Research on the Principle and Suppression Method of Micro-Vibration Generation in a Spatial Optoelectronic Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
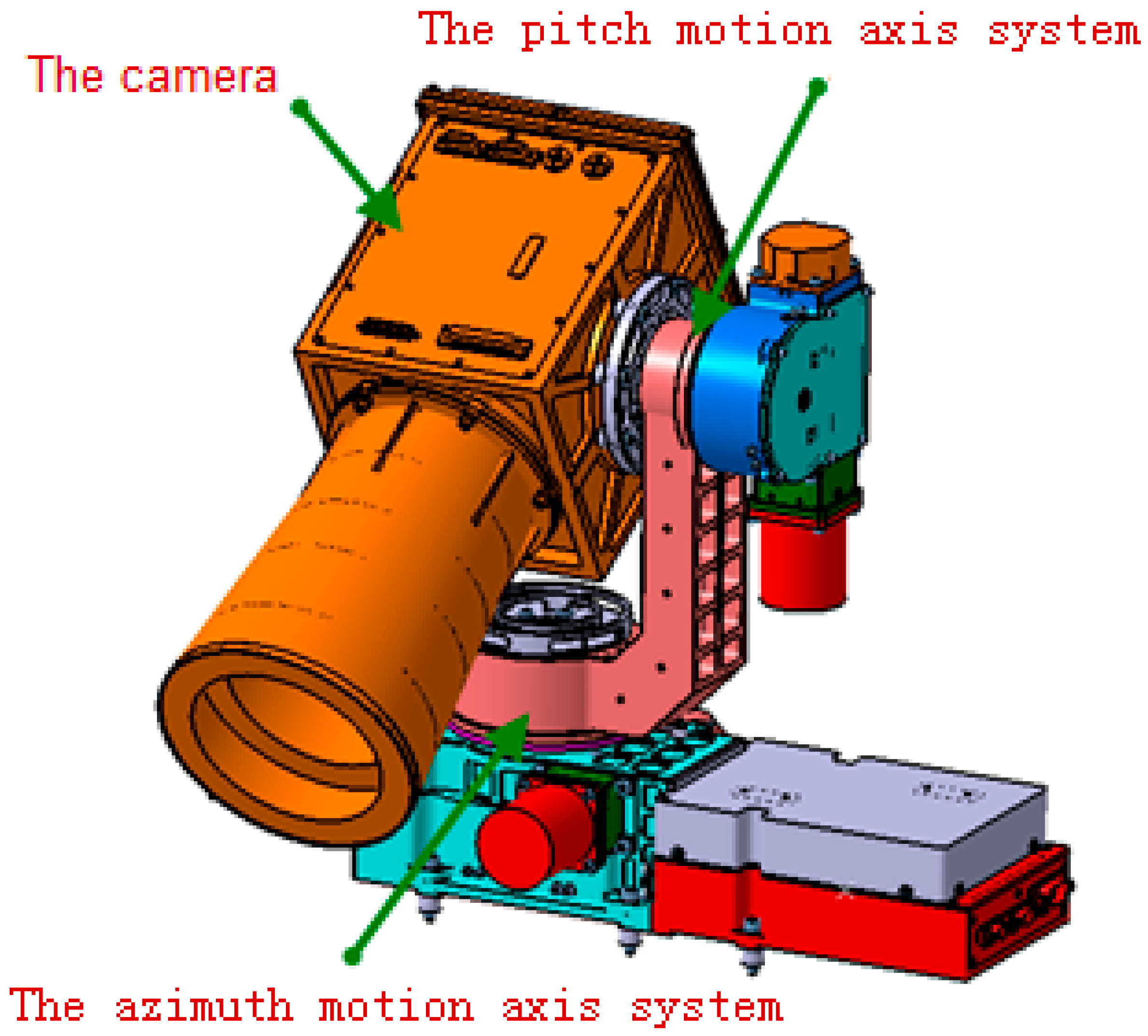
2. Design of Spatial Optoelectronic Scanning Mechanism
3. Analysis of the Principle of Micro-Vibration Generation
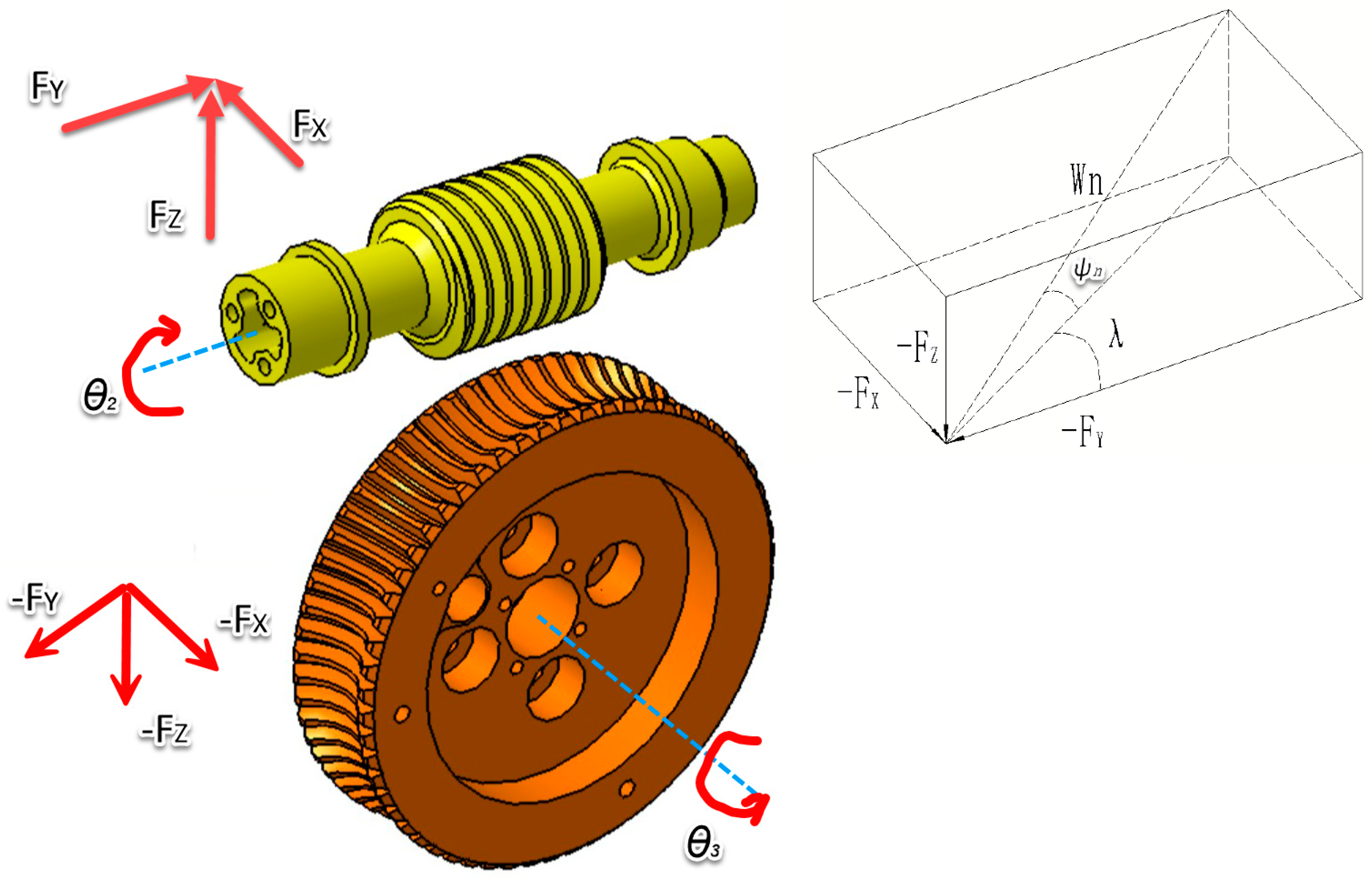
3.1. Dynamic Modeling of Worm and Worm Gear
3.2. Micro-Vibration Dynamics Analysis of Worm and Worm Gear Motion Mechanism
3.2.1. Camera Runs from+90° to XX°
3.2.2. Camera Runs from XX° to +90°
3.2.3. Camera Runs from −20° to YY°
3.2.4. Camera Runs from YY° to −20°
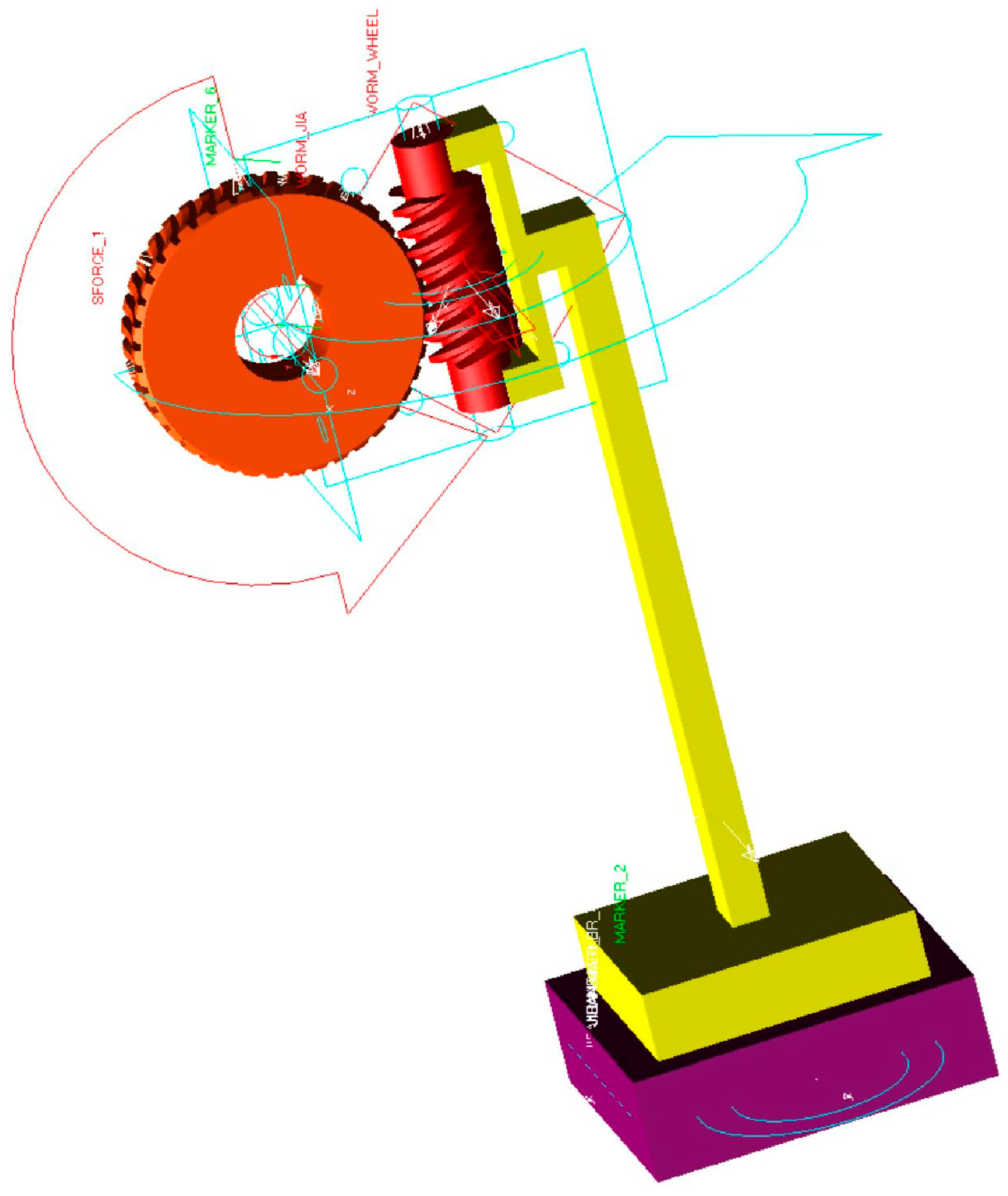
3.3. ADAMS Simulation Analysis of Micro-Vibration in Worm Gear Mechanism Motion
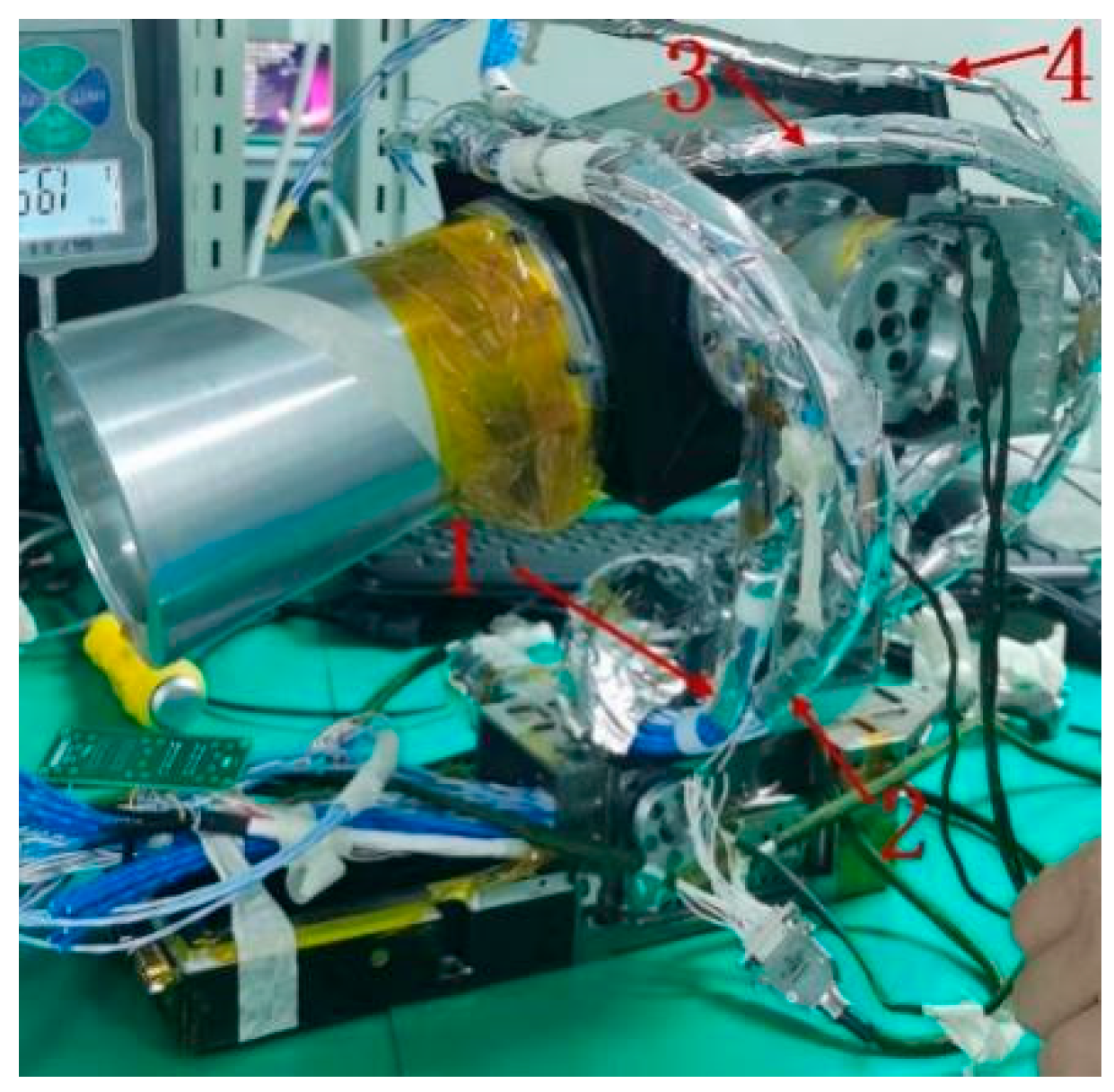
4. Experimental Verification of the Principle of Micro-Vibration Generation
4.1. The Influence of Wire-Winding Torque on Micro-Vibration
4.2. The Influence of Worm Gear and Worm Meshing Gap on Micro-Vibration
4.3. Experimental Summary
5. Optimization Design of Optoelectronic Scanning Mechanism Structure
6. Summary
7. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Y. Advances in spacecraft micro-vibration suppression methods. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2023, 138, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.; Zheng, R.; Wu, Y.; Sui, J.; Zhong, J. Micro-vibration suppression methods and key technologies for high-precision space optical instruments. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 180, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addari, D.; Aglietti, G.S.; Remedia, M. Investigating micro-vibration sources modelling. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Spacecraft Structures, Materials & Environmental Testing (ECSSMET), Braunschweig, Germany, 1–4 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Xie, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, L. Development of active micro-vibration isolation system for precision space payload. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elasha, F.; Ruiz-Cárcel, C.; Mba, D.; Kiat, G.; Nze, I.; Yebra, G. Pitting detection in worm gearboxes with vibration analysis volume. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 42, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A. A Review on Fault Detection of Gearbox by using Vibration Analysis. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 14627–14633. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahim, E.; Payam, J.; Nasrolah, A.; Majid, H.; Mojtaba, B.; Mohammad Hadi, J.; Ali, Z. Developing an intelligent fault diagnosis of MF285 tractor gearbox using genetic algorithm and vibration signals. Mod. Mech. Eng. 2013, 3, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elforjani, M.; Mba, D.; Muhammad, A.; Sire, A. Condition monitoring of worm gears. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vähäoja, P.; Lahdelma, S.; Leinonen, J. On the condition monitoring of worm gears Engineering Asset Management. In Proceedings of the 1st World Congress on Engineering Asset Management; Springer: London, UK, 2006; pp. 332–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, T.J.; Wu, F.K. Modeling and robust control of worm-gear driven systems. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2009, 17, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Research on Dynamics Simulation and Vibration Characteristics of Deceleration Mechanism of Steering Gear. Fire Control Command Control 2023, 48, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xia, Y.Z. Modal analysis of worm gear based on ANSYS workbench. J. Jiamusi Univ. 2017, 35, 246–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.M. Modal analysis of worm gear transmission performance based on finite element method. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 2016, 29, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Tian, C.L.; Liu, T.; Kong, F. Modal analysis of prestressed worm gear. Ind. Technol. Innov. 2015, 2, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, A.; Singh, R. Non-linear dynamics of a spur gear pair. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 142, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, P.; Zhao, C. Research on Meshing Force Simulation of Worm Transmission Mechanism for Screw Jack Mechanism. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2016, 2, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, K. Planetary Gear Train Dynamics. J. Mech. Des. 1994, 116, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ma, J.; Wu, D. Simulation study on contact stress of gear tooth. J. Mech. Transm. 