Approaches for Preventing Tool Wear in Sheet Metal Forming Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
- duration of contact;
- relative sliding speeds of bodies in contact;
- amount of the load;
- environmental parameters (humidity, temperature).
- mechanical properties—yield stress, tensile strength, hardness;
- thermal expansion of material;
- properties of the surface layer of the deformed material—hardness, chemical composition of protective coating, surface roughness;
- properties of the surface layer of the tool—hardness, chemical composition of protective coating, surface roughness, delamination resistance;
- geometry of contact.
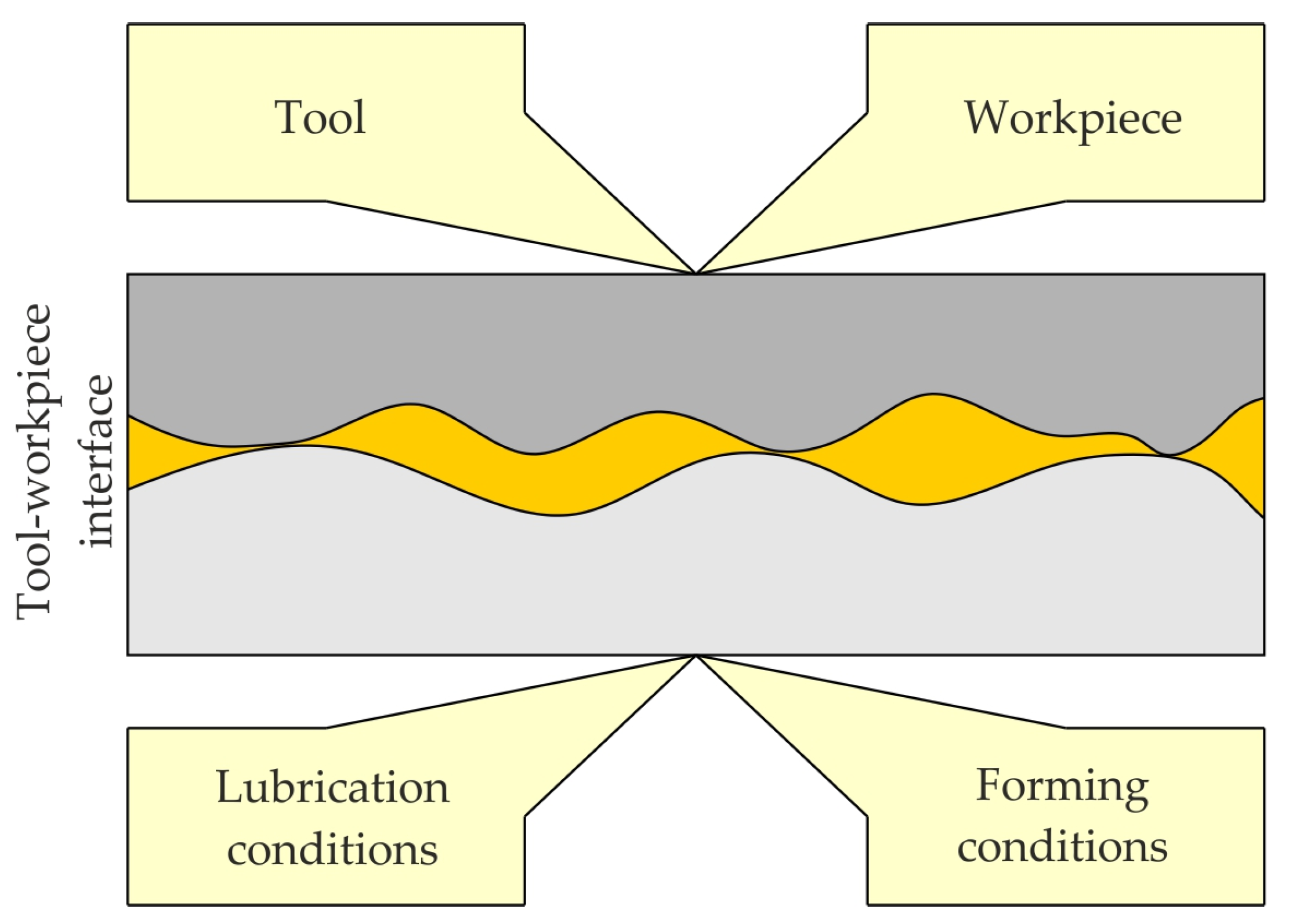
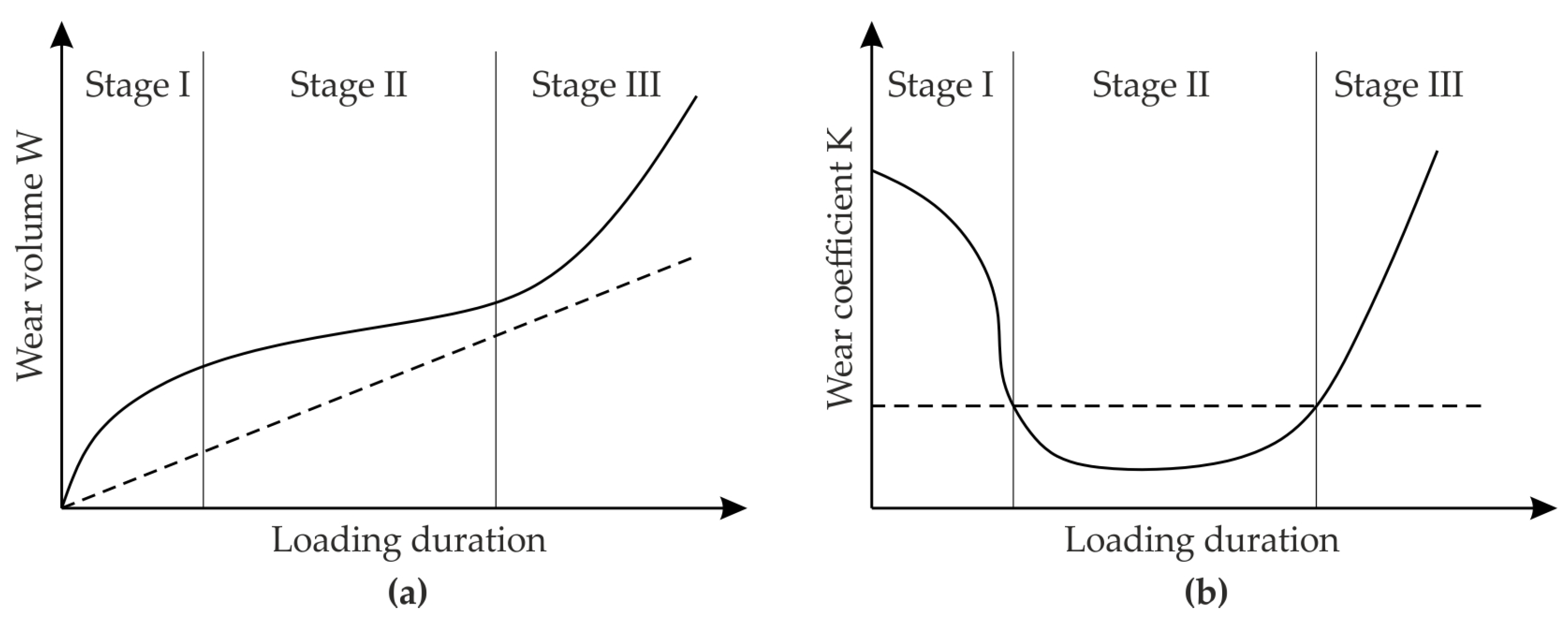
2. Tool Wear in SMF
2.1. Wear Mechanisms
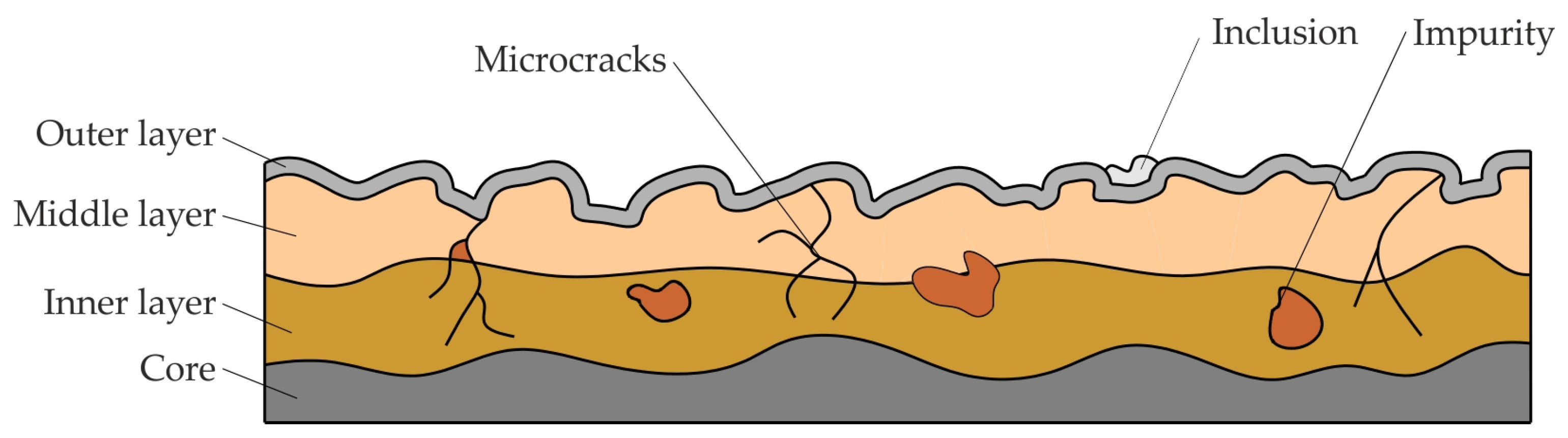
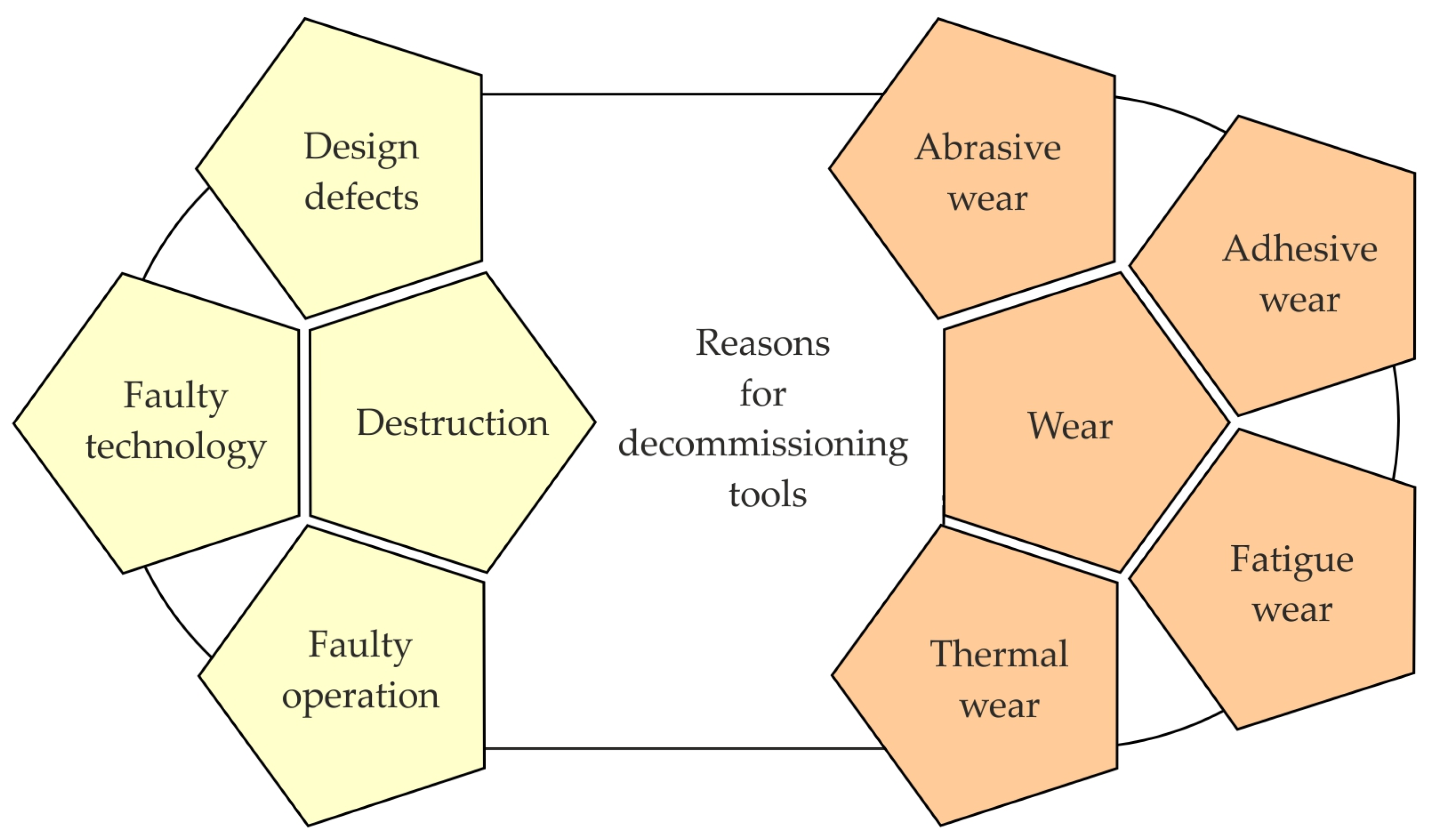
2.2. Causes of Tool Failure
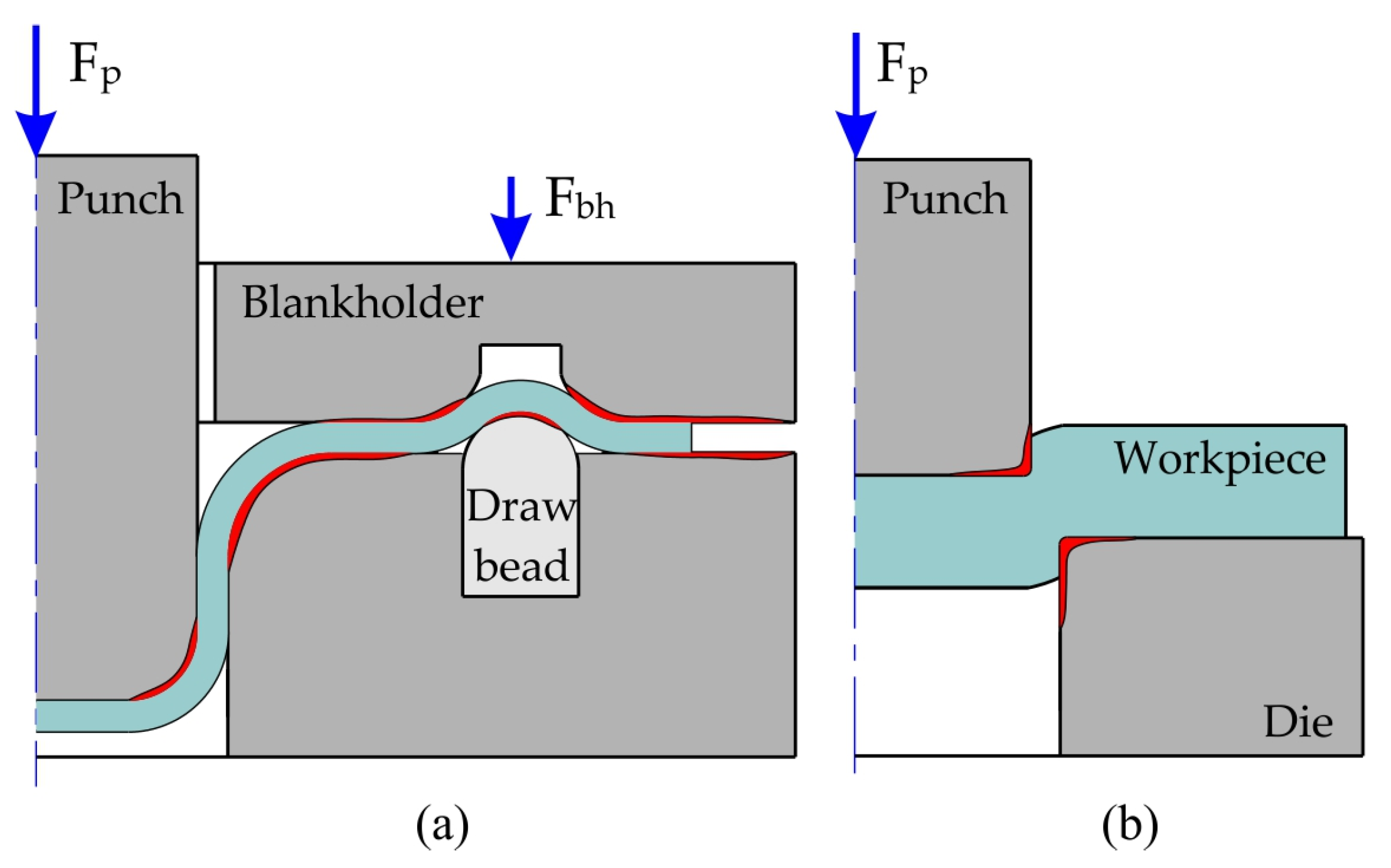
3. Lubrication
4. Protective Coatings for Tools
4.1. Methods of Constituting Surface Layers
- mechanical methods—burnishing, shot peening, hammering, cold working;
- physical methods—vapour deposition by sputtering, spraying and evaporation techniques, ion implantation;
- thermal methods—heat treatment (hardening, annealing, tempering), surfacing;
- thermal–mechanical methods—gas and plasma spraying, spray deposition, hot plastic working;
- thermal–chemical methods—diffusion alloying with non-metallic elements (nitriding, carburising, boronisation, carbonitriding), diffusion alloying with metallic elements (tin plating, aluminising, galvanising), laser and electron-beam alloying;
- chemical and electrochemical methods—conversion deposition of phosphate, oxide and chromate coatings, electrolytic deposition of metals or alloys (i.e., nickel plating, chrome plating, zinc plating), plating and chemical or electrolytic etching.
4.2. High-Energy Techniques
4.3. Coatings Produced in PVD and CVD Processes
4.4. Functional Coatings
| Coating | Ra, μm | Hardness, GPa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient Temperature | 400 °C | ||
| TiAlN | 0.03 | 33.5 | 30.5 |
| AlTiCrN | 0.05 | 18 | 16.4 |
| TiAlCrCN | 0.07 | 28 | 27.6 |
| DLC | 0.03 | 28 | 27.6 |
| AlTiCrN+CN | 0.03 | 29 | 27.2 |
| AlCrSiN+CN | 0.02 | 27 | 25.8 |
| AlTiCrN | 0.04 | 38 | 29 |
5. Self-Lubricating Materials and Coatings
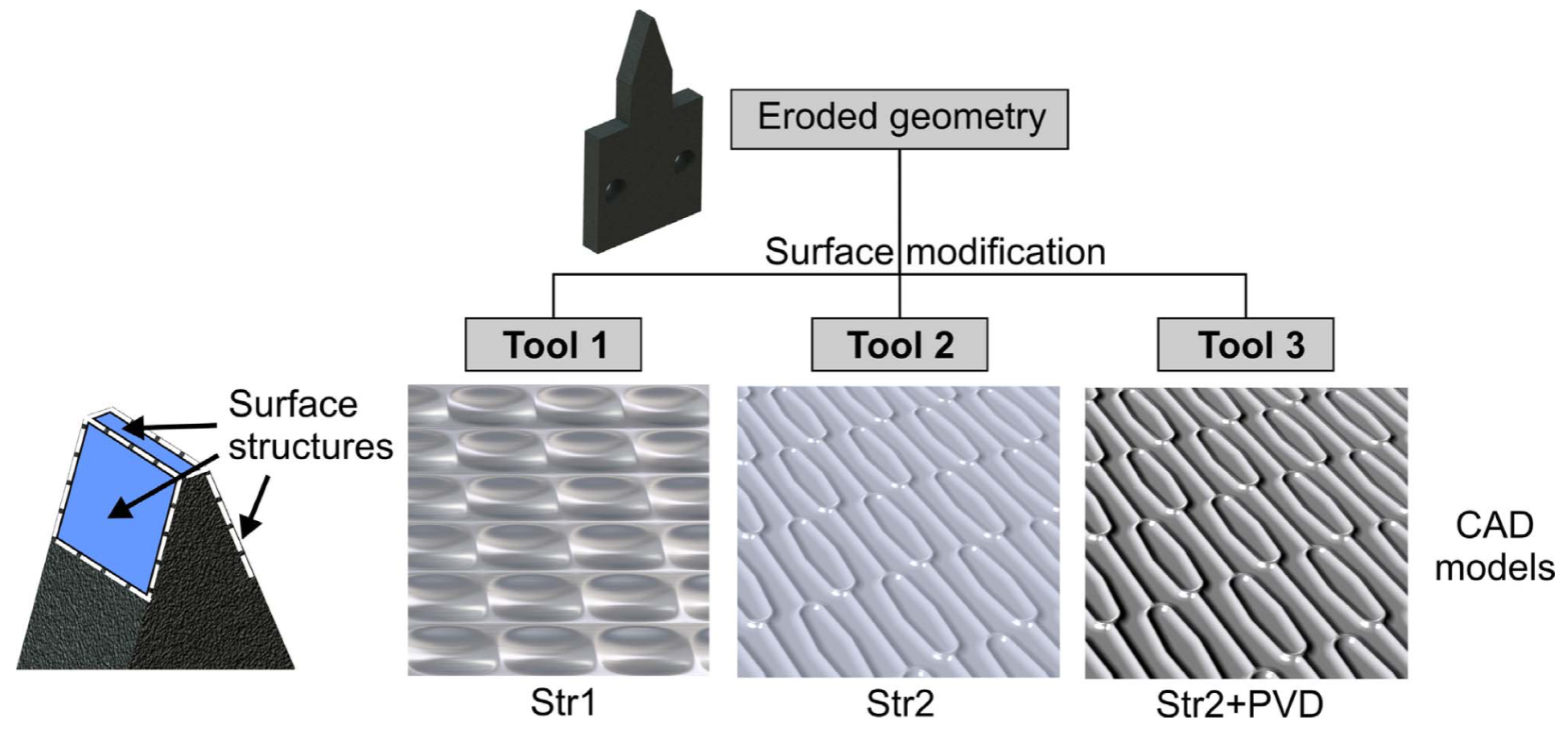
6. Structured and Textured Tool Surfaces
7. Summary
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czichos, H.; Habig, K.H. Tribologie-Handbuch-Tribologie, Tribomaterialien, Tribotechnik, 3rd ed.; ViehwegþTeubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, J.; Song, J.; Bae, G.; Park, N.; Lee, M.; Kim, H. Quantitative evaluation of experimental wear behaviour for CrN-coated tool steels in sheet metal forming process of TRIP 1180. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 50, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Kim, M.; Bae, G.; Song, J.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, M.G. Quantitative Evaluation of Tool Wear in Cold Stamping of Ultra-High-Strength Steel Sheets. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, V.D.; Santos, A.J.D.; Câmara, M.A.; Rodrigues, P.C.D.M. Influence of Different Contact Conditions on Friction Properties of AISI 430 Steel Sheet with Deep Drawing Quality. Coatings 2023, 13, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cora, Ö.N.; Koç, M. Wear resistance evaluation of hard-coatings for sheet blanking die. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 15, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Kaščák, L. Assessment of frictional performance of deep drawing quality steel sheets used in automotive industry. Technol. Autom. Montażu 2022, 115, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, A.; Kirkhorn, L.; Andersson, M.; Stahl, J.E. Improved tool wear properties in sheet metal forming using Carbide Steel, a novel abrasion resistant cast material. Wear 2011, 271, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, H.; Kumar, R.; Chohan, J.S. Parametric optimization and wear analysis of AISI D2 steel components. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żaba, K.; Kuczek, Ł.; Puchlerska, S.; Wiewióra, M.; Góral, M.; Trzepieciński, T. Analysis of Tribological Performance of New Stamping Die Composite Inserts Using Strip Drawing Test. Adv. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2023, 40, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonnikov, D.A.; Semenov, I.E. Thin sheet metal forming with composite material. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 734, 012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Malinowski, T.; Pieja, T. Experimental and numerical analysis of industrial warm forming of stainless steel sheet. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondini, F.; Basso, A.; Arinbjarnar, U.; Nielsen, C.V. The Performance of 3D Printed Polymer Tools in Sheet Metal Forming. Metals 2021, 11, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.; Santos, A.D.; Teixeira, P.; Bolt, P.J. Study on the usability and robustness of polymer and wood materials for tooling in sheet metal forming. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2008, 202, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joghan, H.D.; Hahn, M.; Sehrt, J.T.; Tekkaya, A.E. Hybrid additive manufacturing of metal laminated forming tools. CIRP Ann. 2022, 71, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
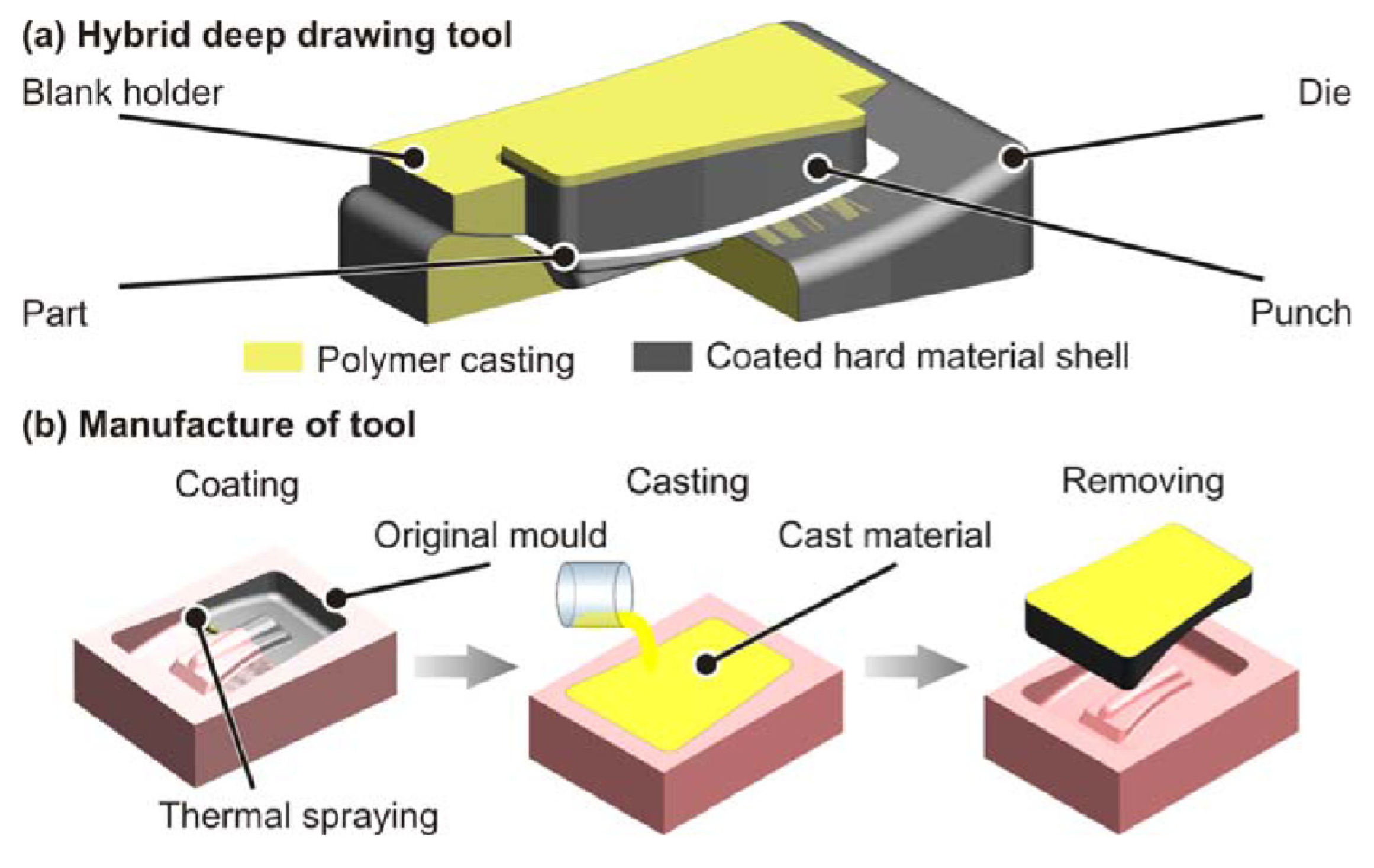
- Witulski, J.; Trompeter, M.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Kleiner, M. High wear resistant deep drawing tools made of coated polymers. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.H.C.; Liewald, M. Analysis of the tribological behaviour of polymer composite tool materials for sheet metal forming. Wear 2010, 268, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, U.; Zhu, Y.; Abbasi, S.; Lewis, R.; Lewis, S. Tribology of the wheel-rail contact aspects of wear, particle emission and adhesion. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2013, 51, 1091–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.H.; Farahana, R.N.; Bienk, K.; Nielsen, C.V.; Bay, N. Effects of DLC/TiAlN-coated die on friction and wear in sheet-metal forming under dry and oil-lubricated conditions: Experimental and numerical studies. Wear 2019, 438–439, 203040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geueke, M.; Frohn-Sörensen, P.; Reuter, J.; Padavu, N.; Reinicke, T.; Engel, B. Structural optimization of additively manufactured polymer tools for flexible sheet metal forming. Procedia CIRP 2021, 104, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepiecinski, T.; Lemu, H.G. Recent Developments and Trends in the Friction Testing for Conventional Sheet Metal Forming and Incremental Sheet Forming. Metals 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Najm, S.M.; Oleksik, V.; Vasilca, D.; Paniti, I.; Szpunar, M. Recent Developments and Future Challenges in Incremental Sheet Forming of Aluminium and Aluminium Alloy Sheets. Metals 2022, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Szpunar, M.; Dzierwa, A.; Żaba, K. Investigation of Surface Roughness in Incremental Sheet Forming of Conical Drawpieces from Pure Titanium Sheets. Materials 2022, 15, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, M.; Szwajka, K.; Trzepieciński, T. Frictional Characteristics of Deep-Drawing Quality Steel Sheets in the Flat Die Strip Drawing Test. Materials 2022, 15, 5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Z. Tool Wear Prediction Modelling for Sheet Metal Stamping Die in Automotive Manufacture. Ph.D. Thesis, Swinburne University of Technology, Hawthorn, Australia, 24 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shanbhag, V.V.; Pereira, P.M.; Rolfe, F.B.; Arunachalam, N. Time series analysis of tool wear in sheet metal stamping using acoustic emission. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 896, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinbjarnar, U.; Nielsen, C.V. Effect of workpiece pre-straining on tribological performance of surface coatings in sheet metal forming. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H. Tribological properties of titanium-based alloy. In Surface Engineering of Light Alloys; Dong, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2010; pp. 58–80. [Google Scholar]
- Trzepieciński, T. Tarcie i Smarowanie w Procesach Kształtowania Blach; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D. Technologie kształtowania struktury i własności powierzchni materiałów inżynierskich przez nanoszenie powłok z fazy gazowej. In Kształtowanie Struktury i Własności Powierzchni Materiałów Inżynierskich i Biomedycznych; Dobrzański, L.A., Ed.; International OCSCO World Press: Gliwice, Poland, 2009; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fejkiel, R.; Goleń, P. Application of the Finite Element Method to Simulate the Friction Phenomenon in a Strip Drawing Test. Adv. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2023, 40, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemu, H.G.; Trzepieciński, T. Numerical and experimental study of frictional behavior in bending under tension test. Stroj. Vestn.-J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 59, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Kubit, A.; Slota, J.; Fejkiel, R. An experimental study of the frictional properties of steel sheets using the drawbead simulator test. Materials 2019, 12, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Lemu, H.G. Frictional conditions of AA5251 aluminium alloy sheets using drawbead simulator tests and numerical methods. Stroj. Vestn.-J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 60, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Kelly, G.; Rolfe, B.F.; Pereira, M.P. The effect of temperature on sliding wear of steel-tool steel pairs. Wear 2012, 282–283, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Recklin, V.; Groche, P. Strain Induced Surface Change in Sheet Metal Forming: Numerical Prediction, Influence on Friction and Tool Wear. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Kim, M.; Bae, G.; Kim, H.-G.; Lee, M.-G.; Song, J. Efficient Wear Simulation Methodology for Predicting Nonlinear Wear Behavior of Tools in Sheet Metal Forming. Materials 2022, 15, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gåård, A. Wear in Sheet Metal Forming. Ph.D. Thesis, Karlstad University, Karlstad, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski, J.; Mucha, J.; Trzepieciński, T. Kształtowanie Trwałości Eksploatacyjnej Narzędzi do Przeróbki Plastycznej Metali; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Rzeszowskiej: Rzeszów, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowski, L. Stale Szybkotnące na Narzędzia do Obróbki Plastycznej; Instytut Obróbki Plastycznej: Poznań, Poland, 1994.
- Masen, M. Abrasive Tool Wear in Metal Forming Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 15 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D. Obróbka powierzchni materiałów inżynierskich. Zmiany struktury i własności powierzchni materiałów inżynierskich w wyniku eksploatacji. Open Access Libr. 2011, 5, 368–416. [Google Scholar]
- Podgornik, B.; Leskovšek, V. Wear mechanisms and surface engineering of forming tools. Mater. Technol. 2015, 49, 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.P.; Yan, W.; Rolfe, B.F. Sliding distance, contact pressure and wear in sheet metal stamping. Wear 2010, 268, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard G98-91; Standard Test Method for Galling Resistance of Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1991.
