Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of HGYGT
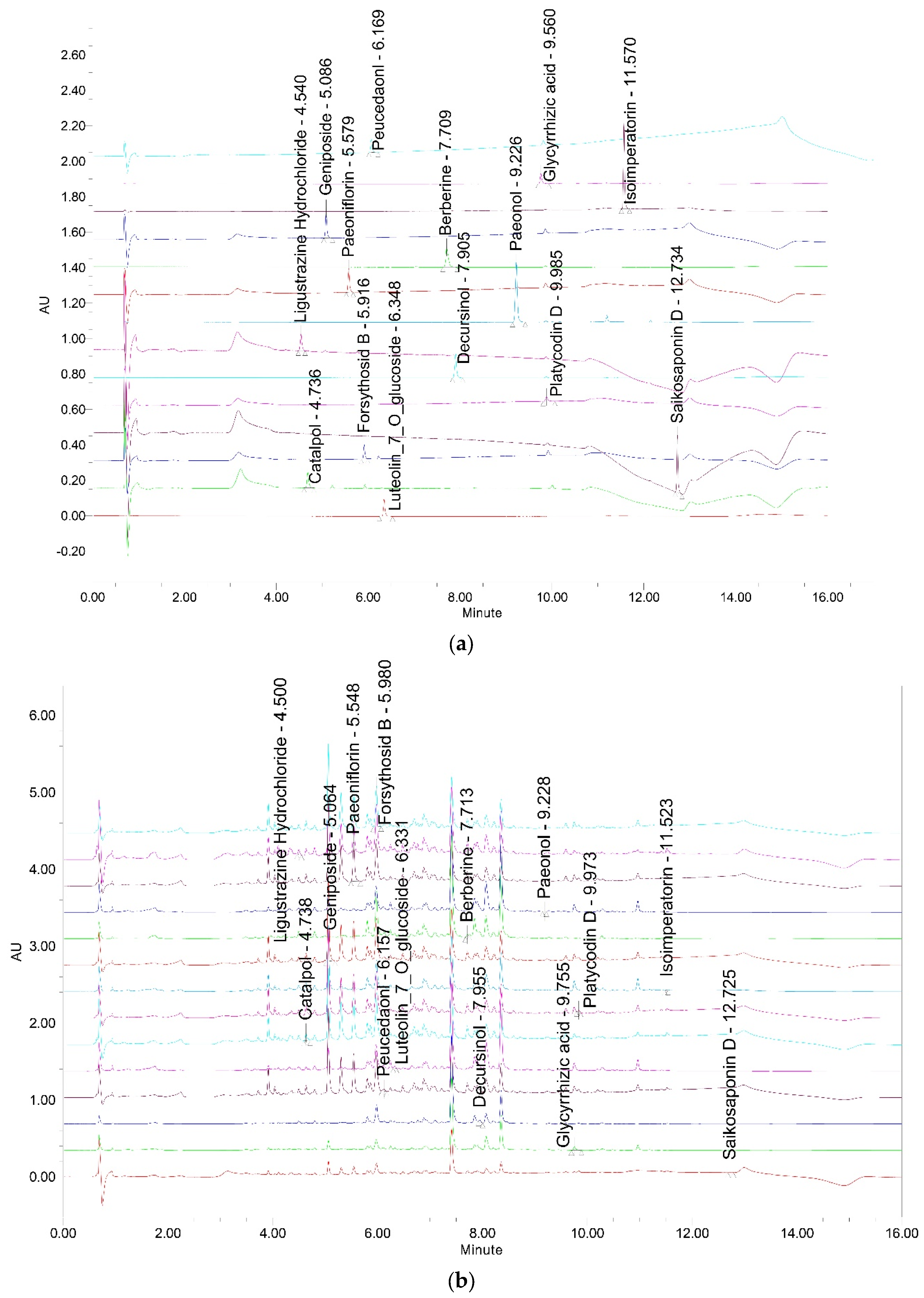
2.3. Chemical Profiling of HGYGT by UPLC
2.3.1. Chromatographic Conditions
2.3.2. Preparation of Sample and Standard Solutions
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. MTT Assay for Cell Viability
2.6. Measurement of NO
2.7. IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and PGE2 Assays
2.8. Preparation of Whole-Cell Extracts and Nuclear Fractions and Immunoblot Analysis
2.9. CA-Induced Paw Edema
2.10. Histological Evaluation
2.11. Blood Biochemistry
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of HGYGT
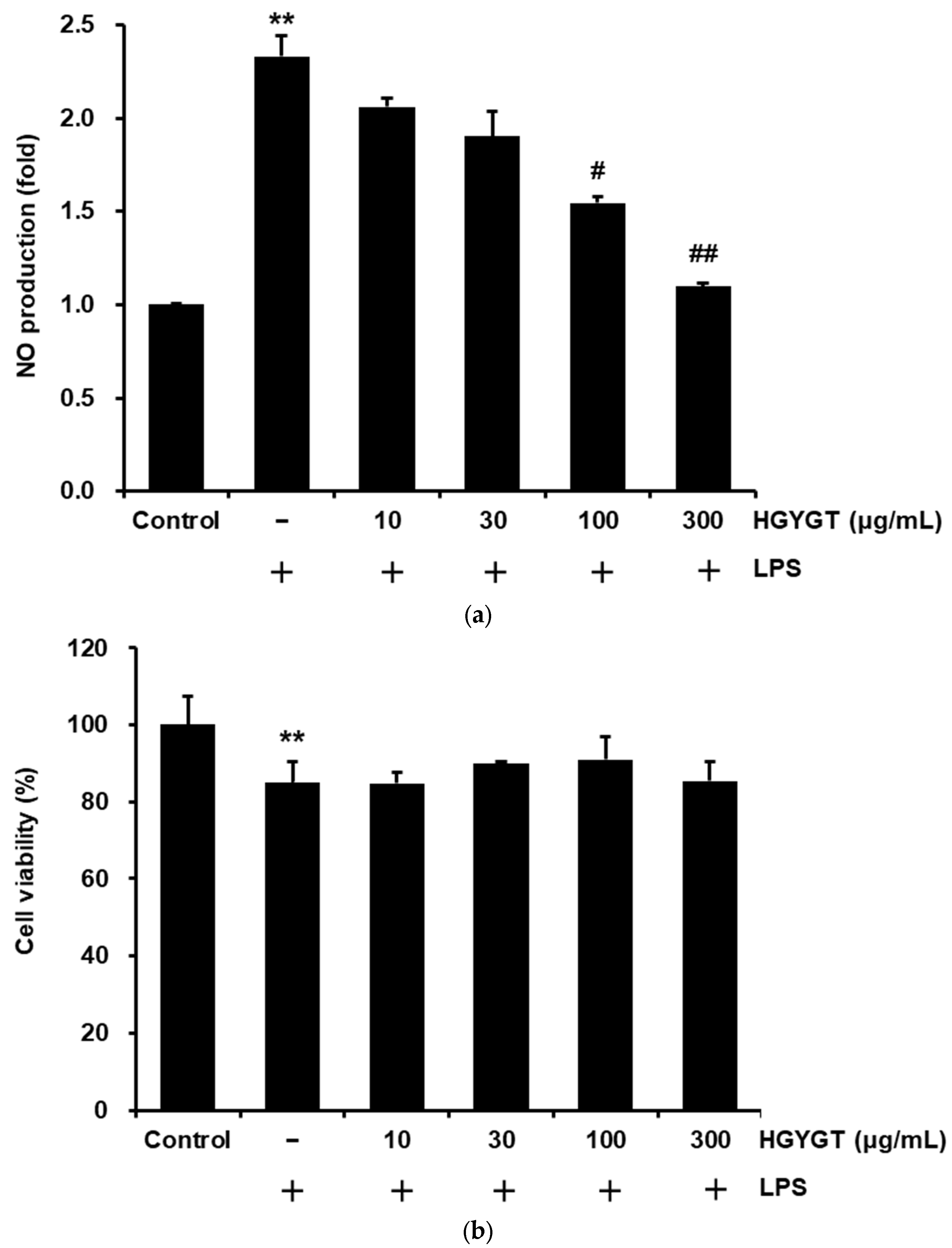
3.2. Effects of HGYGT on LPS-Stimulated NO Production and Cell Viability
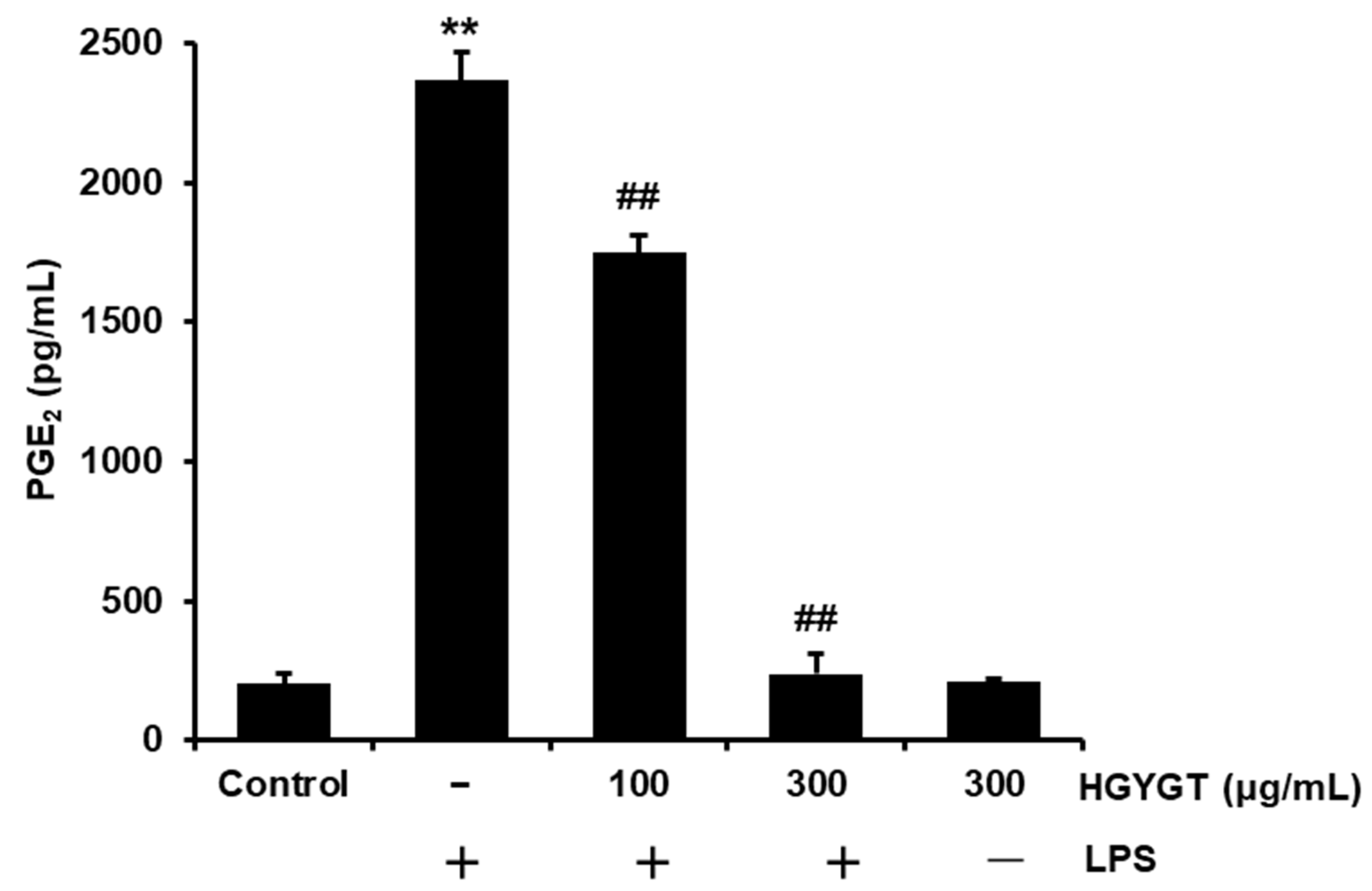
3.3. Effects of HGYGT on LPS-Induced PGE2 Production
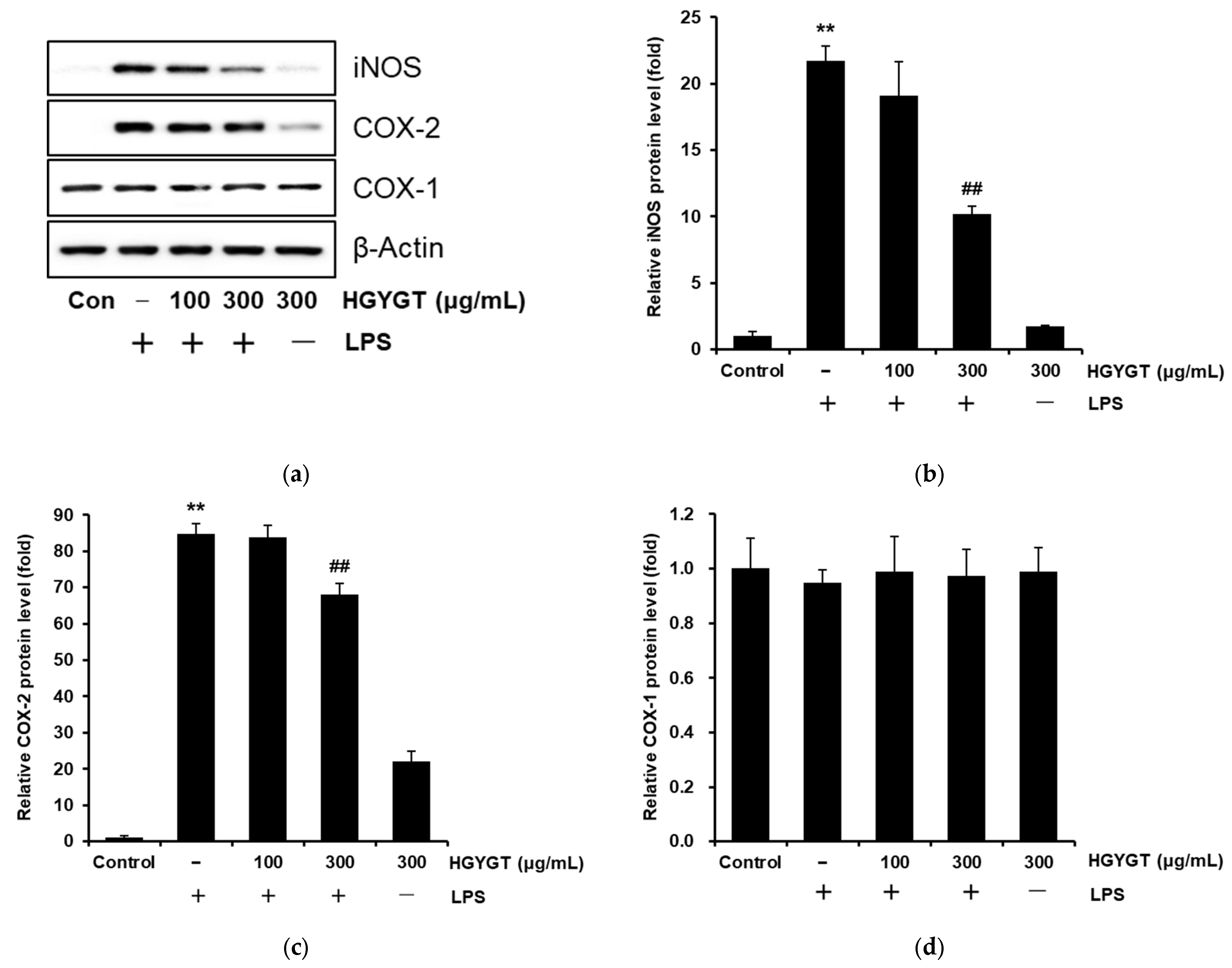
3.4. Effects of HGYGT on LPS-Stimulated iNOS, COX-1, and COX-2 Protein Expression
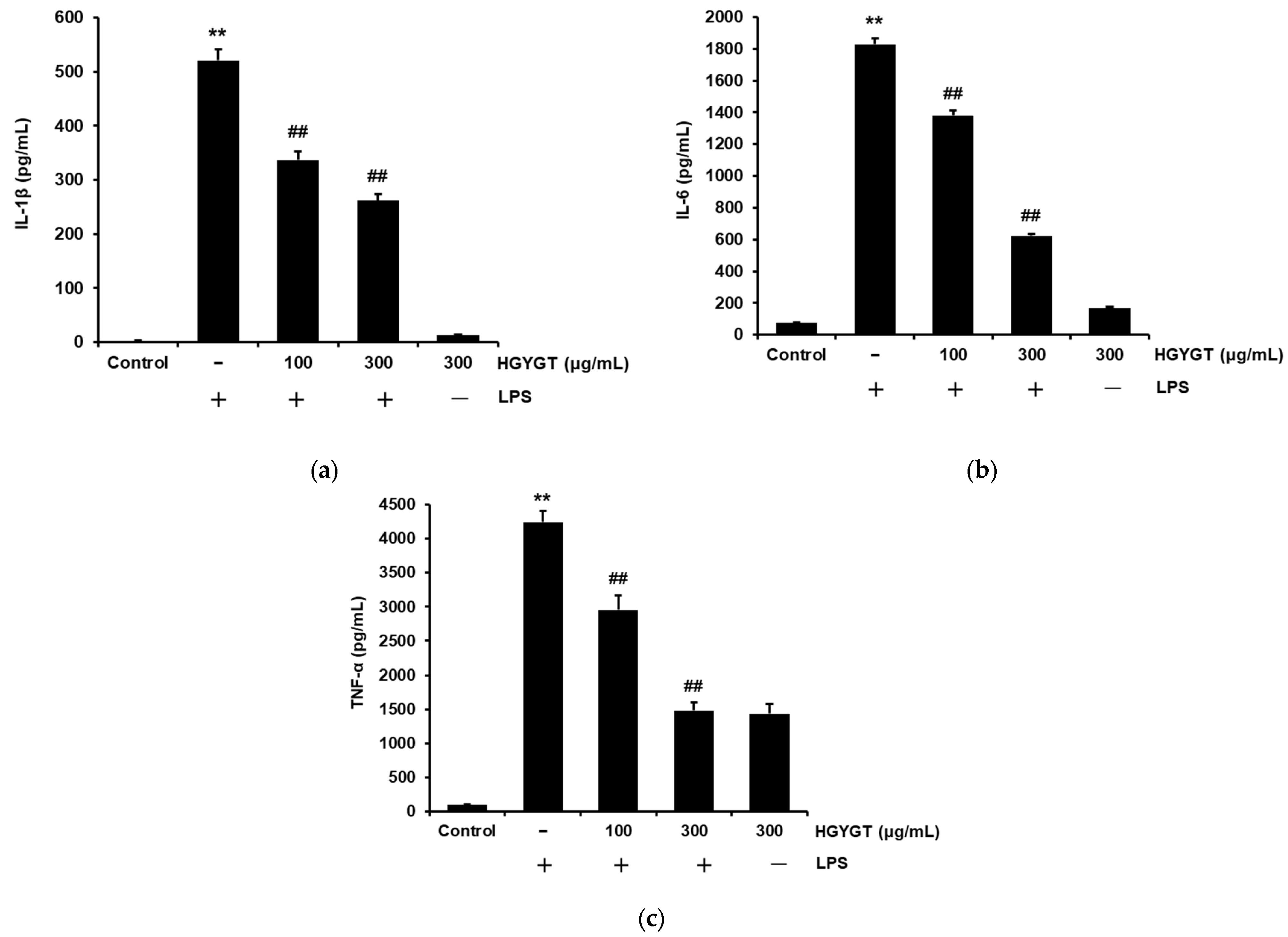
3.5. Effects of HGYGT on LPS-Induced IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α Production
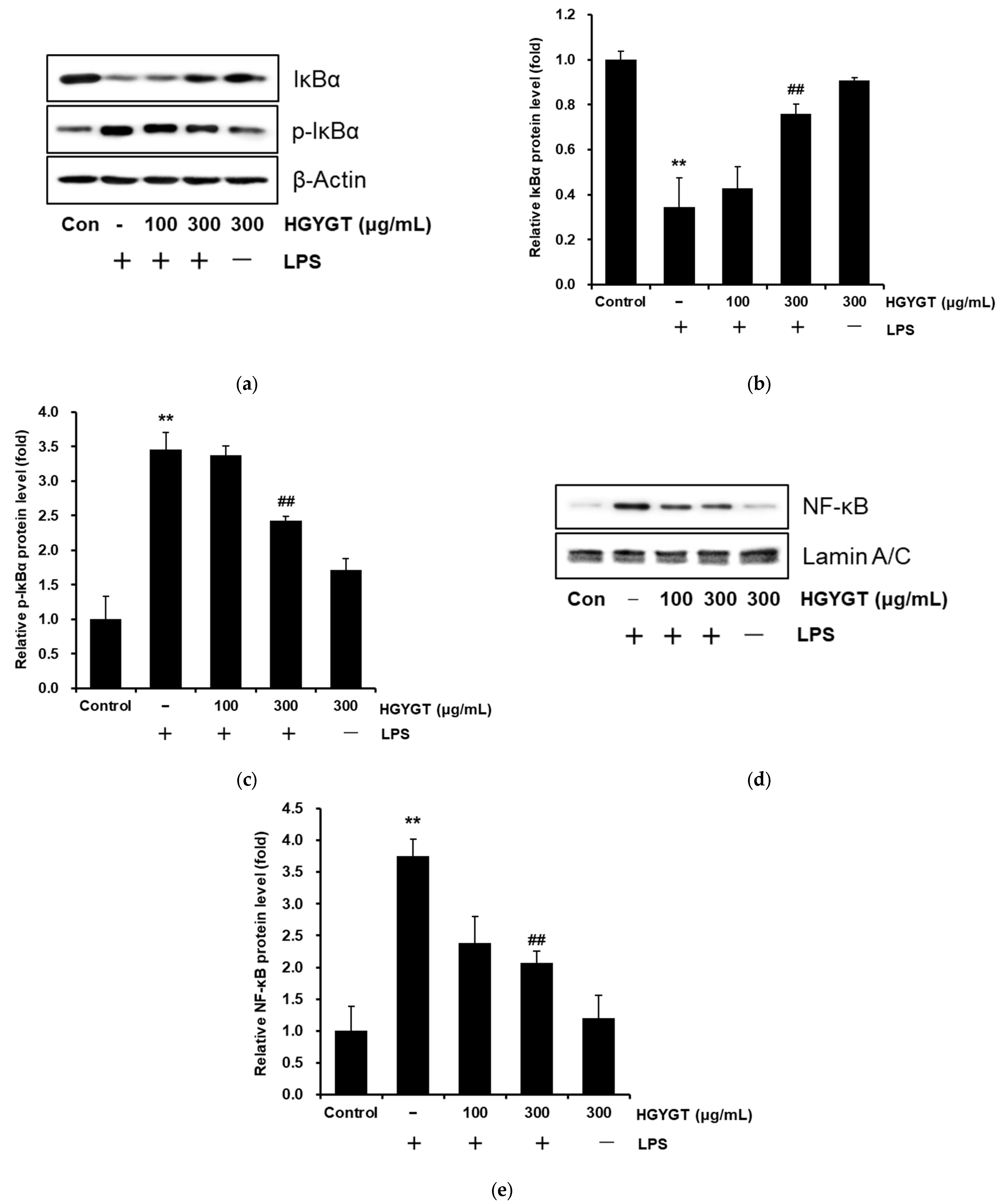
3.6. Effects of HGYGT on LPS-Stimulated Activation of NF-κB
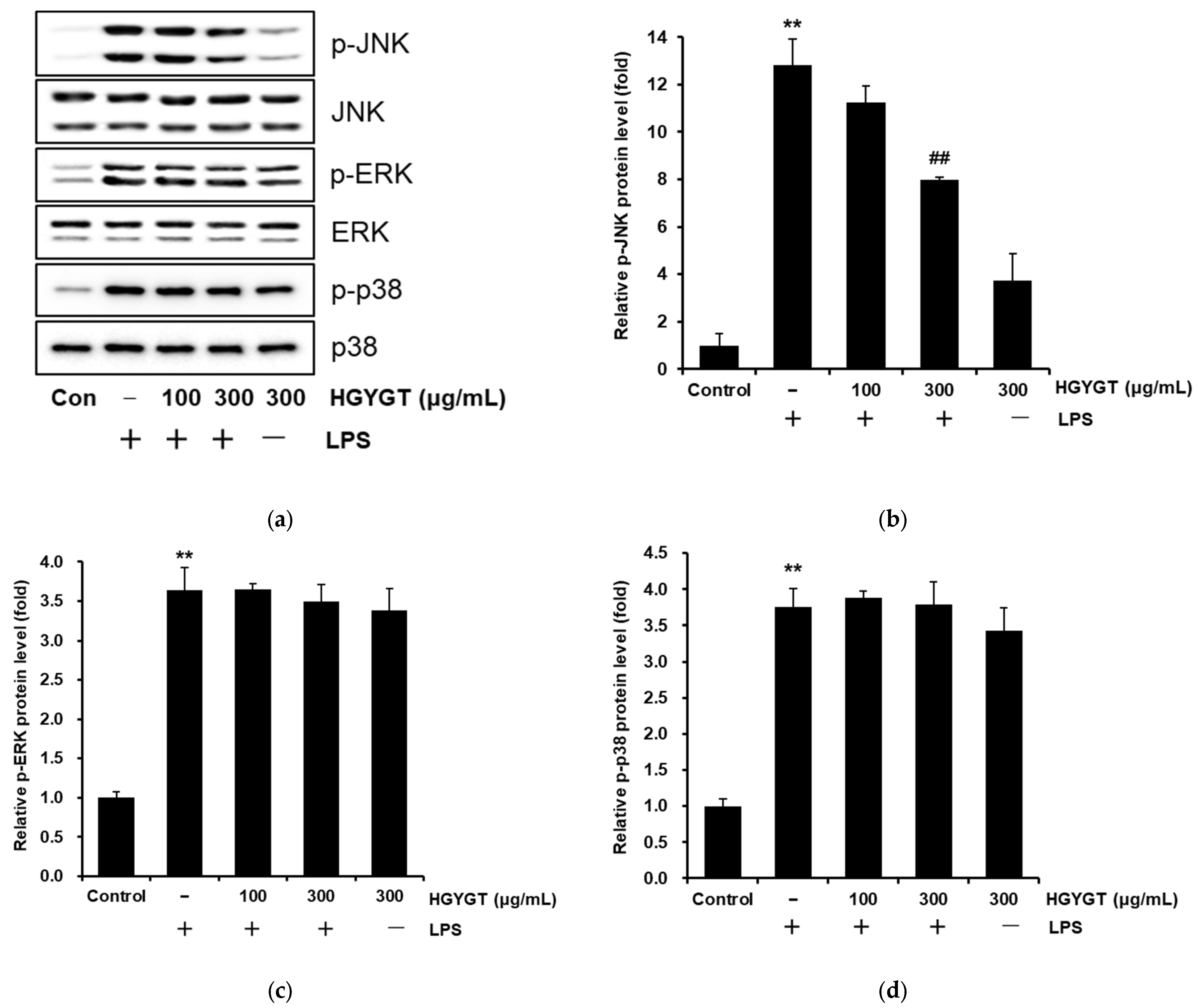
3.7. Inhibitory Effects of HGYGT on LPS-Stimulated Phosphorylation of MAPKs
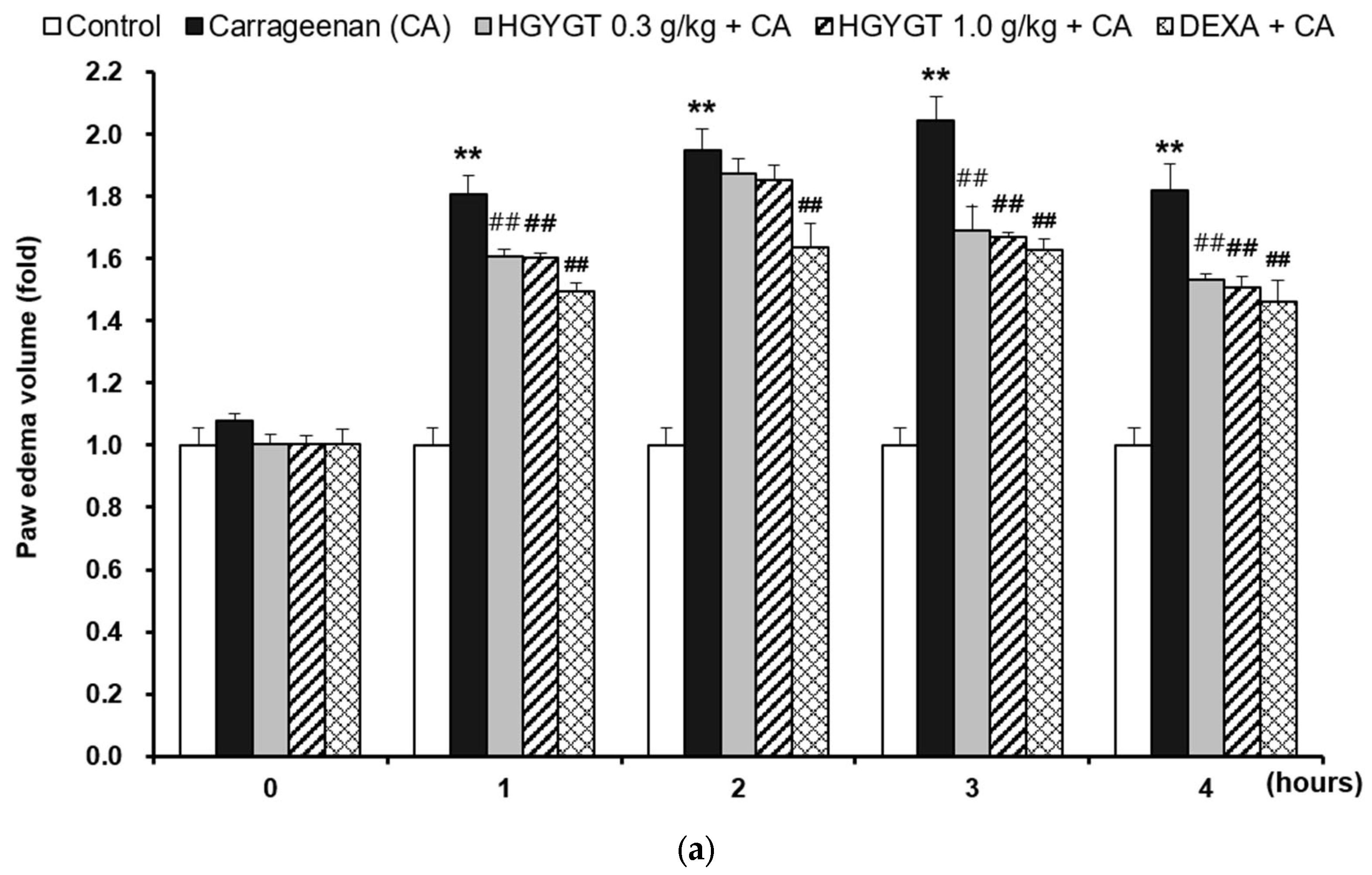
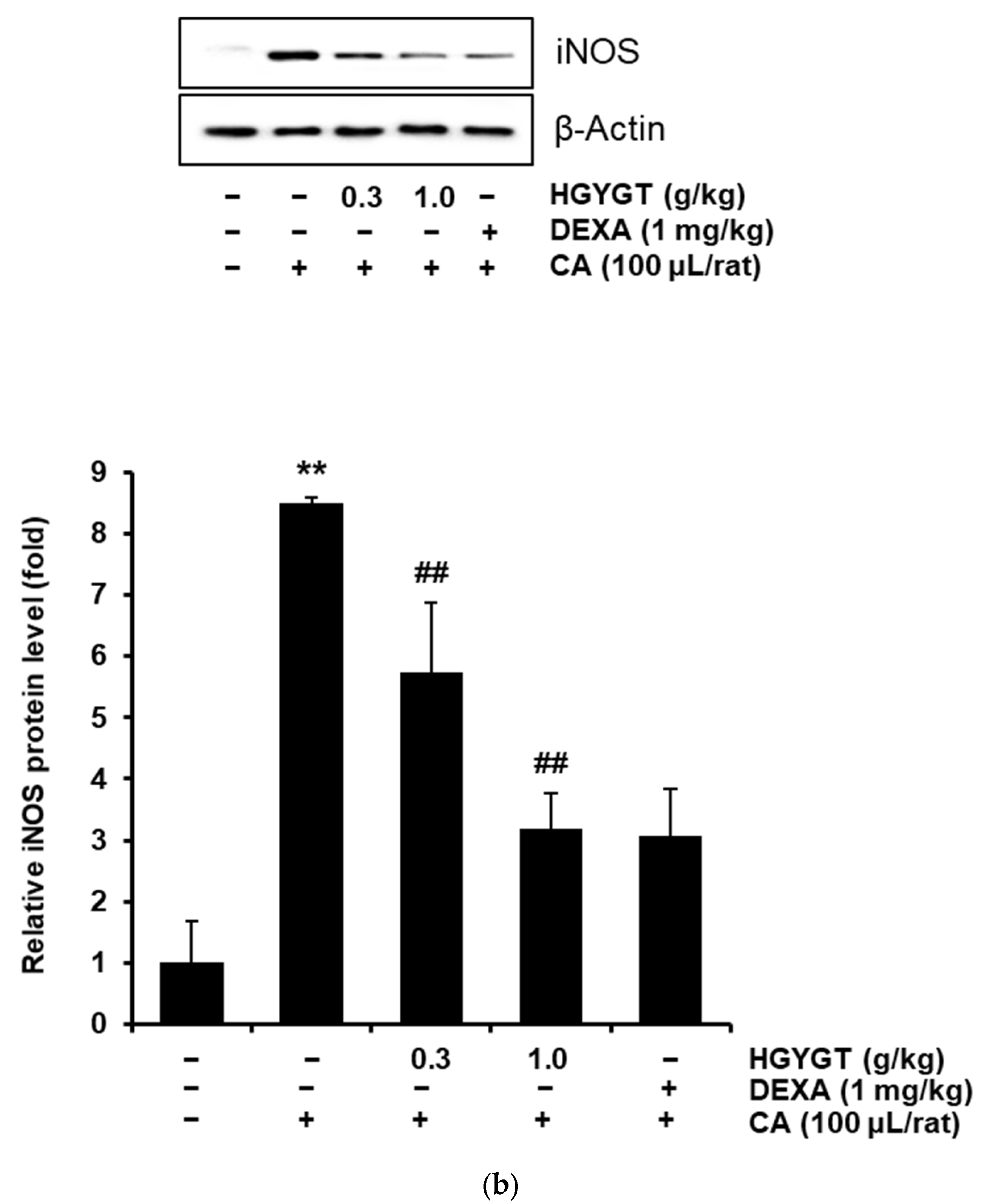
3.8. Effects of HGYGT on CA-Induced Paw Edema and Expression of iNOS Protein by CA in the Paw Tissues
3.9. Effects of HGYGT on Plasma Levels of ALT and AST
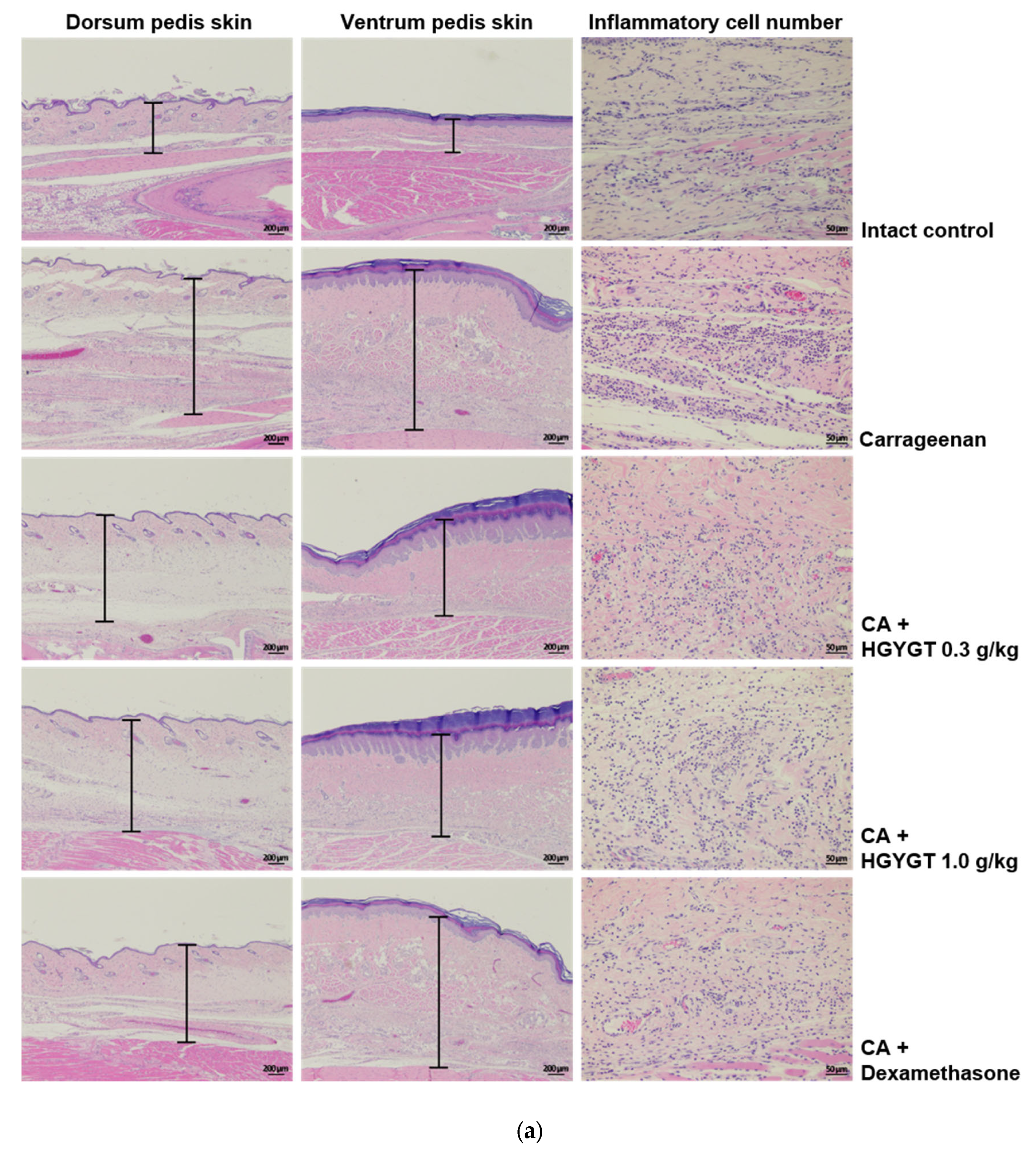
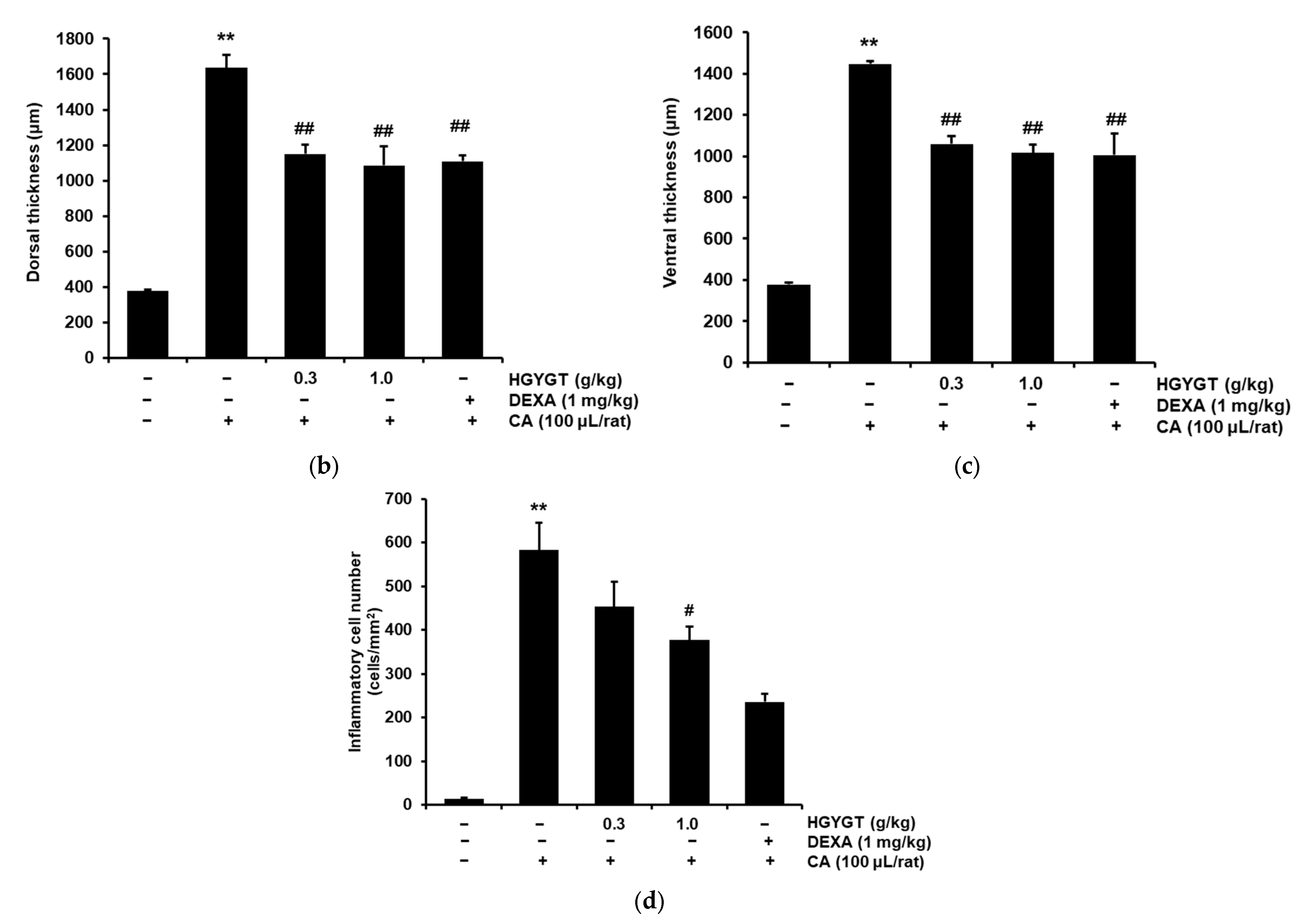
3.10. Effects of HGYGT on CA-Induced Paw Edema Through Histological Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Acid |
| CA | Carrageenan |
| COX | Cyclooxygenase |
| DEXA | Dexamethasone |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FA | Formic acid |
| FBS; | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| HGYGT | hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| IκBα | Inhibitor of κB alpha |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal Kinase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NC membrane | Nitrocellulose Membrane |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B cells |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PDA | Photodiode Array |
