Lubrication Mechanism and Establishment of a Three-Phase Lubrication Model for SCCO2-MQL Ultrasonic Vibration Milling of SiCp/Al Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lubrication Mechanism of SCCO2-MQL
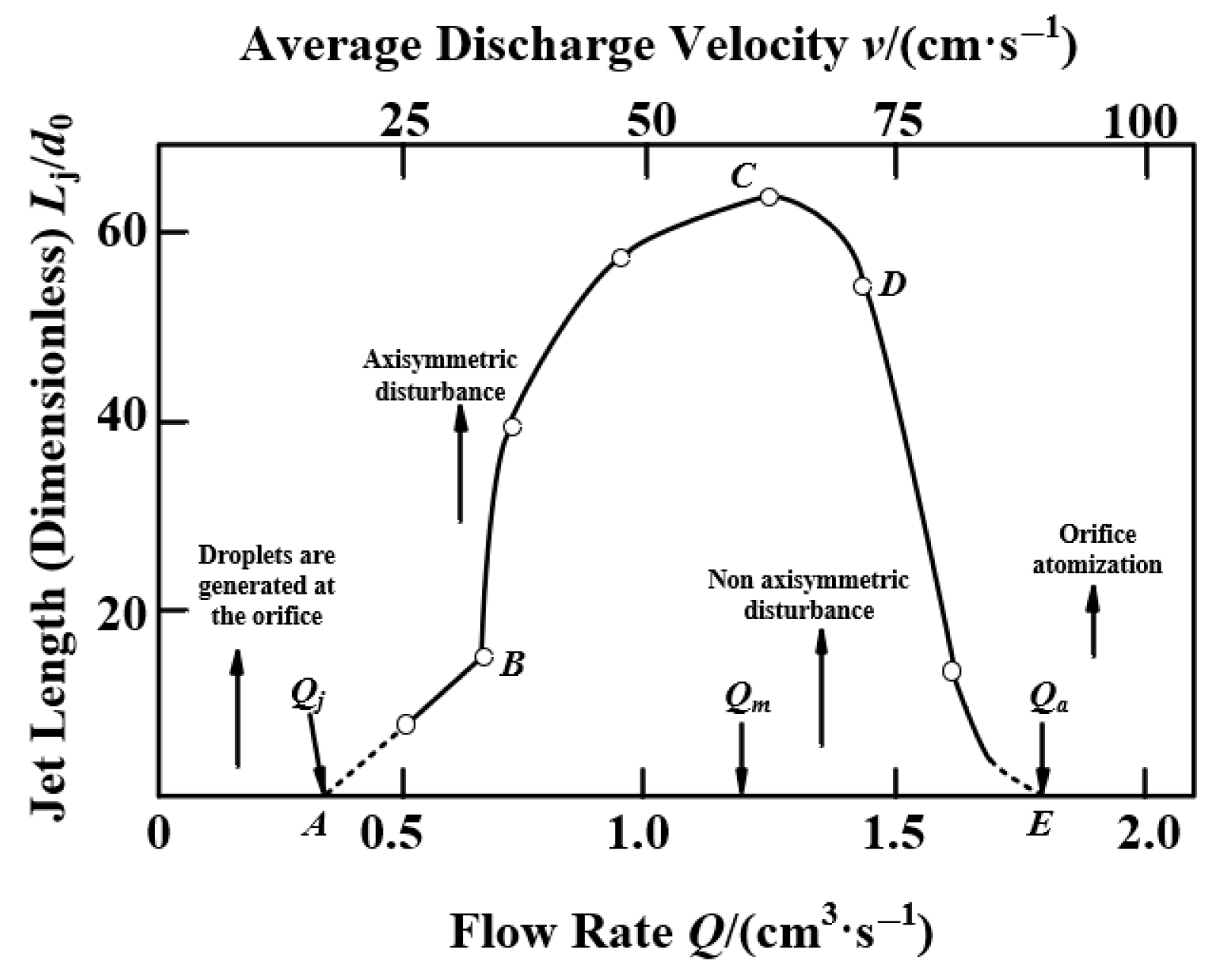
