The Anatomy of the Internet of Digital Twins: A Symbiosis of Agent and Digital Twin Paradigms Enhancing Resilience (Not Only) in Manufacturing Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Digital Twins
2.2. Multi-Agent Systems
- Ingenias: is based on the well-known and established software development process, the Unified Process, and the definition of metamodels [45].
- Mase: uses a set of graphical models to describe system goals, behaviors, types of agents, and agent communication interfaces [46].
- Prometheus: is specifically designed to build intelligent agents [49].
- Passi: is a step-by-step methodology for the design and development of multi-agent partnerships, with the integration of design models and concepts from software engineering approaches using the UML notation [50].
- Decaf: is a flexible MAS, i.e., a set of software tools for the rapid design, development, and execution of intelligent agents for complex software systems [51].
2.3. Digital Twin Realizations through Multi-Agent Systems
- The sharing of data collection and intelligence capabilities across multiple DTs,
- The execution of collaboration models,
- The evolution and reconfiguration of the system based on emergent and self-organizing processes that use a plug-and-play strategy on the fly.
3. The Digital Twin Reference Model
4. Architecture
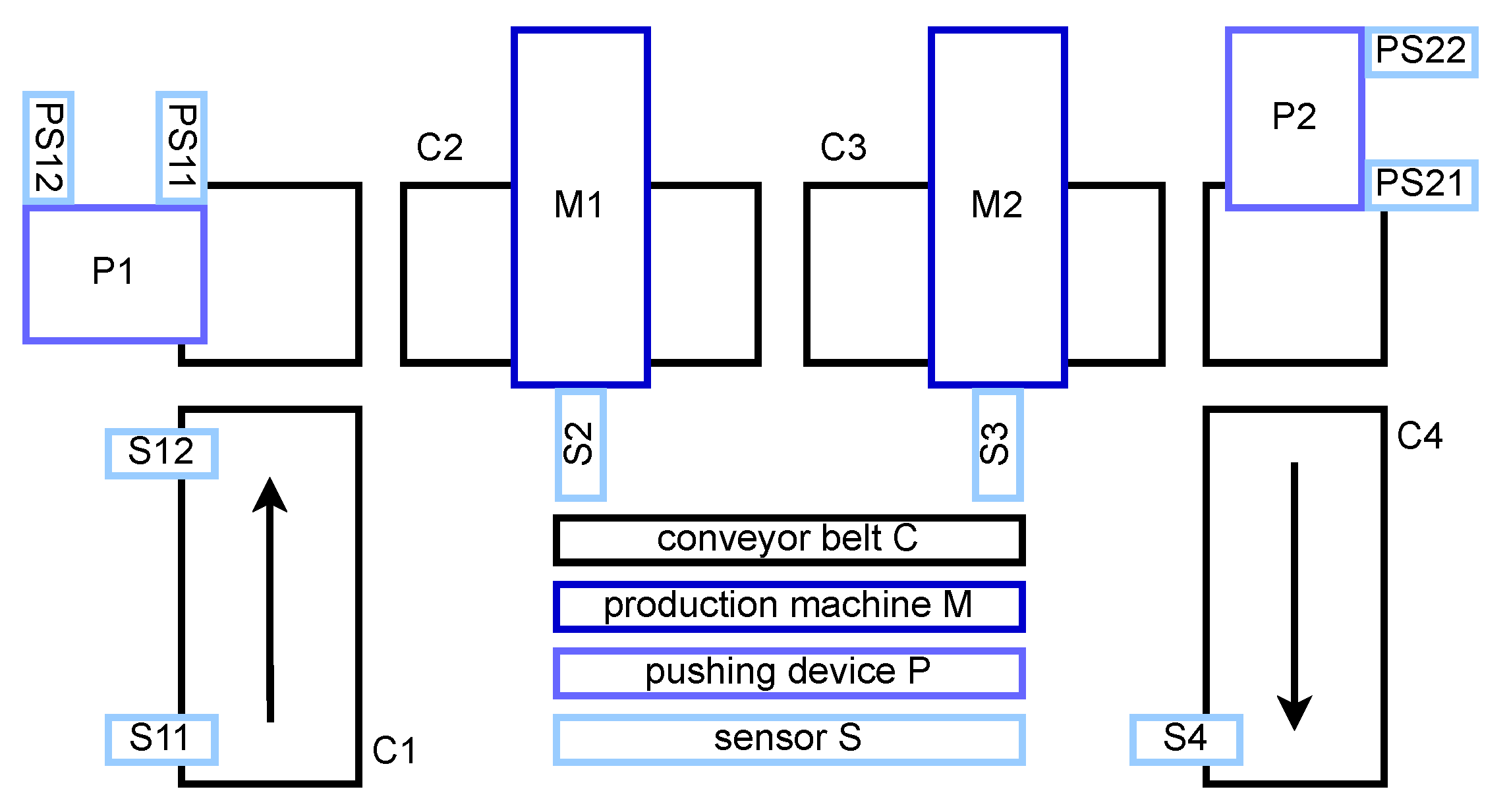
5. Use Case Description—Choreography of Production Processes
- Step A: Thrilling process,
- Step B: Milling process,
- Step C: Drilling process.
