Performance of Multifunctional Smart PV-Based Domestic Distributed Generator in Dual-Mode Operation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
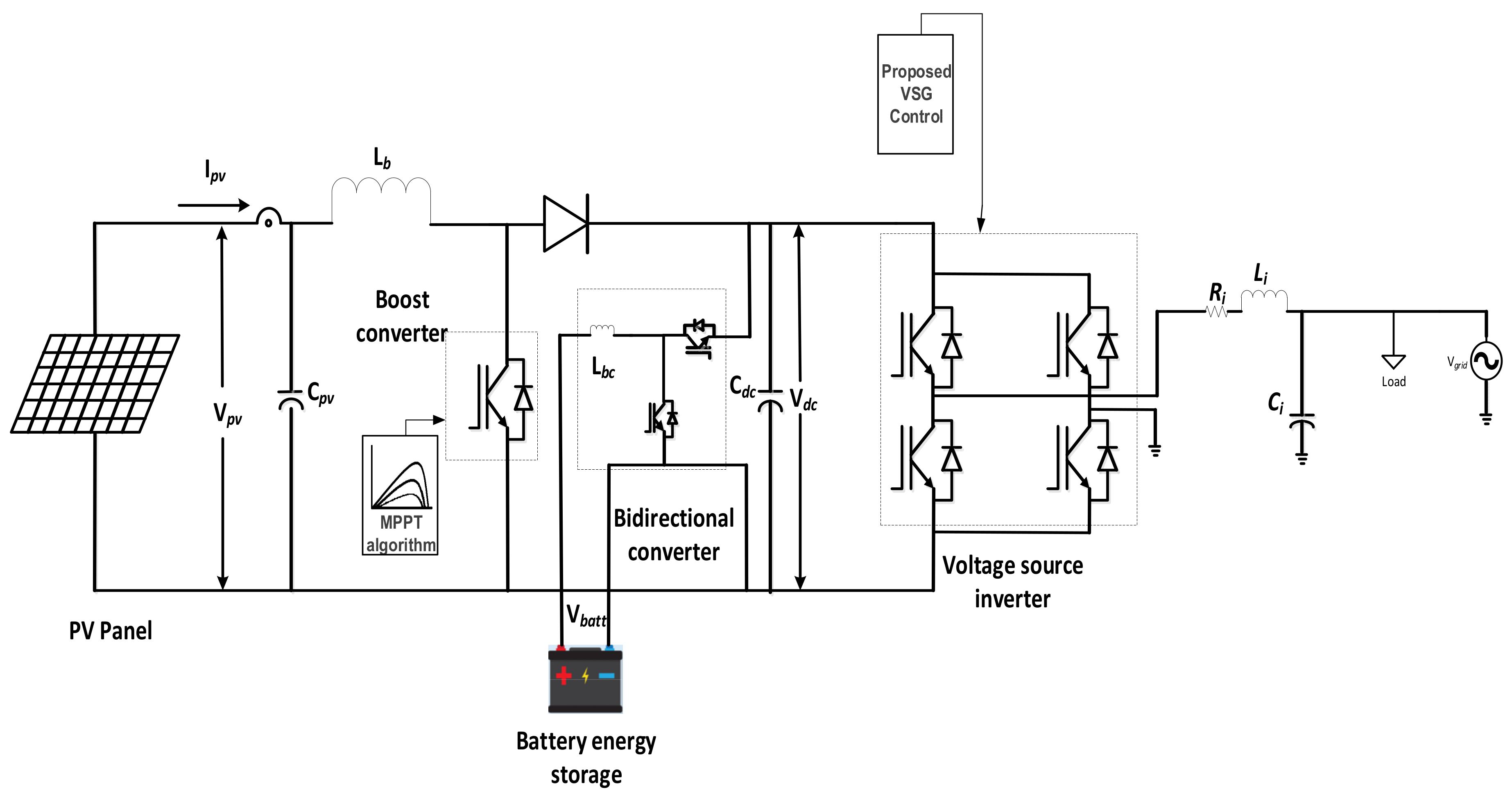
2. Smart Multifunctional Domestic Solar PV System
3. System Modelling
3.1. PV, MPPT, and DC Link Control
3.2. Single-Phase Inverter
3.3. Battery-Energy-Storage System
