Spaceflight and Medical Microbiology: Possible Implications for Standard Infection Diagnostics and Therapy
Abstract
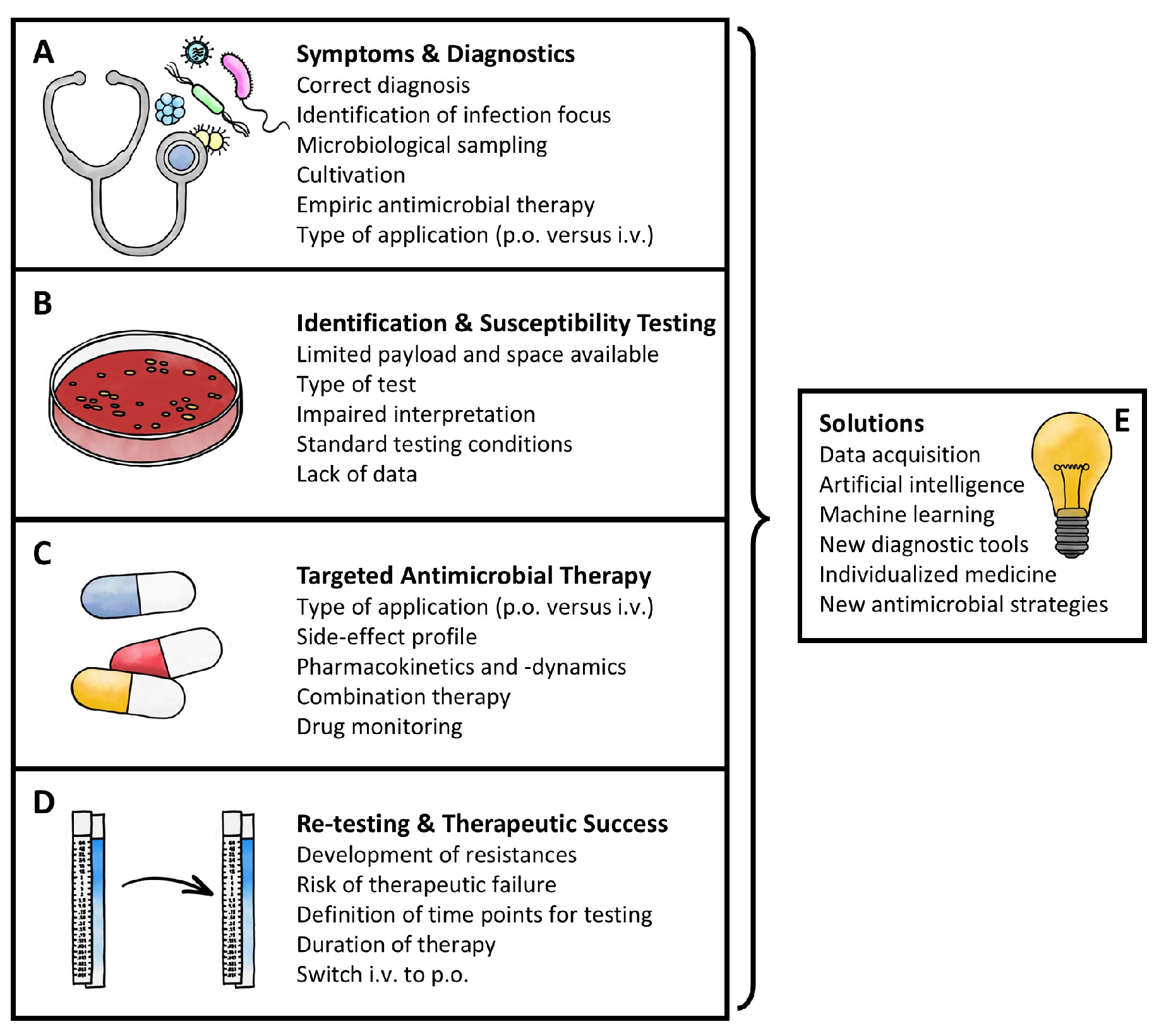
1. Introduction
2. Symptoms and Diagnostics
3. Identification and Susceptibility Testing
4. Targeted Antimicrobial Therapy
5. Re-Testing and Therapeutic Success
6. Outlook and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C. | Candida |
| ECOFF | Epidemiological cut-off |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| ISS | International Space Station |
| i.v. | Intravenous |
| P. | Pseudomonas |
| p.o. | Per os |
| POCT | Point-of-care testing |
| S. | Staphylococcus |
| UTI | Urinary tract infection |
References
- Nickerson, C.A.; Medina-Colorado, A.A.; Barrila, J.; Poste, G.; Ott, C.M. A vision for spaceflight microbiology to enable human health and habitat sustainability. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 7, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.R. Space microbiology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1974, 28, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horneck, G.; Klaus, D.M.; Mancinelli, R.L. Space Microbiology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 121–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choukèr, A. Stress Challenges and Immunity in Space: From Mechanisms to Monitoring and Preventive Strategies, 2nd ed.; 2012 Edition; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cowen, D.; Zhang, R.; Komorowski, M. Infections in long-duration space missions. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Sommer, A. Towards rational treatment of bacterial infections during extended space travel. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermel, L.A. Infection Prevention and Control During Prolonged Human Space Travel. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3.0 Health and Medical Care—NASA. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/reference/3-0-health-and-medical-care/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Mora, M.; Mahnert, A.; Koskinen, K.; Pausan, M.R.; Oberauner-Wappis, L.; Krause, R.; Perras, A.K.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Berg, G.; Moissl-Eichinger, C. Microorganisms in Confined Habitats: Microbial Monitoring and Control of Intensive Care Units, Operating Rooms, Cleanrooms and the International Space Station. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlani, S.; Stephens, E.; Singh, N.K.; Venkateswaran, K.; Wang, C.C. Advances in space microbiology. iScience 2021, 24, 102395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salido, R.A.; Zhao, H.N.; McDonald, D.; Mannochio-Russo, H.; Zuffa, S.; Oles, R.E.; Aron, A.T.; El Abiead, Y.; Farmer, S.; González, A.; et al. The International Space Station has a unique and extreme microbial and chemical environment driven by use patterns. Cell 2025, 188, 2022–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Laudenslager, M.L.; Stowe, R.P.; Crucian, B.E.; Feiveson, A.H.; Sams, C.F.; Pierson, D.L. Latent virus reactivation in astronauts on the international space station. npj Microgravity 2017, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, B.V.; Crucian, B.E.; Pierson, D.L.; Laudenslager, M.L.; Mehta, S.K. Herpes Virus Reactivation in Astronauts During Spaceflight and Its Application on Earth. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucian, B.; Babiak-Vazquez, A.; Johnston, S.; Pierson, D.L.; Ott, C.M.; Sams, C. Incidence of clinical symptoms during long-duration orbital spaceflight. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2016, 9, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, K.-A.; Pollock, N.W.; Dion, P.-M.; Lapierre, M.; Tremblay, S.; Witteman, W.; Rhéaume, C.; Lafond, D.; Fortier, F.-A.; Marion, A.; et al. Managing Select Medical Emergencies During Long-Duration Space Missions. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2025, 96, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, K.J.; Williams, T.J.; Schneiderman, J.S.; Whitmire, A.M.; Picano, J.J.; Leveton, L.; Schmidt, L.; Shea, C. Evidence Report: Risk of Adverse Cognitive or Behavioral Conditions and Psychiatric Disorders. 2016. Available online: https://humanresearchroadmap.nasa.gov/evidence/reports/bmed.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Wilson, N. A Microbial Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy: Researchers race to understand effects of deep space on microbiome. BioScience 2019, 69, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, V. Microbiological status of cosmonauts during orbital spaceflights on Salyut and Mir orbital stations. Acta Astronaut. 2005, 56, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.R. Recovery of medically important microorganisms from Apollo astronauts. Aerosp. Med. 1974, 45, 824–828. [Google Scholar]
