NGF-TrkA Axis Enhances PDGF-C-Mediated Angiogenesis in Osteosarcoma via miR-29b-3p Suppression: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy Using Larotrectinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis of mRNA Expression Profiles from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)
2.3. Cell Cultures
2.4. MicroRNA Database Searches
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Cell Transfection
2.7. Harvesting OS Conditioned Medium (CM)
2.8. HUVEC Cells Tube Formation and Quantification
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
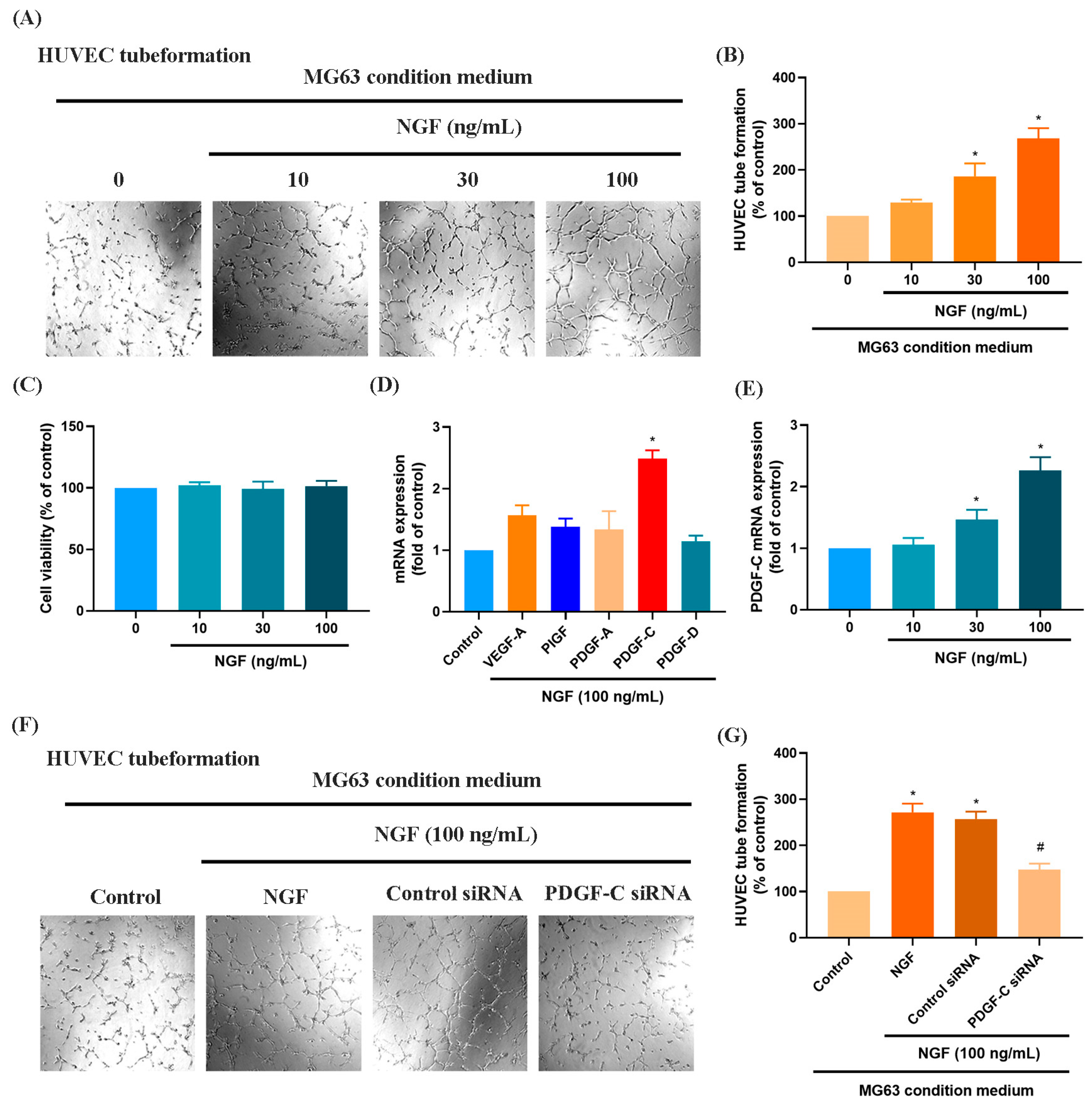
3.1. NGF Induces the Expression of PDGF-C to Promote Angiogenesis
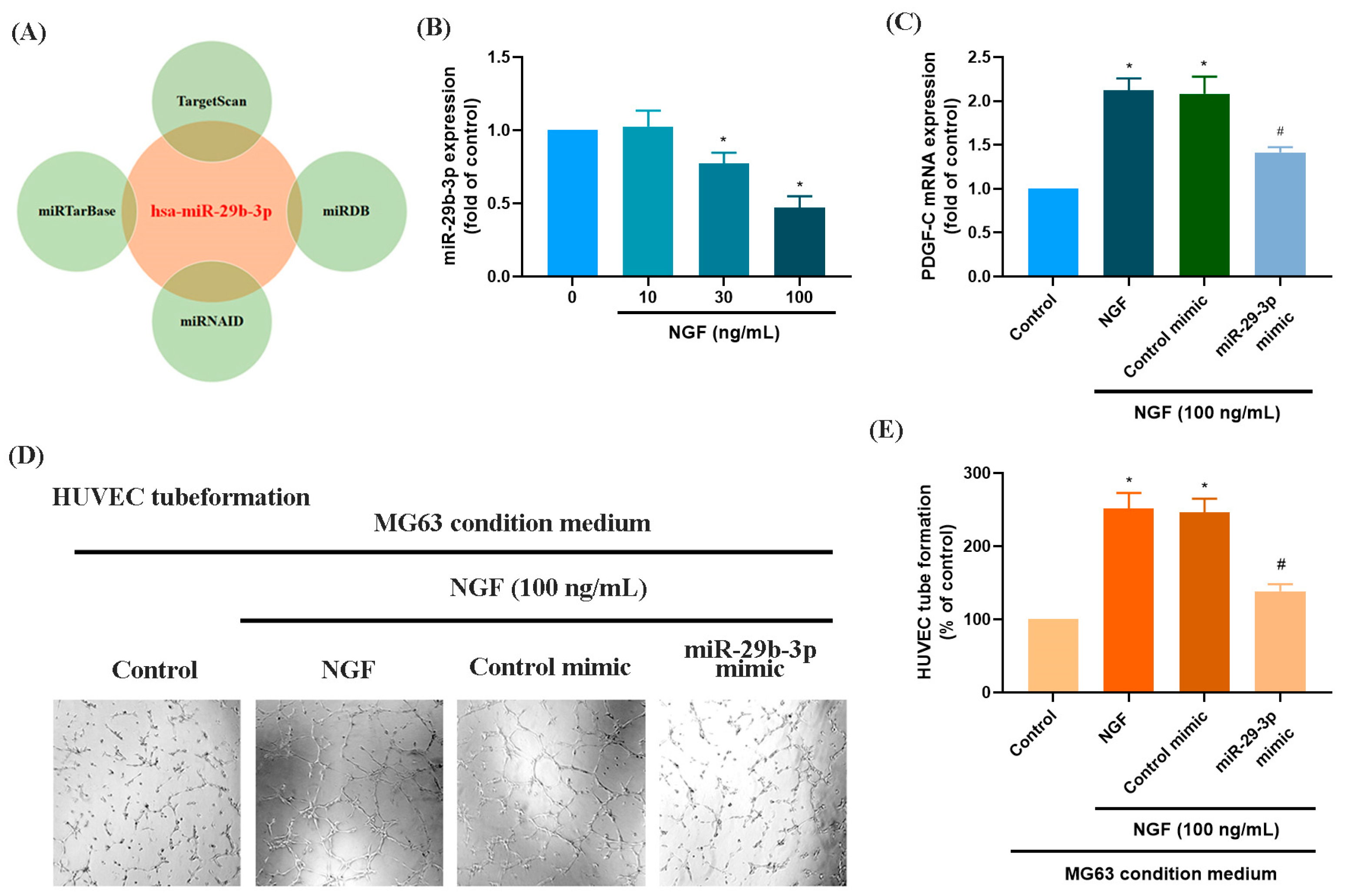
3.2. The miR-29b-3p/PGDF-C Axis Regulates NGF-Enhanced Angiogenesis in MG63 Cells
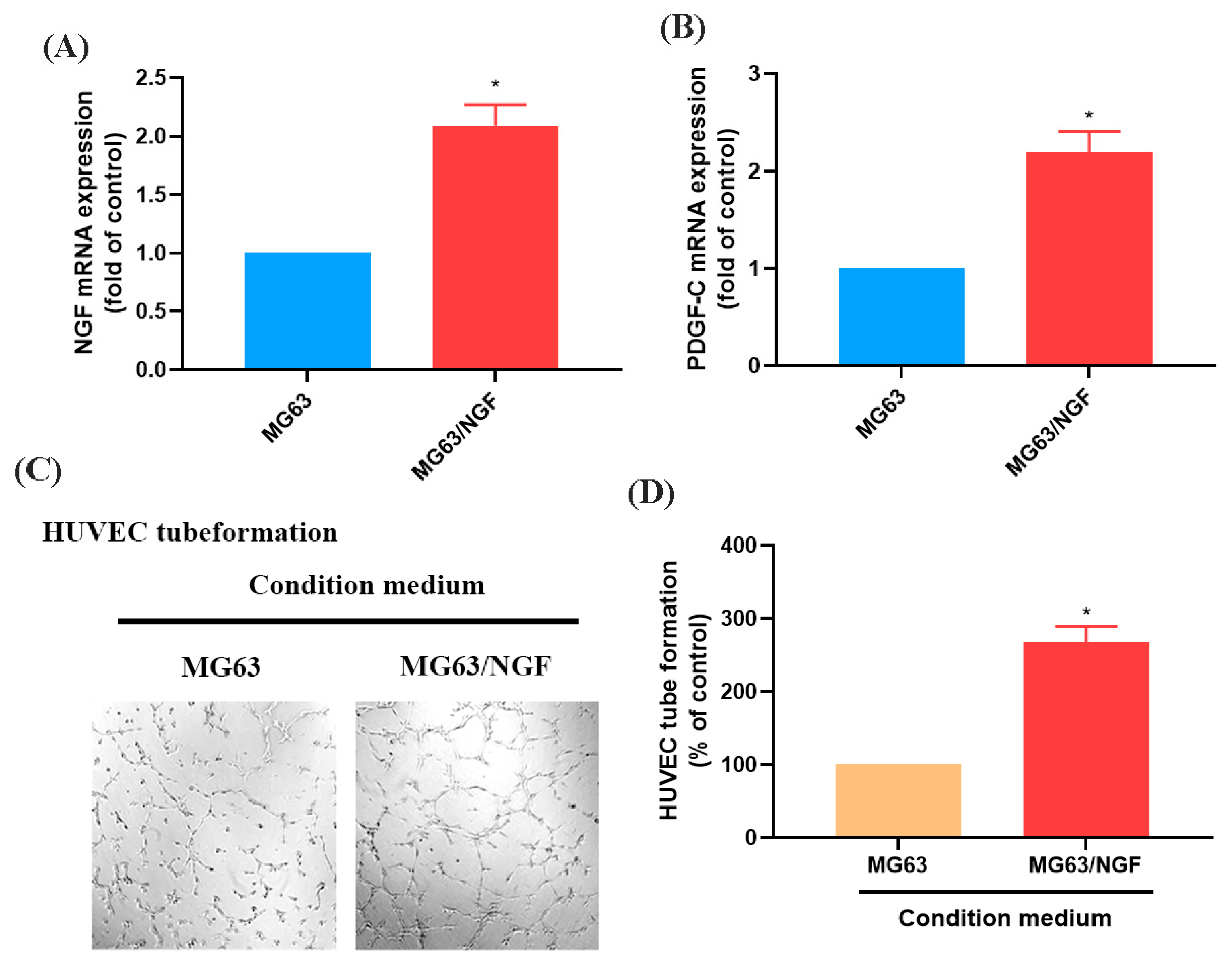
3.3. The NGF-Overexpressing MG63 Cell Line (MG63/NGF) Enhances HUVEC Tube Formation
3.4. Larotrectinib Inhibits NGF-Induced Angiogenesis in MG63 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durfee, R.A.; Mohammed, M.; Luu, H.H. Review of Osteosarcoma and Current Management. Rheumatol. Ther. 2016, 3, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabello, L.; Troisi, R.J.; Savage, S.A. Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer 2009, 115, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, G.; Longhi, A.; Versari, M.; Mercuri, M.; Briccoli, A.; Picci, P. Prognostic factors for osteosarcoma of the extremity treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: 15-year experience in 789 patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2006, 106, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Hou, C.H.; Lin, F.L.; Tsao, Y.T.; Hou, S.M. Nimbolide Induces ROS-Regulated Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Migration in Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23405–23424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.H.; Chen, W.L.; Lin, C.Y. Targeting nerve growth factor-mediated osteosarcoma metastasis: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities using larotrectinib. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Serra, M. An update on chemotherapy for osteosarcoma. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 2727–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.H.; Lin, F.L.; Hou, S.M.; Liu, J.F. Cyr61 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis of osteosarcoma by Raf-1/MEK/ERK/Elk-1/TWIST-1 signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, A.; Errani, C.; De Paolis, M.; Mercuri, M.; Bacci, G. Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State of the art. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E. Update on Survival in Osteosarcoma. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 47, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhead, M.L.; Clark, J.C.; Myers, D.E.; Dass, C.R.; Choong, P.F. The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: A review. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 959248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perivoliotis, K.; Ntellas, P.; Dadouli, K.; Samara, A.A.; Sotiriou, S.; Ioannou, M.; Tepetes, K. Microvessel Density (MVD) in Patients with Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Investig. 2024, 42, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Gao, T.; Bai, C.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, G. AOC3 accelerates lung metastasis of osteosarcoma by recruiting tumor-associated neutrophils, neutrophil extracellular trap formation and tumor vascularization. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, G.S. Targeted anti-angiogenesis therapy for advanced osteosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1413213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Cerasuolo, A.; Starita, N.; Amiranda, S.; Cimmino, T.P.; Bonelli, P.; Tuccillo, F.M.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Buonaguro, L.; Tornesello, M.L. Emerging role of endogenous peptides encoded by non-coding RNAs in cancer biology. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025, 10, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.D.; He, F.; Tong, C.J.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Zhu, S.Z.; Luo, J.Z.; Yuan, B. HIF-1alpha-mediated augmentation of miRNA-18b-5p facilitates proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma through attenuation PHF2. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Yang, M.; Xing, P.; Huang, T. MicroRNA miR-331-3p suppresses osteosarcoma progression via the Bcl-2/Bax and Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling pathways and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (MGAT1). Bioengineered 2022, 13, 14159–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesheh, M.M.; Bayat, M.; Kobravi, S.; Lotfalizadeh, M.H.; Heydari, A.; Memar, M.Y.; Baghi, H.B.; Kermanshahi, A.Z.; Ravaei, F.; Taghavi, S.P.; et al. MicroRNAs and human viral diseases: A focus on the role of microRNA-29. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Sahebi, U.; Nazarian, H.; Majdi, L.; Bayat, M. Oncogenic MicroRNAs: Key players in human prostate cancer pathogenesis, a narrative review. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 42, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Geng, P.; Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P. miR-29 promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration by targeting PTEN. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, J.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tang, T.; Zheng, L. Evaluation of miR-29c inhibits endotheliocyte migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells by suppressing the insulin like growth factor 1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; van der Meer, A.J.; Patick, A.K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, B.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Han, M.M.; Yang, C.W.; Zhu, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.J.; Fu, T.; et al. Nerve Growth Factor/Tyrosine Kinase A Receptor Pathway Enhances Analgesia in an Experimental Mouse Model of Bone Cancer Pain by Increasing Membrane Levels of delta-Opioid Receptors. Anesthesiology 2024, 140, 765–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2000, 10, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Bai, J.; Qin, T.; Wang, Z.; Han, L. NGF from pancreatic stellate cells induces pancreatic cancer proliferation and invasion by PI3K/AKT/GSK signal pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5901–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.E.; Tieftrunk, E.; Schorn, S.; Friess, H.; Ceyhan, G.O. Nerve growth factor & TrkA as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2016, 1866, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; DuBois, S.G.; Kummar, S.; Farago, A.F.; Albert, C.M.; Rohrberg, K.S.; van Tilburg, C.M.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Berlin, J.D.; Federman, N.; et al. Larotrectinib in patients with TRK fusion-positive solid tumours: A pooled analysis of three phase 1/2 clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, N.T.N.; Lai, C.Y.; Tsai, H.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Liu, S.