balogh, E.; Kocsy, G.; Tóbiás, I.; Gullner, G. Transcriptome profiling of pepper leaves by RNA-Seq during an incompatible and a compatible pepper-tobamovirus interaction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Liu, S.; Somssich, I.E. Transcriptional events defining plant immune responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.J. WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.U.; Lee, G.-J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Paek, K.-H. Capsicum annuum transcription factor WRKYa positively regulates defense response upon TMV infection and is a substrate of CaMK1 and CaMK2. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Zhong, K.; Jin, P.; Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. NbWRKY40 Positively Regulates the Response of Nicotiana benthamiana to Tomato Mosaic Virus via Salicylic Acid Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 603518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: Latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, L.C.; Heine, S.; Wendt, L.; Wegele, E.; Schomerus, J.T.; Schulze, J.; Hehl, R. Genomic distribution and context dependent functionality of novel WRKY transcription factor binding sites. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, F.; Zhou, A.; Somssich, I.E. Stimulus-Dependent, Promoter-Specific Binding of Transcription Factor WRKY1 to Its Native Promoter and the Defense-Related Gene PcPR1-1 in Parsley. Plant Cell. 2004, 16, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, W.-P.; Wang, S.-B.; Liu, J.-B.; Pan, B.-G.; Guo, G.-J.; Wei, G. Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in pepper. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2015, 42, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yao, Z.P.; Ruan, M.Y.; Ye, Q.J.; Wang, R.Q.; Zhou, G.Z.; Luo, J. In silico identification and characterization of the WRKY gene superfamily in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Genet. Mol. Res. GMR 2016, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, F.; Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Dai, X.; Yang, B.; Zou, X.; Ma, Y. Identification, expression, alternative splicing and functional analysis of pepper WRKY gene family in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, J.; Guo, J.; Lin, M.; Jin, C.; Huang, J.; Tang, W.; Guan, D.; He, S. The transcriptional reprograming and functional identification of WRKY family members in pepper’s response to Phytophthora capsici infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-J.; Shin, Y.-C.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, K.-J.; Kim, J.-K.; Paek, K.-H. A hot pepper gene encoding WRKY transcription factor is induced during hypersensitive response to Tobacco mosaic virus and Xanthomonas campestris. Planta 2006, 223, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Park, C.-J.; Huh, S.U.; Choi, L.M.; Lee, G.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Paek, K.-H. Capsicum annuum WRKYb transcription factor that binds to the CaPR-10 promoter functions as a positive regulator in innate immunity upon TMV infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.U.; Choi, L.M.; Lee, G.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Paek, K.-H. Capsicum annuum WRKY transcription factor d (CaWRKYd) regulates hypersensitive response and defense response upon Tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Sci. Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 2012, 197, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-K.; Yi, S.Y.; Yu, S.H.; Moon, J.S.; Park, J.M.; Choi, D. CaWRKY2, a chili pepper transcription factor, is rapidly induced by incompatible plant pathogens. Mol. Cells 2006, 22, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-K.; Baek, K.-H.; Park, J.M.; Yi, S.Y.; Yu, S.H.; Kamoun, S.; Choi, D. Capsicum annuum WRKY protein CaWRKY1 is a negative regulator of pathogen defense. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, I.; Fraser, R.S.S.; Gerwitz, A. The gene-for-gene relationship between Capsicum annuum L. and tobacco mosaic virus: Effects on virus multiplication, ethylene synthesis and accumulation of pathogenesis-related proteins. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1989, 35, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rys, M.; Juhász, C.; Surówka, E.; Janeczko, A.; Saja, D.; Tóbiás, I.; Skoczowski, A.; Barna, B.; Gullner, G. Comparison of a compatible and an incompatible pepper-tobamovirus interaction by biochemical and non-invasive techniques: Chlorophyll a fluorescence, isothermal calorimetry and FT-Raman spectroscopy. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 83, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullner, G.; Künstler, A.; Király, L.; Pogány, M.; Tóbiás, I. Up-regulated expression of lipoxygenase and divinyl ether synthase genes in pepper leaves inoculated with Tobamoviruses. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 74, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, C.; Tóbiás, I.; Ádám, A.L.; Kátay, G.; Gullner, G. Pepper 9- and 13-lipoxygenase genes are differentially activated by two tobamoviruses and by hormone treatments. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 92, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, E.; Juhász, C.; Dankó, T.; Fodor, J.; Tóbiás, I.; Gullner, G. The expression of several pepper fatty acid desaturase genes is robustly activated in an incompatible pepper-tobamovirus interaction, but only weakly in a compatible interaction. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziurka, M.; Janeczko, A.; Juhász, C.; Gullner, G.; Oklestková, J.; Novák, O.; Saja, D.; Skoczowski, A.; Tóbiás, I.; Barna, B. Local and systemic hormonal responses in pepper leaves during compatible and incompatible pepper-tobamovirus interactions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczko, A.; Dziurka, M.; Gullner, G.; Kocurek, M.; Rys, M.; Saja, D.; Skoczowski, A.; Tóbiás, I.; Kornas, A.; Barna, B. Comparative studies of compatible and incompatible pepper–Tobamovirus interactions and the evaluation of effects of 24-epibrassinolide. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, R.; Sekine, K.-T.; Mizumoto, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Murai, J.; Kiba, A.; Hikichi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kobayashi, K. Genetic basis for the hierarchical interaction between Tobamovirus spp. and L resistance gene alleles from different pepper species. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. MPMI 2011, 24, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenleaf, W.H.; Cook, A.A.; Heyn, A. Resistance to Tobacco mosaic virus in Capsicum, with reference to the Samsun latent strain. Phytopathology 1964, 54, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.D.; Goodwin, P.H.; Hsiang, T. Induction of glutathione S-transferase genes of Nicotiana benthamiana following infection by Colletotrichum destructivum and C. orbiculare and involvement of one in resistance. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavelu, M.; Belostotsky, D.; Bevan, M.W.; Flavell, R.B.; Rogers, H.J.; Lonsdale, D.M. Partial characterization of the Nicotiana tabacum actin gene family: Evidence for pollen-specific expression of one of the gene family members. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1993, 240, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods San Diego Calif. 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, J.L.; Temple, G.F.; Brasch, M.A. DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, K.W.; Haag, J.R.; Pontes, O.; Opper, K.; Juehne, T.; Song, K.; Pikaard, C.S. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Depicker, A.; Hilson, P. Recombinational cloning with plant gateway vectors. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, B.A.; Vanderhaeghen, R.; Whitford, R.; Town, C.D.; Hilson, P. Simultaneous high-throughput recombinational cloning of open reading frames in closed and open configurations. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2006, 4, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, J.N. Tobamovirus Cross Protection Using a Potexvirus Vector. Virology 1996, 226, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Brader, G.; Palva, E.T. The WRKY70 transcription factor: A node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell. 2004, 16, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihama, N.; Yoshioka, H. Post-translational regulation of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihama, N.; Yamada, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Katou, S.; Yoshioka, H. Phosphorylation of the Nicotiana benthamiana WRKY8 transcription factor by MAPK functions in the defense response. Plant Cell. 2011, 23, 1153–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Zhang, S. Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade induces WRKY family of transcription factors and defense genes in tobacco. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 38, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapila, J.; De Rycke, R.; Van Montagu, M.; Angenon, G. An Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression system for intact leaves. Plant Sci. 1997, 122, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wydro, M.; Kozubek, E.; Lehmann, P. Optimization of transient Agrobacterium-mediated gene expression system in leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2006, 53, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashandy, H.; Jalkanen, S.; Teeri, T.H. Within leaf variation is the largest source of variation in agroinfiltration of Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Methods 2015, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibbe, M.; Qu, N.; Galis, I.; Baldwin, I.T. Induced Plant Defenses in the Natural Environment: Nicotiana attenuata WRKY3 and WRKY6 Coordinate Responses to Herbivory. Plant Cell. 2008, 20, 1984–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, L.C.; van Strien, E.A. The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities, and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1999, 55, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, M.I.; Galdeano, M.M.; Gilardi, P.; García-Luque, I.; Serra, M.T. Proteomic analysis of pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs) induced by compatible and incompatible interactions of pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) in Capsicum chinense L3 plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutt, J.R.; Harpster, D.C.; Dixon, M.H.; Carr, J.P.; Dunsmuir, P.; Klessig, D.F. Disease response to tobacco mosaic virus in transgenic tobacco plants that constitutively express the pathogenesis-related PR1b gene. Virology 1989, 173, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-S.; Fu, S.-F.; Li, Z.; Murphy, A.M.; Dobson, E.A.; Garland, L.; Chaluvadi, S.R.; Lewsey, M.G.; Nelson, R.S.; Carr, J.P. Salicylic acid treatment and expression of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 transgene inhibit lethal symptoms and meristem invasion during tobacco mosaic virus infection in Nicotiana benthamiana. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collum, T.D.; Culver, J.N. Tobacco mosaic virus infection disproportionately impacts phloem associated translatomes in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana. Virology 2017, 510, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Target Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Product Length (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaWRKY2 (DQ402421) | accactgttacggagggtgt | cgaacgaaaggaaactgcta | 182 | 58 |
| CaWRKY2rt (DQ402421) | gcacaagtccaggatgtcca | tgagatgtcacggagggtct | 205 | 60 |
| M13 | gtaaaacgacggccag | caggaaacagctatgac | n.d. | 52 |
| TMV-CP (AF165190) | cttgtcatcagcgtgggc | aagtcactgtcagggaac | 165 | 47 |
| NbACS2 (Niben101Scf09512g03008) | aggtttgtgggtgttaagaa | ctaattcctccagtttaagtt | 191 | 58 |
| NbACS6 (Niben101Scf02334g00004) | aggagcaaacttcagatcag | ctgcacaaaatgggataa | 231 | 58 |
| NbGSTF (degenerate primers) * | ctggkgawcacaagaagc | gccaaratatcagcacacc | n.d. | 50 |
| NbGSTU1 (degenerate primers) * | gatggcagaagtgaagttg | ctcctagccaaaatscca | n.d. | 50 |
| NbLOX1 (KC585517) | gcctgttaaagttccatata | gcctacagcattacatcc | 231 | 58 |
| NtPR-1a (D90196) | taaaaagcaacttaaagtcaa | caagtagctagaccatcaaca | 194 | 58 |
| NtPR-1b (X03465) | cagggaagtggcgattttatg | agaccacttggactttttacagat | 400 | 60 |
| NbPR-10 (KF841443) | cagtgaaggcaaagatcaagc | caagcccttaggaactcttag | 253 | 60 |
| NbWRKY1 (Niben101Scf02430Ctg025) | ctcgtcggggtcttacatga | ttacagctgccaaccaatct | 277 | 60 |
| CaUBI-3 (AY486137 | tgtccatctgctctctgttg | caccccaagcacaataagac | 204 | 60 |
| Nt actin (X69885) ** | cggaatccacgagactacatac | gggaagccaagatagagc | 230 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juhász, C.; Szatmári, Á.; Bozsó, Z.; Barna, B.; Gullner, G. Transient Overexpression of the Pepper WRKY2 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana Markedly Delays the Systemic Necrosis Caused by Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Life 2025, 15, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040669
Juhász C, Szatmári Á, Bozsó Z, Barna B, Gullner G. Transient Overexpression of the Pepper WRKY2 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana Markedly Delays the Systemic Necrosis Caused by Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Life. 2025; 15(4):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040669
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuhász, Csilla, Ágnes Szatmári, Zoltán Bozsó, Balazs Barna, and Gábor Gullner. 2025. "Transient Overexpression of the Pepper WRKY2 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana Markedly Delays the Systemic Necrosis Caused by Tobacco Mosaic Virus" Life 15, no. 4: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040669
APA StyleJuhász, C., Szatmári, Á., Bozsó, Z., Barna, B., & Gullner, G. (2025). Transient Overexpression of the Pepper WRKY2 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana Markedly Delays the Systemic Necrosis Caused by Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Life, 15(4), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040669




