Influence of Hybridization Ratio on Field Back-EMF Ripple in Switched Flux Hybrid Excitation Machines
Abstract
1. Introduction
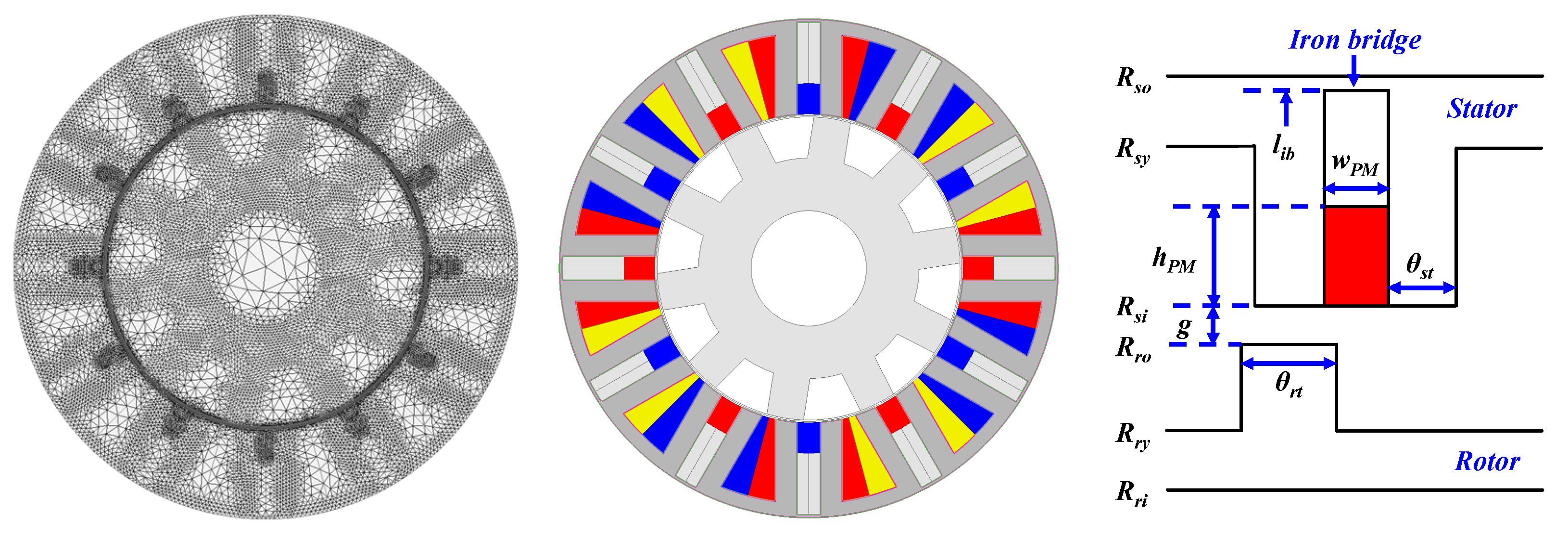
2. Machine Topology and Operation Principle
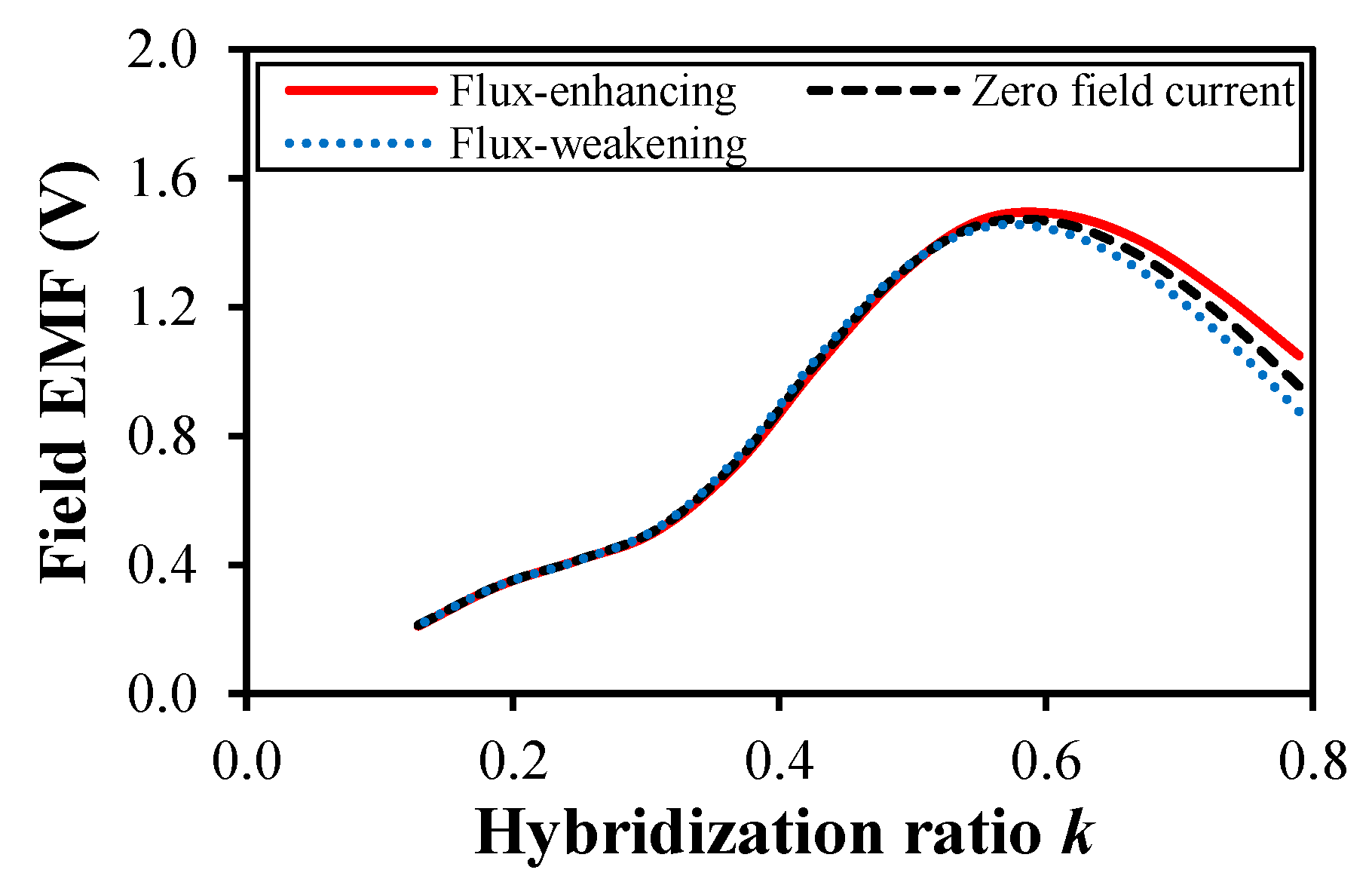
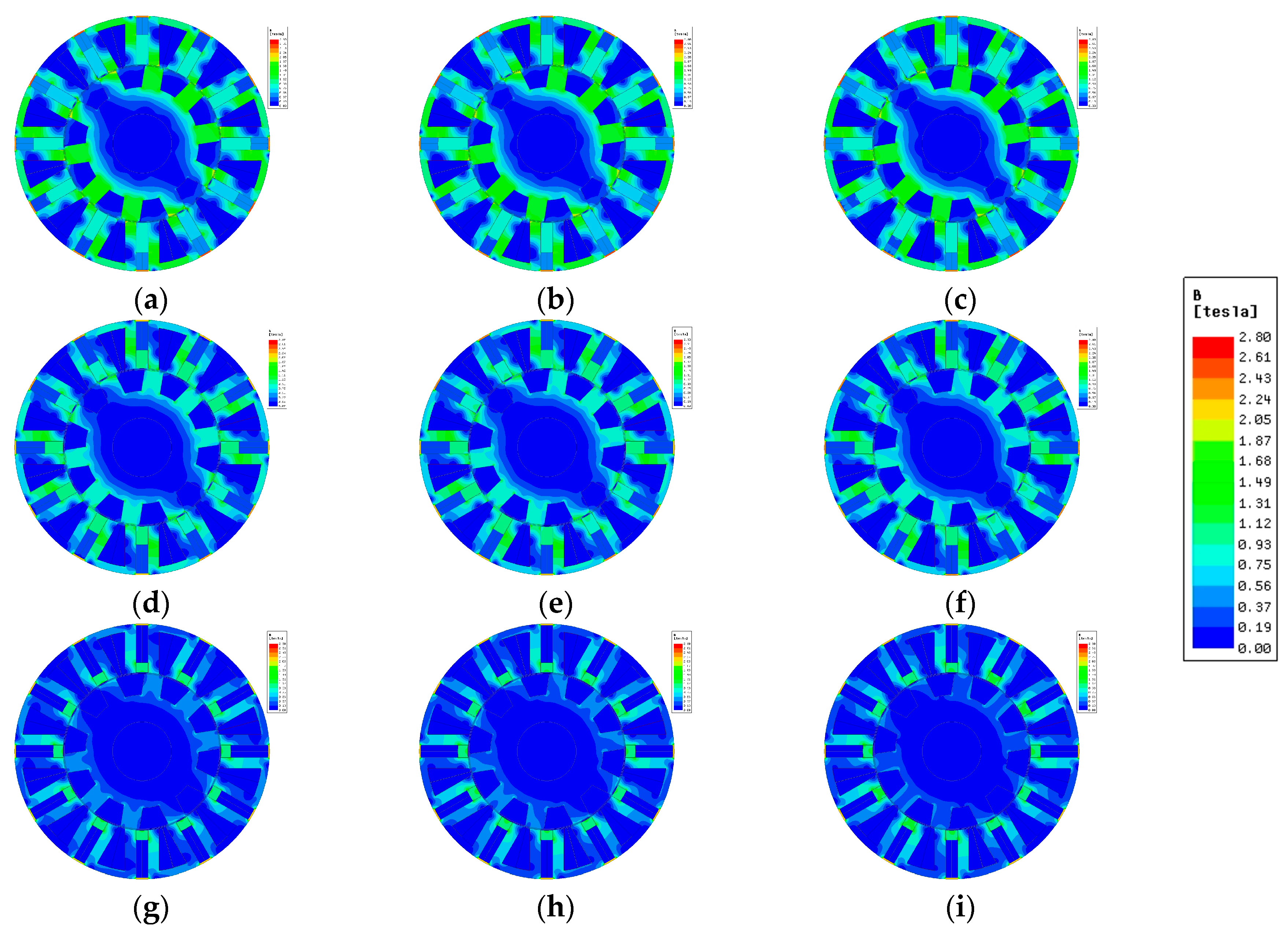
3. Influence of Hybridization Ratio on Field Back-EMF Ripple in HESF Machines
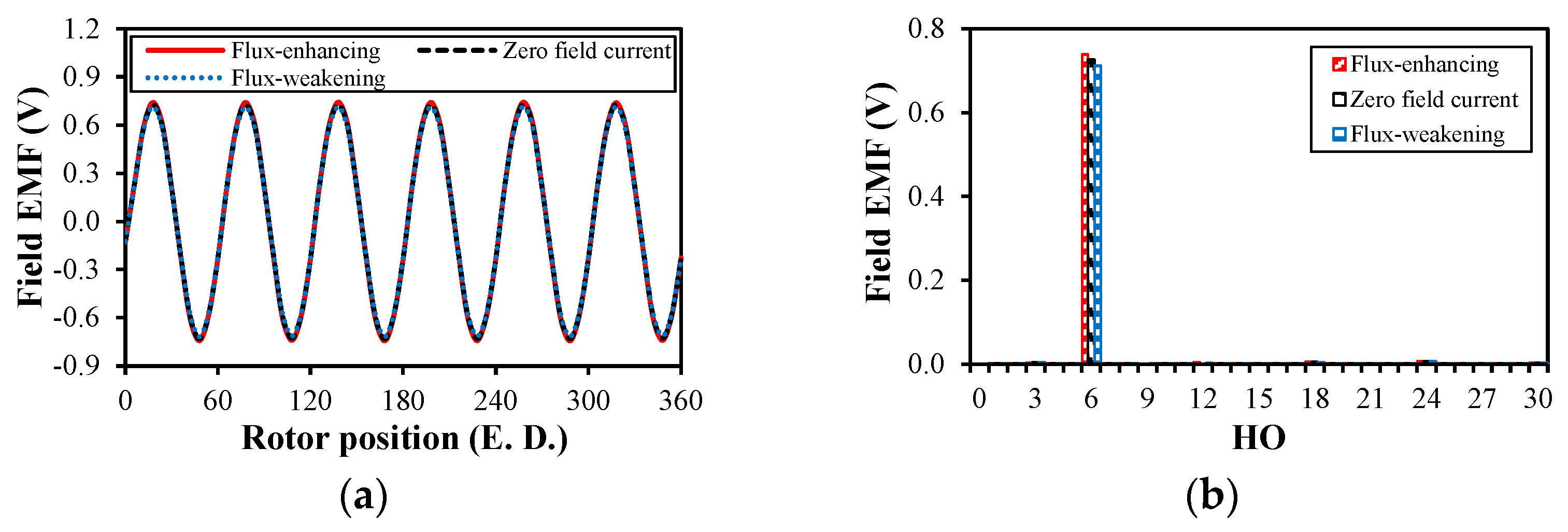
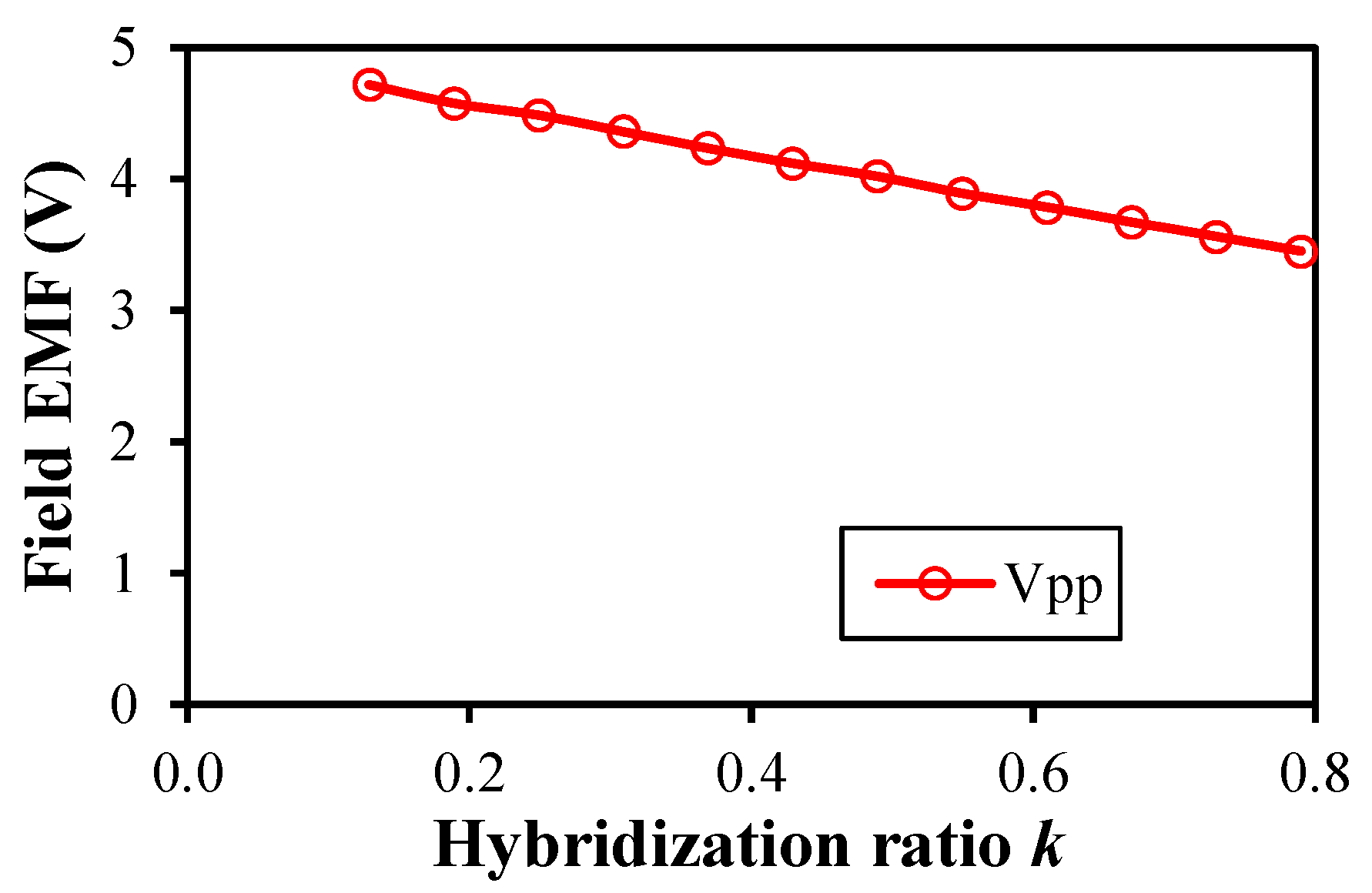
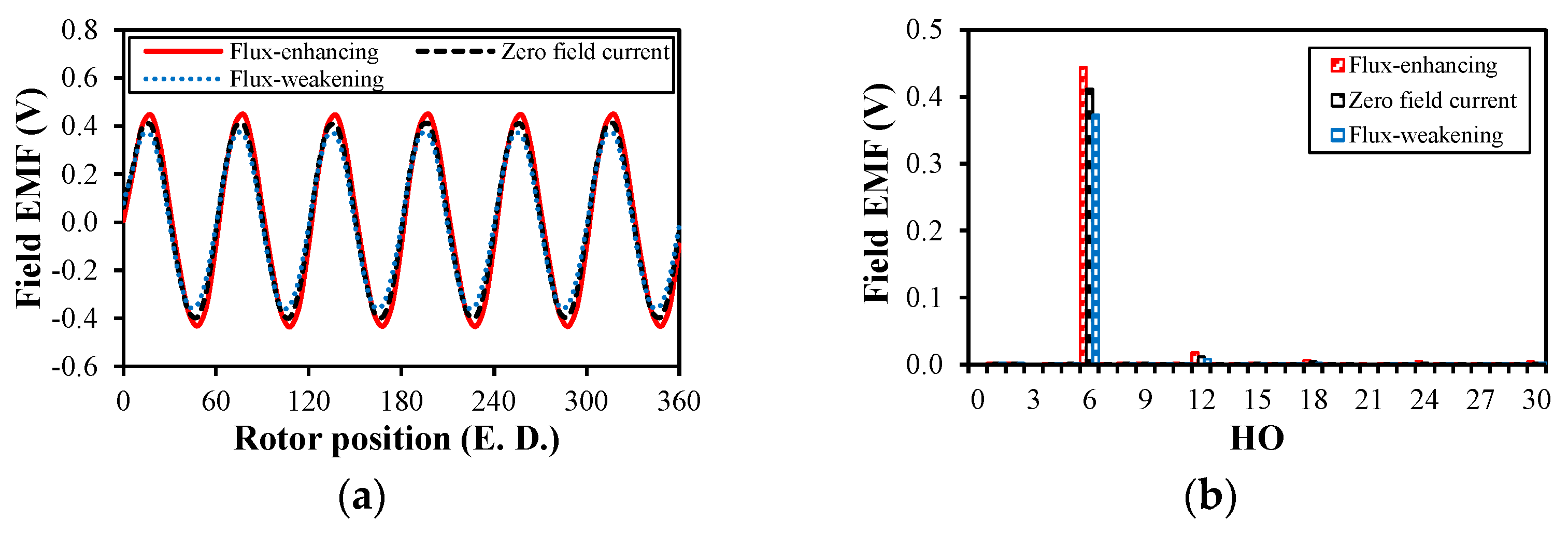
3.1. Open-Circuit Condition
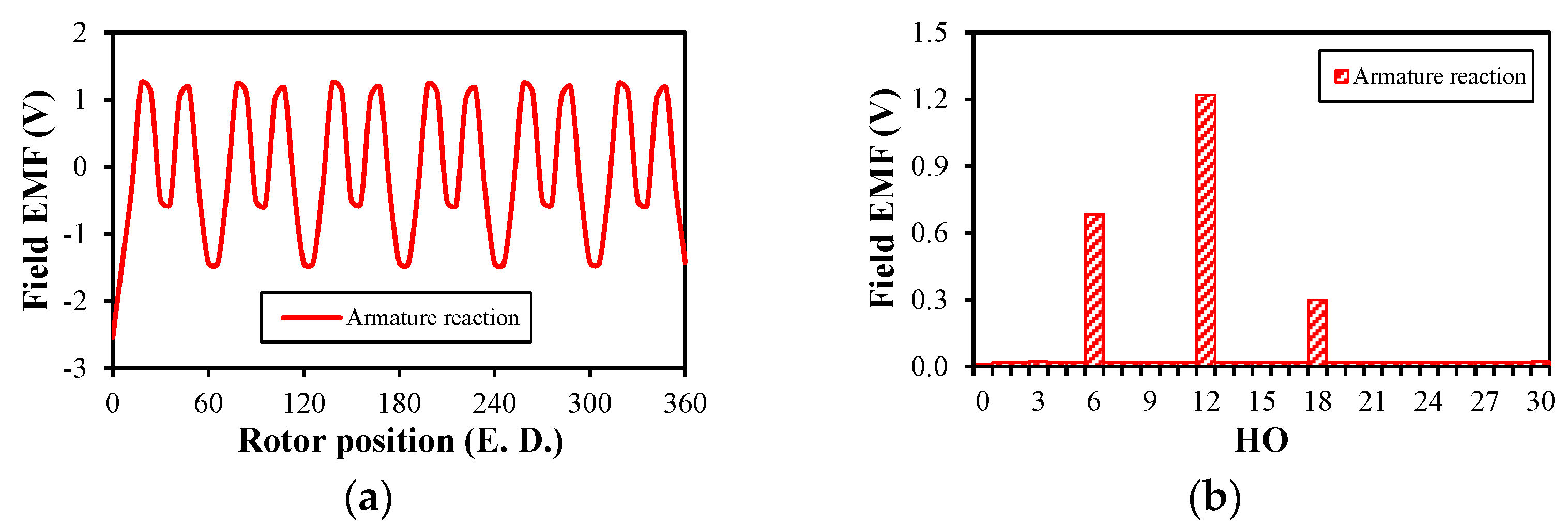
3.2. Armature Reaction Condition
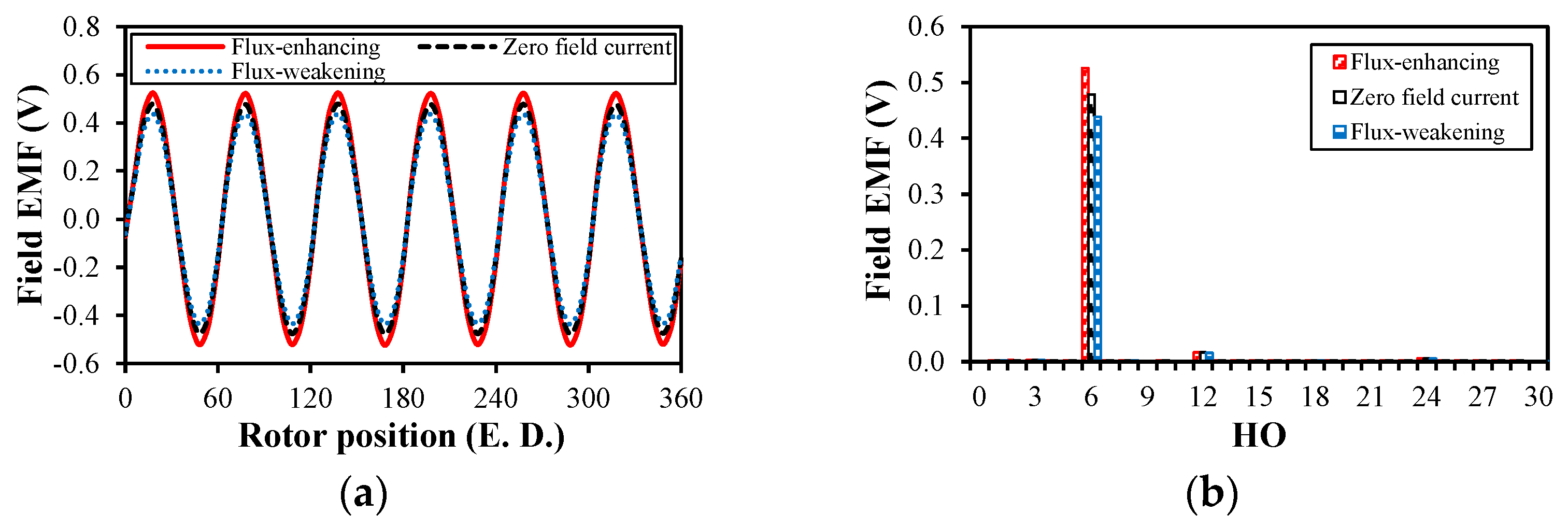
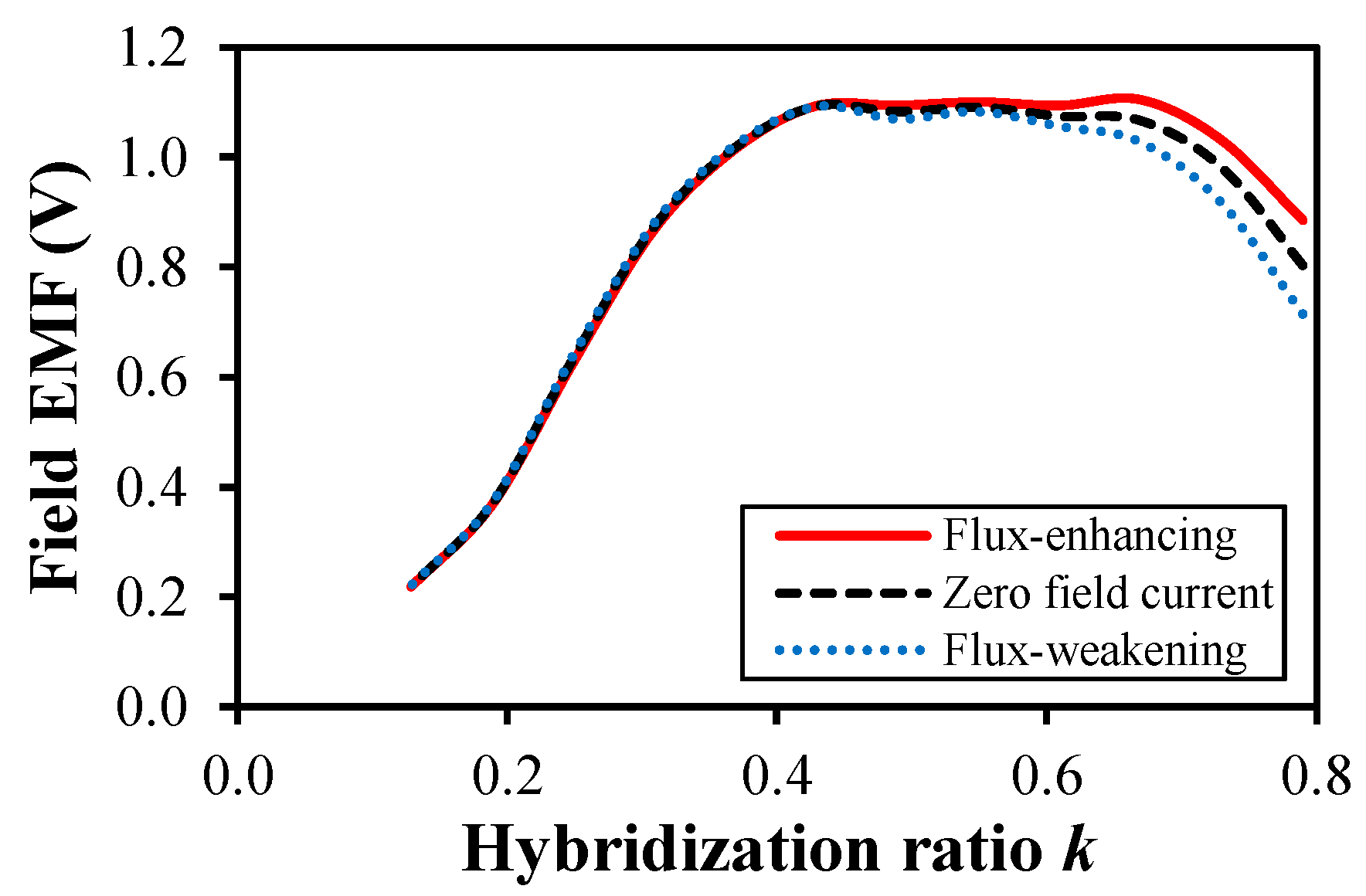
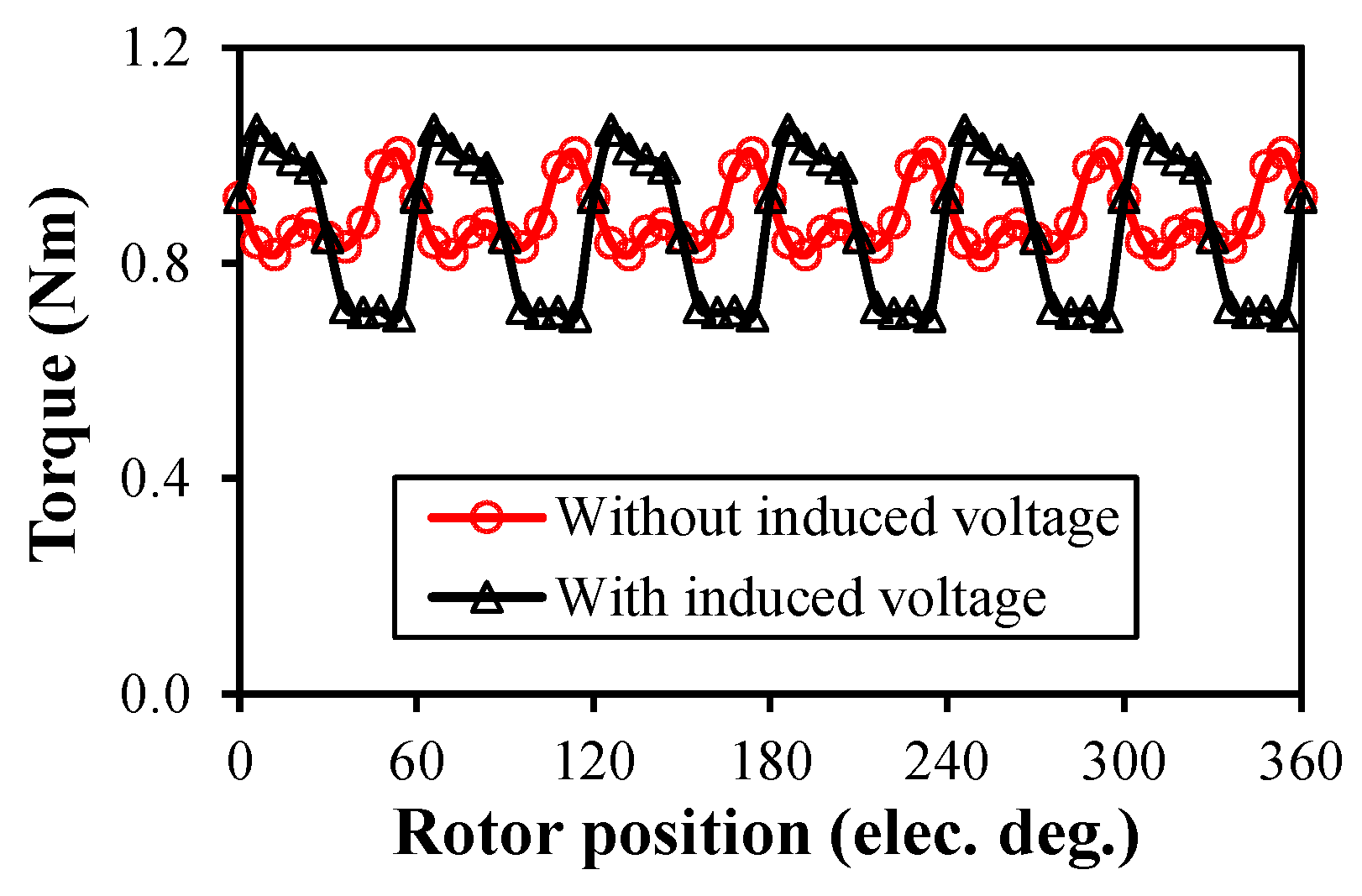
3.3. On-Load Condition
4. Comparison of HESF and WFSF Machines
4.1. Open-Circuit Condition
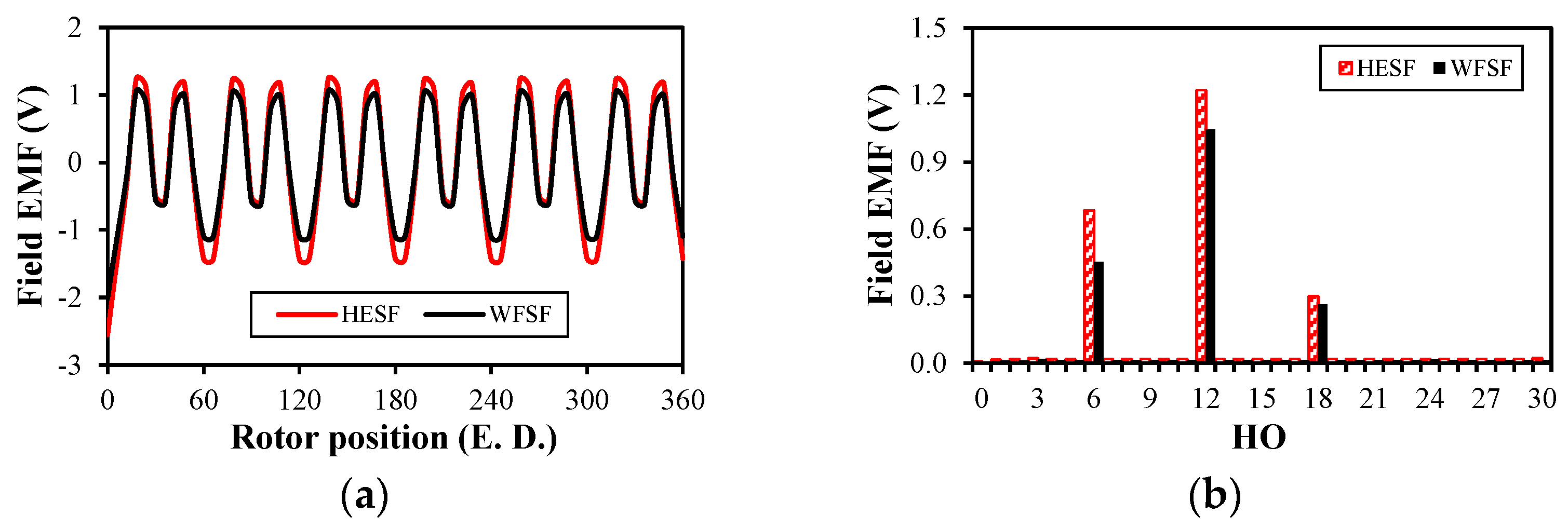
4.2. Armature Reaction Condition
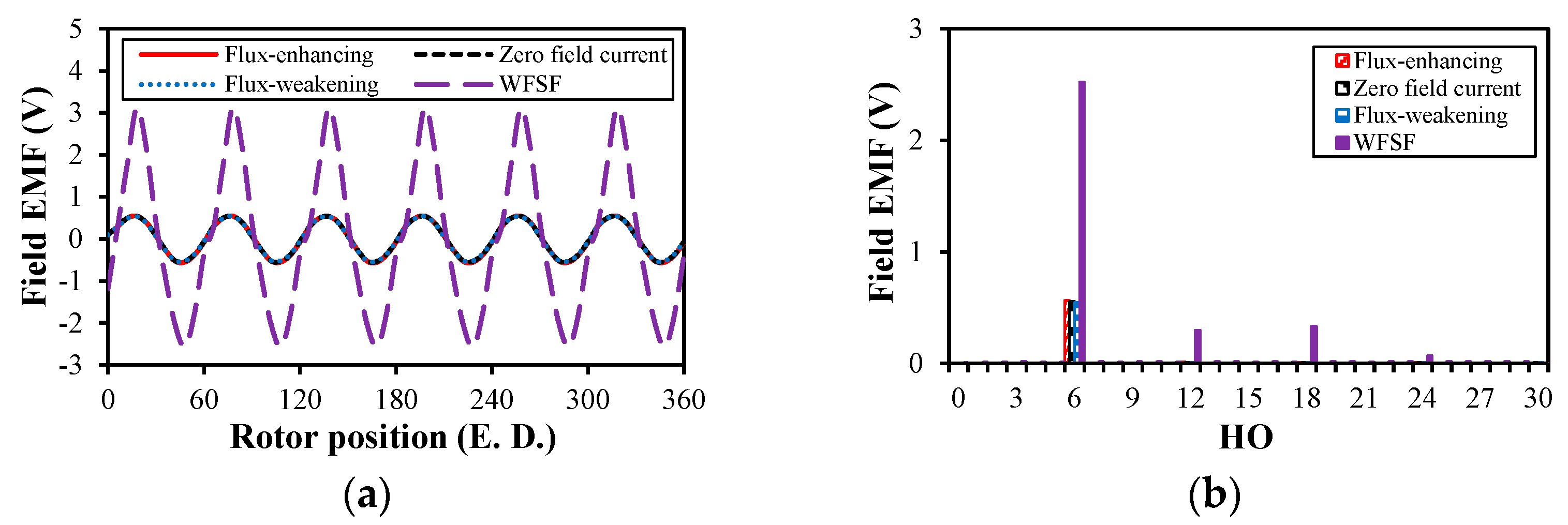
4.3. On-Load Condition
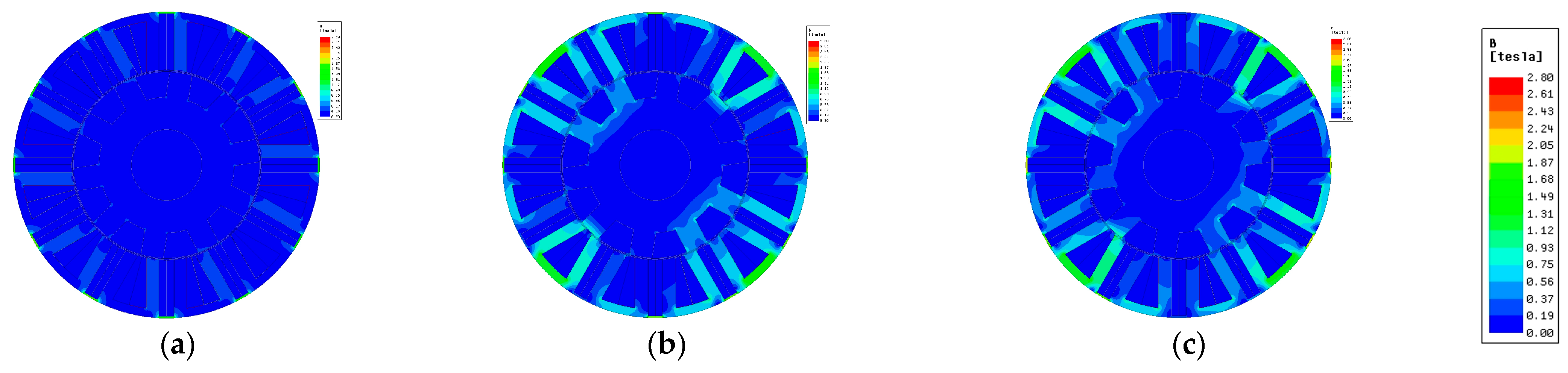
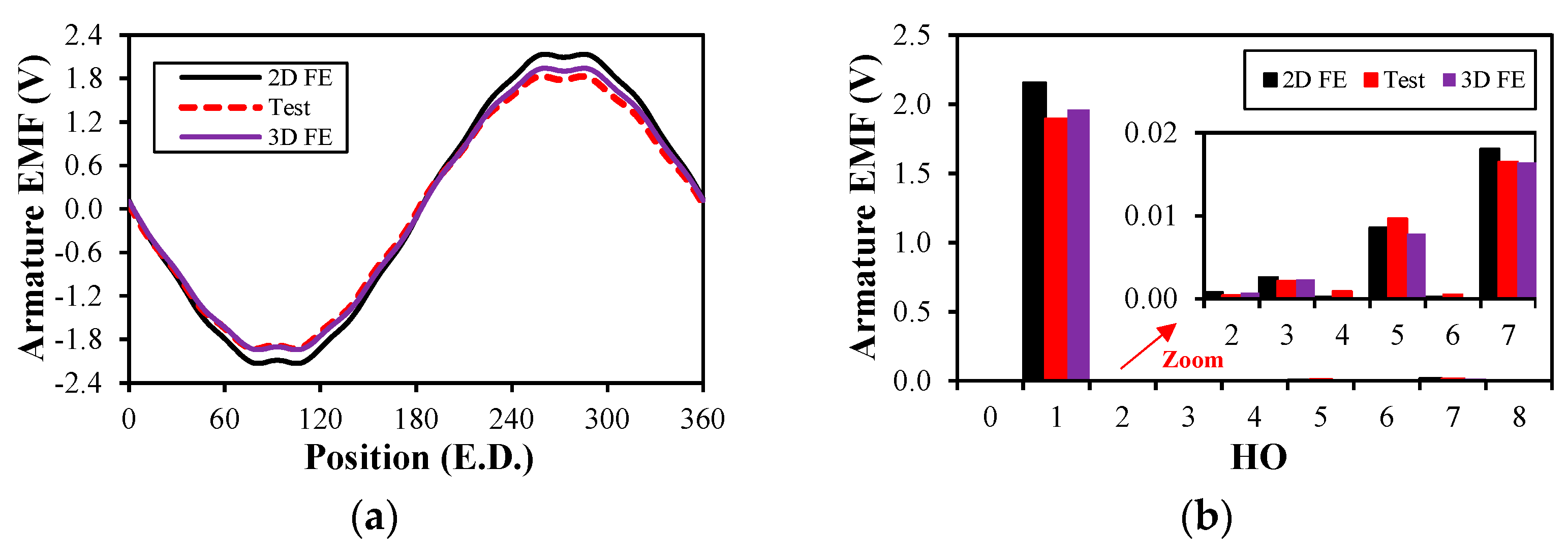
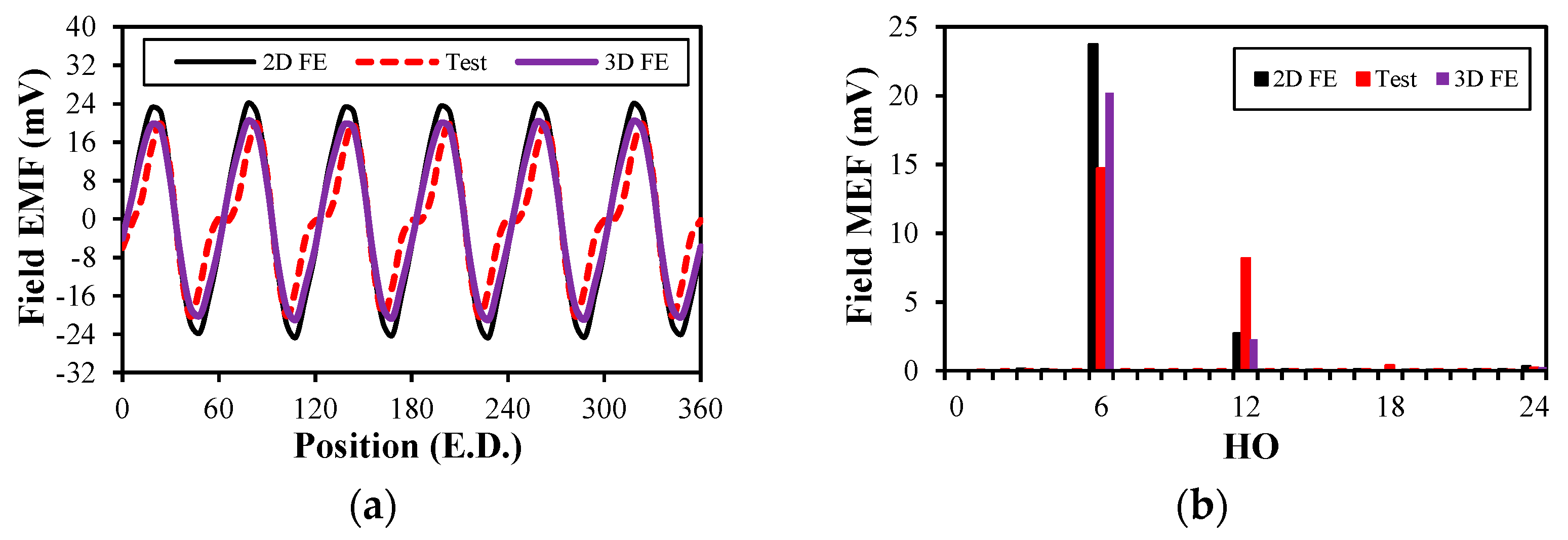
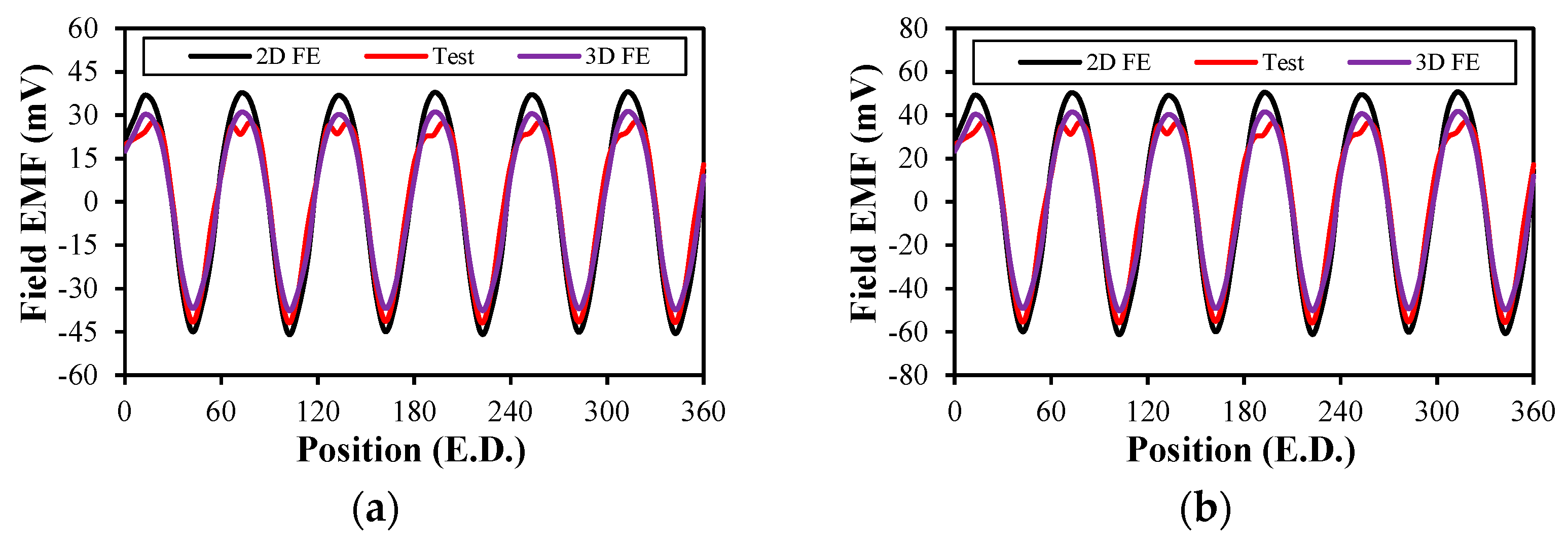
