Drug-Induced Complete Atrioventricular Block in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Highlighting Digoxin-Beta Blocker Interactions and a Paradoxical State
Abstract
1. Introduction
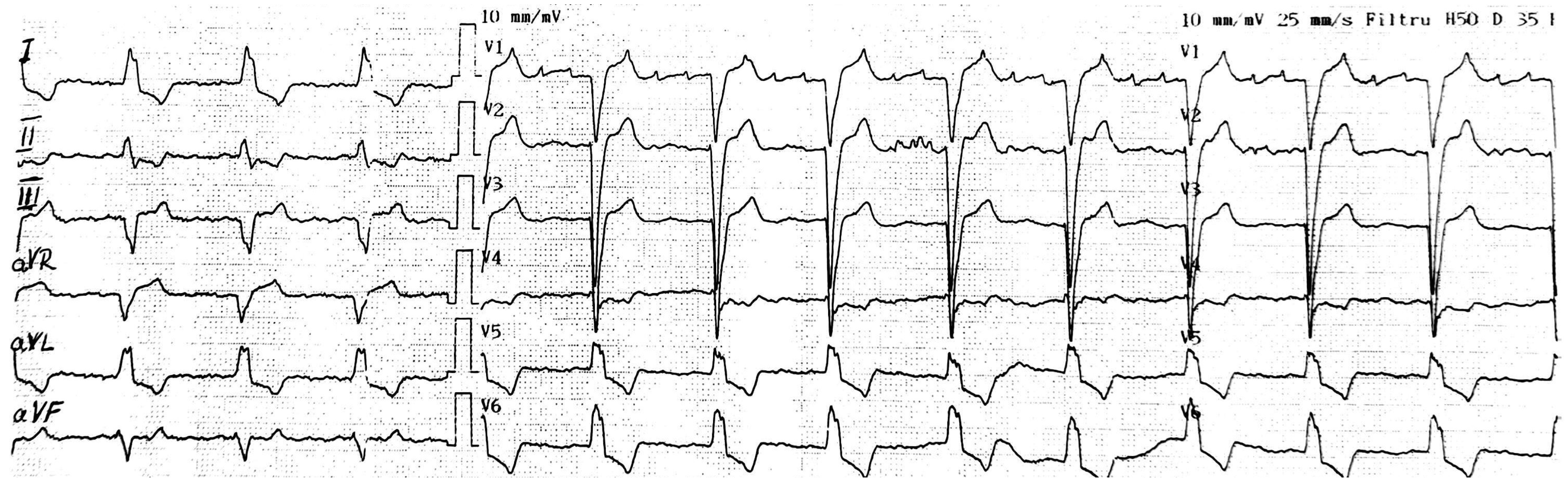
2. Detailed Case Description
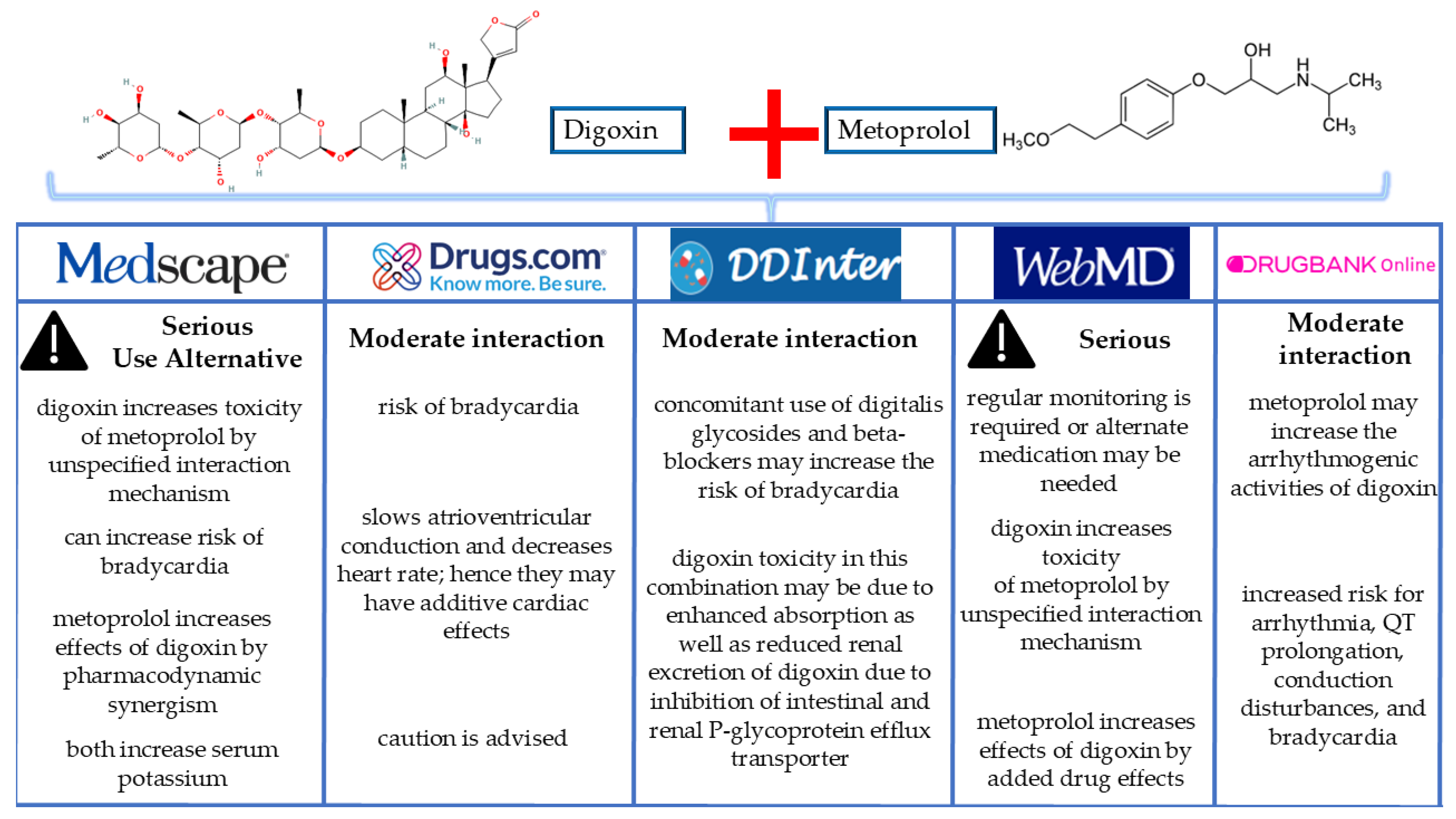
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| CHB | Complete heart block |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
References
- Vogler, J.; Breithardt, G.; Eckardt, L. Bradyarrhythmias and Conduction Blocks. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2012, 65, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarakis, G.; Gheni, A.; Hashim, H.T. Complete Heart Block (CHB). In Clinical and Surgical Aspects of Congenital Heart Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 141–146. ISBN 9783031230615. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, A.E.; DiMarco, J.P.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Estes, N.A.M., 3rd; Freedman, R.A.; Gettes, L.S.; Gillinov, A.M.; Gregoratos, G.; Hammill, S.C.; Hayes, D.L.; et al. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, e1–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashou, A.H.; Goyal, A.; Nguyen, T.; Ahmed, I.; Chhabra, L. Atrioventricular Block. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459147/ (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Merchant, F.M.; Hoskins, M.H.; Musat, D.L.; Prillinger, J.B.; Roberts, G.J.; Nabutovsky, Y.; Mittal, S. Incidence and Time Course for Developing Heart Failure With High-Burden Right Ventricular Pacing. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2017, 10, e003564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, S.N.C.; Providência, R.; Paiva, L.; Nascimento, J.; Marques, A.L. A Review on Advanced Atrioventricular Block in Young or Middle-Aged Adults. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundhu, M.; Yildiz, M.; Syed, M.; Shah, B.; Gul, S.; Afzal, O.; Castle, L. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Ischemic and Non-Ischemic Complete Heart Block. Cureus 2017, 9, e1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, P.; Gupta, T.; Palaniswamy, C.; Kolte, D.; Khera, S.; Mujib, M.; Aronow, W.S.; Ahn, C.; Sule, S.; Jain, D.; et al. Complete Heart Block Complicating ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 1, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsheh, A.; Shimony, D.; Bogot, N.; Nesher, G.; Breuer, G.S. Complete Heart Block in Lupus. Lupus 2019, 28, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, U.; Lazoglu, Z.; Kalkan, K.; Topcu, S.; Tanboga, I.H. A Life-Threatening Condition: Hyperkalemia-Induced Complete Heart Block. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 121, e161–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.J.; Bockenstedt, L.K. Lyme Disease and the Heart. Circulation 2013, 127, e451–e454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knabben, V.; Chhabra, L.; Slane, M. Third-Degree Atrioventricular Block. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545199/ (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, M.; Zhang, M.; Yao, F.; Cheng, Y. Incidence and Risk Factors Associated with Atrioventricular Block in the General Population: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study and Cardiovascular Health Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abo-EL-Sooud, K.; Aleya, L.; Bungau, S.G.; Najda, A.; Saluja, R. Alleviation of Drugs and Chemicals Toxicity: Biomedical Value of Antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6276438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G.; Corb Aron, R.A.; Tarce, A.G.; Bodog, R.; Bodog, T.M.; Radu, A. Deciphering the Intricate Interplay in the Framework of Antibiotic-Drug Interactions: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, J.E.; Chung, M.K.; Campbell, K.B.; Hammadah, M.; Joglar, J.A.; Leclerc, J.; Rajagopalan, B.; American Heart Association Clinical Pharmacology Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing. Drug-Induced Arrhythmias: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 142, e214–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, J.P.; Rigby, J.; Harper, A.C.; Rowland, R. Cardiovascular Monitoring with Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: A Clinical Protocol. Adv. Psychiatr. Treat. 2007, 13, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Ariff, A.M.; Abd Hadi, H.; Win, N.T.; Thoulath, M.I.; Aktifanus, A.T.J.; Mutaya, S.M.; Nalliah, S.; Mohamed Yusof, A.K. AHMAD Prevalence of Drug to Drug Interactions in Critical Cardiac Patients. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, Z.; Rehman, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Atif, M.; Ahmad, N. Potential Drug–Drug Interactions in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases: Findings from a Prospective Observational Study. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.H.M.; Romiti, G.F.; Olshansky, B.; Chao, T.-F.; Huisman, M.V.; Lip, G.Y.H. Combination Therapy of Beta-Blockers and Digoxin Is Associated with Increased Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Report from the GLORIA-AF Registry. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatnick, W.; Jelic, T. Calcium Channel Blocker and Beta Blocker Overdose, and Digoxin Toxicity Management. Emerg. Med. Pract. 2020, 22, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchier, L.; Grimard, C.; Pierre, B.; Nonin, E.; Gorin, L.; Rauzy, B.; Cosnay, P.; Babuty, D.; Charbonnier, B. Comparison of Beta Blocker and Digoxin Alone and in Combination for Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. J. Am. Coll. Dent. 2014, 81, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumoto, F.M.; Schoenfeld, M.H.; Barrett, C.; Edgerton, J.R.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Gold, M.R.; Goldschlager, N.F.; Hamilton, R.M.; Joglar, J.A.; Kim, R.J.; et al. 