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Tzeng, H.E.; Tang, C.H. Apelin promotes osteosarcoma metastasis by upregulating PLOD2 expression via the Hippo signaling pathway and hsa_circ_0000004/miR-1303 axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Chen, P.C.; Chang, T.M.; Hou, C.H. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 promotes cancer cell migration via c-Raf/MAPK/AP-1 pathway and MMP-9 production in osteosarcoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2020, 39, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Chen, P.C.; Chang, T.M.; Hou, C.H. Thrombospondin-2 stimulates MMP-9 production and promotes osteosarcoma metastasis via the PLC, PKC, c-Src and NF-kappaB activation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12826–12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, L.M.; Valenzuela Alvarez, M.; Yang, Y.; Spinelli, F.; Cantero, M.J.; Alaniz, L.; Garcia, M.G.; Kleinerman, E.S.; Correa, A.; Bolontrade, M.F. Up-regulation of pro-angiogenic molecules and events does not relate with an angiogenic switch in metastatic osteosarcoma cells but to cell survival features. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Jia, M.; Liu, W.; Zhu, W. Synergistic anti-tumour activity of ginsenoside Rg3 and doxorubicin on proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis in osteosarcoma by modulating mTOR/HIF-1alpha/VEGF and EMT signalling pathways. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 75, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, W. Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis of 16 studies. Medicine 2018, 97, e13051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Quan, H.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y. MicroRNA-143 expression inhibits the growth and the invasion of osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghish, A.S.; Elballal, M.S.; Elazazy, O.; Elesawy, A.E.; Shahin, R.K.; Midan, H.M.; Sallam, A.M.; Elbadry, A.M.M.; Mohamed, A.K.I.; Ishak, N.W.; et al. miRNAs as potential game-changers in bone diseases: Future medicinal and clinical uses. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 245, 154440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Zheng, W.; Liu, H.; Xu, S.; Yong, T.; et al. Targeted intervention in nerve-cancer crosstalk enhances pancreatic cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, K.; He, J.; Deng, Q.