| p-ERK | Phosphorylated Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| p-IκBα | Phosphorylated Inhibitor of κB alpha |
| p-JNK | Phosphorylated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase |
| p-p38 | Phosphorylated p38 MAPK |
| RAW | Research Applications of Wistar Institute |
| SDS-PAGE: | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| TCMTNF-α | Traditional Chinese medicineTumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| Tukey’s HSD test | Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference test |
| UPLC | Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Shin, J.Y. Bangyakhappyeon Haeseol; Singwang Munhwasa: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1989; p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.I.; Chae, B.Y. Effects of Heounggaeyeoungyotang and Kamiheounggaeyeoungyo tang on the Analgesic, Antipyretic and Antiinflammatory action. KH Univ. O. Med. J. 1986, 9, 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.S.; Jin, Y.S.; Jeong, G.M. Study of the effects of Hyunggaeyeungyotang on the Anti-allergic effect in rats and mice. J. Korean Orient. Pediatr. 1990, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.J.; Shin, S.Y. Effects of Hyunggyeyungyotang and Kamihyunggyeyungyotang administration on the anti-inflammation, analgesia and anti-allergic reaction in mice. J. Korean Orient. Pediatr. 1997, 111, 249–273. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, S.C.; Jee, S.Y. Inhibitory Effect of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang Water Extract on production of Nitric Oxide, IL-6 and Expression of iNOS, COX-2 in LPS-Activated Raw 264.7 Cells. Korean J. Orient. Physiol. Pathol. 2007, 21, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Park, B.K.; Gim, S.B.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, D.H. The effects of HYGB on various immunological factors related to pathogenesis of allergic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. J. Haehwa Med. 2009, 18, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, R.Y.; Park, B.K.; Gim, S.B.