Novel and Efficient Methodology for Drop Placement Accuracy Testing of Robot-Guided Inkjet Printing onto 3D Objects
Abstract
1. Introduction
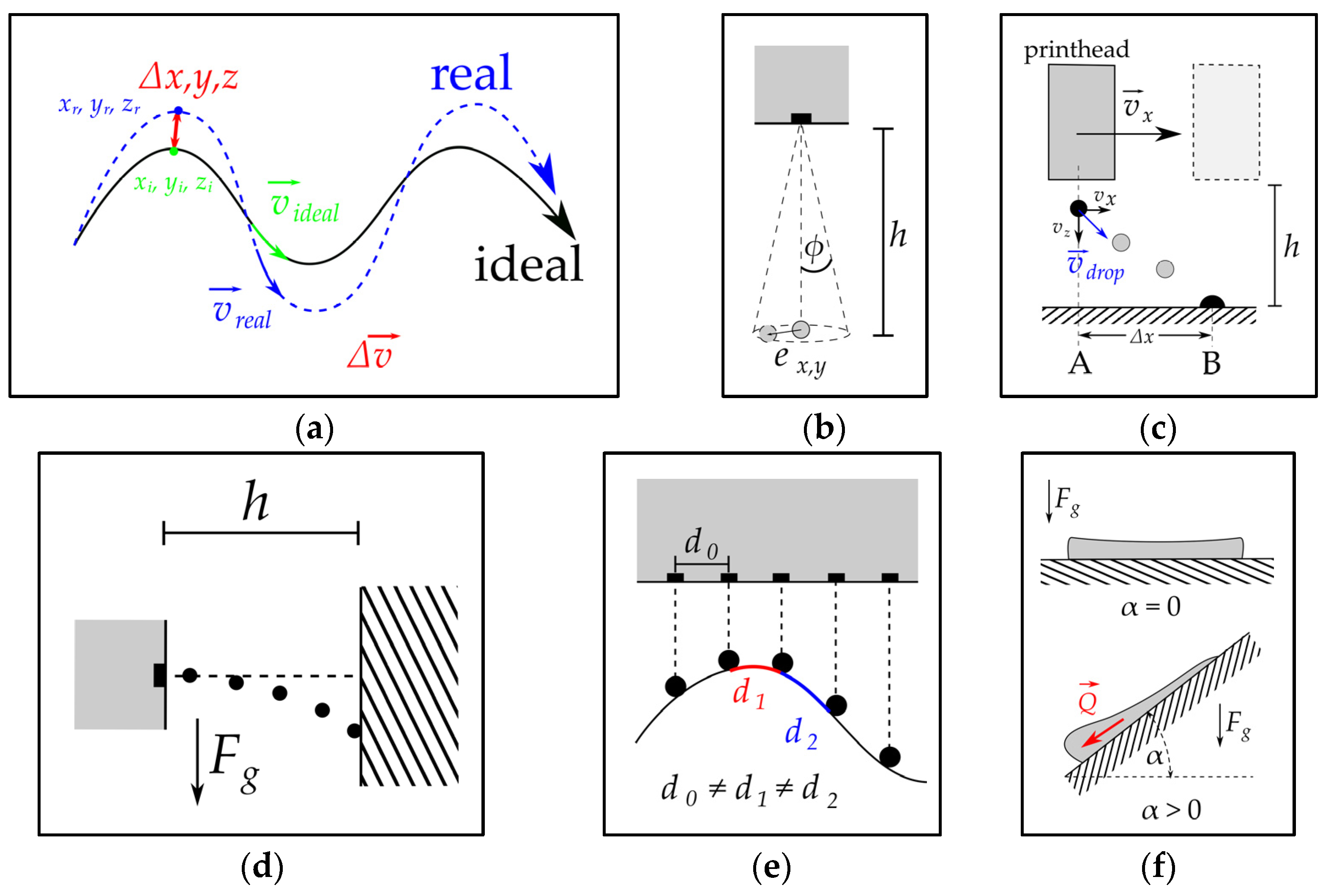
2. Sources of Error for Inkjet Drop Placement on Curved Surfaces
2.1. Robot Motion, Path Planning, and Scanning System
2.2. Inkjet Printing Process
2.2.1. Jet Straightness in Relation to Print Distance
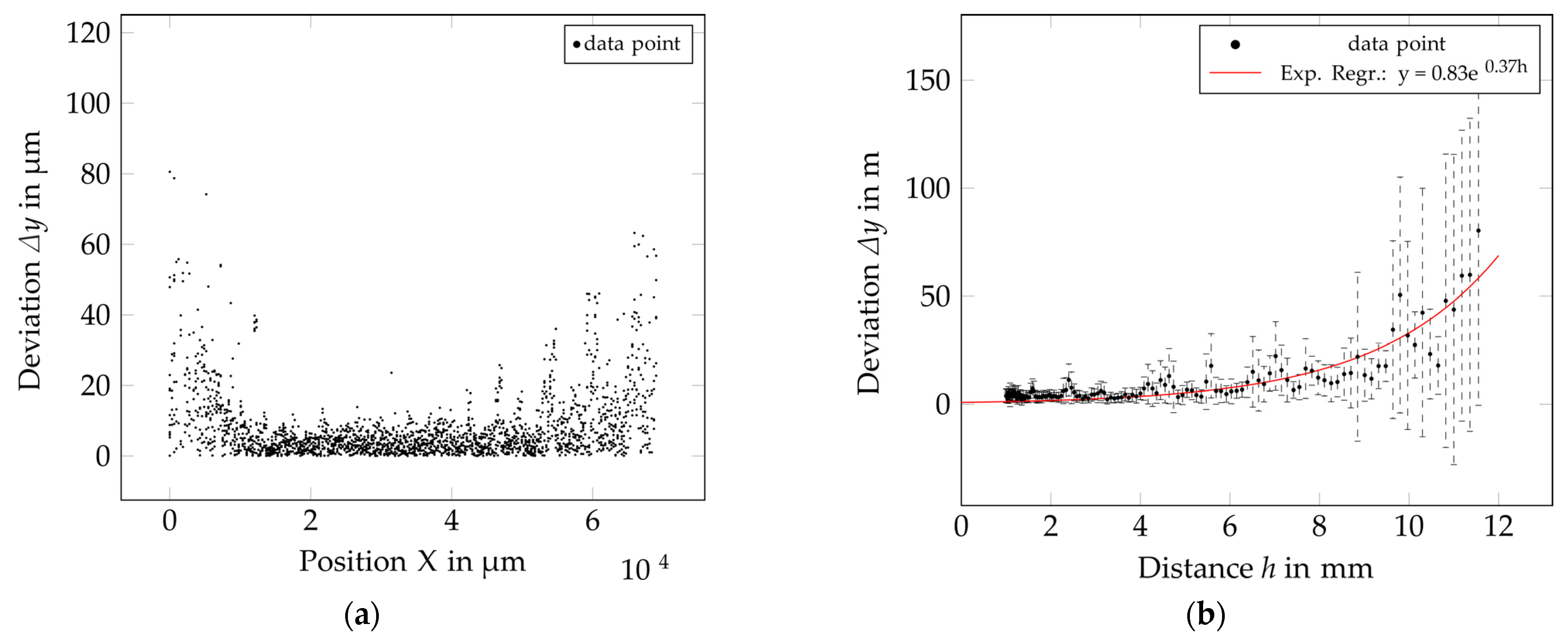
2.2.2. Drop Motion in Print Direction
2.2.3. Printhead Spatial Orientation
2.3. Layer Formation
