Bringing Antimicrobial Strategies to a New Level: The Quorum Sensing System as a Target to Control Streptococcus suis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
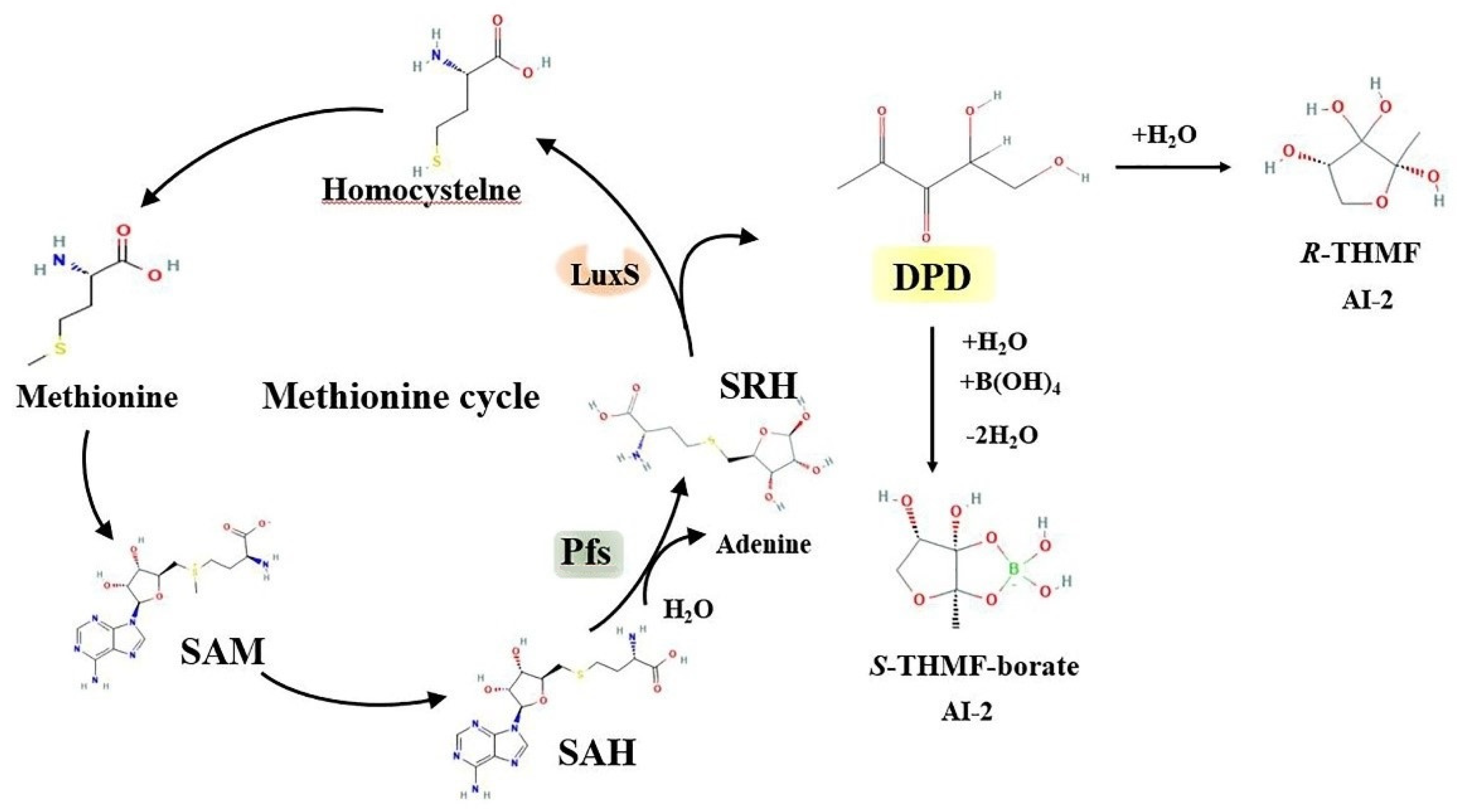
2. LuxS/AI-2 QS System
2.1. Streptococcus suis LuxS/AI-2 QS System
2.2. LuxS/AI-2 QS System Participates in the Regulation of Bacterial Function
3. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors in Streptococcus suis
4. Potential Drug Target of LuxS/AI-2 QS System to Inhibit Streptococcus suis
4.1. Potential Drug Target: AI-2 Production
4.2. Potential Drug Target: AI-2 Transmission
4.3. Potential Drug Target: LuxS Protein
4.4. Potential Drug Target: Blockage of AI-2 Binding to Receptors
4.5. Potential Drug Target: AI-2-Mediated QS
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Loughlin, C.; Miller, L.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.; Bassler, B. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, L.; Dong, X.; Grenier, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. Research progress of bacterial quorum sensing receptors: Classification, structure, function and characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum Sensing in Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouillaut, L.; Perchat, S.; Arold, S.; Zorrilla, S.; Slamti, L.; Henry, C.; Gohar, M.; Declerck, N.; Lereclus, D. Molecular basis for group-specific activation of the virulence regulator PlcR by PapR heptapeptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3791–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, C.; Thompson, J.; Xavier, K. AI-2-mediated signalling in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haleis, A.; Alfa, M.; Gottschalk, M.; Bernard, K.; Manickam, K. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 14, North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L. The LuxS/AI-2 system of Streptococcus suis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7231–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, M.; Khan, S.; Wani, M.Y.; Ahmad, A. Quorum Sensing-A Stratagem for Conquering Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2835–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lu, C. Biological activity and identification of a peptide inhibitor of LuxS from Streptococcus suis serotype 2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.B.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.Y.; Bai, J.W.; Chen, J.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, Y.H. Emodin affects biofilm formation and expression of virulence factors in Streptococcus suis ATCC700794. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Waters, C.M. A Tangled Web: Regulatory Connections between Quorum Sensing and Cyclic Di-GMP. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Regulation of Uptake and Processing of the Quorum-Sensing Autoinducer AI-2 in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.A.; Oliveira, R.A.; Djukovic, A.; Ubeda, C.; Xavier, K.B. Manipulation of the quorum sensing signal AI-2 affects the antibiotic-treated gut microbiota. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Hao, L.; Ke, H.; Liang, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. LuxS/AI-2 in Streptococcus agalactiae reveals a key role in acid tolerance and virulence. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Qiu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, H.; Xue, T.; Cai, G.; Sun, B. AI-2 quorum sensing negatively regulates rbf expression and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taga, M.E.; Semmelhack, J.L.; Bassler, B.L. The LuxS-dependent autoinducer AI-2 controls the expression of an ABC transporter that functions in AI-2 uptake in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L. Regulatory Mechanisms of the LuxS/AI-2 System and Bacterial Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01186-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Lu, C. Functional analysis of luxS in Streptococcus suis reveals a key role in biofilm formation and virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Ding, C.; Mao, X.; Lu, C. Crystal Structure and Identification of Two Key Amino Acids Involved in AI-2 Production and Biofilm Formation in Streptococcus suis LuxS. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, H.; Lu, C. Over expression of luxS Cannot Increase Autoinducer-2 Production, Only Affect the Growth and Biofilm Formation in Streptococcus suis. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 924276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Gong, S.; Dong, X.; Mao, C.; Yi, L. LuxS/AI-2 system is involved in fluoroquinolones susceptibility in Streptococcus suis through overexpression of efflux pump SatAB. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 233, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, B.L.; Wright, M.; Showalter, R.E.; Silverman, M.R. Intercellular signalling in Vibrio harveyi: Sequence and function of genes regulating expression of luminescence. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 9, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealson, K.H.; Hastings, J.W. Bacterial bioluminescence: Its control and ecological significance. Microbiol. Rev. 1979, 43, 496–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.M.; Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Global effects of the cell-to-cell signaling molecules autoinducer-2, autoinducer-3, and epinephrine in a luxS mutant of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4875–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, S.; Schmidt-Dannert, C. Applications of quorum sensing in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ku, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, F.; Zeng, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; He, Q. The AI-2/luxS Quorum Sensing System Affects the Growth Characteristics, Biofilm Formation, and Virulence of Haemophilus parasuis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. LuxS/AI-2 Quorum Sensing System in Edwardsiella piscicida promotes Biofilm Formation and Pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 2020, 88, e00907-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Weng, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Lin, S. Biofilm formation and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus mitis in response to luxS/AI-2 signaling. Int. J. Stomatol. 2017, 44, 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q. Screening and Effects on the Virulence Genes and LuxS of Chinese Herbal Extracts against Streptococcus suis Biofilm; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Drayton, M.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Straus, S.K. Towards Robust Delivery of Antimicrobial Peptides to Combat Bacterial Resistance. Molecules 2020, 25, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W.; Li, X.; Ding, K.; Li, J. A Kind of Streptococcus suis Density Sensing System Blocking Polypeptide and Its Application: China. China Patent CN106957353A, 27 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, X. A Novel Polypeptide Capable of Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Its Application: China. China Patent CN102942617A, 18 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X. Study on the Quorum Sensing of luxS/AI-2 of Streptococcus suis Serotype2; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Fan, Q.; Jin, M.; Mao, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L.; Hou, X.; et al. Paeoniflorin reduce /AI-2 system-controlled biofilm formation and virulence in luxS. Virulence 2021, 12, 3062–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Effect of Rhizoma Coptidis and Its Monomers on the LuxS and Virulence Genes against Streptococcus suis Biofilm; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Crowder, T.; Rinaldo-Matthis, A.; Ho, M.C.; Almo, S.C.; Schramm, V.L. Transition state analogs of 5 ‘-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase disrupt quorum sensing. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Shi, W.; Almo, S.C.; Evans, G.B.; Furneaux, R.H.; Tyler, P.C.; Painter, G.F.; Lenz, D.H.; Mee, S.; Zheng, R.; et al. Structure and inhibition of a quorum sensing target from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 12929–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tedder, M.E.; Nie, Z.; Margosiak, S.; Chu, S.; Feher, V.A.; Almassy, R.; Appelt, K.; Yager, K.M. Structure-based design, synthesis, and antimicrobial activity of purine derived SAH/MTA nucleosidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 14, 3165–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Ryu, E.J.; Li, L.