Prediction of Vehicle Interior Wind Noise Based on Shape Features Using the WOA-Xception Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
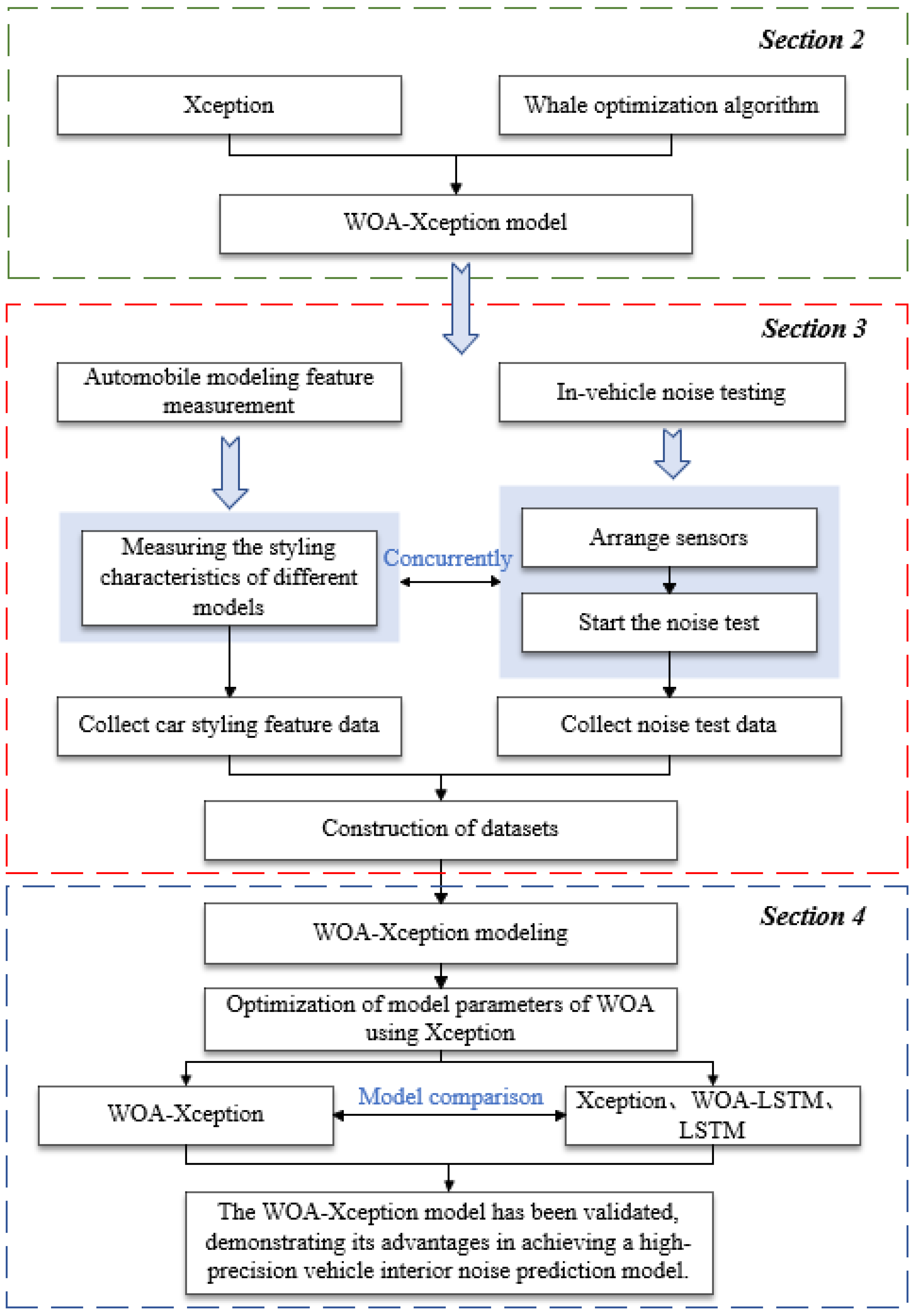
2. Models and Methods
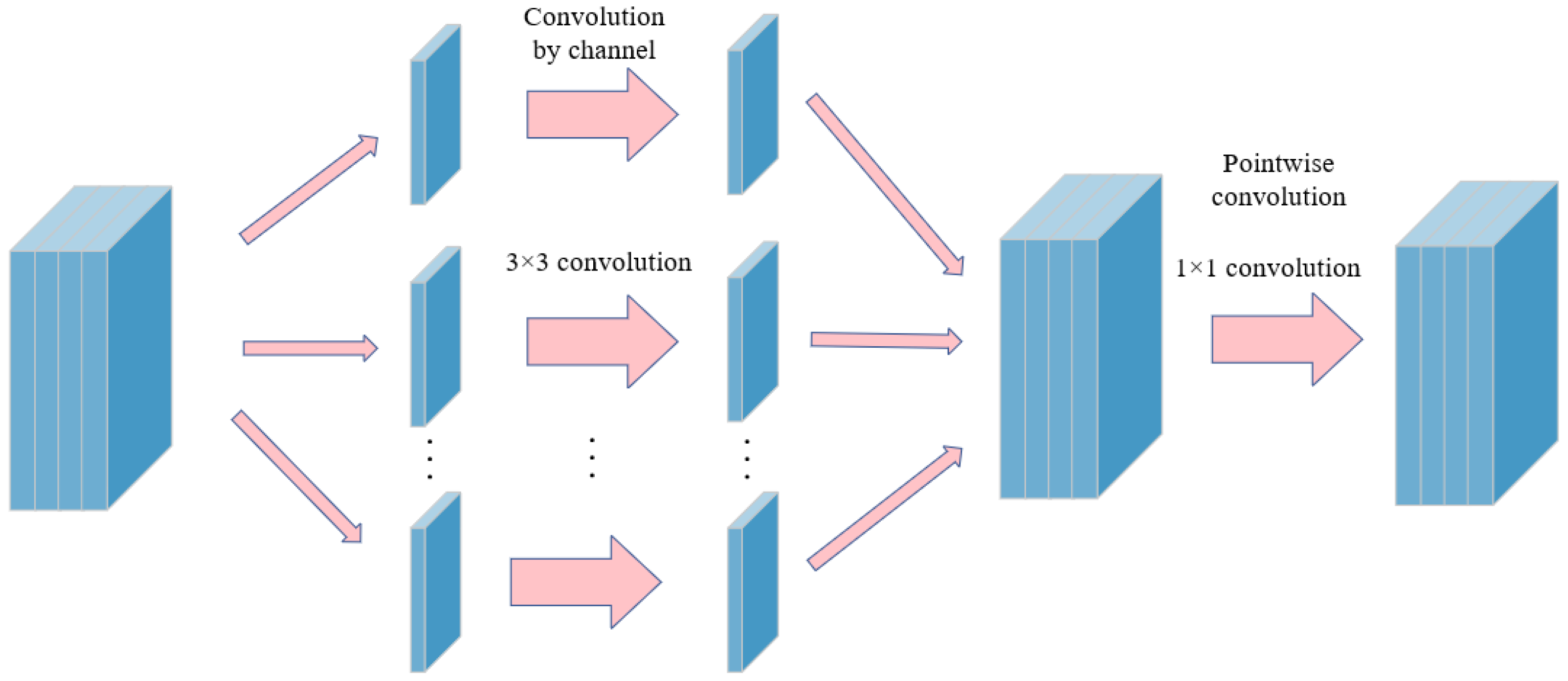
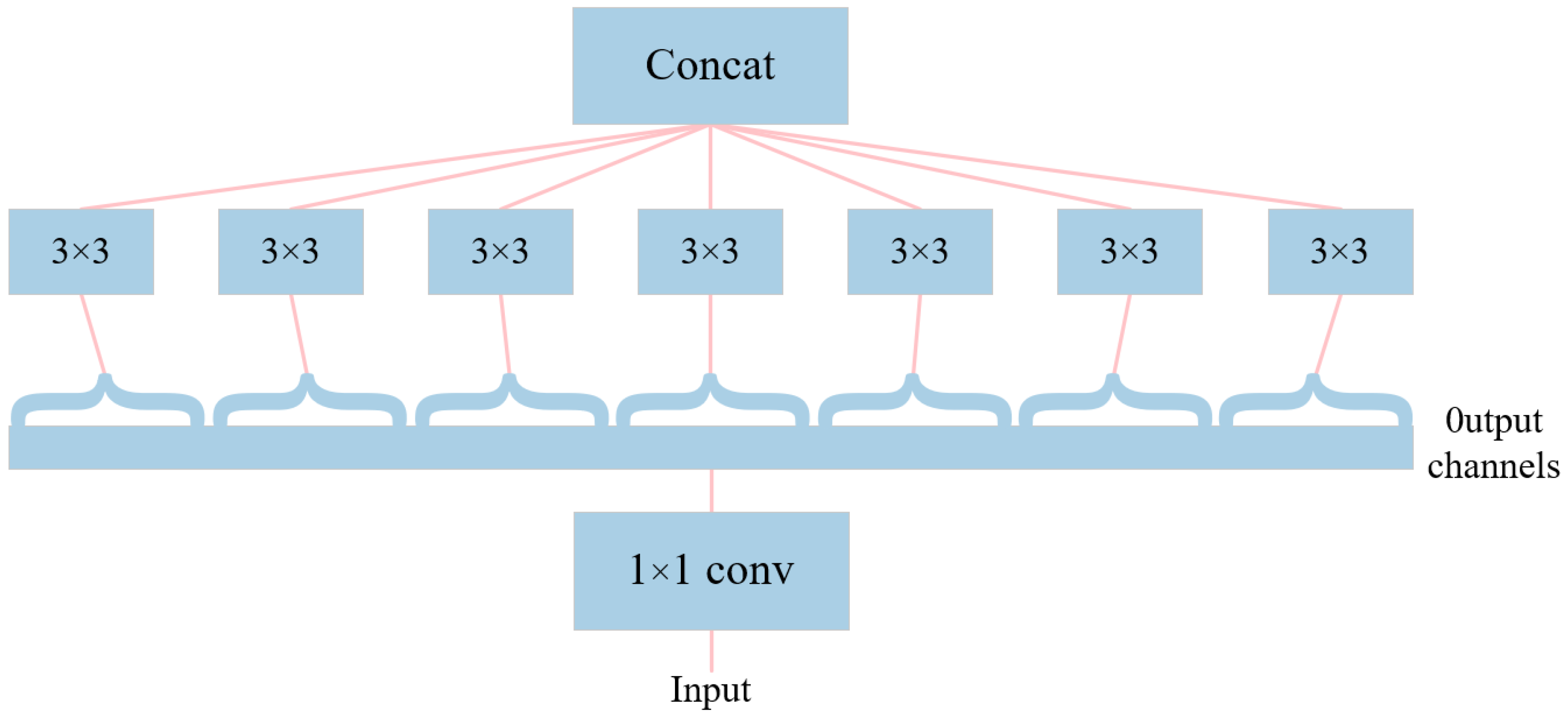
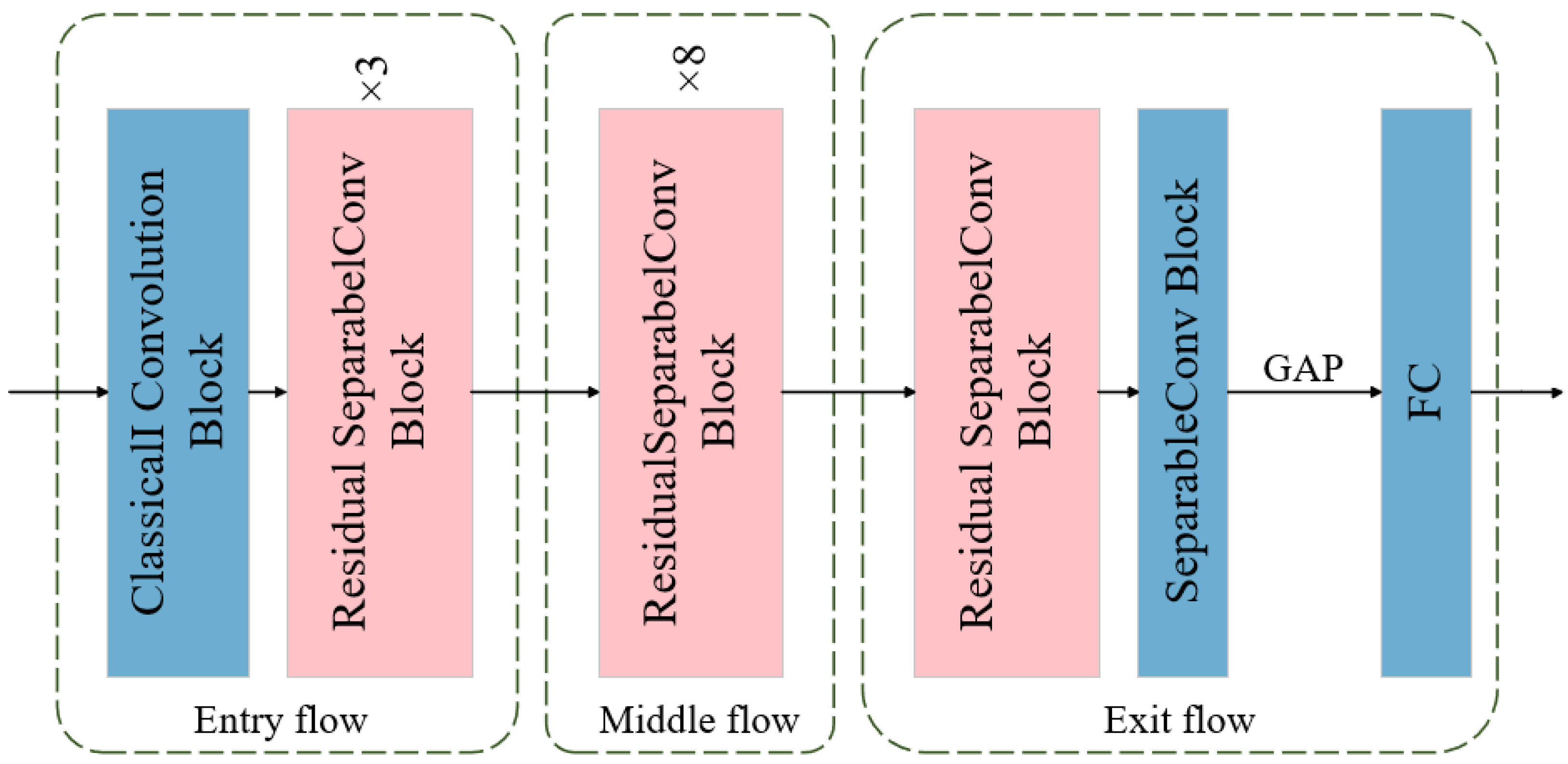
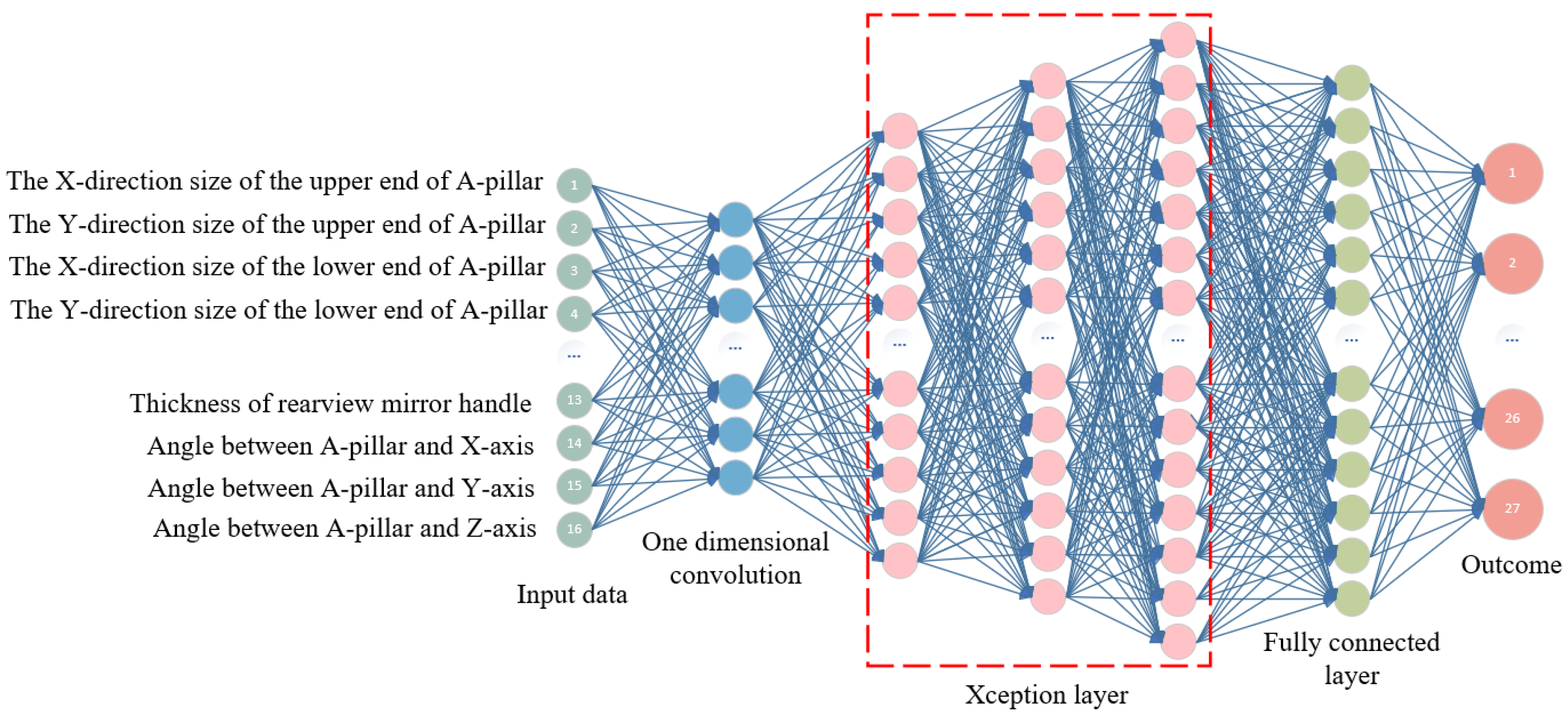
2.1. Xception Method
2.2. WOA-Xception Method
3. In-Vehicle Master Driving Noise Test
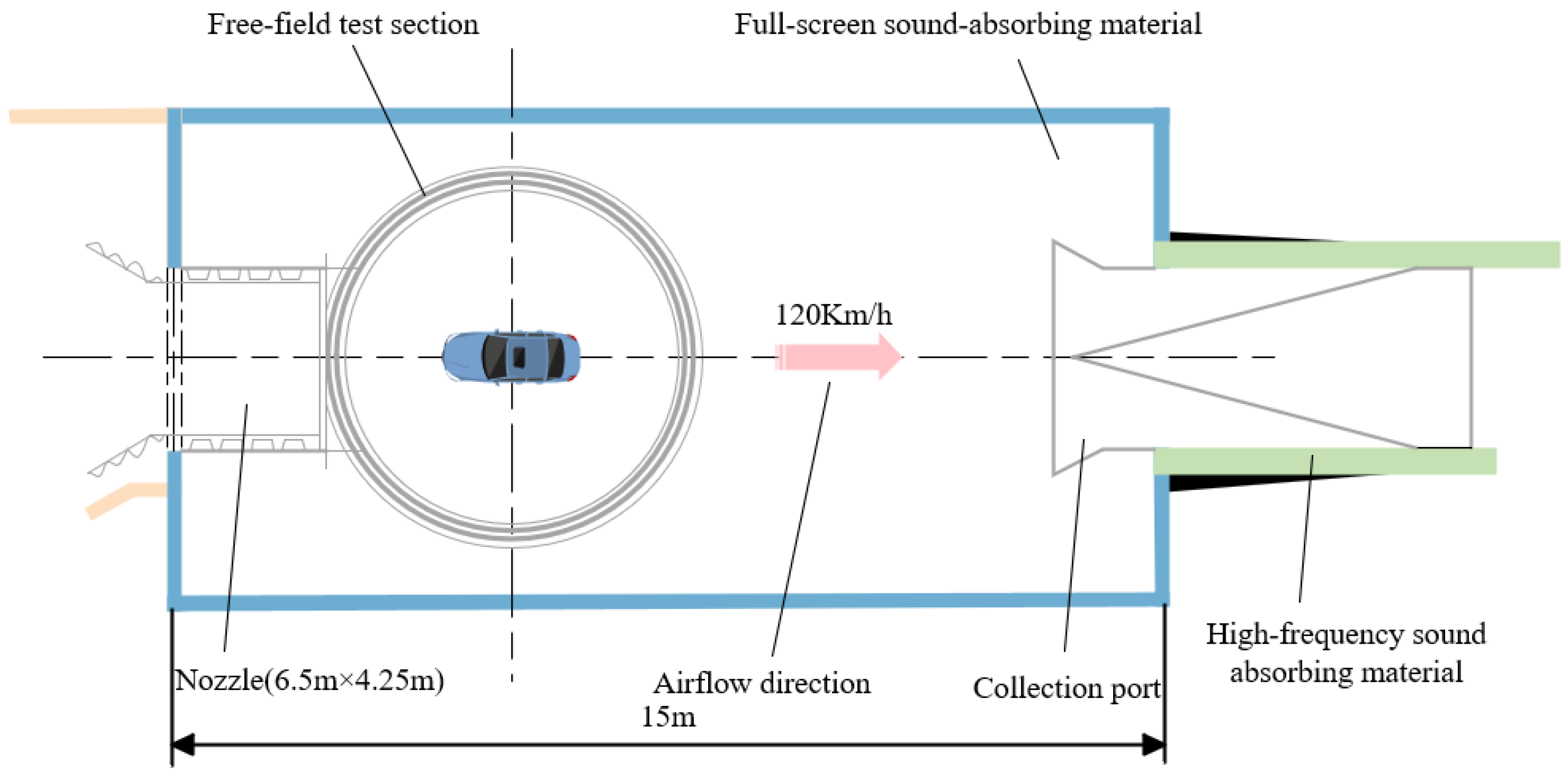
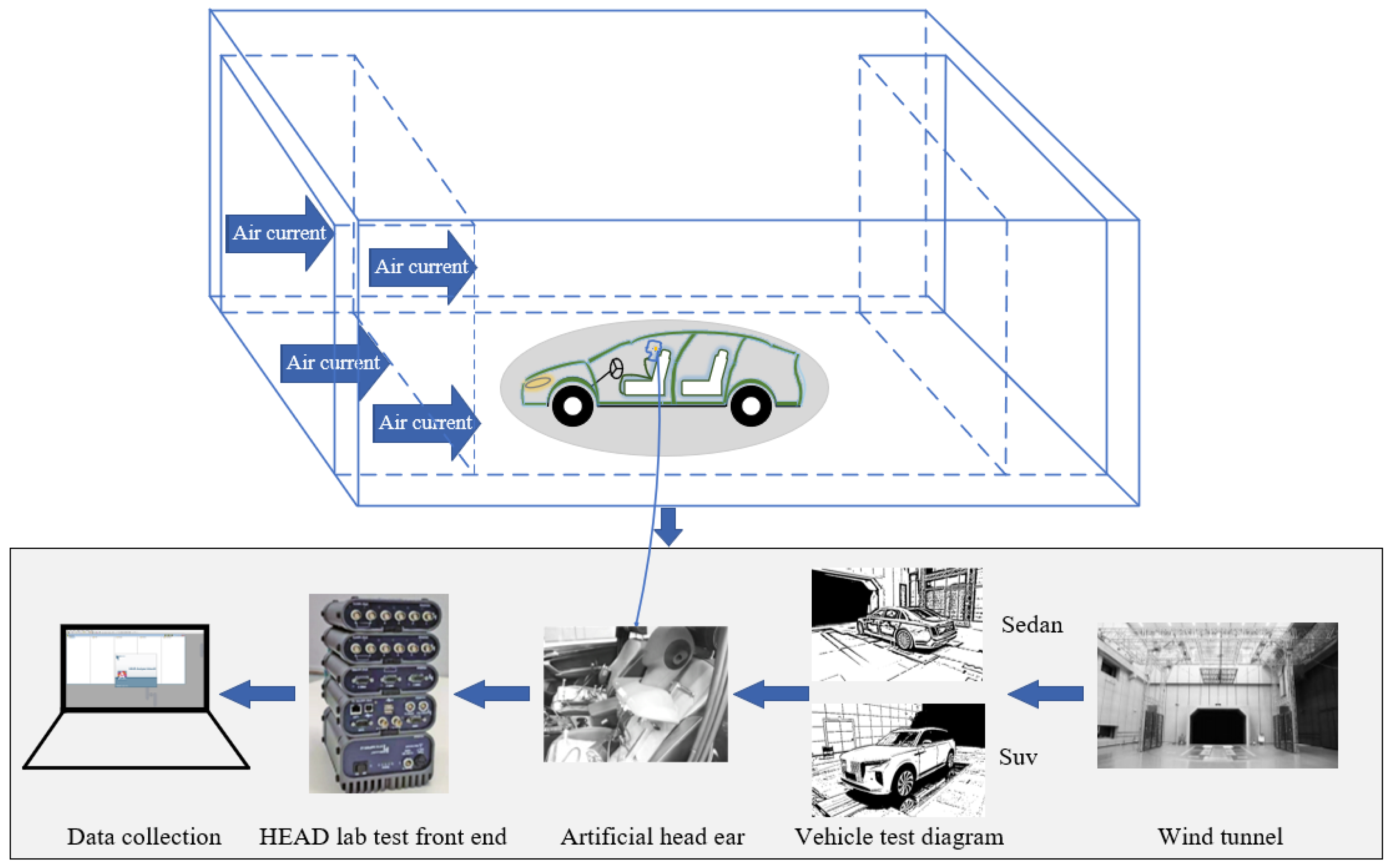
3.1. Test Platform
3.2. Test Method
3.3. Test Results for Noise in the Driver’s Right Ear Inside the Vehicle
4. Prediction and Verification of In-Vehicle Main Driving Noise Based on WOA-Xception
4.1. WOA-Xception Model Establishment
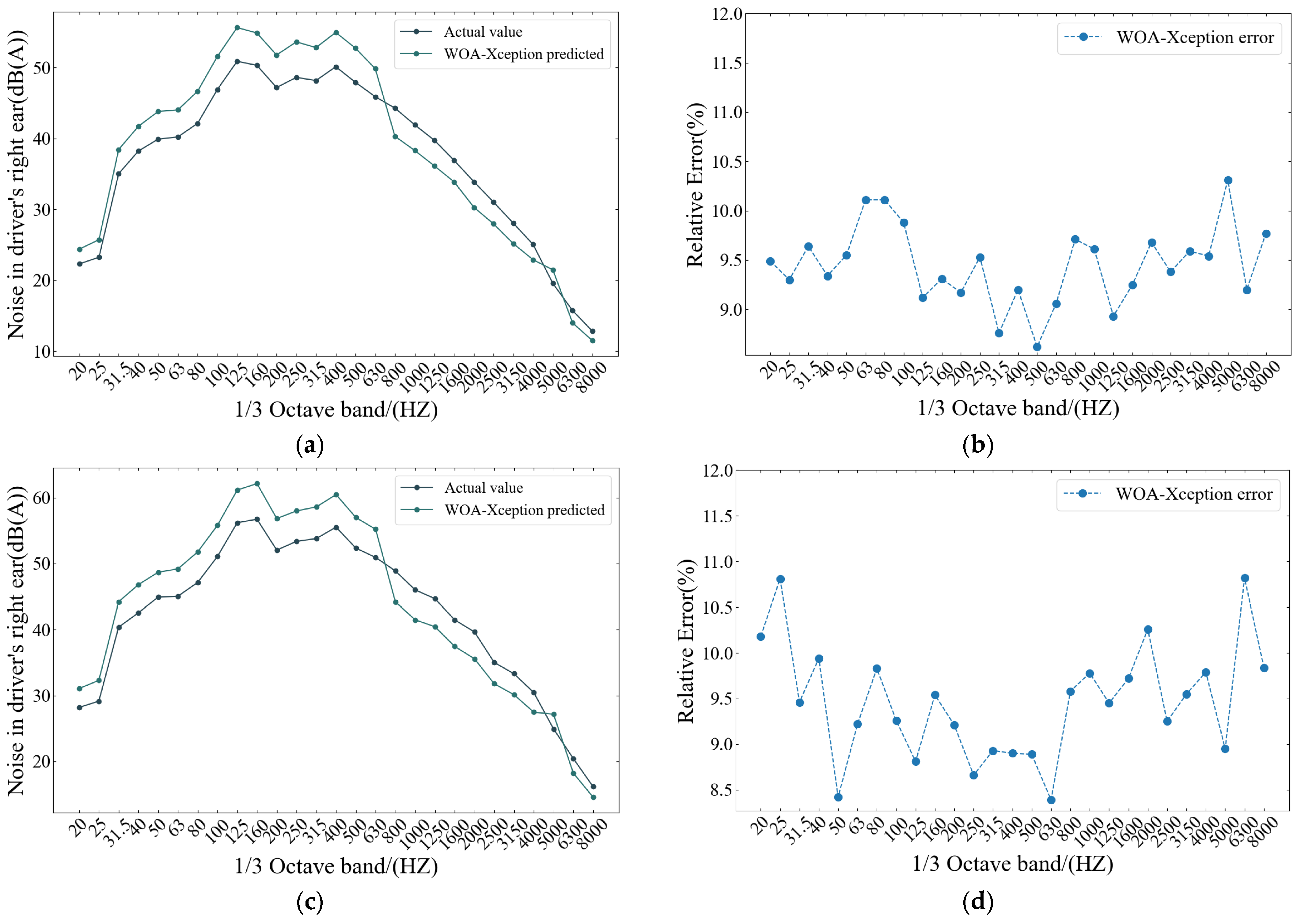
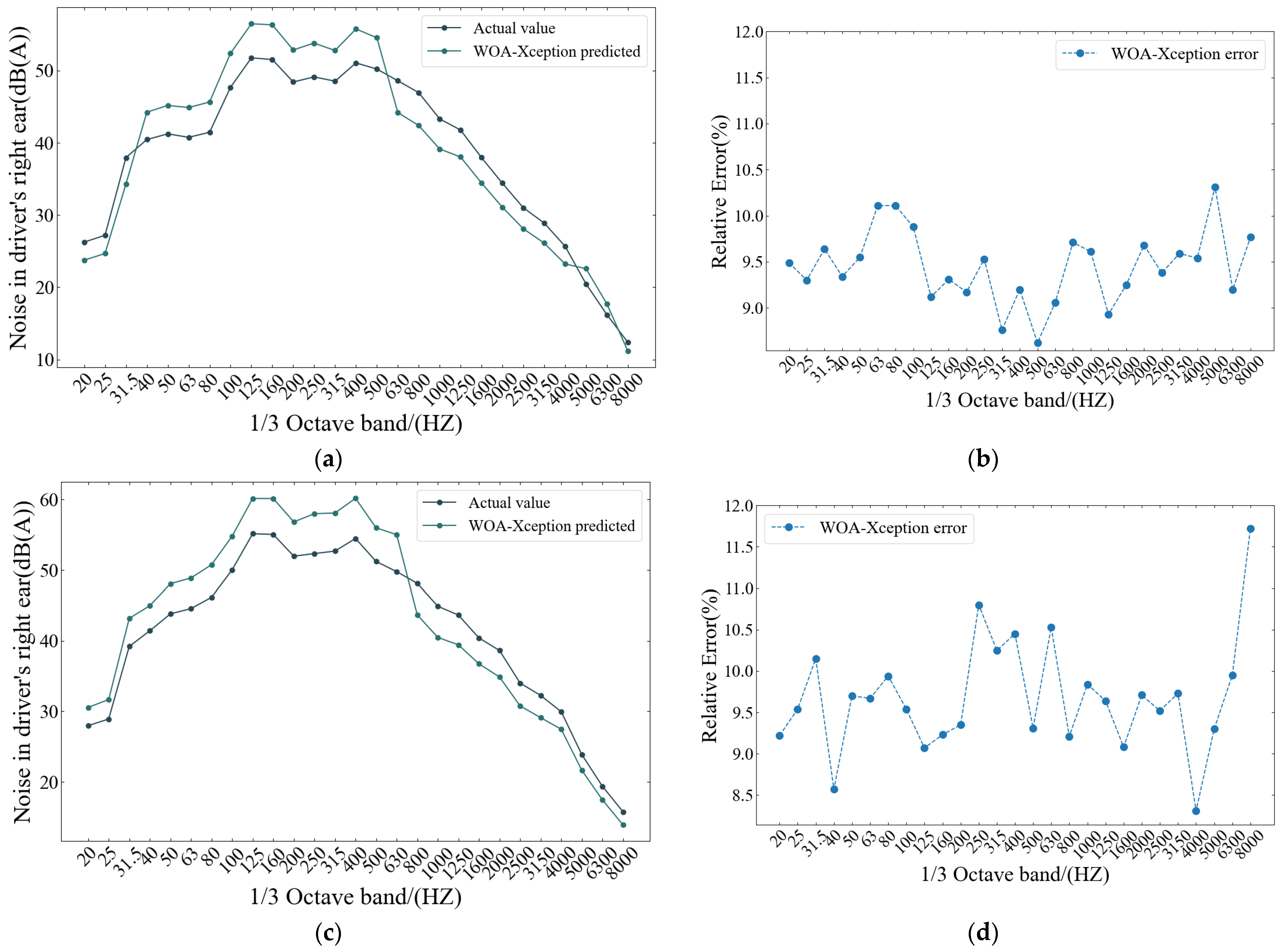
4.2. Prediction Analysis of WOA-Xception Model
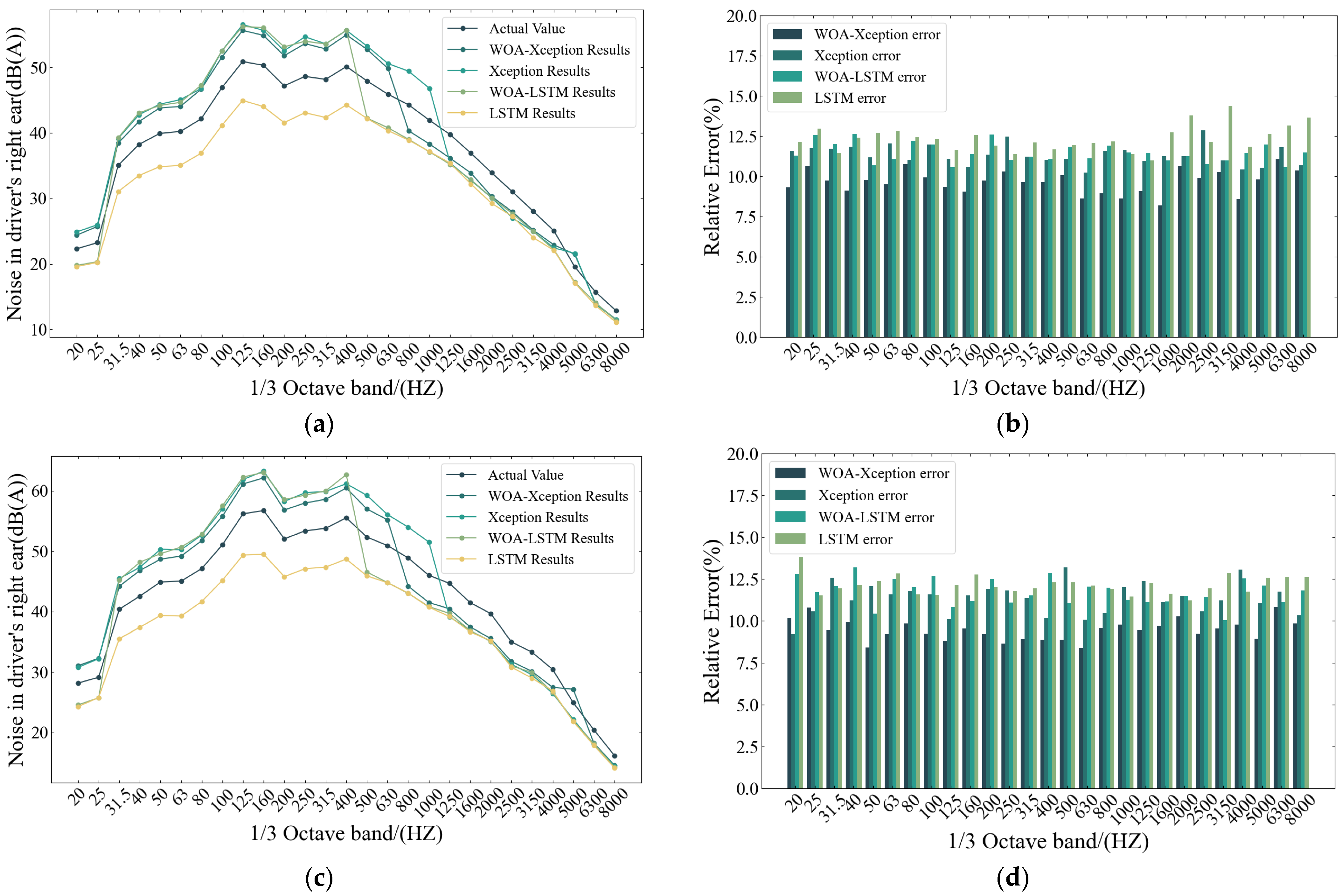
4.3. Compare Other Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NVH | Noise, Vibration, and Harshness |
| WOA | Whale Optimization Algorithm |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
References
- Huang, H.B.; Huang, X.R.; Li, R.X.; Lim, T.C.; Ding, W.P. Sound quality prediction of vehicle interior noise using deep belief networks. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 113, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Pang, J.; Huang, H. Improving of pure electric vehicle sound and vibration comfort using a multi-task learning with task-dependent weighting method. Measurement 2024, 233, 114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qatu, M.S. Recent research on vehicle noise and vibration. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 2012, 8, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lim, T.C.; Wu, J.; Ding, W.; Pang, J. Multitarget prediction and optimization of pure electric vehicle tire/road airborne noise sound quality based on a knowledge-and data-driven method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 197, 110361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuit, K. The sound quality of vehicle interior noise: A challenge for the NVH-engineers. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 2004, 1, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Guo, H.; Yuan, T.; Ma, L.F.; Wang, C. Electromagnetic noise analysis and optimization for permanent magnet synchronous motor used on electric vehicles. Eng. Comput. 2021, 38, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dai, P.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H. Predicting and optimizing pure electric vehicle road noise via a locality-sensitive hashing transformer and interval analysis. ISA Trans. 2025, 157, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, J.R.; George, A.R. Measurement and Analysis of Automobile Wind Noise (No. 930299); SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighthill, M.J. On sound generated aerodynamically I. General theory. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1952, 211, 564–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.R. Automobile aerodynamic noise. In Proceedings of the International Congress & Exposition, Detroit, MI, USA, 26 February–2 March 1990; pp. 434–457. [Google Scholar]
- Masri, J.; Amer, M.; Salman, S.; Ismail, M.; Elsisi, M. A survey of modern vehicle noise, vibration, and harshness: A state-of-the-art. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Ding, W.; Yang, M.; Fan, D.; Pang, J. Uncertainty optimization of pure electric vehicle interior tire/road noise comfort based on data-driven. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 165, 108300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Dai, P.; Yang, M.; Jia, W.; Jia, X.; Huang, H. Research on maglev vibration isolation technology for vehicle road noise control. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2022, 6, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Ristovska, G.; Dadvand, P. WHO environmental noise guidelines for the European Region: A systematic review on environmental noise and adverse birth outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Ding, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, X.; Pang, J. Vehicle vibro-acoustical comfort optimization using a multi-objective interval analysis method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, S.; Khreis, H. Burden of disease from transportation noise and motor vehicle crashes: Analysis of data from Houston, Texas. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T/CSAE113-2019; Test Method for Interior Wind Noise Measurement in Full-Vehicle Aeroacoustic Wind Tunnel Testing. China Society of Automotive Engineers: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Mukkera, S.; Premkumar, S.R.; Samar, D. A Test Methodology for Vehicle Wind Noise Reduction and Acoustic Quality Improvement (No. 2019-26-0216); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.; Krueger, L.; Lentzen, M.; Woodiga, S.; Chalupa, K.; Hupertz, B.; Lewington, N. Development and initial testing of a full-scale DrivAer generic realistic wind tunnel correlation and calibration model. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars-Mech. Syst. 2018, 11, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditcheva, O.; Lofdahl, L.C.; Sebben, S.; Harling cEng, P.; Bernhardsson, H. On the Possibilities and Limitations of Wind Noise Testing in the Aerodynamical Wind Tunnel at Volvo Cars (No. 2016-01-1807); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Johnson, J.; Dietschi, U.; Khalighi, B. Wind noise measurements for automotive mirrors. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars-Mech. Syst. 2009, 2, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovedatti, V.; Milhorn, J.; DeJong, R.; Ebbitt, G. Vehicle wind noise measurements in a wind tunnel with a contoured top profile. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars-Mech. Syst. 2016, 9, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Nusser, K.; Oswald, M. Aero-Vibro-Acoustic Wind Noise-Simulation Based on the Flow Around a Car (No. 2016-01-1804); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, A.; Ikeda, J.; Nakasato, K.; Kamiwaki, T.; Wakamatsu, J.; Oshima, M.; Li, C.; Tsubokura, M. Numerical Simulation of Fluctuating Wind Noise of a Vehicle in Reproduced on-Road Wind Condition (No. 2024-01-2353); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukkera, S.; Pandey, A.; Krishna, K.A.; Patil, S.; Prasad, P.L.N. Prediction of Mirror Induced Wind Noise Using CFD-FEM Approach (No. 2017-26-0221); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, D.; Golota, A.; Zerbib, N.; Mebarek, L. Wind Noise Source Characterization and How It Can Be Used to Predict Vehicle Interior Noise (No. 2014-01-2052); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moron, P.; Wu, L.; Powell, R.; Senthooran, S. Numerical simulation of on-road wind conditions for interior wind noise of passenger vehicles. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Tokyo, Japan, 2023; Volume 266, pp. 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Moron, P.; Balasubramanian, G.; Neuhierl, B.; Senthooran, S.; Crouse, B.; Freed, D.; Kain, C.; Ullrich, F. Simulation of underbody contribution of wind noise in a passenger automobile. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars-Mech. Syst. 2013, 6, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, W.; Yang, M.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.; Jin, T. Distributed Drive Autonomous Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Control Based on Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Lim, T.C.; Yang, M.; Ding, W. Pure electric vehicle nonstationary interior sound quality prediction based on deep CNNs with an adaptable learning rate tree. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 148, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Ding, W.; Huang, H. Exploratory study on sound quality evaluation and prediction for engineering machinery cabins. Measurement 2025, 253, 117684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ding, W.; Yang, M. Multi-objective prediction and optimization of vehicle acoustic package based on ResNet neural network. Sound Vib. 2023, 57, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, D.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; He, Y.; Grabner, G. Deep learning-based wind noise prediction study for automotive clay model. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 045302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Wind turbine airfoil noise prediction using dedicated airfoil database and deep learning technology. Appl. Energy 2024, 364, 123165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ding, W.; Pang, J. Prediction and optimization of pure electric vehicle tire/road structure-borne noise based on knowledge graph and multi-task ResNet. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kužnar, D.; Možina, M.; Giordanino, M.; Bratko, I. Improving vehicle aeroacoustics using machine learning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Ding, W.; Huang, H. Evaluation and prediction of vibration comfort in engineering machinery cabs using random forest with genetic algorithm. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2024, 8, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, C.; Calloni, M.; Golota, A.; Zerbib, N. Aero-Vibro-Acoustic Simulation Methodologies for Vehicle Wind Noise Reduction (No. 2019-26-0202); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, M.; Ding, W. Sound quality prediction and improving of vehicle interior noise based on deep convolutional neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 160, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Chollet, F. Depthwise separable convolutions for neural machine translation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülmez, B. A novel deep neural network model based Xception and genetic algorithm for detection of COVID-19 from X-ray images. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 328, 617–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.G.; Quan, C.; Lee, H.D.; Kang, U. Falcon: Lightweight and accurate convolution based on depthwise separable convolution. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2023, 65, 2225–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, R.; Mahesh, T.R.; Bhatia Khan, S.; Malibari, A.A.; Asiri, F.; Rehman, A.U.; Al Malwi, W. Employing Xception convolutional neural network through high-precision MRI analysis for brain tumor diagnosis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1487713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, K.; Fan, S.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y. A multi-strategy whale optimization algorithm and its application. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 108, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawi, M.; Zawbaa, H.M.; Emary, E. Feature selection approach based on whale optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Doha, Qatar, 4–6 February 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, E.G.; Kharazi, A.; Muller, S.; Ebeling, W.; Mercker, E. The BMW AVZ Wind Tunnel Center (No. 2010-01-0118); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, S.A.; Aroussi, A.; Rice, E. Simulation of road vehicle natural environment in a climatic wind tunnel. Simul. Pract. Theory 2001, 8, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, E.; Yen, J.; Arnette, S.; Walter, J. Recent advances in large scale aeroacoustic wind tunnels. In Proceedings of the 8th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference & Exhibit, Breckinridge, CO, USA, 17–19 June 2002; p. 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fago, B.; Lindner, H.; Mahrenholtz, O. The effect of ground simulation on the flow around vehicles in wind tunnel testing. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1991, 38, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Uddin, M.; Zhang, C. Computational analyses of the effects of wind tunnel ground simulation and blockage ratio on the aerodynamic prediction of flow over a passenger vehicle. Vehicles 2020, 2, 318–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.Y. Test and evaluation method for low wind noise level of automobiles. Qual. Certif. 2025, 2, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 532-1:2017; Acoustics—Methods for Calculating Loudness—Part 1: Zwicker Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Blanchet, D.; Golota, A. Combining Modeling Methods to Accurately Predict Wind Noise Contribution (No. 2015-01-2326); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, S.G.K.; Sahu, K.K. Normalization: A preprocessing stage. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.06462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Vehicle Model | Wind Velocity (km/h) | Sampling Frequency (HZ) | Sampling Time (s) | Yaw Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUV | 120 | 48k | 15 | 0 |
| Sedan | 120 | 48k | 15 | 0 |
| Algorithm Type | Parameter Type | Numerical |
|---|---|---|
| Xception | Input dimension | 1 |
| Maximum number of iterations | 500 | |
| Number of Xception layers | 3 | |
| Learning rate optimization range | [0.001, 0.01] | |
| Batch size optimization range | [32, 128] | |
| WOA | Maximum number of iterations | 5 |
| Number of whales | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Yi, H.; Ma, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Y. Prediction of Vehicle Interior Wind Noise Based on Shape Features Using the WOA-Xception Model. Machines 2025, 13, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060497
Ma Y, Yi H, Ma L, Deng Y, Wang J, Wu Y, Peng Y. Prediction of Vehicle Interior Wind Noise Based on Shape Features Using the WOA-Xception Model. Machines. 2025; 13(6):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060497
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yan, Hongwei Yi, Long Ma, Yuwei Deng, Jifeng Wang, Yudong Wu, and Yuming Peng. 2025. "Prediction of Vehicle Interior Wind Noise Based on Shape Features Using the WOA-Xception Model" Machines 13, no. 6: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060497
APA StyleMa, Y., Yi, H., Ma, L., Deng, Y., Wang, J., Wu, Y., & Peng, Y. (2025). Prediction of Vehicle Interior Wind Noise Based on Shape Features Using the WOA-Xception Model. Machines, 13(6), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060497