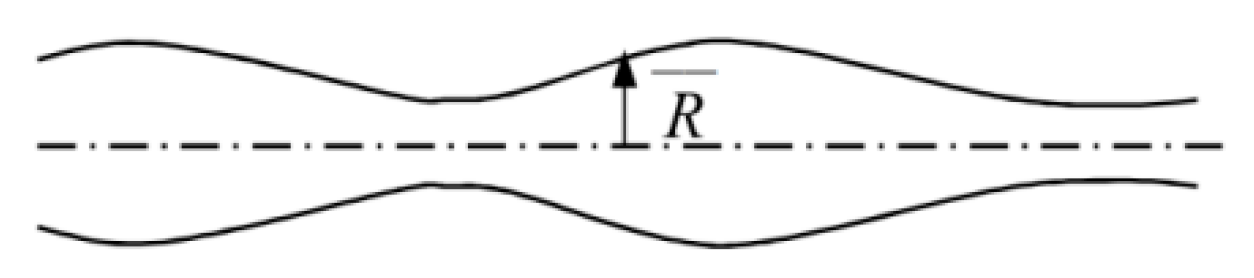
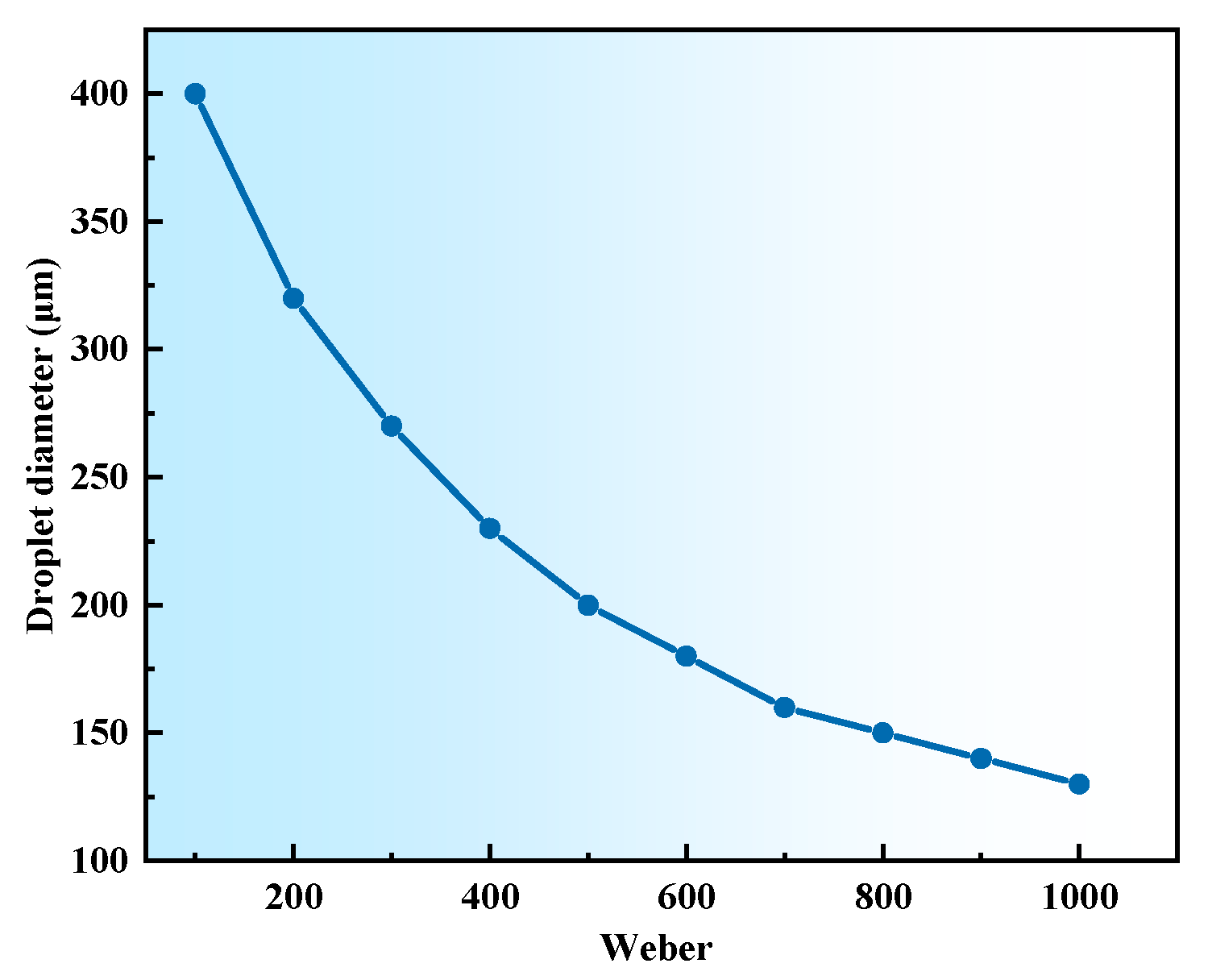
2.1. Liquid Atomization Mechanism
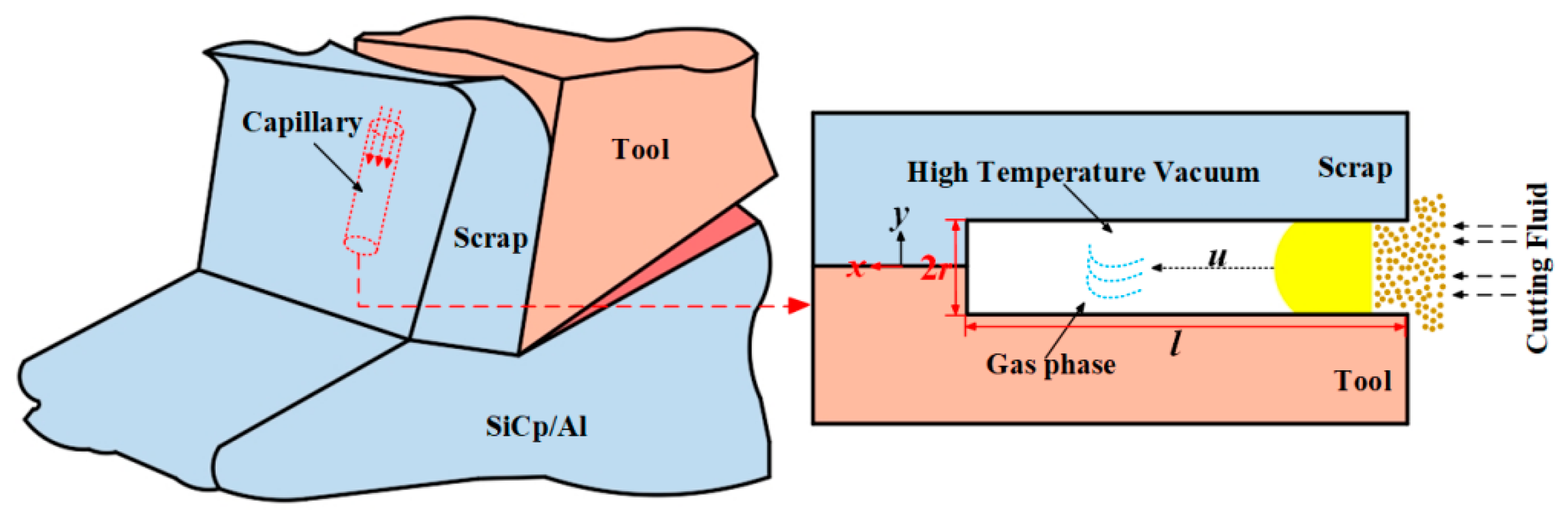
2.2. Capillary Infiltration Dynamics
2.3. Boundary Layer Theory
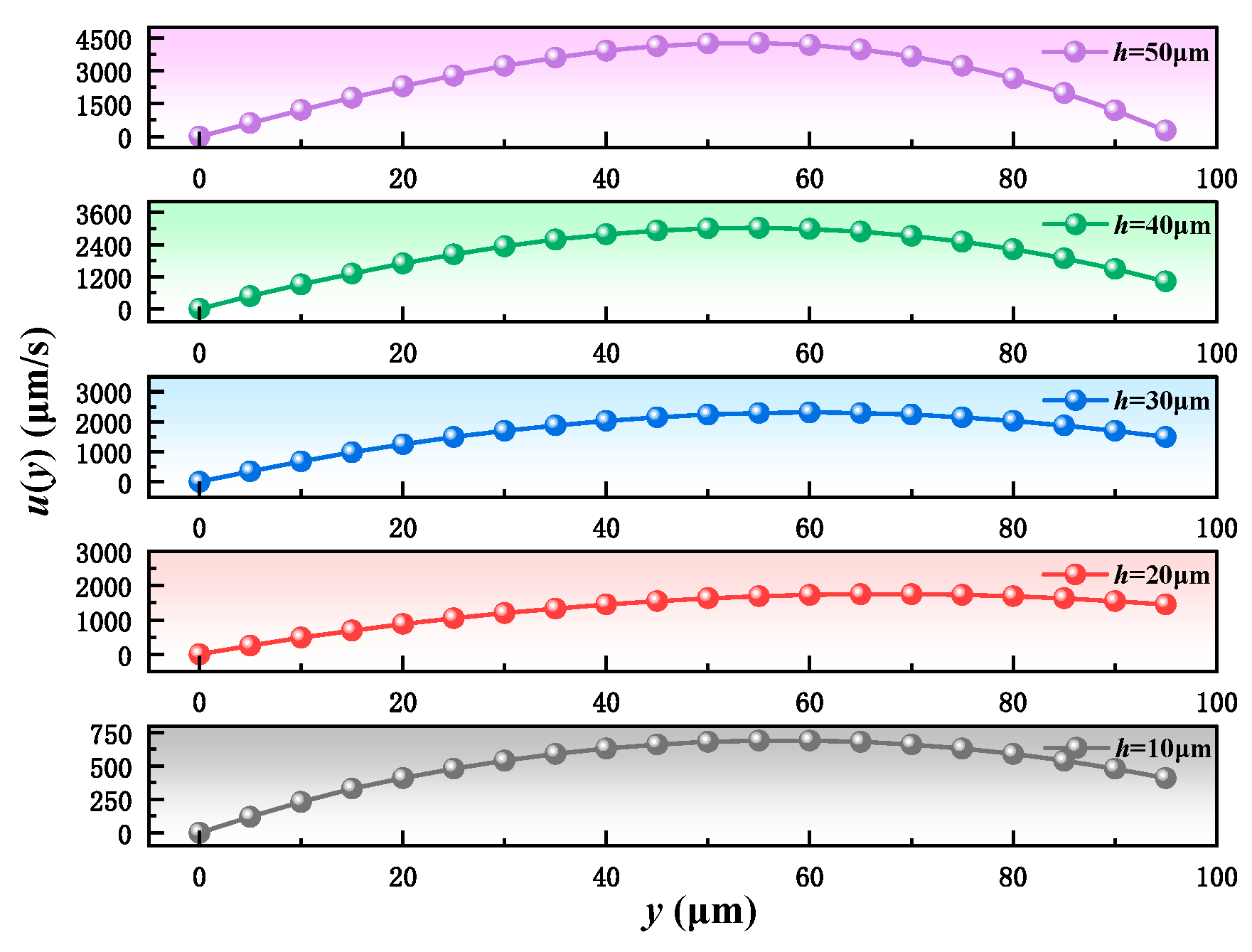
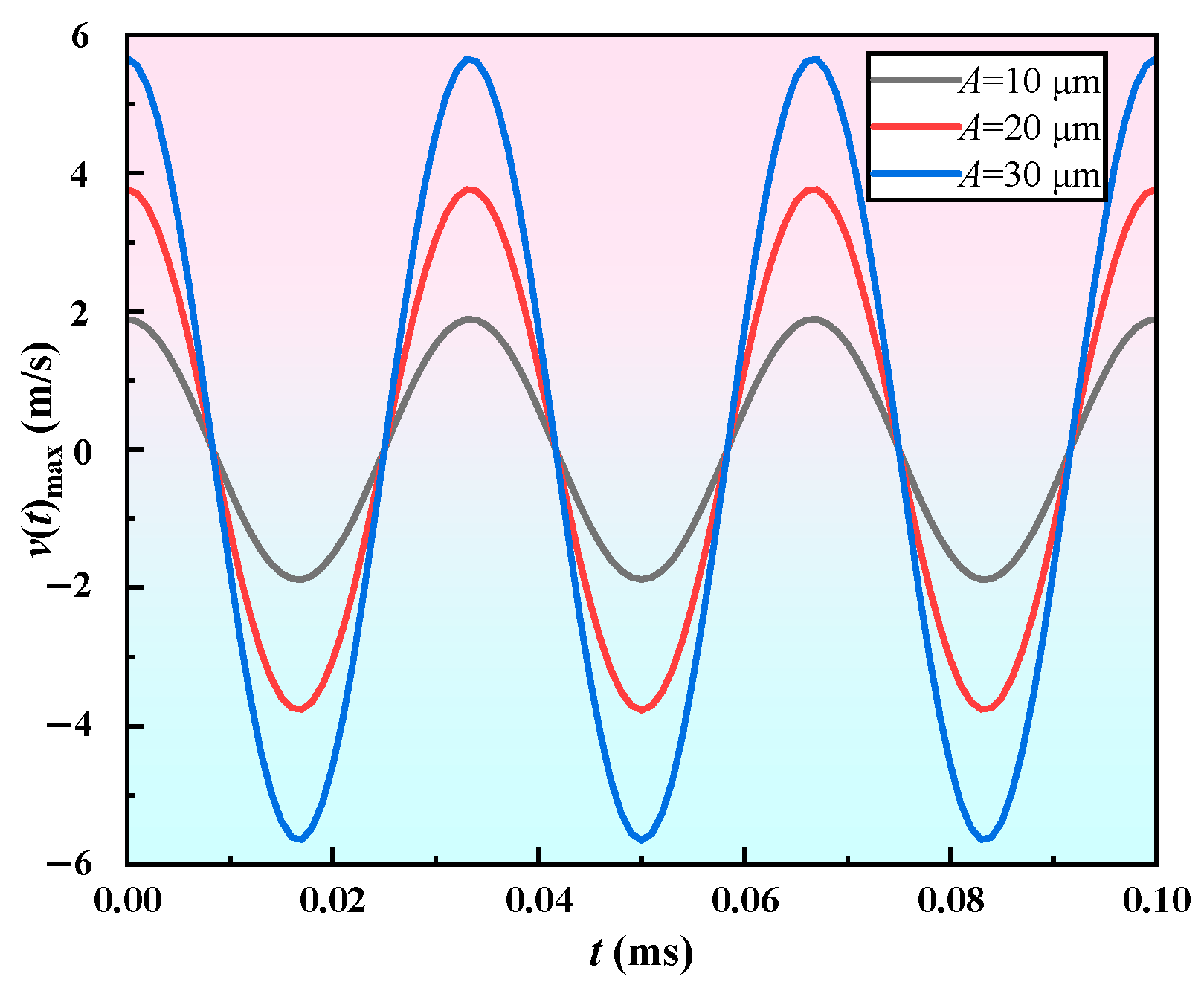
