Tissue Culture—A Sustainable Approach to Explore Plant Stresses
Abstract
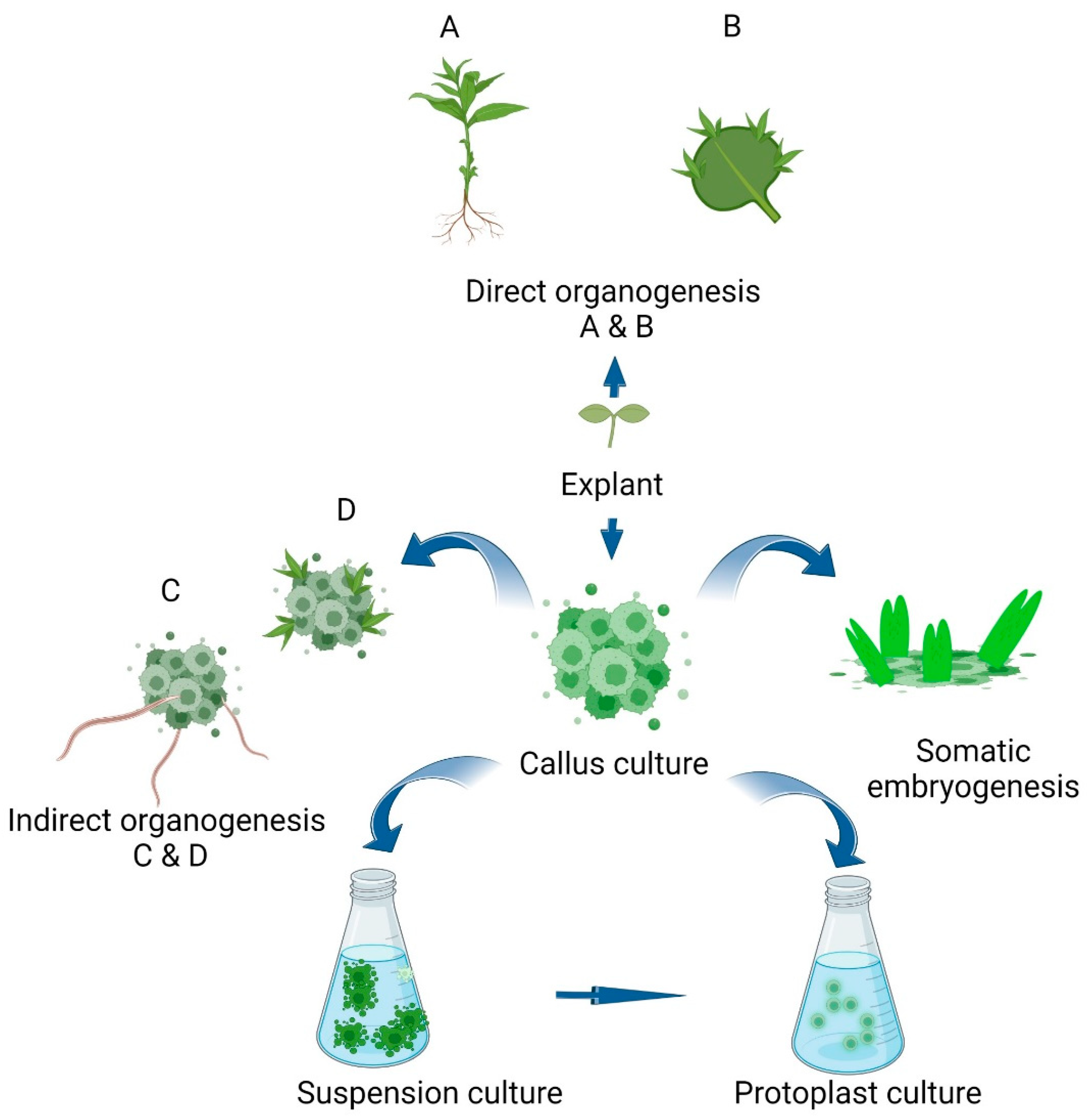
1. Introduction
2. In Vitro Screening of Drought Tolerance
3. In Vitro Screening of Salinity Tolerance
4. In Vitro Screening of Disease Resistance
5. In Vitro Screening of Metal Hyperaccumulators
6. Stress Tolerance through Transgenic Technology
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.P.; Loh, C.S. Plant Tissue Culture for Biotechnology. In Plant Biotechnology and Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wijerathna-Yapa, A.; Ramtekey, V.; Ranawaka, B.; Basnet, B.R. Applications of in Vitro Tissue Culture Technologies in Breeding and Genetic Improvement of Wheat. Plants 2022, 11, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamborg, O.L. Plant Tissue Culture. Biotechnology. Milestones. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 2002, 38, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathna-Yapa, A.; Pathirana, R. Sustainable Agro-Food Systems for Addressing Climate Change and Food Security. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.D.; Mishra, R.; Maurya, K.K.; Singh, R.B.; Wilson, D.W. Estimates for World Population and Global Food Availability for Global Health. In The Role of Functional Food Security in Global Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Valoppi, F.; Agustin, M.; Abik, F.; Morais de Carvalho, D.; Sithole, J.; Bhattarai, M.; Varis, J.J.; Arzami, A.N.; Pulkkinen, E.; Mikkonen, K.S. Insight on Current Advances in Food Science and Technology for Feeding the World Population. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 626227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Hiti-Bandaralage, J.C.A.; Ahlawat, J.; Gaur, N.; Diwan, B. 13—Nanobioremediation: An Introduction. In Nano-Bioremediation: Fundamentals and Applications; Iqbal, H.M.N., Bilal, M., Nguyen, T.A., Eds.; (Micro and Nano Technologies); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 263–279. ISBN 978-0-12-823962-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pessarakli, M. Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fahad, S.; Nie, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiong, D.; Saud, S.; Hongyan, L.; Cui, K.; Huang, J. Crop Plant Hormones and Environmental Stress. In Sustainable Agriculture Review; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 15, pp. 371–400. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, T.A. History of Plant Tissue Culture. Mol. Biotechnol. 2007, 37, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Tang, L.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.S. Plant Cell Totipotency: Insights into Cellular Reprogramming. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A. Callus, Dedifferentiation, Totipotency, Somatic Embryogenesis: What These Terms Mean in the Era of Molecular Plant Biology? Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smỳkal, P.; Valledor, L.; Rodriguez, R.; Griga, M. Assessment of Genetic and Epigenetic Stability in Long-Term in Vitro Shoot Culture of Pea (Pisum Sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, M.J.M.; De Klerk, G.J. Epigenetics in Plant Tissue Culture. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 63, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Marum, L. An Epigenetic View of Plant Cells Cultured in Vitro: Somaclonal Variation and Beyond. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3713–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, S.; Bajwa, A.A.; Nazir, U.; Anjum, S.A.; Farooq, A.; Zohaib, A.; Sadia, S.; Nasim, W.; Adkins, S.; Saud, S.; et al. Crop Production under Drought and Heat Stress: Plant Responses and Management Options. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Rico-Medina, A.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. The Physiology of Plant Responses to Drought. Science 2020, 368, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, G.; Hall, J. Crop Yield Sensitivity of Global Major Agricultural Countries to Droughts and the Projected Changes in the Future. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, A.; Sita, K.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Kumar, R.; Bhogireddy, S.; Varshney, R.K.; HanumanthaRao, B.; Nair, R.M.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Nayyar, H. Drought or/and Heat-Stress Effects on Seed Filling in Food Crops: Impacts on Functional Biochemistry, Seed Yields, and Nutritional Quality. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, F.A.; Golovina, E.A.; Buitink, J. Mechanisms of Plant Desiccation Tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattivelli, L.; Rizza, F.; Badeck, F.-W.; Mazzucotelli, E.; Mastrangelo, A.M.; Francia, E.; Marè, C.; Tondelli, A.; Stanca, A.M. Drought Tolerance Improvement in Crop Plants: An Integrated View from Breeding to Genomics. Field Crops Res. 2008, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badu-Apraku, B.; Obisesan, O.; Abiodun, A.; Obeng-Bio, E. Genetic Gains from Selection for Drought Tolerance during Three Breeding Periods in Extra-Early Maturing Maize Hybrids under Drought and Rainfed Environments. Agronomy 2021, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccio, M.L.; Paul, M.; Bate, N.J.; Cohn, J.; Cutler, S.R. Where Are the Drought Tolerant Crops? An Assessment of More than Two Decades of Plant Biotechnology Effort in Crop Improvement. Plant Sci. 2018, 273, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, S.; Ram, T.; Yadaw, R.B.; Mishra, K.K.; Mandal, N.P. Breeding High-Yielding Drought-Tolerant Rice: Genetic Variations and Conventional and Molecular Approaches. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6265–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xiong, L. Genetic Engineering and Breeding of Drought-Resistant Crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 715–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahaya, M.A.; Shimelis, H. Drought Stress in Sorghum: Mitigation Strategies, Breeding Methods and Technologies—A Review. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2022, 208, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmandar, M.N.; Rasouli, F.; Giglou, M.T.; Zahedi, S.M.; Aazami, M.A. In Vitro Screening of Cucmis Melo L. Against Drought Mediated by PEG and Sorbitol. Res. Squre 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, A.; Ragab, R.; Ahmed, K.; Omar; Dakhly, F.; Mohamed, S. In Vitro Selection for Tomato Plants for Drought Tolerance via Callus Culture under Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and Mannitol Treatments. In Proceedings of the 8th African Crop Science Society Conference, El-Minia, Egypt, 27–31 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Iwama, K. In Vitro Screening of Potato against Water-Stress Mediated through Sorbitol and Polyethylene Glycol. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarina, L.; Matskiv, A.; Simonyan, T.; Koninskaya, N.; Malyarovskaya, V.; Gvasaliya, M.; Malyukova, L.; Tsaturyan, G.; Mytdyeva, A.; Martinez-Montero, M.E.; et al. Biochemical and Genetic Responses of Tea (Camellia Sinensis (L.) Kuntze) Microplants under Mannitol-Induced Osmotic Stress In Vitro. Plants 2020, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, E.; Végh, B.; Khalil, R.; Marček, T.; Szalai, G.; Pál, M.; Janda, T. Metabolic Responses of Wheat Seedlings to Osmotic Stress Induced by Various Osmolytes under Iso-Osmotic Conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekko, K.; Timasheff, S.N. Mechanism of Protein Stabilization by Glycerol: Preferential Hydration in Glycerol-Water Mixtures. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 4667–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingsle, G.; Karpinski, S.; Hällgren, J.E. Low Temperature, High Light Stress and Antioxidant Defence Mechanisms in Higher Plants. PHYTON-HORN- 1999, 39, 253–268. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response Mechanism of Plants to Drought Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C. Sucrose Accumulation in Sugar Beet Under Drought Stress. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2010, 196, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, T.; Ohsumi, C.; Iuchi, S.; Seki, M.; Kasuga, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Important Roles of Drought- and Cold-Inducible Genes for Galactinol Synthase in Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant J. 2002, 29, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Sun, M.; Ma, Q.; Kang, H.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Y.; You, C. MdSWEET17, a Sugar Transporter in Apple, Enhances Drought Tolerance in Tomato. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunaryo, W.; Widoretno, W.; Nurhasanah, N.; Sudarsono, S. Drought Tolerance Selection of Soybean Lines Generated from Somatic Embryogenesis Using Osmotic Stress Simulation of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG). Nusant. Biosci. 2016, 8, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Tripathi, M.K.; Tiwari, S.; Tripathi, N.; Sapre, S.; Ahuja, A.; Tiwari, S. Cell Suspension Culture and In Vitro Screening for Drought Tolerance in Soybean Using Poly-Ethylene Glycol. Plants 2021, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Sidari, M.; Anastasi, U.; Santonoceto, C.; Maggio, A. Effect of PEG-Induced Drought Stress on Seed Germination of Four Lentil Genotypes. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Handa, A.K. Resistance of Cultured Higher Plant Cells to Polyethylene Glycol-Induced Water Stress. Plant Sci. Lett. 1981, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva Neto, V.B.; Otoni, W.C. Carbon Sources and Their Osmotic Potential in Plant Tissue Culture: Does It Matter? Sci. Hortic. 2003, 97, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, N.S.; Delporte, F.; Muhovski, Y.; Djekoun, A.; Watillon, B. In Vitro Screening of Durum Wheat against Water-Stress Mediated through Polyethylene Glycol. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouiamrine, E.H.; Diouri, M. Response of Durum Wheat (Triticum Durum Desf.) Callus Culture to Osmosis- Induced Drought Stress Caused by Polyethylene Glycol (PEG). Ann. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 4555–4563. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, R.R.; Waskom, R.M.; Nabors, M.W. In Vitro Screening and Field Evaluation of Tissue-Culture-Regenerated Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench) for Soil Stress Tolerance. Euphytica 1995, 85, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, I.; Razzaq, A.; Ashraf, M.; Hafiz, I.A.; Kaleem, S.; Qayyum, A.; Ahmad, M. In Vitro Selection of Tissue Culture Induced Somaclonal Variants of Wheat for Drought Tolerance. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 50, 03681157. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; Nawar, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.E.; El-Shamarka, A.; Selim, M.M.; Fahmi, A.I. Using Tissue Culture to Select for Drought Tolerance in Bread Wheat. In Proceedings of the 4th International Crop Science Congress, Brisbane, Australia, 26 September 2004; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Harris, P.J.; Henderson, J. In Vitro Selection and Characterisation of a Drought Tolerant Clone of Tagetes Minuta. Plant Sci. 2000, 159, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Javed, R.; Adeel, M.; Rizwan, M.; Yang, Y. PEG 6000-Stimulated Drought Stress Improves the Attributes of In Vitro Growth, Steviol Glycosides Production, and Antioxidant Activities in Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni. Plants 2020, 9, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmesa, D.; Dechassa, N.; Mohammed, W.; Gebre, E.; Monneveux, P.; Bündig, C.; Winkelmann, T. In Vitro Screening of Potato Genotypes for Osmotic Stress Tolerance. Open Agric. 2017, 2, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.; Sofi, P.; Gosal, S.; Singh, N. In Vitro Screening of Rice (Oryza Sativa L) Callus for Drought Tolerance. Commun. Biometry Crop Sci. 2010, 5, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, J.; Chowdhury, B.; Bhattacharya, A.; Mandal, A.B. In Vitro Screening for Increased Drought Tolerance in Rice. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 2002, 38, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushotham, M.G.; Patil, V.; Chandrashekra Raddey, P.; Prasad, T.G.; Vajranabhaiah, S.N. Development of in Vitro PEG Stress Tolerant Cell Lines in Two Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea L.) Genotypes. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 1998, 3, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gangopadhyay, G.; Basu, S.; Gupta, S. In Vitro Selection and Physiological Characterization of NaCl- and Mannitol-Adapted Callus Lines in Brassica Juncea. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1997, 50, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunaratne, S.; Santha, S.; Kovoor, A. An in Vitro Assay for Drought-Tolerant Coconut Germplasm. Euphytica 1991, 53, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errabii, T.; Gandonou, C.B.; Essalmani, H.; Abrini, J.; Idaomar, M.; Skali-Senhaji, N. Growth, Proline and Ion Accumulation in Sugarcane Callus Cultures under Drought-Induced Osmotic Stress and Its Subsequent Relief. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, P.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Effect of Salinity Stress on Plants and Its Tolerance Strategies: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4056–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.-K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of Plant Responses and Adaptation to Soil Salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Hou, X.; Liang, X. Response Mechanisms of Plants Under Saline-Alkali Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 667458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Peng, T.; Xue, S. Mechanisms of Plant Saline-Alkaline Tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 281, 153916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL Sabagh, A.; Hossain, A.; Barutçular, C.; Iqbal, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Fahad, S.; Sytar, O.; Çiğ, F.; Meena, R.S.; Erman, M. Consequences of Salinity Stress on the Quality of Crops and Its Mitigation Strategies for Sustainable Crop Production: An Outlook of Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. In Environment, Climate, Plant and Vegetation Growth; Fahad, S., Hasanuzzaman, M., Alam, M., Ullah, H., Saeed, M., Ali Khan, I., Adnan, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 503–533. ISBN 978-3-030-49732-3. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.-H.; Foster, K.J. Energy Costs of Salt Tolerance in Crop Plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.V. Genetic Sources for the Development of Salt Tolerance in Crops. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 89, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, A.; Benazir, I.; Kumar, G. Reassessing the Role of Ion Homeostasis for Improving Salinity Tolerance in Crop Plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Wu, L. Breeding for Salinity Tolerance in Plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1994, 13, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A.; Mirodjagh, S.-S. Response of Durum Wheat Cultivars to Immature Embryo Culture, Callus Induction and in Vitro Salt Stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1999, 58, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadhira, D.; Zapata-Arias, F.J.; Gregorio, G.B.; Alejar, M.S.; de la Cruz, H.C.; Padolina, T.F.; Galvez, A.M. Development of the First Salt-Tolerant Rice Cultivar through Indica/Indica Anther Culture. Field Crops Res. 2002, 76, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, L.; Caligari, P.D.S. Androgenesis of the Salt Tolerant Shrub Atriplex Glauca. Plant Cell Rep. 1996, 15, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, M. Effect of Salt Stress on in Vitro Organogenesis from Nodal Explant of Limnophila Aromatica (Lamk.) Merr. And Bacopa Monnieri (L.) Wettst. And Their Physio-Morphological and Biochemical Responses. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannachi, S.; Werbrouck, S.; Bahrini, I.; Abdelgadir, A.; Siddiqui, H.A.; Van Labeke, M.C. Obtaining Salt Stress-Tolerant Eggplant Somaclonal Variants from In Vitro Selection. Plants 2021, 10, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, N.; Kikuchi, A.; Watanabe, K.N. Assessment of Somaclonal Variation for Salinity Tolerance in Sweet Potato Regenerated Plants. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 7256–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.S.; Widholm, J.M. Comparison of Tissue Culture and Whole Plant Responses to Salinity in Potato. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 1993, 33, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabou, R.; Fergani, M.A.; Azzam, C.R.; Morsi, N. Devolopment of Some Canola Genotypes to Salinity Tolerance Using Tissue Culture Technique. Egypt. J. Agron. 2017, 39, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazami, M.A.; Rasouli, F.; Ebrahimzadeh, A. Oxidative Damage, Antioxidant Mechanism and Gene Expression in Tomato Responding to Salinity Stress under in Vitro Conditions and Application of Iron and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Z.; Mandal, A.K.A.; Datta, S.K.; Biswas, A.K. Development of NaCl-Tolerant Line in Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat. Through Shoot Organogenesis of Selected Callus Line. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 129, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, N.K.; Bas, B.; Koc, M.; Kusek, M. Investigations of in Vitro Selection for Salt Tolerant Lines in Sour Orange (Citrus Aurantium L.). Biotechnology 2009, 8, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandonou, C.B.; Errabii, T.; Abrini, J.; Idaomar, M.; Senhaji, N.S. Selection of Callus Cultures of Sugarcane (Saccharum Sp.) Tolerant to NaCl and Their Response to Salt Stress. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2006, 87, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Jaiswal, U.; Jaiswal, V.S. In Vitro Selection of NaCl-Tolerant Callus Lines and Regeneration of Plantlets in a Bamboo (Dendrocalamus Strictus Nees.). Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 2003, 39, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełkowska, A.; Grzebelus, E.; Lis-Krzyścin, A.; Maćkowska, K. Application of the Salt Stress to the Protoplast Cultures of the Carrot (Daucus Carota L.) and Evaluation of the Response of Regenerants to Soil Salinity. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2019, 137, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajrabhaya, M.; Thanapaisal, T.; Vajrabhaya, T. Development of Salt Tolerant Lines of KDML and LPT Rice Cultivars through Tissue Culture. Plant Cell Rep. 1989, 8, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Sathasivam, R.; Nguyen, B.V.; Baek, S.-A.; Yeo, H.J.; Park, Y.E.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Metabolic Profiling of Primary Metabolites and Galantamine Biosynthesis in Wounded Lycoris Radiata Callus. Plants 2020, 9, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, P.; Jayabalam, N. Selection and Regeneration of Groundnut Plants Resistant to the Pathotoxic Culture Filtrate OfCercosporidium Personation through Tissue Culture Technology. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1997, 61, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, A.; Tribulato, E.; Continella, G.; Vardi, A. Differential Responses of Citrus Calli and Protoplasts to Culture Filtrate and Toxin of Phoma Tracheiphila. Theoret. Appl. Genet. 1992, 83, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayatri, M.C.; Darshini, V.R.; Kavyashree, R. Selection of Turmeric Callus Tolerant to Culture Filtrate of Pythium Graminicolum and Regeneration of Plants. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2005, 83, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, M.; Jayabalan, N. Isolation of Disease-Tolerant Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L. Cv. SVPR 2) Plants by Screening Somatic Embryos with Fungal Culture Filtrate. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2006, 87, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A.S.; Thind, K.S.; Kumar, B.; Pallavi, M.; Gosal, S.S. In Vitro Selection at Cellular Level for Red Rot Resistance in Sugarcane (Saccharum Sp.). Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 58, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Huang, D. Studies on Somaclonal Variants for Resistance to Scab in Bread Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) through in Vitro Selection for Tolerance to Deoxynivalenol. Euphytica 1998, 101, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, S.; Li, Z.; Gray, D.J. In-Vitro Selection of Vitis Vinifera `Chardonnay’ with Elsinoe Ampelina Culture Filtrate is Accompanied by Fungal Resistance and Enhanced Secretion of Chitinase. Planta 2000, 211, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, M.E.; Ward, K.T. Field Performance of Populus Expressing Somaclonal Variation in Resistance to Septoria Musiva. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Long, G.; Luo, L.; Li, R.; Deng, Z. Production of Sweet Orange Somaclones Tolerant to Citrus Canker Disease by in Vitro Mutagenesis with EMS. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2015, 123, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschlag, F.A.; Ognjanov, V. Somaclonal Variation in Peach: Screening for Resistance to Xanthomonas Campestris Pv. Pruni and Pseudomonas Syringae Pv. Syringae. Acta Hortic. 1990, 280, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P.J.; Scowcroft, W.R. Somaclonal Variation—A Novel Source of Variability from Cell Cultures for Plant Improvement. Theoret. Appl. Genet. 1981, 60, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J.E.; Schoeman, M.H.; Berjak, P.; Watt, M.P.; Toerien, A.J. In Vitro Selection and Commercial Release of Guava Wilt Resistant Rootstocks. In Proceedings of the XXV International Horticultural Congress, Part 3: Culture Techniques with Special Emphasis on Environmental Implications 513, Brussels, Belgium, 2–7 August 1998; pp. 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Capuana, M. Heavy Metals and Woody Plants-Biotechnologies for Phytoremediation. Iforest-Biogeosci. For. 2011, 4, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donohue, B.; Hiti-Bandaralage, J.; Gleeson, M.; O’Brien, C.; Harvey, M.-A.; van der Ent, A.; Pinto Irish, K.; Mitter, N.; Hayward, A. Tissue Culture Tools for Selenium Hyperaccumulator Neptunia Amplexicaulis for Development in Phytoextraction. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2022, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan-Goldhirsh, A.; Barazani, O.; Nepovim, A.; Soudek, P.; Smrcek, S.; Dufkova, L.; Krenkova, S.; Yrjala, K.; Schröder, P.; Vanek, T. Plant Response to Heavy Metals and Organic Pollutants in Cell Culture and at Whole Plant Level. J. Soils Sediments 2004, 4, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, M.; Balestrazzi, A.; Bisoffi, S.; Carbonera, D. In Vitro Culture and Genetic Engineering of Populus spp.: Synergy for Forest Tree Improvement. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 72, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafzadeh, S.; Leung, D.W.M. Novel Potato Plants with Enhanced Cadmium Resistance and Antioxidative Defence Generated after in Vitro Cell Line Selection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantaray, S.; Rout, G.R.; Das, P. In Vitro Selection and Regeneration of Zinc Tolerant Calli from Setaria italica L. Plant Sci. 1999, 143, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, P.; Bouharmont, J. Use of Somaclonal Variation and in Vitro Selection for Chilling Tolerance Improvement in Rice. Euphytica 1997, 96, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Mandal, A.B. Towards Development of Al-Toxicity Tolerant Lines in Indica Rice by Exploiting Somaclonal Variation. Euphytica 2005, 145, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sint Jan, V.; Costa de Macedo, C.; Kinet, J.-M.; Bouharmont, J. Selection of Al-Resistant Plants from a Sensitive Rice Cultivar, Using Somaclonal Variation, in Vitro and Hydroponic Cultures. Euphytica 1997, 97, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Samantaray, S.; Das, P. In Vitro Selection and Biochemical Characterisation of Zinc and Manganese Adapted Callus Lines in Brassica Spp. Plant Sci. 1999, 146, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S.; Rout, G.R.; Das, P. Induction, Selection and Characterization of Cr and Ni-Tolerant Cell Lines of Echinochloa Colona (L.) Link in Vitro. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Sahoo, S. In Vitro Selection and Plant Regeneration of Copper-Tolerant Plants from Leaf Explants of Nicotiana Tabacum L. Cv. ‘Xanthi’. Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasic, K.; Korban, S.S. Expression of Arabidopsis Phytochelatin Synthase in Indian Mustard (Brassica Juncea) Plants Enhances Tolerance for Cd and Zn. Planta 2007, 225, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang Zhu, Y.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.; Jouanin, L.; Terry, N. Overexpression of Glutathione Synthetase in Indian Mustard Enhances Cadmium Accumulation and Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzilli, M.; Di Santo, P.; Palumbo, G.; Maiuro, L.; Paura, B.; Tognetti, R.; Cocozza, C. Cd and Cu Accumulation, Translocation and Tolerance in Populus Alba Clone (Villafranca) in Autotrophic in Vitro Screening. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10058–10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çetin, B.; Ay, Ç. Determination of CD (İİ) and ZN (İİ) Tolerance and Phytoremediation Ability of Prunella Vulgaris L. In Plant Tissue Culture Conditions; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Di Santo, P.; Cocozza, C.; Tognetti, R.; Palumbo, G.; Iorio, E.D.; Paura, B. A Quick Screening to Assess the Phytoextraction Potential of Cadmium and Copper in Quercus Pubescens Plantlets. iForest-Biogeosci. For. 2016, 10, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lonardo, S.; Capuana, M.; Arnetoli, M.; Gabbrielli, R.; Gonnelli, C. Exploring the Metal Phytoremediation Potential of Three Populus Alba L. Clones Using an in Vitro Screening. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berková, V.; Berka, M.; Griga, M.; Kopecká, R.; Prokopová, M.; Luklová, M.; Horáček, J.; Smýkalová, I.; Čičmanec, P.; Novák, J.