Effects of Invasive Solidago canadensis and Biochar on the Remediation of Soil Cd Contamination and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Site
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.2.1. Preparation of Biochar
2.2.2. Soil Sample Preparation
2.2.3. Selection of Test Plants
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Gas Sampling and Analysis
2.3.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
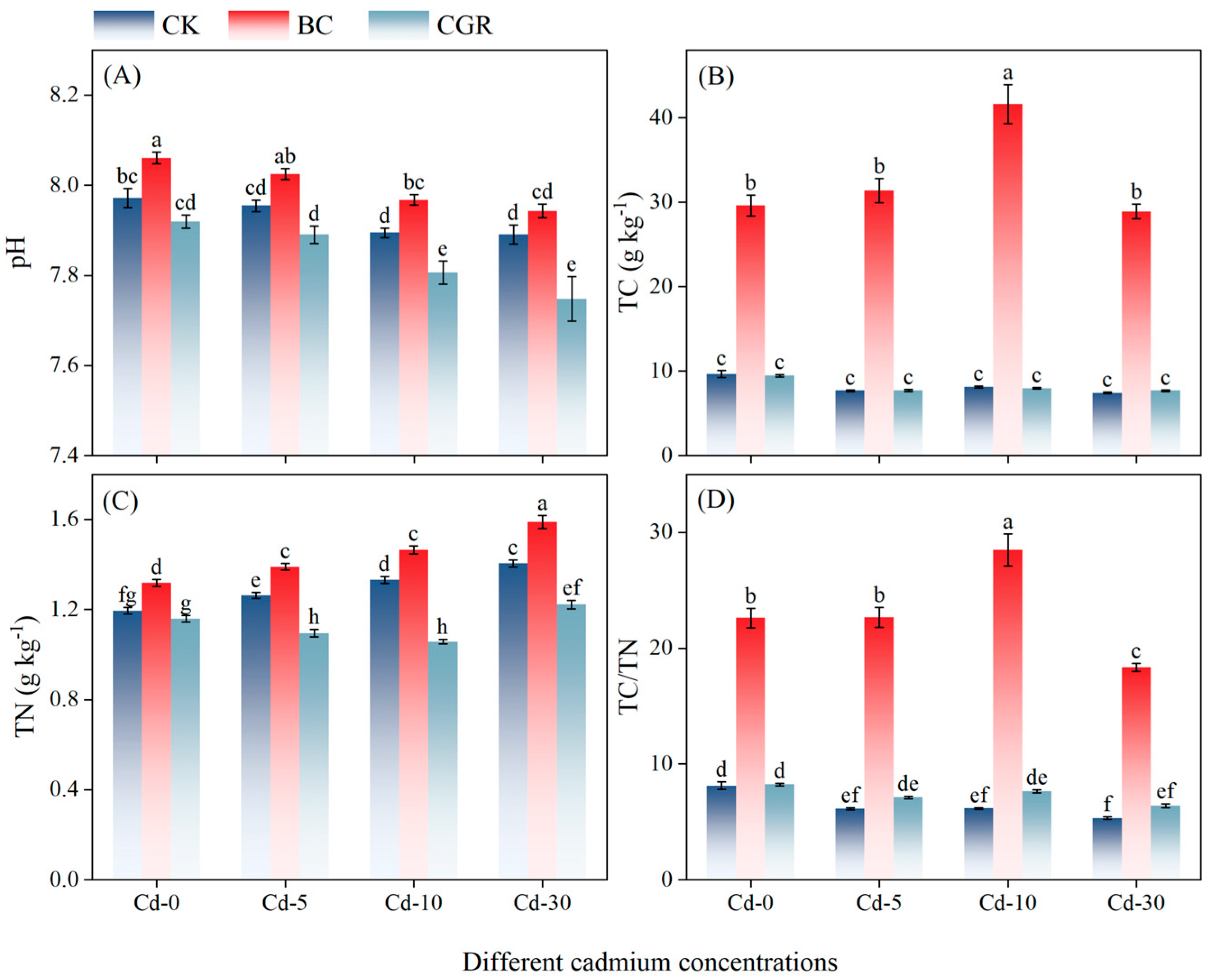
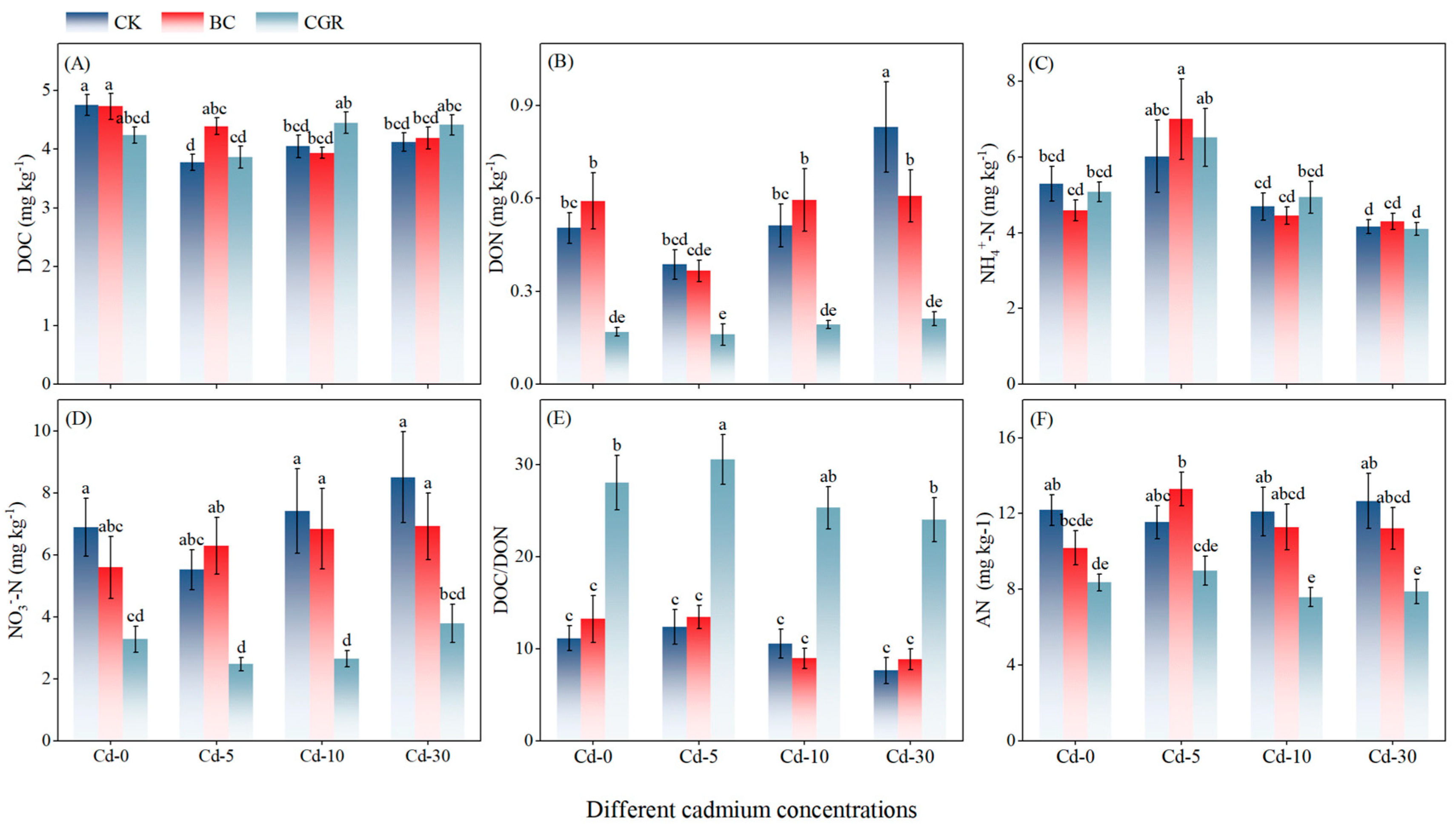
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
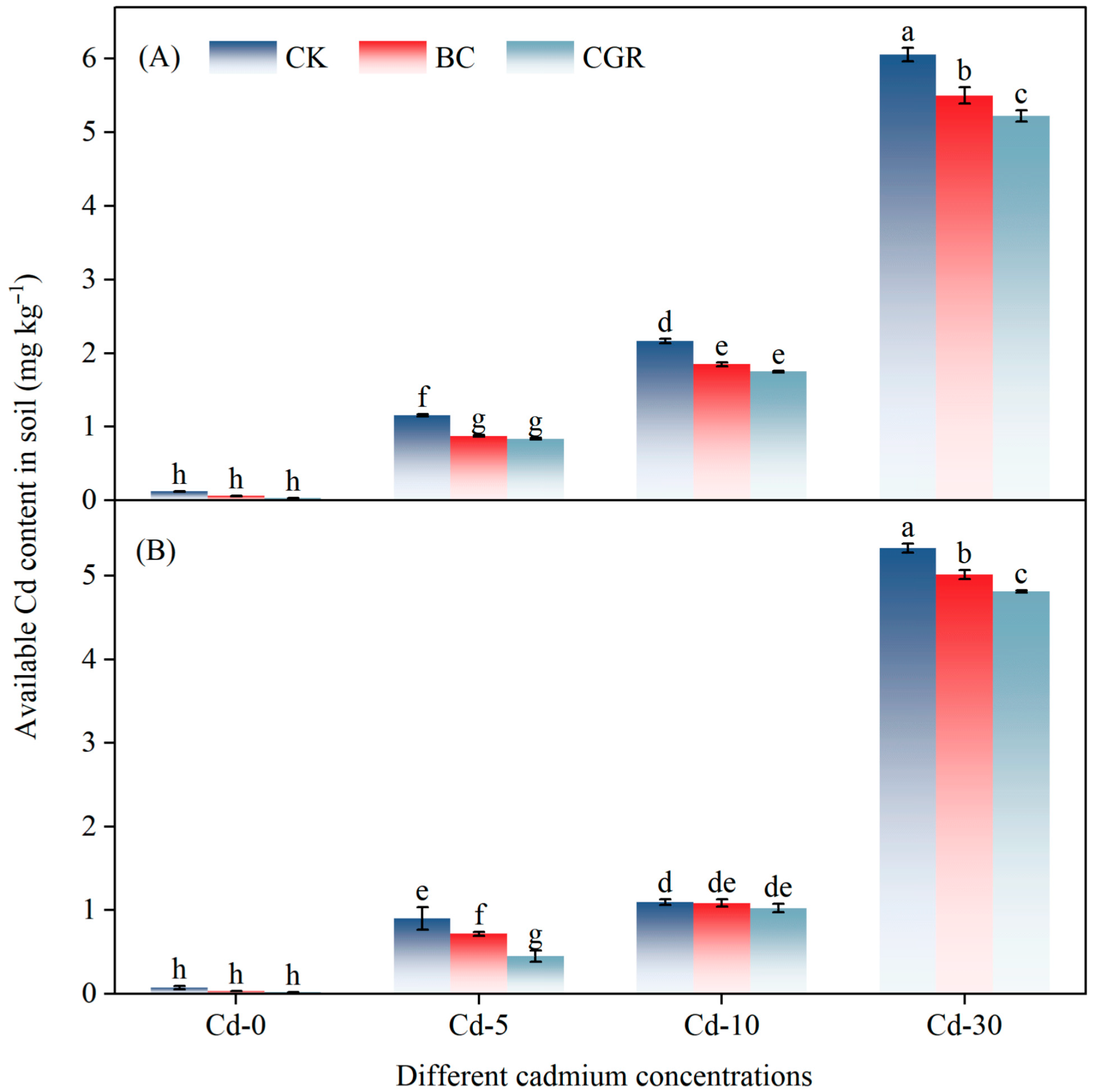
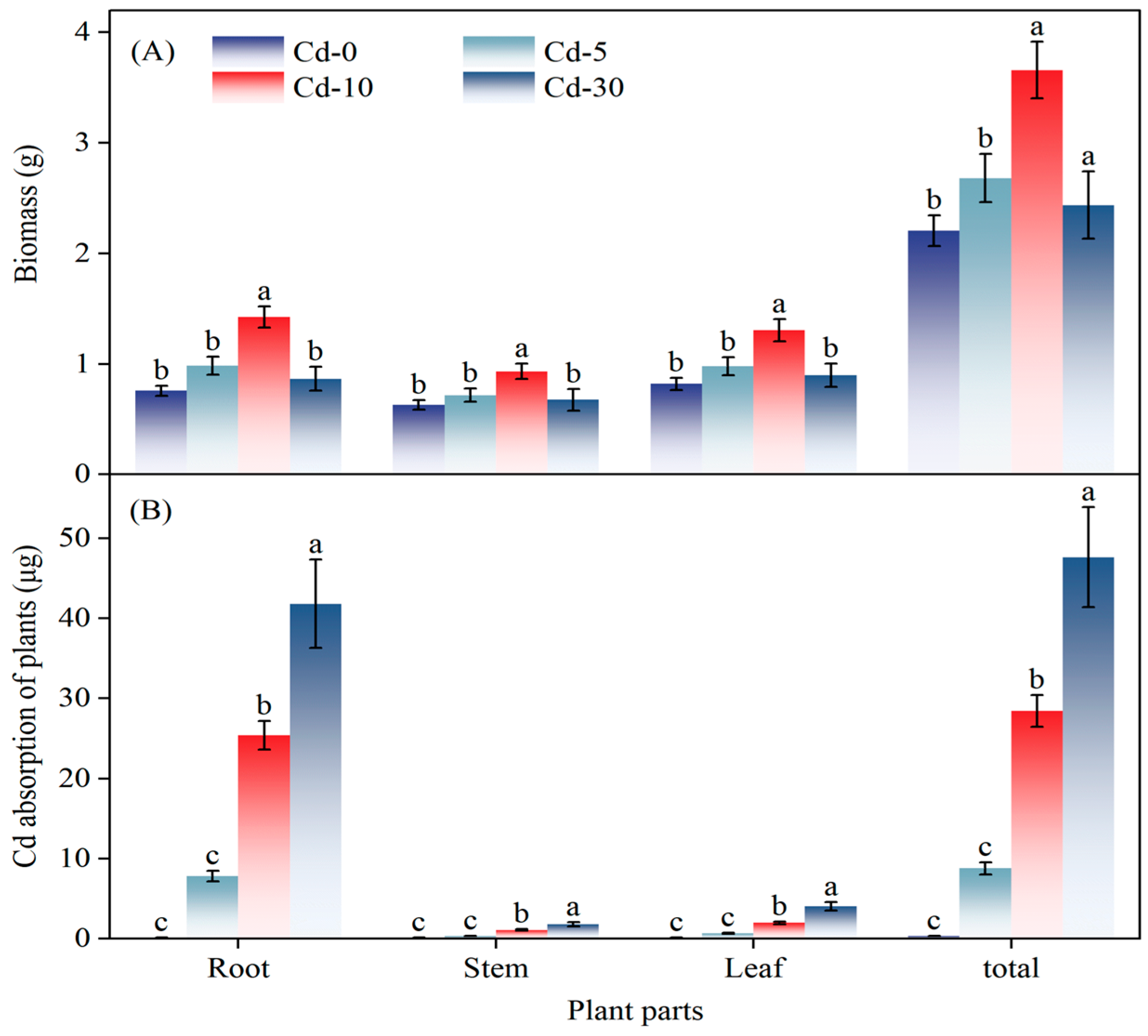
3.2. Soil-Available Cadmium
3.3. Plant Cadmium Content
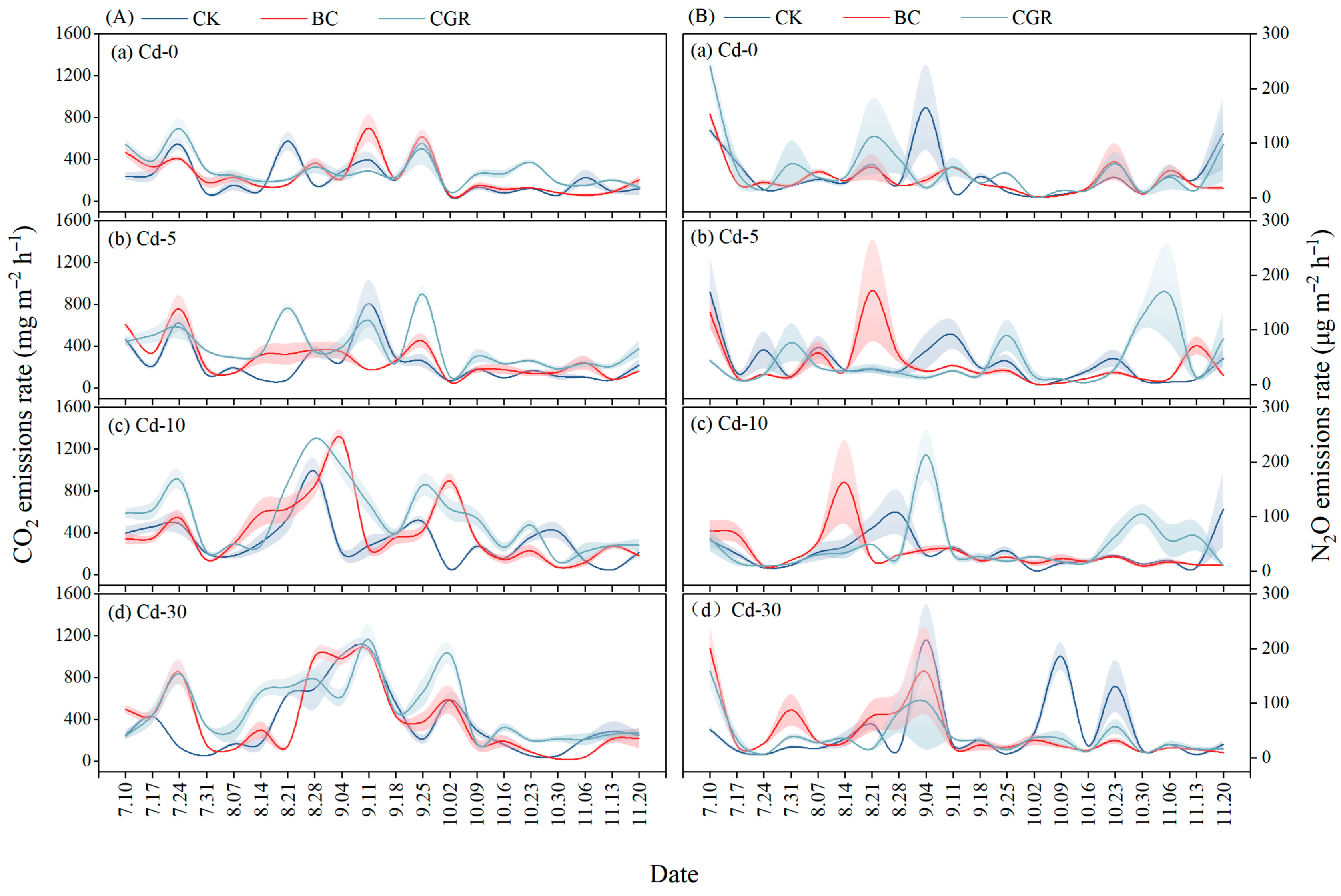
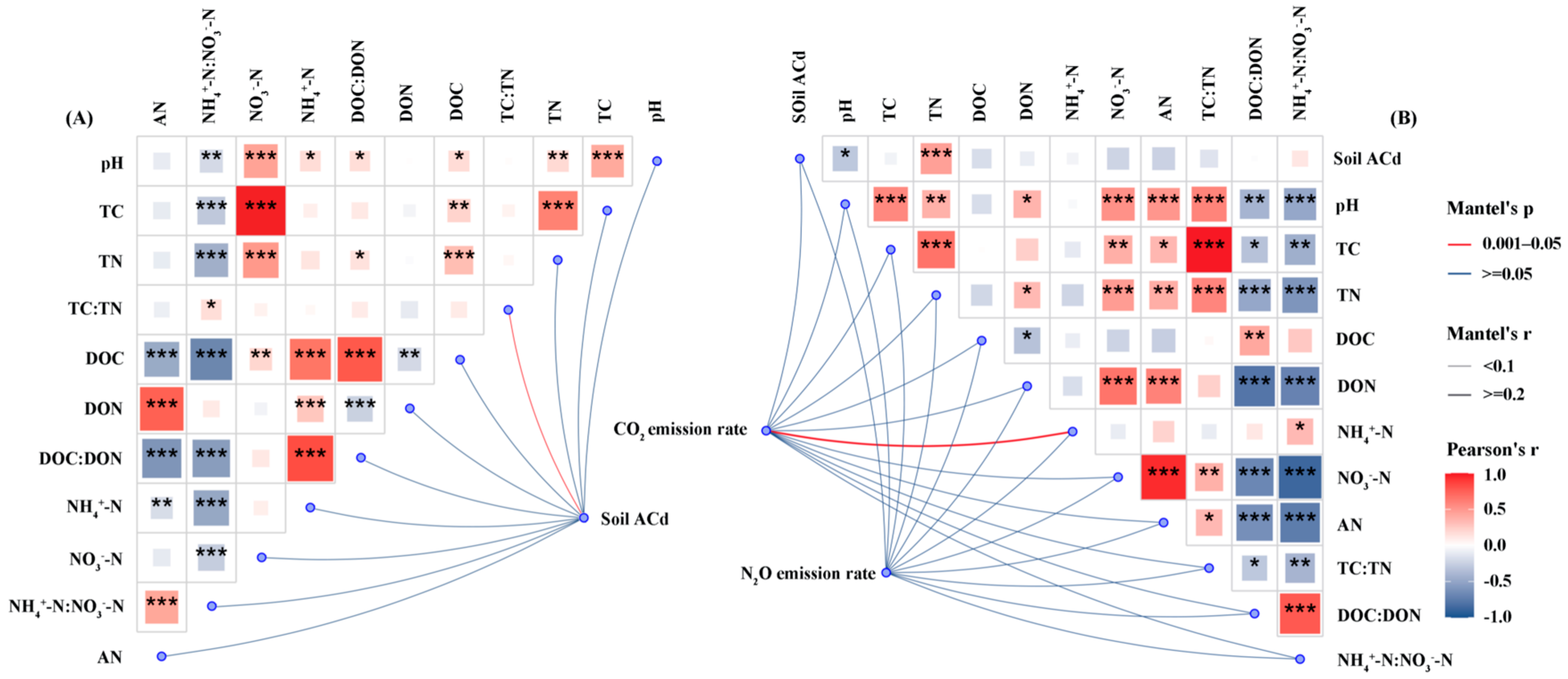
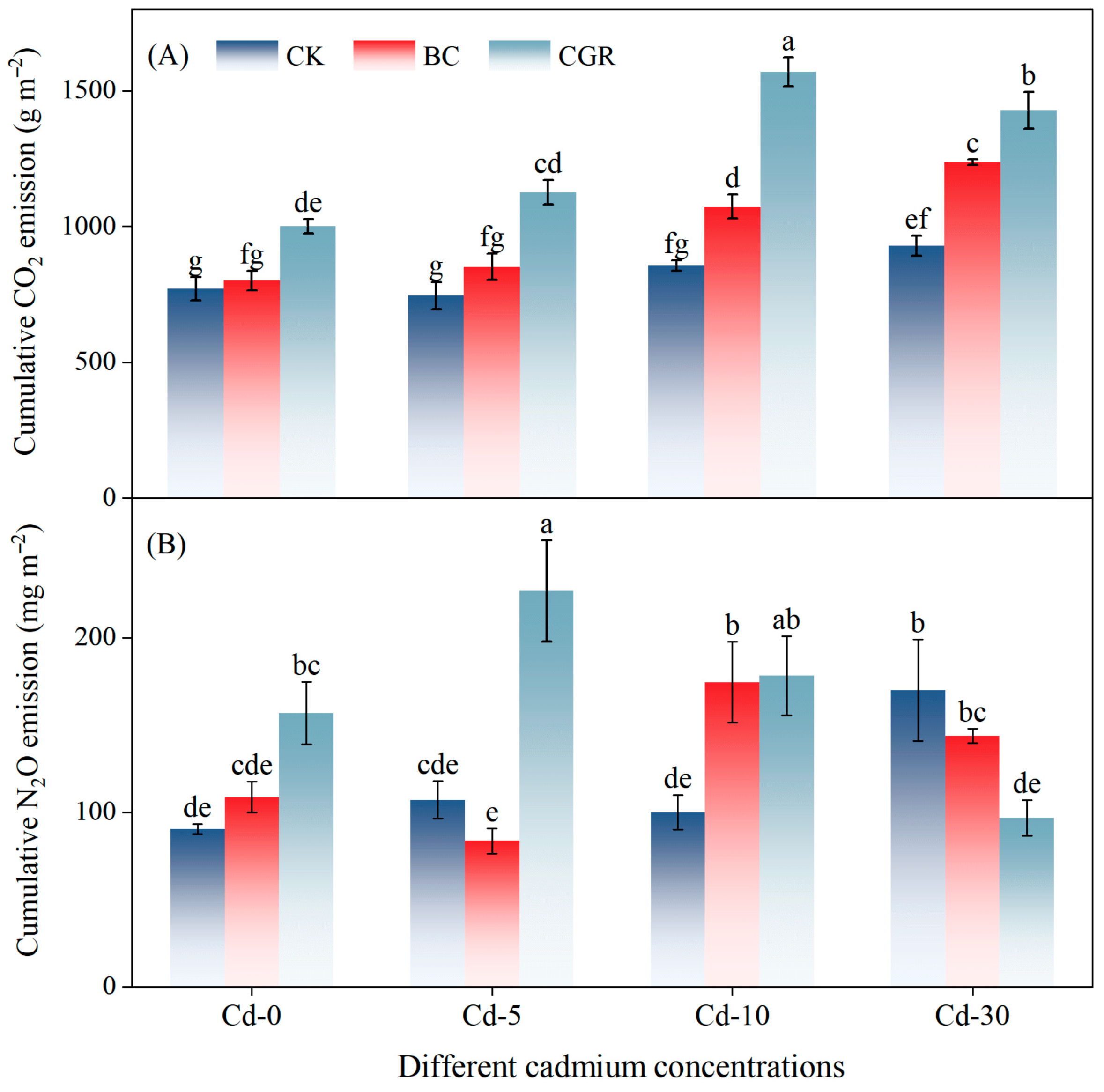
3.4. Effect on Soil GHG
3.4.1. CO2 Emission
3.4.2. N2O Emission
4. Discussion
4.1. Remediation Effects of CGR and BC on Cd-Contaminated Soil
4.2. Effects of CGR and BC on CO2 and N2O Emissions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sun, S.; Fan, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Song, F. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Influence the Uptake of Cadmium in Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, L.; Ye, Y.; Tang, F.; Wang, F.; Bao, H.; Jiang, Q.; Peng, W.; Zhang, L.; et al. Regulation of Cadmium Accumulation and Tolerance by Receptor-Like Kinase OsSRK and Putative Ligand OsTDL1B in Rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Food Safety in China: Effects, Sources and Removing Technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Review of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in China: Spatial Distribution, Primary Sources, and Remediation Alternatives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elik, Ü.; Gül, Z. Accumulation Potential of Lead and Cadmium Metals in Maize (Zea mays L.) and Effects on Physiological-Mor phological Characteristics. Life 2025, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabesch, S.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Kappler, A.; Fendorf, S.; Muehe, E.M.; León-Ninin, J.; Lezama-Pacheco, J. Coupled Cadmium and Climatic Stress Increase Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions. In Goldschmidt2021 Abstracts; European Association of Geochemistry: Aubière, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Reshaping Agriculture Eco-Efficiency in China: From Greenhouse Gas Perspec tive. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, R.; Du, Y.; Han, H.; Guo, S.; Song, X.; Ju, X. Significant Increases in Nitrous Oxide Emissions under Simulated Extreme Rainfall Events and Straw Amendments from Agricultural Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Dentener, F.; Bergamaschi, P.; Pagliari, V.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Peters, J.A.H.W.; et al. EDGAR v4.3.2 Global Atlas of the Three Major Greenhouse Gas Emissions for the Period 1970–2012. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 959–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhu, B.; Davis, S.J.; Ciais, P.; Guan, D.; Gong, P.; Liu, Z. Global Carbon Emissions and Decarbonization in 2024. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Xu, J. Dynamics of Soil Microbial N-Cycling Strategies in Response to Cadmium Stress. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14305–14315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, S.; Pang, Q.; Abdalla, M.; Karbin, S.; Qi, S.; Hu, J.; Qiu, H.; Song, X.; Smith, P. Metagenomic Insights into the Influence of Soil Microbiome on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Paddy Fields under Varying Irrigation and Fertilisation Regimes. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 393, 127129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, P.D.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Thi, K.V.; Quang, P.N. Insights into the Remediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Vegetable Soil: Co-Application of Low-Cost by-Products and Microorganism. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optimizing Biochar Production: A Review of Recent Progress in Lignocellulosic Biomass Pyrolysis. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 148–172. [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, J. Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Biochar in Aqueous Solution: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 968, 178898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Hu, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, D.; Lu, X.; Mi, B. Comparison of Properties, Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms to Cd(II) on Lignin-Derived Biochars under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures by Microwave Heating. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z. Modification of Arsenic and Cadmium Species and Accumu lation in Rice Using Biochar-Supported Iron-(Oxyhydr)Oxide and Layered Double Hydroxide: Insight from Fe Plaque Conversion and Nano-Bioassembly in the Root. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 152847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Geng, N.; Hou, X.