2.4. Hydrodynamics
3. Modeling and Simulation of Three-Phase Lubrication Mechanism in SCCO2-MQL
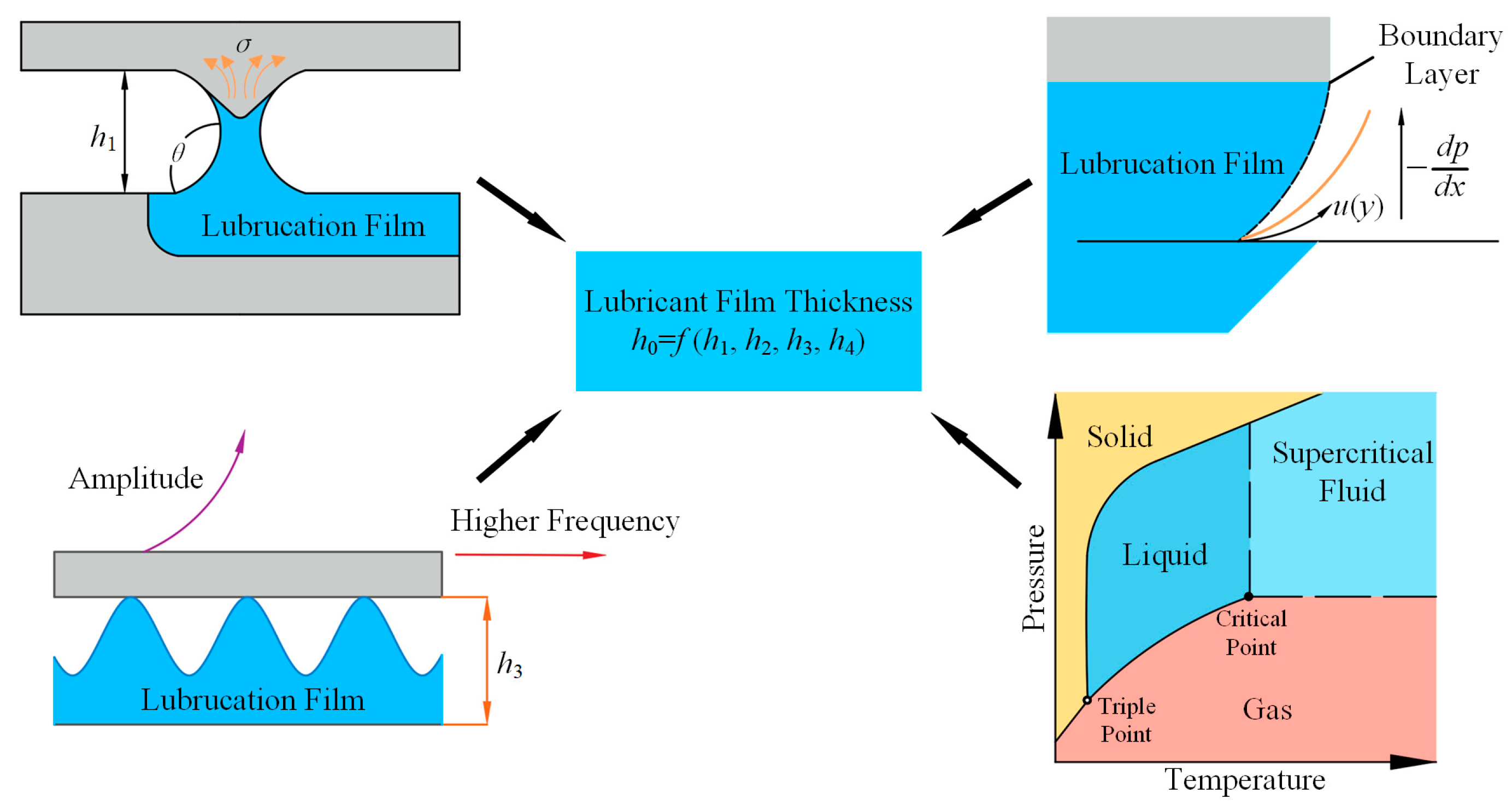
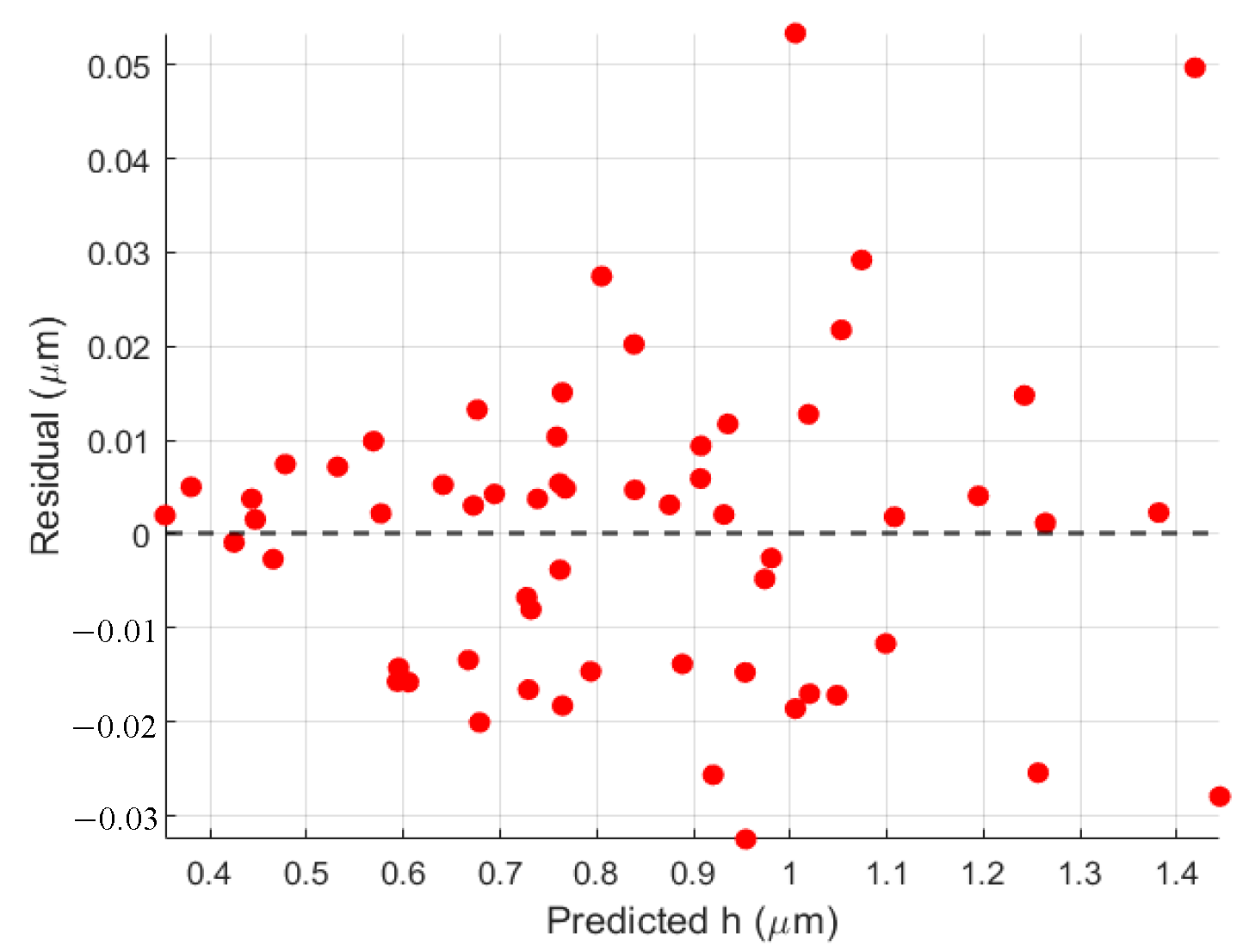
3.1. Mathematical Modeling of Lubrication Film Thickness
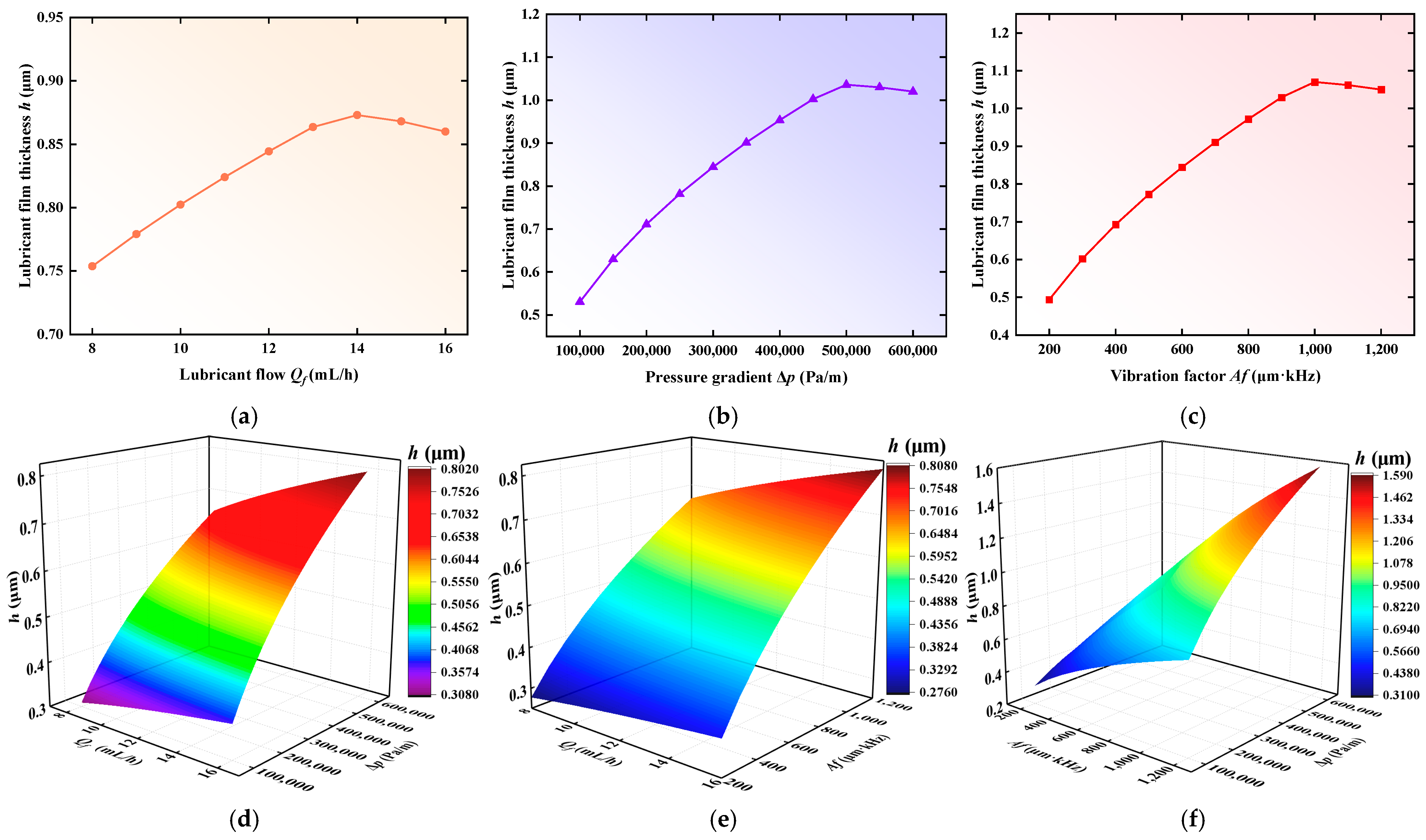