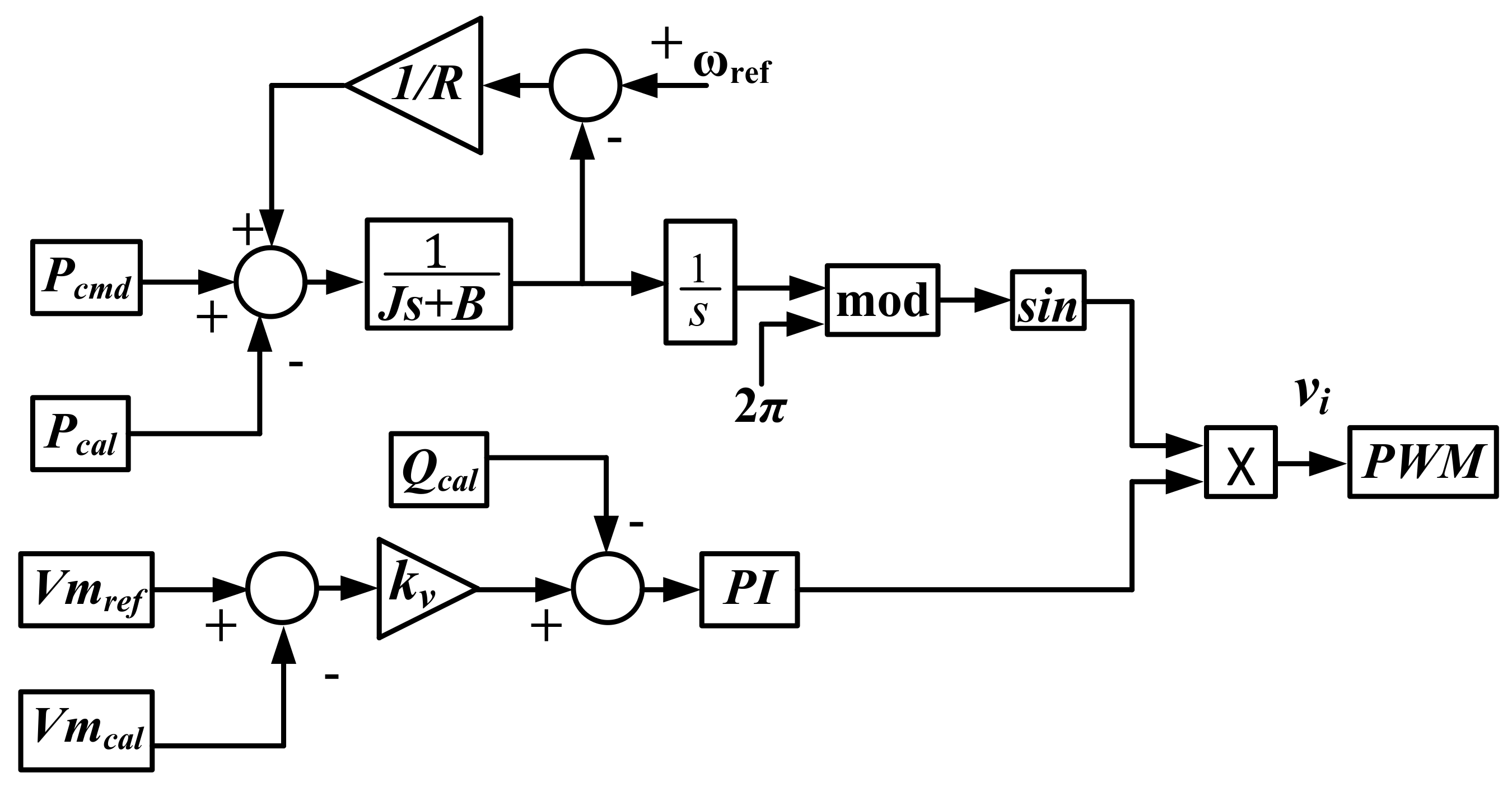
4. Control Schematic and Design
- ➢
- Real and reactive power control in both modes of operation, following the standards and making the static source to behave like a rotating synchronous generator.
- ➢
- Supply frequency and voltage support during abnormal conditions.
- ➢
- Meeting the power commands under varying insolation conditions.