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, D.H. The effects of HYT on various immunological factors related to pathogenesis of allergic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice induced by Biostir AD. J. Haehwa Med. 2009, 18, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Gim, S.B.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, D.H. Effect of Hyunggaeyunkyotang balhyobang (HYBH) on Atopic Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice Model. J. Haehwa Med. 2011, 19, 65–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.G.; Park, B.K.; Gim, S.B.; Lee, Y.K.; Jin, M.R.; Kim, D.H. Experimental Research of Hyunggaeyunkyotanggamibalhyobang (HYGBH) on Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. J. Haehwa Med. 2011, 19, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Hong, S.U. The effects of Hyunggaeyungyo-tang of suppression of iNOS production on RAW 264.7cell. J. Korean Med. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. Dermatol. 2011, 24, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Hong, S.U. The Effects of Hyunggaeyungyo-tang of Suppression of iNOS Production on Mice with Allergic Rhinitis. J. Korean Med. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. Dermatol. 2012, 25, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.H.; Kim, S.R.; Choi, H.S.; Ku, J.M.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.-G. Effects of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis model. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 418705. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, S.G.; Cho, N.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, H.S.; Kim, K.K. Investigation of Antimicrobial and Anti-inflammatory Activities of the Hyeonggaeyeongyotang Gagambang. Korea J. Herbol. 2018, 33, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D. Progress of research into the pharmacological effect and clinical application of the traditional Chinese medicine Rehmanniae Radix. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115809. [Google Scholar]