3.2. Model Simulation and Parameter Response Analysis
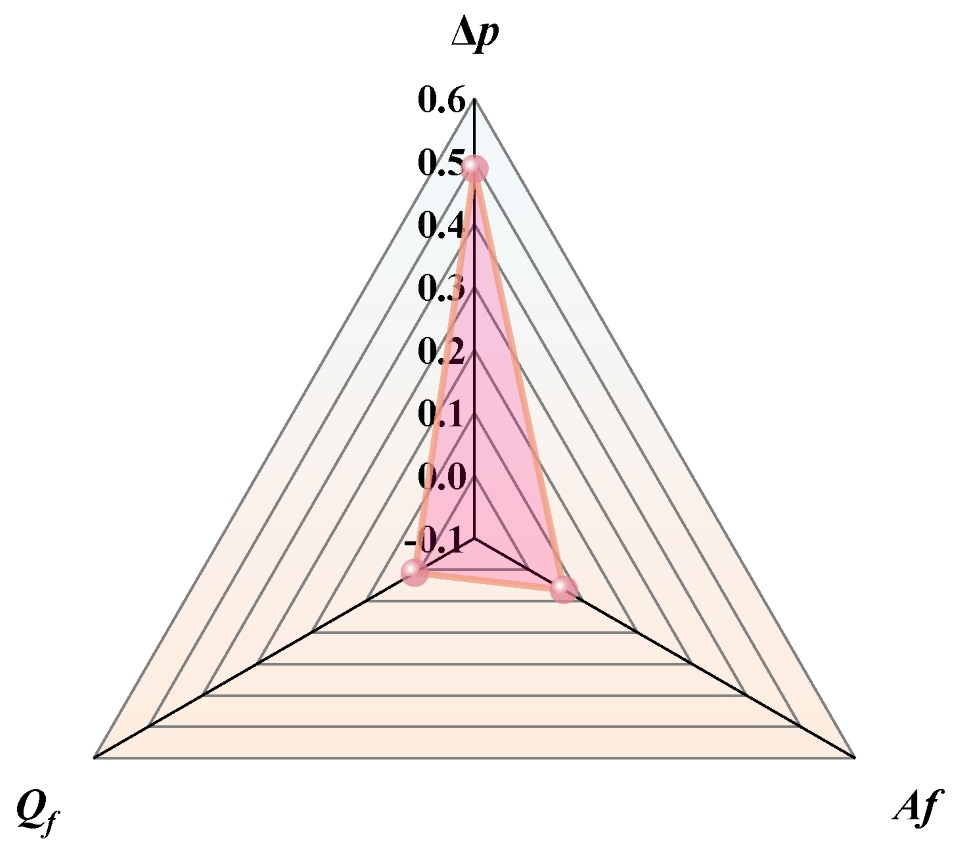
3.3. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A multiphysics-coupled lubrication film thickness prediction model was proposed, systematically characterizing the film-forming behavior of the lubricant under ultrasonic vibration and SCCO2 three-phase conditions. The model integrates droplet atomization scale, lubricant penetration path, shear spreading capacity, and CO2 phase state variation, revealing the key influencing factors and nonlinear response characteristics of film formation, and is finally expressed as a regression-based predictive formulation (Equation (18)), providing a quantitative tool that can be directly applied for subsequent parameter analysis and process optimization.