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, B.M. New bicyclic brominated furanones as potent autoinducer-2 quorum-sensing inhibitors against bacterial biofilm formation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 137, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.Y.; Yuan, M.; Cui, Z.Q.; Wu, Z.M.; Yu, Z.J.; Song, K.; Tang, B.; Fu, B.D. Rutin inhibits quorum sensing, biofilm formation and virulence genes in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 119, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, A.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, S.; Jianyu, S.U. Inhibitory effects of citral, cinnamaldehyde, and tea polyphenols on mixed biofilm formation by foodborne Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enteritidis. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girennavar, B.; Cepeda, M.L.; Soni, K.A.; Vikram, A.; Patil, B.S. Grapefruit juice and its furocoumarin inhibits autoinducer signaling and biofilm formation in bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Xia, F.; Fu, Y.X.; Wu, Y.L.; Leng, C.Q.; Yi, P.F.; Shen, H.Q.; Wei, X.B. Andrographolide interferes quorum sensing to reduce cell damage caused by avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Heredia, N.; García, S. 2(5H)-Furanone, epigallocatechin gallate, and a citric-based disinfectant disturb quorum-sensing activity and reduce motility and biofilm formation of Campylobacter jejuni. Folia Microbiol. 2015, 60, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Inhibitors and antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29, 65–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.; Fernandes, R.; Tsao, C.; Bentley, W. Cross species quorum quenching using a native AI-2 processing enzyme. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Rajan, R.; Zhu, J.; Bell, C.; Pei, D. Design and synthesis of substrate and intermediate analogue inhibitors of S-ribosylhomocysteinase. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, J.; Zhang, T.; Wynn, D.; Karschner, E.; Zhou, Z. Synthesis of LuxS inhibitors targeting bacterial cell-cell communication. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3043–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Gu, W.; Yu, J. Virtual screening and in vitro experimental verification of LuxS inhibitors from natural products for Lactobacillus reuteri. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, F. Research Progress on Bacterial Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Chem. Bioeng. 2016, 33, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, N.; Choudhary, G.; Li, M.; Wang, B. A new phenothiazine structural scaffold as inhibitors of bacterial quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannick, D.E.; Mohamad, S.; Arnaud, C.; Laurent, S.; Yves, Q.; Yves, D.; Valérie, H.; Denis, F. N,N’-alkylated Imidazolium-derivatives act as quorum-sensing inhibitors targeting the Pectobacterium atrosepticum-induced symptoms on potato tubers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19976–19986. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, V.; Smith, J.; Wang, J.; Stewart, J.; Bentley, W.; Sintim, H. Synthetic analogs tailor native AI-2 signaling across bacterial species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11141–11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Jie, J.; Zeng, M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and anti-quorum sensing activities of pummelo peel flavonoid extract. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ni, N.; Chou, H.; Lu, C.; Tai, P.; Wang, B. Structure-based discovery and experimental verification of novel AI-2 quorum sensing inhibitors against Vibrio harveyi. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Du, M.; Fox, L.; Zhu, M.J. Bactericidal effects of Cinnamon cassia oil against bovine mastitis bacterial pathogens. Food Control 2016, 66, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Santhakumari, S.; Ravi, A.V. In vitro antibiofilm efficacy of Piper betle against quorum sensing mediated biofilm formation of luminescent Vibrio harveyi. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowery, C.A.; Abe, T.; Park, J.; Eubanks, L.M.; Sawada, D.; Kaufmann, G.F.; Janda, K.D. Revisiting AI-2 Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: Direct Comparison of Alkyl-DPD Analogues and a Natural Product Fimbrolide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Zuo, R.; Gonzalez Barrios, A.F.; Bedzyk, L.A.; Eldridge, G.R.; Pasmore, M.E.; Wood, T.K. Differential gene expression for investigation of Escherichia coli biofilm inhibition by plant extract ursolic acid. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4022–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defoirdt, T.; Crab, R.; Wood, T.K.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Quorum sensing-disrupting brominated furanones protect the gnotobiotic brine shrimp Artemia franciscana from pathogenic Vibrio harveyi, Vibrio campbellii, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6419–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouyahya, A.; Dakka, N.; Et-Touys, A.; Abrini, J.; Bakri, Y. Medicinal plant products targeting quorum sensing for combating bacterial infections. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, V.; Tamizh Manoharan, M.; Raj Chellappan, D.; Adline, P.S. Fructose furoic acid ester: An effective quorum sensing inhibitor against uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, E.; Sim, J.; Sim, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, B. D-Galactose as an autoinducer 2 inhibitor to control the biofilm formation of periodontopathogens. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.; van Gennip, M.; Phipps, R.; Shanmugham, M.; Christensen, L.; Alhede, M.; Skindersoe, M.; Rasmussen, T.; Friedrich, K.; Uthe, F.; et al. Ajoene, a sulfur-rich molecule from garlic, inhibits genes controlled by quorum sensing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Li, M. Recent progresses on AI-2 bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wan, W.; Mansouri, S.; Alfaro, J.; Bassler, B.; Cornell, K.; Zhou, Z. Chemical synthesis of S-ribosyl-L-homocysteine and activity assay as a LuxS substrate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 3897–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnuk, S.F.; Robert, J.; Sobczak, A.J.; Meyers, B.P.; Malladi, V.L.A.; Zhu, J.; Gopishetty, B.; Pei, D. Inhibition of S-ribosylhomocysteinase (LuxS) by substrate analogues modified at the ribosyl C-3 position. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6699–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soni, K.; Jesudhasan, P.; Cepeda, M.; Widmer, K.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Patil, B.; Hume, M.; Pillai, S. Identification of ground beef-derived fatty acid inhibitors of autoinducer-2-based cell signaling. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, J.; Fu, X.; Ma, C.; Lu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, X.; et al. Effect of 3,4-dibromo-2(5H)-furanone as a natural quorum sensing inhibitor on biofilm formation of Pseudomonas Fluourcens. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff, M.J.; Bassler, B.L. SnapShot: Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Cell 2018, 174, 1328–1328.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratnam, S.; Millette, M.; Mcfarland, L.V.; Dupont, H.L.; Lacroix, M. Potential role of probiotics in reducing Clostridioides difficile virulence: Interference with quorum sensing systems. Microb. Pathog 2021, 153, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T. Quorum-Sensing Systems as Targets for Antivirulence Therapy. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 26, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Brackman, G.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors: How strong is the evidence? Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| QSI | Source | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emodin | Rhubarb | Down-regulates the luxS gene, inhibits AI-2 synthesis | [10] |
| TTMHSIRTNRHN | Synthetic | Inhibits AI-2 synthesis | [31,32] |
| HSIRTGSKKPVPIIY | |||
| TNRHNPHHLHHV | |||
| Temprine-La(s)(T-La(s)) | Synthetic | Decreases AI-2 concentrations and down-regulates biofilm-related genes | [33] |
| Temprine-La(Fs)(T-La(Fs)) | |||
| RGD-T-La(s) | |||
| RGD-T-La(Fs) | |||
| Paeoniflorin | Peony | Reduces the binding rate of AI-2 to receptors | [34] |
| Coptis water extract | Huanglian | Inhibits the expression of the luxS, gdh, fbps, and mrp genes | [35] |
| QSI | Source | Bacteria | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrographolide | Andrographis | Escherichia coli | Decreases AI-2 activity | [38] |
| Citral | Lemon | Vibrio harveyi | Reduces the synthesis of AI-2, inhibits the formation of biofilm | [41] |
| Furanocoumarin | Grapefruit | Vibrio harveyi | Reduces the synthesis of AI-2 | [42] |