- Tafrihi, M.; Imran, M.; Tufail, T.; Gondal, T.A.; Caruso, G.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, R.; Atanassov, M.; Atanassov, L.; Fokou, P.V.T.; et al. The Wonderful Activities of the Genus Mentha: Not Only Antioxidant Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Zhao, R.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.R.; Cho, I.J.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.C. Anti-inflammatory effects of liquiritigenin as a consequence of the inhibition of NF-kappaB-dependent iNOS and pro-inflammatory cytokines production. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.W.; Park, S.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Jegal, K.H.; Lee, J.R.; Cho, I.J.; Ku, S.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Ahn, Y.T.; Son, Y.; et al. Biomolecular evidence of anti-inflammatory effects by Clematis mandshurica Ruprecht root extract in rodent cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.W.; Park, S.M.; Zhao, R.; Lee, C.; Chun, W.; Son, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jegal, K.H.; Cho, I.J.; et al. Hederagenin, a major component of Clematis mandshurica Ruprecht root, attenuates inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cells and in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 528–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.M.; Hwangbo, M.; Lee, J.R.; Byun, S.H.; Ku, S.K.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C.; Jee, S.Y.; Park, S.J. Cheongsangbangpung-tang ameliorated the acute inflammatory response via the inhibition of NF-κB activation and MAPK phosphorylation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Kubes, P. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: A little bit of good in all of us. Gut 2000, 47, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, W.F.; Chou, C.J.; Chen, C.F. Camptothecin suppresses nitric oxide biosynthesis in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 625–635. [Google Scholar]
