Abstract
This paper presents an adaptive sliding mode controller (ASMC) with the implication of a forgetting factor for a two-degree-of-freedom (2-DOF) arm robot manipulator trajectory tracking. The proposed approach builds upon conventional sliding mode control (SMC), which is well known for its robustness and low tracking error. The controller dynamically adjusts this parameter by introducing an adaptive mechanism to enhance trajectory tracking, guarantee high robustness, and reduce chattering effects. In order to mitigate gain drift, a forgetting factor is incorporated into the adaptation law, ensuring stable and reliable control performance. Stability is validated using Lyapunov theory, and the effectiveness of the proposed ASMC is evaluated through numerical simulations. The simulations are conducted in MATLAB R2023b using a dynamic model of the 2-DOF robotic manipulator. Comparative results with conventional SMC confirm that the adaptive approach significantly improves tracking accuracy, noise robustness, and chattering suppression.
1. Introduction
In recent years, control strategies for robotic manipulators have received a lot of attention, especially in the context of systems with limited degrees of freedom, where researchers can isolate and understand the behavior of new control techniques and algorithms under controlled conditions before extending them to more complex robots. Robotic manipulators, also known as robotic arms, are fundamental elements in the development of automated systems because of their ability to perform precise and repeatable movements, which makes them valuable in both academic research and industrial settings [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. A key challenge in robotic manipulation is not the mechanical design alone, but the development of robust control algorithms that ensure accurate trajectory tracking, disturbance rejection, and adaptability to uncertain dynamics.
Trajectory tracking control in robotic arms plays a pivotal role in ensuring precise and efficient motion. Over time, various control strategies have been developed to enhance performance. Traditional controllers, such as proportional–integral (PI) and proportional–integral–derivative (PID), remain widely used due to their simplicity and ease of implementation [8,9,10]. However, these controllers face challenges when dealing with the nonlinearity of the system, variations in parameters, and external disturbances, often leading to inaccuracies of follow-up [11]. In contrast, SMC, known for its robustness against uncertainties, offers a promising alternative. Yet, its primary drawback is the chattering phenomenon, undesired oscillations that can cause mechanical wear. To address this, high-order sliding-mode control (HOSMC) was introduced, effectively minimizing chattering while preserving the robustness of SMC. However, its increased computational complexity poses challenges for real-time implementation [12]. Hybrid control approaches, such as PI-Fuzzy and SMC-Fuzzy controllers, attempt to merge the benefits of conventional and intelligent control techniques. Despite their potential, their effectiveness depends heavily on the precise tuning of fuzzy rules, which can be complex. Furthermore, controllers based on neural networks (NN) offer adaptability and excel in managing nonlinearities, they require extensive training and significant computational power [13]. Additionally, iterative learning control (ILC) has gained attention in robotic control for its ability to improve performance over repeated tasks, addressing challenges such as disturbances and system uncertainties by refining control inputs based on past experiences [14].
Numerous control strategies have been proposed in the literature to address the challenges of accurate trajectory tracking in robotic manipulators. For instance, Djaneye-Boundjou et al. [15] employed an adaptive particle swarm optimization (APSO) algorithm to optimize PID gains in high-degree-of-freedom (H-DOF) and multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems, effectively accounting for joint coupling effects. Their approach was validated through simulations on a 2-DOF robotic arm. Likewise, Wazzan et al. [16] utilized the social spider algorithm (SSA) to improve PID control and integrated fuzzy logic (FL) to minimize steady-state error and improve tracking accuracy. Their MATLAB-based implementation, which included forward and inverse kinematics, achieved precise circular trajectory tracking. These works illustrate the benefits of combining intelligent optimization techniques with classical control methods to improve robustness and system performance. Milind et al. [17] designed a PID controller for a flexible two-link robotic manipulator operating in 3D space. The 2-DOF system, modeled as a planar mechanism with motion in the x-y plane, used a base motor for the first link and a shoulder motor for the second. MATLAB Simulink simulations demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed controller with minimal control errors. Zakia et al. [18] introduced a hybrid control strategy combining PID and SMC for a 2-DOF planar manipulator. In this design, the PID parameters were used to construct the sliding surface, allowing the controller to benefit from the simplicity of PID and the fast convergence and robustness of SMC, thus improving stability and tracking performance. Silva et al. [19] studied PID and PID 2-DOF controllers for a cylindrical manipulator’s rotational joint. They identified a first-order system model using the non-recursive least squares method and tuned it with Ziegler–Nichols (ZN), Chien–Hrones–Reswick (CHR), internal model control (IMC), and Skogestad IMC (SIMC). Performance evaluation showed CHR and IMC yielded the best results for both controllers. Azar et al. [20] proposed a control strategy for position control and trajectory tracking in robotic manipulators, using