- (2)
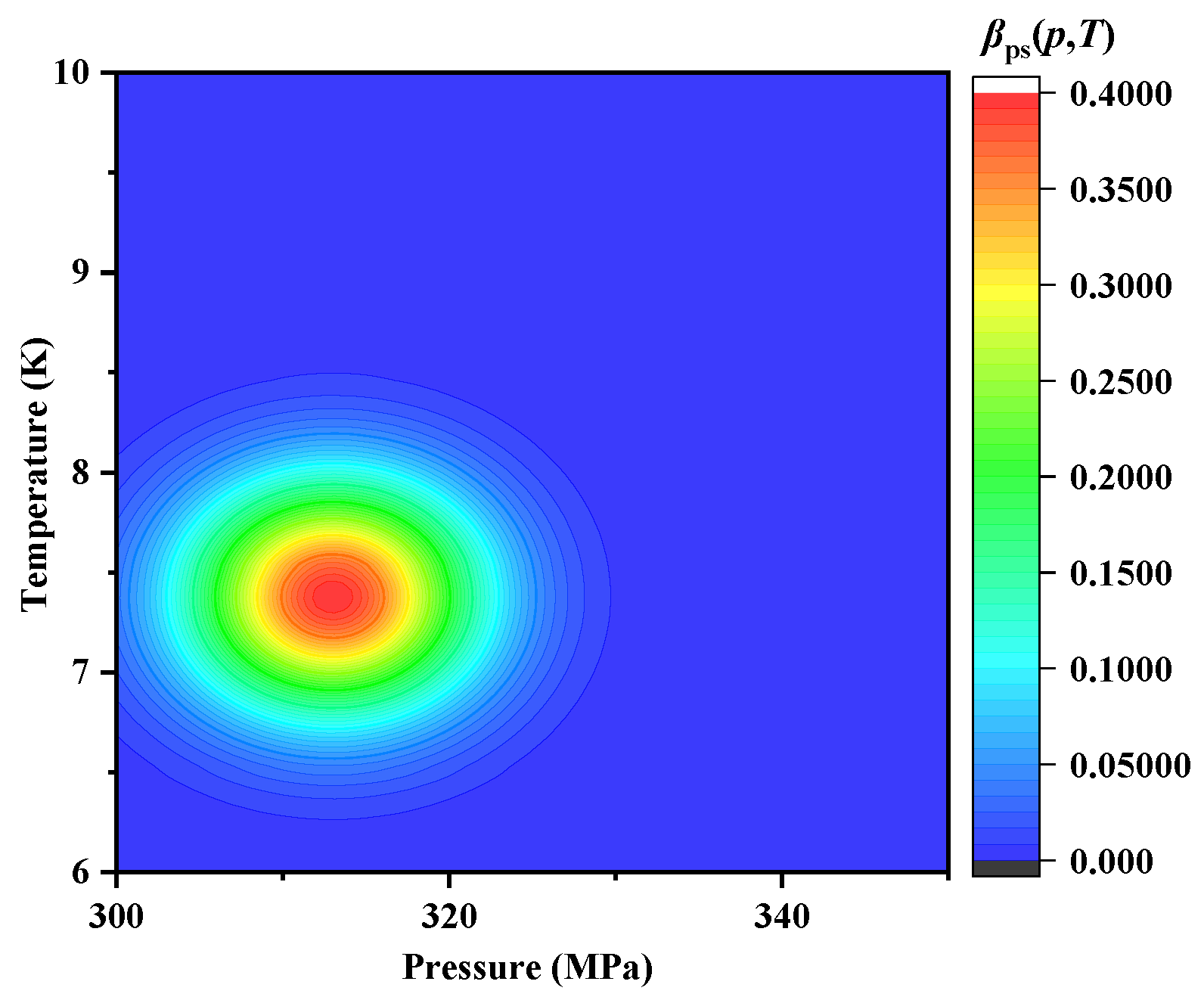
- A pseudo-phase enhancement factor βps(p,T) was introduced to characterize the phase transition behavior of supercritical CO2 in the critical region. The results reveal that density fluctuations and phase stratification significantly enhance the liquid-phase lubrication capacity, playing a critical role in lubrication film formation and effectively improving film stability and lubrication efficiency.
- (3)
- Simulation analysis showed that when the vibration factor Af < 1200 μm·kHz, shear spreading is continuously enhanced, whereas exceeding this threshold causes film instability. A pressure gradient Δptot below 6.0 × 105 Pa/m promotes the formation of a complete lubrication film, while excessive values may disrupt the boundary layer. The optimal lubrication effect of the flow rate Qf is observed around 16 mL/h, whereas oversupply may lead to lubricant backflow or film thickness saturation.