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Flax (Linum Usitatissimum L.) Tolerance to Cadmium: A Case Study of Proteome and Metabolome of Four Different Flax Genotypes. Plants 2022, 11, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hradilová, J.; Řehulka, P.; Řehulková, H.; Vrbová, M.; Griga, M.; Brzobohatý, B. Comparative Analysis of Proteomic Changes in Contrasting Flax Cultivars upon Cadmium Exposure. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smykalova, I.; Vrbova, M.; Tejklova, E.; Vetrovcova, M.; Griga, M. Large Scale Screening of Heavy Metal Tolerance in Flax/Linseed (Linum Usitatissimum L.) Tested in Vitro. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 32, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, A.F.; Byrt, C.S.; Roy, S.J.; Whitney, S.M.; Mortimer, J.C.; Ankeny, R.A.; Gilliham, M.; Zhang, D.; Millar, A.A.; Rebetzke, G.J.; et al. Potential Abiotic Stress Targets for Modern Genetic Manipulation. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.C. Biolistic Plant Transformation. Physiol. Plant. 1990, 79, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiei, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Komari, T. Progress of Cereal Transformation Technology Mediated by Agrobacterium Tumefaciens. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazian, M.; Sadat Noori, S.A.; Galuszka, P.; Mortazavian, S.M.M. Tissue Culture-Based Agrobacterium-Mediated and in Planta Transformation Methods. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2017, 53, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes de Melo, B.; Lourenço-Tessutti, I.T.; Morgante, C.V.; Santos, N.C.; Pinheiro, L.B.; de Jesus Lins, C.B.; Silva, M.C.M.; Macedo, L.L.P.; Fontes, E.P.B.; Grossi-de-Sa, M.F. Soybean Embryonic Axis Transformation: Combining Biolistic and Agrobacterium-Mediated Protocols to Overcome Typical Complications of In Vitro Plant Regeneration. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.-L.; Dong, L.; Wang, Z.-P.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Han, C.-Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.-C.; Chen, Q.-J. A CRISPR/Cas9 Toolkit for Multiplex Genome Editing in Plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svitashev, S.; Schwartz, C.; Lenderts, B.; Young, J.K.; Mark Cigan, A. Genome Editing in Maize Directed by CRISPR–Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein Complexes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, L.; Narula, A. Gene Editing and Crop Improvement Using CRISPR-Cas9 System. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Ueta, R.; Osakabe, Y.; Osakabe, K. Precision Genome Editing in Plants: State-of-the-Art in CRISPR/Cas9-Based Genome Engineering. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.-L.; Cohen, D.; Atkinson, R.; Richardson, K.; Morris, B. Regeneration of Transgenic Plants from the Commercial Apple Cultivar Royal Gala. Plant Cell Rep. 1995, 14, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norelli, J.L.; Aldwinckle, H.S.; Destéfano-Beltrán, L.; Jaynes, J.M. Transgenic ‘Mailing 26′Apple Expressing the Attacin E Gene Has Increased Resistance to Erwinia Amylovora. Euphytica 1994, 77, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Câmara Machado, M.L.; da Câmara Machado, A.; Hanzer, V.; Weiss, H.; Regner, F.; Steinkellner, H.; Mattanovich, D.; Plail, R.; Knapp, E.; Kalthoff, B. Regeneration of Transgenic Plants of Prunus Armeniaca Containing the Coat Protein Gene of Plum Pox Virus. Plant Cell Rep. 1992, 11, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, R.; Levy, L.; Damsteegt, V.; Yepes, L.M.; Cordts, J.; Hadidi, A.; Slightom, J.; Gonsalves, D. Transformation of Plum with the Papaya Ringspot Virus Coat Protein Gene and Reaction of Transgenic Plants to Plum Pox Virus. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1995, 120, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, R.; Ravelonandro, M.; Callahan, A.M.; Cordts, J.M.; Fuchs, M.; Dunez, J.; Gonsalves, D. Transgenic Plums (Prunus Domestica L.) Express the Plum Pox Virus Coat Protein Gene. Plant Cell Rep. 1994, 14, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Liang, X.; Song, W.; Chen, Q.; Lai, J.; Jiang, C. A Retrotransposon in an HKT1 Family Sodium Transporter Causes Variation of Leaf Na+ Exclusion and Salt Tolerance in Maize. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosh Kumar, V.V.; Verma, R.K.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Watts, A.; Rao, M.V.; Chinnusamy, V. CRISPR-Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing of Drought and Salt Tolerance (OsDST) Gene in Indica Mega Rice Cultivar MTU1010. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar-Mathur, P.; Vadez, V.; Jyostna Devi, M.; Lavanya, M.; Vani, G.; Sharma, K.K. Genetic Engineering of Chickpea (Cicer Arietinum L.) with the P5CSF129A Gene for Osmoregulation with Implications on Drought Tolerance. Mol. Breed. 2009, 23, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochatt, S.J.; Power, J.B. Selection for Salt and Drought Tolerance in Protoplast- and Explant-Derived Tissue Cultures of Colt Cherry (Prunus Avium × Pseudocerasus). Tree Physiol. 1989, 5, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirzadeh-Khorzoghi, E.; Jahanbakhshian-Davaran, Z.; Seyedi, S.M. Direct Somatic Embryogenesis of Drought Resistance Pistachio (Pistacia Vera L.) and Expression Analysis of Somatic Embryogenesis-Related Genes. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 121, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, R.; Wingender, R. Gene-transfer and plant-regeneration (techniques). Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant Species | Marial Screened under In Vitro Conditions | In Vitro Screening Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean (Glycine max) Cultivars: B 3731, MLG 2999, MSC 8606,Tidar | Immature cotyledons were used as explant/Somatic embryogenesis | Subjected to 15% PEG 6000. The application of PEG was terminated after the plants were 28 days old. | [39] |