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zhuge, Y. Potassium Permanganate-Hematite-Modified Biochar Enhances Cadmium and Zinc Passivation and Nutrient Availability and Promotes Soil Microbial Activity in Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; He, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, J. Iron-Silicon Modified Biochar for Remediation of Cadmium/Arsenic Co-Contam inated Paddy Fields: Is It Possible to Kill Two Birds with One Stone? J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Hu, H.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Xing, Z.; Ali, U.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu Contaminated Soil by Co-Pyrolysis Biochar Derived from Rape Straw and Orthophosphate: Speciation Transformation, Risk Evaluation and Mechanism Inquiry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprivica, M.; Petrović, J.; Simić, M.; Dimitrijević, J.; Ercegović, M.; Trifunović, S. Characterization and Evaluation of Biomass Waste Biochar for Turfgrass Growing Medium Enhancement in a Pot Experiment. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; De Almeida Moreira, B.R.; Bai, Y.; Nadar, C.G.; Feng, Y.; Yadav, S. Assessing Biochar’s Impact on Greenhouse Gas Emis sions, Microbial Biomass, and Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Soils through Meta-Analysis and Machine Learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 963, 178541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasar, B.J.; Agarwala, N. Unravelling the Role of Biochar-Microbe-Soil Tripartite Interaction in Regulating Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Budget: A Panacea to Soil Sustainability. Biochar 2025, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Zou, J.; Siemann, E. Perennial Forb Invasions Alter Greenhouse Gas Balance between Ecosys tem and Atmosphere in an Annual Grassland in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kama, R.; Javed, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Iqbal, B.; Diatta, S.; Sun, J. Effect of Soil Type on Native Pterocypsela Laciniata Performance under Single Invasion and Co-Invasion. Life 2022, 12, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhanov, A.; Oliinyk, M.; Pashkevych, N.; Churilov, A.; Kozyr, M. The Role of Flavonoids in Invasion Strategy of Solidago Cana densis L. Plants 2021, 10, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; Hou, X.-Y.; Du, D.-L.; Li, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y. Solidago canadensis Enhances Its Invasion by Modulating Prokaryotic Communities in the Bulk Soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 194, 105881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.P.; Gu, Z.; van Kleunen, M.; Zhou, X. Invasion Impacts in Terrestrial Ecosystems: Global Patterns and Predictors. Science 2025, 390, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.U.; Qi, S.