independent 2-DOF PID controllers for each link of a two-link arm. A type-2 fuzzy compensator is added to improve trajectory tracking and system performance. The study shows that integrating the fuzzy compensator with 2-DOF fractional-order PID (FOPID) controllers enhances performance compared to existing methods, with numerical validation provided. Mohammed et al. [21] developed an adaptive 2-DOF PID controller to handle uncertainties and nonlinearities in real-time robotic manipulation, incorporating a supervisory fuzzy logic system (FLS) for enhanced robustness. MATLAB simulations and practical implementation demonstrated that the adaptive 2-DOF PID controller outperformed traditional fixed-gain controllers, offering better robustness against disturbances and system variations. Bi [22] explored the role of symmetry in robotic dynamics and fault diagnosis, proposing an optimized fuzzy PID algorithm that adjusts the P, I, and D gains based on error rates. They developed a mathematical model for a 2-DOF manipulator and a gradient-based trajectory planning algorithm, with experimental results validating the approach. Tuan et al. [23] studied the control of a 2-DOF robot arm with elastic actuators, enhancing safety by reducing impact forces during collisions. They introduced a two-loop adaptive control strategy, combining ASMC for the outer loop and MRAC for the inner loop, demonstrating a reduction in RMS error and a significant reduction in settling time compared to conventional sliding mode control. Jouila et al. [24] proposed a robust adaptive control for a two-link robot manipulator using a non-singular fast terminal sliding mode (NFTSM) controller combined with a wavelet neural network (WNN) to handle uncertainties and disturbances. A compensation term and online adaptation improved tracking and reduced chattering, with Lyapunov theory ensuring stability. Simulations demonstrated superior performance over other controllers. Sun et al. [25] proposed an adaptive fuzzy backstepping controller for a 2-DOF manipulator to improve trajectory tracking and reduce jitter and positioning errors. Simulation results showed enhanced precision and stability under disturbances. Rahmani et al. [26] developed a hybrid PD-SMC controller optimized using the extended grey wolf optimizer (EGWO), which effectively balanced robustness and simplicity. Simulation results demonstrated superior performance compared to conventional SMC and PDSMC methods. Hameed et al. [27] developed an ASMC approach for a 2-DOF robotic manipulator, emphasizing the method’s robustness to uncertainties and external disturbances. The proposed controller was designed to improve tracking accuracy, reduce steady-state error, and suppress chattering. Experimental results showed strong performance, achieving an error rate of and system efficiency exceeding , validating the effectiveness and reliability of the control strategy. Similarly, Balthazar et al. [28] examined various control techniques—such as linear–quadratic regulator (LQR), feedforward, and integral control—in order to improve positioning precision and vibration reduction in 2-DOF robotic manipulators. Their findings demonstrated enhanced control of motor current and smoother link motion, contributing to overall system stability and accuracy. Zafer et al. [29] proposed a 2-DOF planar robot control using a fuzzy logic controller (FLC) optimized by particle swarm optimization (PSO). The PSO-tuned FLC outperformed the PSO-tuned PID controller in trajectory control and robustness under varying conditions and noise. Girgis et al. [30] proposed a fractional-order adaptive PID (FOAPID) controller to improve the stability and tracking performance of a 2-DOF robotic manipulator. By combining fractional calculus with the EFRLS algorithm, the controller adaptively adjusts its gains. Lyapunov analysis ensures stability, and the method shows strong robustness against uncertainties and disturbances.
In addition to robust trajectory tracking, contour accuracy is another key concern, especially in manufacturing applications. Several studies have focused on minimizing contour errors using traditional control methods with servo matching [31,32], cross-coupled control (CCC) strategies [33], and task coordinate system approaches [34]. These methods offer high contour precision and can be complementary to robust tracking control techniques such as the one proposed in this study.
In this paper, an adaptive sliding mode controller (ASMC) is implemented to track the trajectory of the 2-DOF arm robot. The main contributions of the proposed ASMC scheme are summarized as follows:
- The ASMC is implemented to overcome the limitations of conventional SMC, particularly in terms of robustness and chattering reduction.
- By dynamically adjusting the control gain, the ASMC enhances disturbance rejection capabilities while improving tracking accuracy.
- The proposed approach ensures precise trajectory tracking with reduced control effort, making it a more effective solution for robotic arm control.
- A novel adaptation law with a forgetting factor is proposed to prevent gain drift when the sliding surface becomes small.
- The implication of the forgetting mechanism stabilizes the gain, avoids high-frequency oscillations, and improves controller reliability in practical implementations.
- Comparative simulations with traditional SMC demonstrate that the ASMC achieves superior performance in terms of tracking precision and robustness.
- The results confirm the effectiveness of the ASMC in addressing the drawbacks of conventional SMC.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents an in-depth analysis of the dynamic modeling of a 2-DoF robotic manipulator. Section 3 outlines the proposed control strategies and their implementation. Section 4 discusses the simulation results. Finally, the conclusion, Section 5, highlights the main findings and contributions of the study.