| mangiferin | Mango | Lactobacillus reuteri | inhibitor of LuxS protein | [49] |
| Naringin | Grapefruit | Vibrio harveyi | Inhibits the AI-2-mediated QS system | [54] |
| Cassia | Cassia oil | Escherichia coli | Inhibits the production of AI-2 | [56] |
| Hexadecanoic acid | Black pepper | Vibrio harveyi | Suppresses the QS system | [57] |
| Apigenin | Celery | Vibrio harveyi | Inhibits the AI-2-mediated QS system | [61] |
| Fructose furoate | Plants | Escherichia coli | Inhibits the expression of QS system-related genes (fimA, csgA, espA) | [62] |
| D-Galactose | Lactose | Vibrio harveyi | Reduces the synthesis of AI-2 | [63] |
| Ajoene | Garlic | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Suppresses the QS system | [64] |
| QSI | Structure Diagram | Bacteria | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-TolT-ImmA | 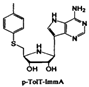 | Streptococcus pneumoniae | Inhibits the MTAN enzyme, blocks the production of SRH and AI-2 signal molecules | [36,65] |
| EtT-ImmA | 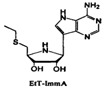 | |||
| MeT-ImmA | 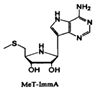 | Streptococcus pneumoniae | Inhibits the MTAN enzyme, blocks the production of SRH and AI-2 signal molecules | [36,65] |
| p-C1-PhT-DADMe-ImmA | 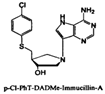 | Vibrio cholerae Escherichia coli O157:H7 Streptococcus pneumoniae | ||
| MT-DADMe-immucillin-A | 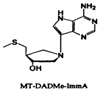 | |||
| EtT-DADMe-immucillin-A | 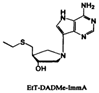 | Vibrio cholerae | ||
| BuT-DADMe-immucillin-A |  | Vibrio cholerae Escherichia coli O157:H7 | ||
| S-anhydroribosyl-L-homocysteine | 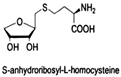 | unknown | SRH analogues, as substrates of the LuxS protein, exhibit inhibitory activity against the LuxS protein | [48,66] |
| S-homoribosyl-L-cysteine | 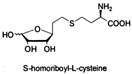 | |||
| Aromatic sulfones | 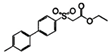 | Vibrio harveyi | Suppresses the AI-2 QS system | [55] |
| Sulfones(S-1) | 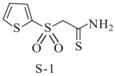 | |||
| Sulfones(S-2) |  | |||
| SRH analog-1 |  | Bacillus subtilis | Reversible competitive inhibitors of luxS | |
| SRH analog-2 | 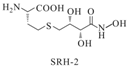 | Bacillus subtilis | [47] | |
| SRH analogs | 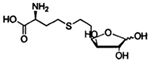 | Vibrio harveyi | [67] | |
| 2-Methylpropyl-DPD | 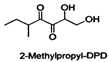 | Vibrio harveyi Salmonella typhimurium | Inhibits the AI-2-mediated QS system | [53] |
| Isopropyl-DPD | 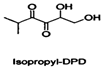 | |||
| Neopentyl-DPD |  | Vibrio harveyi Salmonella typhimurium | Inhibits the AI-2-mediated QS system | [53] |
| Pentyl-DPD | 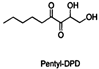 | |||
| Linoleic acid | 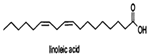 | Vibrio harveyi | Inhibits AI-2 QS and the formation of bacterial biofilms | [68] |
| Oleic acid |  | |||
| Palmitic acid | 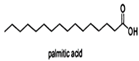 | |||
| 3, 4-dibromo-2 (5H)-furanone |  | Campylobacter jejuni | Interfere with QS system activity | [69] |
| 2(5H)-furanone | 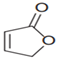 | Inhibiting the activity of AI-2 | [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, B.; Shen, Y.; Zuo, J.; Song, D.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y. Bringing Antimicrobial Strategies to a New Level: The Quorum Sensing System as a Target to Control Streptococcus suis. Life 2022, 12, 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122006
Xue B, Shen Y, Zuo J, Song D, Fan Q, Zhang X, Yi L, Wang Y. Bringing Antimicrobial Strategies to a New Level: The Quorum Sensing System as a Target to Control Streptococcus suis. Life. 2022; 12(12):2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122006
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Bingqian, Yamin Shen, Jing Zuo, Dong Song, Qingying Fan, Xiaoling Zhang, Li Yi, and Yang Wang. 2022. "Bringing Antimicrobial Strategies to a New Level: The Quorum Sensing System as a Target to Control Streptococcus suis" Life 12, no. 12: 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122006
APA StyleXue, B., Shen, Y., Zuo, J., Song, D., Fan, Q., Zhang, X., Yi, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). Bringing Antimicrobial Strategies to a New Level: The Quorum Sensing System as a Target to Control Streptococcus suis. Life, 12(12), 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122006







