Evaluation of Immune Response Dynamics: Analyzing the Parameters of Complete Blood Count (CBC) in Experimental Borreliosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
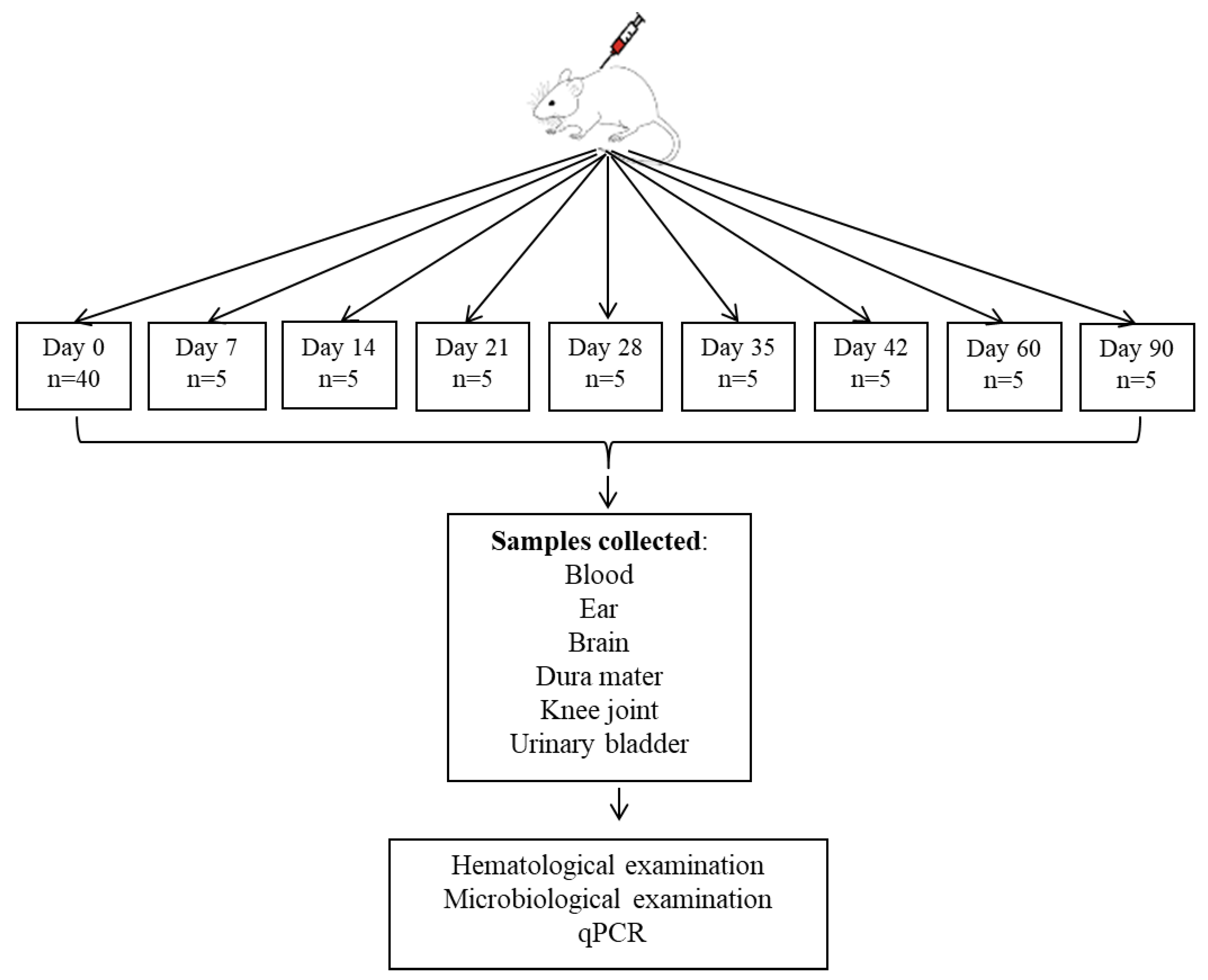
2.2. Study Design
2.2.1. Borrelia Strain and Genetic Modification
2.2.2. Inoculum Preparation and Bacterial Quantification
2.2.3. Animal Inoculation Technique
2.2.4. The Hematological Analysis
2.2.5. The Microbiological Analysis
2.2.6. DNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.3. Animal Selection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Generative AI Tools
3. Results
3.1. Microbiological Examination and qPCR Analysis
3.2. Hematological Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SII | Systemic immuno-inflammatory index |
| CBC | Complete blood count |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gammaNF |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| BAF | Băneasa Animal Facility |
| CI | Cantacuzino National Military Medical Institute for Research and Development |
| GFP | Green Fluorescence Protein |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| NEU | Neutrophils |
| LYM | Lymphocytes |
| MONO | Monocytes |
| BASO | Basophils |
| PLT | Platelet count |
References
- Thippani, S.; Patel, N.J.; Jathan, J.; Filush, K.; Socarras, K.M.; DiLorenzo, J.; Balasubramanian, K.; Gupta, K.; Ortiz Aleman, G.; Pandya, J.M.; et al. Evidence for the Presence of Borrelia burgdorferi Biofilm in Infected Mouse Heart Tissues. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perronne, C. Lyme and associated tick-borne diseases: Global challenges in the context of a public health threat. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, G.; Strle, F. Lyme borreliosis-from tick bite to diagnosis and treatment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugeler, K.J.; Schwartz, A.M.; Delorey, M.J.; Mead, P.S.; Hinckley, A.F. Estimating the frequency of lyme disease diagnoses, United States, 2010–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunfeld, K.P.; Kraiczy, P.; Norris, D.E.; Lohr, B. The In Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato: Shedding Light on the Known Unknowns. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Fedorova, N.; Becker, N.S.; Kleinjan, J.E.; Marosevic, D.; Krebs, S.; Hui, L.; Fingerle, V.; Lane, R.S. Borrelia maritima sp. nov., a novel species of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex, occupying a basal position to North American species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.; Cinco, M.; Trevisini, S.; di Meo, N.; Chersi, K.; Ruscio, M.; Forgione, P.; Bonin, S. Borreliae Part 1: Borrelia Lyme Group and Echidna-Reptile Group. Biology 2021, 10, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitova, Y.; Rar, V.; Tikunov, A.; Yakimenko, V.