- Gröesch, S.; Maier, T.J.; Schiffmann, S.; Geisslinger, G. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) independent anticarcinogenic effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 736–747. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichman, A.H. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 5th ed.; Saunders: Philadelpia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 243–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J. The role of interleukin-1 family in fibrotic diseases. Cytokine 2023, 165, 156161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aliyu, M.; Zohora, F.T.; Anka, A.U.; Ali, K.; Maleknia, S.; Saffarioun, M.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-6 cytokine: An overview of the immune regulation, immune dysregulation, and therapeutic approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiegs, G.; Horst, A.K. TNF in the liver: Targeting a central player in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 445–459. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, W.Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenosides from Panax ginseng as Key Modulators of NFκB Signaling Are Powerful Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6119. [Google Scholar]
- Solt, L.A.; May, M.J. The IκB kinase complex: Master regulator of NF-κB signaling. Immunol. Res. 2008, 42, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.L.; Lapadat, R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 2002, 298, 1911–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Han, J.; Hui, L. MAPK signaling in inflammation-associated cancer development. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Gamache, D.A.; Povlishock, J.T.; Ellis, E.F. Carrageenan-induced brain inflammation. Characterization of the model. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J.; Sedgwick, A.D.; Edwards, J.C.; Lees, P. A comparative study of the cellular, exudative and histological responses to carrageenan, dextran and zymosan in the mouse. Int. J. Tissue React. 1991, 13, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, R.L.C.; Moore, P.K. A comparison of the effects of L-NAME, 7-NI and L-NIL on carrageenan-induced hind paw oedema and NOS activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Mazumder, U.K.; Gomathi, P.; Selvan, V.T. Anti-inflammatory evaluation of leaves of Plumeria acuminate. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.V.; Verma, A.R.; Gupta, P.K.; Vijayakumar, M. Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities of Fumaria indica whole plant extract in experimental animals. Acta Pharm. 2007, 57, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Lian, Q. Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of osthole in rats. Zhong Yao Cai 2005, 28, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Beloeil, H.; Ababneh, Z.; Chung, R.; Zurakowski, D.; Mulkern, R.V.; Berde, C.B. Effects of bupivacaine and tetrodotoxin on carrageenan-induced hind paw inflammation in rats (Part 1): Hyperalgesia, edema, and systemic cytokines. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. Forsythoside B attenuates neuro-inflammation and neuronal apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB and p38-MAPK signaling pathways through activating Nrf2 post spinal cord injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, L. Platycodin D relieves rheumatoid arthritis by promoting apoptosis of mitochondria to inhibit activation of hedgehog pathway. Autoimmunity 2023, 56, 2205053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Huang, C.S.; Wang, F.; Gong, J.Y.; Pan, Z.H. Effect of ligustrazine hydrochloride on coagulation reaction and inflammation reaction in single valve replacement patients with rheumatic heart disease undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2014, 34, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, W. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xie, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, K.; Guan, X.; Ni, C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, L. Paeonol allevites ulcerative colitis in mice by increasing short-chain fatty acids derived from Clostridium butyricum. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155056. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Shi, Z.; You, L.; Du, Y.; Ni, J.; Yan, D. Neuroprotective Effect of Catalpol via Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 690. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Yin, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Si, H.; Xia, D. Inhibition of inflammation by berberine: Molecular mechanism and network pharmacology analysis. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.S. Pharmacological effect of decursin, decursinol angelate, and decursinol derived from Angelica gigas Nakai. J. Life Sci. 2021, 31, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; He, W.; Shen, L.; Zhang, R. Glycyrrhizic acid alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury by regulating angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and caveolin-1 signaling pathway. Inflammation 2022, 45, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, N.; Chang, W. Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220541. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhao, R. Geniposide ameliorates psoriatic skin inflammation by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway and MMP9. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 133, 112082. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, H.; Wei, X.; Dong, X.; Chi, L. Anti-inflammatory effect of luteolin-7-O-glucoside via the JAK1/STAT6/SOCS1 pathway in ulcerative colitis treatment. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2022, 18, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.N.; Yuan, Z.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Yan, R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Liao, M.; Chen, J.X. Saikosaponin a and its epimer saikosaponin d exhibit anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, I.G.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.G.; Oh, M.S. Comparative study of Bang-poong (root of Saposhnikovia divaricata Schischkin) and related species on neuroprotective and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effects. Korea J. Herbol. 2019, 34, 29–37. [Google Scholar]

| Scientific Name | Dose (g) |
|---|---|
| Schizonepeta tenuifolia Briq | 1.875 g |
| Bupleurum falcatum L. | 1.875 g |
| Cnidium officinale Makino | 1.875 g |
| Angelica gigas Nakai | 1.875 g |
| Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC | 1.875 g |
| Paeonia lactiflora Pall | 1.875 g |
| A. dahurica (Hoffm.) Benth. & Hook.f. ex Franch. and Sav | 1.875 g |
| Saposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz.) Schischk | 1.875 g |