| Soybean (Glycine max) Cultivars: JS335, JS9305 | Calli/cell clumps/embryoids rose from the immature and mature embryonic axis and cotyledons | Subjected to discontinuous exposure to a lethal dose of 20% PEG6000 | [40] |
| Durum wheat (Triticum durum) Cultivars: Waha, Oued Zenati, Djenah Khetifa | Immature embryo-derived calli | Subjected to 10% and 20% PEG 6000 | [44] |
| Durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) Cultivars: Karim, Sebou, Ourigh, Anouar | Immature embryo-derived calli | Subjected to 10% and 20% PEG 10000 | [45] |
| Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) | Embryogenic callus | Subjected to a range of 0–15% PEG 8000 | [46] |
| Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Cultivar: GA-2002 | Immature embryo-derived calli | Subjected to a range of PEG 6000 | [47] |
| Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Cultivars: Sakha 8, Sakha 69, Giza 157, Sids 1, West bred, Falke, Hahn/Turaco, and Kauz/Gen | Immature embryo-derived calli | Subjected to a range of Mannitol | [48] |
| Tagetes (Tagetes minuta) | Calli-derived from cotyledon explants | Subjected to a range of Mannitol | [49] |
| Sweet leaf (Stevia rebaudiana) | Nodal shoot/micro propagated shoots | Subjected to a range of PEG 6000 | [50] |
| Potato (Solanum tuberosum) 27 CIP different cultivars | Nodal cuttings | Subjected to a range of Sorbitol | [51] |
| Rice (Oryza sativa) Cultivars: PA U 201 and PR 116 | Embryogenic calli | Subjected to a range of (0–2%) PEG 6000 | [52] |
| Potato (Solanum tuberosum) Cultivars: IWA-1, IWA-3, IWA-5 | Well-sprouted microtubers | Subjected to a range of Sorbitol and PEG 6000 | [30] |
| Rice (Oryza sativa) Cultivars: IR 18351-229-3, IR 3185-6-3-3-2, SR 26-B, Nona Bokra, and C 14-8 | Seed-derived calli | Subjected to a range of PEG 6000 | [53] |
| Ground nut (Arachis hypogaea) Cultivars: TMV2, JL24 | Hypocotyl-derived calli | Subjected to a range of PEG (0.0, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0 MPa) | [54] |
| Brown mustard (Brassica juncea Czern) Cultivars: RW-85-59 | Cotyledon-derived calli | Subjected to a range of Mannitol | [55] |
| Coconut (Cocos nucifera) Variety: Sri Lanka tall | Embryo cultures | Subjected to a range of PEG 6000 (1–5%) | [56] |
| Sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) Cultivars: R570 and CP59-73 | Calli cultures | Subjected to a range of Mannitol | [57] |
| Plant Species | Marial Screened under In Vitro Conditions | In Vitro Screening/ Mutagenesis Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limnophila aromatica (Lamk.) Merr. | In vitro organogenesis from nodal explant | Nodal explants subjected to callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 0–100 mM | [71] |
| Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. | In vitro organogenesis from nodal explant | Nodal explants subjected to callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 0–100 mM | [71] |
| Aubergine (Solanum melongena) Cultivar: Bonica | Leaf segment-derived calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 40–120 mM | [72] |
| Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) Cultivar: Shiroyutaka | Embryogenic calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 25–200 mM | [73] |
| Potato (Solanum tuberosum) Cultivars: Kennebec, Norchip, Red Pontiac, Russet Burbank, Russet Norkotah, and Superior | Stem cuttings, Leaf rachis originated callus-derived cell cultures | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 0.25–0.5 M | [74] |
| Canola (Brassica napus) Cultivars: Bingo Torpe, Conny and Siberian. | Hypocotyls and Cotyledonary-derived calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 4000, 8000, 12,000, and 16,000 ppm | [75] |
| Tomato (Solanum lycopersicom) Cultivars: Nora, PS-10, Peto, Roma | Hypocotyl-derived calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 5, 50, 75, and 100 mM | [76] |
| Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.) Cultivar: Maghi Yellow | Ray floret-derived calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 50, 75 and 100 mM | [77] |
| Sour Orange (Citrus aurantium L.) | Embryogenic calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 100–300 mM | [78] |
| Sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) Cultivar: CP65-357 | Young leaf-derived callus | Callus formation on a 68 mM NaCl concentration | [79] |
| Bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus Nees) | Embryogenic calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mM | [80] |
| Carrot (Daucus carota subsp. sativus L.) Cultivars: Dolanka and two Iranian landraces (DAL and NL) | Protoplasts | Protoplast culture in a series of NaCl concentrations 10–400 mM | [81] |
| Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars: KDML and LPT | Embryogenic calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 1–2% | [82] |