2. Dynamic of a 2-DoF Arm Robot Manipulator
As illustrated in Figure 1, a 2-DOF robot arm manipulator is a robotic system with two independent joints, typically consisting of a base joint and an elbow joint, enabling motion in a planar workspace [35]. This type of manipulator is widely used in industrial automation, robotic research, and precision tasks requiring controlled motion. The manipulator consists of two rigid links of lengths and , with masses and , respectively, connected through rotary joints. The dynamic model of a 2-DOF robotic manipulator can be derived using Lagrange’s formulation, considering joint torques, inertia, Coriolis, centrifugal forces, and external disturbances. The general equation of motion for a 2-DOF robot arm is given as follows [36,37]:
In this representation, the vectors , , and correspond to the joint positions, velocities, and accelerations, respectively. The inertia matrix is denoted by , while is the vector of Coriolis and centrifugal forces. The gravitational forces acting on the system are represented by . The applied joint torques are given by . The explicit expressions for , , and can be found in Appendix A. Consequently, the system dynamics can be expressed as follows [38]:
The dynamic behavior of the 2-DOF robotic manipulator can be succinctly expressed in the following form as follows:
where , , and represents the control input vector. To account for parameter variations and uncertainties in the system, the equation is modified as follows [39]:
where and denote the uncertainties associated with the system parameters. The equation can be further expressed as follows:
where .
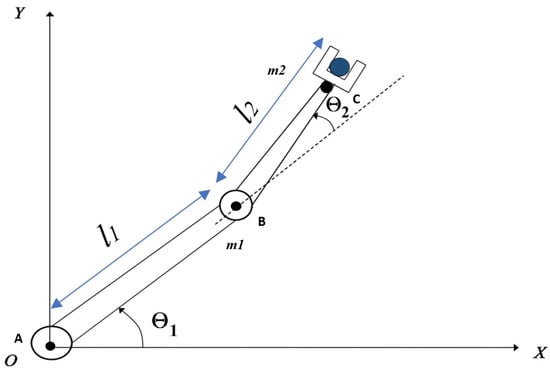

Figure 1.
The 2 DoF rigid-link robot manipulator [40].
3. Control Design
This section presents the design of an adaptive sliding mode controller (ASMC) for a 2-DOF robotic arm, as illustrated in Figure 2. The ASMC is implemented on a proportional-derivative (PD) surface, which is utilized in both proposed controllers. The PD surface is chosen in order to minimize steady-state error, while the derivative term improves transient response, leading to enhanced tracking performance. The ASMC approach dynamically adjusts the control gains to enhance robustness and mitigate chattering, ensuring better adaptation to system uncertainties and disturbances.
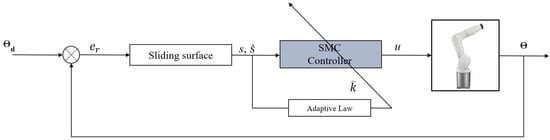
Figure 2.
Block diagram illustrates the proposed control strategy.
3.1. Sliding Mode Control Scheme
SMC is a nonlinear control approach known for its robustness, ease of implementation and precision. Its framework is structured to guide the system states toward a predefined surface in the state space, referred to as the sliding surface. The design of this surface, denoted as , is a critical aspect of the SMC technique. A common approach to designing the sliding surface in SMC is through the use of a proportional-derivative (PD) structure. This method enhances stability and improves tracking performance by shaping the system dynamics on the sliding surface. The general form of a PD sliding surface is given as follows [40]:
where is the tracking error vector between the actual position and the desired position , is the derivative of the tracking error vector, and are diagonal positive proportional and derivative gains matrices, respectively, which designed to influence the convergence rate and stability of the system. Since the sliding surface s is a vector, each component of the sliding surface, denoted as (where i = 1,2 …m), is associated with a separate degree of freedom of the manipulator. This formulation ensures that when the system reaches the sliding surface , the error dynamics behave like a proportional-derivative control system, leading to improved tracking accuracy and robustness.