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICEs | Internal combustion engines |
| HEVs/EVs | Hybrid/full electric vehicles |
| HEMs | Hybrid-excited synchronous machines |
| WFSMs | Wound field synchronous machines |
| DSBLDC | Doubly salient brushless DC |
| HESF | Hybrid excited switched flux machines |
| SFPMM | Switched flux permanent magnet machine |
| PMSMs | Permanent magnet synchronous machines |
| WFSF | Switched flux wound field machine |
| MMFs | Magnetomotive forces |
| HOs | Harmonic orders |
| RMS | Root mean square |
References
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Electrical machines and drives for electric, hybrid, and fuel cell vehicles. Proc. IEEE. 2007, 95, 746–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C. The state of the art of electric, hybrid, and fuel cell vehicles. Proc. IEEE. 2007, 95, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S.; Carraro, E.; Castiello, M.; Fornasiero, E. Electric vehicle traction based on synchronous reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4762–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Hua, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W. Overview of stator-permanent magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5087–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C.; Chau, K.T.; Jiang, J.Z.; Xia, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R. Novel permanent magnet motor drives for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, M. Development of traction drive motors for the Toyota hybrid system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 126, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Okubo, T.; Abe, M.; Tamai, K. Development of High Response Motor and Inverter System for the Nissan LEAF Electric Vehicle; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wilden, R.; Gudergan, S.P. The impact of dynamic capabilities on operational marketing and technological capabilities: Investigating the role of environmental turbulence. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, W.L.; Ertugrul, N. Field-weakening performance of interior permanent-magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, Y.; Vido, L.; Gabsi, M.; Hoang, E.; Ahmed, A.; Lecrivain, M. Hybrid excitation synchronous machines: Energy-efficient solution for vehicles propulsion. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Atiq, S.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.I. PM assisted, brushless wound rotor synchronous machine. J. Magn. 2016, 21, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.Q.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Stone, D.A.; Foster, M.P. Investigation on operational envelops and efficiency maps of electrically excited machines for electrical vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Shima, K.; Momiyama, M.; Kawamura, M. A multipole synchronous machine with nonoverlapping concentrated armature and field windings on the stator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Shima, K.; Momiyama, M.; Kawamura, M. Development of a low-speed multi-pole synchronous machine with a field winding on the stator side. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical (ICEM), Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Afinowi, A.A.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Guan, Y.; Mipo, J.C.; Farah, P. Hybrid-excited doubly salient synchronous machine with permanent magnets between adjacent salient stator poles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Mipo, J.C.; Personna, S. A novel parallel hybrid excited machine with enhanced flux regulation capability. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussens, B.; Hoang, E.; Lecrivain, M.; Manfe, P.; Gabsi, M. A hybrid-excited flux-switching machine for high-speed DC-alternator applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2976–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, E.; Lecrivain, M.; Gabsi, M. A new structure of a switching flux synchronous polyphased machine with hybrid excitation. In Proceedings of the 2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wang, C.; Mipo, J.C.; Personnaz, S.; Farah, P. Reduction of open-circuit DC winding induced voltage in wound field switched flux machines by skewing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wang, C.; Mipo, J.C.; Personnaz, S.; Farah, P. Analysis and reduction of on-load DC winding induced voltage in wound field switched flux machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Hua, W.; Akehurst, S.; Zhu, X.F.; Zhang, W.T.; Hu, J.; Li, H.Y.; Zhu, J.M. Analysis and suppression of induced voltage pulsation in DC winding of five-phase wound-field switched flux machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1890–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wang, C. Reduction of on-load dc winding-induced voltage in partitioned stator wound field switched flux machines by dual three-phase armature winding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 5409–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, B. Reduction of field-winding-induced voltage in a doubly salient brushless dc generator with stator-damper winding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 7767–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Investigation of DC winding induced voltage in hybrid-excited switched-flux permanent magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 3594–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Cai, S.; Wang, L.; Wei, F.R.; Shao, B. Influence of stator slot and rotor pole number combination on field winding induced voltage ripple in hybrid excitation switched flux machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wei, F.R. Voltage pulsation induced in DC field winding of different hybrid excitation switched flux machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 4815–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Analysis of open-circuit DC winding induced voltage in partitioned-stator hybrid-excited switched-flux machine. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fourteenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte-Carlo, Monaco, 8–10 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Analysis and suppression of on-load excitation winding voltage pulsating in partitioned-stator hybrid-excited switched-flux machine. In Proceedings of the 10th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2020), Nottingham, UK, 15–17 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
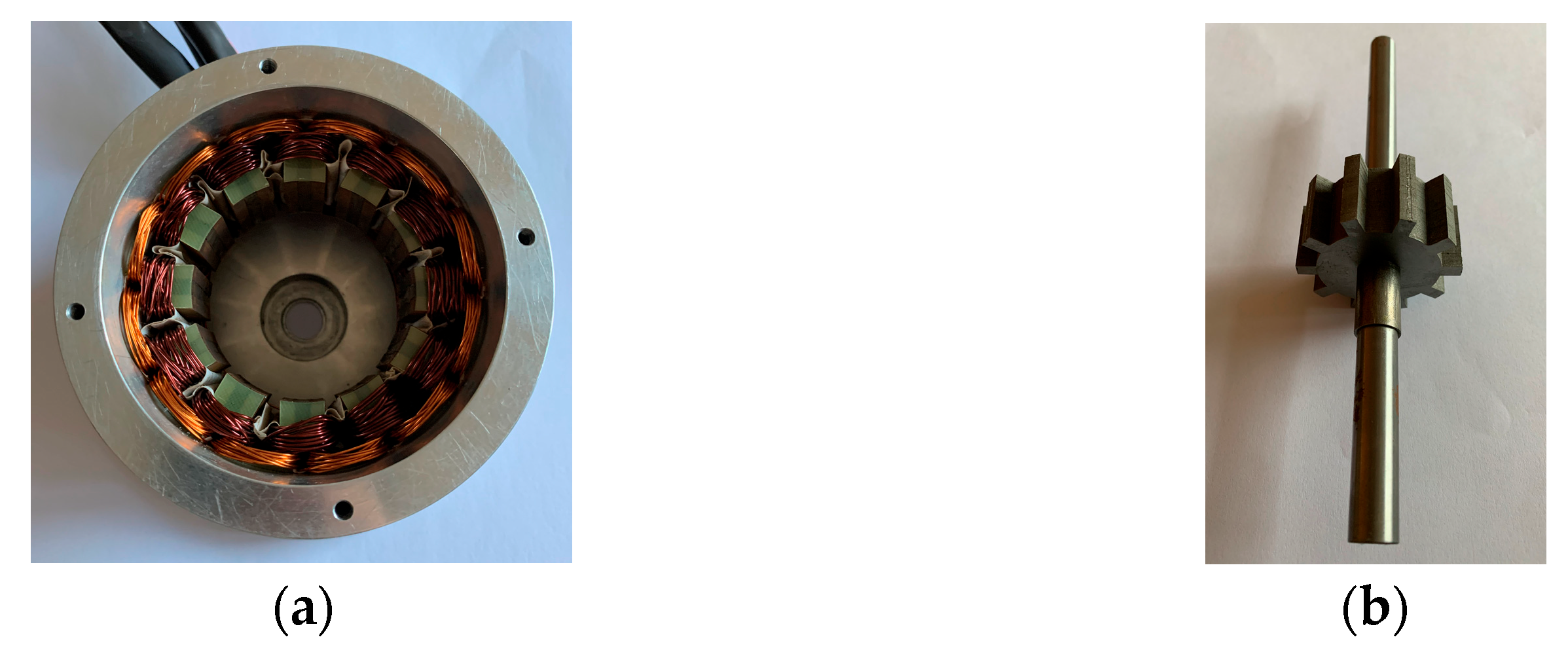


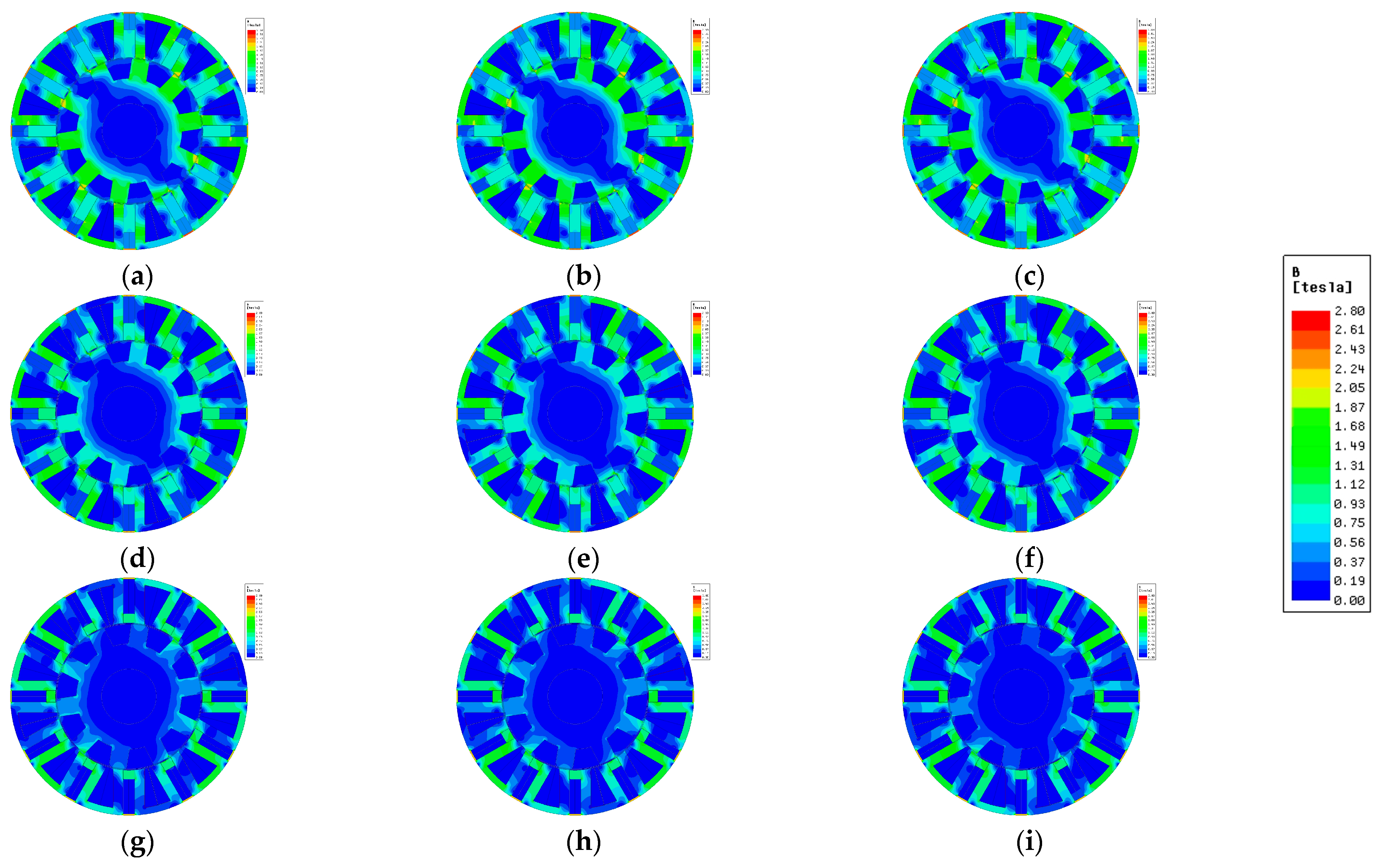






| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator outer radius | 45 mm | Stator pole number | 12 |
| Active axial length | 25 mm | Rotor pole number | 10 |
| Air gap length | 0.5 mm | Iron bridge length | 1 mm |
| Rotor outer radius | 26.5 mm | PM length | 7.5 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Han, R.; Shang, R.; Yang, Z. Influence of Hybridization Ratio on Field Back-EMF Ripple in Switched Flux Hybrid Excitation Machines. Machines 2025, 13, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060473
Sun X, Han R, Shang R, Yang Z. Influence of Hybridization Ratio on Field Back-EMF Ripple in Switched Flux Hybrid Excitation Machines. Machines. 2025; 13(6):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060473
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xiaoyong, Ruizhao Han, Ruyu Shang, and Zhiyu Yang. 2025. "Influence of Hybridization Ratio on Field Back-EMF Ripple in Switched Flux Hybrid Excitation Machines" Machines 13, no. 6: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060473
APA StyleSun, X., Han, R., Shang, R., & Yang, Z. (2025). Influence of Hybridization Ratio on Field Back-EMF Ripple in Switched Flux Hybrid Excitation Machines. Machines, 13(6), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060473