2.3.1. Distortion by Geometrical Projection
2.3.2. Liquid Flow Behavior
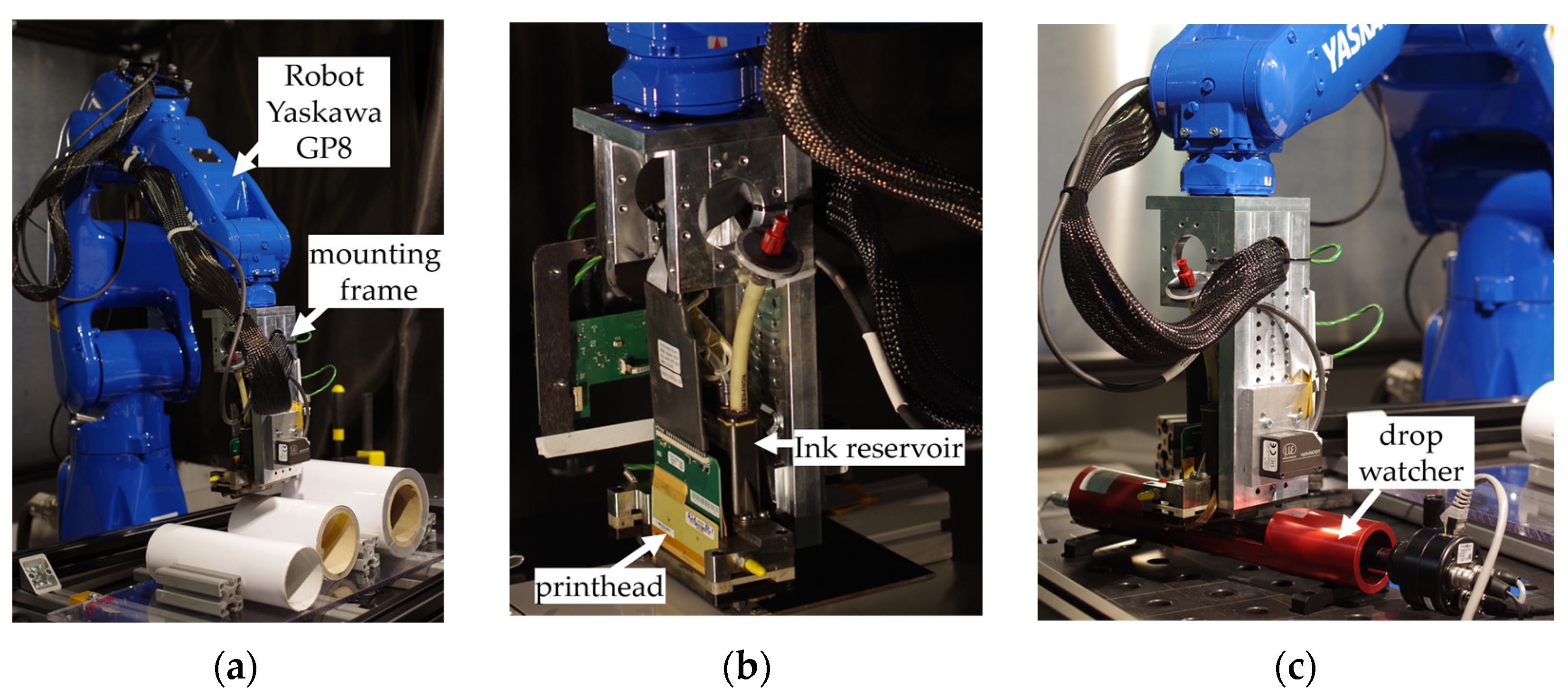
3. Experimental Setup and Methodology
- [AGF]—a black UV-curable ink from Agfa (Altamira Pack LMX) with a density of 1.09 g/cm3, 9–11 mPa·s viscosity (T = 45 °C), and 22.5 mN/m ± 1 mN/m (T = 25 °C) surface tension;
- [PVN]—a silver nanoparticle ink from PV Nanocell (I40DM-106) with a density of 1.62 g/cm3, 10 mPa·s viscosity (T = 25 °C), and a silver load of 40%. The surface tension was not determined.