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.; Livanova, N.; Tikunova, N. Detection and genetic characterization of a putative novel Borrelia genospecies in Ixodes apronophorus / Ixodes persulcatus / Ixodes trianguliceps sympatric areas in Western Siberia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grąźlewska, W.; Holec-Gąsior, L. Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease. Antibodies 2023, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Reynolds, S. Borrelia bavariensis: Vector Switch, Niche Invasion, and Geographical Spread of a Tick-Borne Bacterial Parasite. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donta, S.T. Borrelia burgdorferi 0755, a Novel Cytotoxin with Unknown Function in Lyme Disease. Toxins 2024, 16, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornero, R.; Irfan, S.S.; Cachaco, S.; Zhou, W.; Byne, A.; Howard, M.; McIntyre, H.; Birkaya, B.; Liotta, L.; Luchini, A. Identification of Unambiguous Borrelia Peptides in Human Urine Using Affinity Capture and Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2742, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.; Lloyd, V.K.; Robichaud, G.A. Development, Optimization, and Validation of a Quantitative PCR Assay for Borrelia burgdorferi Detection in Tick, Wildlife, and Human Samples. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.; Sürth, V.; Röttgerding, F.; Zipfel, P.F.; Fritz-Wolf, K.; Kraiczy, P. Elucidating the Immune Evasion Mechanisms of Borrelia mayonii, the Causative Agent of Lyme Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcón-Chino, M.E.T.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Gazeta, G.S.; Carvalho, J.P.R.S.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Durans, A.M.; Souza, A.L.A.; De-Simone, S.G. New Epitopes for the Serodiagnosis of Human Borreliosis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Tang, X.; Hart, T.; Homer, R.; Belperron, A.A.; Bockenstedt, L.K.; Ring, A.; Nakamura, A.; Fikrig, E. Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor influences periarticular joint inflammation in B. burgdorferi-infected mice. eLife 2025, 14, RP104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.C.; Maylor-Hagen, H.; Ma, Y.; Weis, J.H.; Weis, J.J. The Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi utilizes multiple ligands, including RNA, for interferon regulatory factor 3-dependent induction of type I interferon-responsive genes. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3144–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Bramwell, K.K.; Lochhead, R.B.; Paquette, J.K.; Zachary, J.F.; Weis, J.H.; Teuscher, C.; Weis, J.J. Borrelia burgdorferi arthritis-associated locus Bbaa1 regulates Lyme arthritis and K/B×N serum transfer arthritis through intrinsic control of type I IFN production. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 6050–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batheja, S.; Nields, J.A.; Landa, A.; Fallon, B.A. Post-Treatment Lyme Syndrome and Central Sensitization. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 25, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Cavallo, I.; Bordignon, V.; D’Agosto, G.; Pontone, M.; Trento, E.; Gallo, M.T.; Prignano, G.; Pimpinelli, F.; Toma, L.; et al. The Emerging Role of Microbial Biofilm in Lyme Neuroborreliosis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.R.; Reiner, S.L. Genetic control of experimental lyme arthritis in the absence of specific immunity. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barthold, S.W.; Persing, D.H.; Armstrong, A.L.; Peeples, R.A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1991, 139, 263–273. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Barthold, S.W.; Bockenstedt, L.K. Passive immunizing activity of sera from mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4696–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M. The critical role of laboratory medicine during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and other viral outbreaks. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, L.K.; Rupert, J. Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Shin, T.G.; Jo, I.J.; Jeon, K.; Suh, G.Y.; Lee, T.R.; Yoon, H.; Cha, W.C.; Sim, M.S. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in critically-ill septic patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jager, C.P.; van Wijk, P.T.; Mathoera, R.B.; de Jongh-Leuvenink, J.; van der Poll, T.; Wever, P.C. Lymphocytopenia and neutrophil-lymphocyte count ratio predict bacteremia better than conventional infection markers in an emergency care unit. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebman, A.W.; Yang, T.; Zenilman, J.M.; Soloski, M.J.; Aucott, J.N. A sex-based analysis of complete blood count features during acute, untreated Lyme disease. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1454858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, L.V.; Spanou, V.M.; Katsogiannou, E.G.; Katsoulos, P.D. Hematological Features in Sheep with IgG and IgM Antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. Pathogens 2021, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljøstad, U.; Mygland, Å. CSF B–lymphocyte chemoattractant (CXCL13) in the early diagnosis of acute Lyme neuroborreliosis. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Wang, G.; Schwartz, I.; Wormser, G.P. Diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 484–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strle, F.; Lusa, L.; Ružić-Sabljić, E.; Maraspin, V.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Cimperman, J.; Ogrinc, K.; Rojko, T.; Zorman, J.V.; Stupica, D. Clinical characteristics associated with Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato skin culture results in patients with erythema migrans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajkowska, J.; Moniuszko, A.; Czupryna, P.; Ptaszyńska-Sarosiek, I.; Pancewicz, S.; Kondrusik, M.; Grygorczuk, S.; Swierzbińska-Pijanowska, R.; Dunaj, J.; Czupryna, P. Evaluation of CXCL8, CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL12 and CXCL13 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuroborreliosis. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 136, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Stanek, G.; Wormser, G.P.; Gray, J.; Strle, F. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, T.J.; Norman, M.U.; Colarusso, P.; Bankhead, T.; Kubes, P.; Chaconas, G. Real-time high resolution 3D imaging of the lyme disease spirochete adhering to and escaping from the vasculature of a living host. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, D.S. Electrotransformation of the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Methods Mol. Biol. 1995, 47, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P.A.; Jewett, M.W. Genetic Manipulation of Borrelia. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 42, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, J.W.; Kostelnik, L.M.; Zeidner, N.S.; Massung, R.F. Multiplex real-time PCR for detection of anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3164–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, F.; Shang, B.; Speich, J.E.; Wan, Y.Y.; Hashida, H.; Braun, T.; Sadoughi, A.; Puehler, T.; Lue, T.F.; et al. Reporting quality of animal research in journals that published the ARRIVE 1.0 or ARRIVE 2.0 guidelines: A cross-sectional analysis of 943 studies. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 14, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, G.; Fingerle, V.; Hunfeld, K.P.; Jaulhac, B.; Kaiser, R.; Krause, A.; Kristoferitsch, W.; O’Connell, S.; Ornstein, K.; Strle, F.; et al. Lyme borreliosis: Clinical case definitions for diagnosis and management in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, C.; Ancuta, D.L.; Ionita, F.M.; Caracoti, I.V.; Caracoti, C.; Muntean, A.A.; Popa, M.I. Development of A Murine Model Of Neuroborreliosis Induced By Human Borrelia Strain. Sci. Work. Ser. C Vet. Med. 2024, 70, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Coburn, J.; Garcia, B.; Hu, L.T.; Jewett, M.W.; Kraiczy, P.; Norris, S.J.; Skare, J. Lyme Disease Pathogenesis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 42, 473–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Guan, G.