Once the sliding surface is designed, the next step is to determine the control law that drives the system states toward and maintains them on this surface. In general, the control law in SMC comprises two components: the equivalent control and the switching control . The equivalent control ensures exact linearization, while the switching control is responsible for stabilizing the system by compensating for model uncertainties and rejecting disturbances. The overall control law is given by [40]:
where ensures that the nominal system dynamics follow the desired trajectory. introduces robustness, compensating for uncertainties and external disturbances. This formulation guarantees that the system converges to the sliding surface and maintains stability despite model uncertainties and perturbations. The nonlinear system under consideration can be expressed in state-space form as follows:
where and are continuous functions defining the system dynamics, and u is the control input. The objective of SMC is to design a control law that ensures the system state reaches and remains on a predefined sliding surface . As previously mentioned, the control input is decomposed into and (Equation (7)). The equivalent control is obtained by enforcing the sliding condition , ensuring that the system dynamics remain on the sliding surface. Substituting Equation (6) and the system dynamics of Equation (8) into condition, leads to the general expression for as follows [41]:
This formulation ensures that the nominal system behavior follows the desired trajectory while maintaining stability. Using Equations (5), (6), and (9). Therefore, with negligible uncertainties, the equivalent control is given as follows:
The nonlinear component is designed in order to guarantee that the control variable moves toward the sliding surface while satisfying the convergence condition, which is given as follows [41]:
This condition ensures that the system state moves toward and remains on the sliding surface, satisfying stability requirements. The switching control condition is given by [42]:
where is diagonal positive matrix defined as . Finally, using Equations (7), (10), and (12), the total control input u is given by following:
In order to guarantee the stability of the SMC controller, Lyapunov theory is applied. A commonly used Lyapunov candidate function is chosen as follows [43]:
Differentiating the Lyapunov function with respect to time yields
Substituting Equations (7) and (13) into Equation (15) yields the following:
Since eliminates the corresponding terms in , Equation (15) simplifies to
Thus,
3.2. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control
The adaptive sliding mode control (ASMC) is an advanced control strategy designed to enhance the robustness and performance of SMC by dynamically adjusting the control gains in response to system uncertainties and disturbances [44]. Traditional SMC offers high robustness but suffers from chattering due to the high-frequency switching of the control input [45]. ASMC reduces this issue by incorporating an adaptive law that regulates the control parameters in real time, ensuring an optimal balance between robustness and smooth control action. By continuously tuning the control gains based on system states and tracking errors, ASMC improves convergence speed and reduces steady-state error. The complete control law using adaptive SMC is formulated as follows [46,47]:
where the equivalent control is defined in (10), while the adaptive control is provided as follows [46]:
where is the switching adaptive gain defined as . In order to enhance robustness and reduce chattering, ASMC employs an adaptive gain adjustment strategy. The element of the switching gain vector is updated according to the following adaptation law as follows [46]:
where and is the adaptive learning rate [46]. The adaptation law in (21) allows the control gain to increase based on the magnitude of the sliding variable s. However, this formulation has a critical drawback: Since is always positive when , the gain will increase continuously over time, leading to an effect known as gain drift [48]. The uncontrolled increase in arises because the adaptation law relies merely on , meaning that as long as remains nonzero, continues to grow indefinitely. This can lead to excessively high gains, which may cause instability or high-frequency control actions in practical implementations. To address this issue, a forgetting factor is introduced to regulate the growth of and ensure its boundedness over time. By incorporating a damping term, the adaptation law prevents excessive accumulation of while still allowing it to adapt effectively according to the system tracking error. In order to mitigate gain drift, a forgetting factor is introduced into the adaptation law, leading to the following modified update rule [49]:
where is a positive diagonal matrix that acts as a damping term that counteracts the continuous increase of . When grows too large, the term reduces its rate of increase, ensuring that remains bounded. This modification allows the controller to retain the benefits of adaptive tuning while avoiding excessive control gains that could degrade performance. Now, using Equations (10), (19) and (20), the final ASMC control law is expressed as
In order to demonstrate the proposed ASMC controller stability, a Lyapunov candidate is chosen as follows [50]:
In the same manner, through simplification and substitution Equations (7) and (23) into Equation (24). Therefore, the time derivative of the Lyapunov is as follows:
The term becomes negative if is chosen to be sufficiently large; thus,
4. Results and Discussion
This section presents a comparative analysis of the control performance of the ASMC and SMC applied to a 2-DOF arm robot manipulator. The evaluation focuses on trajectory tracking accuracy, chattering elimination, and overall system response to the desired motion trajectories under noise application. Table 1 represents the initial values and proposed controller parameters.

Table 1.
Initial values and parameters for ASMC and SMC.
After tuning the ASMC and SMC controllers parameters using the trial-and-error method, the results demonstrate that ASMC consistently and significantly improves the tracking performance of the robotic arm over different initial conditions. Table 2 shows a comprehensive comparison of indices for both controllers under two distinct scenarios: , and , . For the first case, where and , ASMC achieves lower trajectory errors, with an RMSE of for and for , contrast to SMC, which records higher RMSE values of and , corresponding to improvements of and , respectively. Additionally, ASMC exhibits superior integral performance, achieving lower ITAE values of for and for , while SMC results in higher ITAE values of and , represents enhancements of and . The IAE metric further highlights the ASMC advantage, with values of and for and , respectively, in contrast to SMC, which yields and . Moreover, ASMC achieves lower ISE values of and , whereas SMC shows significantly higher ISE values of and . Likewise, the IAE and ISE values for ASMC are consistently better, achieving reductions of and in IAE, and and in ISE for and , respectively. The maximum absolute error for ASMC is rad for both and , which is similar to the SMC maximum absolute error of rad for and rad for . In the second case, with initial conditions and , a similar trend is observed. ASMC again outperforms SMC, achieving lower RMSE values of for and for , corresponding to improvements of and over SMC. The ITAE values improve by for and for , while the IAE values improve by and , respectively. Furthermore, ASMC achieves notable reductions in ISE, improving by for and for compared to the corresponding SMC values. These results confirm that ASMC provides enhanced accuracy and control efficiency in trajectory tracking for robotic arms.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of ASMC and SMC for different initial conditions.
