Estimation Model for Cotton Canopy Structure Parameters Based on Spectral Vegetation Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measuring Methods
2.1.1. Spectral Measuring Method
2.1.2. Measuring of LAI
2.1.3. Biomass Measurements
2.2. Spectral Data Analysis and Technique Method
2.2.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2.2.2. Spectral Vegetation Indices
3. Results
3.1. Research of NDVI in Retrieval of LAI
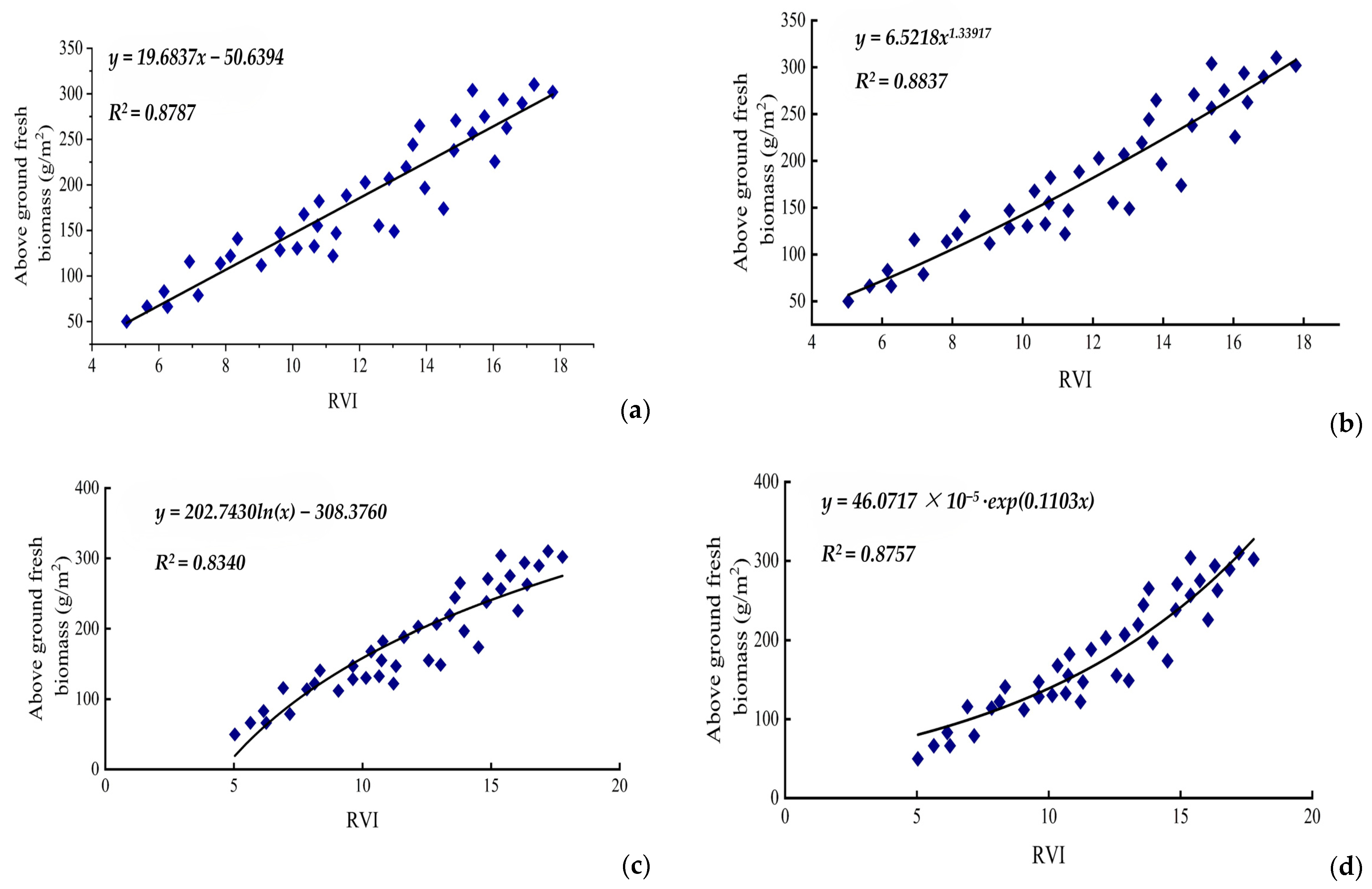
3.2. Spectral Data Testing Model of RVI to Above-Ground Biomass
3.3. Spectral Data Testing Model of RVI to Above-Ground Fresh Biomass
3.4. Spectral Data Testing Model of RVI to Above-Ground Dry Biomass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pena, M.; Brenning, A.; Sagredo, A. Constructing satellite-derived hyperspectral indices sensitive to canopy structure variables of a Cordilleran Cypress (Austrocedrus chilensis) forest. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kross, A.; McNairn, H.; Lapen, D.; Sunohara, M.; Champagne, C. Assessment of RapidEye vegetation indices for estimation of leaf area index and biomass in corn and soybean crops. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xiao, J.; Hou, J.; Duan, B. Rape yields estimation research based on spectral analysis for UAV image. J. Geomat. 2017, 42, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.J.; Köhler, P.; Magney, T.S.; Frankenberg, C.; Fung, I.; Cohen, R.C. A double peak in the seasonality of California’s photosynthesis as observed from space. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, S. The Role of Cotton in China’s Agricultural Economy. Chin. Agric. Sci. 2017, 14, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Smith, R.B.; De Pauw, E. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and their relationships with agricultural crop characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 71, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Lu, J. Estimating biomass of winter oilseed rape using vegetation indices and texture metrics derived from UAV multispectral images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 166, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A. Reflectance wavebands and indices for remote estimation of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance in pine canopies—A promising technique to rapidly determine nitrogen and cholophyll content. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 63, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ahmed, N.; Zhang, L. Applications of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing in Cotton Cultivation: A Review. J. Remote Sens. Appl. 2019, 12, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Chen, Y.; Sui, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C. Mechanism analysis of leaf biochemical concentration by high spectral remote Sensing. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 4, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ahmed, N.; Zhang, L. Remote Sensing Technology for Monitoring Crop Growth. Remote Sens. Appl. 2019, 12, 78–91. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.K.; Chai, L.; Singh, R.P. Crop yield estimation model for Iowa using remote sensing and surface parameters. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, D.T.; Kumar, P.; Long, S.P. Simultaneous improvement in productivity, water use, and albedo through crop structural modification. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, A.; Myrgiotis, V.; Florence, A.; Hoad, S.; Rees, R.; MacArthur, A.; Williams, M. Combining process modelling and LAI observations to diagnose winter wheat nitrogen status and forecast yield. Agronomy 2021, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, D.T.; Kumar, P.; Long, S.; Bernacchi, C.; Liang, X.; Sivapalan, M. Ecohydrological responses of dense canopies to environmental variability: 1. Interplay between vertical structure and photosynthetic pathway. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, G04022–G04025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Park, H.; Lee, J. Leaf Area Index as an Indicator of Canopy Structure and Growth Dynamics. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 182, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Feng, H.; Xu, L.; Miao, M.; Long, H.; Yue, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Yang, X.; Fan, L. Estimation of Crop Growth Parameters Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, M.; Xing, W.; Han, Y.; Bai, Q.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wei, Z.; Wu, W. The Optimal Soil Water Content Models Based on Crop-LAI and Hyperspectral Data of Winter Wheat. Irrig. Sci. 2021, 39, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Monitoring Changes in Leaf Area Index for Crop Fertilization Strategies. J. Crop Sci. 2020, 28, 112–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Q. Rice Nitrogen Nutrition Estimation with RGB Images and Machine Learning Methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Huang, C. Estimating of cotton canopy fraction of Photosyn The tically active radiation and leaf area index based on hyperspectral remote sensing data. Cotton Sci. 2009, 21, 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. Utilizing Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Cotton Canopy Structure Monitoring. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2019, 18, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Development of a Spectral Cognition Retrieval Model for Cotton Canopy Structure Parameters. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 34, 56–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, G. Enhancing Precision Cotton Cultivation through Hyperspectral Remote Sensing: A Machine Learning Approach. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2020, 8, 132–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, G.; Han, L.; Li, Z.; Feng, H.; Xu, B.; Wu, J.; Lei, L. Estimation of Maize Above-Ground Biomass Based on Stem-Leaf Separation Strategy Integrated with LiDAR and Optical Remote Sensing Data. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Liu, S. Resarch of remote sensing monitoring model for winter wheat Biomass. J. Arid. Land. Resour. Environ. 