- . Bruce, R.J.; Ott, C.M.; Skuratov, V.M.; Pierson, D.L. Microbial surveillance of potable water sources of the International Space Station. SAE Trans. 2005, 114, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, M.E.; Kerstman, E.L. Quantification of Medical Risk on the International Space Station Using the Integrated Medical Model. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2020, 91, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, M.; Topi, S.; Palmirotta, R.; D’agostino, D.; Charitos, I.A.; Lovero, R.; Santacroce, L. An Overview of the Microbiota of the Human Urinary Tract in Health and Disease: Current Issues and Perspectives. Life 2023, 13, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.; Oertlin, C.; Baselet, B.; Westerberg, L.S.; Frippiat, J.-P.; Baatout, S. Next generation of astronauts or ESA astronaut 2.0 concept and spotlight on immunity. npj Microgravity 2023, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.F.; Youngstein, T.; Kirrane, M.D.; Lonsdale, D.O. Diagnostic challenges in sepsis. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, M.L.; Patel, M.; Claypool, S. Sepsis as a model for improving diagnosis. Diagnosis 2018, 5, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, K.M.; Dy-Boarman, E.A.; Haase, K.K.; Maxvill, K.; Pass, S.E.; Alvarez, C.A. Challenges with Diagnosing and Managing Sepsis in Older Adults. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresta, F.; Bergamini, C.; Podda, M.; Campanile, F.C.; Anania, G.; Volpato, S.; Nobili, A.; Costa, G.; Puzziello, A.; Corcione, F. How to Define an Elderly and Frail Patient? In Emergency Laparoscopic Surgery in the Elderly and Frail Patient; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Campisi, M.; Cannella, L.; Pavanello, S. Cosmic chronometers: Is spaceflight a catalyst for biological ageing? Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 95, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeschger, T.; McCloskey, D.; Kopparthy, V.; Singh, A.; Erickson, D. Point of care technologies for sepsis diagnosis and treatment. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massara, M.; De Caridi, G.; Serra, R.; Barillà, D.; Cutrupi, A.; Volpe, A.; Cutrupi, F.; Alberti, A.; Volpe, P. The role of procalcitonin as a marker of diabetic foot ulcer infection. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, D.J.; Miller, R.S.; Crucian, B.E.; Valentine, R.W.; Cristoforetti, S.; Bearg, S.B.; Sipic, Z.; Cheng, J.; Yu, R.; Calaway, K.M.; et al. Single drop cytometry onboard the International Space Station. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, J.-H.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.-J.; Wang, S.-N.; Wang, J.-M. Biomarkers for diagnosis of sepsis in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Al-Amin, Y.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Lucy, I.B. Conventional methods and future trends in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, A.; Aabenhus, R. Urine sampling techniques in symptomatic primary-care patients: A diagnostic accuracy review. BMC Fam. Pract. 2016, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, S. MIQ 02: Harnwegsinfektionen: Qualitätsstandards in der Mikrobiologisch-Infektiologischen Diagnostik; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bilsen, M.P.; Jongeneel, R.M.H.; Schneeberger, C.; Platteel, T.N.; van Nieuwkoop, C.; Mody, L.; Caterino, J.M.; Geerlings, S.; Köves, B.; Wagenlehner, F.; et al. Definitions of Urinary Tract Infection in Current Research: A Systematic Review. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, E.E.; Parnell, L.K.; Wang, D.; Stapleton, A.E.; Lukacz, E.S. Microbial threshold guidelines for UTI diagnosis: A scoping systematic review. Pathol. Lab. Med. Int. 2023, 15, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddeo, T.A.; Gilmore, S.; Armstrong, C.W. Spaceflight Medical Systems. In Principles of Clinical Medicine for Space Flight; Barratt, M.R., Baker, E.S., Pool, S.