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhyth. Circulation 2019, 140, e382–e482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Awuah, D.; Deliwala, S.; Alkotob, M.L.; Seedahmed, E.; Bachuwa, G. The Management of Acute Onset Complete Heart Block and Atrial Flutter in a Patient with COVID-19. Eur. J. Case Reports Intern. Med. 2022, 9, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Murakawa, Y.; Ajiki, K.; Omata, M. Incidence of Induced Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter in Complete Atrioventricular Block. A Concept of “atrial-Malfunctioning” Atrio-Hisian Block. Circulation 1997, 95, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georger, F.; De Roy, L.; Sorea, C.; Albenque, J.-P.; Boveda, S.; Belhassen, B. Unusual Mechanism of Complete Atrioventricular Block Following Atrial Flutter Ablation. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2015, 1, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprasad, N.; Johnson, F.; Venugopal, K. Congenital Complete Heart Block and Maternal Connective Tissue Disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 112, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gona, S.R.; Rosenberg, J.; Fyffe-Freil, R.C.; Kozakiewicz, J.M.; Money, M.E. Review: Failure of Current Digoxin Monitoring for Toxicity: New Monitoring Recommendations to Maintain Therapeutic Levels for Efficacy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1179892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, J.B.; Wingate, S.; Zolty, R.; Rich, M.W.; Hauptman, P.J. Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Digoxin Toxicity. Am. J. Med. 2025, 138, 25–33.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, C.-H.; Liu, M.-W. A Case of Digoxin Intoxication Caused by Short-Term Massive Overdose: Case Report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2024, 103, e37034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, R.H.; Pegu, B.; Bansal, H.; Soni, K.D. Falling into Complexity: A Case of Digitalis-Induced Fall, Trauma, Symptomatic Bradycardia, and Syncope. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2024, 13, 3431–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.; Ioannou, A.; Dickinson, B.; Metaxa, S.; Amin, F.R.; Mandal, A.K.J.; Missouris, C.G. Drug-Related Bradycardia Precipitating Hospital Admission in Older Adults: An Ongoing Problem. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. Sci. Pract. 2022, 29, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.M.; Bae, M.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.; Heo, J.-H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yang, D.H.; Park, H.S.; et al. Prognosis and Natural History of Drug-Related Bradycardia. Korean Circ. J. 2009, 39, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchier, L.; Laborie, G.; Clementy, N.; Babuty, D. Beta-Blockers or Digoxin for Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure? Card. Fail. Rev. 2016, 2, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.C.; Tran, V.N.; Yaqub, S.; Basbayraktar, B.; Farid, A.; Sleem, M. Digoxin Toxicity in a Patient with Sick Sinus Syndrome: A Case Complicated by Acute Kidney Injury and Concurrent Amiodarone Use. Chest 2024, 166, A669–A670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoishi, H.; Uesawa, Y.; Ishii-Nozawa, R. Evaluation of β-Blocker-Induced Bradyarrhythmia Using an Analysis of the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report Database. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 47, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, G.; Toth, P.P.; Bungau, S.; Behl, T.; Ilie, M.; Stoian, A.P.; Bratu, O.G.; Bacalbasa, N.; Rus, M.; Diaconu, C.C. Cardiovascular Risk and Statin Therapy Considerations in Women. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Yang, Z.; Yi, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; et al. DDInter: An Online Drug-Drug Interaction Database towards Improving Clinical Decision-Making and Patient Safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1200–D1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachuer, C.; Corny, J.; Bézie, Y.; Ferchichi, S.; Durand-Gasselin, B. Complete Atrioventricular Block in an Elderly Patient Treated with Low-Dose Lacosamide. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2018, 18, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medscape Interactions Checker. Drug Interactions Between Digoxin and Metoprolol. Available online: https://reference.medscape.com/drug-interactionchecker (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Drugs.Com Interactions Checker. Drug Interactions between Digoxin and Metoprolol. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/interactions-check.php?drug_list=883-0,1615-0 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- WebMD Interactions Checker. Drug Interactions between Digoxin and Metoprolol. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/interaction-checker/default.htm (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- DrugBank Interactions Checker. Drug Interactions between Digoxin and Metoprolol. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drug-interaction-checker#results (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- DDInter Interactions Checker. Drug Interactions between Digoxin and Metoprolol. Available online: https://ddinter.scbdd.com/inter-checker/ (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Dasbiswas, A.; Reddy, P.K.M.; Gajapati, V.; Rawat, C.R.; Dharmadhikari, A. Efficacy & Tolerability of Bisoprolol in Comparison to Metoprolol in Indian Patients with Stage-1 Hypertension: Multicentre, Parallel Group, Open Labelled, Randomised Noninferiority Clinical Study. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3005. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, S.; Ihle, P.; Harder, S.; Schubert, I. Risk of Hyperkalemia and Combined Use of Spironolactone and Long-Term ACE Inhibitor/Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Therapy in Heart Failure Using Real-Life Data: A Population- and Insurance-Based Cohort. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2015, 24, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wong, L.Y.F.