4. Experiments and Modeling
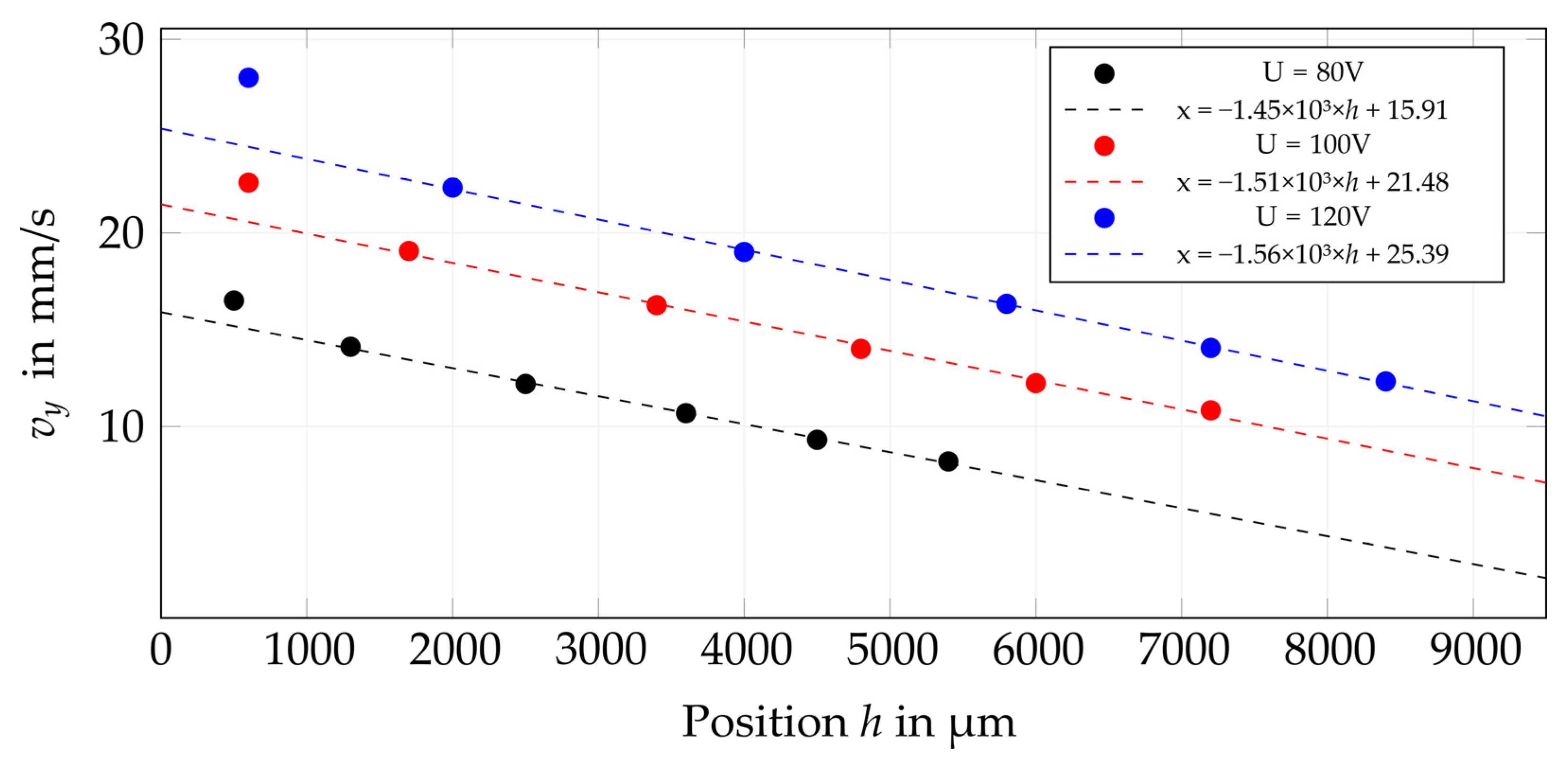
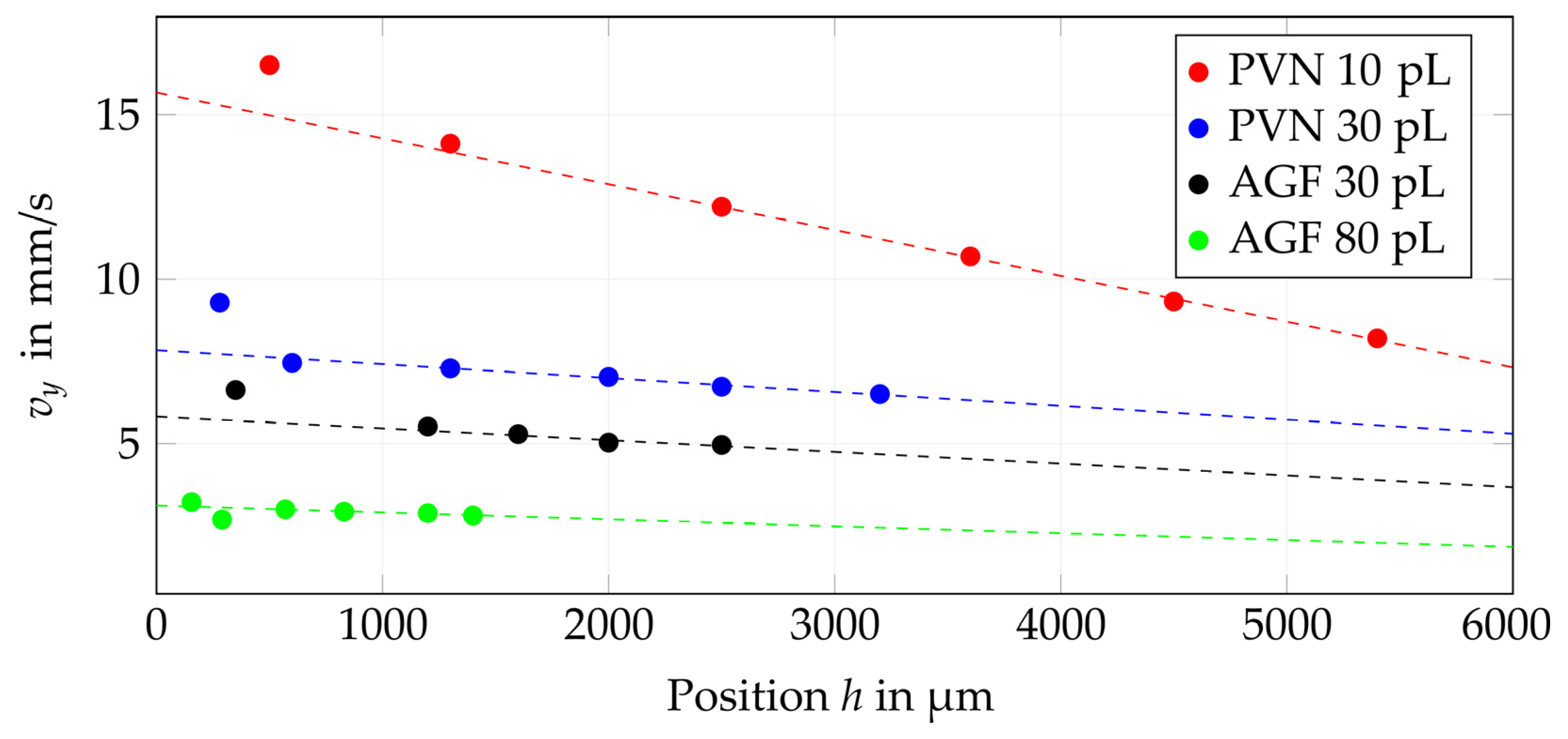
4.1. Drop Watching
4.2. Printing onto a Cylinder and Modeling
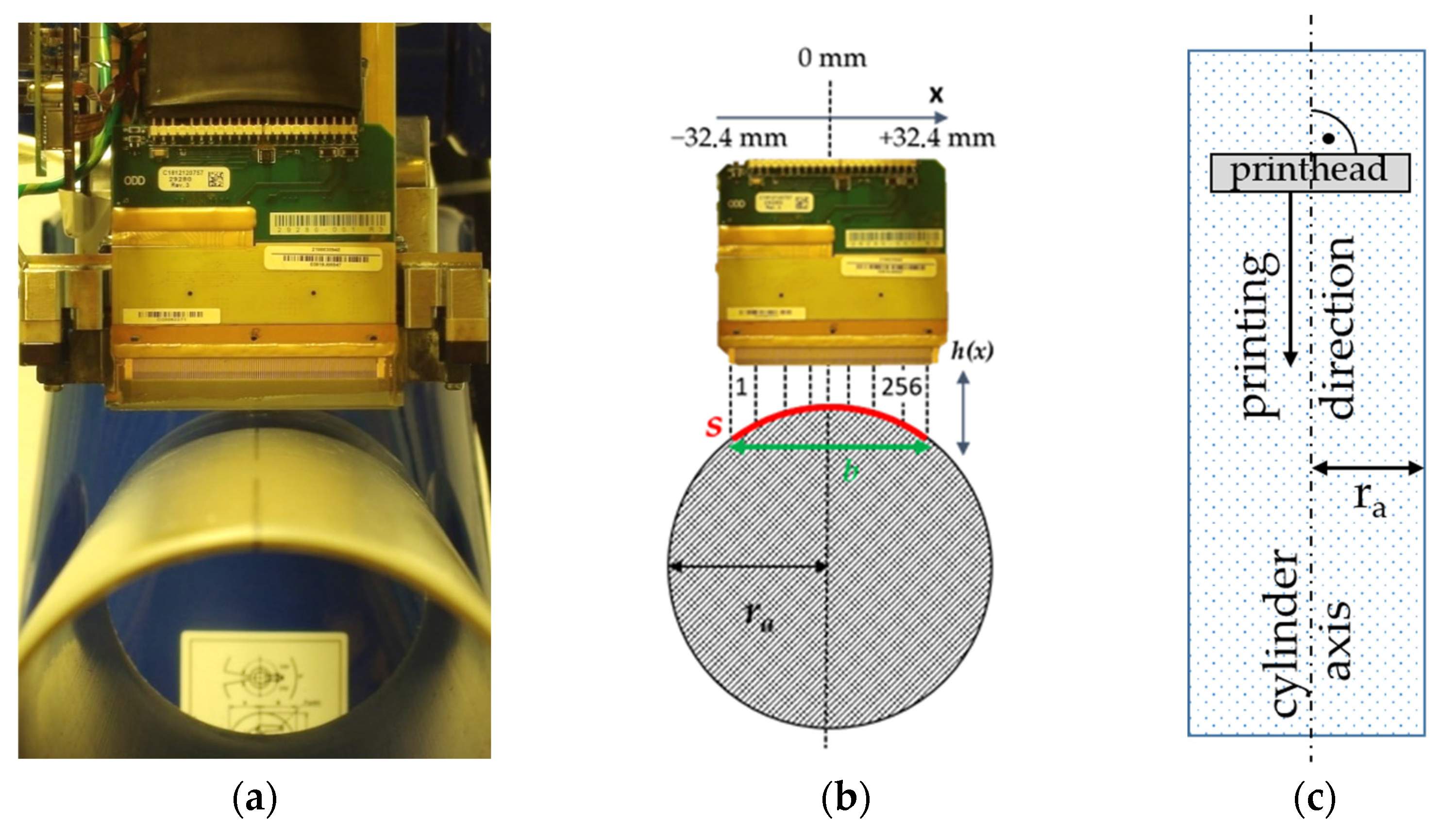
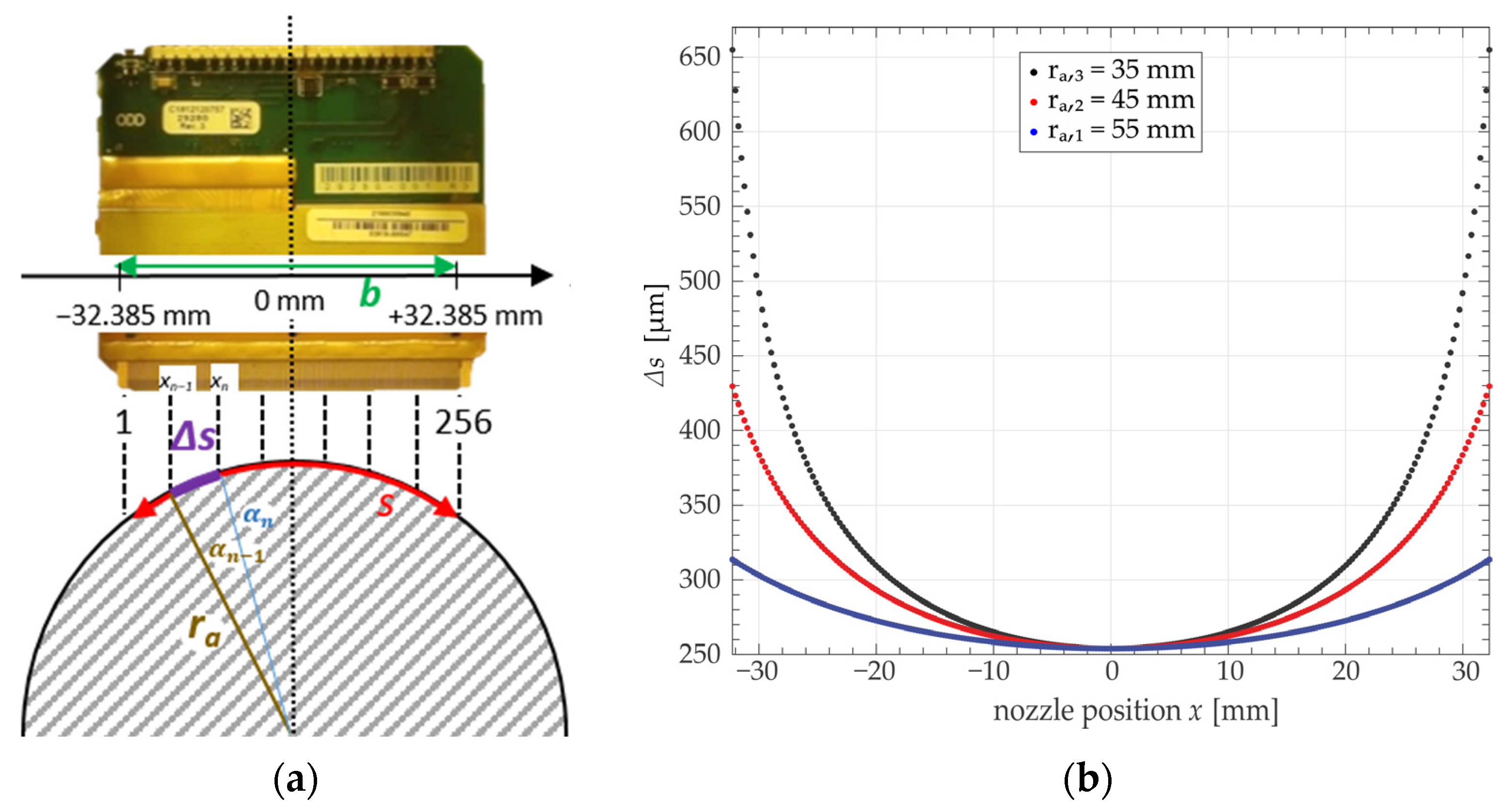
4.2.1. Print Setup
4.2.2. Modeling
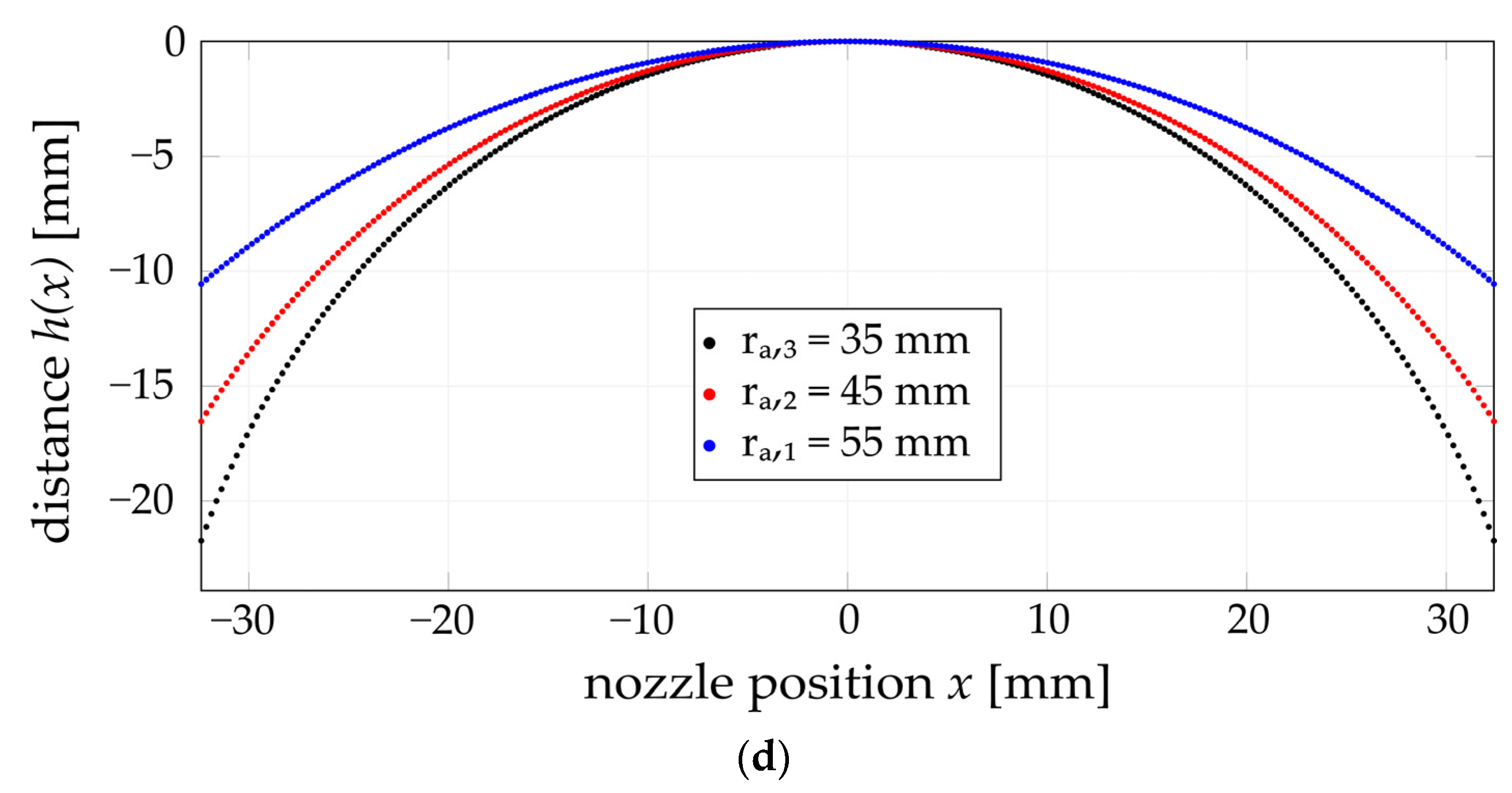
Print Distance
Deviation in Relation to Print and Drop Speed
Image Distortion
Summarized Model Equation
4.2.3. Determination of Displacement and Maximum Height
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Drop Watching
- An increase in piezo voltage will increase the main drop velocity and the jetting distance;
- With increasing drop volume, the drop speed decreases (at a constant piezo voltage level);
- Piezo voltage influences the drop volume of the main drop and the development of the satellite drops.
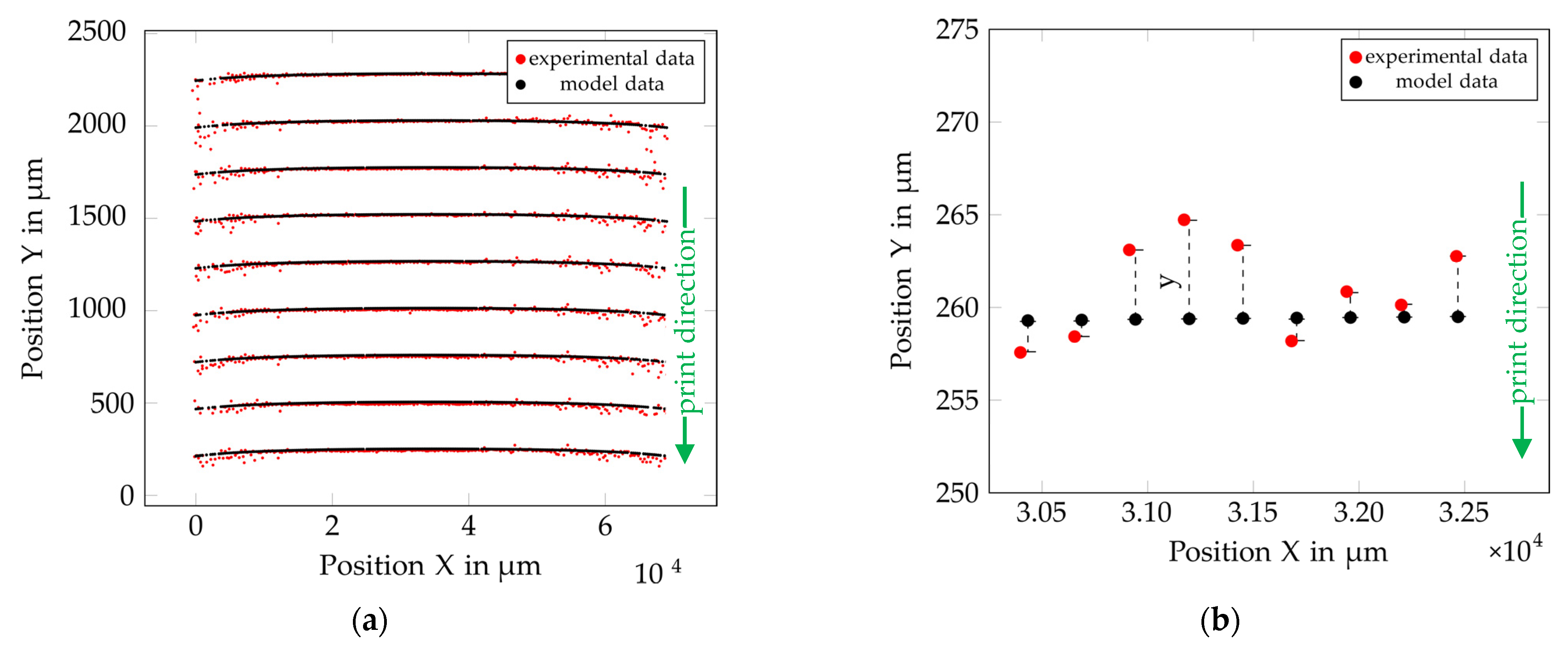
5.2. Printing onto a Cylinder
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummins, G.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Inkjet Printing of Conductive Materials: A Review. Circuit World 2012, 38, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Lee, D.-G.; Lee, B.-Y.; Hur, S. Classifications and Applications of Inkjet Printing Technology: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 140079–140102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Pei, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Xu, T. Inkjet Bioprinting of Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10793–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, I.M.; Martin, G.D. Introduction to Inkjet Printing for Manufacturing. In Inkjet Technology for Digital Fabrication; Hutchings, I.M., Martin, G.D., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-0-470-68198-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cie, C. The Development