| Durum wheat (Triticum turgidum var. durum) | Immature embryogenic calli | Callus formation on a series of NaCl concentrations 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, and 2.1% w/v | [68] |
| Plant Species | Marial Screened under In Vitro Conditions | In Vitro Screening/Investigation Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lycoris radiata | Callus induced from meristem tissue of dried bulbs | Wounding stress imposed to analyse the accumulation of galantamine content as a measure of abiotic stress response in plants | [83] |
| Ground nut (Arachis hypogaea) Cultivars: VRI-2, TMV-7 | Immature leaf-derived calli | Culture filtrate of Cercosporidium personation | [84] |
| Femminello’ lemon (Citrus limon L.) Burro. f. Tarocco’ orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osb.) | Nucellar calli | Culture filtrate and toxin of Phoma tracheiphila | [85] |
| Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Cultivar: Suguna | Non-embryogenic propagule-derived calli | Culture filtrate of Pythium graminicolum | [86] |
| Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Cultivar: SVPR 2 | Hypercotyl-derived somatic embryos | Culture filtrate of Fusarium oxysporum and Alternaria macrospora | [87] |
| Sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) Cultivars: CoJ 88 and CoJ 64 | Apical spindle tips-derived calli | Culture filtrate of Colletotrichum falcatum | [88] |
| Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Varieties: Sumai 3 (P1), Mianyang 11 (P2), and their reciprocal F1 hybrids | Embryo-derived calli | Deoxynivalenol | [89] |
| grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Cultivar: Chardonnay | Proembryogenic masses derived calli | Culture filtrate of Elsinoe ampelina | [90] |
| Populus nigra × trichocarpa | Internode-derived callus, Somaclonal selection | Culture filtrate of Septoria musiva | [91] |
| Sweet orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) | embryogenic callus mutagenesis with EMS by somaclones tolerant | Culture filtrate of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri | [92] |
| Peach (Prunus persica) Cultivars: Sunhigh, Redhaven | Embryo-derived calli | Culture filtrate of Xanthomonas campestris pv. pruni | [93] |
| Plant Species | Tissue Culture Method | Stress | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Cultivar: Iwa | Micropropagation in vitro cell line selection | Cadmium | [100] |
| Foxtail millet (Setaria Italica) | Leaf base and mesocotyl explant-derived calli | Zinc | [101] |
| Rice (Oryza sativa L.) | Embryo-derived calli | Aluminium | [102,103,104] |
| Brassica campestris cv. M27 Brassica juncea cv. Pusabold | Cotyledon-derived calli | Zinc | [105] |
| Jungle rice (Echinochloa colona) | Leaf base-derived calli | Chromium, Nickel | [106] |
| Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Cultivar: Xanthi | Leaf-derived calli | Copper | [107] |
| Mustard (Brassica juncea) | Hypocotyl-derived calli | Cadmium | [108,109] |
| Silver poplar (Populus alba) | Microshoot cultures | Cadmium, Copper | [110] |
| Prunella vulgaris | Shoot-tip explants | Cadmium, Zinc | [111] |
| Downy oak (Quercus pubescens) | Seedlings | Cadmium, Copper | [112] |
| Silver poplar (Populus alba) | Microshoots culture | Arsenic, Copper, Cadmium, Zinc | [113] |
| Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) | Cell culture/Calli/shoot-tip culture | Cadmium | [114,115,116] |
| Crop | Trait | Trasformation Tissue Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) Cultivar Royal Gala. | Herbicide resistance | Callus/Organogenesis | [126] |
| Apple (Malus domestica) Cultivar: Mailing 26 | Resistance to Erwínía amylovora | Callus/Organogenesis | [127] |
| Apricot (Prunus armeniaca) Cultivar: Kecskemeter | Plum pox virus resistance | Callus/Organogenesis | [128] |
| European plum (Prunus domestica) Cultivar: Stanley | Papaya ringspot virus resistance | Callus/Organogenesis | [129,130] |
| Maize (Zea mays) | Salt resistance | Embryo culture/Organogenesis | [131] |
| Rice (Oryza sativa) | Salt resistance | Callus/Organogenesis | [132] |
| Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) Cultivar: C 235 (desi type) | Drought resistance | Callus/Direct organogenesis | [133] |
| Colt cherry (Prunus avium × pseudocerasus) | Salt and drought resistance | Protoplast | [134] |
| Pistachio (Pistacia vera) Cultivar: Sarakhs | Drought resistance | Somatic embryogenesis | [135] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijerathna-Yapa, A.; Hiti-Bandaralage, J. Tissue Culture—A Sustainable Approach to Explore Plant Stresses. Life 2023, 13, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030780
Wijerathna-Yapa A, Hiti-Bandaralage J. Tissue Culture—A Sustainable Approach to Explore Plant Stresses. Life. 2023; 13(3):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030780
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijerathna-Yapa, Akila, and Jayeni Hiti-Bandaralage. 2023. "Tissue Culture—A Sustainable Approach to Explore Plant Stresses" Life 13, no. 3: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030780
APA StyleWijerathna-Yapa, A., & Hiti-Bandaralage, J. (2023). Tissue Culture—A Sustainable Approach to Explore Plant Stresses. Life, 13(3), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030780