6. Implementation and Proof of Concept
7. Discussion and Evaluation
- Active: The IDTs are generated from the DT in the Intranet of Digital Twins, and they are supplied with all data relevant for collaboration. Depending on the workload and the status of the physical machine, the DT updates and provides its IDT as a subset of its available information. These current data reflect the perceived context of the PT, and thus form the basis for negotiating with other IDTs. Once an Order Demand IDT enters the marketplace, the IDTs proactively try to find its production optimum, depending on the desired negotiation strategy.
- Online: Due to the available interfaces between the levels of the DTRM, all entities involved are mutually up to date. Since the IDT acts only as a proxy for the DT, it cannot directly affect the PT. This still requires a controlling instance for confirmation, but this is required anyway for functional safety and security reasons.
- Goal seeking: Without an overarching goal, intelligence to proactively solve problems would not be needed either. Therefore, the overall goal in the marketplace is to fulfill the optimal production flow of the order demands. Depending on the desired negotiation strategy, the IDT can be provided with various sub-goals regarding its bargaining behavior in a human-like and social manner.
- Anticipatory: In order to optimize for future negotiation scenarios, another award mechanism is implemented between DTs and their IDTs. Feedback from the evaluation of the production process provides the basis for self-adaptation to meet future goals more efficiently.
8. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | Asset Administration Shell |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| BDI | Belief, Desire, and Intention |
| CPS | Cyber-Physical System |
| CPPS | Cyber-Physical Production Systems |
| DT | Digital Twin |
| DTRM | Digital Twin Reference Model |
| EU | European Union |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| IDT | Intelligent Digital Twin |
| IIC | Industrial Internet Consortium |
| IIRA | Industrial Internet Reference Architecture |
| IoDT | Internet of Digital Twins |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| MAS | Multi-Agent System |
| MQTT | Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| OPC UA | Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture |
| PLC | Programmable Logic Controller |
| PLM | Product Lifecycle Management |
| PT | Physical Twin |
| RAMI 4.0 | Reference Architectural Model Industry 4.0 |
References
- Abbass, K.; Zeeshan Qasim, M.; Song, H.; Murshed, M.; Mahmood, H.; Younis, I. A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures. In Environmental Science and Pollution Research; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 29, Number 28; pp. 42539–42559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Du, W. An Analysis on the Crisis of “Chips shortage” in Automobile Industry—Based on the Double Influence of COVID-19 and Trade Friction. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1971, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Trollman, H.; Trollman, F.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Parra-López, C.; Duong, L.; Martindale, W.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Hdaifeh, A.; et al. The Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Its Implications for the Global Food Supply Chains. Foods 2022, 11, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breque, M.; De Nul, L.; Petridis, A. Industry 5.0: Towards a Sustainable, Human Centric and Resilient European Industry; Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, F.; Padovano, A.; Umbrello, S. Value-Oriented and Ethical Technology Engineering in Industry 5.0: A Human-Centric Perspective for the Design of the Factory of the Future. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Thiel, R.; Jain, P.; Singh, V.; Fischer, M. Digital Twin: Where do humans fit in? Autom. Constr. 2023, 148, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahavandi, S. Industry 5.0—A Human-Centric Solution. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Wang, L. Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception and perception. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 61, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J. Enabling Technologies for Industry 5.0: Results of a Workshop with Europe’s Technology Leaders; Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehe, R.; Waltersmann, L.; Sauer, A.; Bauernhansl, T. Sustainable production and the role of digital twins–Basic reflections and perspectives. J. Adv. Manuf. Process. 