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, F. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) Can Be an Early Indicator for Predicting the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 9483–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalkılınç Hökenek, U.; Kılıç, M.; Alışkan, H. Investigation of the prognostic role of systemic immunoinflammatory index in patients with acute pancreatitis. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023, 29, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuța, D.L.; Lovati, A.B.; Coman, C. The clinical significance of inflammatory biomarkers, IL6 cytokine, and systemic immune inflammatory index in rabbit model of acute and chronic Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis-induced osteomyelitis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preac Mursic, V.; Marget, W.; Busch, U.; Pleterski Rigler, D.; Hagl, S. Kill kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi and bacterial findings in relation to the treatment of Lyme borreliosis. Infection 1996, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, R.; Cinco, M. Induction of cystic forms by different stress conditions in Borrelia burgdorferi. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2004, 112, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthold, S.W.; Hodzic, E.; Imai, D.M.; Feng, S.; Yang, X.; Luft, B.J. Ineffectiveness of tigecycline against persistent Borrelia burgdorferi. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockenstedt, L.K.; Wooten, R.M.; Baumgarth, N. Immune Response to Borrelia: Lessons from Lyme Disease Spirochetes. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 42, 145–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.R.; Reiner, S.L. Clearance of Borrelia burgdorferi may not be required for resistance to experimental Lyme arthritis. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, M.W.; Dunham-Ems, S.M.; Caimano, M.J.; Belperron, A.A.; Bockenstedt, L.K.; Fu, H.C.; Radolf, J.D.; Wolgemuth, C.W. The heterogeneous motility of the Lyme disease spirochete in gelatin mimics dissemination through tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3059–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, D.M.; Samuels, D.S.; Feng, S.; Hodzic, E.; Olsen, K.; Barthold, S.W. The early dissemination defect attributed to disruption of decorin-binding proteins is abolished in chronic murine Lyme borreliosis. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunev, S.S.; Hastey, C.J.; Hodzic, E.; Feng, S.; Barthold, S.W.; Baumgarth, N. Lymphoadenopathy during lyme borreliosis is caused by spirochete migration-induced specific B cell activation. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group Analyzed on Euthanasia Day | Microbiological Examination (Culture) | qPCR |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | + (head) | + (head and body) |