The figures presented are split into two parts: part (a) corresponds to Case 1 with initial conditions , , and part (b) corresponds to Case 2 with , . Figure 3 illustrates the position tracking control of and using ASMC in comparison with SMC. It is evident from the figure that ASMC achieves a quicker and more efficient alignment with the reference trajectory than SMC. The 2-DoF arm robot manipulator, when controlled by ASMC, reaches the desired trajectory more swiftly and accurately, whereas SMC also demonstrates satisfactory performance. Figure 4 depicts the position tracking error of and under ASMC and SMC. As shown in Figure 4, ASMC results in a smaller tracking error compared to SMC, indicating improved precision. Figure 5 illustrates the sliding surface for both ASMC and SMC over time. According to this figure, both controllers successfully drive the system to the sliding surface, maintaining it at zero. However, noticeable chattering is observed in the SMC response, whereas ASMC achieves a smoother trajectory without chattering. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the adaptive mechanism in ASMC, which mitigates high-frequency oscillations while ensuring precise tracking. The velocity of joints and under the applied controllers is shown in Figure 6. According to Figure 6, ASMC enables the 2-DOF arm robot manipulator to settle more quickly to the set point compared to SMC. Additionally, ASMC bears and eliminates the chattering, with velocity fluctuations nearly vanishing, in contrast to SMC, where noticeable chattering is present. However, it should be noted that, in order to reduce the chattering effect typically encountered in conventional SMC, the discontinuous sign function can be replaced with a continuous approximation such as the saturation function or the hyperbolic tangent function tanh(s) [51]. This modification smooths the control signal and makes the controller more suitable for practical implementations, where high-frequency switching can lead to actuator wear or undesirable vibrations. However, such continuous approximations cause the system to converge to a boundary layer around the sliding surface rather than reaching exactly, which may slightly reduce tracking accuracy. In contrast, the proposed ASMC technique dynamically adjusts the switching gain in response to the tracking error, improving robustness and adaptability and significantly mitigating chattering while maintaining a high level of tracking precision. Figure 7 illustrates the control output signals for ASMC and SMC, highlighting differences in their performance. The SMC controller shows significant oscillations in its control signal, particularly after s, indicating less stable control behavior. These oscillations could lead to undesirable effects in real-world applications such as heat, energy losses, and system instability. In contrast, ASMC maintains a smooth control signal, reflecting its stability and precision. In order to evaluate the robustness of the proposed ASMC and SMC controllers, random noise is introduced into the system. Figure 8 and Figure 9 illustrate the effect of noise on the error signal for SMC and ASMC, respectively. As shown in Figure 8, the SMC controller maintains stability for noise levels ranging from to . However, when subjected to , , and , the error signal exhibits significant fluctuations, exceeding the range of for and for under high noise value of . In contrast, Figure 9 demonstrates that the ASMC controller provides enhanced stability under the same conditions. Even with high noise applied, the error variations remain more controlled, within the range of for and for . This indicates that ASMC exhibits superior resilience to high noise levels compared to SMC, ensuring more reliable performance in the presence of external disturbances.
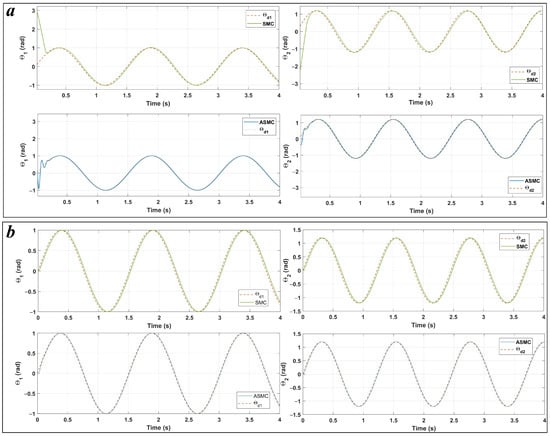
Figure 3.
Position tracking joints under ASMC and SMC for Case 1 (a), and Case 2 (b).
