Radiomics Results for Adrenal Mass Characterization Are Stable and Reproducible Under Different Software
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.2. Statistical Comparison and Correlation Analysis
2.3. Visualization
2.4. Model Training and Evaluation
- Logistic Regression: A linear model used for binary classification.
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA): A linear classifier that assumes normal distribution of the data and equal covariance matrices for each class.
- Linear Support Vector Machine (SVM): A linear classifier that finds the hyperplane that best separates the data into classes.
- Accuracy: The proportion of correctly classified instances.
- Precision: The proportion of true positive instances among the instances classified as positive.
- Recall: The proportion of true positive instances among the actual positive instances.
- F1 Score: The harmonic mean of precision and recall.
2.5. Feature Importances
2.6. Statistical Significance of Model Performance
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Comparison and Correlation Analysis
3.2. Visualization
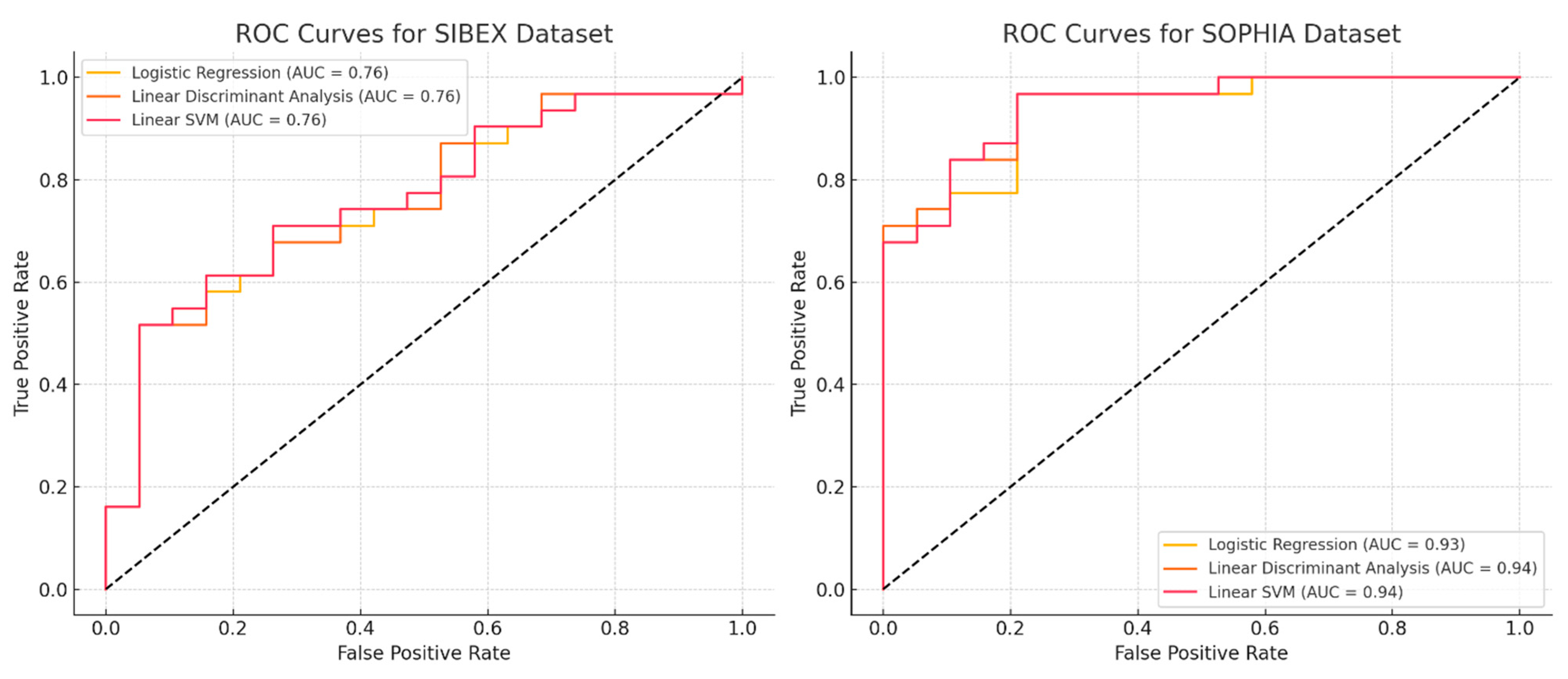
3.3. Model Performance
- Logistic Regression: Accuracy 0.72, Precision 0.730, Recall 0.871, F1 Score 0.794
- Linear Discriminant Analysis: Accuracy 0.72, Precision 0.718, Recall 0.903, F1 Score 0.800
- Linear SVM: Accuracy 0.66, Precision 0.719, Recall 0.742, F1 Score 0.730
- Logistic Regression: Accuracy 0.90, Precision 0.882, Recall 0.968, F1 Score 0.923
- Linear Discriminant Analysis: Accuracy 0.84, Precision 0.871, Recall 0.871, F1 Score 0.871
- Linear SVM: Accuracy 0.90, Precision 0.882, Recall 0.968, F1 Score 0.923
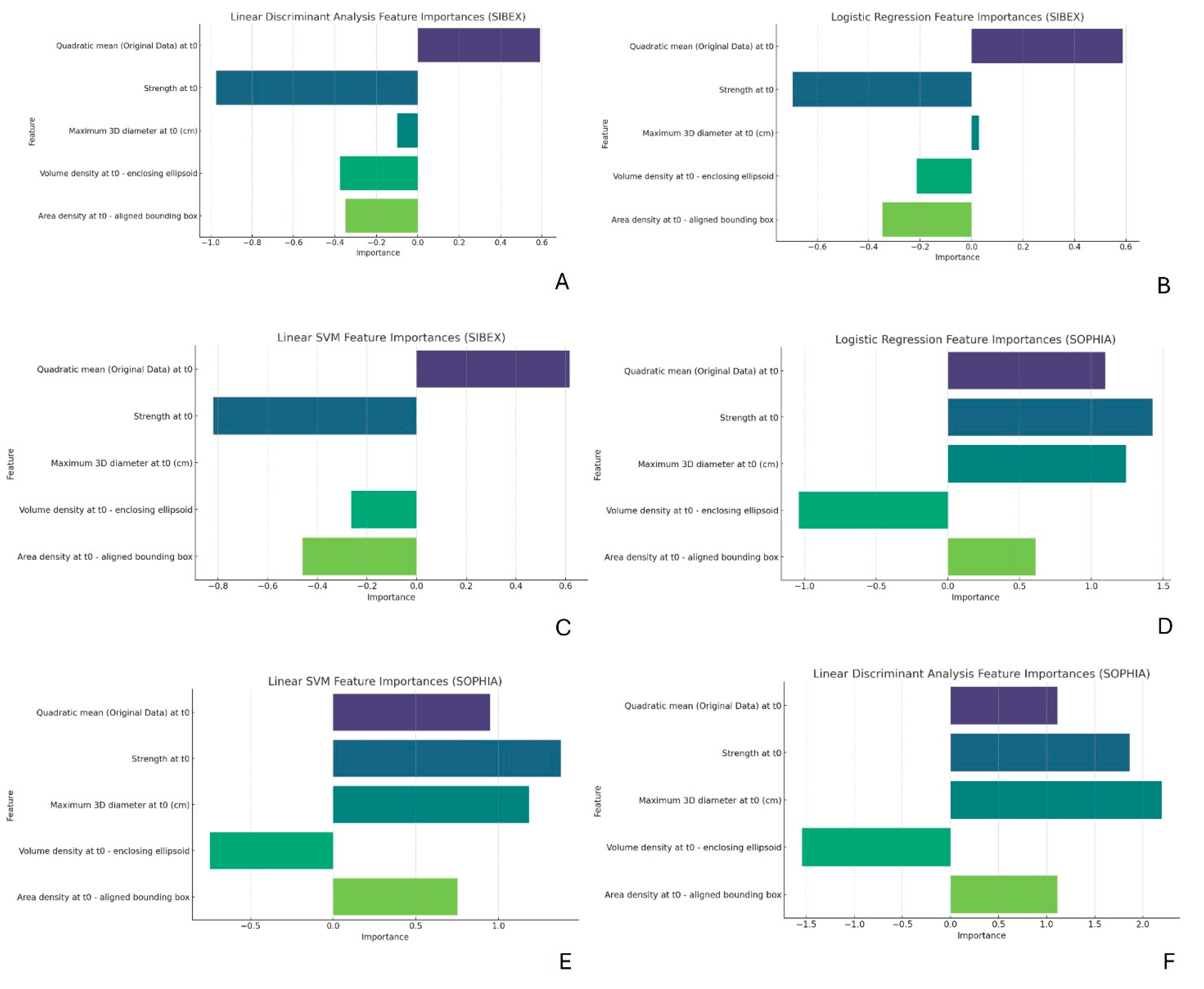
3.4. Feature Importances
3.5. Statistical Significance of Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| IBSI | Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
References
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in Medical Imaging—“How-to” Guide and Critical Reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliciani, G.; Mellini, L.; Carnevale, A.; Sarnelli, A.; Menghi, E.; Piccinini, F.; Scarpi, E.; Loi, E.; Galeotti, R.; Giganti, M.; et al. The Potential Role of MR Based Radiomic Biomarkers in the Characterization of Focal Testicular Lesions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Urso, L.; Bianconi, F.; Palumbo, B.; Marzola, M.C.; Evangelista, L.; Schillaci, O. Radiomics and Theranostics with Molecular and Metabolic Probes in Prostate Cancer: Toward a Personalized Approach. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Palumbo, D.; De Cobelli, F.; Fiorino, C. Does Radiomics Play a Role in the Diagnosis, Staging and Re-Staging of Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma? Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lei, H.; Pang, J. Diagnostic Performance of Radiomics in Adrenal Masses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 975183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, K.; Wei, R.; Zuo, M.; Yao, W.; Zheng, Z.; He, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, C.; An, C.; et al. A Multitask Deep Learning Radiomics Model for Predicting the Macrotrabecular-Massive Subtype and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kui, X.; Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J. Computed Tomography-Derived Intratumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics in Predicting EGFR Mutation in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciani, G.; Serra, F.; Menghi, E.; Ferroni, F.; Sarnelli, A.; Feo, C.; Zatelli, M.C.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Giganti, M.; Carnevale, A. Radiomics in the Characterization of Lipid-Poor Adrenal Adenomas at Unenhanced CT: Time to Look beyond Usual Density Metrics. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Jin, S.; Yang, J.; Pan, W.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Ji, W. Can Radiomics Provide Additional Diagnostic Value for Identifying Adrenal Lipid-Poor Adenomas From Non-Adenomas on Unenhanced CT? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 888778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klontzas, M.E. Radiomics Feature Reproducibility: The Elephant in the Room. Eur. J. Radiol. 2024, 175, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B. Understanding Sources of Variation to Improve the Reproducibility of Radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 633176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-Based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligero, M.; Jordi-Ollero, O.; Bernatowicz, K.; Garcia-Ruiz, A.; Delgado-Muñoz, E.; Leiva, D.; Mast, R.; Suarez, C.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Calvo, N.; et al. Minimizing Acquisition-Related Radiomics Variability by Image Resampling and Batch Effect Correction to Allow for Large-Scale Data Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traverso, A.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Gillies, R. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, L.; Fiz, F.; Laudicella, R.; Bianconi, F.; Castello, A.; Guglielmo, P.; Liberini, V.; Manco, L.; Frantellizzi, V.; Giordano, A.; et al. PET Radiomics and Response to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Cancers 2023, 15, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennestrì, F.; De Crea, C.; Voloudakis, N.; Raffaelli, M. Laparoscopic Transabdominal Anterior Bilateral Adrenalectomy (La-TABA): An Alternative Approach for Severe Cushing’s Syndrome. Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, R.W.; Nepute, J.C.; Hayek, M.E.; Albert, S.G. Adrenal Incidentalomas: Clinical Controversies and Modified Recommendations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Smith, W.W.; Song, J.H.; Boland, G.L.; Francis, I.R.; Israel, G.M.; Mazzaglia, P.J.; Berland, L.L.; Pandharipande, P.V. Management of Incidental Adrenal Masses: A White Paper of the ACR Incidental Findings Committee. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-B.; Huang, Y.-S.; Yan, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.-H.; Gu, G.-L. Comparison of Lateral Transperitoneal versus Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy for Pheochromocytoma: A Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-García, J.J.; Gil Navarro, R.; Franco Campello, M.; Costa Navarro, R.; Gomis Martín, A.; Villodre Tudela, C.; Zaragoza Zaragoza, C.; Carrión Tomás, A.; Ramia-Ángel, J.M. A Novel Study, Textbook Outcome in Adrenalectomy: Retrospective Observational Study in an Endocrine Surgical Unit. Updates Surg. 2024, 76, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, M.; Tsagarakis, S.; Terzolo, M.; Tabarin, A.; Sahdev, A.; Newell-Price, J.; Pelsma, I.; Marina, L.; Lorenz, K.; Bancos, I.; et al. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas, in Collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 189, G1–G42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Carnevale, A.; Angileri, S.A.; Pellegrino, F.; Renzulli, M.; Golfieri, R.; Zhang, D.; Sun, H.; Giganti, M.; Dionigi, G.; et al. Outcomes Following Minimally Invasive Imagine-Guided Percutaneous Ablation of Adrenal Glands. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Elbanan, M.G.; Luna, A.; Haider, M.A.; Smith, A.D.; Sabottke, C.F.; Spieler, B.M.; Turkbey, B.; Fuentes, D.; Moawad, A.; et al. Radiomics in Abdominopelvic Solid-Organ Oncologic Imaging: Current Status. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Del Giudice, C.; Coppola, A.; Carnevale, A.; Giganti, M.; Renzulli, M.; Tacher, V.; Urbano, J.; Kobeiter, H.; Loffroy, R.; et al. Gastrointestinal Hemorrhages in Patients with COVID-19 Managed with Transarterial Embolization. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Gu, X.; Huang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, L.; Luo, N.; Lin, H.; Jin-yuan, L. Nomogram Based on Clinical and Preoperative CT Features for Predicting the Early Recurrence of Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma: A Multicenter Study. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, A.; Galatola, R.; Cuocolo, R.; Romeo, V.; Verde, F.; Mainenti, P.P.; Brunetti, A.; Maurea, S. Radiomics in Cross-Sectional Adrenal Imaging: A Systematic Review and Quality Assessment Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santinha, J.; Pinto dos Santos, D.; Laqua, F.; Visser, J.J.; Groot Lipman, K.B.W.; Dietzel, M.; Klontzas, M.E.; Cuocolo, R.; Gitto, S.; Akinci D’Antonoli, T. ESR Essentials: Radiomics—Practice Recommendations by the European Society of Medical Imaging Informatics. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Leger, S.; Agolli, L.; Pilz, K.; Troost, E.G.C.; Richter, C.; Löck, S. Assessing Robustness of Radiomic Features by Image Perturbation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Bussink, J.; Lambin, P.