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, F.; Jiang, Z. PRELP inhibits colorectal cancer progression by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis via the inactivation of the FGF1/PI3K/AKT pathway. Apoptosis 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, S. G-CSF promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in TAM. Aging 2024, 16, 10799–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, P.; Shi, R. Anlotinib as a molecular targeted therapy for tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xie, L.; Guo, W. PDGF/PDGFR effects in osteosarcoma and the “add-on” strategy. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Appiah-Kubi, K.; Wu, M.; Yao, X.; Qian, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. The platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) and their receptors (PDGFRs) are major players in oncogenesis, drug resistance, and attractive oncologic targets in cancer. Growth Factors 2016, 34, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shang, G. The Roles of Noncoding RNAs in the Development of Osteosarcoma Stem Cells and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 773038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.J.; Li, L.J.; Huo, H.F.; Liu, X.Q.; Cui, H.W.; Jiang, D.M. MicroRNA-29b sensitizes osteosarcoma cells to doxorubicin by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) in osteosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Vares, G.; Ohno, T.; Takahashi, A.; Uzawa, A.; Seo, S.J.; Sai, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying the enhancement of carbon ion beam radiosensitivity of osteosarcoma cells by miR-29b. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4357–4371. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Guo, J.; Gu, R.; Lei, B.; Ding, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, G. MicroRNA-29b-3p inhibits cell proliferation and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA and PDGFB in retinal microvascular endothelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2020, 26, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Niu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Svatek, R.; Rodriguez, R.; et al. Y-Box Binding Protein 1 Regulates Angiogenesis in Bladder Cancer via miR-29b-3p-VEGFA Pathway. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 9913015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mu, N.; Qu, N. Methylation of the miR-29b-3p promoter contributes to angiogenesis, invasion, and migration in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Le, A.T.; Doebele, R.C. TRKing down an old oncogene in a new era of targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, B.; Nie, W.; Hu, J.; Fan, Y.; Nie, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. A novel c-Met/TRK inhibitor 1D228 efficiently inhibits tumor growth by targeting angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatu, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target mRNA | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| VEGF-A | AGGGCAGAATCATCACGAAGT | AGGGTCTCGATTGGATGGCA |
| PIGF | TGACATGGTTGTGCATCTGTT | ACTCTATCAGTGGTGCTCCATAC |
| PDGF-A | GCAAGACCAGGACGGTCATTT | GGCACTTGACACTGCTCGT |
| PDGF-C | ATTTGGGCTTGAAGACCCAGA | CCAGCGCCCTAATATAGTTCCA |
| PDGF-D | ACGGATACAGCTAGTGTTTGACA | GTCCACACCATCGTCCTCTAATA |
| GAPDH | ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC | TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA |
| Target miRNA | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | |
| has-miR-29b-3p | TAGCACCATTTGAAATCAGTGTT | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, S.-M.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-L.; Chang, E.-M.; Lin, C.-Y. NGF-TrkA Axis Enhances PDGF-C-Mediated Angiogenesis in Osteosarcoma via miR-29b-3p Suppression: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy Using Larotrectinib. Life 2025, 15, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010099
Hou S-M, Cheng C-Y, Chen W-L, Chang E-M, Lin C-Y. NGF-TrkA Axis Enhances PDGF-C-Mediated Angiogenesis in Osteosarcoma via miR-29b-3p Suppression: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy Using Larotrectinib. Life. 2025; 15(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010099
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Sheng-Mou, Ching-Yuan Cheng, Wei-Li Chen, En-Ming Chang, and Chih-Yang Lin. 2025. "NGF-TrkA Axis Enhances PDGF-C-Mediated Angiogenesis in Osteosarcoma via miR-29b-3p Suppression: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy Using Larotrectinib" Life 15, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010099
APA StyleHou, S.-M., Cheng, C.-Y., Chen, W.-L., Chang, E.-M., & Lin, C.-Y. (2025). NGF-TrkA Axis Enhances PDGF-C-Mediated Angiogenesis in Osteosarcoma via miR-29b-3p Suppression: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy Using Larotrectinib. Life, 15(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010099