- Groche, P.; Moeller, N.; Hoffmann, H.; Suh, J. Influence of gliding speed and contact pressure on the wear of forming tools. Wear 2011, 271, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, P.; Gåård, A.; Krakhmalev, P.; Bergström, J. Galling resistance and wear mechanisms for cold-work tool steels in lubricated sliding against high strength stainless steel sheets. Wear 2012, 286–287, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelcastre, L. Hot Forming Tribology: Galling of Tools and Associated Problems; Luleå University of Technology: Lulea, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, R.G. A general model for sliding wear in electrical contacts. Wear 1993, 162–164, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.K. Wear equation for polymers sliding against metal surfaces. Wear 1970, 16, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gåård, A.; Krakhmalev, P.; Bergström, J. Influence of tool steel microstructure on origin of galling initiation and wear mechanisms under dry sliding against a carbon steel sheet. Wear 2009, 267, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy-Nürnberg, K.; Nürnberg, G.; Golle, M.; Hoffmana, H. Simulation of wear on sheet metal forming tools—An energy approach. Wear 2008, 265, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubhayaratne, I.; Pereira, M.P.; Xiang, Y.; Rolfe, B.F. Audio signal analysis for tool wear monitoring in sheet metal stamping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 809–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, V.V.; Rolfe, B.F.; Arunachalam, N.; Pereira, M.P. Investigating galling wear behaviour in sheet metal stamping using acoustic emissions. Wear 2018, 414–415, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, C.; Molitor, D.A.; Rojahn, M.; Groche, P. Towards a real-time tool state detection in sheet metal forming processes validated by wear classification during blanking. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1238, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitor, D.A.; Kubik, C.; Hetfleisch, R.H.; Groche, P. Workpiece image-based tool wear classification in blanking processes using deep convolutional neural networks. Prod. Eng. 2022, 16, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, C.; Becker, M.; Molitor, D.A.; Groche, P. Towards a systematical approach for wear detection in sheet metal forming using machine learning. Prod. Eng. 2023, 17, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
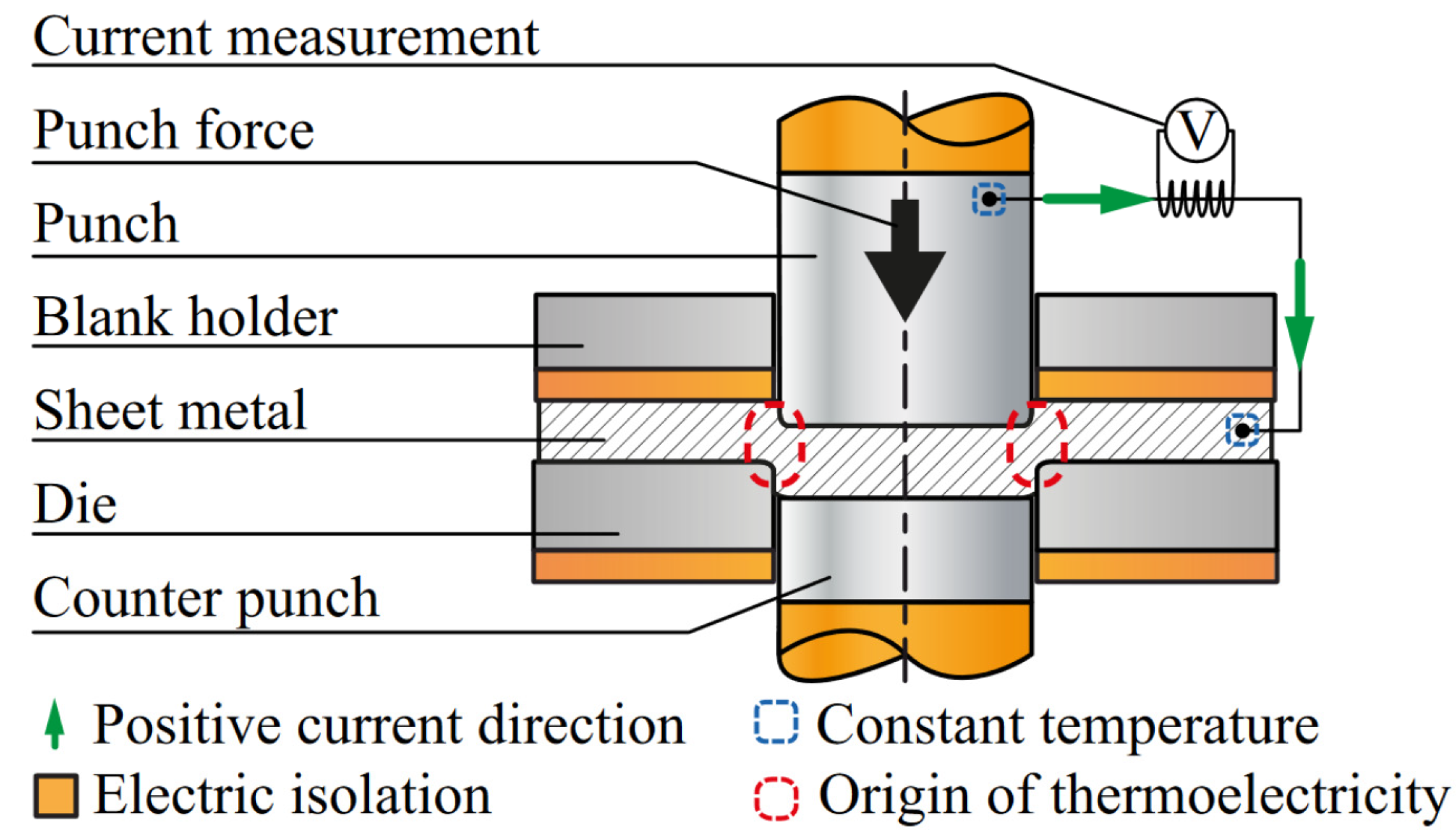
- Tröber, P.; Demmel, P.; Hoffman, H.; Golle, R.; Volk, W. On the influence of Seebeck coefficients on adhesive tool wear during sheet metal processing. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groche, P.; Christiany, M.; Wu, Y. Load-dependent wear in sheet metal forming. Wear 2019, 422–423, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieczkarek, P.; Wernicke, S.; Gies, S.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Krebs, E.; Wiederkehr, P.; Biermann, D.; Tillmann, W.; Stangier, D. Wear behavior of tribologically optimized tool surfaces for incremental forming processes. Tribol. Int. 2016, 104, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewe, M.; Wilbuer, H.; Menzel, A. Simulation of wear and effective friction properties of microstructured surfaces. Wear 2021, 464–465, 203491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierzyńska, M. Tarcie, Zużycie i Smarowanie w Obróbce Plastycznej Metali; Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bong, H.J.; Barlat, F.; Ahn, D.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.G. Formability of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels at warm forming temperature. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2013, 75, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.P.; Weiss, M.; Rolfe, B.F.; Hilditch, T.B. The effect of the die radius profile accuracy on wear in sheet metal stamping. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 66, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.P.; Yan, W.; Rolfe, B.F. Wear at the die radius in sheet metal stamping. Wear 2012, 274–275, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, B.A.; Maier, H.J.; Hübner, S.; Bonk, C.; Almohallami, A.; Lummer, C.; Schein, P.; Scheland, H.; Micke-Camuz, M. Wear Behavior of MoS2 Lubricant Layers During Sheet Metal Forming. Procedia Eng. 2017, 183, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Masood, S.H. Investigation of die radius arc profile on wear behaviour in sheet metal processing of advanced high strength steels. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, V.D.; de Matos Rodrigues, P.C. Failure analysis of AISI 430 stainless steel sheet under stretching and bending conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, V.D.; de Matos Rodrigues, P.C. Design of a Tribo-Simulator for Investigation of the Tribological Behavior of Stainless-Steel Sheets Under Different Contact Conditions. Mater. Res. 2022, 25, e20210220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, S. Kompozycje Smarów Plastycznych i Stałych w Procesie Tarcia Stalowych Węzłów Maszyn; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Wrocławskiej: Wrocław, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, D.O.; Walton, S. Surface topography and lubrication in sheet metal forming. Tribol. Int. 1987, 20, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T. Recent developments and trends in sheet metal forming. Metals 2020, 10, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żaba, K.; Puchlerska, S.; Kuczek, Ł.; Trzepieciński, T.; Maj, P. Effect of Step Size on the Formability of Al/Cu Bimetallic Sheets in Single Point Incremental Sheet Forming. Materials 2023, 16, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemu, H.G.; Trzepieciński, T.; Kubit, A.; Fejkiel, R. Friction modeling of Al-Mg alloy sheets based on multiple egression analysis and neural networks. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2017, 11, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Szpunar, M.; Kašcák, L. Modeling of friction phenomena of Ti-6Al-4V sheets based on backward elimination regression and multi-layer artificial neural networks. Materials 2021, 14, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilkiran, D.; Wulff, D.; Almohallami, A.; Özkaya, F.; Bouguecha, A.; Hübner, S.; Möhwald, K.; Maier, H.J.; Behrens, B.A. Wear behaviour of thermally oxidised tool surfaces as low-friction separation layers for dry sheet metal forming. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podstawy Techniki Smarowniczej. Available online: https://totalenergies.pl/system/files/atoms/files/rozdzial_02_podstawy_techniki_smarowniczej.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Płaza, S.; Margilewski, L.; Celichowski, G. Wstęp do Tribologii i Tribochemii; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego: Łódź, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Renevier, N.M.; Hampshire, J.; Fox, V.C.; Allen, T.; Teer, D.G. Advantage of using self-lubricating, hard, wear-resistant MoS2-based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuna, F.J.; Dabai, M.U.; Sokoto, M.A.; Dangoggo, S.M.; Bagudo, B.U.; Birnin-Yauri, U.A.; Hassan, L.G.; Sada, I.; Abubukar, A.L.; Jibrin, M.S. Chemical modification of vegetable oils for the production of biolubricants using trimethylolpropane: A review. Egypt. J. Pet. 2020, 29, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T. Tribological performance of environmentally friendly bio-degradable lubricants based on a combination of boric acid and bio-based oils. Materials 2020, 13, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biresaw, G.; Erhan, S.M. Solid lubricant formulations containing starch-soybean oil composites. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bexell, U.; Olsson, M.; Johansson, M.; Samuelsson, J.; Sundell, P.E. A tribological study of a novel pre-treatment with linseed oil bonded to mercaptosilane treated aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 166, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareh-Desari, B.; Davoodi, B. Assessing the lubrication performance of vegetable oil-based nano-lubricants for environmentally conscious metal forming processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, M.; Szwajka, K. Assessment of the Tribological Performance of Bio-Based Lubricants Using Analysis of Variance. Adv. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2023, 40, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, N.K.B.M.P.; Narayanan, R.G. Friction and lubrication in sustainable metal forming. In Sustainable Material Forming and Joining; Narayanan, R.G., Gunasekera, J.S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, N.J.; Tyrer, B.; Stachowiak, G.W. Boundary lubrication performance of free fatty acids in sunflower oil. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 16, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, H.M.; Mohamad, E.N.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Al Mahmud, K.A.H.; Habibullah, M.; Ashraful, A.M. The prospects of biolubricants as alternatives in automotive applications. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. Tribological behaviors of surfactant-functionalized carbon nanotubes as lubricant additive in water. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 25, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Chen, X.H.; Xu, L.S.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.H. Modification of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with fatty acid and their tribological properties as lubricant additive. Carbon 2005, 43, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelio, J.A.C.; Cuervo, P.; Palacio, L.M.H.; Lara-Romero, J.; Toro, A. Tribological properties of carbon nanotubes as lubricant additive in oil and water for a wheel—Rail system. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.V.; Hulwan, D.B.; Mandale, M.B. Recent advancements in synthesis, rheological characterization, and tribological performance of vegetable oil-based lubricants enhanced with nanoparticles for sustainable lubrication. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppar, R.; Dinesha, P.; Kumar, S. A critical review on vegetable oil-based bio-lubricants: Preparation, characterization, and challenges. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokar, D.; Radek, N.; Mikina, A.; Kalinowski, A. Właściwości Powłok DLC Teksturowanych Laserowo. Available online: https://www.iskra-zmils.com.pl/library/2021/03/11/wlasciwosci-powlok-dlc-teksturowanych-laserowo.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Lovell, M.R.; Deng, Z. Characterization of interfacial friction in coated sheet steels: Influence of stamping process parameters and wear mechanisms. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Han, B.; Yan, Q.; Altan, T. Evaluation of tool materials, coatings and lubricants in forming galvanized advanced high strength steels (AHSS). CIRP Ann. 2008, 57, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A. Ogólna klasyfikacja warstw powierzchniowych i procesów ich wytwarzania. In Kształtowanie Struktury i Własności Powierzchni Materiałów Inżynierskich i Biomedycznych; Dobrzański, L.A., Ed.; International OCSCO World Press: Gliwice, Poland, 2009; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Jonda, E.; Labisz, K. Foresight methods application for evaluating laser treatment of hot-work steels. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2010, 43, 750–773. [Google Scholar]
- De Hosson, J.T.M.; Ocelik, V. Functionally graded materials produced with high power laser. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 426–432, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, J.; Trzepieciński, T. Możliwości Zapewnienia Jakościowego Wykonania Narzędzi z Oszczędnościowej Stali Szybkotnącej; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Rzeszowskiej: Rzeszów, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil, K.P.; Jegadheesan, C.; Somasundaram, P.; Praveen, K.S.; Vivek, A.A.; Ajit, P.S.; Jeyaprakash, N. State of art: Review on laser surface hardening of alloy metals. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Bonek, M.; Piec, M.; Jonda, E. Diode laser modification of surface gradient layer properties of a hot-work tool steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 532–533, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakowski, T.; Wierzchoń, T. Inżynieria Powierzchni Metali. Podstawy, Urządzenia, Technologia; Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Temmler, A.; Cortina, M.; Ross, I.; Küpper, M.E.; Rittinghaus, S.K. Evolution of Surface Topography and Microstructure in Laser Polishing of Cold Work Steel 1.2379 (AISI D2) Using Quadratic, Top-Hat Shaped Intensity Distributions. Materials 2022, 15, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, D.J.; Weber, R.; Holder, D.; Graf, T. Estimation of the depth limit for percussion drilling with picosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 11546–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, T.; Heberle, J.; Hautmann, H.; Zhao, R.; Tenner, J.; Tremmel, S.; Merklein, M.; Schmidt, M. Effect of Picosecond Laser Based Modifications of Amorphous Carbon Coatings on Lubricant-free Tribological Systems. JLMN-J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2017, 12, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähnig, T.; Mousavi, A.; Steinhorst, M.; Roch, T.; Brosius, A.; Lasagni, A.F. Friction reduction in dry forming by using tetrahedral amorphous carbon coatings and laser micro-structuring. Dry Met. Form. 2019, 5, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbruch, H.; Lu, Y.; Messaoudi, H.; Mehner, A.; Vollertsen, F. Tribological Properties of Multi-Layer a-C:H:W/a-C:H PVD-Coatings Micro-Structured by Picosecond Laser Ablation. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 809, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, M.; Reichardt, G.; Weber, R.; Graf, T.; Liewald, M. Dry Metal Forming Using Volatile Lubricants Injected into the Forming Tool Through Flow-Optimized, Laser-Drilled Microholes. JOM 2020, 72, 2517–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Kwaśny, W.; Brytan, Z.; Shishkov, R.; Tomov, B. Structure and properties of the Ti + Ti(C,N) coatings obtained in the PVD process on sintered high speed steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 157–158, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liewald, M.; Wagner, S.; Becker, D. Anisotropie des tribologischen verhaltens beim tiefziehen von Feinblechen. Tribol. Schmier. 2010, 57, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liewald, M.; Becker, D. Effects of rolling direction and lubricant on friction in sheet metal forming. J. Tribol. 2009, 131, 042101042108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PVD czy CVD—Metody Nanoszenia Powłok na Narzędzia. Available online: https://magazynprzemyslowy.pl/artykuly/pvd-czy-cvd-metody-nanoszenia-powlok-na-narzedzia (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Sitek, W. Metodologia Projektowania Stali Szybkotnących z Wykorzystaniem Narzędzi Sztucznej Inteligencji; International OCSCO World Press: Gliwice, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Burakowski, T.; Wierzchoń, T. Surface Engineering of Metals—Principles, Equipment, Technologies; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, D.R.; McFall, W.D.; Sainty, W.G.; Yin, Y.; Durandet, A.; Boswell, R.W. New technology for PACVD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 82, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarde, D.; Powell, M.J.; Quesada-Cabrera, R.; Wilson, R.L.; Carmalt, C.J.; Sankar, G.; Parkin, I.P.; Palgrave, R.G. Optimized Atmospheric-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition Thermochromic VO2 Thin Films for Intelligent Window Applications. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkko, J.G.; Qiu, R.; Bäcke, O.; Forslund, A.; Halvarsson, M.; Larsson, H.; Boman, M. Low-pressure CVD of (Tix,W1-x)Ny from WF6, TiCl4 and NH3. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 438, 128394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, B.C.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Mueller, R.; Lora, F.A.; Nascimento, M.L.F.; Pinto, H.C.; Coelho, R.S. Tribological Investigations on Tool Surfaces for Temperature-Supported Forming of Magnesium AZ31 Sheets. Materials 2020, 13, 2465. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann, W.; Stangier, D. Application of Nanostructured Bionic Thin Layers to Enhance the Wear and Friction Behavior of Tools for Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming. In Sheet Bulk Metal Forming; Merklein, M., Tekkaya, A.E., Behrens, B.A., Eds.; TCRC73 2020, Lecture Notes in Production Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 216–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, M. Vanadium carbide diffusion coatings for tool and die components. ASM Proc. Heat Treat. 2006, 2006, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Janoss, B.J. PVD/CVD coatings for stamping and forming of stainless steels. In Technical Papers-Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Proceedings of the 1999 Conference Forming and Fabricating Stainless Steel, Springfield, MA, USA, 2-4 June 1999; Society of Manufacturing Engineers: Dearborn, MI, USA, 1999; pp. 99–199. [Google Scholar]