| Mentha arvensis L. | 1.875 g |
| Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis | 1.875 g |
| Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | 1.875 g |
| Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC | 1.875 g |
| Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl | 1.875 g |
| Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch | 1.125 g |
| Time (min) | 0.1% FA/Water (%) | 0.1% FA/Acetonitrile (%) | Flow Rate (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| 1.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| 2.0 | 90 | 10 | 0.40 |
| 5.0 | 65 | 35 | 0.40 |
| 6.0 | 50 | 50 | 0.40 |
| 7.0 | 50 | 50 | 0.40 |
| 9.0 | 30 | 70 | 0.40 |
| 13.0 | 10 | 90 | 0.40 |
| 14.0 | 2 | 98 | 0.40 |
| 15.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| 16.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.40 |
| Compound | Content (μg/g) |
|---|---|
| Forsythoside B | 93.842 ± 0.649 |
| Platycodin D | 39.998 ± 1.363 |
| Ligustrazine Hydrochloride | 5.687 ± 0.207 |
| Paeoniflorin | 42.873 ± 2.632 |
| Paeonol | 0.417 ± 0.044 |
| Catalpol | 11.057 ± 0.645 |
| Berberine | 2.660 ± 0.086 |
| Decursinol | 2.977 ± 0.280 |
| Glycyrrhizic acid | 21.279 ± 1.244 |
| Isoimperatorin | 0.369 ± 0.021 |
| Geniposide | 71.665 ± 4.486 |
| Luteolin-7-glucopyranoside | 10.437 ± 0.428 |
| Saikosaponin D | 2.054 ± 0.135 |
| Peucedanol | 20.507 ± 0.375 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.H.; Kim, M.H.; Nam, H.J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Life 2025, 15, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040587
Lee KH, Kim MH, Nam HJ. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Life. 2025; 15(4):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040587
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Keun Hee, Min Hee Kim, and Hae Jeong Nam. 2025. "Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies" Life 15, no. 4: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040587
APA StyleLee, K. H., Kim, M. H., & Nam, H. J. (2025). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Life, 15(4), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040587






