Optimization and Control of a Planar Three Degrees of Freedom Manipulator with Cable Actuation
Abstract
1. Introduction
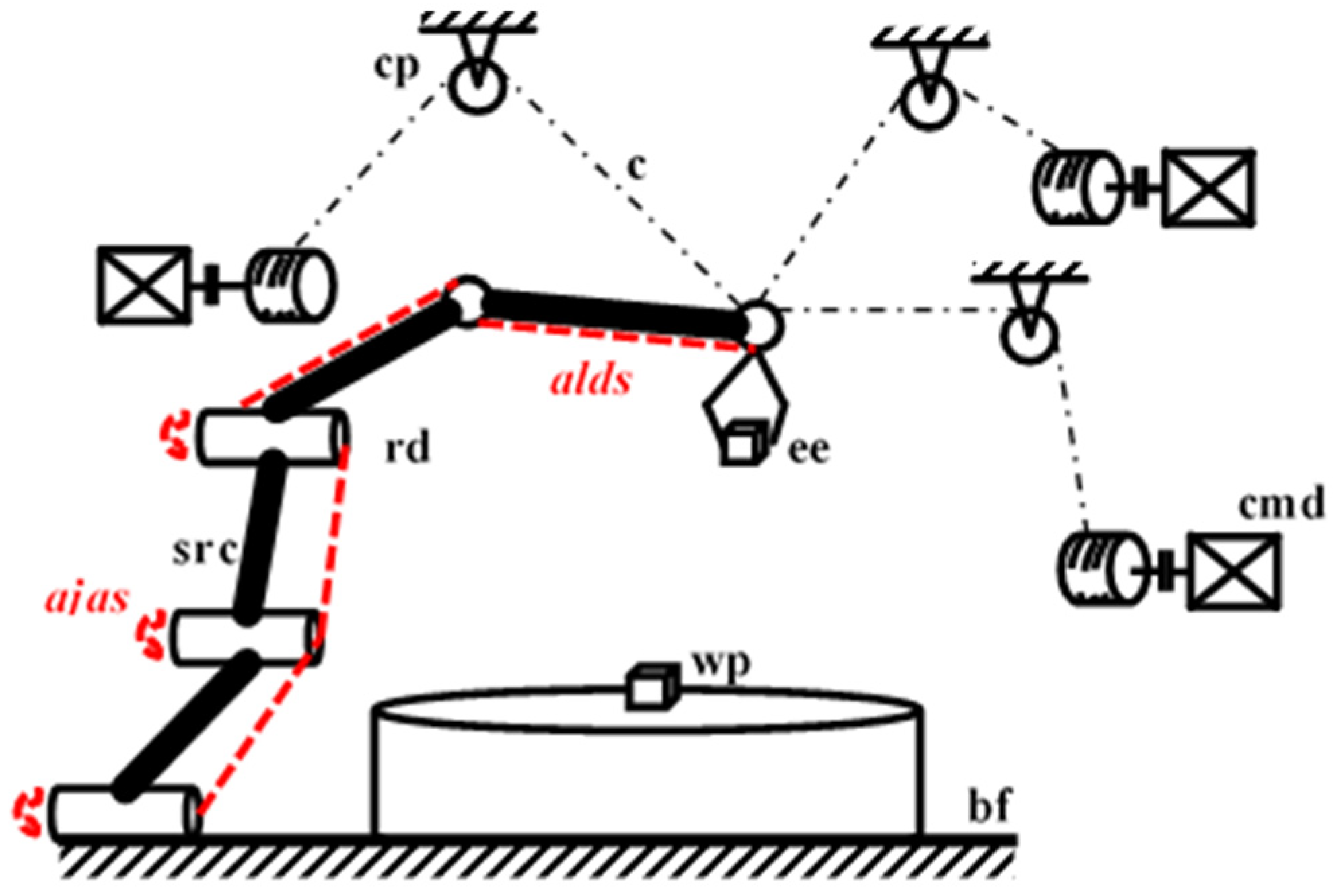
2. Design of the Cable-Driven Manipulator
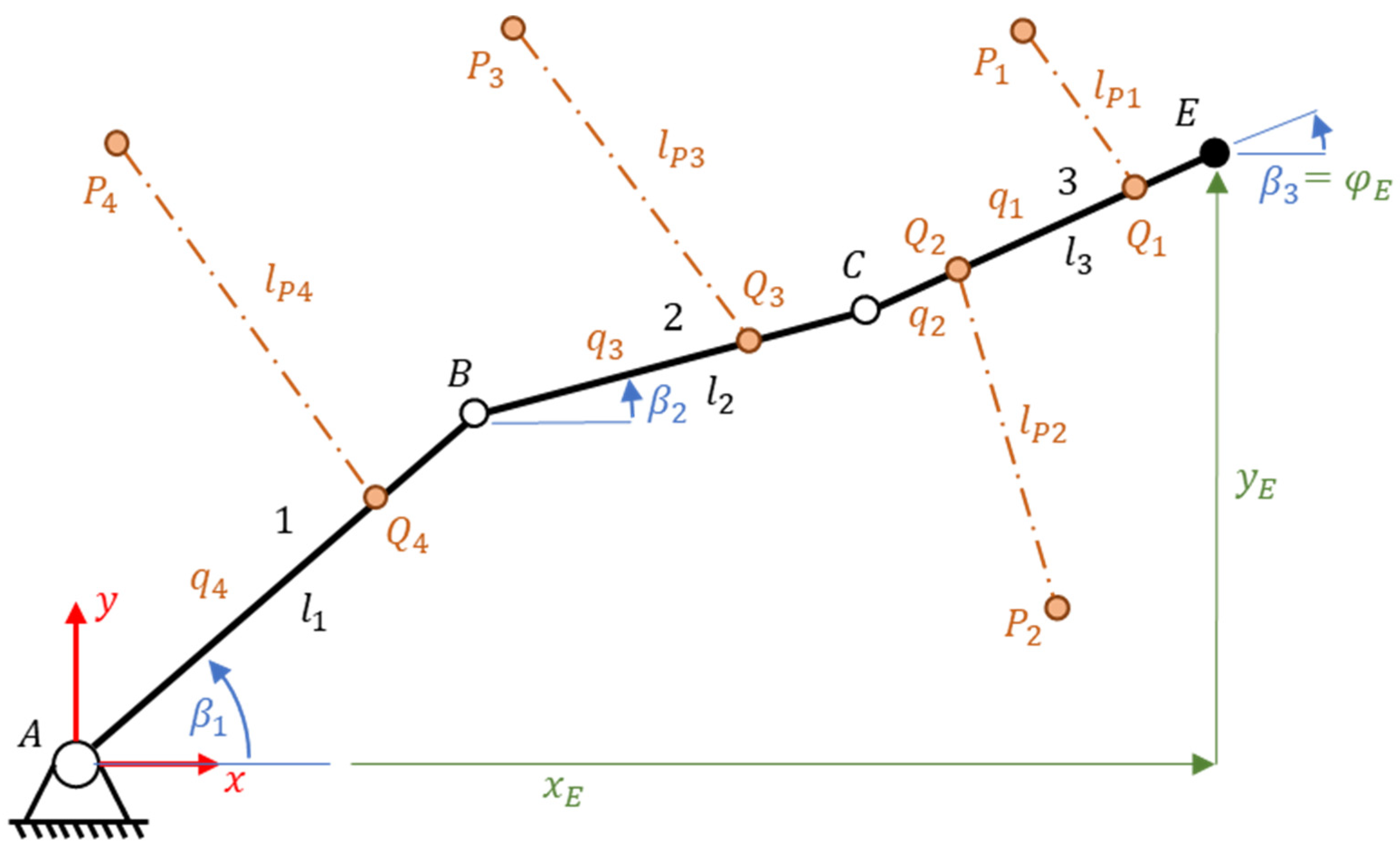
2.1. Three Degrees of Freedom Planar Manipulator
- Absolute angle of every link: , , control algorithm
- Absolute angle and position of the end-effector: optimization algorithm
2.2. Number of Cables of the Manipulator
2.3. Cable Placement/Connection with Serial Structure
2.4. Cables Tension and Force Distribution
- For any dimension of the vector of unknown the pseudoinversion of the matrix of the solution is calculated in the sense of minimizing the Euclidean norm .
- If the matrix has dependent columns (more unknowns than equations), then the pseudoinversion determines the solution in the sense of minimizing the Euclidean norm .
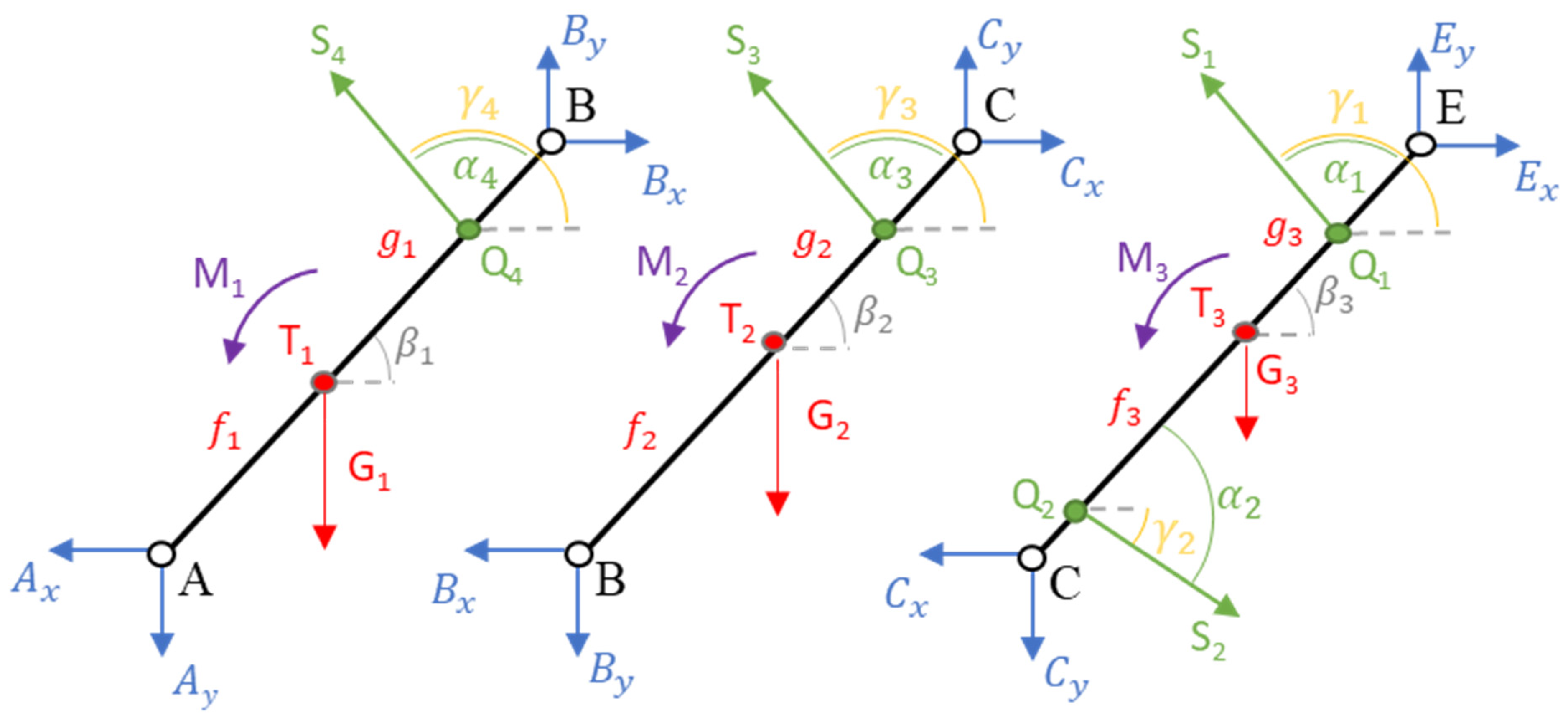
3. Dynamic Model of the Manipulator
- Vector method (constraints between dependent and independent coordinates)
- Newton–Euler dynamics Equations
- Accelerations of mass centers of each link
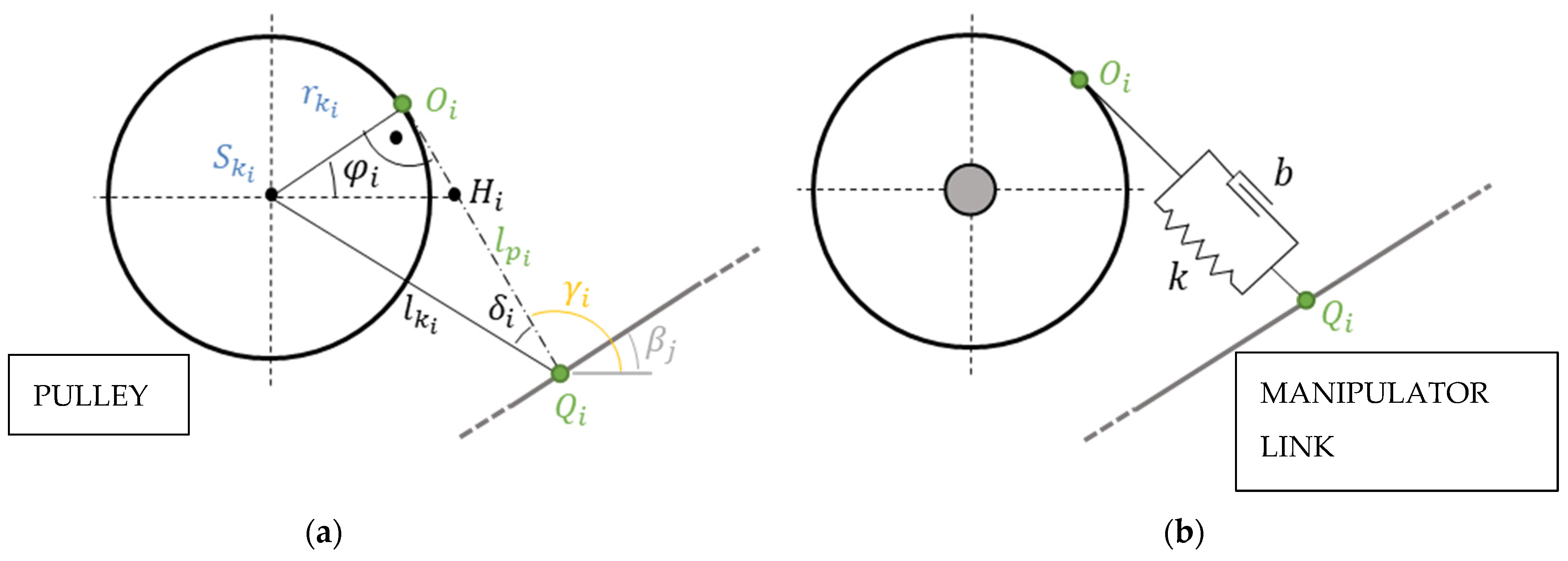
3.1. Geometrical Extension for a Pulley
3.2. Extensible Cable Model with Pulley