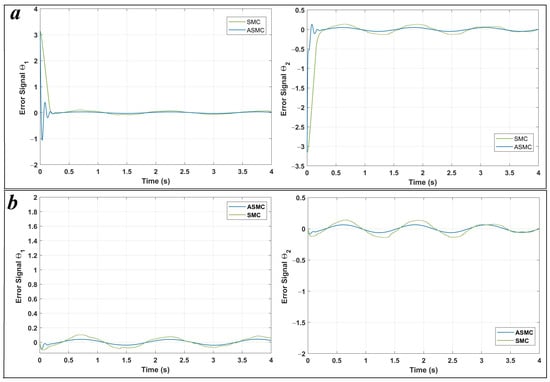
Figure 4.
Position tracking error joints under ASMC and SMC controllers for Case 1 (a), and Case 2 (b).
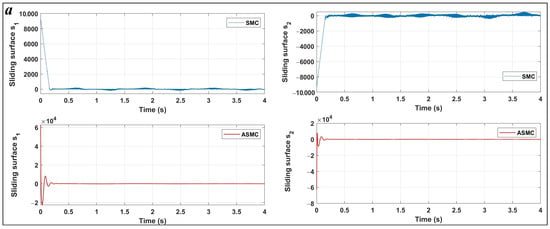
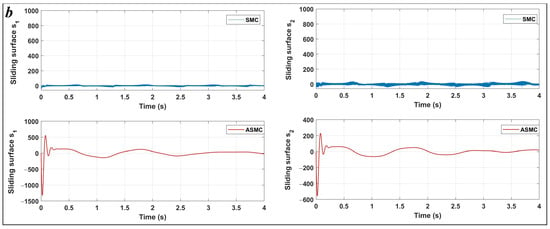
Figure 5.
Sliding surfaces for ASMC and SMC for Case 1 (a), and Case 2 (b).
Figure 6.
Velocity joints under ASMC and SMC controllers for Case 1 (a), and Case 2 (b).

Figure 7.
Control signals of the ASMC and SMC controllers for Case 1 (a), and Case 2 (b).
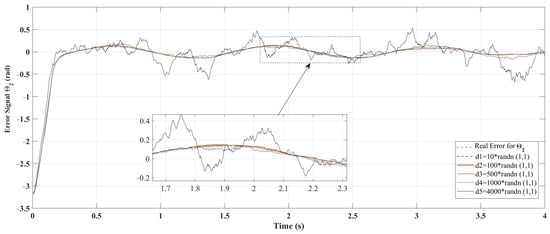
Figure 8.
Position tracking error of joints of the SMC controller under random noises application for Case 1.
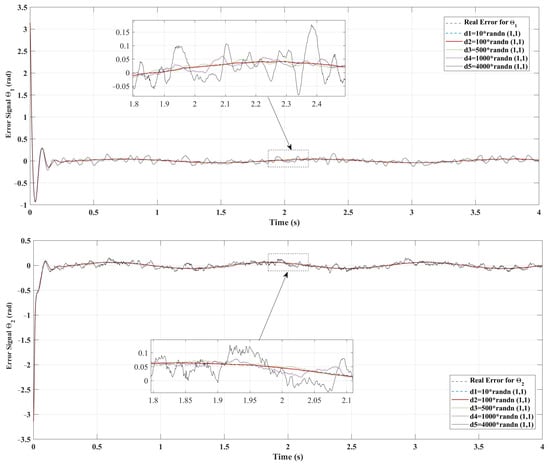
Figure 9.
Position tracking error of joints of the proposed ASMC under random noises application for Case 1.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents an advanced control approach for a 2-DoF robot manipulator, using an adaptive sliding mode controller (ASMC) to enhance trajectory tracking performance and a solution for the chattering phenomenon. The proposed ASMC method significantly reduces tracking errors and mitigates chattering, addressing a key challenge in sliding mode control. Unlike conventional SMC, which often suffers from high-frequency oscillations, ASMC improves system stability while maintaining robust performance. Moreover, the robustness of ASMC is evaluated under the influence of high external noise, demonstrating its ability to maintain accurate trajectory tracking and system stability despite disturbances. The numerical simulations demonstrate the superiority of ASMC over SMC, highlighting its improved tracking accuracy, lower error indices, and enhanced resilience to noise. For future research, experimental validation and the extension of the proposed control strategy to multi-DOF robotic systems and real-world applications are planned.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y.S.; methodology, M.Y.S.; software, M.Y.S.; validation, M.Y.S., A.B. and O.B.; formal analysis, M.Y.S. and O.B.; investigation, M.Y.S., A.B. and O.B.; resources, O.B.; data curation, M.Y.S. and O.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.S.; writing—review and editing, M.Y.S., A.B., O.B. and I.R.; visualization, M.Y.S., O.B. and A.B.; supervision, O.B.; project administration, M.Y.S.; funding acquisition, O.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Basque Government, through the project EKOHEGAZ II (ELKARTEK KK-2023/00051), to the UPV/EHU, through the project GIU23/002, and to the MobilityLab Foundation (CONV23/14) for supporting this work.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the projects supported by the Telecommunications Signals and Systems Laboratory (TSS), University Amar Telidji. The authors would like to thank all the associates who have contributed to this work directly or indirectly. The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Basque Government, through the project EKOHEGAZ II (ELKARTEK KK-2023/00051), to the UPV/EHU, through the project GIU23/002, and to the MobilityLab Foundation (CONV23/14) for supporting this work. During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used OpenAI and Grammarly for language editing and improving the clarity of the manuscript. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations and nomenclatures are used in this manuscript:
| 2-DoF | 2-Degree-of-Freedom |
| ASMC | Adaptive Sliding Mode Control |
| SMC | Sliding Mode Control |
| PID | Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
| FLC | Fuzzy Logic Controller |
| APSO | Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization |
| SPA | Social Spider Algorithm |
| HOSMC | High-Order Sliding Mode Control |
| NNC | Neural Network Control |
| ZN | Ziegler–Nichols |
| IMC | Internal Model Control |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| MIMO | Multi-Input Multi-Output |
| DSSMC | Dual Surface Sliding Mode Controller |
| NFTSM | Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode |
| WNN | Wavelet Neural Network |
| MRAC | Model Reference Adaptive Controllers |
| NFTSM | Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode |
Appendix A
The parameters dynamics of the 2-DoF arm robot manipulator, as expressed in Equation (1), are determined as follows [10,52]:
- where , , and .
References
- Billard, A.; Kragic, D. Trends and challenges in robot manipulation. Science 2019, 364, eaat8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garriz, C.; Domingo, R. Development of trajectories through the kalman algorithm and application to an industrial robot in the automotive industry. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 23570–23578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrat, S.; Kang, T.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Yi, S. Artistic robotic arm: Drawing portraits on physical canvas under 80 seconds. Sensors 2023, 23, 5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.M.; Atia, M.R. A lead through approach for programming a welding arm robot using machine vision. Robotica 2022, 40, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Wan, W.; Koyama, K.; Harada, K. A dual-arm robot that manipulates heavy plates with the support of a vacuum lifter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 2808–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Cui, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Q. Research progress and development trend of surgical robot and surgical instrument arm. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2021, 17, e2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coloma, S.; Peralta, P.E.; Redondo, V.; Morono, A.; Vila, R.; Ferre, M. The effect of ionizing radiation on robotic trajectory movement and electronic components. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 4191–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibjoo, A.D.; Shakibjoo, M.D. 2-DOF PID with reset controller for 4-DOF robot arm manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Intelligent Systems (ARIS), Taipei, Taiwan, 29–31 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Adar, N.; Kozan, R. Comparison between real time PID and 2-DOF PID controller for 6-DOF robot arm. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 130, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Barambones, O.; Bencherif, A. A novel adaptive PID controller design for a PEM fuel cell using stochastic gradient descent with momentum enhanced by whale optimizer. Electronics 2022, 11, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.W.; Lee, I.B. Limitations and countermeasures of PID controllers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 2596–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Amrr, S.M.; Saidi, A.S.; Banerjee, A.; Nabi, M. Finite-time adaptive higher-order SMC for the nonlinear five DOF active magnetic bearing system. Electronics 2021, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Bencherif, A.; Barambones, O. Indirect Adaptive Control Using Neural Network and Discrete Extended Kalman Filter for Wheeled Mobile Robot. Actuators 2024, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, D.A.; Alleyne, A.G. A high precision motion control system with application to microscale robotic deposition. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaneye-Boundjou, O.; Xu, X.; Ordóñez, R. Automated particle swarm optimization based PID tuning for control of robotic arm. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON) and Ohio Innovation Summit (OIS), Dayton, OH, USA, 25–29 July 2016; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wazzan, A.N.; Basil, N.; Raad, M.; Mohammed, H.K. PID controller with robotic arm using optimization algorithm. Int. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 7, 3746–3751. [Google Scholar]
- Milind, J.S.; Arunkumar, G.; Manjunath, T. PID control of a double link (2-link) flexible robotic manipulator (2-DOF) in the 3 DE space. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Mangalore, India, 27–28 October 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zakia, U.; Moallem, M.; Menon, C. PID-SMC controller for a 2-DOF planar robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox’sBazar, Bangladesh, 7–9 February 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F.; Batista, J.; Souza, D.; Lima, A.; dos Reis, L.; Barbosa, A. Control and identification of parameters of a joint of a manipulator based on PID, PID 2-DOF, and least squares. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, A.T.; Serrano, F.E. Fractional order two degree of freedom pid controller for a robotic manipulator with a fuzzy type-2 compensator. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.A.; El-Nagar, A.M.; Elsheikh, E.A.; El-Bardini, M. Embedded adaptive 2-DoF PID controller for robot manipulator using a supervisory fuzzy logic system. Menoufia J. Electron. Eng. Res. 2022, 31, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M. Control of robot arm motion using trapezoid fuzzy two-degree-of-freedom PID algorithm. Symmetry 2020, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, H.M.; Sanfilippo, F.; Hao, N.V. A novel adaptive sliding mode controller for a 2-DOF elastic robotic arm. Robotics 2022, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouila, A.; Nouri, K. An adaptive robust nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode controller based on wavelet neural network for a 2-DOF robotic arm. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 13259–13282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, W.K. Research on Adaptive Fuzzy Backstepping Control Method of 2-DOF Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Intelligent Informatics and Biomedical Sciences (ICIIBMS), Oita, Japan, 25–27 November 2021; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, M.; Komijani, H.; Rahman, M.H. New sliding mode control of 2-DOF robot manipulator based on extended grey wolf optimizer. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2020, 18, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, W.N.; Khawwaf, J.O. Robust sliding mode control for 2-Dof robot manipulator position control system. IET Conf. Proc. 2024, 18, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar, J.M.; de Oliveira, C.; da Rosa, R.A.; Gonçalves, G.; Lenzi, G.G.; Tusset, A.M. Efficiency comparative of linear controllers in positioning control of a robotic manipulator with two degrees of freedom. Math. Eng. Sci. Aerosp. (MESA) 2024, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Bingül, Z.; Karahan, O. A Fuzzy Logic Controller tuned with PSO for 2 DOF robot trajectory control. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, M.E.; Nasr, A.E. Trajectory tracking of 2DOF robotic manipulator system based on adaptive exponential forgetting recursive least squares fractional-order PID control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Syst. Control Eng. 2024, 38, 09596518251322228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Mannan, M.A.; Poo, A. Tracking and contour error control in CNC servo systems. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, G.; Li, W.; Li, M. Research on servo matching of a five-axis hybrid machine tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kong, X.; Yu, G.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Jiang, A. Error estimation and cross-coupled control based on a novel tool pose representation method of a five-axis hybrid machine tool. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2022, 182, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yao, B.; Wang, Q. Global task coordinate frame-based contouring control of linear-motor-driven biaxial systems with accurate parameter estimations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5195–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, I.S.; Ingram, J.N.; Wolpert, D.M. A modular planar robotic manipulandum with end-point torque control. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 181, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, S.; Swarnkar, P. Intelligent fractional order sliding mode based control for surgical robot manipulator. Electronics 2023, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Bao, D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, W. Adaptive Dynamic Boundary Sliding Mode Control for Robotic Manipulators under Varying Disturbances. Electronics 2024, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Nethi, A.; Jetta, M. Multiplicative Gaussian Noise Removal using Partial Differential Equations and Activation Functions: A Robust and Stable Approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Algorithms, Computing and Systems, Larissa, Greece, 19–21 October 2023; pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Shi, P.; Wang, P.; He, C.; Zhang, H. Non-singular terminal sliding mode controller with nonlinear disturbance observer for robotic manipulator. Electronics 2023, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Barambones, O.; Bencherif, A. Robust adaptive sliding mode control using stochastic gradient descent for robot arm manipulator trajectory tracking. Electronics 2024, 13, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.I.; Vadim, I. Sliding mode control. Var. Struct. Syst. Princ. Implement. 2004, 66, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın, M. Real-Time Sliding Mode and Moving Sliding Mode Control of 3-DOF Linear Parallel Robot. Machines 2025, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.X.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Compensation Function Observer-Based Backstepping Sliding-Mode Control of Uncertain Electro-Hydraulic Servo System. Machines 2024, 12, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Mohammad, A.; Mohsen, E. Continuous nonsingular terminal sliding mode control based on adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer for uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 2019, 109, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B. Adaptive super-twisting fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control with ESO for high-pressure electro-pneumatic servo valve. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 134, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Khayati, K. Adaptive sliding mode control with smooth switching gain. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 27th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Toronto, ON, Canada, 4–7 May 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Bencherif, A.; Barambones, O. A novel robust adaptive sliding mode control using stochastic gradient descent for PEMFC power system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 17277–17292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, P.A.; Kokotovic, P.V. Instability analysis and improvement of robustness of adaptive control. Automatica 1984, 20, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, P.A. Adaptive control of linear time-invariant systems. In Encyclopedia of Systems and Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, M.; Maiti, A. Adaptive sliding mode resilient control of multi-robot systems with a leader–follower model under byzantine attacks in the context of the industrial Internet of things. Machines 2024, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Lan, Q. Finite-Time Integral Sliding Mode Control for Motion Control of Permanent-Magnet Linear Motors. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 567610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Lee, J.; Chang, P.H.; Choi, C. Practical nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of robot manipulators for high-accuracy tracking control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3593–3601. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).