| 14 | + (head) | + (head and body) |
| 21 | + (body) | + (body) |
| 28 | - | - |
| 35 | - | - |
| 42 | - | - |
| 60 | - | + (head and body) |
| 90 | - | + (head and body) |
| The Evolutionary Phase of Borreliosis | Immunological Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Early phase (D0–D14) | Positive detection of Borrelia by both methods (culture and qPCR) |
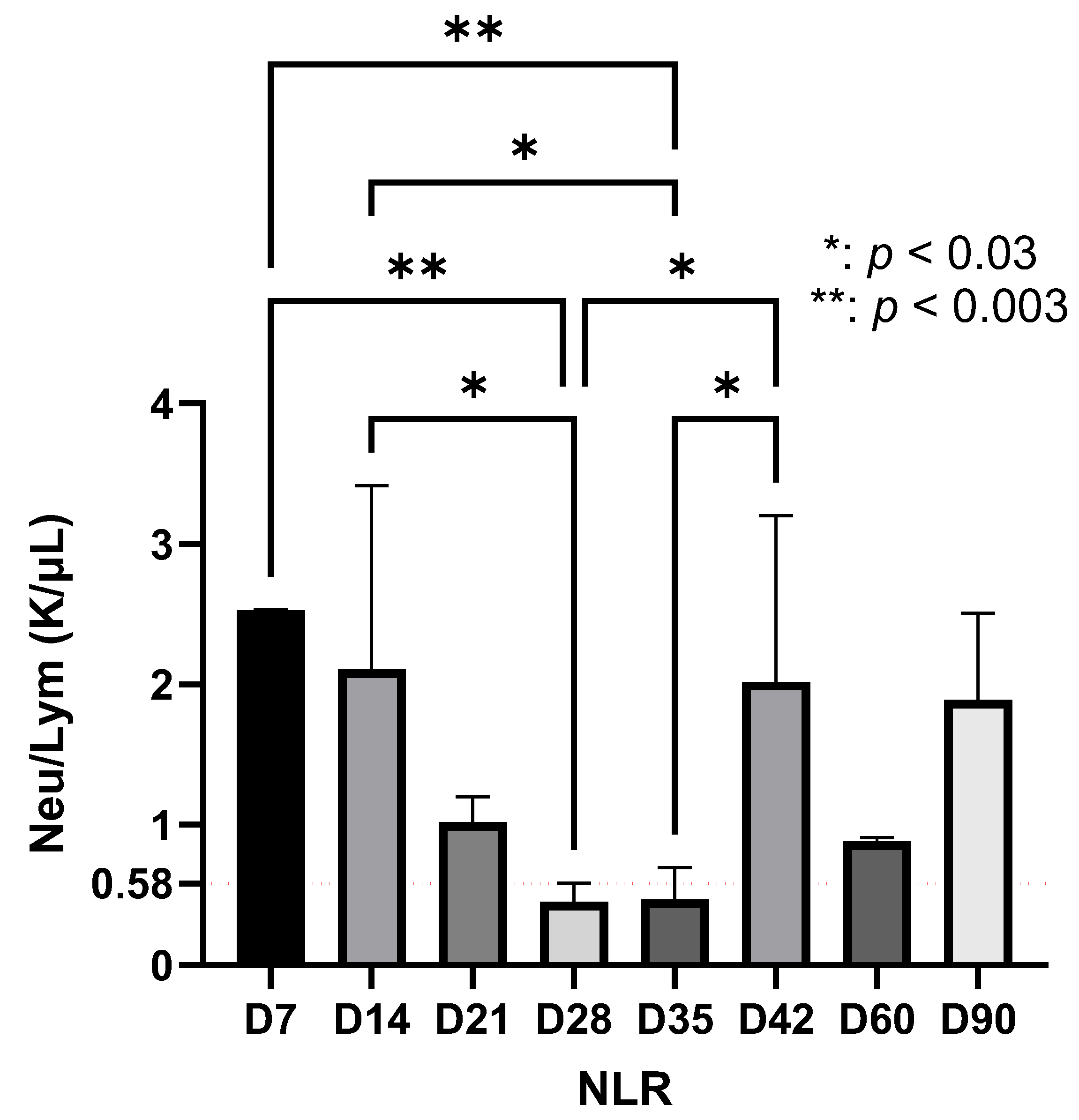
| Significant increase in NLR at D7 | |
| Maximum systemic immuno-inflammatory index at D7 (p < 0.0001) | |
| Dominant innate immune response, reflected by neutrophil mobilization | |
| This phase corresponds to the period of active dissemination of spirochetes | |
| Intermediate phase (D14–D35) | Presence of Borrelia confirmed until D21, then negative |
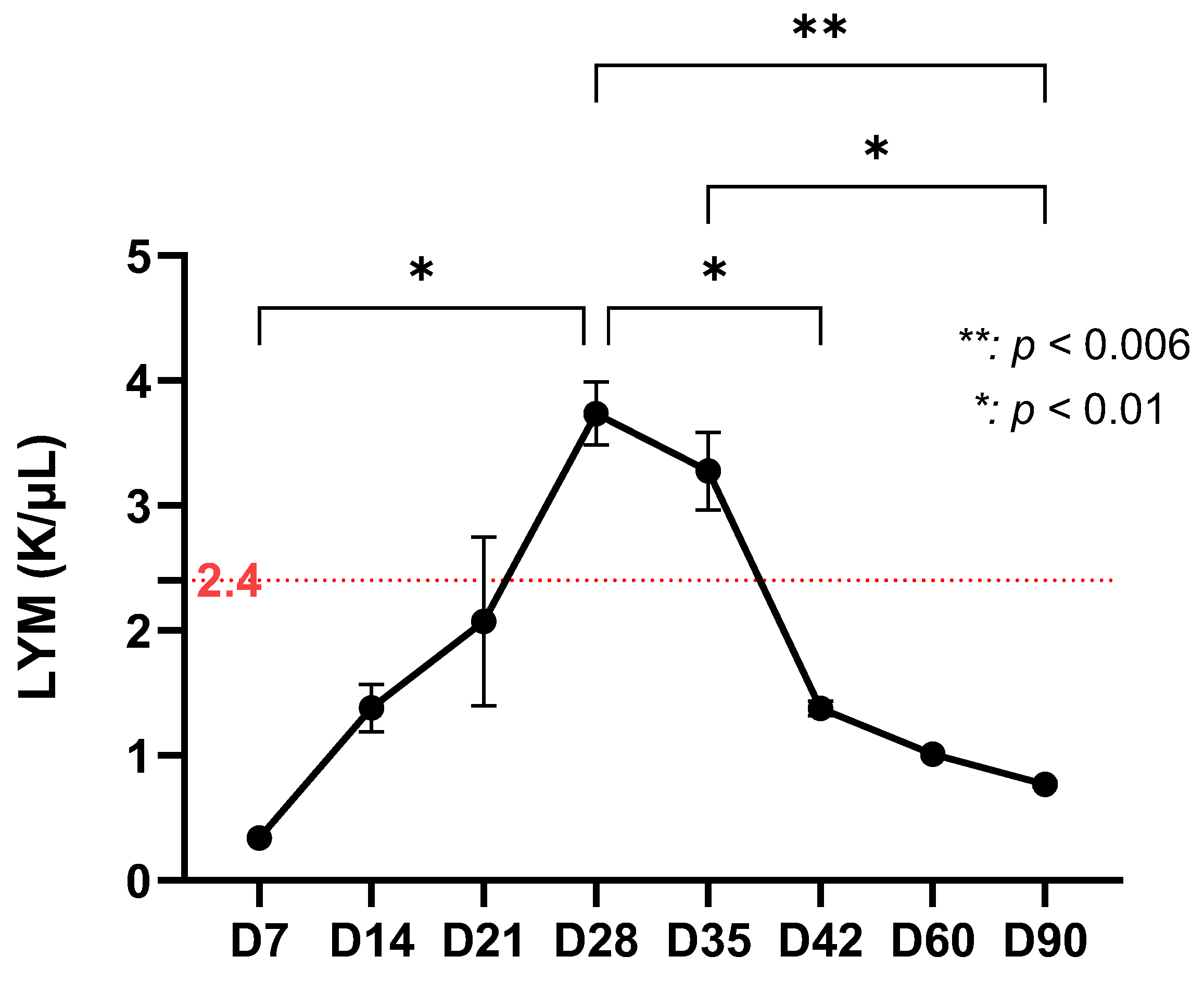
| Significant increase in lymphocytes (p < 0.01) at D28–D35 Increase in monocytes with peak at D35 (p < 0.01) Decrease in systemic immuno-inflammatory index Transition to adaptive immune response | |
| Late phase (D35–D90) | Detection of Borrelia only by qPCR at D60 and D90 NLR reactivation at D42 (p < 0.03) Decrease and stabilization of lymphocytes after D42 Fluctuations in the immuno-inflammatory index Suggests bacterial persistence and development of immunological memory |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexandru, D.M.; Ancuţa, D.L.; Coman, C. Evaluation of Immune Response Dynamics: Analyzing the Parameters of Complete Blood Count (CBC) in Experimental Borreliosis. Life 2025, 15, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111758
Alexandru DM, Ancuţa DL, Coman C. Evaluation of Immune Response Dynamics: Analyzing the Parameters of Complete Blood Count (CBC) in Experimental Borreliosis. Life. 2025; 15(11):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111758
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexandru, Diana Mihaela, Diana Larisa Ancuţa, and Cristin Coman. 2025. "Evaluation of Immune Response Dynamics: Analyzing the Parameters of Complete Blood Count (CBC) in Experimental Borreliosis" Life 15, no. 11: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111758
APA StyleAlexandru, D. M., Ancuţa, D. L., & Coman, C. (2025). Evaluation of Immune Response Dynamics: Analyzing the Parameters of Complete Blood Count (CBC) in Experimental Borreliosis. Life, 15(11), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111758