1997, 11, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Shihezi. Available online: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%9F%B3%E6%B2%B3%E5%AD%90%E5%B8%82/4776421?fromtitle=%E7%9F%B3%E6%B2%B3%E5%AD%90&fromid=348362 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Pu, R.; Gong, P. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing and Its Application; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Q. Study on imaging spectrometer remote sensing information for wetland vegetation. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 1, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brantley, S.T.; Zinnert, J.C.; Young, D.R. Application of hyperspectral vegetation indices to detect variations in high leaf area index temperate shrub thicket canopies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.D.; Johnson, A.B.; Brown, E.F.; Davis, M.G. Remote Sensing of Vegetation: Principles, Applications, and Future Prospects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 7020–7045. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.B.; Smith, C.D. Advances in Remote Sensing Applications for Agriculture. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.B.; Smith, C.D.; Brown, E.F. Remote Sensing Techniques for Estimating Leaf Area Index: A Review. Remote Sens. Rev. 2019, 40, 298–316. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Pavlic, G.; Brown, L.; Cihlar, J.; Leblanc, S.G.; White, P.H.; Hall, R.J.; Peddle, D.R.; King, D.J.; Trofymow, J.A.; et al. Derivation and validation of Canada-wide coarse-resolution leaf area index maps using high-resolution satellite imagery and ground measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 55, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broge, N.H.; Leblanc, E. Comparing prediction power and stability of broadband and hyperspectral vegetation indices for estimation of green leaf area index and canopy chlorophyll density. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 76, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z. Analysis of multi-temporal and multi-spatial character of NDVI and crop Condition models development. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2000, 16, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Correlation analysis between vegetation near-ground reflectance spectral characteristics and biomass for inner-mongolia steppe. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2004, 28, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Casanova, D.; Epema, G.F.; Goudriaan, J. Monitoring rice reflectance at field level for estimating biomass and LAI. Field Crops Res. 1998, 55, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Huang, J.F. Rice Yield Estimation; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2002; Volume 5, pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.F.; Johnson, A.B.; Smith, C.D. Modeling Biomass Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Remote Sens. Rev. 2019, 25, 321–335. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q. Estimating the maize biomass by crop height and narrowband vegetation indices derived from UAV-based hyperspectral images. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnyp, M.L.; Miao, Y.X.; Yuan, F.; Ustin, S.L.; Yu, K.; Yao, Y.K.; Huang, S.Y.; Bareth, G. Hyperspectral canopy sensing of paddy rice aboveground biomass at different growth stages. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross Validation. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html (accessed on 1 February 2010).