2007, 31, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.H.; Kwak, Y.K.; Kim, S.H. On the frequency bandwidth change of a servo system with a gear reducer due to backlash and motor input woltage. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2003, 73, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, G.; Gong, L.; Huang, Q. Variable inertial damper and its application in zero-drive gear hobbing machine. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2006, 19, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Dhupia, J.S. A time-domain fault detection method based on an electrical machine stator current measurement for planetary gear-sets. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME international Conference on Advanced inteligent Mechatronics, Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 9–12 July 2013; pp. 1631–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Benabid, Y.; Mansouri, S. Dynamics study and diagnostics with vibration analysis from worm gear manufactured by reverse engineering techniques. J. Vibroeng. 2016, 18, 4458–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.Y.; Shaw, D. Parametric study of dynamics of worm and worm-gear set under suddenly applied rotating angle. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 304, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





















| Serial Number | Backlash | Unbalanced Force of Wire Winding (N) | Micro-Vibration Data (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03 mm | 5.4 (+90°), 4.18 (−20°) | 14.5 |
| 2 | 0.03 mm | 3.12 (+90°), 2 (−20°) | 9.8 |
| 3 | 0.03 mm | 1.21 (+90°), 1.3 (−20°) | 7 |
| 4 | 0.03 mm | 0 | 3.2 |
| 5 | 0.01 mm | 3.12 (+90°), 2 (−20°) | 12 |
| 6 | 0.03 mm | 3.12 (+90°), 2 (−20°) | 9.8 |
| 7 | 0.05 mm | 3.12 (+90°), 2 (−20°) | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; Yang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Y. Research on the Principle and Suppression Method of Micro-Vibration Generation in a Spatial Optoelectronic Mechanism. Machines 2024, 12, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120857
Gao B, Yang H, Chen W, Wang H, Qi Z, Liu Y. Research on the Principle and Suppression Method of Micro-Vibration Generation in a Spatial Optoelectronic Mechanism. Machines. 2024; 12(12):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120857
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Bo, Hongtao Yang, Weining Chen, Hao Wang, Zimiao Qi, and Yang Liu. 2024. "Research on the Principle and Suppression Method of Micro-Vibration Generation in a Spatial Optoelectronic Mechanism" Machines 12, no. 12: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120857
APA StyleGao, B., Yang, H., Chen, W., Wang, H., Qi, Z., & Liu, Y. (2024). Research on the Principle and Suppression Method of Micro-Vibration Generation in a Spatial Optoelectronic Mechanism. Machines, 12(12), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120857