4. Optimization of the Manipulator Structure
4.1. Optimization Parameters
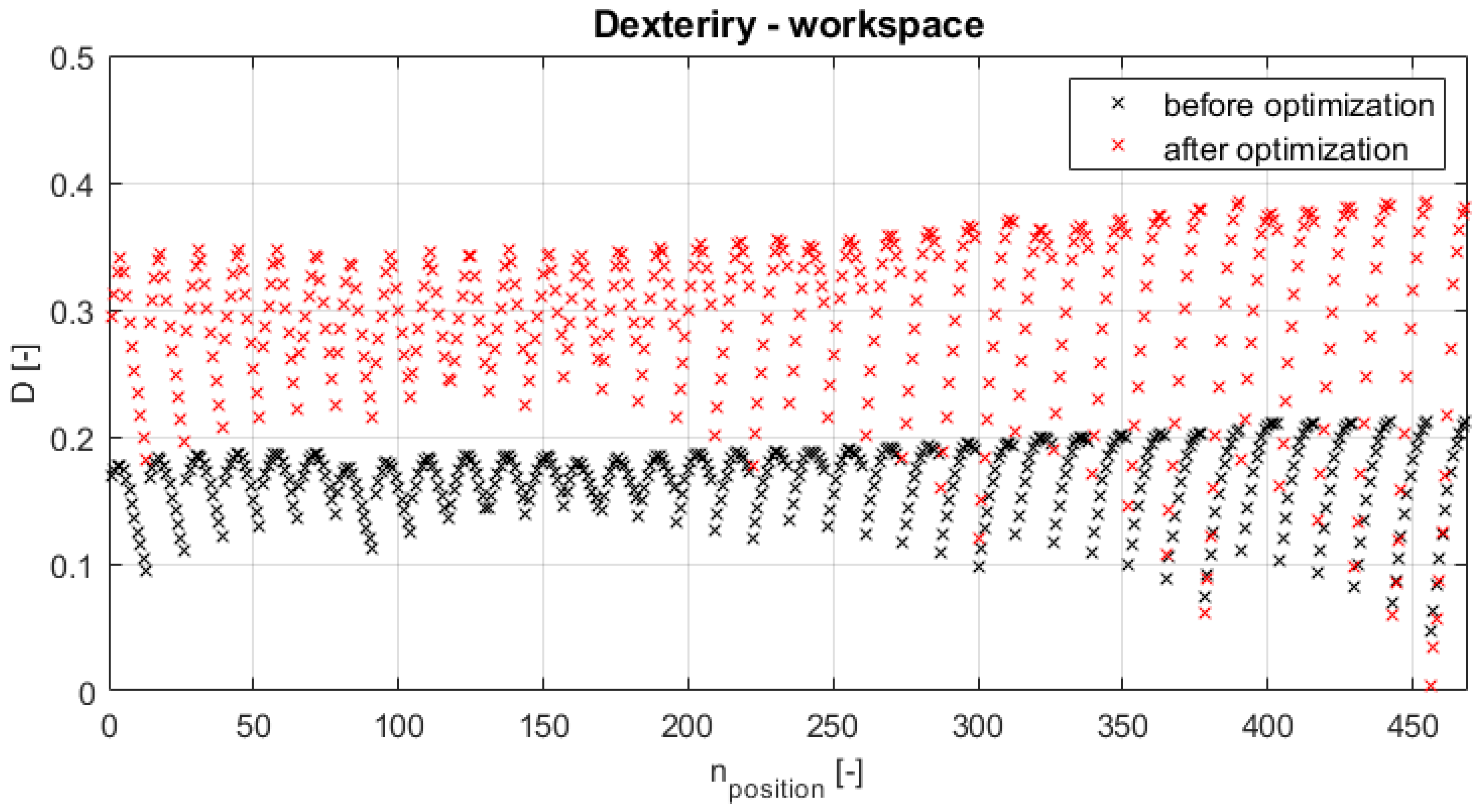
4.2. Workspace
4.3. Cost Function (CF)
4.3.1. –Dexterity
4.3.2. –Uniform Distribution of Dexterity
4.3.3. –The Ratio of the Workspace to the Built-Up Manipulator Space
4.3.4. and Normalization and Scaling
4.4. Optimization Results
5. Control Algorithm
5.1. Computed Torque Control
5.2. Inverse Dynamics
5.3. Wrenchian
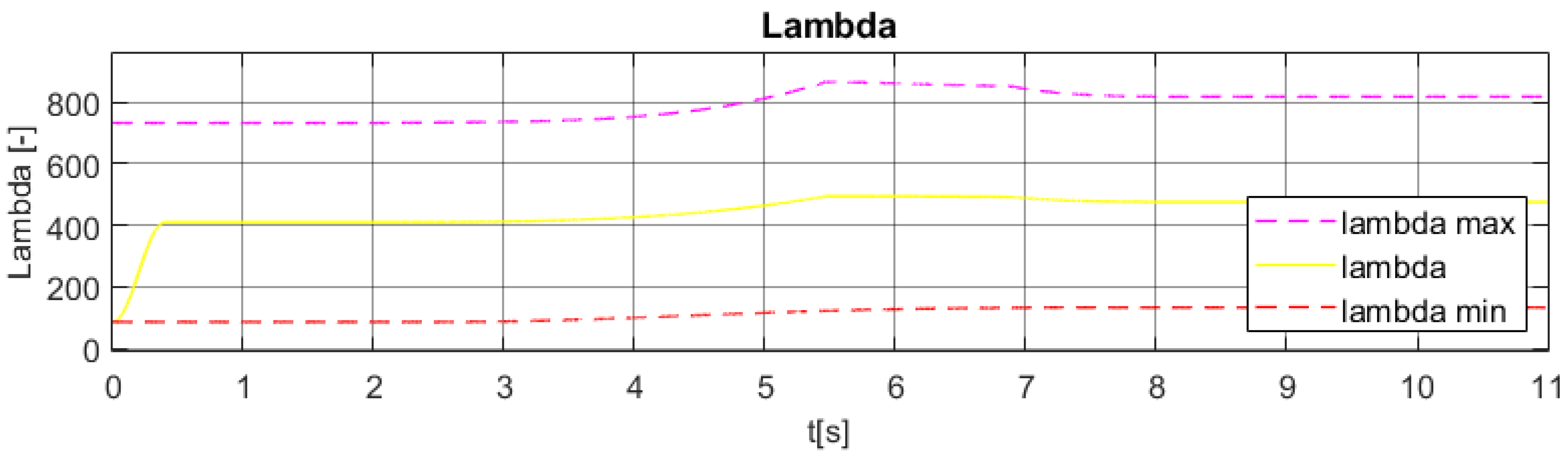
5.4. Cable Force Distribution
SVD Decomposition
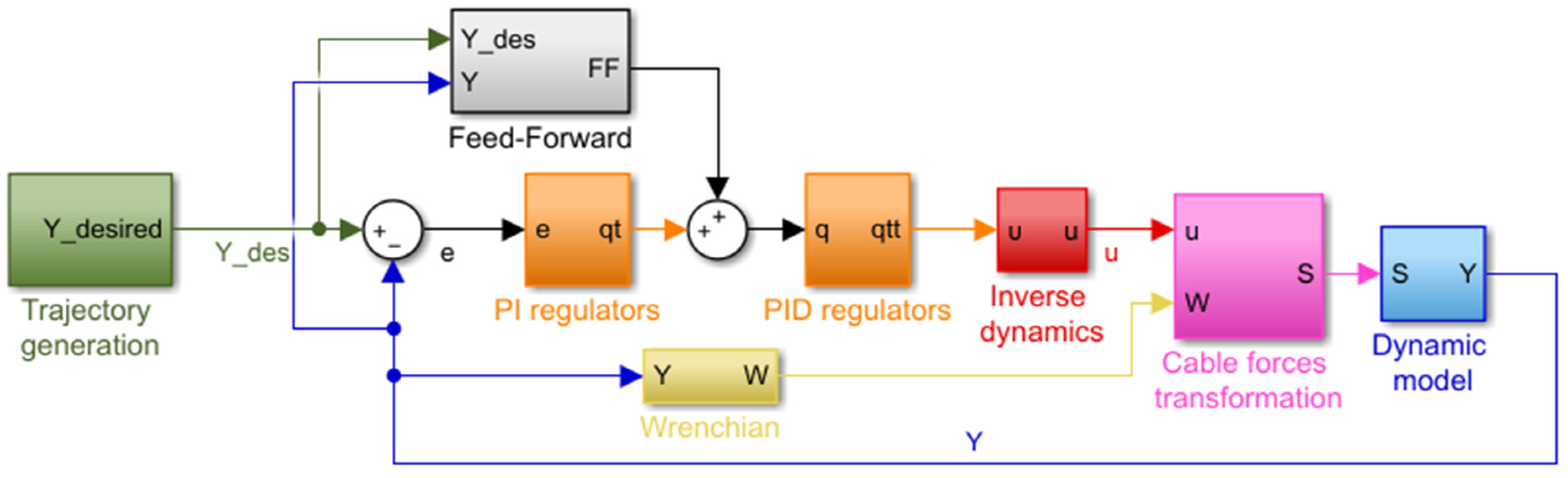
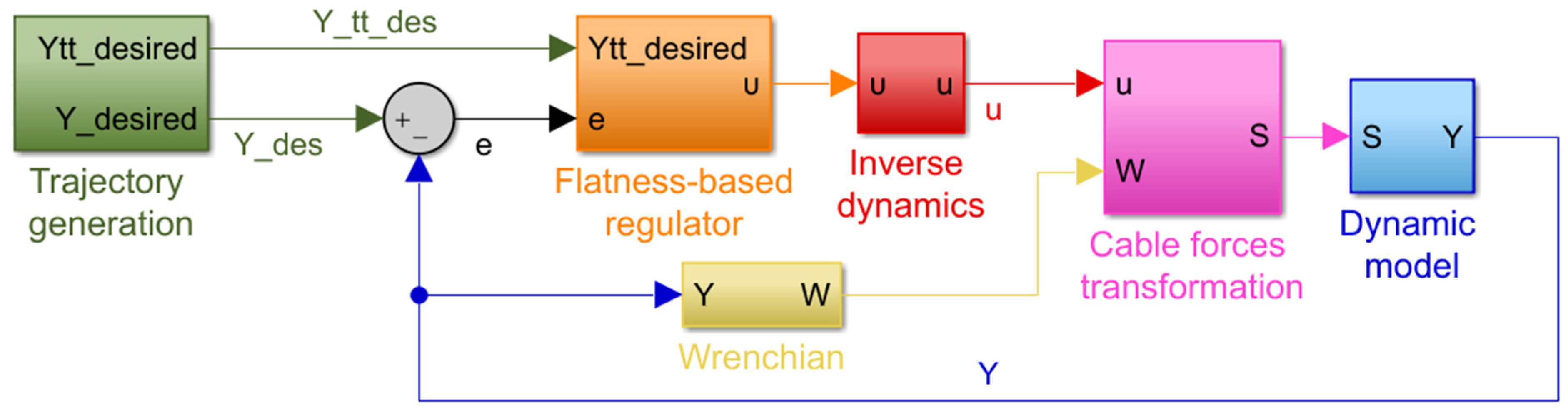
5.5. Two Different Regulators
5.5.1. PI and PID Cascade with Feed-Forward (FF)
5.5.2. Flatness Based Regulator
- All the coefficients of the equation should have the same sign
- There should be no missing term
5.6. Trajectory Generation
6. Simulation Testing
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vahrenkamp, N.; Asfour, T. Representing the robot’s workspace through constrained manipulability analysis. Auton. Robot. 