- (4)
- Parameter sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the pressure gradient Δptot is the dominant factor influencing film thickness, with a normalized sensitivity reaching 0.488, which is significantly higher than that of the vibration factor (Af = 0.065) and the flow rate (Qf = 0.010). This indicates that rational regulation of the pressure gradient is the key pathway to improving lubrication performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Nie, S.; Huang, H.; Liu, Z. Study on thermal balance of supercritical CO2-assisted machining based on mass flow-rate optimization. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 60, 367–376. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, J.; Niu, Q.; Gao, H.; Jing, L.; Tang, S.; Zhang, S. Optimization of MQL parameters and cutting performance in titanium alloy milling. Aeronaut. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 67, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, H.; Luo, T.; Xu, W.; Zhu, C. Surface defects in ultrasonic vibration assisted cutting of TiCp/TC4 with PCD tool. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2023, 43, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Lin, J.; Wu, D.; Ren, J. Surface integrity and fatigue behavior when turning γ-TiAl alloy with optimized PVD-coated carbide inserts. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapoglou, N.; Taylor, C.; Makris, C. Milling of aerospace alloys using supercritical CO2 assisted machining. Procedia CIRP 2021, 101, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wika, K.K.; Gurdal, O.; Litwa, P.; Hitchens, C. Influence of supercritical CO2 cooling on tool wear and cutting forces in the milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Procedia CIRP 2019, 82, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Xu, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Cui, X.; Li, B.; Liu, M.; Gao, T.; et al. SiCp/Al composites from conventional to empowered machining: Mechanisms and processability. Compos. Struct. 2024, 346, 118433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, E.A.; Rahim, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.R.; Mohid, Z. Experimental investigation of supercritical carbon dioxide (SCCO2) performance as a sustainable cooling technique. Procedia CIRP 2016, 40, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, J.; Ming, W.; An, Q.; Chen, M. Feasibility of supercritical CO2-based minimum quantity lubrication to improve the surface integrity of 50% Sip/Al composites. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 73, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, R.A.; He, N.; Jamil, M.; Gupta, M.K. Tribological and machining characteristics of milling SiCp/Al MMC composites under sustainable cooling conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 2613–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Analytical modeling of temperature distribution in lead-screw whirling milling considering the transient un-deformed chip geometry. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 157–158, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Tabor, D. The role of lubricants in machining. Wear 1977, 43, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, E.; Wang, R. Lubrication Mechanism of scCO2-MQL in the Assisted Machining of Titanium Alloys. Machines 2023, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H. Study on Spray Atomization Characteristics and Permeation Lubrication Mechanism in MQL Cutting. Ph.D. Thesis, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Sharma, A. Development of a friction model and its application in finite element analysis of minimum quantity lubrication machining of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 238, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, B.-Z.; Liang, S.Y. Analysis of Thermal and Mechanical Effects on Residual Stress in Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) Machining. J. Mech. 2018, 34, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-X.; Wang, X.-D.; Lee, D.-J. Pseudo-phases of supercritical CO2 at supercritical CO2-subcritical H2O interface: A molecular dynamics simulation. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 122026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousti, S. A compressible hydrodynamic analysis of journal bearings lubricated with supercritical carbon dioxide. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles, San Antonio, TX, USA, 28–31 March 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wahap, M.A.A.; Nasir, F.M.; Sa’aT, F.A.-Z.M.; Wae-Hayee, M.; Yong, K.T.L.; Anuar, M.R. A comparison of multiphase Ansys-Fluent models in performing supercritical CO2 extraction simulation. CFD Lett. 2025, 17, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, C.; An, Q.; Ming, W.; Chen, M. Surface layer microstructure and mechanical characteristics analysis of cast iron during milling process under supercritical CO2-MQL. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhuang, B.; Wu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Ding, W.; Su, H. Development of an ultrasonic vibration-assisted MQL device and its effects on the milling performance of ultra-high strength steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 135, 4765–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Rong, J.; Jing, L.; Gao, H.; Tang, S.; Qiu, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Dai, F. Study on force-thermal characteristics and cutting performance of titanium alloy milled by ultrasonic vibration and minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 95, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.C.; Pandey, P.M.; Dixit, U.S. An experimental study on surface roughness and frictional property of ultrasonic-vibration-assisted milled surface. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 4187–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, H.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V. Evaluation of Cutting Force and Surface Roughness of Inconel 718 Using a Hybrid Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Turning and Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL). In Advances in Unconventional Machining and Composites; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.J.; Zou, Y.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, G. Experimental study on MQL high-speed turning of 18Cr2Ni4WA alloy steel. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 2017, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, D.; Mu, K.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Cai, C. High-performance liquid metal-based SiC/Graphene-Mo hybrid nanofluid for hydraulic transmission. Tribol. Int. 2024, 198, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresme, F.; Kornyshev, A.A.; Perkin, S.; Urbakh, M. Electrotunable friction with ionic liquid lubricants. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marian, M.; Bartz, M.; Wartzack, S.; Rosenkranz, A. Non-Dimensional Groups, Film Thickness Equations and Correction Factors for Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication: A Review. Lubricants 2020, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Zhang, H. Lubrication Mechanism and Establishment of a Three-Phase Lubrication Model for SCCO2-MQL Ultrasonic Vibration Milling of SiCp/Al Composites. Machines 2025, 13, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090879
Wang B, Zhang H. Lubrication Mechanism and Establishment of a Three-Phase Lubrication Model for SCCO2-MQL Ultrasonic Vibration Milling of SiCp/Al Composites. Machines. 2025; 13(9):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090879
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bowen, and Huiping Zhang. 2025. "Lubrication Mechanism and Establishment of a Three-Phase Lubrication Model for SCCO2-MQL Ultrasonic Vibration Milling of SiCp/Al Composites" Machines 13, no. 9: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090879
APA StyleWang, B., & Zhang, H. (2025). Lubrication Mechanism and Establishment of a Three-Phase Lubrication Model for SCCO2-MQL Ultrasonic Vibration Milling of SiCp/Al Composites. Machines, 13(9), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090879