4.1. Active Power Control Loop
4.2. PCC Voltage Control
4.3. System Stability
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. VSG Operation and Frequency Support
5.2. Set Point Change to Active Power
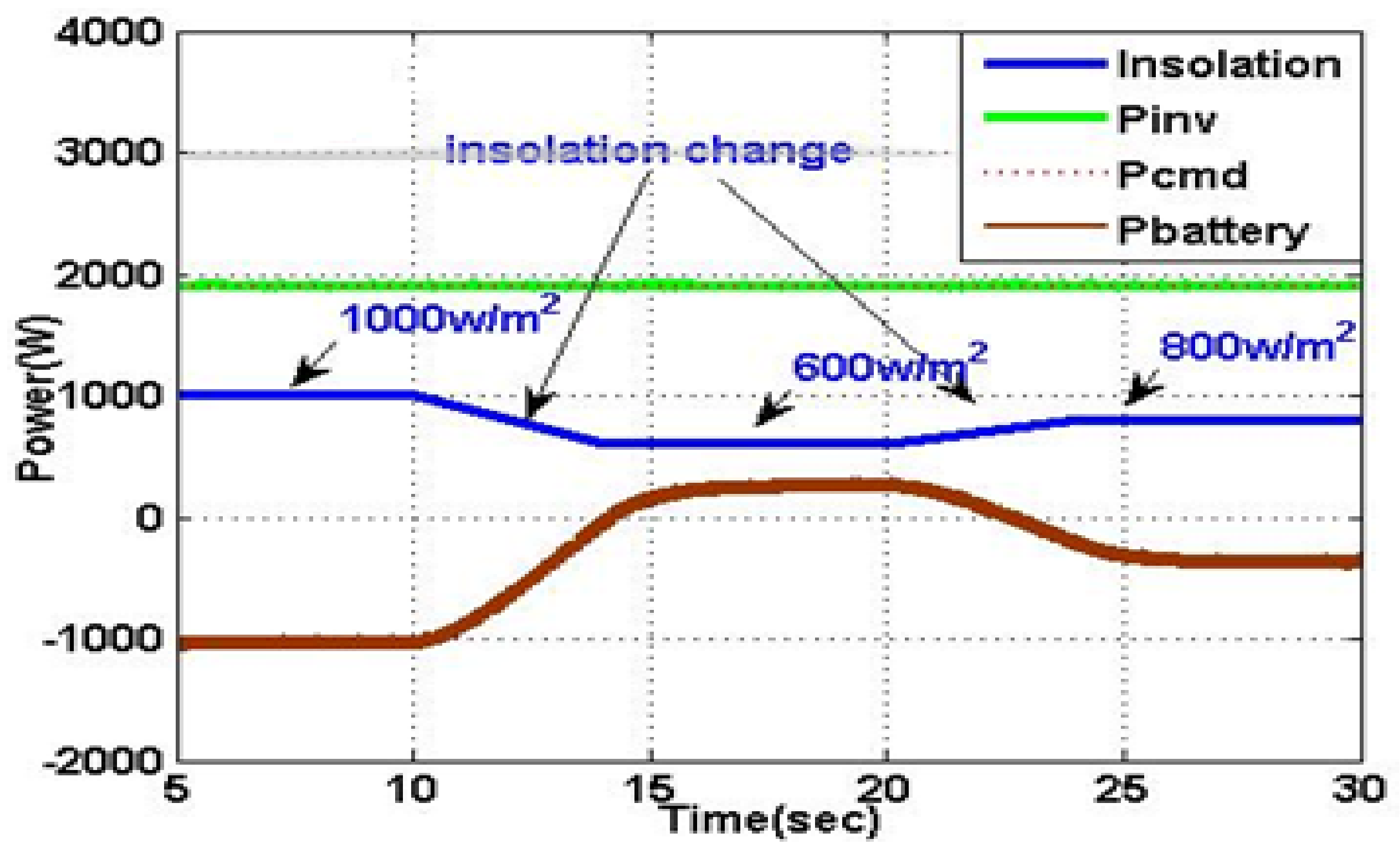
5.3. Insolation Changes
5.4. Voltage Support
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| VSG | Virtual Synchronous Generatorsynchronous generator |
| PI | Proportional Integralintegral |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimizationswarm optimization |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| PLL | Phase Locked Loop-locked loop |
| MPPT | Maximum Power Point Trackingpower point tracking |
| INC | Incremental Conductanceconductance |
| Ni-Cad | Nickel Cadmiumcadmium |
| SOGI | Second Order Generalized Integrator-order generalized integrator |
| PCC | Point of Common Couplingcommon coupling |
| MPP | Maximum Power Pointpower point |
References
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Renewable Energy Statistics 2019; Technical Reports; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-92-9260-137-9. [Google Scholar]
- A Report on. Off-Grid and Decentralized Solar Application Scheme: Operational Guidelines for Grid Connected Rooftop and Small Solar Power Plants Programme; Government of India, Ministry of New & Renewable Energy: New Delhi, India, 2014.