2015, 38, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volech, J.; Mráz, L.; Šika, Z.; Valášek, M. Model of Flexible Robot with Deformation Detection. Procedia Eng. 2014, 96, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fareh, R.; Saad, M.; Saad, M. Distributed control strategy for flexible link manipulators. Robotica 2014, 33, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, R.; Oliveira, M. Tensegrity Systems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- SunSpiral, V.; Agogino, A.; Atkinson, D. Super Ball Bot-Structures for Planetery Landing and Exploration for NASA Innovation Advanced Concepts (NIAC) Program; NASA Ames Research Center: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fadeyev, D.; Zhakatayev, A.; Kuzdeuov, A.; Varol, H.A. Generalized Dynamics of Stacked Tensegrity Manipulators. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63472–63484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, J.B.; Skelton, R.E. Backlash-free motion control of robotic manipulators driven by tensegrity motor networks. In Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–15 December 2006; pp. 2300–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Svatoš, P.; Šika, Z.; Valášek, M.; Zicha, J.; Bauma, V.; Rada, V. Fiber Driven Tilting Mechanism. In The Latest Methods of Construction Design; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Valášek, M.; Karásek, M. HexaSphere with Cable Actuation. In Recent Advances in Mechatronics; Springer: Singapore, 2010; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Skopec, T.; Šika, Z.; Valášek, M. Calibration using adaptive model complexity for parallel and fiber-driven mechanisms. Robot. 2016, 34, 1416–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, F.; Mishra, A.K.; Naselli, G.A.; Mazzolai, B. Simplified Sensing and Control of a Plant-Inspired Cable Driven Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Korea, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, S.; Yang, G.; Lim, W. Design and analysis of cable-driven manipulators with variable stiffness. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 69, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Hufnagel, T. Model-based control of redundantly actuated parallel manipulators in redundant coordinates. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2012, 60, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, X.; Cuvillon, L.; Gangloff, J. Active vibration canceling of a cable-driven parallel robot in modal space. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1599–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.