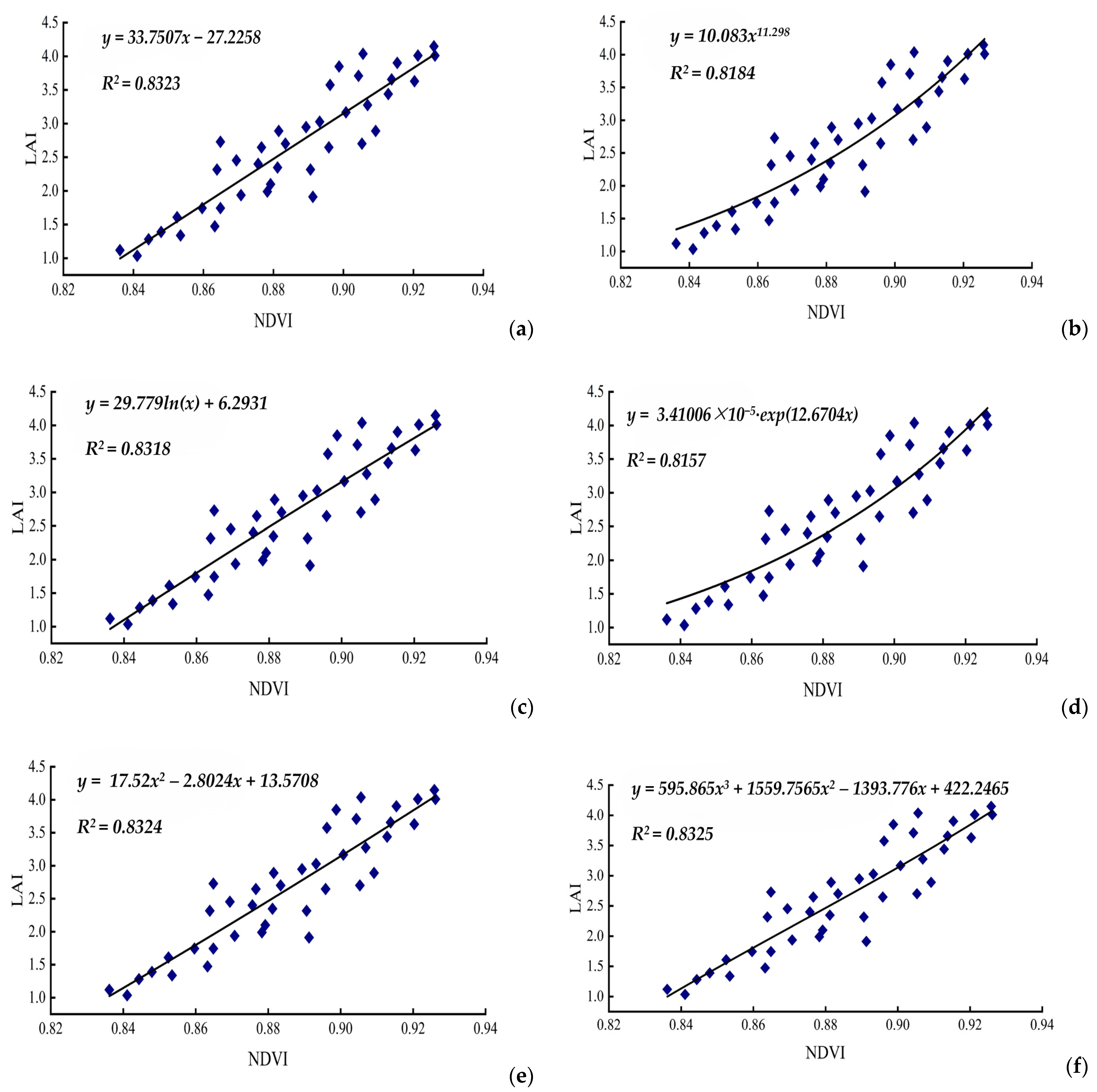


| Model Function | Regression Function | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | y = a + bx | y = 33.7507x − 27.2258 | 0.8323 | 0.3967 |
| 2 | y = axb | y = 10.083x11.298 | 0.8184 | 0.3613 |
| 3 | y = a + bln(x) | y = 29.779ln(x) + 6.2931 | 0.8318 | 0.3965 |
| 4 | y = a∙exp(bx) | y = 3.41006 × 10−5∙exp(12.6704x) | 0.8157 | 0.3634 |
| 5 | y = ax2 + bx + c | y = 17.52x2 – 2.8024x + 13.5708 | 0.8324 | 0.4527 |
| 6 | y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d | y = 595,865x3 + 1559.7565x2 – 1393.776x + 422.2465 | 0.8325 | 0.4499 |
| Model Function | Regression Function | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | y = a + bx | y = 19.6837x − 50.6394 | 0.8787 | 0.3653 |
| 2 | y = axb | y = 6.5218x1.33917 | 0.8837 | 0.1033 |
| 3 | y = a + bln(x) | y = 202.7430ln(x) − 308.3760 | 0.8340 | 0.1068 |
| 4 | y = a∙exp(bx) | y = 46.0717 × 10−5∙exp(0.1103x) | 0.8757 | 0.2985 |
| 5 | y = ax2 + bx + c | y = 0.4762x2 + 8.7352x + 6.3519 | 0.8747 | 0.4824 |
| 6 | y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d | y = 0.038x3 + 0.8566x2 − 23.0176x + 40.7481 | 0.8851 | 0.2985 |
| Model Function | Regression Function | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | y = a + bx | y = 4.1927x − 11.8051 | 0.8558 | 0.4473 |
| 2 | y = a xb | y = 1.2493x1.3721 | 0.8587 | 0.1177 |
| 3 | y = a + b ln(x) | y = 42.9131ln(x) − 66.3749 | 0.8193 | 0.3117 |
| 4 | y = a∙ exp(bx) | y = 9.1565 × 10−5∙exp(1.1146x) | 0.8456 | 0.0076 |
| 5 | y = ax2 + bx + c | y = 0.0764x2 − 2.4660x + 2.8662 | 0.8588 | 0.3932 |
| 6 | y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d | y = −8.5670x3 + 0.1051x2 − 2.1642x + 1.8818 | 0.8588 | 0.3924 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shen, C.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; et al. Estimation Model for Cotton Canopy Structure Parameters Based on Spectral Vegetation Index. Life 2025, 15, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010062
Qi Y, Chen X, Chen Z, Zhang X, Shen C, Chen Y, Peng Y, Chen B, Wang Q, Liu T, et al. Estimation Model for Cotton Canopy Structure Parameters Based on Spectral Vegetation Index. Life. 2025; 15(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yaqin, Xi Chen, Zhengchao Chen, Xin Zhang, Congju Shen, Yan Chen, Yuanying Peng, Bing Chen, Qiong Wang, Taijie Liu, and et al. 2025. "Estimation Model for Cotton Canopy Structure Parameters Based on Spectral Vegetation Index" Life 15, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010062
APA StyleQi, Y., Chen, X., Chen, Z., Zhang, X., Shen, C., Chen, Y., Peng, Y., Chen, B., Wang, Q., Liu, T., & Zhang, H. (2025). Estimation Model for Cotton Canopy Structure Parameters Based on Spectral Vegetation Index. Life, 15(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010062