2021, 3, e10078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Bagheri, B.; Kao, H.A. A Cyber-Physical Systems architecture for Industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Manuf. Lett. 2015, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M. Intelligent digital twins and the development and management of complex systems [version 1; peer review: 4 approved]. Digit. Twin 2022, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, L.; Leitao, P.; De la Prieta, F. Towards the Digitization using Asset Administration Shells. In Proceedings of the IECON 2021—47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–16 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Snider, C.; Nassehi, A.; Yon, J.; Hicks, B. Characterising the Digital Twin: A systematic literature review. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgärtel, H. The role of Semantics and Semantic Web Technologies for Digital Twins in Industry 4.0 Systems. In Proceedings of the Workshop Management for Industry 4.0, IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium (NOMS), Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, L.; Leitao, P.; la Prieta, F.D. Agent-Based Asset Administration Shell Approach for Digitizing Industrial Assets. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafto, M.; Conroy, M.; Doyle, R.; Glaessgen, E.; Kemp, C.; LeMoigne, J.; Wang, L. Modeling, Simulation, Information Technology and Processing Roadmap; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Grieves, M.; Vickers, J. Digital Twin: Mitigating Unpredictable, Undesirable Emergent Behavior in Complex Systems. In Transdisciplinary Perspectives on Complex Systems; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piascik, B.; Vickers, J.; Lowry, D.; Scotti, S.; Stewart, J.; Calomino, A. Technology Area 12: Materials, Structures, Mechanical Systems, and Manufacturing Road Map; NASA Headquarters: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Lehmann., J.; Lober., A.; Rache., A.; Baumgärtel., H.; Reichwald., J. Collaboration of Semantically Enriched Digital Twins based on a Marketplace Approach. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems—WINSYS, INSTICC, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–13 July 2022; SciTePress: Setúbal, Portugal; pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Xiao, S.; Hu, L. A review of the technology standards for enabling digital twin. Digit. Twin 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauer, J.; Schweigert-Recksiek, S.; Engel, C.; Spreitzer, K.; Zimmermann, M. What is a digital twin?—Definitions and insights from an industrial case study in technical product development. Proc. Des. Soc. DESIGN Conf. 2020, 1, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Fuenmayor, E.; Hinchy, E.; Qiao, Y.; Murray, N.; Devine, D. Digital Twin: Origin to Future. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjarov, M.; Lechler, T.; Fuchs, J.; Brossog, M.; Selmaier, A.; Faltus, F.; Donhauser, T.; Franke, J. The Digital Twin Concept in Industry—A Review and Systematization. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Vienna, Austria, 8–11 September 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barricelli, B.R.; Casiraghi, E.; Fogli, D. A Survey on Digital Twin: Definitions, Characteristics, Applications, and Design Implications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 167653–167671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Schorz, S.; Rache, A.; Häußermann, T.; Rädle, M.; Reichwald, J. Establishing Reliable Research Data Management by Integrating Measurement Devices Utilizing Intelligent Digital Twins. Sensors 2023, 23, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massonet, A.; Kiesel, R.; Schmitt, R.H. Der Digitale Zwilling über den Produktlebenszyklus. Z. Für Wirtsch. Fabr. 2020, 115, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazdi, N.; Talkhestani, B.A.; Maschler, B.; Weyrich, M. Realization of AI-enhanced industrial automation systems using intelligent Digital Twins. Procedia CIRP 2021, 97, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Valk, H.; Haße, H.; Möller, F.; Otto, B. Archetypes of Digital Twins. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2021, 64, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.M.; Shah, S.A.; Shukla, D.; Bentafat, E.; Bakiras, S. The Role of AI, Machine Learning, and Big Data in Digital Twinning: A Systematic Literature Review, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32030–32052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relekar, A.; Smolira, P.; Petrova, E.; Svidt, K. Enabling Digital Twin with Advanced Visualization and Contextualization of Sensor Data with BIM and Web Technologies. In Proceedings of the Conference CIB W, Luxembourg, 11–15 October 2021; Volume 78, pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Haddadi, H.; Mortier, R.; McAuley, D.; Crowcroft, J. Human-Data Interaction; Technical Report UCAM-CL-TR-837; University of Cambridge, Computer Laboratory: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, M.; Coulton, P.; Pilling, F.; Gradinar, A.; Pilling, M.; Forrester, I. More-than-Human-Data Interaction. In Proceedings of the 25th International Academic Mindtrek Conference, Tampere, Finland, 16–18 November 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, A.; Nee, A.Y.C. Digital Twin in Industry: State-of-the-Art. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel-Heuser, B.; Ocker, F.; Weiß, I.; Mieth, R.; Mann, F. Potential for combining semantics and data analysis in the context of digital twins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2021, 379, 20200368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlab, N.; Kamm, S.; Muller, T.; Jazdi, N.; Weyrich, M. Knowledge Graphs as Enhancers of Intelligent Digital Twins. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), Victoria, BC, Canada, 10–12 May 2021; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, G.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, W. A data- and knowledge-driven framework for digital twin manufacturing cell. Procedia CIRP 2019, 83, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. I. 4.0. Details of the Asset Administration Shell Part 1; Plattform Industrie 4.0; Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi): Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ocker, F.; Urban, C.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Diedrich, C. Leveraging the Asset Administration Shell for Agent-Based Production Systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, M.J. An Introduction to MultiAgent Systems, Second Edition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, A.; Gehlhoff, F.; Seitz, M.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Baumgaertel, H.; Diedrich, C.; Lüder, A.; Schöler, T.; Sutschet, G.; Verbeet, R. Agents for the Realisation of Industrie 4.0—VDI Status Report; VDI Verein Deutscher Ingenieure: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, M.E.P.; Domínguez, J.P.; Rojas, C.A.; Barroso, R.J.D.; de Miguel Jiménez, I.; de Queiroz, J.M.; Leitao, P. A brief review on multi-agent system approaches and methodologies. In Proceedings of the IV Workshop on Disruptive Information and Communication Technologies for Innovation and Digital Transformation, Online, 18 June 2021; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wooldridge, M.; Jennings, N.; Kinny, D. The Gaia Methodology For Agent-Oriented Analysis And Design. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2000, 3, 285–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambonelli, F.; Jennings, N.R.; Wooldridge, M. Developing Multiagent Systems: The Gaia Methodology. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2003, 12, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, J.; Gomez-Sanz, J.J.; Fuentes, R. The Ingenias Methodology and Tools; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 236–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloach, S.; Wood, M.; Sparkman, C. Multiagent Systems Engineering. Int. J. Softw. Eng. Knowl. Eng. 2001, 11, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, P.; Perini, A.; Giorgini, P.; Giunchiglia, F.; Mylopoulos, J. Tropos: An Agent-Oriented Software Development Methodology. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2004, 8, 203–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunchiglia, F.; Mylopoulos, J.; Perini, A. The Tropos Software Development Methodology: Processes, Models and Diagrams. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agent-Oriented Software Engineering III, Bologna, Italy, 15–19 July 2002; pp. 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Padgham, L.; Winikoff, M. Prometheus: A Methodology for Developing Intelligent Agents. In Proceedings of the Agent-Oriented Software Engineering III, Bologna, Italy, 15–19 July 2003; pp. 174–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chella, A.; Cossentino, M.; Sabatucci, L.; Seidita, V. Agile passi: An agile process for designing agents. Int. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2006, 21, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.; Decker, K.; Mersic, M. DECAF - A flexible multi agent system architecture. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2003, 7, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sycara, K.; Pannu, A.; Willamson, M.; Zeng, D.D.; Decker, K. Distributed Intelligent Agents. IEEE Expert 1997, 11, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sycara, K.P.; Paolucci, M.; Velsen, M.V.; Giampapa, J.A. The RETSINA MAS Infrastructure. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2003, 7, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, P.; Karnouskos, S.; Ribeiro, L.; Lee, J.; Strasser, T.; Colombo, A.W. Smart Agents in Industrial Cyber–Physical Systems. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnouskos, S.; Leitao, P.; Ribeiro, L.; Colombo, A.W. Industrial Agents as a Key Enabler for Realizing Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems: Multiagent Systems Entering Industry 4.0. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2020, 14, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Salazar, L.A.; Ryashentseva, D.; Lüder, A.; Vogel-Heuser, B. Cyber-physical production systems architecture based on multi-agent’s design pattern—comparison of selected approaches mapping four agent patterns. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 4005–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeet, R.; Baumgärtel, H. Implementierung von autonomen I4.0-Systemen mit BDI-Agenten. In Handbuch Industrie 4.0: Produktion, Automatisierung und Logistik; ten Hompel, M., Vogel-Heuser, B., Bauernhansl, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, V.; de la Prieta, F.; Leitao, P. Alignment of Digital Twin Systems with the RAMI 4.0 Model Using Multi-agent Systems. In Proceedings of the Service Oriented, Holonic and Multi-Agent Manufacturing Systems for Industry of the Future, Bucharest, Romania, 22–23 September 2022; pp. 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada, L.; Leitão, P. Multi-Agent Systems to Implement Industry 4.0 Components. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Industrial Cyberphysical Systems (ICPS), Tampere, Finland, 10–12 June 2020; Volume 1, pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.; Casquero, O.; Estévez, E.; Leitão, P.; Marcos, M. Towards the generic integration of agent-based AASs and Physical Assets: A four-layered architecture approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 19th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 21–23 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel-Heuser, B.; Ocker, F.; Scheuer, T. An approach for leveraging Digital Twins in agent-based production systems. Automatisierungstechnik 2021, 69, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambra, T.; Macharis, C. Agent-Based Digital Twins (ABM-DT) in Synchromodal Transport and Logistics: The Fusion of Virtual and Pysical Spaces. In Proceedings of the 2020 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–18 December 2020; pp. 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ambra, T.; Caris, A.; Macharis, C. Should I Stay or Should I Go? Assessing Intermodal and Synchromodal Resilience from a Decentralized Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambra, T.; Caris, A.; Macharis, C. Do You See What I See? A Simulation Analysis of Order Bundling within a Transparent User Network in Geographic Space. J. Bus. Logist. 2021, 42, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittler, D.; Lierhammer, P.; Braun, D.; Müller, T.; Jazdi, N.; Weyrich, M. An Agent-based Realisation for a continuous Model Adaption Approach in intelligent Digital Twins. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.03681. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz, C.; Lopez, J. Digital Twin: A Comprehensive Survey of Security Threats. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1475–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/DIS 23247-1:2020(E); Automation Systems and Integration—Digital Twin Framework for Manufacturing—Overview and General Principles. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ISO/DIS 23247-2:2021(E); Automation Systems and Integration—Digital Twin Framework for Manufacturing—Reference Architecture. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.I.K.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Digital Twin-driven smart manufacturing: Connotation, reference model, applications and research issues. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheleroff, S.; Xu, X.; Zhong, R.Y.; Lu, Y. Digital Twin as a Service (DTaaS) in Industry 4.0: An Architecture Reference Model. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 47, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Bottani, E.; Ciarapica, F.E.; Costantino, F.; Donato, L.D.; Ferraro, A.; Mazzuto, G.; Monteriù, A.; Nardini, G.; Ortenzi, M.; et al. Digital Twin Reference Model Development to Prevent Operators’ Risk in Process Plants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.M.; El Saddik, A. C2PS: A Digital Twin Architecture Reference Model for the Cloud-Based Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN SPEC 91345; Reference Architecture Model Industrie 4.0 (RAMI4.0). DIN German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Plattform Industrie 4.0. RAMI4.0—A Reference Framework for Digitalisation. 