-J. Flexible robot manipulator path design to reduce the endpoint residual vibration under torque constraints. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 275, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preumont, A. Mechatronics: Dynamics of Electromechanical and Piezoelectric Systems; Springer: Dordrech, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Z.; Liu, T.; Xu, W.; Lou, Y.; Liang, B. Dynamic feedforward control of spatial cable-driven hyper-redundant manipulatorsfor on-orbit servicing. Robotica 2019, 37, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlet, J.-P. On the Redundancy of Cable-Driven Parallel Robots; Springer: Singapore, 2015; pp. 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Merlet, J.-P. The kinematics of cable-driven parallel robots with sagging cables: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1593–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Carricato, M.; Merlet, J.-P. Stability Analysis of Underconstrained Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 29, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouttefarde, M.; Lamaury, J.; Reichert, C.; Bruckmann, T. A Versatile Tension Distribution Algorithm for n -DOF Parallel Robots Driven by n+2 Cables. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, K. Redundant Cable Manipulator. Master’s Thesis, Prague, Czech Republic, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brdička, M.; Hladík, A. Theoretical Mechanics; Academia: Prague, Czech Republic, 1987. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Lederer, P. Theory and Optimization of Mechanical Systems II; Editorial Centre CTU: Prague, Czech Republic, 1988. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Lederer, P. Theory and Optimization of Mechanical Systems I; Editorial Centre CTU: Prague, Czech Republic, 1987. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Hynek, J. Genetic Algorithms and Genetic Programming; Grada Publishing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2008. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, O. Genetic Algorithm Essentials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 679. [Google Scholar]
- Elisha, D.; John, T.; Adisa, A. Flat control of industrial robotic manipulators. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 87, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Rouchon, P.; Murray, M.; Matin, P. Flat Systems, Equivalence and Trajectory Generation. Available online: http://www.cds.caltech.edu/~murray/preprints/mmr03-cds.