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Machine Learning Methods for Quantitative Radiomic Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tăbăcaru, G.; Moldovanu, S.; Răducan, E.; Barbu, M. A Robust Machine Learning Model for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Tăbăcaru, G.; Moldovanu, S.; Barbu, M. Texture Analysis of Breast US Images Using Morphological Transforms, Hausdorff Dimension and Bagging Ensemble Method. In Proceedings of the 32nd Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Chania, Greece, 11–14 June 2024. [Google Scholar]

| Radiomic Feature | t_stat | p_value |
|---|---|---|
| Quadratic mean | −0.84 | 1.00 |
| Strength | 0.97 | 1.00 |
| Maximum 3D diameter | 2.20 | 1.00 |
| Volume density—enclosing ellipsoid | −0.81 | 1.00 |
| Area density—aligned bounding box | −0.39 | 1.00 |
| Radiomic Feature | Spearman Correlation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Quadratic mean | 0.81 | <0.01 |
| Strength | 0.74 | <0.01 |
| Maximum 3D diameter | 0.97 | <0.01 |
| Volume density—enclosing ellipsoid | 0.48 | <0.01 |
| Area density—aligned bounding box | 0.51 | <0.01 |
| SIBEX software | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.87 | 0.79 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.90 | 0.80 |
| Linear SVM | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.73 |
| SOPHIA software | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
| Logistic Regression | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.92 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| Linear SVM | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feliciani, G.; Mascolo, F.; Cossu, A.; Urso, L.; Feletti, F.; Menghi, E.; Sarnelli, A.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Giganti, M.; Carnevale, A. Radiomics Results for Adrenal Mass Characterization Are Stable and Reproducible Under Different Software. Life 2025, 15, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040560
Feliciani G, Mascolo F, Cossu A, Urso L, Feletti F, Menghi E, Sarnelli A, Ambrosio MR, Giganti M, Carnevale A. Radiomics Results for Adrenal Mass Characterization Are Stable and Reproducible Under Different Software. Life. 2025; 15(4):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040560
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeliciani, Giacomo, Francesca Mascolo, Alberto Cossu, Luca Urso, Francesco Feletti, Enrico Menghi, Anna Sarnelli, Maria Rosaria Ambrosio, Melchiore Giganti, and Aldo Carnevale. 2025. "Radiomics Results for Adrenal Mass Characterization Are Stable and Reproducible Under Different Software" Life 15, no. 4: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040560
APA StyleFeliciani, G., Mascolo, F., Cossu, A., Urso, L., Feletti, F., Menghi, E., Sarnelli, A., Ambrosio, M. R., Giganti, M., & Carnevale, A. (2025). Radiomics Results for Adrenal Mass Characterization Are Stable and Reproducible Under Different Software. Life, 15(4), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040560








