A Decade of Progress in Ultrasound Assessments of Subcutaneous and Total Body Fat: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
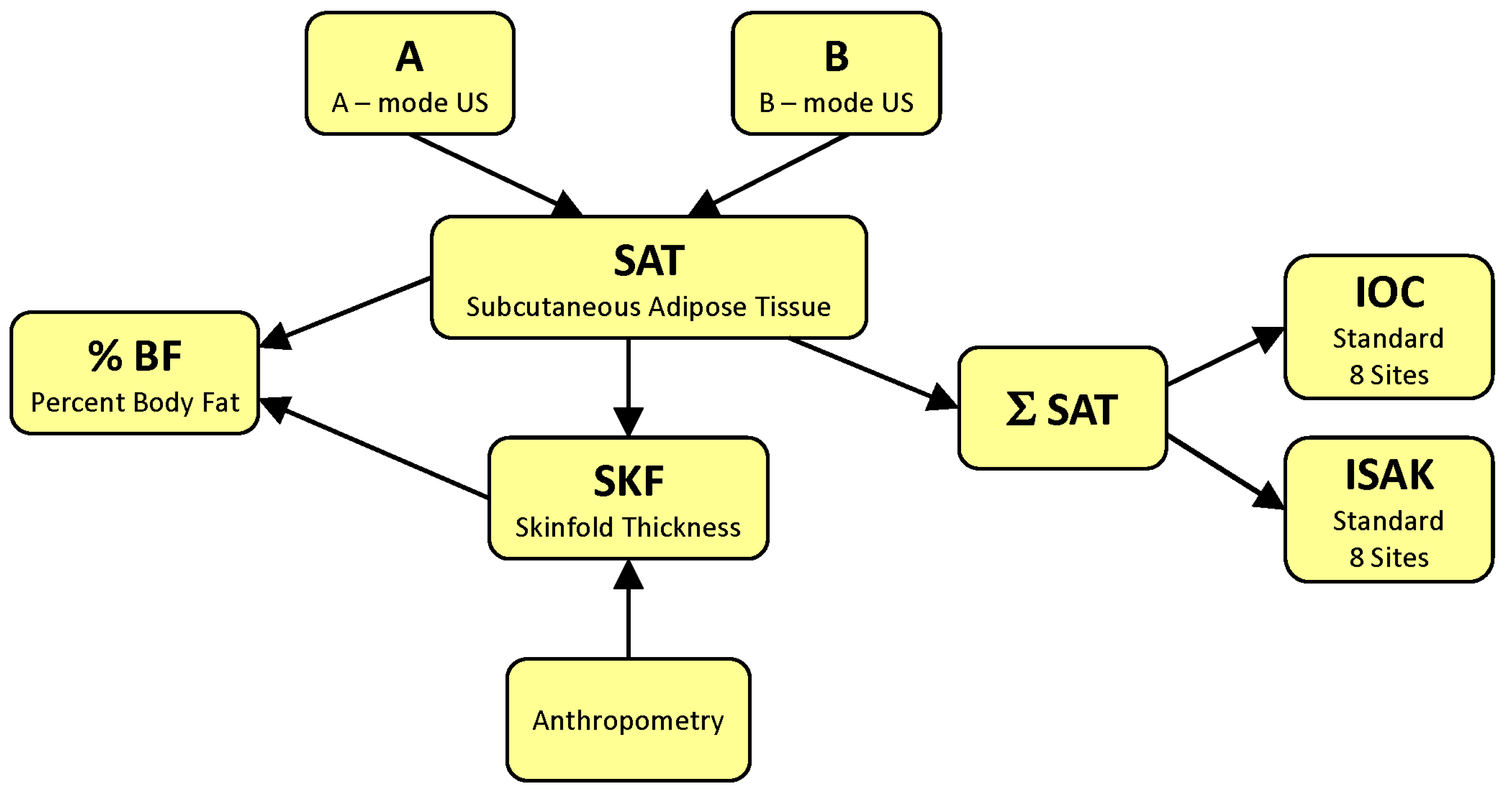
2. Basics
3. Methods
3.1. Eligibility Criteria
3.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
3.3. Document Selection and Data Collection
4. Results
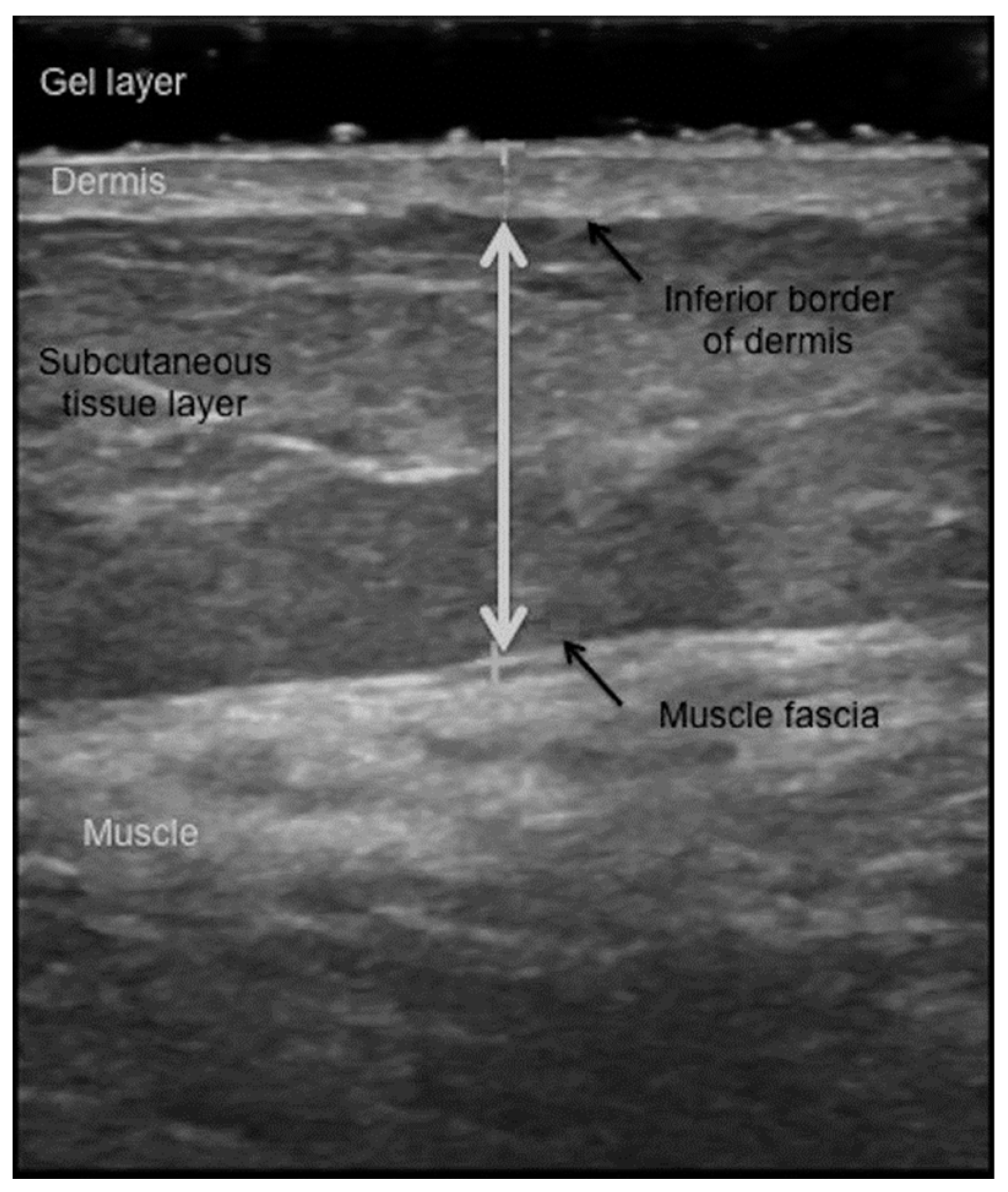
4.1. Ultrasound Measures of the Subcutaneous Fat Layer Thickness
4.2. A-Mode Ultrasound Assessments of the Total Body Fat Content
4.2.1. Validity of Body Fat Content Estimates via A-Mode Ultrasound
4.2.2. Reliability of %BF Estimation by A-Mode US
4.3. B-Mode Ultrasound Evaluations of Body Fat Content
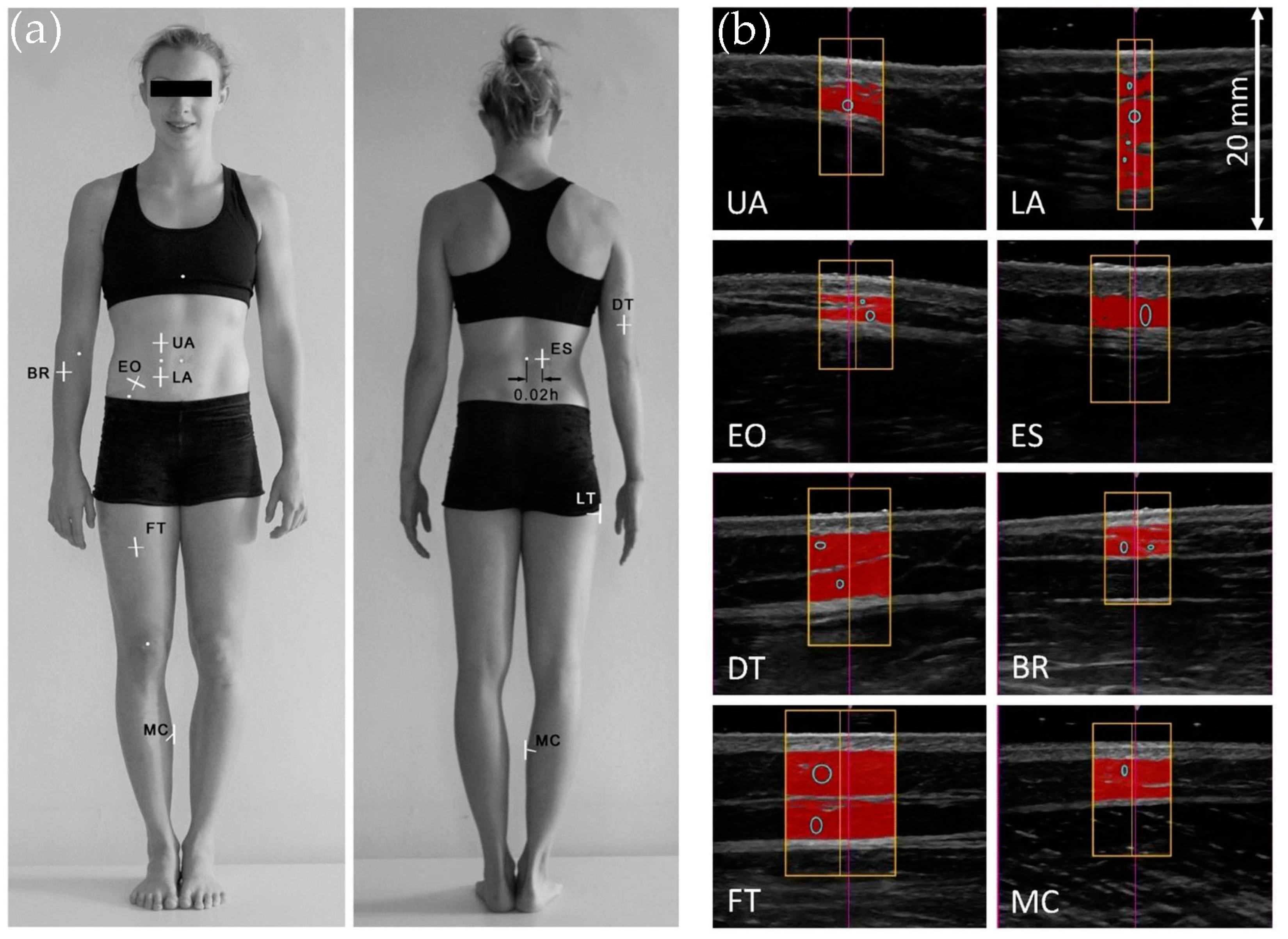
4.4. Ultrasound-Based Characterization of Subcutaneous Fat Patterning
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| 2, 3, 4C | 2, 3, 4-compartment model |
| %BF | percent body fat |
| ADP | air displacement plethysmography |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| A-mode | amplitude-mode |
| B-mode | brightness-mode |
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BMI | body mass index |
| Bic1 | one-point biceps |
| BIS | bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy |
| BM | body mass |
| BR | brachioradialis |
| CE | constant error |
| CT | computed tomography |
| D | body density |
| DT | distal triceps |
| DW4 | 4-site Durnin and Womersley |
| DXA | dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| EO | external oblique |
| ES | erector spinae |
| F | female |
| FFM | fat-free mass |
| FM | fat mass |
| FS4 | 4-site Forsyth–Sinning |
| FT | front thigh |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HW | hydrostatic weighing |
| ICC | intraclass correlation coefficient |
| IOC | International Olympic Committee |
| ISAK | International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry |
| JP3, 4, 7 | 3, 4, 7-site Jackson and Pollock |
| LA | lower abdomen |
| LoA | limits of agreement |
| LT | lateral thigh |
| M | male |
| MC | medial calf |
| MDC | minimal detectable change |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NHCA4 | 4-site National Health Center of America |
| P3 | 3-site Pollock |
| P9 | 9-site Parrillo |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| S2 | 2-site Sloan |
| SAT | subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| SEE | standard error of estimate |
| SEM | standard error of measurement |
| SKF | skinfold |
| TE | total error |
| UA | upper abdomen |
| US | ultrasound |
References
- Heymsfield, S.B. Advances in body composition: A 100-year journey. Int. J. Obes. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Enderle, J.; Pourhassan, M.; Braun, W.; Eggeling, B.; Lagerpusch, M.; Glüer, C.-C.; J Kehayias, J.; Kiosz, D.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Metabolic adaptation to caloric restriction and subsequent refeeding: The Minnesota Starvation Experiment revisited. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.J.; Braun, W.; Enderle, J.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Beyond BMI: Conceptual Issues Related to Overweight and Obese Patients. Obes. Facts 2016, 9, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechanick, J.I.; Butsch, W.S.; Christensen, S.M.; Hamdy, O.; Li, Z.; Prado, C.M.; Heymsfield, S.B. Strategies for minimizing muscle loss during use of incretin-mimetic drugs for treatment of obesity. Obes. Rev. 2024, 26, e13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeland, I.J.; Linge, J.; Birkenfeld, A.L. Changes in lean body mass with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies and mitigation strategies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackland, T.R.; Lohman, T.G.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Maughan, R.J.; Meyer, N.L.; Stewart, A.D.; Müller, W. Current status of body composition assessment in sport. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheja, L.; Heeren, J. The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Meyer, N.L.; Lohman, T.G.; Ackland, T.R.; Maughan, R.J.; Stewart, A.D.; Müller, W. How to minimise the health risks to athletes who compete in weight-sensitive sports review and position statement on behalf of the Ad Hoc Research Working Group on Body Composition, Health and Performance, under the auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G. Skinfolds and body density and their relation to body fatness: A review. Hum. Biol. 1981, 53, 181–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lohman, T.G. Assessment of body composition in children. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1989, 1, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri, W.E. Body composition from fluid spaces and density: Analysis of methods. In Techniques for Measuring Body Composition; Brozek, J., Hanschel, A., Eds.; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; pp. 223–244. [Google Scholar]
- Lohman, T.G. Applicability of Body Composition Techniques and Constants for Children and Youths. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 1986, 14, 325–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blue, M.N.M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Ryan, E.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. Validity of Body-Composition Methods across Racial and Ethnic Populations. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnke, A.R., Jr.; Feen, B.G.; Welham, W.C. The specific gravity of healthy men: Body weight ÷ volume as an index of obesity. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1942, 118, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, P.; Aitkens, S. A new air displacement method for the determination of human body composition. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, M.A.; Gomez, T.D.; Bernauer, E.M.; Mole, P.A. Evaluation of a new air displacement plethysmograph for measuring human body composition. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Kotler, D.P.; Wielopolski, L.; Withers, R.T.; Pierson, R.N., Jr.; Heymsfield, S.B. Multicomponent methods: Evaluation of new and traditional soft tissue mineral models by in vivo neutron activation analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, B.S.; Tinsley, G.M.; Esco, M.R. Validity of Field and Laboratory Three-Compartment Models in Healthy Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, A.M.; Langan-Evans, C. Come Back Skinfolds, All Is Forgiven: A Narrative Review of the Efficacy of Common Body Composition Methods in Applied Sports Practice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra-Andrade, J.H.; Ripka, W.L.; Heymsfield, S.B. Skinfold calipers: Which instrument to use? J. Nutr. Sci. 2023, 12, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Campa, F.; Stagi, S.; Gobbo, L.A.; Buffa, R.; Toselli, S.; Silva, D.A.S.; Gonçalves, E.M.; Langer, R.D.; Guerra-Júnior, G.; et al. The bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) international database: Aims, scope, and call for data. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 77, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, R.A.D.; Goddard, B.A.; Paton, A. Measurement of fat thickness in man: A comparison of ultrasound, Harpenden calipers and electrical conductivity. Br. J. Nutr. 1966, 20, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullen, B.A.; Quaade, F.; Olessen, E.; Lund, S.A. Ultrasonic reflections used for measuring subcutaneous fat in humans. Hum. Biol. 1965, 37, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borkan, G.A.; Hults, D.E.; Cardarelli, J.; Burrows, B.A. Comparison of ultrasound and skinfold measurements in assessment of subcutaneous and total fatness. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1982, 58, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, M.T.; Kuczmarski, R.J. Ultrasound as an approach to assessing body composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 39, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R. Ultrasound as a Tool to Assess Body Fat. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 280713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzocchi, A.; Filonzi, G.; Ponti, F.; Albisinni, U.; Guglielmi, G.; Battista, G. Ultrasound: Which role in body composition? Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, F.; De Cinque, A.; Fazio, N.; Napoli, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Bazzocchi, A. Ultrasound imaging, a stethoscope for body composition assessment. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1699–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, R.M.; Teigell-Muñoz, F.J.; Porcel, J.M.; Lázaro, J.R.; Rubio, S.G. Ultrasound for body composition assessment: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Nishioka, S.; Maeda, K.; Wakabayashi, H. Ultrasound utilized by registered dietitians for body composition measurement, nutritional assessment, and nutritional management. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Almeida, J.M.; García-García, C.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Ballesteros Pomar, M.D.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.M.; Fernández Medina, B.; de Luis Román, D.A.; Bellido Guerrero, D.; Bretón Lesmes, I.; Tinahones Madueño, F.J. Nutritional ultrasound®: Conceptualisation, technical considerations and standardisation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Y Nutr. (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 70, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.F.; Silva, E.B.d.; Bomfim, A.B.C. Validity and reliability of portable A-mode ultrasound in measuring body fat percentage: A systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0292872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzi, A.J.; Lafrenière, A.S.; Gilardino, M.; Hemmerling, T. Ultrasonography Technique in Abdominal Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Measurement: A Systematic Review. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; O’Brien, K.K. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 2010, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremkau, F.W. Sonography Principles and Instruments E-Book, 10th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- El-Brawany, M.A.; Nassiri, D.K.; Terhaar, G.; Shaw, A.; Rivens, I.; Lozhken, K. Measurement of thermal and ultrasonic properties of some biological tissues. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2009, 33, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.R.; Bamber, J.C.; Haar, G.R. Physical Principles of Medical Ultrasonics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W.; Horn, M.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Kainz, P.; Kröpfl, J.M.; Maughan, R.J.; Ahammer, H. Body composition in sport: A comparison of a novel ultrasound imaging technique to measure subcutaneous fat tissue compared with skinfold measurement. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Horn, M.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Kainz, P.; Kröpfl, J.M.; Ackland, T.R.; Lohman, T.G.; Maughan, R.J.; Meyer, N.L.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; et al. Body composition in sport: Interobserver reliability of a novel ultrasound measure of subcutaneous fat tissue. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Lohman, T.G.; Stewart, A.D.; Maughan, R.J.; Meyer, N.L.; Sardinha, L.B.; Kirihennedige, N.; Reguant-Closa, A.; Risoul-Salas, V.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; et al. Subcutaneous fat patterning in athletes: Selection of appropriate sites and standardisation of a novel ultrasound measurement technique: Ad hoc working group on body composition, health and performance, under the auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.G.; Jeong, D.W.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, I.J.; Yi, Y.H. Association between uterine leiomyoma and metabolic syndrome in parous premenopausal women: A case-control study. Medicine 2016, 95, e5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, M.J.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, A.J.; Cintineo, H.P.; Sanders, D.J.; McFadden, B.A.; Arent, M.A.; Monaco, R.; Arent, S.M. Agreement between B-Mode Ultrasound and Air Displacement Plethysmography in Preprofessional Ballet Dancers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, R.S.; Wagner, D.R.; Bigler, M. Evaluation of Body Fat Prediction Equations from a Portable A-Mode Ultrasound Compared to Air Displacement Plethysmography. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 9, e91750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, P.; Miclos-Balica, M.; Macavei, G.A.; Munteanu, O.; Neagu, A.; Neagu, M. Anthropometric Formulas Repurposed to Predict Body Fat Content from Ultrasound Measurements of Subcutaneous Fat Thickness. Symmetry 2024, 16, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Rodriguez, C.; White, S.J.; Williams, A.D.; Stratton, M.T.; Harty, P.S.; Smith, R.W.; Dellinger, J.R.; Johnson, B.A. A Field-based Three-Compartment Model Derived from Ultrasonography and Bioimpedance for Estimating Body Composition Changes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R.; Cain, D.L.; Clark, N.W. Validity and Reliability of A-Mode Ultrasound for Body Composition Assessment of NCAA Division I Athletes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, S.; Toomey, C.; McCreesh, K.; O’Neill, C.; Jakeman, P. Ultrasound measurement of subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness accurately predicts total and segmental body fat of young adults. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Blue, M.N.M.; Trexler, E.T.; Hirsch, K.R. Utility of ultrasound for body fat assessment: Validity and reliability compared to a multicompartment criterion. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Marfell-Jones, M.; Olds, T.; De Ridder, J. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment, 3rd ed.; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Lower Hutt, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kopinski, S.; Engel, T.; Cassel, M.; Fröhlich, K.; Mayer, F.; Carlsohn, A. Ultrasound Applied to Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Measurements in International Elite Canoeists. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.J.; Smith, R.W.; Stratton, M.T.; Harty, P.S.; Rodriguez, C.; Siedler, M.R.; White, S.J.; Williams, A.D.; Dellinger, J.R.; Keith, D.S.; et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry fat mass. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2021, 41, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.N.; Ducker, K.J.; Furzer, B.J.; Dymock, M.; Landers, G.J. Measures of body composition via Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, ultrasound and skinfolds are not impacted by the menstrual cycle in active eumenorrheic females. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2022, 25, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.C.; Landers, G.J.; Binnie, M.J.; Goods, P.S.R.; Fulton, S.K.; Ackland, T.R. Body composition assessment in athletes: Comparison of a novel ultrasound technique to traditional skinfold measures and criterion DXA measure. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R.; Cotter, J.D. Ultrasound Measurements of Subcutaneous Fat Thickness Are Robust Against Hydration Changes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2021, 31, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomey, C.; McCreesh, K.; Leahy, S.; Jakeman, P. Technical considerations for accurate measurement of subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness using B-mode ultrasound. Ultrasound 2011, 19, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Ricci, C.; Cocco, G.; Donati, D.; Farì, G.; Mezian, K.; Naňka, O.; Özçakar, L. From histology to sonography in skin and superficial tissue disorders: EURO-MUSCULUS/USPRM* approach. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 237, 154003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Ricci, C.; Gervasoni, F.; Giulio, C.; Farì, G.; Andreoli, A.; Özçakar, L. From physical to ultrasound examination in lymphedema: A novel dynamic approach. J. Ultrasound 2022, 25, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.C.; Cronin, O.; O’Neill, S.B.; Woods, T.; Keohane, D.M.; Molloy, M.G.; Falvey, E.C. Application of a Sub-set of Skinfold Sites for Ultrasound Measurement of Subcutaneous Adiposity and Percentage Body Fat Estimation in Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L. An introduction to Ultrasound and the BodyMetrix System; IntelaMetrix: Livermore, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, D.R.; Teramoto, M. Interrater reliability of novice examiners using A-mode ultrasound and skinfolds to measure subcutaneous body fat. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R.; Thompson, B.J.; Anderson, D.A.; Schwartz, S. A-mode and B-mode ultrasound measurement of fat thickness: A cadaver validation study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.R.; Teramoto, M.; Judd, T.; Gordon, J.; McPherson, C.; Robison, A. Comparison of A-mode and B-mode Ultrasound for Measurement of Subcutaneous Fat. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Hong, S.U.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.Y. Estimation of Validity of A-Mode Ultrasound for Measurements of Muscle Thickness and Muscle Quality. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.S.; Pollock, M.L. Generalized equations for predicting body density of men. Br. J. Nutr. 1978, 40, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.S.; Pollock, M.L.; Ward, A. Generalized equations for predicting body density of women. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1980, 12, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti de Oliveira, G.; Fernandes, L.V.; Vasques, A.C.J.; Corona, L.P. Exploring the use of portable mode A ultrasound for body composition assessment: A narrative review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2024, 13, e13813144888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utter, A.; Hager, M. Evaluation of ultrasound in assessing body composition of high school wrestlers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loenneke, J.P.; Barnes, J.T.; Wagganer, J.D.; Pujol, T.J. Validity of a portable computer-based ultrasound system for estimating adipose tissue in female gymnasts. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Fultz, S.N.; Melvin, M.N.; Wingfield, H.L.; Woessner, M.N. Reproducibility and Validity of A-Mode Ultrasound for Body Composition Measurement and Classification in Overweight and Obese Men and Women. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, N.; Davison, J.; Schiller, L.; Willey, M. Reliability and Validity of A-Mode Ultrasound to Quantify Body Composition. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totosy de Zepetnek, J.O.; Lee, J.J.; Boateng, T.; Plastina, S.E.; Cleary, S.; Huang, L.; Kucab, M.; Paterakis, S.; Brett, N.R.; Bellissimo, N. Test–retest reliability and validity of body composition methods in adults. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2021, 41, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.E.; Miller, B.; Juvancic-Heltzel, J.A.; Agnor, S.E.; Kiger, D.L.; Kappler, R.M.; Otterstetter, R. Agreement between ultrasound and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in assessing percentage body fat in college-aged adults. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.E.; Miller, B.; Gibson, A.L.; McLain, T.A.; Juvancic-Heltzel, J.A.; Kappler, R.M.; Otterstetter, R. A comparison of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, air displacement plethysmography and A-mode ultrasound to assess body composition in college-age adults. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranauskas, M.N.; Johnson, K.E.; Juvancic-Heltzel, J.A.; Kappler, R.M.; Richardson, L.; Jamieson, S.; Otterstetter, R. Seven-site versus three-site method of body composition using BodyMetrix ultrasound compared to dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinto, M.; Lins, V.C.; Rocha, G.; Dourado, M.A.; Dutra, M. Practical but Inaccurate? A-Mode Ultrasound and Bioelectrical Impedance Underestimate Body Fat Percentage Compared to Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Male College Students. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Park, J.-H.; Seo, M.-W.; Jung, H.C.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, J.-M. Validity of the Portable Ultrasound BodyMetrix™ BX-2000 for Measuring Body Fat Percentage. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripka, W.L.; Gewehr, P.M.; Ulbricht, L. Fat percentage evaluation through portable ultrasound in adolescents: A comparison with dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. In Proceedings of the IECBES 2016—IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ripka, W.L.; Ulbricht, L.; Menghin, L.; Gewehr, P.M. Portable A-Mode Ultrasound for Body Composition Assessment in Adolescents. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, J.C.; Bouslah, M. Prediction of body fat in male athletes from ultrasound and anthropometric measurements versus DXA. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2020, 60, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, J.C. Prediction of percent body fat in adult men using ultrasonic and anthropometric measurements versus dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Gazz. Medica Ital. Arch. Per Le Sci. Mediche 2022, 181, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielemann, R.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Orlandi, S.P.; Xavier, M.O.; Bergmann, R.B.; Formoso Assunção, M.C. Estimation of body fat in adults using a portable A-mode ultrasound. Nutrition 2016, 32, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Aragon, A.A.; Moon, J.; Krieger, J.W.; Tiryaki-Sonmez, G. Comparison of amplitude-mode ultrasound versus air displacement plethysmography for assessing body composition changes following participation in a structured weight-loss programme in women. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridge, A.D.; Brown, J.; Snider, H.; Rowan, S.N.; Skelly, L.E.; Josse, A.R. Comparison of Body Composition Assessment Using Air-Displacement Plethysmography and A-Mode Ultrasound before and after a 12-Week Exercise Intervention in Normal Weight Adult Males. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 25, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M. Five-component model validation of reference, laboratory and field methods of body composition assessment. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.M.; Deurenberg, P.; Guo, S.S.; Pietrobelli, A.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N., Jr.; Heymsfield, S.B. Six-compartment body composition model: Inter-method comparisons of total body fat measurement. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1998, 22, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, K.L.; Fukuda, D.H.; Hyde, P.N.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Moon, J.R.; Stout, J.R. Estimating fat-free mass in elite-level male rowers: A four-compartment model validation of laboratory and field methods. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, P.; Neagu, M.; Amaricai, E.; Haragus, H.G.; Onofrei, R.R.; Neagu, A. Using A-Mode Ultrasound to Assess the Body Composition of Soccer Players: A Comparative Study of Prediction Formulas. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.W.; Hickey, G.L.; Head, S.J. Statistical primer: Multivariable regression considerations and pitfalls†. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 55, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondareva, E.; Parfenteva, O.; Vasileva, A.; Kulemin, N.; Gadzhiakhmedova, A.; Kovaleva, O.; Khromov-Borisov, N. Agreement of bioimpedance analysis and ultrasound scanning for fat mass, fat free mass and body fat percentage evaluation in the group of adult women. Biol. Commun. 2023, 68, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondareva, E.A.; Parfenteva, O.I.; Troshina, E.A.; Ershova, E.V.; Mazurina, N.V.; Komshilova, K.A.; Kulemin, N.A.; Ahmetov, I.I. Agreement between bioimpedance analysis and ultrasound scanning in body composition assessment. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2024, 36, e24001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.J.; Lal, S.; Gittins, M.; Strauss, B.J.G.; Burden, S.T. Practical measurement of body composition using bioelectrical impedance, air displacement plethysmography and ultrasound in stable outpatients with short bowel syndrome receiving home parenteral nutrition: Comparison of agreement between the methods. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 32, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krkeljas, Z.; Engelbrecht, L.; Terblanche, E. Differences in Resting Metabolic Rate between BodyMetrix™ and Indirect Calorimetry in South African Adults. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 23, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasziw, M.; Young, S.L.; Woodbury, M.G.; Fryday-Field, K. Statistical Methodology for the Concurrent Assessment of Interrater and Intrarater Reliability: Using Goniometric Measurements as an Example. Phys. Ther. 1994, 74, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollman, J.H.; Beckman, B.A.; Brandt, R.A.; Merriwether, E.N.; Williams, R.T.; Nordrum, J.T. Minimum Detectable Change in Gait Velocity during Acute Rehabilitation following Hip Fracture. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2008, 31, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, K.O.; Wong, S.P. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol. Methods 1996, 1, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loenneke, J.P.; Barnes, J.T.; Wagganer, J.D.; Wilson, J.M.; Lowery, R.P.; Green, C.E.; Pujol, T.J. Validity and reliability of an ultrasound system for estimating adipose tissue. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirita-Emandi, A.; Dobrescu, A.; Papa, M.; Puiu, M. Reliability of Measuring Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Thickness Using Ultrasound in Non-Athletic Young Adults. Maedica 2015, 10, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Chiriţă-Emandi, A.; Papa, M.C.; Abrudan, L.; Dobrescu, M.A.; Puiu, M.; Velea, I.P.; Paul, C. A novel method for measuring subcutaneous adipose tissue using ultrasound in children—Interobserver consistency. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Miclos-Balica, M.; Muntean, P.; Schick, F.; Haragus, H.G.; Glisici, B.; Pupazan, V.; Neagu, A.; Neagu, M. Reliability of body composition assessment using A-mode ultrasound in a heterogeneous sample. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.E. Reliability of air displacement plethysmography. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondareva, E.A.; Parfent’eva, O.I.; Vasil’eva, A.A.; Kulemin, N.A.; Popova, E.V.; Gadzhiakhmedova, A.N.; Kovaleva, O.N.; Khromov-Borisov, N.N. Reproducibility of Body Fat and Fat-Free Mass Measurements by Bioimpedance and Ultrasound Scanning Analysis in a Group of Young Adults. Hum. Physiol. 2023, 49, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, M.; Wagner, D.R.; Lowry, R.S. Interdevice Reliability of A-Mode Ultrasound to Measure Body Composition. Sport Mont 2022, 20, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, A.W. Estimation of body fat in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 1967, 23, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Kondo, M.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukunaga, T. Prediction equations for body composition of Japanese adults by B-mode ultrasound. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 1994, 6, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaud, R.S.; Abe, T.; Loenneke, J.P.; Fujita, E.; Akamine, T. Body fat percentage assessment by ultrasound subcutaneous fat thickness measurements in middle-aged and older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Loenneke, J.P.; Thiebaud, R.S. An Ultrasound Prediction Equation to Estimate DXA-Derived Body Fatness for Middle-Aged and Older Caucasian Adults. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Perez, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Mourtzakis, M.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Ridlon, J.; Gaskins, H.R.; Mutlu, E. Comparison between handheld ultrasound and regional and whole-body dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for body fat assessment. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgutalp, Ş.; Korkusuz, F. Abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness measured by ultrasound as a predictor of total fat mass in young-and middle-aged adults. Acta Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, P.N.; Kendall, K.L.; Fairman, C.M.; Coker, N.A.; Yarbrough, M.E.; Rossi, S.J. Use of B-Mode Ultrasound as a Body Fat Estimate in Collegiate Football Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3525–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heyward, V.H.; Wagner, D.R. Applied Body Composition Assessment; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, A.J.; Dona, S.T.; Cintineo, H.P.; McFadden, B.A.; Sanders, D.J.; Monaco, R.; Arent, S.M. Intra-and inter-rater reliability of assessing body composition using B-mode ultrasound in conjunction with artificial intelligence software. J. Exerc. Nutr. 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.P.; Klawitter, L.; Carver, E.; Johnson, Z.; McGrath, R.; Stastny, S.; Christensen, B.; Hackney, K.J. Reliability of a Novel Automated Ultrasound Technology for Body Composition Assessment and Comparisons with Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2023, 16, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, K.; Metoyer, C.J.; Winchester, L.J.; Esco, M.R.; Fedewa, M.V. Agreement between ultrasound protocols for the estimation of body fat percentage: Comparison to a four-compartment model. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2023, 43, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechelli, F.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Stokes, M.; Agyapong-Badu, S. Validity of ultrasound imaging versus magnetic resonance imaging for measuring anterior thigh muscle, subcutaneous fat, and fascia thickness. Methods Protoc. 2019, 2, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechelli, F.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Stokes, M.; Agyapong-Badu, S. Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of ultrasound imaging for measuring quadriceps muscle and non-contractile tissue thickness of the anterior thigh. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2019, 5, 037002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Herreros, S.; López Gómez, J.J.; Cebria, A.; Izaola, O.; Salvador Coloma, P.; Nozal, S.; Cano, J.; Primo, D.; Godoy, E.J.; de Luis, D. Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Ultrasound Imaging System for Quantifying Muscle Architecture Parameters of the Rectus Femoris in Disease-Related Malnutrition (DRM). Nutrients 2024, 16, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti de Oliveira, G.; Vilar Fernandes, L.; Summer Chen, X.; Drumond Andrade, F.C.; Scarlazzari Costa, L.; Junqueira Vasques, A.C.; Pires Corona, L. Intra- and inter-rater reliability of muscle and fat thickness measurements obtained using portable ultrasonography in older adults. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 60, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toni, L.; Petre, G.C.; Garolla, A.; De Santis, I.; Valente, U.; Foresta, C.; De Rocco Ponce, M. Prognostic Value of Ultrasound Stratigraphy in Long-Term Weight Loss: Results from a Nutritional Counseling Program. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Maughan, R.J. The need for a novel approach to measure body composition: Is ultrasound an answer? Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1001–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Ahammer, H.; Lohman, T.G.; Meyer, N.L.; Sardinha, L.B.; Stewart, A.D.; Maughan, R.J.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Müller, T.; et al. Relative Body Weight and Standardised Brightness-Mode Ultrasound Measurement of Subcutaneous Fat in Athletes: An International Multicentre Reliability Study, Under the Auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Störchle, P.; Müller, W.; Sengeis, M.; Ahammer, H.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Bachl, N.; Lackner, S.; Mörkl, S.; Holasek, S. Standardized Ultrasound Measurement of Subcutaneous Fat Patterning: High Reliability and Accuracy in Groups Ranging from Lean to Obese. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelso, A.; Trájer, E.; Machus, K.; Treff, G.; Müller, W.; Steinacker, J.M. Assessment of subcutaneous adipose tissue using ultrasound in highly trained junior rowers. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2017, 17, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengeis, M.; Müller, W.; Störchle, P.; Führhapter-Rieger, A. Body weight and subcutaneous fat patterning in elite judokas. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1774–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, A.; Müller, W.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Sengeis, M.; Ahammer, H.; Steinacker, J.M. High inter-observer reliability in standardized ultrasound measurements of subcutaneous adipose tissue in children aged three to six years. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, A.; Vogel, K.; Steinacker, J.M. Ultrasound measurements of subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness show sexual dimorphism in children of three to five years of age. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Zalaudek, K.; Brix, B.; Sengeis, M.; Jantscher, A.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Müller, W.; Matjuda, E.N.; Mungamba, M.M.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.; Fredriksen, P.M.; et al. Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Measured by B-Mode Ultrasound to Assess and Monitor Obesity and Cardio–Metabolic Risk in Children and Adolescents. Biology 2021, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Meier-Allard, N.; Mörkl, S.; Müller, W.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Mangge, H.; Zelzer, S.; Holasek, S. Hypercarotenemia in Anorexia Nervosa Patients May Influence Weight Balance: Results of a Clinical Cross-Sectional Cohort Study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 758300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Mörkl, S.; Müller, W.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Oberascher, A.; Lehofer, M.; Bieberger, C.; Wonisch, W.; Amouzadeh-Ghadikolai, O.; Moser, M.; et al. Novel approaches for the assessment of relative body weight and body fat in diagnosis and treatment of anorexia nervosa: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörkl, S.; Lackner, S.; Müller, W.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Kashofer, K.; Oberascher, A.; Painold, A.; Holl, A.; Holzer, P.; Meinitzer, A.; et al. Gut microbiota and body composition in anorexia nervosa inpatients in comparison to athletes, overweight, obese, and normal weight controls. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.N.; Ducker, K.J.; Furzer, B.J.; Dymock, M.; Landers, G.J. Food and fluid intake and hydration status does not affect ultrasound measurements of subcutaneous adipose tissue in active adults. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2022, 25, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.N.; Ducker, K.J.; Furzer, B.J.; Dymock, M.; Landers, G.J. Acute exercise affects dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition estimates but not standardised ultrasound measurements of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2023, 43, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Tanaka, F.; Kawakami, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Fukunaga, T. Total and segmental subcutaneous adipose tissue volume measured by ultrasound. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Loenneke, J.P.; Thiebaud, R.S.; Fujita, E.; Akamine, T.; Loftin, M. Prediction and Validation of DXA-Derived Appendicular Fat-Free Adipose Tissue by a Single Ultrasound Image of the Forearm in Japanese Older Adults. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Gallagher, D.; Kotler, D.P.; Wang, Z.; Allison, D.B.; Heshka, S. Body-size dependence of resting energy expenditure can be attributed to nonenergetic homogeneity of fat-free mass. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E132–E138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Thiele, J.; Kwast, S.; Borger, M.A.; Schröter, T.; Falz, R.; Busse, M. Measurement of subcutaneous fat tissue: Reliability and comparison of caliper and ultrasound via systematic body mapping. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, S.L.; Abe, T.; Counts, B.R.; Dankel, S.J.; Barnett, B.E.; Loenneke, J.P. Muscle and fat mapping of the trunk: A case study. J. Ultrasound 2015, 18, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Störchle, P.; Müller, W.; Sengeis, M.; Lackner, S.; Holasek, S.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A. Measurement of mean subcutaneous fat thickness: Eight standardised ultrasound sites compared to 216 randomly selected sites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Thiele, J.; Kwast, S.; Borger, M.A.; Schröter, T.; Schmidt, J.; Busse, M. A new approach to quantify visceral fat via bioelectrical impedance analysis and ultrasound compared to MRI. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, A.M.; Kara, M.; Kara, Ö.; Kaymak, B.; Akıncı, A.; Özçakar, L. Ultrasonographic measurements of the skin, fat and muscle in vitamin D deficiency. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, C.H.; Nanaiah, S.P.; Ramaiah, R.; Prathap, N.; Prasad, S. Maternal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness by Ultrasonography and Its Effect on Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes. J. South Asian Fed. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2024, 16, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, M.S.; Kahramanoglu, I.; Vitale, S.G.; Akgol, S.; Dilek, M.E.; Kartal, S.; Caruso, S.; Kahveci, B.; Obut, M.; Bademkiran, M.H.; et al. Maternal abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness as a simple predictor for gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Perinat. Med. 2019, 47, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvery, N.; Wan, H.T.; Dirr, M.A.; Christensen, R.E.; Weil, A.; Raja, S.; Reynolds, K.A.; Kyllo, R.L.; Makin, I.R.S.; Poon, E.; et al. Utility of high-resolution ultrasound in measuring subcutaneous fat thickness. Lasers Surg. Med. 2022, 54, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Wong, V.; Bell, Z.W.; Spitz, R.W.; Dankel, S.J.; Loenneke, J.P. Subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution and serum lipid/lipoprotein in unmedicated postmenopausal women: A B-mode ultrasound study. Imaging 2021, 13, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetyo, M.; Andreas, S.; Sunardi, D.; Prihartono, J.; Imanuel Setiawan, S.; Christian, A. Ultrasonographic measurement of abdominal and gluteal-femoral fat thickness as a predictor for android/gynoid ratio. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 154, 110387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Bard, R.; Goldfarb, R.; Shiloh, A.; Kenolova, D. Ultrasound Assessment of Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat Thickness after Treatments with a High-Intensity Focused Electromagnetic Field Device: A Multicenter Study. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenteva, O.I.; Kulemin, N.A.; Bondareva, E.A.; Ahmetov, I.I. Prevalence and Predictors of Normal-Weight Obesity among Women. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze, A.; Nowak, J.; Słoboda, K.; Mlosek, R.K.; Dobruch-Sobczak, K.; Woźniak, W.; Ciostek, P. Sex and body mass index implications on gluteofemoral subcutaneous tissue morphology visualized by ultrasonography—Preliminary study. J. Ultrason. 2019, 19, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Anwar, M.; Hertwig, A.; Hahn, R.; Pesta, M.; Timmermann, I.; Siebenrock, T.; Liebau, K.; Hiesmayr, M. Ultrasound method of the USVALID study to measure subcutaneous adipose tissue and muscle thickness on the thigh and upper arm: An illustrated step-by-step guide. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2020, 32, 38–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.T.; Mourtzakis, M. Development of a bedside-applicable ultrasound protocol to estimate fat mass index derived from whole body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scans. Nutrition 2019, 57, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, B.J.; Lombardi, A.; Kwon, S.; Loeb, M.; Cho, H.; He, K.; Wei, D.; Park, J. Ultrasound for assessing paediatric body composition and nutritional status: Scoping review and future directions. Acta Paediatr. 2025, 114, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Rolfe, E.D.L.; Mak, E.; Sengupta, A.; Powell, R.; Watson, L.P.E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Shepherd, J.A.; Wareham, N.; Brage, S.; et al. Prediction of total and regional body composition from 3D body shape. Npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blue, M.N.; Trexler, E.T.; Hirsch, K.R.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. A profile of body composition, omega-3 and Vitamin D in National Football League players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R. Oversimplification of the Relationship between Ultrasound and Skinfold Measurements of Subcutaneous Fat Thickness. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Chandler, A.J.; Arent, S.M. Response. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, K.; Kuribayashi, M.; Hirayama, K.; Yabuzaki, J.; Kurosumi, M.; Hamanaka, Y. Examination of age-related changes of viscoelasticity in the dermis and subcutaneous fat layer using ultrasound elastography. Ski. Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, A.S.; Kashyap, N.K.; Trivedi, S.; Choudhary, R.; Suryavanshi, G.; Thangaraju, P.; Bagale, K.R. Assessment of Body Fat Percentage Using B-Mode Ultrasound Technique versus Skinfold Caliper in Obese Healthy Volunteers. Cureus 2022, 14, e22993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, K.; Van der Merwe Reon, A.; Helena Cindy, A.; Nolte Heinrich, W.; Van der Meulen, J. A comparison between skinfold callipers and ultrasound imaging for assessing body composition in recreationally active students. Ergon. SA J. Ergon. Soc. S. Afr. 2016, 28, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pérez-Chirinos Buxadé, C.; Solà-Perez, T.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Roy, A.; Marfell-Jones, M.; Irurtia, A. Assessing subcutaneous adipose tissue by simple and portable field instruments: Skinfolds versus A-mode ultrasound measurements. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan-Stewart, H.; O’Leary, A.; Paine, E.; Faulkner, J.; Jobson, S. The Relationship between Skinfold and Ultrasound Measures of Subcutaneous Fat in Untrained Healthy Males. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuma, I.S.M.; Cambi, M.P.C.; Moraes, T.P.d.; Magro, D.O.; Kotze, P.G. Body fat composition in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: A comparative study between skinfolds and ultrasonography. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2024, 61, e23088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, L.; Neves, E.B.; Ripka, W.L.; Romaneli, E.F.R. Comparison between body fat measurements obtained by portable ultrasound and caliper in young adults. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 1952–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski, Z.; Dychała, E.; Pisula-Lewandowska, A.; Danel, D.P. Comparison of Skinfold Thickness Measured by Caliper and Ultrasound Scanner in Normative Weight Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardo, A.; Tafuri, D.; Corvino, A. Body composition analysis in adolescent male athletes: Skinfold versus ultrasound. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2021, 16, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, Y.; Ohta, M.; Akagi, R.; Kato, E.; Wakahara, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Kanehisa, H. Applicability of ultrasound muscle thickness measurements for predicting fat-free mass in elderly population. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.T. Body Composition Analysis of Computed Tomography Scans in Clinical Populations: The Role of Deep Learning. Lifestyle Genom. 2019, 13, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhakim, T.; Trinh, K.; Mansur, A.; Bridge, C.; Daye, D. Role of Machine Learning-Based CT Body Composition in Risk Prediction and Prognostication: Current State and Future Directions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Feng, J.; Chen, D. A survey on deep learning in medical ultrasound imaging. Front. Phys. 2024, 12, 1398393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, E.; Ulbricht, L.; Ripka, W.; Neves, E. Evaluation of portable ultrasound technology and the correlation with the fat percentage through skinfolds in young adults [Avaliação da tecnologia do ultrassom portátil e sua correlação com o percentual de gordura obtido pelas dobras cutâneas em adultos jovens]. Rev. Bras. Ciências Da Saúde—USCS 2015, 13, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Reference | Population | Study Group | Equation 2 | SEE (%) | TE (%) | CE [LoA] (%) | Criterion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loenneke et al. [74] | athletic | gymnasts, 13F, age 20 ± 1 y | Bic1 JP3 | 3.6 3.9 | 6.7 4.9 | 3.4 5.7 | DXA |
| Smith-Ryan et al. [75] | overweight and obese | 20M, 27F age 37.6 ± 11.6 y | JP7 | - | - | −4.7 | 3C |
| Muntean et al. [49] | general | 107M, 94F age 31.6 ± 10.8 y | JP7 | - | - | −4.8 [−14.2, 4.5] F −4.8 [−14.5, 5.0] M | ADP |
| Hendrickson et al. [76] | general | 21M, 10F age 26.7 ± 3.9 y | JP3 | - | - | −1.0 [−10.0, 8.0] | ADP |
| Totosy de Zepetnek et al. [77] | general | 16M, 33F age 31.4 ± 10.7 y | JP7 | - | - | −0.32 [−7.87, 7.22] | ADP |
| Wagner et al. [51] | athletes | 22M, 23F age 20.1 ± 1.6 y | JP3 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 1.5 for M 4.7 for F | ADP |
| Kendall et al. | athletes FFM (kg) | 23M age 24.6 ± 2.2 y | 3.8 kg | 7.2 kg | 4 kg [−3.2, 11.3] kg | 4C | |
| Johnson et al. [78] | general | 35M, 49F age 23 ± 4.7 y | JP7 | 0.7 | - | −4.4 for M −3.7 for F | DXA |
| Johnson et al. [79] | general FFM (kg) | 33M, 41F age 23.1 ± 4.9 | JP7 | - | - | 0.37kg [−7.9, 8.7] kg | ADP |
| Baranauskas et al. [80] | general | 33M, 43F age 22.08 ± 2.5 y | JP7 JP3 P3 | - - - | - - - | −3.9 −3.6 −5.2 | DXA |
| Olinto et al. [81] | general | 23M age 30.1 ± 7.7 y | JP3 | - | - | −9.6 [−17.1, −2.0] | DXA |
| Kang et al. [82] | general | 105M age 20.01 ± 2.11 y | Bic1 S2 JP3 P3 NHCA4 FS4 DW4 JP7 P9 | - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - | 2.3 [−6.1, 10.7] −7.2 [−16.7, 2.3] −7.0 [−15.9, 2.0] −5.1 [−13.5, 3.2] −6.4 [−15.6, 2.8] −1.4 [−22.1, 19.3] −1.3 [−10.8, 8.2] −6.4 [−14.6, 1.8] −0.4 [−11.3, 10.4] | DXA |
| Lowry et al. [48] | elite, athletic and non-athletic | 42M age 21.4 ± 2.9 y | Bic1 S2 JP3 P3 NHCA4 FS4 DW4 JP7 P9 | 3.67 4.8 4.03 3.25 3.9 4.86 3.82 3.55 4.55 | 7.66 4.72 4.08 3.93 4.16 11.34 7.11 3.69 6.5 | 6.54 −1.23 0.94 1.93 1.68 8.58 6.01 1.23 4.72 | ADP |
| Ripka et al. [83] | adolescents | 143M age 14.8 ± 1.5 y | JP7 new | - 1.45 | - - | −9.37 0.45 [−4.25, 5.16] | DXA |
| Ripka et al. [84] | adolescents | 71M, 34F age 14 ± 2 y M age 13 ± 2.3 y F | new | 1.57 | - | 0.0 [−7.0, 7.0] F 0.2 [−5.4, 5.8] M | DXA |
| Pineau et al. [85] | athletes | 100M; 62M cross-validation | new | 1.6 | - | −0.25 [−4.1, 3.6] | DXA |
| Pineau [86] | general | 63M; 35M cross-validation | new | 2.9 | - | 0.30 [−5.1, 5.7] | DXA |
| Bielemann et al. [87] | general | 102M, 104F age 30 ± 8.1 y M age 31.9 ± 9.9 y F | new | - | - | 0.5 [−6.8, 7.7] M 0.1 [−6.6, 6.7] F | ADP |
| Schoenfeld et al. [88] | general | 20F age 22.4 ± 2.8 y | JP4 | 4.17 | 4.08 | 0.9 [−7.1, 8.9] | ADP |
| Bradley et al. [89] | general | 29M age 18–25 y | JP3 | - | - | 0.0 [−5.3, 5.3] | ADP |
| Reference | Population | Study Group | Equation 2 | SEM (%) | MDC (%) | ICC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loenneke et al. [104] | general | students, 3F, 8M, age 22 ± 3 y | Bic1 JP3 | - - | 2.8 5.6 | 0.977 0.935 |
| Smith-Ryan et al. [75] | general | overweight and obese, 27F, 20M, age 37.6 ± 11.6 y | JP7 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 0.980 |
| Hendrickson et al. [76] | general | adults, 10F, 21M, age 26.7 ± 3.9 y | JP3 JP3 * | - - | - - | 0.800 0.870 |
| Chirita-Emandi et al. [105] | general | adults, 1F, age 31 y, 1M, age 24 y | JP3 JP3 * | 0.78 0.45 | - - | 0.982 0.991 |
| Chirita-Emandi et al. [106] | general | children, 20F, 20M, age 11.9 ± 3.7 y | JP3 * | 0.94 | - | 0.954 |
| Totosy de Zepetnek et al. [77] | general | 16M, 33F age 31.4 ± 10.7 y | JP7 | 0.78 | 2.16 | 0.986 |
| Miclos-Balica et al. [107] | general | adults, 63F, 81M, age 30.4 ± 10.1 y | JP7 JP7 * JP3 JP3 * P3 Bic1 | 1.06 1.24 1.52 1.76 1.57 2.54 | 2.95 3.43 4.21 4.87 4.34 7.05 | 0.979 0.972 0.954 0.938 0.955 0.964 |
| Wagner et al. [51] | athletic | 23F, age 19.6 ± 1.4 y 22M, age 20.6 ± 1.6 y | JP3 JP3 * | - - | 1.80 - | 0.993 0.987 |
| Wagner and Teramoto [65] | general | 32F, age 22.1 ± 1.1 y 48M, age 24.4 ± 1.6 y | JP3 * JP3 * | 1.48 0.94 | 4.10 2.60 | 0.969 0.990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neagu, M.; Neagu, A. A Decade of Progress in Ultrasound Assessments of Subcutaneous and Total Body Fat: A Scoping Review. Life 2025, 15, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020236
Neagu M, Neagu A. A Decade of Progress in Ultrasound Assessments of Subcutaneous and Total Body Fat: A Scoping Review. Life. 2025; 15(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeagu, Monica, and Adrian Neagu. 2025. "A Decade of Progress in Ultrasound Assessments of Subcutaneous and Total Body Fat: A Scoping Review" Life 15, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020236
APA StyleNeagu, M., & Neagu, A. (2025). A Decade of Progress in Ultrasound Assessments of Subcutaneous and Total Body Fat: A Scoping Review. Life, 15(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020236