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Craig, J.J. Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control; Englewood Cliffs: Bergen, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rigatos, G.G. Nonlinear Control and Filtering Using Differential Flatness Approaches. Stud. Syst. Decis. Control. 2015, 25, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Peña, J.M. Characterizations and stable testsfor the Routh–Hurwitz conditionsand for total positivity. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2004, 393, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


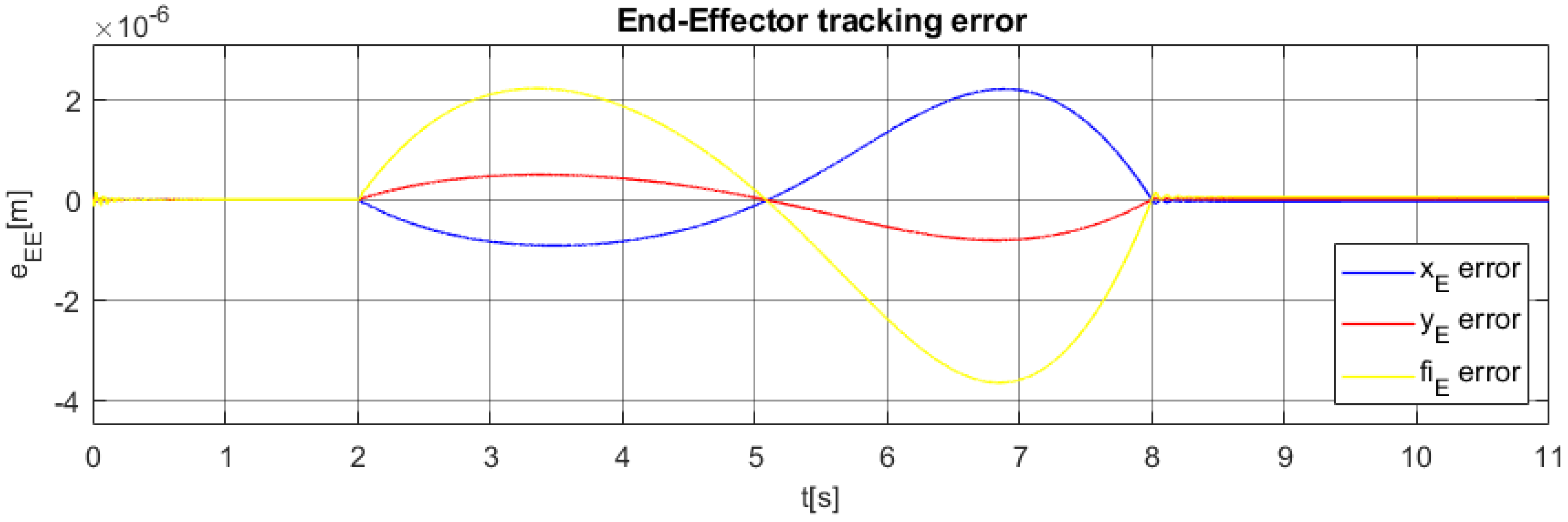
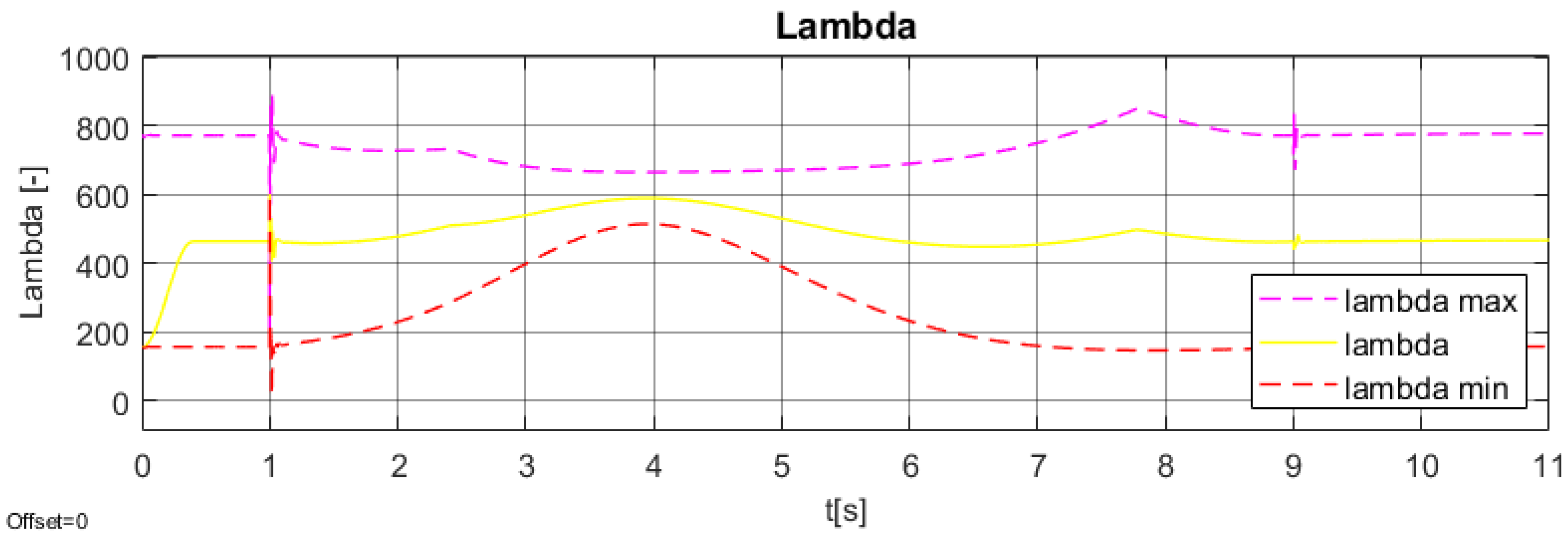
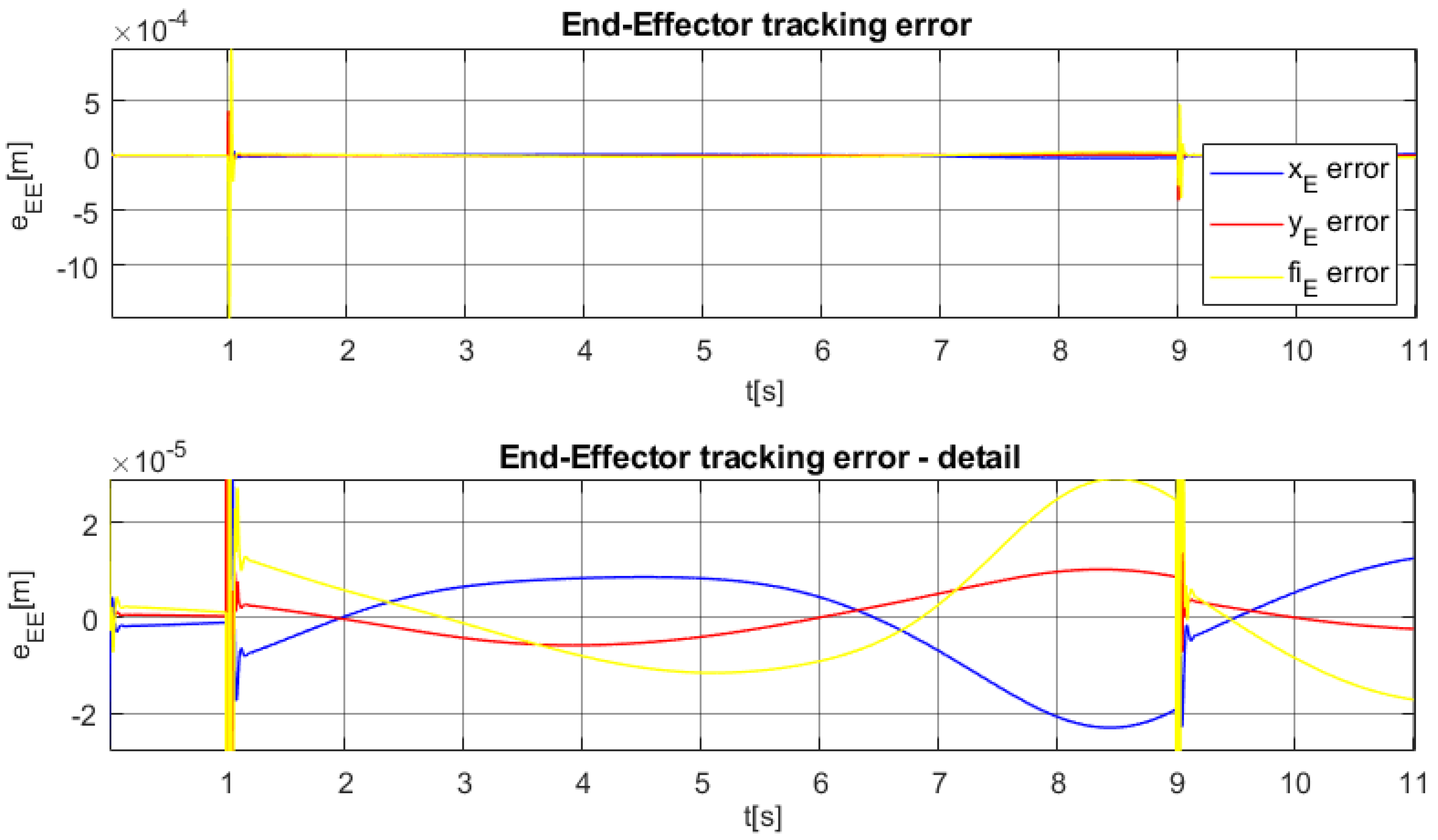
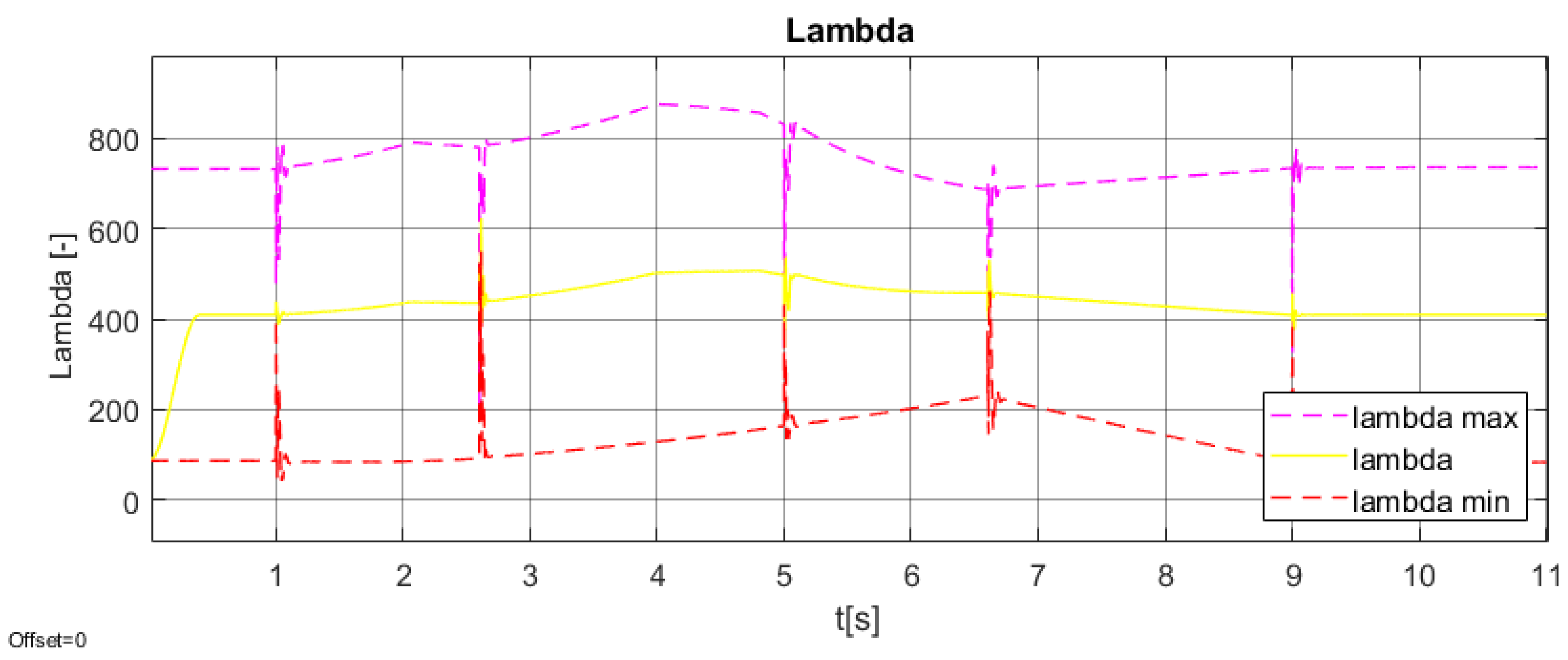
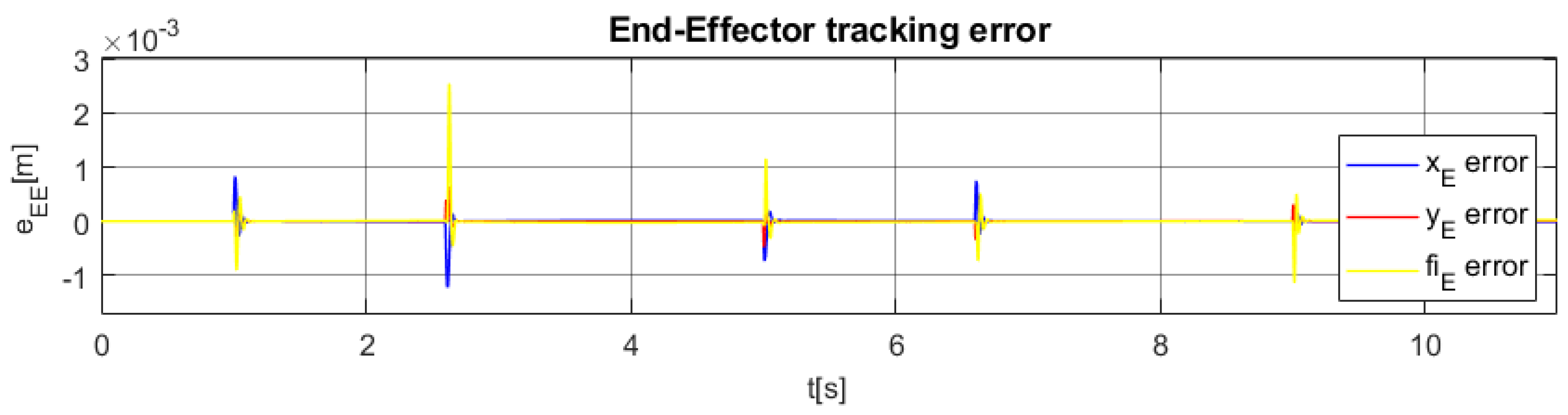
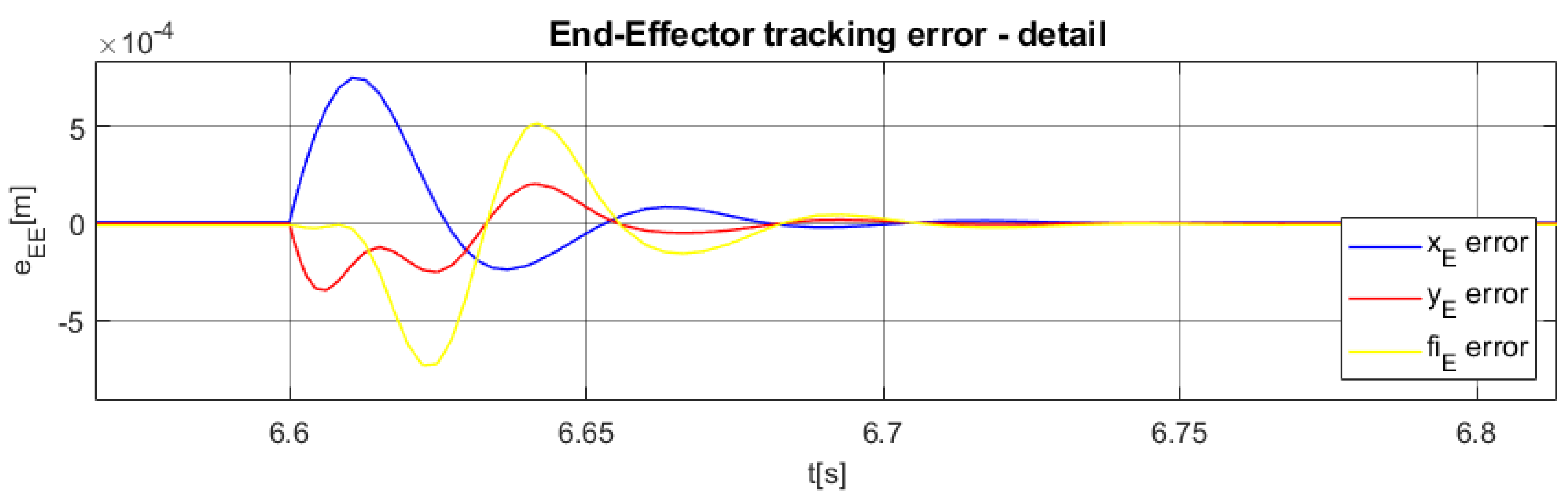
| Index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interval | Interval | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| before | |||
| after |
| Parameter | Optim. Value | Parameter | Optim. Value | Parameter | Optim. Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (m) | (m) | |||
| (m) | (m) | (-) | |||
| (m) | (m) | (-) | |||
| (m) | (m) | (-) | |||
| (m) | (m) | (-) |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg) | (kg·m2) | (N/m) | |||
| (kg) | (kg·m2) | (-) | |||
| (kg) | (kg·m2) | (N·s/m) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krivošej, J.; Šika, Z. Optimization and Control of a Planar Three Degrees of Freedom Manipulator with Cable Actuation. Machines 2021, 9, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120338
Krivošej J, Šika Z. Optimization and Control of a Planar Three Degrees of Freedom Manipulator with Cable Actuation. Machines. 2021; 9(12):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120338
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrivošej, Jan, and Zbyněk Šika. 2021. "Optimization and Control of a Planar Three Degrees of Freedom Manipulator with Cable Actuation" Machines 9, no. 12: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120338
APA StyleKrivošej, J., & Šika, Z. (2021). Optimization and Control of a Planar Three Degrees of Freedom Manipulator with Cable Actuation. Machines, 9(12), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120338