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 201–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.L.; Ledeboer, N.; Burnham, C.-A.D. Clinical Microbiology Is Growing Up: The Total Laboratory Automation Revolution. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wain, J.; Diep, T.S.; Ho, V.A.; Walsh, A.M.; Hoa, N.T.T.; Parry, C.M.; White, N.J. Quantitation of Bacteria in Blood of Typhoid Fever Patients and Relationship between Counts and Clinical Features, Transmissibility, and Antibiotic Resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BD BD BACTECTM Blood Culture Media. Available online: https://www.bd.com/en-us/products-and-solutions/solutions/capabilities/bd-bactec-blood-culture-media (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Abram, T.J.; Cherukury, H.; Ou, C.-Y.; Vu, T.; Toledano, M.; Li, Y.; Grunwald, J.T.; Toosky, M.N.; Tifrea, D.F.; Slepenkin, A.; et al. Rapid bacterial detection and antibiotic susceptibility testing in whole blood using one-step, high throughput blood digital PCR. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Tao, Y.; Shao, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Sun, R. A Comparison of Blood Pathogen Detection Among Droplet Digital PCR, Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing, and Blood Culture in Critically Ill Patients With Suspected Bloodstream Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 641202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.; Mach, K.E.; Shortliffe, L.M.D.; Banaei, N.; Wang, T.-H.; Liao, J.C. New and developing diagnostic technologies for urinary tract infections. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirano, G.; Chen, L.; Nobrega, D.; Finn, T.J.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; DeVinney, R.; Pitout, J.D. Genomic Epidemiology of Global Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli, 2015–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunasri, K.; Adil, M.; Charan, K.V.; Suvro, C.; Reddy, S.H.; Shivaji, S. Effect of Simulated Microgravity on E. coli K12 MG1655 Growth and Gene Expression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.G.; Stodieck, L.; Birdsall, H.H.; Becker, J.L.; Koenig, P.; Hammond, J.S.; Gunter, M.A.; Allen, P.L. Effects of microgravity on the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Candida albicans, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Astrobiology 2013, 13, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiwon, K.; Arends, K.; Rogowski, K.M.; Fürch, S.; Prescha, K.; Sakinc, T.; Van Houdt, R.; Werner, G.; Grohmann, E. Comparison of antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation and conjugative transfer of Staphylococcus and Entero-coccus isolates from International Space Station and Antarctic Research Station Concordia. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, F.; Siems, K.; Walker, S.V.; Bryan, N.C.; Leuko, S.; Moeller, R.; Boschert, A.L. Systematic screening of 42 vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium strains for resistance, biofilm, and desiccation in simulated microgravity. npj Microgravity 2024, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Nascimento, A.; Grenga, L.; Haange, S.-B.; Himmelmann, A.; Arndt, F.S.; Ly, Y.-T.; Miotello, G.; Pible, O.; Jehmlich, N.; Engelmann, B. Human gut microbiome and metabolite dynamics under simulated microgravity. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2259033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkat, G.; Bartoletti, R.; Bruyère, F.; Cai, T.; Geerlings, S.; Köves, B.; Schubert, S.; Wagenlehner, F. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Urological Infections. 2020; EAU: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kranz, J.; Schmidt, S.; Lebert, C.; Schneidewind, L.; Vahlensieck, W.; Sester, U.; Fünfstück, R.; Helbig, S.; Hofmann, W.; Hummers, E.; et al. Epidemiologie, Diagnostik, Therapie, Prävention und Management unkomplizierter, bakterieller, ambulant er-worbener Harnwegsinfektionen bei erwachsenen Patienten: Aktualisierung 2017 der interdisziplinären AWMF S3-Leitlinie. Urologe 2017, 56, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doron, S.; Davidson, L.E. Antimicrobial Stewardship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, C.; Sielaff, A.C.; Frey, K.G.; Allen, J.E.; Singh, N.; Jaing, C.; Wheeler, K.; Venkateswaran, K. Detection of antimicrobial resistance genes associated with the International Space Station environmental surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.W.; Ott, C.M.; Zu Bentrup, K.H.; Ramamurthy, R.; Quick, L.; Porwollik, S.; Cheng, P.; McClelland, M.; Tsaprailis, G.; Radabaugh, T.; et al. Space flight alters bacterial gene expression and virulence and reveals a role for global regulator Hfq. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16299–16304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H. The recent large reduction in space launch cost. In Proceedings of the 48th International Conference on Environmental Systems, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 8–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Ringer, M.; Kotroczó, Z.; Mohácsi-Farkas, C.; Kocsis, T. The Current Level of MALDI-TOF MS Applications in the Detection of Microorganisms: A Short Review of Benefits and Limitations. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschelli, L.; Ciricugno, C.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Romani, A.; Berardinelli, A.; Tartagni, M.; Correale, R. Real-time gas mass spectroscopy by multivariate analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarek, P.; Silberring, J.; Smoluch, M. Miniaturization in mass. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2020, 39, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Life Sciences Glovebox—ISS National Lab. Available online: https://issnationallab.org/facilities/life-sciences-glovebox/ (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Biomérieux. VITEK® SOLUTIONS. Available online: https://www.biomerieux.com/corp/en/our-offer/hospital-laboratory/product-range/vitek-solutions.html (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- BD BD PhoenixTM Automated Identification and Susceptibility. Available online: https://www.bd.com/en-us/products-and-solutions/solutions/capabilities/bd-phoenix-automate-identific (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Datar, R.; Perrin, G.; Chalansonnet, V.; Perry, A.; Perry, J.D.; van Belkum, A.; Orenga, S. Automated antimicrobial susceptibility testing of slow-growing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in the presence of tetrazolium salt WST-1. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 186, 106252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. EUCAST: Calibration and Validation. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_bacteria/calibration_and_validation (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Beysens, D. Transport phenomena in microgravity. Front. Space Technol. 2022, 3, 1092802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vailati, A.; Šeta, B.; Bou-Ali, M.; Shevtsova, V. Perspective of research on diffusion: From microgravity to space exploration. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 229, 125705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. EUCAST: SOPs. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/eucastsops (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- EUCAST. EUCAST: Clinical Breakpoints and Dosing of Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Allen, L.A.; Kalani, A.H.; Estante, F.; Rosengren, A.J.; Stodieck, L.; Klaus, D.; Zea, L. Simulated Micro-, Lunar, and Martian Gravities on Earth—Effects on Escherichia coli Growth, Phenotype, and Sensitivity to Antibiotics. Life 2022, 12, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomartino, R.; Waajen, A.C.; de Wit, W.; Nicholson, N.; Parmitano, L.; Loudon, C.-M.; Moeller, R.; Rettberg, P.; Fuchs, F.M.; Van Houdt, R.; et al. No Effect of Microgravity and Simulated Mars Gravity on Final Bacterial Cell Concentrations on the International Space Station: Applications to Space Bioproduction. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TTaylor, P. Impact of space flight on bacterial virulence and antibiotic susceptibility. Infect. Drug Resist. 2015, 8, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, B.; McCray, R.H.; Best, M.D.; Levine, H.G. A Flight-Rated Petri Dish Apparatus Providing Two Stage Fluid Injection for Aseptic Biological Investigations in Space. SAE Technical Paper. 2001. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2001-01-2286/ (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlmeter, G.; Turnidge, J. Wild-type distributions of minimum inhibitory concentrations and epidemiological cut-off values—Laboratory and clinical utility. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e0010022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlmeter, G.; Turnidge, J. How to: ECOFFs—The why, the how, and the don’ts of EUCAST epidemiological cutoff values. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Wallace, S.L.; Chiu, C.Y.; John, K.K.; Stahl, S.E.; Rubins, K.H.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Dworkin, J.P.; Lupisella, M.L.; Smith, D.J.; Botkin, D.J.; et al. Nanopore DNA Sequencing and Genome Assembly on the International Space Station. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poritz, M.A.; Lingenfelter, B. Multiplex PCR for Detection and Identification of Microbial Pathogens. In Advanced Techniques in Diagnostic Microbiology; Tang, Y.-W., Stratton, C.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, F.J.; Salavert, M.; Cantón, R.; del Pozo, J.L.; Galán-Sánchez, F.; Navarro, D.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, J.C.; Rodríguez-Aguirregabiria, M.; Suberviola, B.; et al. The role of rapid multiplex molecular syndromic panels in the clinical management of infections in critically ill patients: An experts-opinion document. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tixador, R.; Richoilley, G.; Gasset, G.; Planel, H.; Moatti, N.; Lapchine, L.; Enjalbert, L.; Raffin, J.; Bost, R.; Zaloguev, S.; et al. Preliminary results of cytos 2 experiment. Acta Astronaut. 1985, 12, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Lara, S.; del Barrio-Tofiño, E.; López-Causapé, C.; Oliver, A.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Bou, G.; Zamorano, L.; Sánchez-Diener, I.; Galán, F.; Gracia, I.; et al. Predicting Pseudomonas aeruginosa susceptibility phenotypes from whole genome sequence resistome analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, R.; Bard, J.D.; Simner, P.J. The Genotype-to-Phenotype Dilemma: How Should Laboratories Approach Discordant Susceptibility Results? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, A.J.; Barsottini, M.R.d.O.; Rocha, R.R.; Laurindo, M.V.; de Moraes, F.L.L.; da Rocha, S.L. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: Virulence Factors and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2019, 62, e19180503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre-Femenia, M.À.; Fernández-Muñoz, A.; Gomis-Font, M.A.; Taltavull, B.; López-Causapé, C.; Arca-Suárez, J.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Cantón, R.; Larrosa, N.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa antibiotic susceptibility profiles, genomic epidemiology and resistance mechanisms: A nation-wide five-year time lapse analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 34, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, M.; Fàbrega, A.; Cobos-Trigueros, N.; Zamorano, L.; Ferrer-Navarro, M.; Ballesté-Delpierre, C.; Reustle, A.; Castro, P.; Nicolás, J.M.; Oliver, A.; et al. In vivo evolution of resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients admitted to an intensive care unit: Mechanisms of resistance and antimicrobial exposure. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 3004–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordovana, M.; Pranada, A.B.; Ambretti, S.; Kostrzewa, M. MALDI-TOF bacterial subtyping to detect antibiotic resistance. Clin. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 14, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, W.; Baldeschi, L.; Rizzato, C.; Tavanti, A.; Ghelardi, E.; Lupetti, A. Detection of antibiotic-resistance by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: An expanding area. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrzewa, M.; Sparbier, K.; Maier, T.; Schubert, S. MALDI-TOF MS: An upcoming tool for rapid detection of antibiotic resistance in microorganisms. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Jeong, S.H. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry technology as a tool for the rapid diagnosis of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BfArM—Risikoinformationen—Rote-Hand-Brief zu Systemisch und Inhalativ Angewendeten Fluorchinolonhaltigen Antibiotika: Erinnerung an die Anwendungsbeschränkungen. Available online: https://www.bfarm.de/SharedDocs/Risikoinformationen/Pharmakovigilanz/DE/RHB/2023/rhb-fluorchinolone.html (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- BfArM. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Updates Warnings for Oral and Injectable Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics Due to Disa-Bling Side Effects. 2024. FDA. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-updates-warnings-oral-and-injectable-fluoroquinolone-antibiotics (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- UK Gov. Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: Reminder of the Risk of Disabling and Potentially Long-Lasting or Irreversible Side Effects. GOV.UK. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/drug-safety-update/fluoroquinolone-antibiotics-reminder-of-the-risk-of-disabling-and-potentially-long-lasting-or-irreversible-side-effects (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Simin, D.; Milutinović, D.; Turkulov, V.; Brkić, S. Incidence, severity and risk factors of peripheral intravenous cannula-induced complications: An observational prospective study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2018, 28, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyler, R.F.; Shvets, K. Clinical Pharmacology of Antibiotics. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, H.; Harris, D.; Chirilă, R.M. Pharmacogenomics: Introduction and use in clinical practice. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 58, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandil, H.; Cramp, E.; Vaghela, T. Trends in Antibiotic Resistance in Urologic Practice. Eur. Urol. Focus 2016, 2, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenlehner, F.; Weidner, W.; Naber, K. Antibiotics in Urology—New Essentials. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 35, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaeger, L.N.; Coles, V.E.; Chan, D.C.K.; Burrows, L.L. How to kill Pseudomonas—Emerging therapies for a challenging pathogen. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1496, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Fosse, N.; Frei, R.; Widmer, A.F. Combination therapy for treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, J.; Yu, Y.; Seubert, C.N.; Wotring, V.E.; Derendorf, H. Drugs in space: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in astronauts. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck, E.L.; Grant, M.; Derendorf, H. Effect of simulated microgravity on the disposition and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Mamun, H.A.; Nagano, I.; Masunaga, S.; Kitazawa, D.; Matsuda, H. Antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Risks, current concern, and future thinking. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11054–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paritala, S.T.; Gandhi, G.; Agrawal, K.; Sengupta, P.; Sharma, N. Glycopeptides: Insights Towards Resistance, Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 65, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engberink, R.H.O.; van Oosten, P.J.; Weber, T.; Tabury, K.; Baatout, S.; Siew, K.; Walsh, S.B.; Valenti, G.; Chouker, A.; Boutouyrie, P. The kidney, volume homeostasis and osmoregulation in space: Current perspective and knowledge gaps. npj Microgravity 2023, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blue, R.S.; Bayuse, T.M.; Daniels, V.R.; Wotring, V.E.; Suresh, R.; Mulcahy, R.A.; Antonsen, E.L. Supplying a pharmacy for NASA exploration spaceflight: Challenges and current understanding. npj Microgravity 2019, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Daniels, V.R.; Vaksman, Z.; Boyd, J.L.; Crady, C.; Putcha, L. Evaluation of Physical and Chemical Changes in Pharmaceuticals Flown on Space Missions. AAPS J. 2011, 13, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M. Of Pseudomonas, porins, pumps and carbapenems. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 47, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.A.; Stripling, J.T.; Spellberg, B.; Centor, R.M. Short-course antibiotics for common infections: What do we know and where do we go from here? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L.; Metcalf, S.; Dymock, M.; Robinson, O.; Clark, B.; Nelson, R.; Paterson, D.L.; Yates, P.; Loewenthal, M.; Dewar, D.; et al. Short-versus standard-course intravenous antibiotics for peri-prosthetic joint infections managed with debridement and implant retention: A randomised pilot trial using a desirability of outcome ranking (DOOR) endpoint. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 60, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, K.; Liu, B.M. Impact of Point-of-Care Testing on Diagnosis, Treatment, and Surveillance of Vaccine-Preventable Viral Infections. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimraj, A.; Morgan, R.L.; Shumaker, A.H.; Baden, L.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Edwards, K.M.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gandhi, R.T.; Muller, W.J.; Nakamura, M.M.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients With COVID-19 (September 2022). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, e250–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornely, O.A.; Sprute, R.; Bassetti, M.; Chen, S.C.-A.; Groll, A.H.; Kurzai, O.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Revathi, G.; et al. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of candidiasis: An initiative of the ECMM in cooperation with ISHAM and ASM. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, e280–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; Biswas, R.; Götz, F.; Biswas, L. Impact of Staphylococcus aureus on Pathogenesis in Polymicrobial Infections. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Á.; Smarandache, A.; Iancu, V.; Pascu, M.L. Stability of Antimicrobial Drug Molecules in Different Gravitational and Radiation Conditions in View of Applications during Outer Space Missions. Molecules 2021, 26, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomartino, R.; Averesch, N.J.H.; Bhuiyan, M.; Cockell, C.S.; Colangelo, J.; Gumulya, Y.; Lehner, B.; Lopez-Ayala, I.; McMahon, S.; Mohanty, A. Toward sustainable space exploration: A roadmap for harnessing the power of microorganisms. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putcha, L.; Taylor, P.W.; Boyd, J.L. Biopharmaceutical Challenges of Therapeutics in Space: Formulation and Packaging Considerations. Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriè, E.P.; Baatout, S.; Choukér, A.; Buchheim, J.-I.; Baselet, B.; Russo, C.D.; Wotring, V.; Monici, M.; Morbidelli, L.; Gagliardi, D. The Future of Personalized Medicine in Space: From Observations to Countermeasures. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 739747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.A.; Schmidt, C.M.; Hubbard, R.M.; Mason, C.E. Why personalized medicine is the frontier of medicine and performance for humans in space. New Space 2020, 8, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, V.; Bustos, R.-H.; Pinacho, D.G. Personalized Medicine for Antibiotics: The Role of Nanobiosensors in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgormus, Y.; Okuyan, O.; Dumur, S.; Sayili, U.; Uzun, H. Evaluation of new generation systemic immune-inflammation markers to predict urine culture growth in urinary tract infection in children. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1201368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, S.E.; Martin, K.; Costes, S.V.; Thompson, M.; Suresh, R.; Abadie, L.; Lehnhardt, K.; Easter, B. TOPICAL: Development of Medical Capabilities and Technologies for Health Monitoring, Diagnostics, and Treatment during Human Exploration Spaceflight. 2021. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20210023828 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Kim, J.I.; Maguire, F.; Tsang, K.K.; Gouliouris, T.; Peacock, S.J.; McAllister, T.A.; McArthur, A.G.; Beiko, R.G. Machine Learning for Antimicrobial Resistance Prediction: Current Practice, Limitations, and Clinical Perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0017921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, C.; Heft, N.; Beger, S.; Stewart, L.H. Emergency medicine in spaceflight. In Precision Medicine for Long and Safe Permanence of Humans in Space; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 179–206. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780443222597000266 (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Popov, A.; Fink, W.; Hess, A. Paradigm Shift from Telemedicine to Autonomous Human Health and Performance for Long-Duration Space Missions. Int. J. Progn. Health Manag. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmig, A.; Hagel, S.; Weis, S.; Bahrs, C.; Löffler, B.; Pletz, M.W. Management of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 616524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.; Kesselmeier, M.; Davis, J.; Morris, A.; Lee, S.; Scherag, A.; Hagel, S.; Pletz, M. Cefazolin versus anti-staphylococcal penicillins for the treatment of patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, G.; Gustafsson, E.; Andersson, R. Outcome for invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acton, D.S.; Plat-Sinnige, M.J.T.; van Wamel, W.; de Groot, N.; van Belkum, A. Intestinal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: How does its frequency compare with that of nasal carriage and what is its clinical impact? Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, D.; Frei, R.; Periat, N.; Zimmerli, M.; Battegay, M.; Flückiger, U.; Widmer, A.F. Exclusive Staphylococcus aureus throat carriage: At-risk populations. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilbronner, S.; Foster, T.J. Staphylococcus lugdunensis: A Skin Commensal with Invasive Pathogenic Potential. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- umar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumawat, M.; Verma, V.; Nina, P.B.; Jp, D.; Kumar, S.; Singh, B.; Tiwari, R.R. Futuristic Non-antibiotic Therapies to Combat Antibiotic Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 609459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, Z.; Khoshbayan, A.; Moghadam, M.T.; Farahani, I.; Jazireian, P.; Shariati, A. Bacteriophage therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: A review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Haque, A.; Matsuzaki, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Nakamura, S. The efficacy of phage therapy in a murine model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia and sepsis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 682255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharindwal, S.; Goswami, N.; Jha, P.; Pandey, S.; Jobby, R. Prospective Use of Probiotics to Maintain Astronaut Health during Spaceflight. Life 2023, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.J.; Morici, L.A. Vaccination to Prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bloodstream Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 870104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhour, J.; Haddad, S.F.; Kerbage, A.; Wertheim, H.; Tattevin, P.; Voss, A.; Ünal, S.; Ouedraogo, A.S.; Kanj, S.S. Diagnostic stewardship in infectious diseases: A continuum of antimicrobial stewardship in the fight against antimicrobial resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanov, A.V. Metagenomic analysis of the Dynamic changes in the gut microbiome of the participants of the Mars-500 experiment, simulating long term space flight. Acta Naturae 2013, 5, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.-S.; Chen, P.; Yu, Y.-B.; Zang, P.; Wei, Z. Simulated manned Mars exploration: Effects of dietary and diurnal cycle variations on the gut microbiome of crew members in a controlled ecological life support system. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.A.; Jones, J.A.; Mason, C.E. Optimizing human performance in extreme environments through precision medicine: From spaceflight to high-performance operations on Earth. Camb. Prism. Precis. Med. 2023, 1, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boschert, A.L.; Leuko, S.; Krämer, C.L.; Siems, K.; Ly-Sauerbrey, Y.-T.; Arndt, F. Spaceflight and Medical Microbiology: Possible Implications for Standard Infection Diagnostics and Therapy. Life 2025, 15, 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111757
Boschert AL, Leuko S, Krämer CL, Siems K, Ly-Sauerbrey Y-T, Arndt F. Spaceflight and Medical Microbiology: Possible Implications for Standard Infection Diagnostics and Therapy. Life. 2025; 15(11):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111757
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoschert, Alessa Lalinka, Stefan Leuko, Carolin Luisa Krämer, Katharina Siems, Yen-Tran Ly-Sauerbrey, and Franca Arndt. 2025. "Spaceflight and Medical Microbiology: Possible Implications for Standard Infection Diagnostics and Therapy" Life 15, no. 11: 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111757
APA StyleBoschert, A. L., Leuko, S., Krämer, C. L., Siems, K., Ly-Sauerbrey, Y.-T., & Arndt, F. (2025). Spaceflight and Medical Microbiology: Possible Implications for Standard Infection Diagnostics and Therapy. Life, 15(11), 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111757