of Ink Jet Printing on Textiles. In Ink Jet Textile Printing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 15–27. ISBN 978-0-85709-230-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, I.M. Ink-Jet Printing for the Decoration of Ceramic Tiles: Technology and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the XI Congreso Mundial de la Calidad del Azulejo y del Pavimento, Castellón, Spain, 16 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Geerinckx, J. Achieving Cost-effective, High-volume Digital Printing of Laminates: Key Component Selection and Test Criteria. In Inkjet Printing in Industry; Zapka, W., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1543–1567. ISBN 978-3-527-34780-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Zhao, P.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y. 3D Printing of Functional Magnetic Materials: From Design to Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, T.J.; Pikul, J.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D Printing of Soft Robotic Systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagac, M.; Hajnys, J.; Ma, Q.-P.; Jancar, L.; Jansa, J.; Stefek, P.; Mesicek, J. A Review of Vat Photopolymerization Technology: Materials, Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends of 3D Printing. Polymers 2021, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zichner, R.; Sowade, E.; Baumann, R.R. Inkjet Printed WLAN Antenna for an Application in Smartphones. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 05HB06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, M.; Zichner, R.; Joseph, Y. Inkjet-Printed Wireless Chemiresistive Sensors—A Review. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H.G.; Lee, S.-N.; Kim, J. All-Inkjet-Printed Metal-Insulator-Metal (MIM) Capacitor. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, e14–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowade, E.; Ramon, E.; Mitra, K.Y.; Martínez-Domingo, C.; Pedró, M.; Pallarès, J.; Loffredo, F.; Villani, F.; Gomes, H.L.; Terés, L.; et al. All-Inkjet-Printed Thin-Film Transistors: Manufacturing Process Reliability by Root Cause Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazeau, J.-P.; Said, Z.; Ramirez-Torres, G. A Novel 5-Axis Robot for Printing High Resolution Pictures from Media on 3D Wide Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Churchill, Australia, 10–13 February 2009; IEEE: Gippsland, Australia, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gazeau, J.-P.; Lallemand, J.-P.; Torres, J.R.; Zeghloul, S. Robot for Large-Format, Three-Dimensional Digital Printing on a Fixed Surface and Printing Method Involving at Least One Such Robot. U.S. Patent US20070062383A1, 22 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Herre, F.; Fritz, H.-G.; Wesselky, S. Coating Device and Associated Coating Method. Germany Patent DE102008053178A1, 12 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, T.; Schlörholz, M.; Pitz, H.; Beier, B. Method for Printing Image on Body i.e., Tank of e.g., Passenger Car, Involves Generating Three or Higher-Dimension Raster Matrix Data to Control Inkjet Printhead, and Printing Image with Inkjet Printhead Using Raster Data. Germany Patent DE102012006371A1, 29 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schlörholz, M.; Pitz, H. Methods for Printing a Curved Surface of an Object by Using an Inkjet Head. U.S. Patent US9764573B2, 11 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Junfeng, M.; Lovell, M.R.; Mickle, M.H. Formulation and Processing of Novel Conductive Solution Inks in Continuous Inkjet Printing of 3-D Electric Circuits. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2005, 28, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Wada, H.; Izumi, K.; Tokito, S. Highly Conductive Metal Interconnects on Three-Dimensional Objects Fabricated with Omnidirectional Ink Jet Printing Technology. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 05EA01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Wada, H.; Izumi, K.; Tokito, S. Three-Dimensional Interconnect Layers Inkjet Printed on Plastic Substrates Using Continuous-Wave Xenon Light Sintering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, 016507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulha, P.; Chituurri, N.C.; Kastner, J.; Kurzmann, J.; Mühlberger, M.; Fechtig, D. Inkjet-Printed Capacitive Sensors and Electronic Structures. In Proceedings of the IMAPS flash Conference, Brno, Czech Republic, 24–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fechtig, D. Robot-Based Direct Digital Printing on Freeform Surfaces. In Inkjet Printing in Industry; Zapka, W., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1269–1297. ISBN 978-3-527-34780-3. [Google Scholar]
- Thalheim, R.; Mitra, D.; Kröher, A.-M.; Zichner, R. Printed Electronics on 3D—Prospects and Effects of Inline IR Treatment for Robot Guided Inkjet Printing of Conductive Patterns. In Proceedings of the Fraunhofer Direct Digital Manufacturing Conference DDMC 2023, Berlin, Germany, 16 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Lim, J.W.; Sohn, D.K.; Ko, H.S. Study on Fall Velocity of Continuously Ejected Micro Inkjet Droplet. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 3311–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, P.; Edlund, O. Robust Registration of Point Sets Using Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2014, 58, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ink | Nom. Drop Volume (Printhead) [pL] | Driving Voltage [V] | Drop Volume (Average, Main Drop) [pL] | [m/s] | [1/1000 s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVN | 10 | 80 | 5.1 | 15.9 | −1.5 |