- Escher, C.; Henke, T. New trends in thin coatings for sheet metal forming tools. In Proceedings of the 6th International Tooling Conference: The Use of Tool Steels: Experience and Research, Karlstad University, Karlstad, Sweden, 10–13 September 2002; pp. 919–933. [Google Scholar]
- Balaceanu, M.; Braic, M.; Braic, V.; Pavelescu, G. Properties of arc plasma deposited TiCN/ZrCN superlattice coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.T. TiN/NbN superlattice hard coatings deposited by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 113, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysiecki, M. Nowoczesne Materiały Narzędziowe; Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hovsepian, P.E.; Münz, W.D. Synthesis, structure and applications of nanoscale multilayer/superlattice structured PVD coatings. In Nanostructured Coatings; Cavaleiro, A., De Hosson, J.T.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 555–643. [Google Scholar]
- Hultman, L. Synthesis, structure and properties of superhard superlattice coatings. In Nanostructured Coatings; Cavaleiro, A., De Hosson, J.T.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 539–554. [Google Scholar]
- Czechowski, K.; Wrońska, I. Powłoki nanostrukturalne na narzędzia skrawające. Mechanik 2011, 84, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Spain, E.; Avelar-Batista, J.C.; Letch, M.; Housden, J.; Lerga, B. Characterization and application of Cr-Al-N coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Vinh, P.V.; Kim, J.H.; Ngoc, T. Deposition of superhard TiAlSiN thin films by cathodic arc plasma deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, A.E.; Derfinger, V.H.; Hanselmann, B.; Bachmann, T.; Sartory, B. Investigation of the properties of Al1-xCrxN coatings by cathodic arc evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.; Keunecke, M.; Bewilogua, K.; Chudoba, T.; Kölker, W.; van den Berg, H. Cubic boron nitride based coating systems with different interlayers for cutting inserts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Temperature dependent friction and wear of magnetron sputtered coating TiAlN/VN. Wear 2011, 271, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Wang, D.Y.; Hung, C.Y. Structural and mechanical properties of nanolayered TiAlN/CrN coatings synthesized by arc deposition process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qin, L.; Dong, G.; Hua, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J. An investigation on the lubrication mechanism of MoS2 nano sheet in point contact: The manner of particle entering the contact area. Tribol. Int. 2017, 107, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, D.; Fu, Y.; Pei, Y.T.; De Hosson, J.T.M. Ni—Toughened nc-TiN/a-SiNx nanocomposite thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 194, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Settineri, L.; Faga, M.G.; Gautier, G.; Perucca, M. Evaluation of wear resistance of AlSiTiN and AlSiCrN nanocomposite coatings for cutting tools. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 57, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, M.V.; Thinh, N.T.; Sy, L.V.; Antonov, S. Study on the formability by TPIF technology for aluminium sheet at room temperature. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 207, 05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Baik, Y.J. The crystalline structure, hardness and thermall stability of AlN/CrN superlattice coating prepared by D.C. magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flink, A.; Larsson, T.; Sjölén, J.; Karlsson, L.; Hultman, L. Influence of Si on the microstructure of arc evaporated (Ti, Si)N thin films; evidence for cubic solid solutions and their thermal stability. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Toihara, T.; Wang, M.; Kurosaka, W.; Miyake, S. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of nanoscale TiAlN/SiNx multilayer coating deposited by reactive magnetron sputterin. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 203, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Le, V.V.; Vinh, P.V.; Lee, J.W. Effect of cathode arc current and bias voltage on the mechanical properties CrAlSiN thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 5400–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiotti, A.; Bruschi, S. Tribological behaviour of DLC coatings for sheet metal forming tools. Wear 2011, 271, 2454–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoba, C.H.; Siva Prasad, D. Cathodic arc TiAlN PVD coatings for machining applications. Mater. Sci. Indian J. 2016, 12, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Taube, K. Carbon-based coatings for dry sheet-metal working. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 98, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakawa, M.; Takeuchi, S. Evaluation of tribological properties of DLC films used in sheet forming of aluminum sheet. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakawa, M.; Koga, N.; Watanabe, S.; Takeuchi, S. Tribological behavior of amorphous hard carbon films against zinc-plated steel sheets. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 108–109, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachenfels, K.; Rothammer, B.; Zhao, R.; Tremmel, S.; Merklein, M. Influence of varying sheet material properties on dry deep drawing process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 651, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.C. Coatings for forming dies of advanced high-strength steel. In Coating Technology for Vehicle Applications; Cha, S., Erdemir, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xue, Q. Structure and high temperature tribological behavior of TiAlN/nitride duplex treated coatings on Ti6Al4V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouari, M.; Makich, H. On the physics of machining titanium alloys: Interactions between cutting parameters, microstructure and tool wear. Metals 2014, 4, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Deng, J.; Cui, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J. Friction and wear properties of TiN, TiAlN, AlTiN and CrAlN PVD nitride coatings. Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 2012, 31, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, C.P.; Owens, F.J. Introduction to Nanotechnology; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Gołombek, K.; Pakuła, D.; MIkuła, J.; Staszuk, M.; Żukowska, W. Long-term development directions of PVD/CVD coatings deposited onto sintered tool materials. Open Access Libr. 2011, 6, 278–330. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, D. Wear of nanostructured composite tool coatings. Wear 2013, 304, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Peng, Z.; Yu, X.; Fu, Z.; Yue, W.; Wang, C. Microstructure and tribological performance of self-lubricating diamond/tetrahedral amorphous carbon composite film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3180–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, K.P.; Gonçalves, P.D.C.; Consoni, D.R.; Dias, M.V.G.; De Lima, G.A.; de Mello, J.D.B.; Klein, A.N. Metallurgical aspects of self-lubricating composites containing graphite and MoS2. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.M.; Fazal, M.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Yusof, F.; Masjuki, H.H.; Arslan, A.A. Review to the laser cladding of self-lubricating composite coatings. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2016, 3, 67–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, J.D.B.; Binder, C.; Hammes, G.; Binder, R.; Klein, A.N. Tribological behaviour of sintered iron based self-lubricating composites. Friction 2017, 5, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowe Nanopowłoki Ograniczają Tarcie i Zanieczyszczenia. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/article/id/89519-new-nanocoats-reduce-friction-and-pollution/pl (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Mitsuno, A.; Akhadejdamrong, T.; Aizawa, T. Self-lubrication of Cl-implanted titanium nitride coating for dry metal forming. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotkowiak, M. Samosmarujące Warstwy Stopowane Laserowo i Materiały Spiekane Wytwarzane z Zastosowaniem Fluorków Wapnia i Baru. Ph.D. Thesis, Politechnika Poznańska, Poznań, Poland, 8 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Yu, Y.L.; Li, S.Q. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser clad CaF2/Al2O3 self-lubrication wear-resistant ceramic matrix composite coatings. Scr. Mater. 2002, 47, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, A.H.; Huang, Z.W. Microstructure and properties of HVOF sprayed Ni-based submicron WS2/CaF2 self-lubricating composite coating. trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walck, S.D.; Zabinski, J.S.; McDevitt, N.T. Characterization of air-annealed, pulsed laser deposited ZnO–WS2 solid film lubricants by transmission electron microscopy. Thin Solid Films 1997, 305, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabinski, J.S.; Donley, M.S.; Dyhouse, V.J. Chemical and tribological characterization of PbO–MoS2 films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 1992, 214, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Veovodin, A.A. Molybdenum disulfide as a lubricant and catalyst in adaptive nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 4125–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Brögelmann, T.; Kruppe, N.C.; Hoffmann, D.C.; Bergs, T.; Trauth, D.; Mannens, R.; Hild, R. Self-Lubricating PVD Coatings for Dry Cold Massive Forming. Available online: https://publications.rwth-aachen.de/record/780460/files/780460.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Bobzin, K.; Brögelmann, T.; Kruppe, N.C.; Arghavani, M.; Hoffmann, D.C.; Klocke, F.; Mattfeld, P.; Trauth, D.; Hild, R. Mechanical and tribological characterization of self-lubricating (Cr1-xAlx)N coatings for deposition on complex-shaped forging tools. Dry Met. Form. Open Access J. 2013, 3, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Rajak, D.; Kumar, A.; Behera, A.; Menezes, P. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings: Classification, properties, and applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Reduced wear and friction enabled by graphene layers on sliding steel surfaces in dry nitrogen. Carbon 2013, 59, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasar, A.K.; Xiong, G.; Menezes, P.L. Graphene-reinforced metal and polymer matrix composites. JOM 2018, 70, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J. Tribological properties of h-BN matrix solid-lubricating composites under elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2020, 148, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.; Menezes, P.L. Self-lubricating materials for extreme condition applications. Materials 2021, 14, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majety, S.; Cao, X.K.; Dahal, R.; Pantha, B.N.; Li, J.; Lin, J.Y.; Jiang, H.X. Semiconducting hexagonal boron nitride for deep ultraviolet photonics. Quantum Sens. Nanophotonic Devices 2012, 8268, 607–614. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, H.; Panaitescu, I.; Gangl, R.; Hubmann, R.; Scheerer, M.; Ripoll, M.R. Laser metal deposition of self-lubricating alloys on selective laser melting maraging tools for the high temperature forming of aluminium. Wear 2023, 524–525, 204883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żaba, K.; Tuz, L.; Noga, P.; Rusz, S.; Zabystrzan, R. Effect of Multi-Variant Thermal Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of AlSi10Mg Processed by Direct Metal Laser Sintering and Casting. Materials 2022, 15, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschauer, E.; Riedl, H.; Koller, C.M.; Bolvardi, H.; Arndt, M.; Polcik, P.; Mayrhofer, P.H. Adhesive wear formation on PVD coated tools applied in hot forming of Al-Si coated steel sheets. Wear 2019, 430–431, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschauer, E.; Sackl, S.; Schachinger, T.; Bolvardi, H.; Arndt, M.; Polcik, P.; Riedl, H.; Mayrhofer, P.H. Atomic scale investigations of thermally treated nano-structured Ti-Al-N/Mo-Si-B multilayers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, H.; Koller, C.M.; Limbeck, A.; Kalaš, J.; Polcik, P.; Mayrhofer, P.H. Oxidation behavior and tribological properties of multilayered Ti-Al-N/Mo-Si-B thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2015, 33, 05E129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinwall, D.K.; Wise, M.L.H.; Stout, K.J.; Gho, T.H.A.; Zhao, F.L.; EI-Menshawy, M.F. Electrical discharge texturing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1992, 32, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, J.; Aspinwall, D.K.; Wise, M.L.H.; EI-Menshawy, M.F. Mill roll texturing using EDT. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1994, 45, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podulka, P. The Effect of Surface Topography Feature Size Density and Distribution on the Results of a Data Processing and Parameters Calculation with a Comparison of Regular Methods. Materials 2021, 14, 4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podulka, P. Improved Procedures for Feature-Based Suppression of Surface Texture High-Frequency Measurement Errors in the Wear Analysis of Cylinder Liner Topographies. Metals 2021, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Reinert, L.; Ramos-Moore, E.; Souza, N.; Müser, M.H.; Mücklich, F. Dry friction between laser-patterned surfaces: Role of alignment, structural wavelength and surface chemistry. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijani, D.; Deladi, E.L.; De Rooij, M.B.; Schipper, D.J. The Influence of Surface Texturing on the Film Thickness in Starved Lubricated Parallel Sliding Contacts. Lubricants 2018, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, P.G.; Profito, F.J.; Rosenkranz, A. Multi-scale surface texturing in tribology—Current knowledge and future perspectives. Lubricants 2019, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasegi, N.; Sugimori, H.; Morimoto, H.; Morita, N.; Hori, I. Development of cutting tools with microscale and nanoscale textures to improve frictional behaviour. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, M.; Roth, S.; Becker, W. Influence of laser-produced microstructures on the tribological behavior of ceramics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 100–101, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.E.; Cha, K.H.; Sung, I.H.; Bryan, J. Design of surface micro-structures for friction control in micro-systems applications. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2002, 51, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Hutchings, I.M. Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured steel surfaces under recipro-cating sliding conditions. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Use of structured surfaces for friction and wear control on bearing surfaces. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2014, 2, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aal, H.A. Functional surfaces for tribological applications: Inspiration and design. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2016, 4, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Sperk, T.; Gietzelt, T.; Kunze, T.; Lasagni, A.F.; Brosius, A. Effect of contact area on friction force in sheet metal forming operations. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 767, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varenberg, M.; Halperin, G.; Etsion, I. Different aspects of the role of wear debris in fretting wear. Wear 2002, 252, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakuda, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kanzaki, S.; Yasuda, Y. Effect of surface texturing on friction reduction between ceramic and steel materials under lubricated sliding contact. Wear 2003, 254, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, M.; Stein, P.; Groche, P. Influence of hammer-peened surface textures on friction behavior. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šugár, P.; Šugárová, J.; Frnčík, M. Laser surface texturing of tool steel: Textured surfaces quality evaluation. Open Eng. 2016, 6, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, A.; Galdos, L.; Childs, C.; Llavori, I.; Aginagalde, A.; Mendiguren, J.; Saenz de Argandoña, E. The Interaction between the sheet/tool surface texture and the friction/galling behaviour on aluminium deep drawing operations. Metals 2021, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, V.; Witulski, J.; Brosius, A.; Trompeter, M.; Tekkaya, A.E. Textured surfaces for deep drawing tools by rolling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, M.; Scheil, J.; Müller, C.; Groche, P. Effect of process parameters on surface roughness in hammer peening an deep rolling. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 554–557, 1887–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacini, L.; van Le, N. Effect of impact energy on residua stresses induced by hammer peening of 304L plate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 208, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, W.; Hildebrand, M. Umformtechnische Vorgange in der Wirkfuge unter Berucksichtigung der Bedeutung der Schmier-Stoffe. Schmierung bei den Prozessen der Warm- und Kaltumformung; TU Bergakademie Freiberg: Freiberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwer, C.J. Verschleißreduktion beim Tiefziehen von X5CrNi18-10. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 20 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Šugárová, J.; Šugár, P.; Frnčík, M.; Necpal, M.; Moravčíková, J.; Kusý, M. The influence of the tool surface texture on friction and the surface layers properties of formed component. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2018, 12, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakoti, I.; Kibria, G.; Cep, R.; Pradhan, B.B.; Sharma, A. Laser surface texturing for biomedical applications: A review. Coatings 2021, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhan, M.; Fu, M.W.; Guo, J.; Xu, R.Q.; Lei, X.P. A unique spinning method for grain refinement: Repetitive shear spinning. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlaček, M.; Guštin, A.Z.; Žužek, B. Influence of laser surface texturing sequence on fatigue properties of coated cold work tool steel. Metals 2020, 10, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Sedlaček, M.; Čekada, M.; Jacobson, S.; Zajec, B. Impact of fracture toughness on surface properties of PVD coated cold work tool steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 277, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlaček, M.; Batič, B.Š.; Česnik, D.; Podgornik, B. Influence of the substrate hardness and fracture toughness on the dynamic wear properties of coated tool steels. Mater. Technol. 2019, 53, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshchynsky, V.; Ignatiev, M.; Wisniewska-Weinert, H.; Borowski, J.; Rybak, T.; Dobrovnik, I. Forging tools modification with graphene-like solid lubricant nanoparticles. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2010, 43, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Vorholt, J.; Shimizu, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Heinrich, L.; Flosky, H.; Vollertsen, F.; Yang, M. In-situ observation of lubricant flow on laser textured die surface in sheet metal forming. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 2209–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, A. Problems of modern surface engineering technology implementation. Adv. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2002, 26, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gropper, D.; Wang, L.; Harvey, T.J. Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured surfaces: A review of modeling techniques and key findings. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shi, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C. Recent progress on surface texturing and solid lubricants in tribology: Designs, properties, and mechanisms. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Lin, J.; Politis, D.J.; Den, T.A. An experimental investigation for macro-textured tool in hot stamping. MATEC Web Conf. 2015, 21, 05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, J.; Stein, P.; Kramer, P.; van den Boogaard, A.H. Tool Texturing for Deep Drawing Applications. IOP Sci. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 418, 012095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.H.; Christiansen, P.; Bay, N. The Influence of Tool Texture on Friction and Lubrication in Strip Reduction Testing. Lubricants 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, T.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q. Study on the Anti-friction properties of chemically etched surface texture and its synergistic Anti-friction properties with nano-lubricating oil in sheet metal deep drawing process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 967, 012091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coating for Stamping and Forming Tools. Available online: https://www.thefabricator.com/thefabricator/article/bending/coating-for-stamping-and-forming-tools (accessed on 31 May 2023).
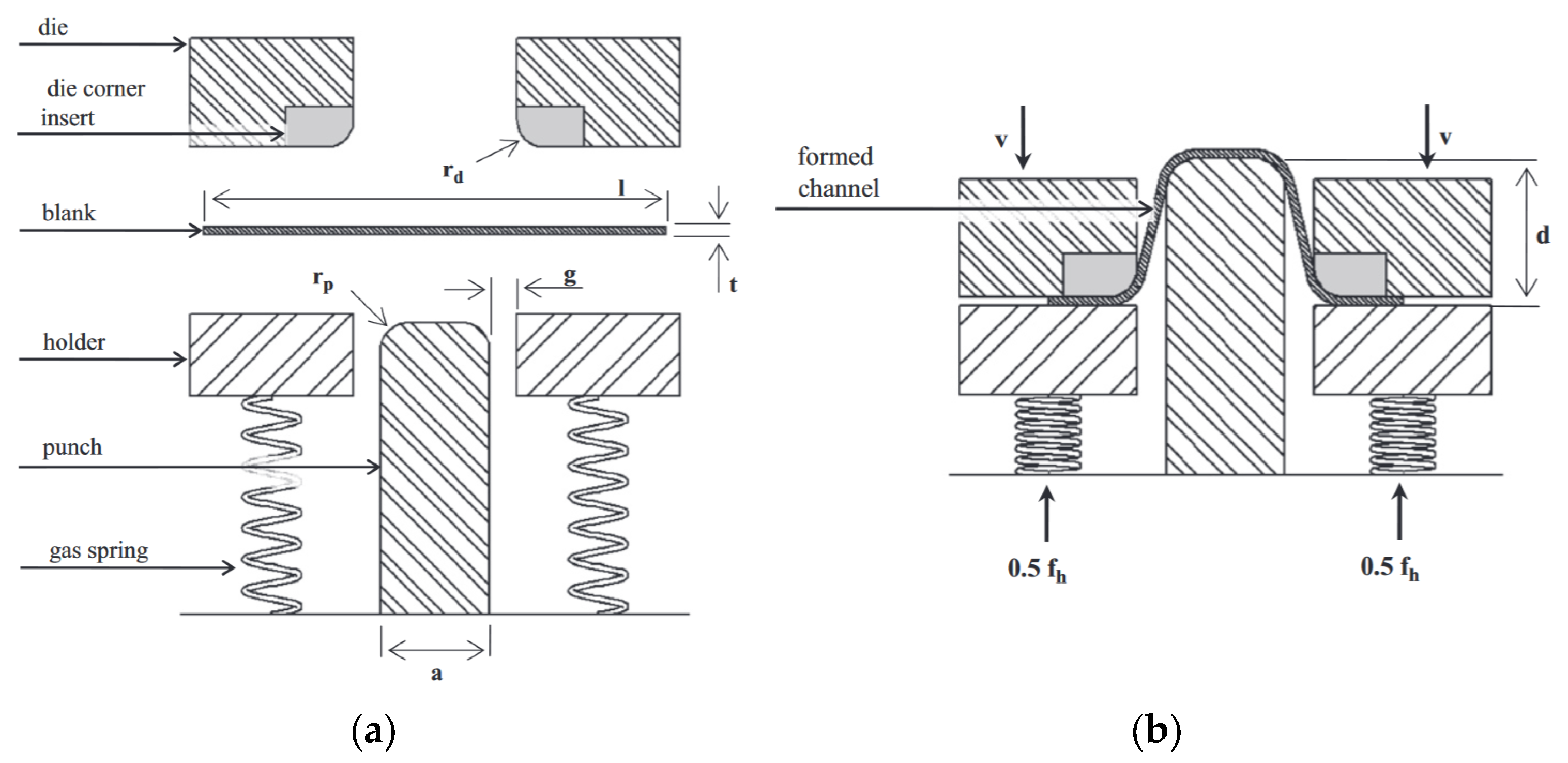
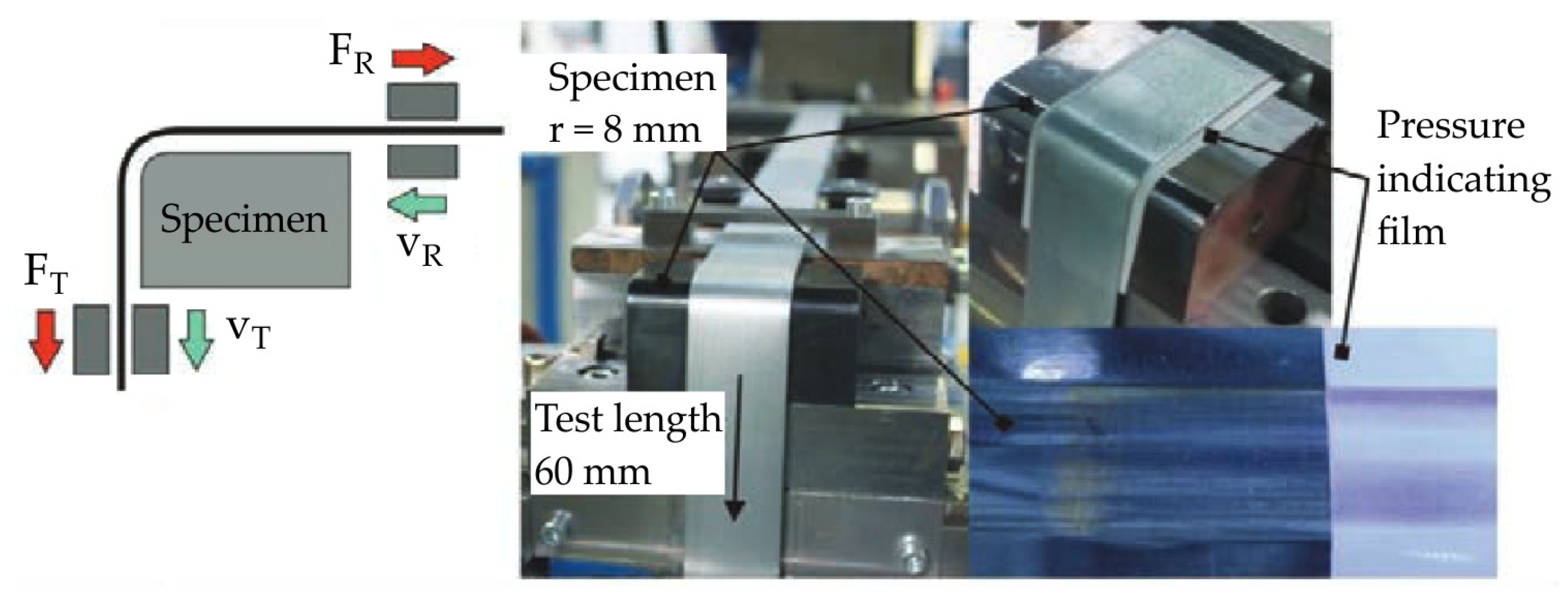
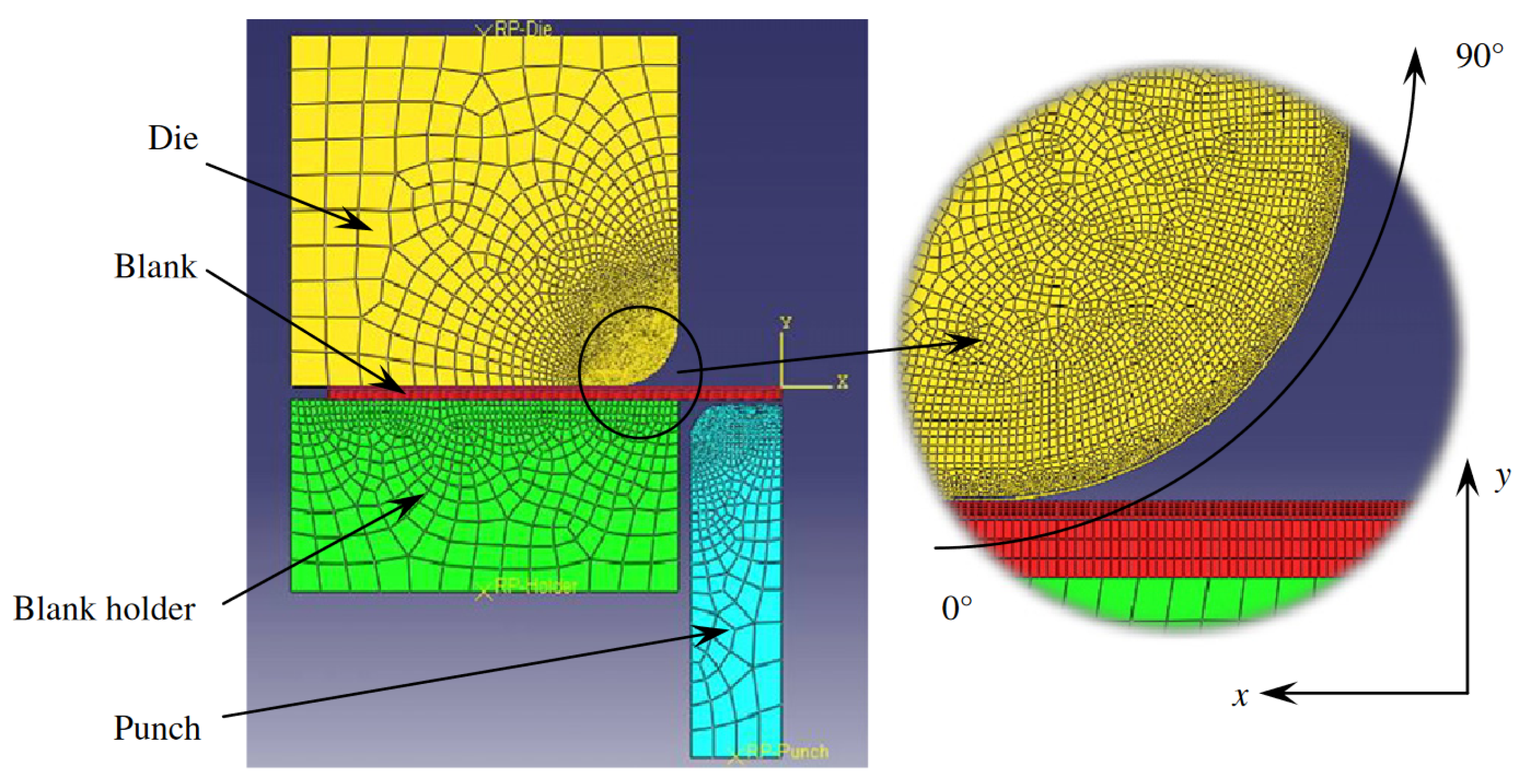
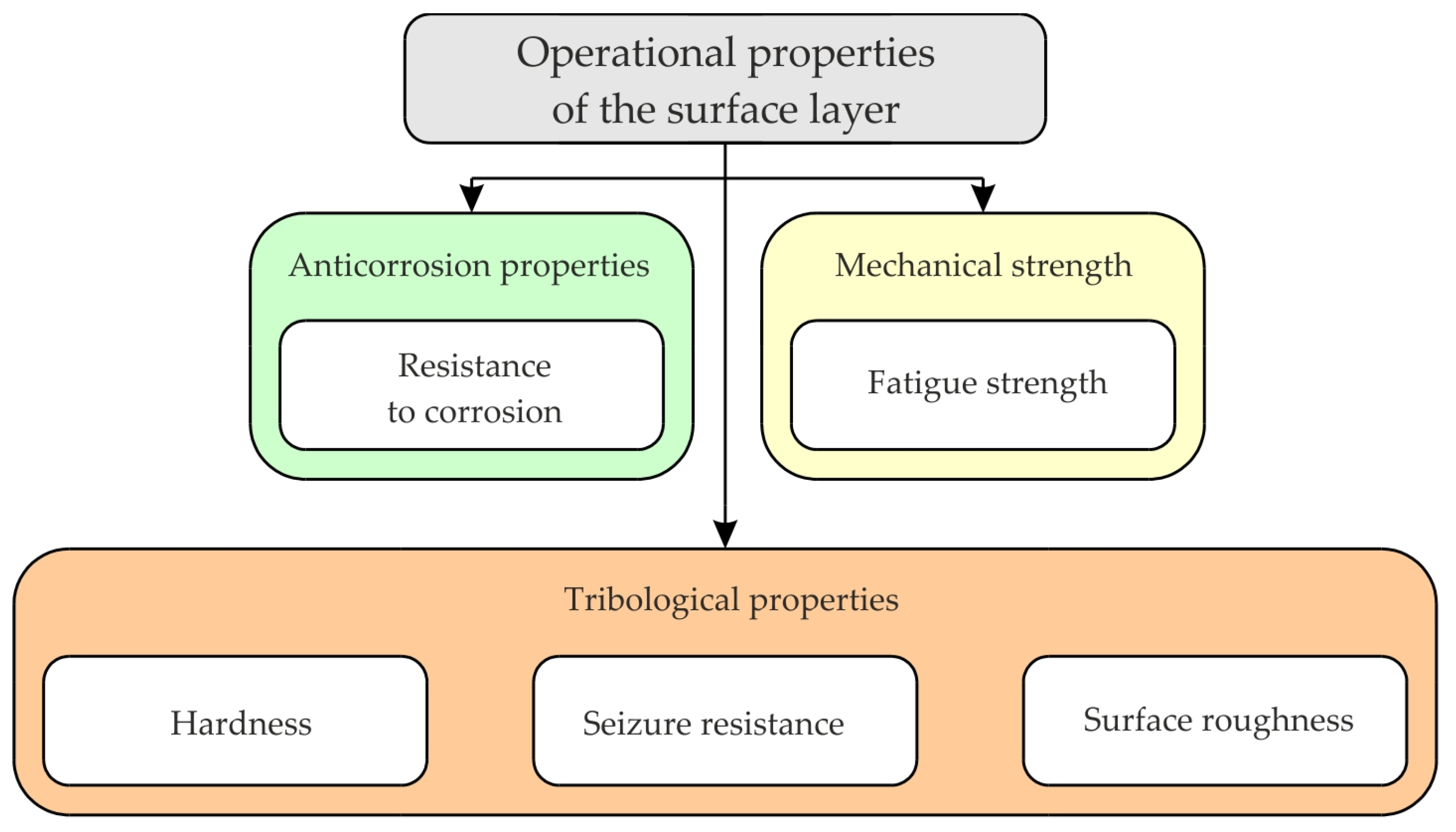
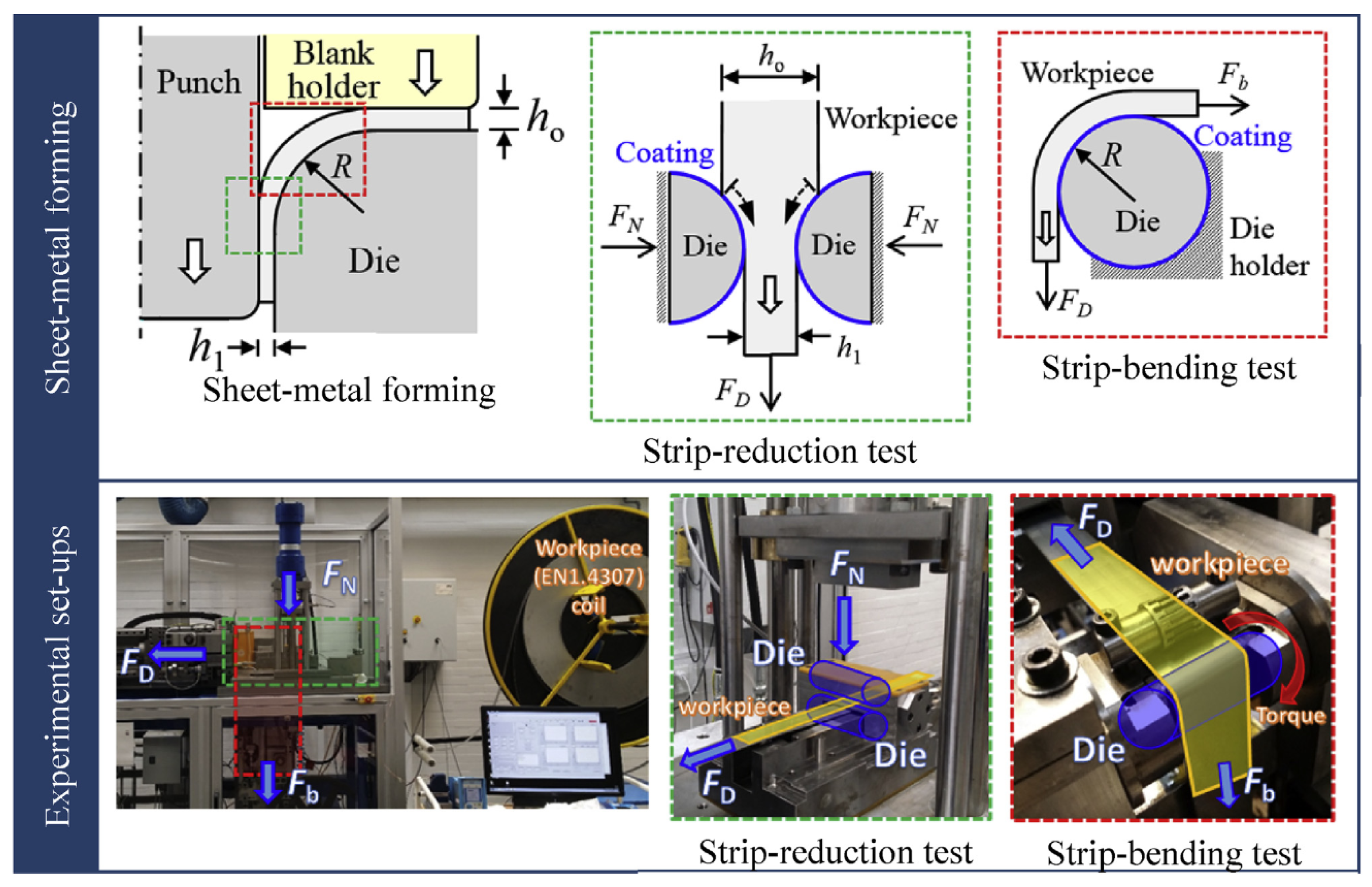
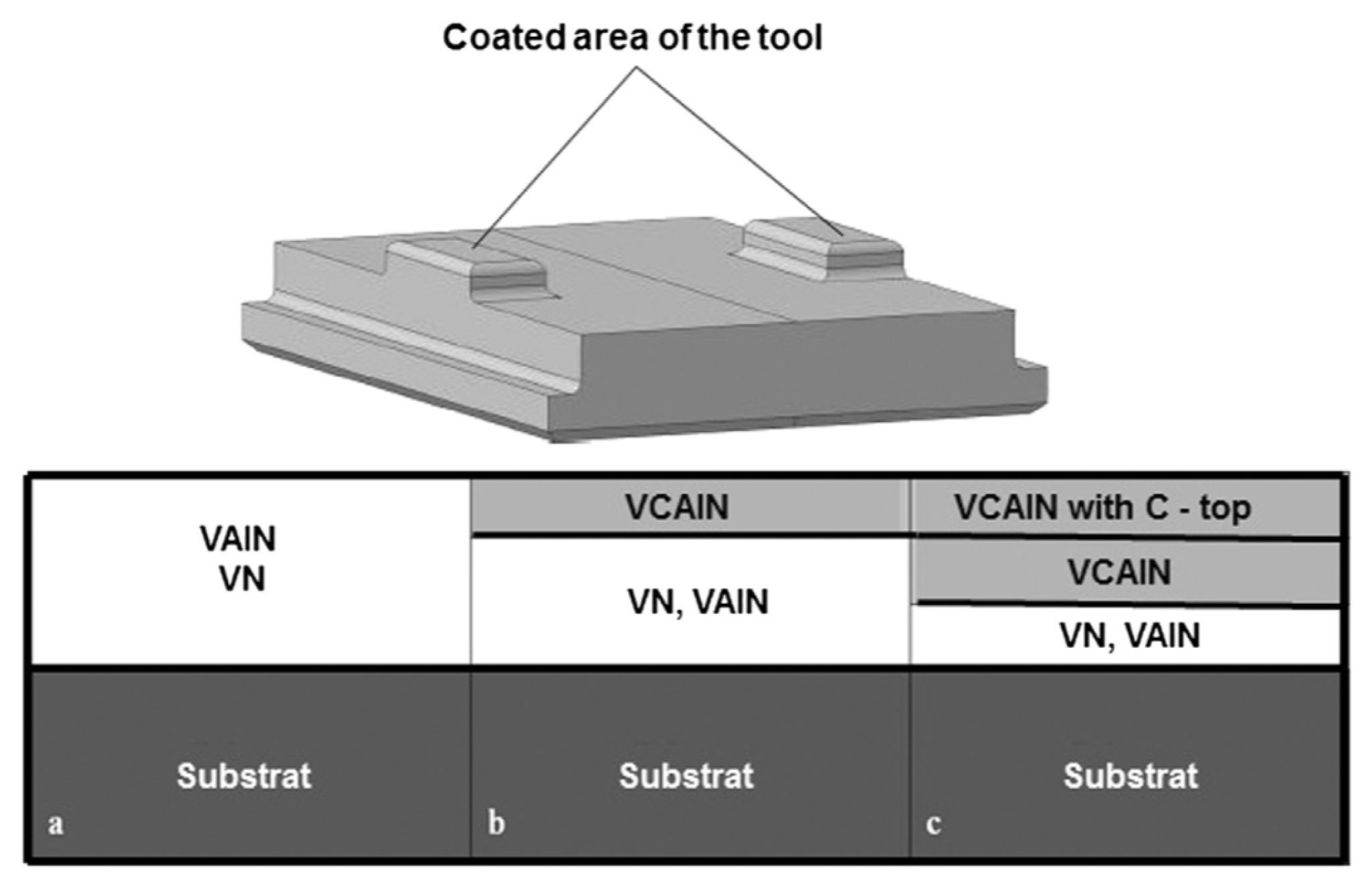


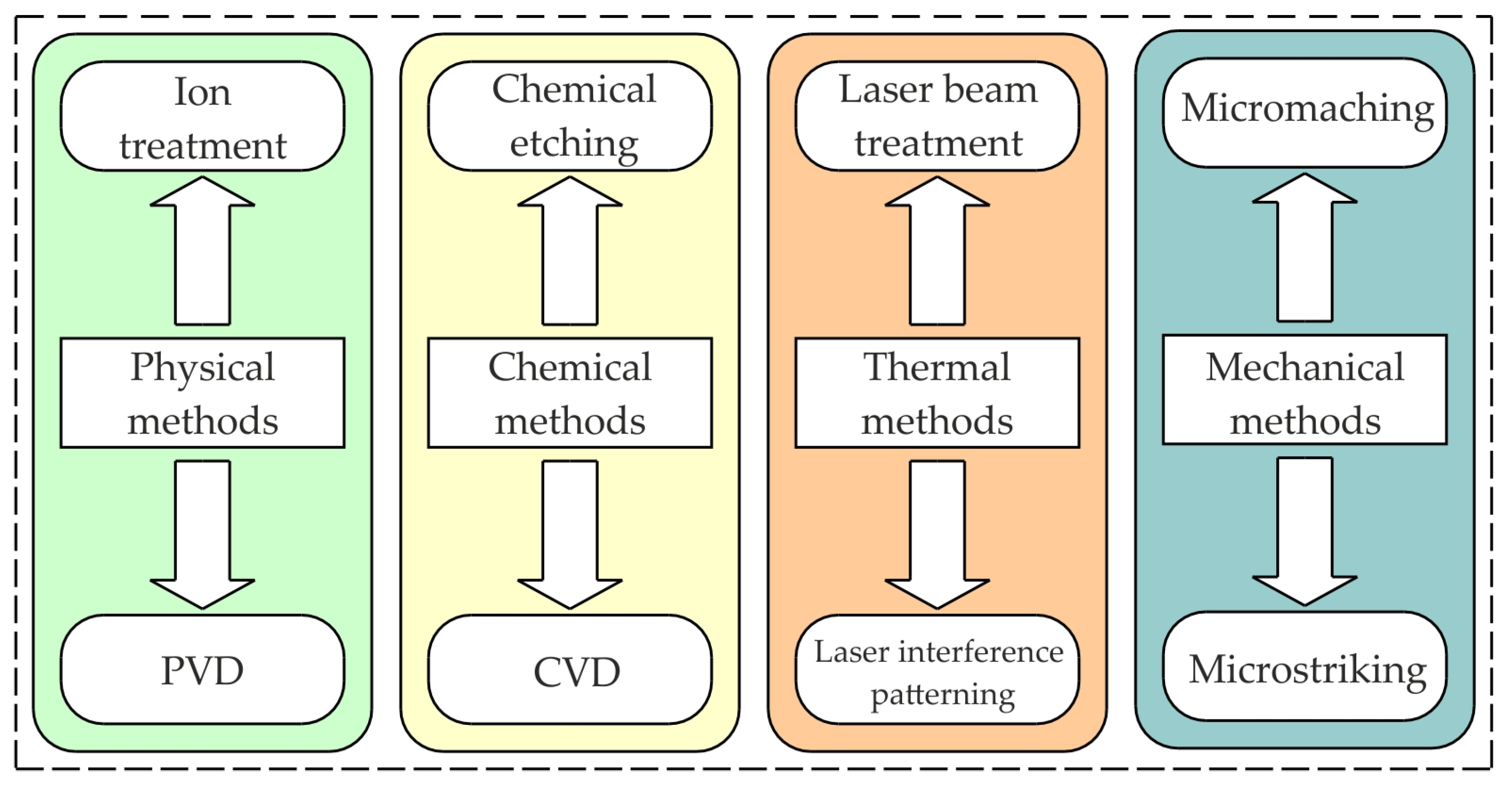

| Structure of Coating | Type of Coating | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Single-layer coating | Cr–Al–N | High oxidation resistance, hardness higher than that of TiN and TiCN [130] |
| Ti–AlSiN | High hardness—48 GPa [131] | |
| Al1-xCrxN | High hardness—38 GPa [132] | |
| Multi-layer coating | TiAlN/cBN, CrTiAlSiN/cBN | Super-hardness—71~75 GPa [133] |
| Superstructure multi-layer coating | TiAlN/ZrN, TiAlN/CrN | Super-hardness—55~78 GPa [127] |
| TiAlN/VN | High hardness—42 GPa, Ra = 0.06 μm [134] | |
| Nanocrystal multi-layer coating | TiAlN/CrN | High hardness—37 GPa [135] |
| Nanolayer coating | CrN/WN | High hardness—31 GPa [136] |
| Nanocomposite coating | Nc-TiN/a-SiNx with addition of Ni | High fracture toughness, hardness—30 GPa [137] |
| AlSiTiN-Si3N4 | High hardness—40 GPa [138] | |
| AlCrSiN | Very high hardness and wear resistance [139] | |
| Superstructure nano-layer coating | AlN/CrN | Very high hardness—40 GPa [140] |
| Nanocrystalline single layer coating | Ti1-xSixN | Very high hardness—40 GPa, temperature resistance up to 900 °C [141] |
| Multi-later nano-coating | lN/SiNx | Hardness—32 GPa, high wear resistance [142] |
| CrAlSiN | High hardness—42 GPa [143] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trzepieciński, T. Approaches for Preventing Tool Wear in Sheet Metal Forming Processes. Machines 2023, 11, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11060616
Trzepieciński T. Approaches for Preventing Tool Wear in Sheet Metal Forming Processes. Machines. 2023; 11(6):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11060616
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrzepieciński, Tomasz. 2023. "Approaches for Preventing Tool Wear in Sheet Metal Forming Processes" Machines 11, no. 6: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11060616
APA StyleTrzepieciński, T. (2023). Approaches for Preventing Tool Wear in Sheet Metal Forming Processes. Machines, 11(6), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11060616