-S.; Gul, F.; Manan, S.; Rono, J.K.; Naz, M.; Shi, X.-N.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.-C.; Du, D.-L. A Green Approach Used for Heavy Metals ‘Phytoremediation’ via Invasive Plant Species to Mitigate Environmental Pollution: A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G. Carbon Sequestration Strategies in Soil Using Biochar: Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 11357–11372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xiang, X.; Yu, X.; Dai, J.; Tian, X. Biochar Superior than Straw in Enhancing Soil Carbon Sequestration via Altering Organic Matter Stability and Carbon Cycle Genes in Cd-Contaminated Soil. Environ. Res. 2025, 287, 123128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Fang, H.; Jiang, N.; Feng, W.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Biochar Is Comparable to Dicyan diamide in the Mitigation of Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Camellia Oleifera Abel. Fields. Forests 2019, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Owens, V.N.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Hong, C.O. Adsorption and Precipitation of Cadmium Affected by Chemical Form and Addition Rate of Phosphate in Soils Having Different Levels of Cadmium. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, C.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Hu, X.; Deng, W.; Wang, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, L. Soil N2O Emission in Cinnamomum Camphora Plantations along an Urbanization Gradient Altered by Changes in Litter Input and Microbial Community Composition. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X.; Niu, D.; Siemann, E. Increases in Soil CO2 and N2O Emissions with Warming Depend on Plant Species in Restored Alpine Meadows of Wugong Mountain, China. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zheng, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Hu, X.; Guo, X.; et al. Effects of Mixing Biochar on Soil N2O, CO2, and CH4 Emissions after Prescribed Fire in Alpine Meadows of Wugong Mountain, China. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3062–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Deng, B.; Liu, X.; Yi, H.; Xiang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, X.; Niu, D. Alpine Meadow Restorations by Non-Dominant Species Increased Soil Nitrogen Transformation Rates but Decreased Their Sensitivity to Warming. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Huang, K.; Cai, H.-H.; Li, J.; Zhai, D.-L.; Dai, Z.-C.; Du, D.-L. Exploring the Potential of Naturalized Plants for Phytore mediation of Heavy Metal Contamination. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Ma, X.; Chu, S.; You, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, T.; et al. Nitrogen Cycle Induced by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Drives “Microbial Partners” to Enhance Cadmium Phytoremediation. Microbiome 2025, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T. Low Molecular Weight Organic Acids in Root Exudates and Cadmium Accumulation in Cadmium Hyperaccumu lator Solanum Nigrum L. and Non-Hyperaccumulator Solanum Lycopersicum L. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 17180–17185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Xu, X. Competition between Roots and Microorganisms for Nitrogen: Mechanisms and Ecological Relevance. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Q. Enhanced Cadmium Accumulation and Tolerance in Transgenic Hairy Roots of Solanum Nigrum L. Expressing Iron-Regulated Transporter Gene IRT1. Life 2020, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xia, R.; Zhong, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Bao, E.; Cao, K.; Chen, Q.; et al. Silicon and Iron Co-Application Modulates Cadmium Accumulation and Cell Wall Composition in Tomato Seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wu, X.; Deng, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; He, T.; Yi, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of Low Cadmium Accumulation in Crops: A Comprehensive Overview from Rhizosphere Soil to Edible Parts. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Metal Tolerance and Homeostasis. Planta 2001, 212, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyšek, P.; Richardson, D.M. Invasive Species, Environmental Change and Management, and Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, W.; Cai, Y.; Chang, S.X. Biochar Effectively Remediates Cd Contamination in Acidic or Coarse- and Medium-Textured Soils: A Global Meta-Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, B.; Ping, M.; Meng, Y.; Luo, W.; Chen, J.; Li, X. Synergistic Superiority of AMF and Biochar in Enhancing Rhizosphere Microbiomes to Support Plant Growth under Cd Stress. Biochar 2025, 7, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Feng, H.; Wan Mahari, W.A.; Yun, F.; Li, M.; Ma, N.L.; Cai, X.; Liu, G.; Liew, R.K.; Lam, S.S. Biochar and Microbial Synergy: Enhancing Tobacco Plant Resistance and Soil Remediation under Cadmium Stress. Biochar 2025, 7, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Chen, C.; Ni, C.; Xiong, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Tan, W. How Different Is the Remediation Effect of Biochar for Cadmium Contaminated Soil in Various Cropping Systems? A Global Meta-Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Sun, X.