- IEEE Standard Committee. IEEE Standard for Interconnection and Interoperability of Distributed Energy Resources with Associated Electric Power Systems Interfaces; IEEE Std. 1547-2018 (Revision of IEEE Std. 1547-2003); Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Recommended Practices and Requirement for Harmonic Control on Electric Power System; IEEE Std 519; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993.
- IEEE Standard Committee. IEEE Standard for Interconnecting Distributed Resources with Electric Power Systems; IEEE Std. 1547; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- International Electro Technical Commission (IEC). Characteristics of the Utility Interface for Photovoltaic (PV) Systems; IEC 61727; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ciobotaru, M.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F. Control of Single-Stage Single-Phase PV Inverter. EPE J. 2006, 16, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Rodriguez, P. Grid Converters for Photovoltaic and Wind Power System; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Malesani, L. Current control techniques for three-phase voltage-source PWM converters: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1998, 45, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyanarayanan, T.; Mishra, S. Performance of FCS-MPC based current controller for VSC based DG sources. In Proceedings of the 20th National Power Systems Conference (NPSC), Tiruchirappalli, India, 14 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzid, A.M.; Guerrero, J.M.; Cheriti, A.; Bouhamida, M.; Sicard, P.; Benghanem, M. A survey on control of electric power distributed generation systems for Microgrid applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Timbus, A.V. Overview of control and grid synchronization for distributed power generation systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, C. Topologies and control strategies of multi-functional grid-connected inverters for power quality enhancement: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 223–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, Y.M. PV power system with multi-mode operation and low-voltage ride-through capability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7524–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Singh, B. Single-phase single-stage multifunctional grid interfaced solar photo-voltaic system under abnormal grid conditions. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2015, 9, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Singh, B. An Adjustable DC Link Voltage Based Control of Multifunctional Grid Interfaced Solar PV System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 5, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kim, K.A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Sangwongwanich, A. Advances in Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Power Conversion Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arab, N.; Kedjar, B.; Javadi, A.; Al-Haddad, K. A Multifunctional Single-Phase Grid-Integrated Residential Solar PV Systems Based on LQR Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Ray, P.K.; Korkua, S.K.; Mishra, S.; Puhan, P.S. Development of PV tied UPQC using PSO based PI tuning Controller based on SOI-QSG PLL. In Proceedings of the IEEE First International Conference on Smart Technologies for Power, Energy and Control (STPEC), Nagpur, India, 25–26 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alluhaybi, K.; Batarseh, I.; Hu, H. Comprehensive Review and Comparison of Single-Phase Grid-Tied Photovoltaic Micro inverters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 1310–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardhi, P.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Chandra, A. Control of Single-Phase Solar Photovoltaic Supply System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 7132–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheepanchakkravarthy, A.; Jawahar, M.R.; Venkatraman, K.; Selvan, M.P.; Moorthi, S. Performance evaluation of FPGA-based predictive current controller for FL-DSTATCOM in electric distribution system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 4400–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.Y.M.; Jalilian, A.; Savaghebi, M.; Josep, M. Guerrero, coordinated control of multifunctional inverters for voltage support and harmonic compensation in a grid-connected microgrid. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 155, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.K.; Gali, V. Development of Modified Hysteresis Current Controller Switching Scheme for Multifunctional Grid-tied Photovoltaic Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Power Electronics and Energy (ICPEE), Bhubaneswar, India, 2–3 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, M.