Comparative Analysis of Intellectual Quotient in Developmental Population with Severe Hearing Loss: Hearing Aids vs. Cochlear Implant Users
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
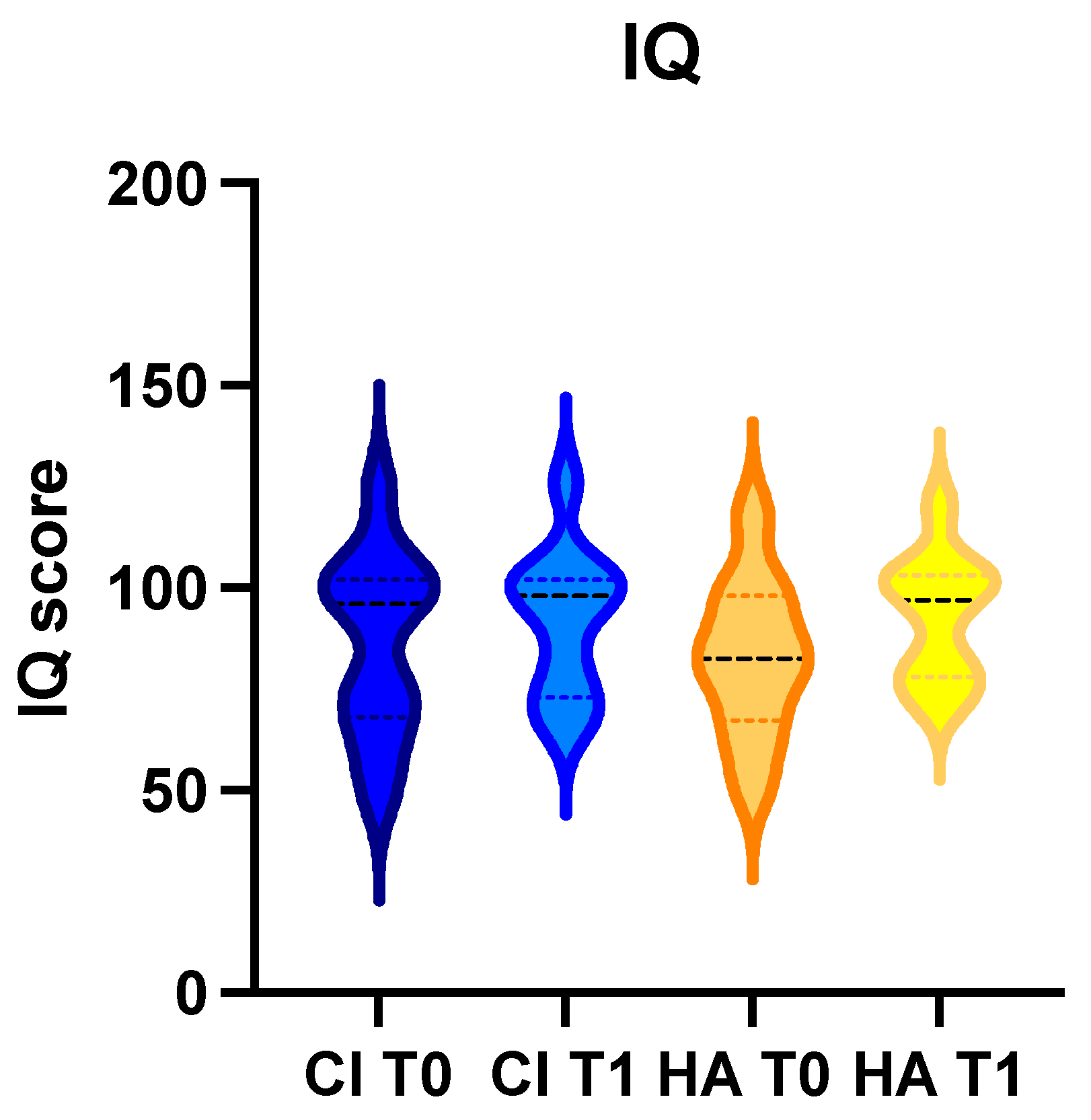
3. Results
3.1. General
3.2. Children with Cochlear Implant
3.3. Children with Hearing Aids
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Wang, H.F.; Zhang, W.; Rolls, E.T.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.H.; Kang, J.; Feng, J.; Yu, J.T.; et al. Hearing impairment is associated with cognitive decline, brain atrophy and tau pathology. eBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, S.A.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.M.; Lee, T.K.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.D. Association of Hearing Loss with Anatomical and Functional Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 149, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stadio, A.; Ralli, M.; Roccamatisi, D.; Scarpa, A.; Della Volpe, A.; Cassandro, C.; Ricci, G.; Greco, A.; Bernitsas, E. Hearing loss and dementia: Radiologic and biomolecular basis of their shared characteristics. A systematic review. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilosi, A.M.; Comparini, A.; Scusa, M.F.; Berrettini, S.; Forli, F.; Battini, R.; Cipriani, P.; Cioni, G. Neurodevelopmental disorders in children with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss: A clinical study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.L. Language facility and theory of mind development in deaf children. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2001, 6, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, T.P.; Dyar, D.; Archbold, S.; O’Donoghue, G.M. Development of spoken language grammar following cochlear im-plantation in prelingually deaf children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.asha.org/practice-portal/clinical-topics/hearing-loss/#collapse_6 (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Di Stadio, A.; Dipietro, L.; Toffano, R.; Burgio, F.; De Lucia, A.; Ippolito, V.; Garofalo, S.; Ricci, G.; Martines, F.; Trabalzini, F.; et al. Working Memory Function in Children with Single Side Deafness Using a Bone-Anchored Hearing Implant: A Case-Control Study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2018, 23, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Volpe, A.; Ippolito, V.; Roccamatisi, D.; Garofalo, S.; De Lucia, A.; Gambacorta, V.; Longari, F.; Ricci, G.; Di Stadio, A. Does Unilateral Hearing Loss Impair Working Memory? An Italian Clinical Study Comparing Patients with and without Hear-ing Aids. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, F.; Al-Momani, M.O.; Garadat, S.; Alqudah, S.; Kassab, M.; Hamadneh, S.; Rauterkus, G.; Gans, R. Cognitive functioning in Deaf children using Cochlear implants. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monshizadeh, L.; Vameghi, R.; Rahimi, M.; Sajedi, F.; Hashemi, S.B.; Yadegari, F.; Kasbi, F. Is There Any Association Between Lan-guage Acquisition and Cognitive Development in Cochlear-Implanted Children? J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2021, 17, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, P.L.; Shinn, J.R.; Davis, G.E.; Sie, K.C. Children with unilateral hearing loss may have lower intelligence quotient scores: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okely, J.A.; Akeroyd, M.A.; Deary, I.J. Associations between Hearing and Cognitive Abilities from Childhood to Middle Age: The National Child Development Study 1958. Trends Hear. 2021, 25, 23312165211053707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.R.; Ferrucci, L.; Metter, E.J.; An, Y.; Zonderman, A.B.; Resnick, S.M. Hearing loss and cognition in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Neuropsychology 2011, 25, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Wechsler WISC IV—Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children; Psychological Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 2004.
- Lang, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Michelotti, C. WISC-IV Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children: Lettura dei Risultati e Interpretazione Clinica; Raffaello Cortina Editor: Lombardia, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, L.A.; Ryan, M.; Martin, R.B.; Ewen, J.; Mostofsky, S.H.; Denckla, M.B.; Mahone, E.M. Working memory influences processing speed and reading fluency in ADHD. Child Neuropsychol. 2011, 17, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, B.; Gibb, R. Brain plasticity and behaviour in the developing brain. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 20, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cardon, G.; Campbell, J.; Sharma, A. Plasticity in the developing auditory cortex: Evidence from children with sensorineural hearing loss and auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2012, 23, 396–411, quiz 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcus, A.; Tuomainen, O.; Campos, A.; Rosen, S.; Halliday, L.F. Functional brain alterations following mild-to-moderate senso-rineural hearing loss in children. Elife 2019, 8, e46965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs-Graham, E.; Walker, E.A.; Eastman, J.A.; Frenzel, M.R.; Joe, T.R.; McCreery, R.W. The impact of mild-to-severe hearing loss on the neural dynamics serving verbal working memory processing in children. Neuroimage Clin. 2021, 30, 102647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandakova, Y.; Hartley, C.A. Mechanisms of learning and plasticity in childhood and adolescence. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 42, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymofiyeva, O.; Gaschler, R. Training-Induced Neural Plasticity in Youth: A Systematic Review of Structural and Functional MRI Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 497245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, A.E.; Moeller, M.P. Treatment efficacy: Hearing loss in children. J. Speech Lang Hear. Res. 1998, 41, S61–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, J.E.C.; Kenna, M.; Anne, S.; Davidson, L. Hearing Loss in Children: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farinetti, A.; Ben Gharbia, D.; Mancini, J.; Roman, S.; Nicollas, R.; Triglia, J.M. Cochlear implant complications in 403 patients: Comparative study of adults and children and review of the literature. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2014, 131, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, A.; Risi, F.; Boyd, P. Potential insertion complications with cochlear implant electrodes. Cochlear Implants Int. 2020, 21, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayalan, M.; Paul, S.P.; Fernando, A.M. Common surgical problems in children. Community Pract. 2013, 86, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riegger, L.Q.; Leis, A.M.; Golmirzaie, K.H.; Malviya, S. Risk Factors for Intraoperative Hypoglycemia in Children: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.M.; Hakim, M.; Ramesh, A.; Rehman, S.; Majid, Y.; Miller, R.; Tumin, D.; Tobias, J.D. Risk factors for post-induction hypotension in children presenting for surgery. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2018, 34, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, M.; Miller, C.; Bräuer, A. Perioperative Hypothermia in Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, R.; Jia, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Bo, L. Research Progress on Risk Factors of Preoperative Anxiety in Children: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public 2022, 19, 9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geers, A.E. Factors influencing spoken language outcomes in children following early cochlear implantation. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 64, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, M.; Ramos, Á.; de Paula Vernetta, C.; Gil-Carcedo, E.; Lassaletta, L.; Sanchez-Cuadrado, I.; Espinosa, J.M.; Batuecas, Á.; Cenjor, C.; Lavilla, M.J.; et al. Guideline on cochlear implants. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2019, 70, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, P.L.; Deep, N.L.; Waltzman, S.B.; Roland, J.T., Jr.; Cushing, S.L.; Papsin, B.C.; Gordon, K.A. Cochlear Implantation in Infants: Why and How. Trends Hear. 2021, 25, 23312165211031751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, S.; Muluk, N.B.; San, T.; Cingi, C. Evaluation of patient satisfaction with different hearing aids: A study of 107 patients. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017, 96, E22–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, S.J.; Gibson, W.P.; Greenberg, S.L.; Bray, M. Comparison of outcomes in a case of bilateral cochlear implantation using devices manufactured by two different implant companies (Cochlear Corporation and Med-El). Cochlear Implants Int. 2011, 12, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogmann, R.J.; Al Khalili, Y. Cochlear Implants. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.S.; Sbeih, F.; Anne, S.; Cohen, M.S.; Schwartz, S.; Liu, Y.C.; Appachi, S. Auditory Outcomes in Children Who Undergo Cochlear Implantation Before 12 Months of Age: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 169, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Wisc IV | |
|---|---|
| Normal | 85–115 |
| Slight deficit | 84–70 |
| Moderate to severe deficit | 69–49 |
| Gender | Age of Implant Months | ABR noWV | PTA (dB) | CA T0 | VU T0 | VPR T0 | WMI T0 | PSI T0 | IQ T0 | CA T1 | VU T1 | VPR T1 | WMI T1 | PSI T1 | IQ T1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 12 | 90 dB | 90 | 112 | 72 | 89 | 85 | 79 | 75 | 124 | 90 | 85 | 94 | 91 | 80 |
| M | 13 | 90 dB | 90 | 80 | 126 | 139 | 130 | 68 | 124 | 92 | 126 | 140 | 130 | 70 | 126 |