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, L.; An, Y.; Luo, Y. Optimal Biochar Selection for Cadmium Pollution Remediation in Chinese Agricultural Soils via Optimized Machine Learning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Fu, Y.; Long, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Guo, L.; Thakur, M.P.; Zhou, X. Invasive C4 Plants Cause Greater Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions than C3 Plants. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocito, F.F.; Espen, L.; Crema, B.; Cocucci, M.; Sacchi, G.A. Cadmium Induces Acidosis in Maize Root Cells. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Meng, B.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, T.; Yin, D.; Li, B.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Coupling of Mercury Contamination and Carbon Emissions in Rice Paddies: Methylmercury Dynamics versus CO2 and CH4 Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 10274–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, B. Solidago Canadensis Invasion Affects Soil N-Fixing Bacterial Communities in Heteroge neous Landscapes in Urban Ecosystems in East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xu, S.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Iqbal, B.; Cheng, P.; et al. Spartina Alterniflora Invasion Altered Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions via Affecting Labile Organic Carbon in a Coastal Wetland. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2024, 203, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrys, A.S.; Wen, Y.; Feng, D.; El-Mekkawy, R.M.; Kong, M.; Qin, X.; Lu, Q.; Dan, X.; Zhu, Q.; Tang, S.; et al. Cadmium Inhibits Carbon and Nitrogen Cycling through Soil Microbial Biomass and Reduces Soil Nitrogen Availability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezabih Beyene, B.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Freeman, C.; Ding, W. Non-Native Plant Invasion Can Accelerate Global Climate Change by Increasing Wetland Methane and Terrestrial Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5453–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omokaro, G.O.; Kornev, K.P.; Nafula, Z.S.; Chikukula, A.A.; Osayogie, O.G.; Efeni, O.S. Biochar for Sustainable Soil Man agement: Enhancing Soil Fertility, Plant Growth and Climate Resilience. Farming Syst. 2025, 3, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, C.; Yang, K.; Sheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, J.; Sun, R.; Zhu, L. Effects of Biochar Aging in the Soil on Its Mechanical Property and Performance for Soil CO2 and N2O Emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalu, S.; Seppänen, A.; Mganga, K.Z.; Sietiö, O.