| 100 | 5.8 | 21.5 | −1.5 | ||
| 120 | 4.4 | 25.4 | −1.6 | ||
| 30 | 80 | 25.8 | 7.7 | −0.4 | |
| 100 | 28.3 | 11.2 | −0.5 | ||
| 120 | 27.2 | 12.9 | −0.6 | ||
| AGF | 30 | 80 | 31.2 | 6.0 | −0.4 |
| 100 | 34.7 | 11.5 | −0.8 | ||
| 120 | 30.3 | 12.5 | −0.9 | ||
| 80 | 80 | 56.3 | 3.1 | −0.2 | |
| 100 | 61.4 | 5.1 | −0.1 | ||
| 120 | 63.4 | 7.2 | −0.5 |
| Ink | Nom. Drop Volume (Printhead) [pL] | Driving Voltage [V] | [mm] | a | f | @Δy = 10 µm [mm] | @Δy = 25 µm [mm] | @Δy = 50 µm [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGF | 30 | 80 | 35 | 14.73 | 0.11 | −3.52 | 4.81 | 11.11 |
| 100 | 35 | 7.84 | 0.11 | 2.21 | 10.54 | 16.84 | ||
| 120 | 35 | 19.37 | 0.0847 | −7.81 | 3.01 | 11.20 | ||
| 80 | 45 | 10.14 | 0.14 | −0.10 | 6.45 | 11.40 | ||
| 100 | 45 | 4.17 | 0.14 | 6.25 | 12.79 | 17.74 | ||
| 120 | 45 | 8.12 | 0.0717 | 2.90 | 15.68 | 25.35 | ||
| 80 | 55 | 9.41 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 6.98 | 11.93 | ||
| 100 | 55 | 4.41 | 0.15 | 5.46 | 11.57 | 16.19 | ||
| 120 | 55 | 4.74 | 0.0805 | 9.27 | 20.66 | 29.27 | ||
| 80 | 80 | 35 | 22.46 | 0.14 | −5.78 | 0.77 | 5.72 | |
| 100 | 35 | 13.01 | 0.0909 | −2.89 | 7.19 | 14.81 | ||
| 120 | 35 | 3.05 | 0.21 | 5.65 | 10.02 | 13.32 | ||
| 80 | 45 | 11.53 | 0.16 | −0.89 | 4.84 | 9.17 | ||
| 100 | 45 | 4.62 | 0.21 | 3.68 | 8.04 | 11.34 | ||
| 120 | 45 | 1.89 | 0.21 | 7.93 | 12.30 | 15.60 | ||
| 80 | 55 | 10.1 | 0.13 | −0.08 | 6.97 | 12.30 | ||
| 100 | 55 | 9.05 | 0.18 | 0.55 | 5.65 | 9.50 | ||
| 120 | 55 | 6.44 | 0.17 | 2.59 | 7.98 | 12.06 | ||
| PVN | 30 | 80 | 35 | 4.85 | 0.13 | 5.57 | 12.61 | 17.95 |
| 100 | 35 | 13.8 | 0.0793 | −4.06 | 7.49 | 16.23 | ||
| 120 | 35 | 17.03 | 0.0586 | −9.09 | 6.55 | 18.38 | ||
