Analysis of MIR27A (rs11671784) Variant Association with Systemic Lupus Erythematous
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. MIR27A rs11671784G>A Genotyping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
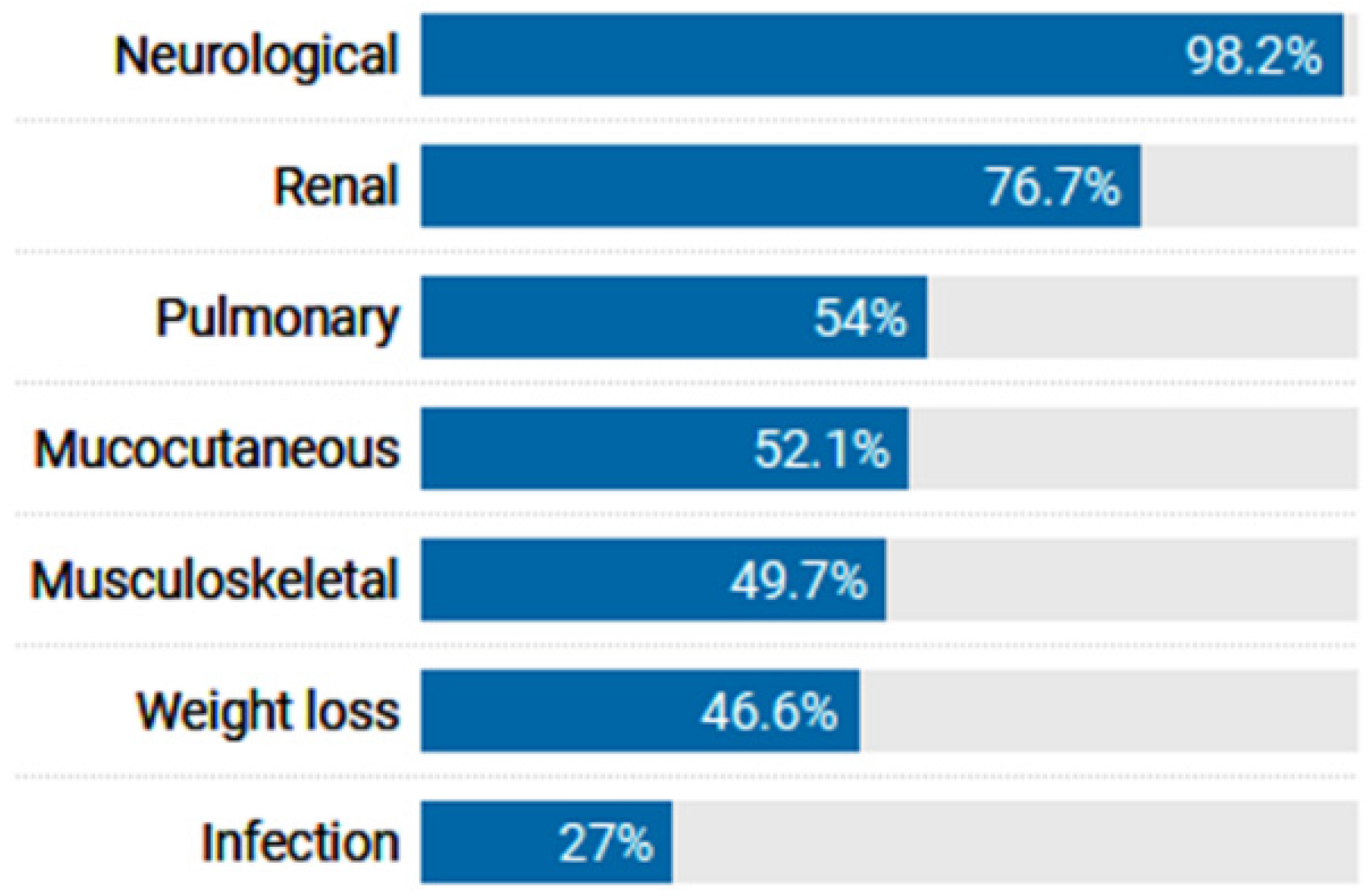
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Allelic Discrimination Analysis
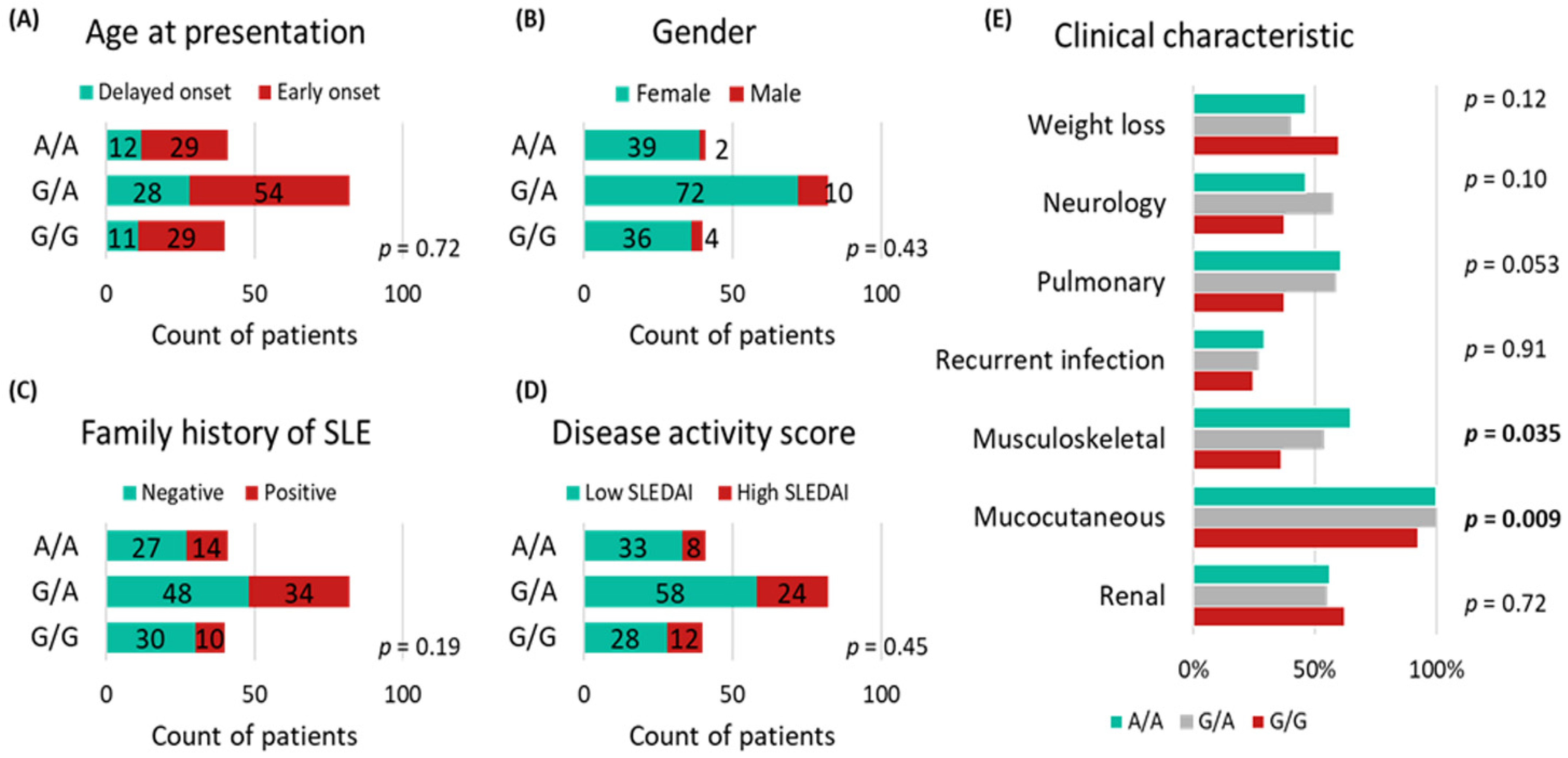
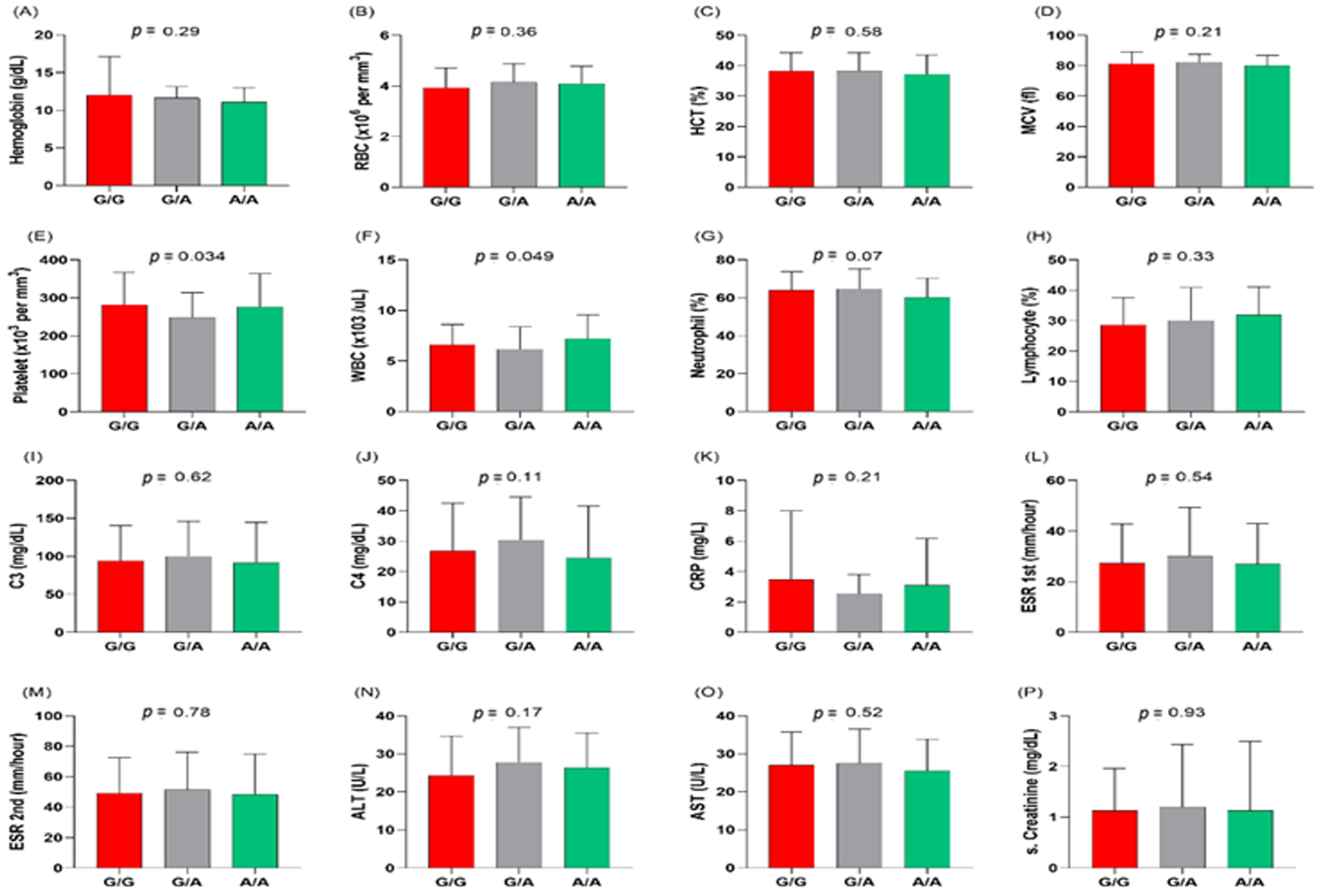
3.3. MIR27A rs11671784G/A Variant Association with Clinicolaboratory Data
3.4. Multivariate Regression Analysis
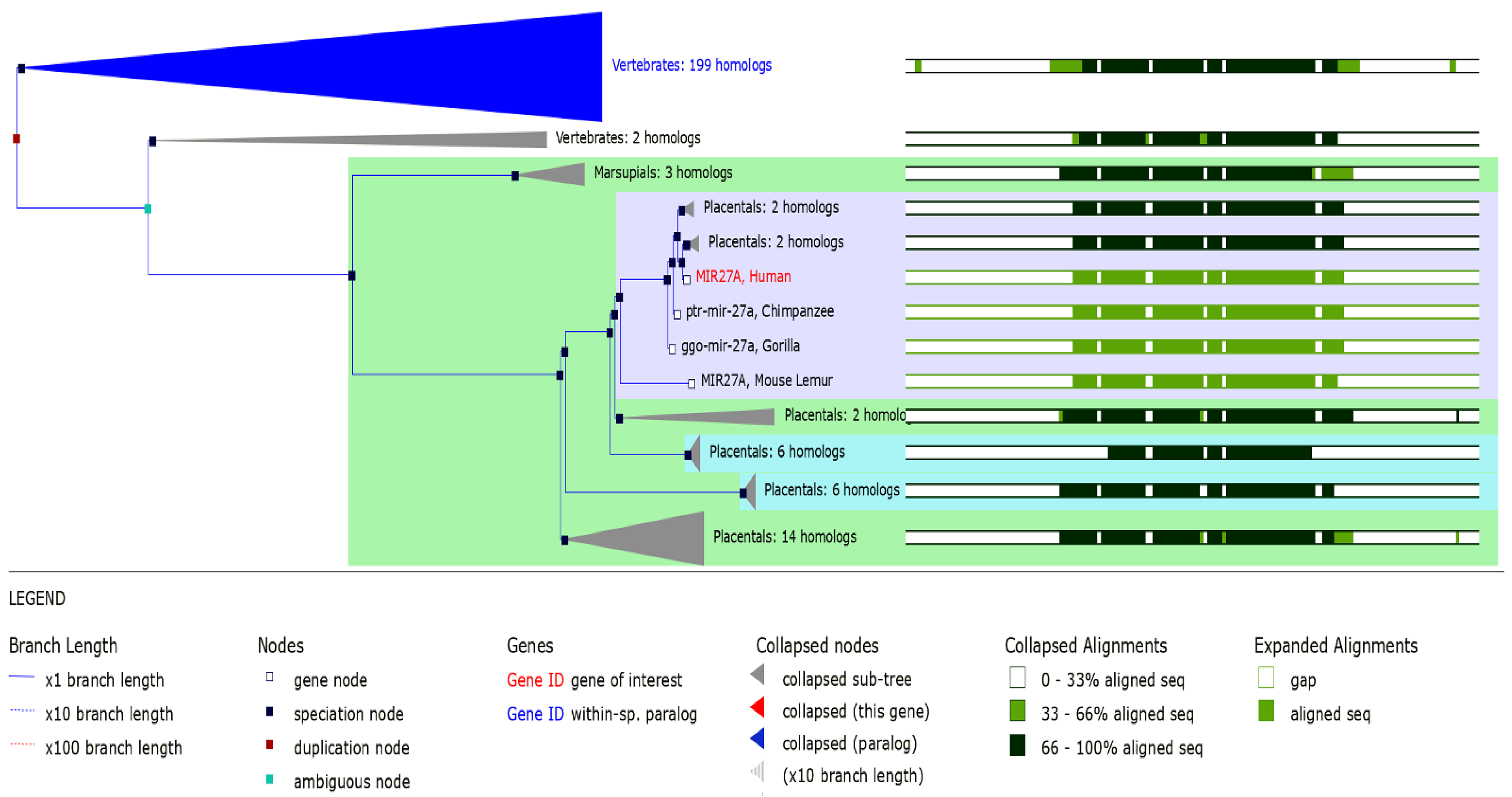
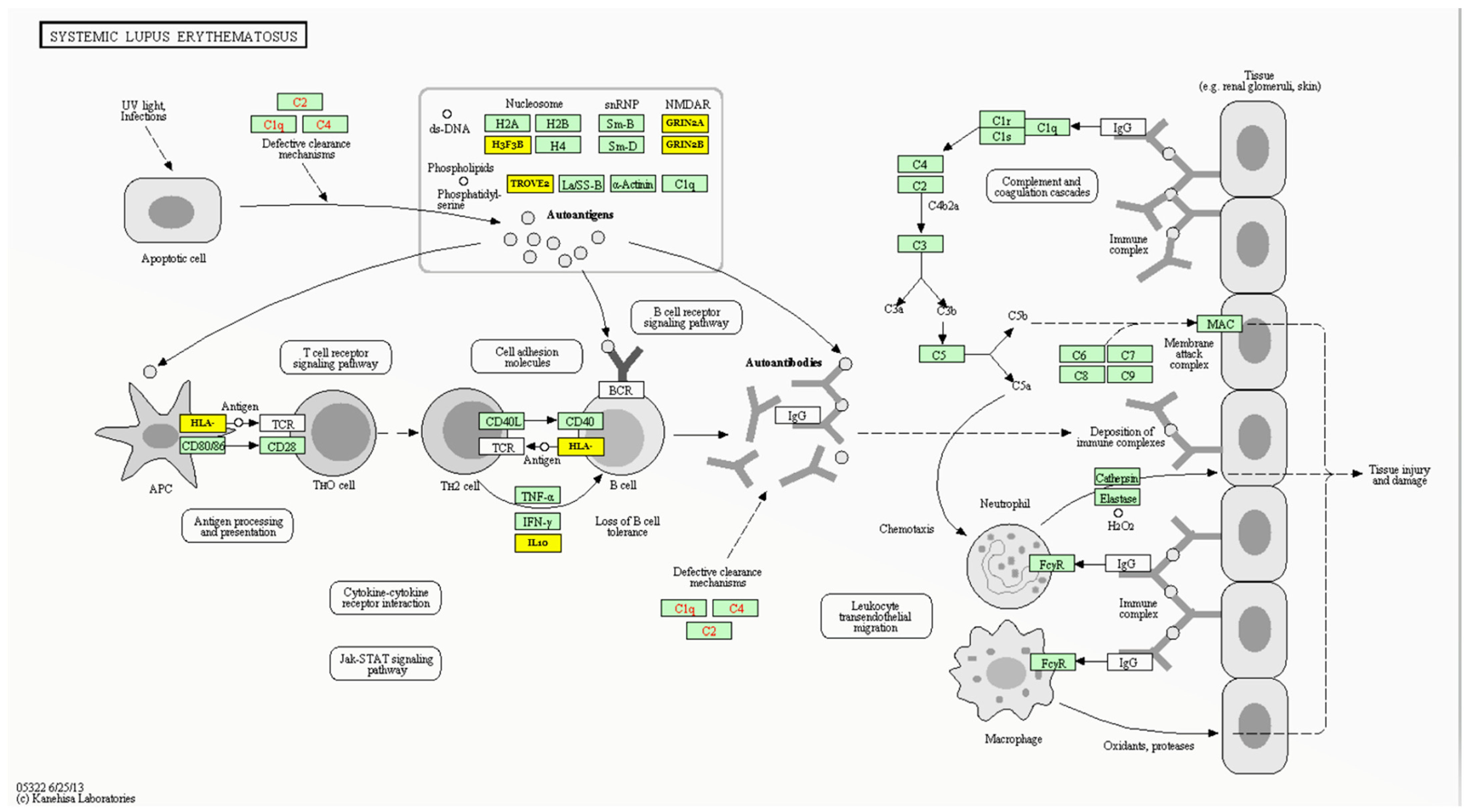
3.5. MIR27A Implication in SLE Etiopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bengtsson, A.A.; Rönnblom, L. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Still a challenge for physicians. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, N.M.; Toraih, E.A.; Mohammad, M.H.S.; Alshammari, E.M.; Fawzy, M.S. Association of microRNA-34a rs2666433 (A/G) Variant with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Female Patients: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, M.; Cojocaru, I.M.; Silosi, I.; Vrabie, C.D. Manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Maedica 2011, 6, 330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Peng, M.; Lu, Q. Translating epigenetics into clinic: Focus on lupus. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkaya, E.; Sahin, S.; Romano, M.; Zhou, Q.; Aksentijevich, I. New Horizons in the Genetic Etiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus-Like Disease: Monogenic Lupus and Beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Gillespie, K.M.; Rodriguez, S. Unravelling the Roles of Susceptibility Loci for Autoimmune Diseases in the Post-GWAS Era. Genes 2018, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarilyo, G.; La Cava, A. miRNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 144, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraih, E.A.; Fawzy, M.S.; Mohammed, E.A.; Hussein, M.H.; El-Labban, M.M. MicroRNA-196a2 Biomarker and Targetome Network Analysis in Solid Tumors. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Quiroz, E.; Pacheco-Lugo, L.; Lorenzi, H.; Díaz-Olmos, Y.; Almendrales, L.; Rico, E.; Navarro, R.; España-Puccini, P.; Iglesias, A.; Egea, E.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Circulating miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Kidney Damage in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraih, E.A.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Hussein, M.H.; Al-Qahtani, S.A.M.; Shaalan, A.A.M. MicroRNA-34a: A Key Regulator in the Hallmarks of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3269379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Yu, X.; Shen, N. Novel insights of microRNAs in the development of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; Aly, N.M.; Abdallah, H.Y.; Al-Qahtani, S.A.; Shaalan, A.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Fawzy, M.S. MicroRNA–target cross-talks: Key players in glioblastoma multiforme. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317726842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, C.; He, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, D.; Tao, Y. Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation, immunity and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraih, E.A.; El-Wazir, A.; Abdallah, H.Y.; Tantawy, M.A.; Fawzy, M.S. Deregulated MicroRNA Signature Following Glioblastoma Irradiation. Cancer Control. 2019, 26, 1073274819847226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, M.S.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Abu AlSel, B.T.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Toraih, E.A. Analysis of microRNA-34a expression profile and rs2666433 variant in colorectal cancer: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Weng, R.; Zhang, K.; He, X.; He, C. Circulating Exosomal microRNAs as Biomarkers of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clinics 2020, 75, e1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; Fawzy, M.S.; Hussein, M.H.; El-Labban, M.M.; Ruiz, E.M.L.; Attia, A.A.; Halat, S.; Moroz, K.; Errami, Y.; Zerfaoui, M.; et al. MicroRNA-Based Risk Score for Predicting Tumor Progression Following Radioactive Iodine Ablation in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients: A Propensity-Score Matched Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, M.S.; Al Ageeli, E.; Al-Qahtani, S.A.; Abu Alsel, B.T.; Kattan, S.W.; Alelwani, W.; Toraih, E.A. MicroRNA-499a (rs3746444A/G) gene variant and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes-associated end-stage renal disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, L.; Dong, L.; Liu, H.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; et al. A regulatory circuit comprising GATA1/2 switch and microRNA-27a/24 promotes erythropoiesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Guo, L. An Exploration of Evolution, Maturation, Expression and Function Relationships in Mir-23∼27∼24 Cluster. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Dubey, R.; Saini, N. Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sourour, S.K.; Aboelenein, H.R.; Elemam, N.M.; Abdelhamid, A.K.; Salah, S.; Abdelaziz, A. Unraveling the expression of microRNA-27a* & NKG2D in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and natural killer cells of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, J.; Raymond, W.; Ostli-Eilertsen, G.; Nossent, J. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) in systemic lupus erythematosus: Relation to disease activity, organ damage and immunological findings. Lupus 2018, 27, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Kronbichler, A.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Han, K.H.; Kang, H.G.; Ha, I.S.; Cheong, H.I.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, G.; et al. Association between Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase- (MMP-) 3 Levels and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-analysis. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 9796735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttilla, I.K.; White, B.A. Coordinate Regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23204–23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Lin, S.-C. Altered FOXO1 Transcript Levels in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardif, G.; Hum, D.; Pelletier, J.-P.; Duval, N.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Gao, Z.; Alarcon, R.M.; Ye, J.; Yun, Z. A role of miR-27 in the regulation of adipogenesis. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Lu, Q. Increased Expression of PPAR-γ Modulates Monocytes into a M2-Like Phenotype in SLE Patients: An Implicative Protective Mechanism and Potential Therapeutic Strategy of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Ye, L.; Guo, G.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Li, B.; Chen, N.; Xue, X. B Cell-Related Circulating MicroRNAs with the Potential Value of Biomarkers in the Differential Diagnosis, and Distinguishment Between the Disease Activity and Lupus Nephritis for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkel, J.; Mimranb, A.; Erez, N.; Kamb, N.; Lohse, A.W.; Hermanna, E.M.; Rotterc, V.; Cohen, I.R. Autoimmunity to the p53 Protein is a Feature of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Related to Anti-DNA Antibodies. J. Autoimmun. 2001, 17, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, J.-M.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, M.-R.; Wang, T.-T.; Lu, Y.-W. Association study between the TP53 Rs1042522G/C polymorphism and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese Han population. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazi, M.S.; Mohammadi, S.; Ebrahimabad, M.Z.; Sedighi, S.; Abdolahi, N.; Tabarraei, A.; Yazdani, Y. Genetic variation in CYP1A1 and AHRR genes increase the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus and exacerbate disease severity in smoker patients. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S. The Role of Adenomatous Polyposis Coli in T Cell Biology: Development, Naïve T Cell Maintenance, and T Cell Homeostatic Proliferation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, A.E.; Wang, W.; Brokamp, E.; Graham, T.B.; Aune, T.M.; Duis, J.B. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis associated with a mutation in GATA3. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 21, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. SMADS-Mediate Molecular Mechanisms in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, U.; Schulenburg, K.; Yurugi, H.; Šolman, M.; Abankwa, D.; Ulges, A.; Tenzer, S.; Bopp, T.; Thiede, B.; Zipp, F.; et al. Targeting prohibitins at the cell surface prevents Th17-mediated autoimmunity. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e99429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; Zabaleta, M.; Toro, F.; Bianco, N.E.; De Sanctis, J.B. Decreased transcription, expression and function of low-density lipoprotein receptor in leukocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 2009, 42, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucio-Eterovic, A.K.; Singh, M.M.; Gardner, J.E.; Veerappan, C.S.; Rice, J.C.; Carpenter, P.B. Role for the nuclear receptor-binding SET domain protein 1 (NSD1) methyltransferase in coordinating lysine 36 methylation at histone 3 with RNA polymerase II function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16952–16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, N.; Haseeb, M.; Kim, M.; Choi, S. Role of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Diseases and Its Therapeutic Outlook. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumimoto, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Onoyama, I.; Imaizumi, K.; Nakayama, K.I. F-box and WD Repeat Domain-containing-7 (Fbxw7) Protein Targets Endoplasmic Reticulum-anchored Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Transcriptional Factors for Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28488–28502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukumo, S.-I.; Subramani, P.G.; Seija, N.; Tabata, M.; Maekawa, Y.; Mori, Y.; Ishifune, C.; Itoh, Y.; Ota, M.; Fujio, K.; et al. AFF3, a susceptibility factor for autoimmune diseases, is a molecular facilitator of immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.-Y.; He, T.-T.; Gao, X.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. ZBTB Transcription Factors: Key Regulators of the Development, Differentiation and Effector Function of T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 713294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, S.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, Q. The roles of PPARγ and its agonists in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 113, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, K.; Van den Haute, C.; Baekelandt, V.; Lucas, S.; Van Horssen, J.; Somers, V.; Van Wijmeersch, B.; Stinissen, P.; Hendriks, J.J.; Slaets, H.; et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor tips the immune balance towards regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, A. Autoimmune Diseases Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2008, 25, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamjanyaporn, P.; Worawichawong, S.; Pisitkun, P.; Khiewngam, K.; Kantachuvesiri, S.; Nongnuch, A.; Assanatham, M.; Sathirapongsasuti, N.; Kitiyakara, C. Predicting treatment response and clinicopathological findings in lupus nephritis with urine epidermal growth factor, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 or their ratios. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Pedersen, B.; Guma, M. Solute carrier nutrient transporters in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 984408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Guo, M. EZH2: Its regulation and roles in immune disturbance of SLE. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1002741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, H.; Yan, X.; Chang, X. Investigate Pathogenic Mechanism of TXNDC5 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauley, K.M.; Cha, S.; Chan, E.K. MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 32, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Tu, Y.; Liu, L.; Qi, J.; He, L. MicroRNA-499 rs3746444 Polymorphism and Autoimmune Diseases Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; Ismail, N.M.; Toraih, A.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Fawzy, M.S. Precursor miR-499a Variant but not miR-196a2 is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility in an Egyptian Population. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yan, J.; Noltner, K.; Feng, J.; Li, H.; Sarkis, D.A.; Sommer, S.S.; Rossi, J.J. SNPs in human miRNA genes affect biogenesis and function. Rna 2009, 15, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammaerts, S.; Strazisar, M.; De Rijk, P.; Del Favero, J. Genetic variants in microRNA genes: Impact on microRNA expression, function, and disease. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, J.B.; De Morais, G.L.; Vieira, T.C.D.S.; Rabelo, N.C.; Llerena, J.C.J.; Gonzalez, S.M.D.C.; De Vasconcelos, A.T.R. miRNA Genetic Variants Alter Their Secondary Structure and Expression in Patients with RASopathies Syndromes. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gawad, A.R.; Shaheen, S.; Babteen, N.A.; Toraih, E.A.; Elshazli, R.M.; Fawzy, M.S.; Gouda, N.S. Association of microRNA 17 host gene variant (rs4284505) with susceptibility and severity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2020, 8, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strafella, C.; Errichiello, V.; Caputo, V.; Aloe, G.; Ricci, F.; Cusumano, A.; Novelli, G.; Giardina, E.; Cascella, R. The Interplay between miRNA-Related Variants and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: EVIDENCE of Association of MIR146A and MIR27A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, Z.S.; Walter, C.E.J.; Prakash, N.; Ramachandiran, K.; C., G.P.D.; Johnson, T. Investigating the role of microRNA-27a gene polymorphisms and its interactive effect with risk factors in gastrointestinal cancers. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Song, B.; Yan, G.; Hao, H. rs11671784 G/A and rs895819 A/G Polymorphisms Inversely Affect Gastric Cancer Susceptibility and miR-27a Expression in a Chinese Population. Experiment 2014, 20, 2318–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Jie, Z.; Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Han, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Y. Genetic variations in miR-27a gene decrease mature miR-27a level and reduce gastric cancer susceptibility. Oncogene 2014, 33, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Bai, H.; Hu, H. rs11671784 G/A variation in miR-27a decreases chemo-sensitivity of bladder cancer by decreasing miR-27a and increasing the target RUNX-1 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardier, C.