2018. Available online: https://www.plattform-i40.de/IP/Redaktion/EN/Downloads/Publikation/rami40-an-introduction.html (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Lin, S.W.; Miller, B.; Durand, J.; Bleakley, G.; Chigani, A.; Martin, R.M.; Murphy, B.; Crawford, M. The Industrial Internet of Things Volume G1: Reference Architecture; Version 1.9. 2019. Available online: https://www.iiconsortium.org/pdf/IIRA-v1.9.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Lin, S.W.; Murphy, B.; Clauer, E.; Loewen, U.; Neubert, R.; Bachmann, G.; Pai, M.; Hankel, M. Architecture Alignment and Interoperability: An Industrial Internet Consortium and Plattform Industrie 4.0 Joint Whitepaper. IIC:WHT:IN3:V1.0:PB:20171205. 2018. Available online: https://www.iiconsortium.org/pdf/JTG2_Whitepaper_final_20171205.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Belyaev, A.; Diedrich, C. Specification, “Demonstrator I4.0-Language” v3.0, Technical Report. IFAT-LIA 07/2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334429449_Specification_Demonstrator_I40-Language_v30 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Lober, A.; Lehmann, J.; Häußermann, T.; Reichwald, J.; Baumgärtel, H. Improving the Engineering Process of Control Systems Based on Digital Twin Specifications. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Emerging Trends in Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering (ELECOM), Reduit, Mauritius, 22–24 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eclipse Foundation. Eclipse Ditto™ Documentation.2021. Available online: https://www.eclipse.org/ditto/intro-overview.html (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Luyen, L.N.; Tireau, A.; Venkatesan, A.; Neveu, P.; Larmande, P. Development of a knowledge system for Big Data. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics, Nimes, France, 13–15 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrgoc, D.; Rojas, C.; Angles, R.; Arenas, M.; Arroyuelo, D.; Aranda, C.B.; Hogan, A.; Navarro, G.; Riveros, C.; Romero, J. MillenniumDB: A Persistent, Open-Source, Graph Database. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.01540. [Google Scholar]






| Characteristics | Description | Matching MAS Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Active | IDTs should actively provide information that is currently needed. This enhances collaboration with humans and other machines. | Through a permanent perception of the environment and continuous exchange with other agents, processed information can be actively incorporated into collaboration processes. |
| Online | In order to ensure active interaction, the IDT must be online and have a continuous connection to the PT’s respective environment perception. | Agents interconnect the physical space and digital space for perception and interaction purposes. |
| Goal-seeking | The goal-seeking, which has always been present, is not to be carried out by human intervention as before, but with the support of the IDT. | Agents can interact autonomously with humans as well as machines or other agents through their social abilities to achieve an overall goal. |
| Anticipatory | The IDT anticipatorily adapts its actions and goals to its self-predicted future based on all its accumulated information and experience. | Agents have the ability to learn, share their knowledge, and adapt their behavior to their future goals. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehmann, J.; Lober, A.; Häußermann, T.; Rache, A.; Ollinger, L.; Baumgärtel, H.; Reichwald, J. The Anatomy of the Internet of Digital Twins: A Symbiosis of Agent and Digital Twin Paradigms Enhancing Resilience (Not Only) in Manufacturing Environments. Machines 2023, 11, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050504
Lehmann J, Lober A, Häußermann T, Rache A, Ollinger L, Baumgärtel H, Reichwald J. The Anatomy of the Internet of Digital Twins: A Symbiosis of Agent and Digital Twin Paradigms Enhancing Resilience (Not Only) in Manufacturing Environments. Machines. 2023; 11(5):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050504
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehmann, Joel, Andreas Lober, Tim Häußermann, Alessa Rache, Lisa Ollinger, Hartwig Baumgärtel, and Julian Reichwald. 2023. "The Anatomy of the Internet of Digital Twins: A Symbiosis of Agent and Digital Twin Paradigms Enhancing Resilience (Not Only) in Manufacturing Environments" Machines 11, no. 5: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050504
APA StyleLehmann, J., Lober, A., Häußermann, T., Rache, A., Ollinger, L., Baumgärtel, H., & Reichwald, J. (2023). The Anatomy of the Internet of Digital Twins: A Symbiosis of Agent and Digital Twin Paradigms Enhancing Resilience (Not Only) in Manufacturing Environments. Machines, 11(5), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050504