-M.; Glaser, B.; Karhu, K. Biochar Reduced the Mineralization of Native and Added Soil Organic Carbon: Evidence of Negative Priming and Enhanced Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency. Biochar 2024, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, T.; Lian, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hamid, Y.; He, Z.; Jeyakumar, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. Simultaneous Mitigation of Cadmium Contamination and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Paddy Soil by Iron-Modified Biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zou, J.; Shen, Z.; Lian, C.; Chen, Y. Analysis of the Long-Term Effectiveness of Biochar Immobilization Remediation on Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil and the Potential Environmental Factors Weakening the Remediation Effect: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Yan, L.; Yu, D. Utilization of Biochar for the Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Gao, W.; Pan, W.; Jiang, C.; Lee, X.; Cheng, J. Response of Soil N2O Production Pathways to Biochar Amend ment and Its Isotope Discrimination Methods. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Bao, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Huang, M.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, Y. Experimental and Numerical Investigations of Biochar-Facilitated Cd2+ Transport in Saturated Porous Media: Role of Solution pH and Ionic Strength. Biochar 2023, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Fang, H.; Cheng, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Pu, H.; Liu, B. Cadmium Accumulation Suppresses Rice Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Inhibiting Rhizosphere Nitrification and Promoting Nitrate Reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 496, 139298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test Materials | pH | TC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | DOC (mg kg−1) | DON (mg kg−1) | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | ACd (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 7.93 ± 0.09 | 8.22 ± 0.15 | 1.29 ± 0.13 | 4.18 ± 0.93 | 0.56 ± 0.05 | 5.04 ± 0.29 | 7.08 ± 0.58 | 0.12 ± 0.03 |