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Diuretic-Induced Hypokalaemia: An Updated Review. Postgrad. Med. J. 2022, 98, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratloo, A.; Haroutunian, P.; Rouhipour, A.; Saeed, S.; Rahmati, F. Hyperkalemia-Induced Complete Heart Block. J. Emerg. Pract. Trauma 2014, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barold, S.S.; Herweg, B. The Effect of Hyperkalaemia on Cardiac Rhythm Devices. EP Eur. 2014, 16, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, P.; Anseeuw, K.; Kotecha, D.; Lapostolle, F.; Thanacoody, R. Diagnosis and Practical Management of Digoxin Toxicity: A Narrative Review and Consensus. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 30, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridwell, R.E.; Baker, K.A.; Hoyte, C.O.; Ng, P.C. Digoxin Toxicity in a Patient with Pacemaker: A Case Report. Cureus 2019, 11, e6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Patel, P.; Patel, N.; Gangwani, J.; Patel, D. Case Report on the Interaction between Furosemide and Digoxin That Caused Digoxin Toxicity. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2022, 12, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul Bag, F.; Yalcin, M.; Vatansev, H.; Comakli, H. Digoxin’s Interactions with Various Drugs and A Case Report. Eur. J. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digiovanni-Kinsley, S.; Duke, B.; Giovane, R.; Paisley, C. A Case of Digoxin Toxicity Due to Acute Renal Failure. Cureus 2021, 13, e17599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.; Maor, E.; Leor, J.; Klempfner, R. Addition of Beta-Blockers to Digoxin Is Associated with Improved 1- and 10-Year Survival of Patients Hospitalized Due to Decompensated Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bustea, C.; Radu, A.-F.; Vesa, C.M.; Radu, A.; Bodog, T.M.; Bodog, R.F.; Maghiar, P.B.; Maghiar, A.M. Drug-Induced Complete Atrioventricular Block in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Highlighting Digoxin-Beta Blocker Interactions and a Paradoxical State. Life 2025, 15, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020215
Bustea C, Radu A-F, Vesa CM, Radu A, Bodog TM, Bodog RF, Maghiar PB, Maghiar AM. Drug-Induced Complete Atrioventricular Block in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Highlighting Digoxin-Beta Blocker Interactions and a Paradoxical State. Life. 2025; 15(2):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleBustea, Cristiana, Andrei-Flavius Radu, Cosmin Mihai Vesa, Ada Radu, Teodora Maria Bodog, Ruxandra Florina Bodog, Paula Bianca Maghiar, and Adrian Marius Maghiar. 2025. "Drug-Induced Complete Atrioventricular Block in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Highlighting Digoxin-Beta Blocker Interactions and a Paradoxical State" Life 15, no. 2: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020215
APA StyleBustea, C., Radu, A.-F., Vesa, C. M., Radu, A., Bodog, T. M., Bodog, R. F., Maghiar, P. B., & Maghiar, A. M. (2025). Drug-Induced Complete Atrioventricular Block in an Elderly Patient: A Case Report Highlighting Digoxin-Beta Blocker Interactions and a Paradoxical State. Life, 15(2), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020215