| 80 | 45 | 7.94 | 0.0721 | 3.20 | 15.91 | 25.52 | ||
| 100 | 45 | 12.06 | 0.0522 | −3.59 | 13.97 | 27.24 | ||
| 120 | 45 | 15.96 | 0.0415 | −11.27 | 10.81 | 27.52 | ||
| 80 | 55 | 2.23 | 0.23 | 6.52 | 10.51 | 13.52 | ||
| 100 | 55 | 2.99 | 0.15 | 8.05 | 14.16 | 18.78 | ||
| 120 | 55 | 4.1 | 0.094 | 9.49 | 19.23 | 26.61 | ||
| 10 | 80 | 35 | 3.3 | 0.21 | 5.28 | 9.64 | 12.94 | |
| 100 | 35 | 7.07 | 0.13 | 2.67 | 9.72 | 15.05 | ||
| 120 | 35 | 9.02 | 0.0922 | 1.12 | 11.06 | 18.57 | ||
| 80 | 45 | 3.53 | 0.22 | 4.73 | 8.90 | 12.05 | ||
| 100 | 45 | 4.18 | 0.2 | 4.36 | 8.94 | 12.41 | ||
| 120 | 45 | 6.49 | 0.11 | 3.93 | 12.26 | 18.56 | ||
| 80 | 55 | 0.83 | 0.37 | 6.73 | 9.20 | 11.08 | ||
| 100 | 55 | 2.78 | 0.24 | 5.33 | 9.15 | 12.04 | ||
| 120 | 55 | 3.11 | 0.18 | 6.49 | 11.58 | 15.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thalheim, R.; Willert, A.; Mitra, D.; Zichner, R. Novel and Efficient Methodology for Drop Placement Accuracy Testing of Robot-Guided Inkjet Printing onto 3D Objects. Machines 2023, 11, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050568
Thalheim R, Willert A, Mitra D, Zichner R. Novel and Efficient Methodology for Drop Placement Accuracy Testing of Robot-Guided Inkjet Printing onto 3D Objects. Machines. 2023; 11(5):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050568
Chicago/Turabian StyleThalheim, Robert, Andreas Willert, Dana Mitra, and Ralf Zichner. 2023. "Novel and Efficient Methodology for Drop Placement Accuracy Testing of Robot-Guided Inkjet Printing onto 3D Objects" Machines 11, no. 5: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050568
APA StyleThalheim, R., Willert, A., Mitra, D., & Zichner, R. (2023). Novel and Efficient Methodology for Drop Placement Accuracy Testing of Robot-Guided Inkjet Printing onto 3D Objects. Machines, 11(5), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050568