| Factors | Remediation Measures | Cd | Remediation Measures × Cd |
|---|---|---|---|
| df | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| pH | 54.693 *** | 21.508 *** | 0.934 |
| TC (g kg−1) | 979.544 *** | 14.118 *** | 15.111 *** |
| TN (g kg−1) | 234.468 *** | 47.457 *** | 8.977 *** |
| DOC (mg kg−1) | 0.642 | 6.054 *** | 3.158 |
| DON (mg kg−1) | 35.95 *** | 6.078 *** | 2.007 |
| NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | 0.048 | 10.491 *** | 0.5 |
| NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | 21.168 *** | 1.623 | 0.472 |
| AN (mg kg−1) | 19.571 *** | 0.723 | 0.894 |
| ACd (mg kg−1) | 12.211 *** | 1343.782 *** | 1.812 |
| TC/TN | 1138.322 *** | 29.38 *** | 17.036 *** |
| DOC/DON | 88.529 *** | 4.326 | 0.237 |
| Factors | Remediation Measures | Cd | Remediation Measures × Cd |
|---|---|---|---|
| df | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| N2O emission rate (μg m−2 h−1) | 0.887 | 0.688 | 0.658 |
| CO2 emission rate (mg m−2 h−1) | 25.731 *** | 24.053 *** | 1.901 |
| Cumulative N2O emission (mg m−2 h−1) | 8.52 *** | 1.79 * | 8.904 *** |
| Cumulative CO2 emission (g m−2 h−1) | 116.42 *** | 50.058 *** | 7.005 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Nie, W.; Hu, Y.; Bai, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, W.; Xiong, L.; Xie, X.; et al. Effects of Invasive Solidago canadensis and Biochar on the Remediation of Soil Cd Contamination and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Life 2025, 15, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121927
Ni X, Yu Y, Liu X, Nie W, Hu Y, Bai J, Yan Z, Li W, Xiong L, Xie X, et al. Effects of Invasive Solidago canadensis and Biochar on the Remediation of Soil Cd Contamination and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Life. 2025; 15(12):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121927
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Xiaokang, Yadi Yu, Xi Liu, Wanqing Nie, Yuli Hu, Jian Bai, Ziyi Yan, Wei Li, Lifei Xiong, Xixian Xie, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Invasive Solidago canadensis and Biochar on the Remediation of Soil Cd Contamination and Greenhouse Gas Emissions" Life 15, no. 12: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121927
APA StyleNi, X., Yu, Y., Liu, X., Nie, W., Hu, Y., Bai, J., Yan, Z., Li, W., Xiong, L., Xie, X., Zhu, Y., Zeng, Z., Yu, Q., Wang, S., Ying, Q., Wu, N., & Zhang, L. (2025). Effects of Invasive Solidago canadensis and Biochar on the Remediation of Soil Cd Contamination and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Life, 15(12), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121927