| M | 14 | 90 dB | 140 | 81 | 100 | 98 | 102 | 100 | 104 | 93 | 100 | 100 | 103 | 100 | 101 |
| F | 11 | 90 dB | 90 | 84 | 54 | 72 | 79 | 71 | 68 | 96 | 76 | 90 | 95 | 90 | 90 |
| F | 13 | 90 dB | 140 | 95 | 62 | 87 | 73 | 56 | 59 | 107 | 70 | 95 | 75 | 60 | 65 |
| F | 14 | 90 dB | 140 | 108 | 62 | 85 | 82 | 65 | 74 | 120 | 62 | 84 | 80 | 64 | 73 |
| M | 12 | 95 dB | 98 | 81 | 102 | 100 | 103 | 103 | 102 | 93 | 102 | 100 | 103 | 103 | 102 |
| M | 13 | 90 dB | 90 | 74 | 104 | 100 | 91 | 88 | 96 | 86 | 104 | 100 | 97 | 94 | 99 |
| M | 14 | 100 dB | 100 | 83 | 60 | 71 | 55 | 59 | 49 | 95 | 72 | 87 | 76 | 74 | 70 |
| F | 12 | 90 dB | 95 | 88 | 100 | 104 | 91 | 91 | 97 | 100 | 100 | 104 | 97 | 91 | 98 |
| F | 13 | 100 dB | 140 | 85 | 106 | 106 | 97 | 91 | 102 | 97 | 106 | 106 | 100 | 100 | 105 |
| Gender | Age Hearing Aids Months | ABR eWV | PTA (dB) | CA T0 | VU T0 | VPR T0 | WMI T0 | PSI T0 | IQ T0 | CA T1 | VU T1 | VPR T1 | WMI T1 | PSI T1 | IQ T1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 14 | 90 dB | 93 | 80 | 108 | 71 | 97 | 65 | 84 | 92 | 110 | 92 | 115 | 80 | 104 |
| M | 15 | 70 dB | 70 | 84 | 110 | 122 | 124 | 67 | 118 | 96 | 120 | 110 | 100 | 70 | 120 |
| F | 13 | 90 dB | 98 | 81 | 90 | 87 | 109 | 56 | 81 | 93 | 102 | 100 | 110 | 64 | 94 |
| F | 15 | 70 dB | 73 | 108 | 75 | 90 | 85 | 72 | 78 | 120 | 77 | 92 | 87 | 74 | 82 |
| M | 16 | 70 dB | 72 | 79 | 60 | 89 | 73 | 65 | 69 | 91 | 70 | 98 | 82 | 71 | 79 |
| M | 1 | 73 dB | 73 | 89 | 62 | 74 | 55 | 59 | 51 | 101 | 78 | 95 | 79 | 68 | 75 |
| M | 13 | 72 dB | 74 | 92 | 76 | 80 | 64 | 62 | 62 | 104 | 84 | 87 | 70 | 68 | 71 |
| F | 12 | 70 dB | 71 | 82 | 98 | 100 | 85 | 79 | 89 | 94 | 102 | 108 | 94 | 91 | 100 |
| F | 11 | 74 dB | 75 | 96 | 104 | 100 | 94 | 88 | 97 | 108 | 108 | 104 | 100 | 94 | 103 |
| F | 13 | 70 dB | 72 | 94 | 108 | 106 | 94 | 88 | 101 | 106 | 108 | 106 | 97 | 91 | 102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Stadio, A.; De Luca, P.; Ippolito, V.; Vedova, P.; Garofalo, S.; Turchetta, R.; Ferlito, S.; della Volpe, A. Comparative Analysis of Intellectual Quotient in Developmental Population with Severe Hearing Loss: Hearing Aids vs. Cochlear Implant Users. Life 2024, 14, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010012
Di Stadio A, De Luca P, Ippolito V, Vedova P, Garofalo S, Turchetta R, Ferlito S, della Volpe A. Comparative Analysis of Intellectual Quotient in Developmental Population with Severe Hearing Loss: Hearing Aids vs. Cochlear Implant Users. Life. 2024; 14(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Stadio, Arianna, Pietro De Luca, Valentina Ippolito, Paola Vedova, Sabina Garofalo, Rosaria Turchetta, Salvatore Ferlito, and Antonio della Volpe. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Intellectual Quotient in Developmental Population with Severe Hearing Loss: Hearing Aids vs. Cochlear Implant Users" Life 14, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010012
APA StyleDi Stadio, A., De Luca, P., Ippolito, V., Vedova, P., Garofalo, S., Turchetta, R., Ferlito, S., & della Volpe, A. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Intellectual Quotient in Developmental Population with Severe Hearing Loss: Hearing Aids vs. Cochlear Implant Users. Life, 14(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010012