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M.; Aamir, M. Selective harmonic elimination in inverters using bio-inspired intelligent algorithms for renewable energy conversion applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2235–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, I.; Vázquez, N.; Vaquero, J.; Vázquez, J.; Hernández, C.; López, H. Multifunctional grid-connected photovoltaic-system controlled by sliding mode. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015-41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gali, V.; Varaprasad, M.V.G.; Gupta, S.K.; Gupta, M. Performance investigation of multifunctional grid connected PV interleaved inverter with power quality enhancement. Energy Syst. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranith, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, B.; Bhatti, T.S. Multimode operation of PV-battery system with renewable intermittency smoothening and enhanced power quality. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 13, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdphol, T.; Rahman, F.S.; Mitani, Y. Virtual Inertia Control Application to Enhance Frequency Stability of Interconnected Power Systems with High Renewable Energy Penetration. Energies 2018, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumder, R.; Shahnia, F.; Ghosh, A.; Ledwich, G.; Wishart, M.; Zare, F. Operation and control of a microgrid containing inertial and non-inertial micro sources. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2009-2009 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Singapore, 23–26 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Im, W.-S.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Kim, J.-M. Distributed virtual inertia based control of multiple photovoltaic systems in autonomous microgrid. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2016, 4, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.T.; Kirschen, D.S. Impact on the Power System of a Large Penetration of Photovoltaic Generation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Eftekharnejad, S.; Vittal, V.; Heydt, G.T.; Keel, B.; Loehr, J. Impact of increased penetration of photovoltaic generation on power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 28, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Ramasubramanian, D.; Sekhar, P.C. A Seamless Control Methodology for a Grid Connected and Isolated PV-Diesel Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4393–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Component | Specified Value |
|---|---|
| Voc of the solar module | 37.3 V |
| Isc of the solar module | 8.2 A |
| VMPP of the solar module | 30.3 V |
| Number of series modules, Ns | 15 |
| Number of parallel modules, Np | 1 |
| DC voltage, Vdc | 400 V |
| Maximum power point, PMPP | 3000 W |
| AC voltage, Vac | 230 V, 50 Hz |
| Time, Command Change | Ppv and Pbat | Pinv |
|---|---|---|
| t = 5–8 s, constant Pcmd | 3000 W and 1000 W charging | 2000 W |
| t = 8–14 s, ramp down Pcmd | 3000 W and ramp up of charging power for battery from 1000 to 1500 W | 2000–1500 W ramp down |
| t = 14 s, step change in Pcmd | 3000 W and change in battery power from 1500 to 300 W | 1500 to 2700 W change (and small overshoot) |
| t = 22 s, ramp down Pcmd | 3000 W and change in battery power from 300 W to 500 W charging | Ramp down from 2700 W to 2500 W |
| Time, Command Change | Ppv and Pbat | Pinv |
|---|---|---|
| t = 5–10 s, constant insolation | 3000 W and 1000 W charging | 2000 W |
| t = 10–14 s, ramp down insolation | Ppv ramp down from 3 kW to 1.7 kW and Pbatt from 1000 W charging to 300 W discharging | 2000 W |
| t = 14–20 s, constant insolation | Ppv 1.7 kW and Pbat 300 W | 2000 W |
| t = 20–24 s, ramp up insolation | Ppv 1.7 kW to 2.4 kW and Pbat 300 W discharging to 400 W charging | 2000 W |
| t = 24–30 s, constant insolation | Ppv 2.4 kW and Pbat 400 W charging | 2000 W |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandrasekaran, K.; Sahayam, J.J.; Thanasingh, S.J.S.D.; Ramalingam, S.; Fayek, H.H.; Ravichandran, N.; Rusu, E. Performance of Multifunctional Smart PV-Based Domestic Distributed Generator in Dual-Mode Operation. Machines 2021, 9, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120356
Chandrasekaran K, Sahayam JJ, Thanasingh SJSD, Ramalingam S, Fayek HH, Ravichandran N, Rusu E. Performance of Multifunctional Smart PV-Based Domestic Distributed Generator in Dual-Mode Operation. Machines. 2021; 9(12):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120356
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandrasekaran, Kumar, Jasper John Sahayam, Sundarsingh Jebaseelan Somasundaram David Thanasingh, Sripriya Ramalingam, Hady H. Fayek, Nagananthini Ravichandran, and Eugen Rusu. 2021. "Performance of Multifunctional Smart PV-Based Domestic Distributed Generator in Dual-Mode Operation" Machines 9, no. 12: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120356
APA StyleChandrasekaran, K., Sahayam, J. J., Thanasingh, S. J. S. D., Ramalingam, S., Fayek, H. H., Ravichandran, N., & Rusu, E. (2021). Performance of Multifunctional Smart PV-Based Domestic Distributed Generator in Dual-Mode Operation. Machines, 9(12), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120356