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B.; Caron, D.; Chang, C.H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, M.S.; Hussein, M.H.; Abdelaziz, E.Z.; Yamany, H.A.; Ismail, H.; Toraih, E.A. Association of MicroRNA-196a2 Variant with Response to Short-Acting β2-Agonist in COPD: An Egyptian Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, X.; Guinó, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleknia, S.; Salehi, Z.; Tabar, V.R.; Sharifi-Zarchi, A.; Kavousi, K. An integrative Bayesian network approach to highlight key drivers in systemic lupus erythematosus. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 22, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, H.; Cao, Q.; Su, G.; Yang, P. Meta-Analysis of miRNA Variants Associated with Susceptibility to Autoimmune Disease. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 9978460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán-Ávila, I.; Jiménez-Morales, M.; Beltrán-Ramírez, O.; Barbosa-Cobos, R.E.; Jiménez-Morales, S.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Valencia-Pacheco, G.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Juárez-Vicuña, Y.; Hernández, D.M.R.-B.; et al. Functional polymorphisms in pre-miR146a and pre-miR499 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus but not with rheumatoid arthritis or Graves’ disease in Mexican patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91876–91886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shal, A.S.; Aly, N.M.; Galil, S.A.; Moustafa, M.A.; Kandel, W.A. Association of microRNAs genes polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Egyptian female patients. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Sun, D.; Lu, F. Association of two polymorphisms of miRNA-146a rs2910164 (G > C) and miRNA-499 rs3746444 (T > C) with asthma: A meta-analysis. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Al Ageeli, E.; Riad, E.; AbdAllah, N.B.; Helal, G.M.; Fawzy, M.S. Structure and functional impact of seed region variant in MIR-499 gene family in bronchial asthma. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Jin, L.; Yan, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Wu, X. Comprehensive review of genetic association studies and meta-analysis on miRNA polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, R.; Lee, W.J.; Ji, J.D. Association between the three functional miR-146a single-nucleotide polymorphisms, rs2910164, rs57095329, and rs2431697, and autoimmune disease susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Su, X.; Jiang, Z.; Rong, X.; Gu, X.; Jia, C.; Zeng, L.; Zheng, H.; Gu, X.; et al. Association between the miRNA-149 rs2292832 T>C polymorphism and Kawasaki disease susceptibility in a southern Chinese population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, X.; Kang, H.; Hong, S. A functional variant of miRNA-149 confers risk for allergic rhinitis and comorbid asthma in Chinese children. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2017, 44, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Rajewsky, K. MicroRNA Control in the Immune System: Basic Principles. Cell 2009, 136, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, T.-Y. The Role of MicroRNAs in Regulatory T Cells and in the Immune Response. Immune Netw. 2011, 11, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. IFN-γ Mediates the Development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7176515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, M.; Ooka, S.; Goto, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimoto, H.; Ishimori, K.; Matsushita, H.; Takakuwa, Y.; Kawahata, K. Anti-IL-10 antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2019, 11, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, K.; Sun, J.; Song, L.; Diao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Wang, X. Excessive activation of the TLR9/TGF-β1/PDGF-B pathway in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Bernal, F.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; García-González, M.; Fernández-Cladera, Y.; González-Rivero, A.F.; de Vera-González, A.; Martín-González, C.; González-Gay, M..; Ferraz-Amaro, I. Serum Levels of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borza, C.M.; Pozzi, A. The role of cell–extracellular matrix interactions in glomerular injury. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wei, W.; Wang, Q. Immuno-hippo: Research progress of the hippo pathway in autoimmune disease. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 230, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, R.; Khanfir, M.S.; Larbi, T.; Zamali, I.; Beldi-Ferchiou, A.; Kammoun, O.; Marzouki, S.; Hamzaoui, S.; Mrad, S.; Barbouche, M.R.; et al. Impaired TGF-β signaling in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with an overexpression of IL-22. Cytokine 2018, 108, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, Q.; Chen, J.; Feng, R.; Yang, C. Upregulating miR-27a-3p inhibits cell proliferation and inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through targeting toll-like receptor 5. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, P.; Kalantari, M.; Assarehzadegan, M.-A.; Poormoghim, H.; Mojtabavi, N. MiR-27a as a diagnostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in systemic sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sode, J.; Krintel, S.B.; Carlsen, A.L.; Hetland, M.L.; Johansen, J.S.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Ellingsen, T.; Burton, M.; Junker, P.; et al. Plasma MicroRNA Profiles in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Responding to Adalimumab plus Methotrexate vs Methotrexate Alone: A Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg: A resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D930–D934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejean, A.S.; Joulia, E.; Walzer, T. The role of Eomes in human CD4 T cell differentiation: A question of context. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, C.N.R.; Barros-Martins, J.; Oberdörfer, L.; Walzer, T.; Prinz, I. Eomes expression reports the progressive differentiation of IFN-γ-producing Th1-like γδ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jiménez, E.; Andrés-León, E. The Implications of ncRNAs in the Development of Human Diseases. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmeesters, A.; Eklund, T.; Leake, D.; Vermeulen, A.; Smith, Q.; Aldred, S.F.; Fedorov, Y. Functional Profiling Reveals Critical Role for miRNA in Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, T. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, Y.; Pawankar, R.; Kawana, S. The role of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and MMP-13 in bullous pemphigoid*1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ami, O.; Pencovich, N.; Lotem, J.; Levanon, D.; Groner, Y. A regulatory interplay between miR-27a and Runx1 during megakaryopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


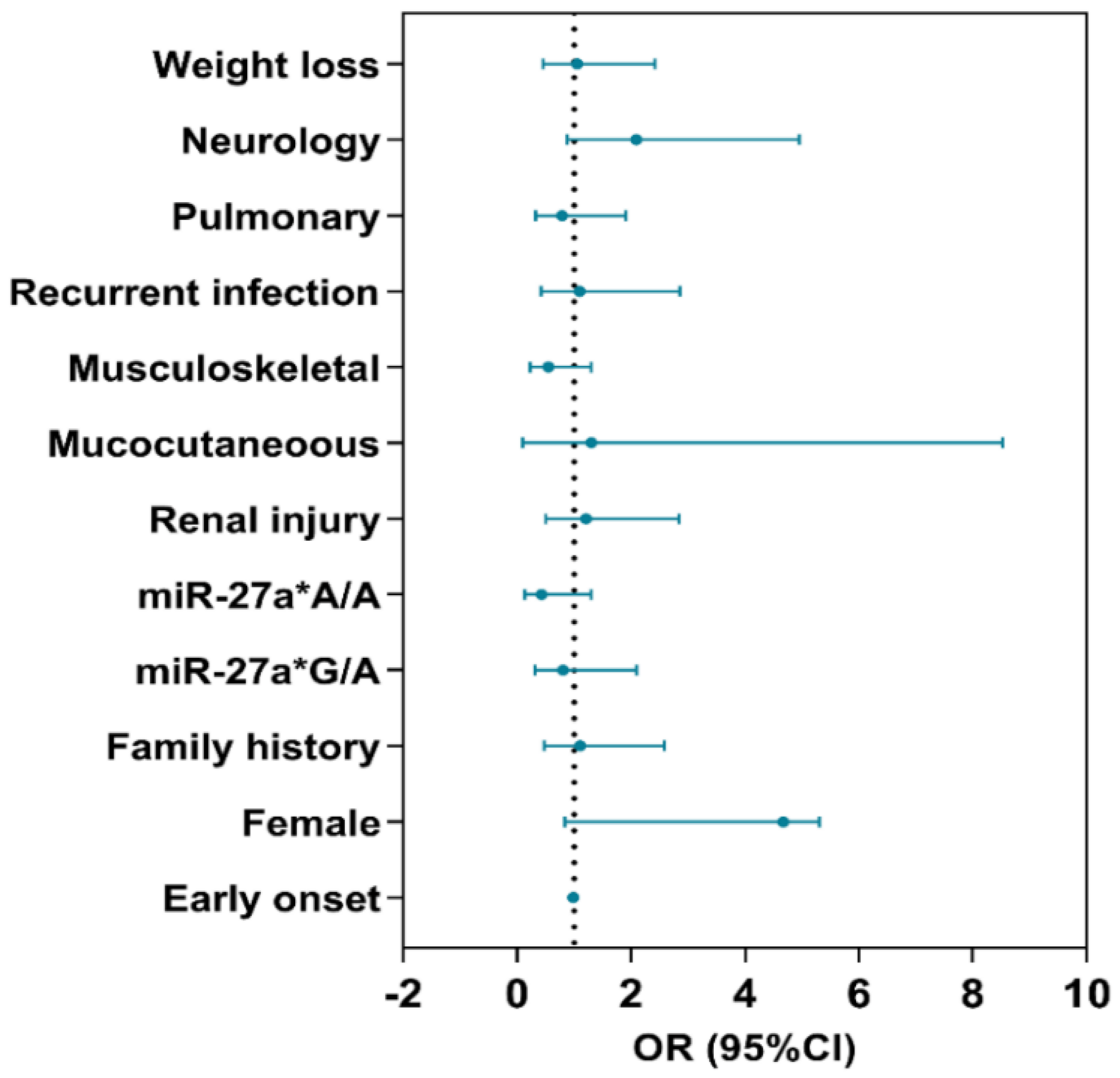

| Model | Genotype | Controls | Cases | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codominant | A/A | 8 (4.9%) | 41 (25.1%) | 1.00 | <0.0001 |
| G/A | 152 (93.2%) | 82 (50.3%) | 0.10 (0.05–0.23) | ||
| G/G | 3 (1.8%) | 40 (24.5%) | 2.56 (0.63–10.36) | ||
| Dominant | A/A | 8 (4.9%) | 41 (25.1%) | 1.00 | <0.0001 |
| G/A-G/G | 155 (95.1%) | 122 (74.8%) | 0.15 (0.07–0.34) | ||
| Recessive | A/A-G/A | 160 (98.2%) | 123 (75.5%) | 1.00 | <0.0001 |
| G/G | 3 (1.8%) | 40 (24.5%) | 17.34 (5.24–57.38) | ||
| Overdominant | A/A-G/G | 11 (6.8%) | 81 (49.7%) | 1.00 | <0.0001 |
| G/A | 152 (93.2%) | 82 (50.3%) | 0.07 (0.04–0.14) | ||
| Log-additive | --- | --- | --- | 1.09 (0.72–1.64) | 0.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khired, Z.A.; Kattan, S.W.; Alzahrani, A.K.; Milebary, A.J.; Hussein, M.H.; Qusti, S.Y.; Alshammari, E.M.; Toraih, E.A.; Fawzy, M.S. Analysis of MIR27A (rs11671784) Variant Association with Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Life 2023, 13, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030701
Khired ZA, Kattan SW, Alzahrani AK, Milebary AJ, Hussein MH, Qusti SY, Alshammari EM, Toraih EA, Fawzy MS. Analysis of MIR27A (rs11671784) Variant Association with Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Life. 2023; 13(3):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030701
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhired, Zenat Ahmed, Shahad W. Kattan, Ahmad Khuzaim Alzahrani, Ahmad J. Milebary, Mohammad H. Hussein, Safaa Y. Qusti, Eida M. Alshammari, Eman A. Toraih, and Manal S. Fawzy. 2023. "Analysis of MIR27A (rs11671784) Variant Association with Systemic Lupus Erythematous" Life 13, no. 3: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030701
APA StyleKhired, Z. A., Kattan, S. W., Alzahrani, A. K., Milebary, A. J., Hussein, M. H., Qusti, S. Y., Alshammari, E. M., Toraih, E. A., & Fawzy, M. S. (2023). Analysis of MIR27A (rs11671784) Variant Association with Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Life, 13(3), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030701







