A Dynamic Self-Attention-Based Fault Diagnosis Method for Belt Conveyor Idlers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sound Feature Analysis of Faulty Idlers
2.2. Dynamic Self-Attention-Based Idler Fault Diagnosis Method
2.3. Time-Frequency Domain Feature Extraction and Preprocessing Method
2.4. Idler Fault Diagnosis Model Based on Dynamic Self-Attention
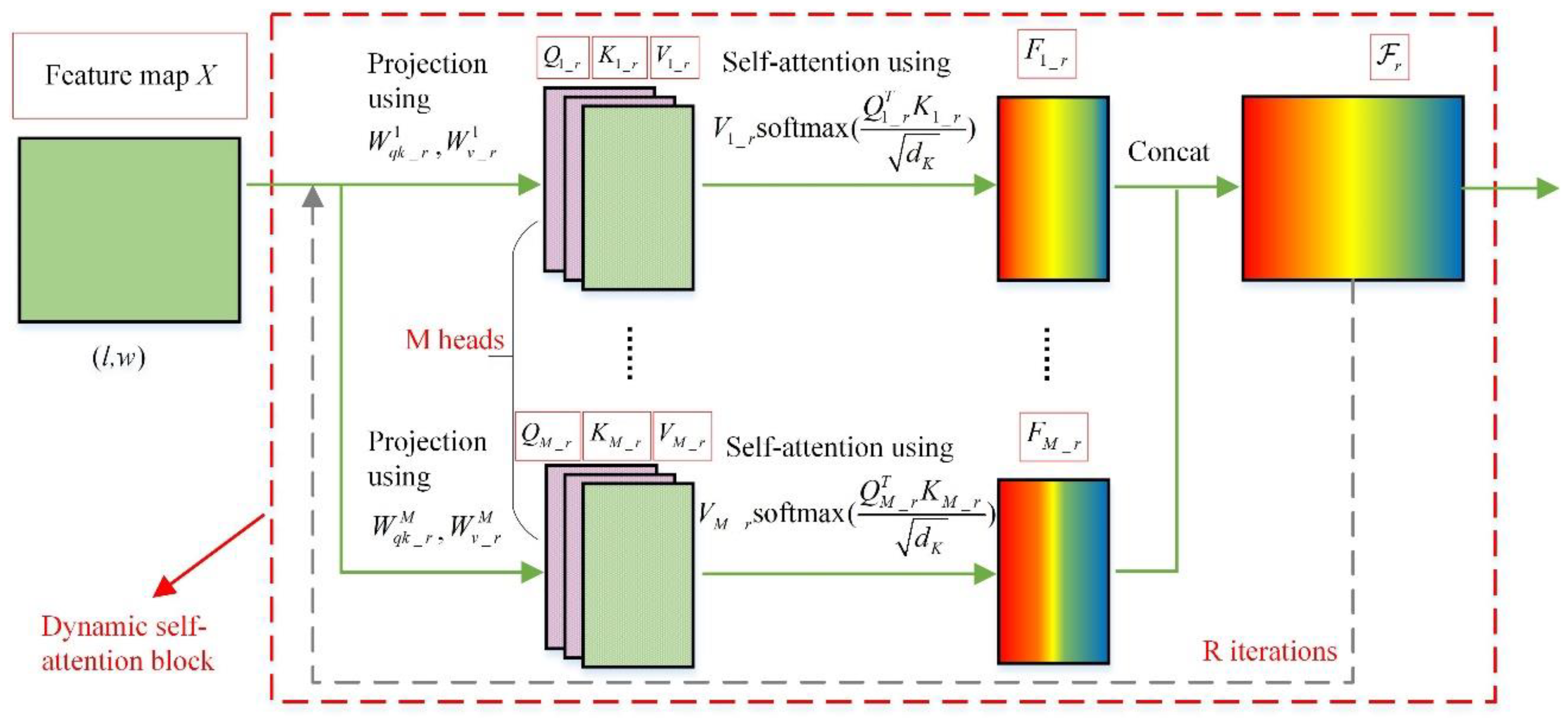
2.4.1. Dynamic Self-Attention
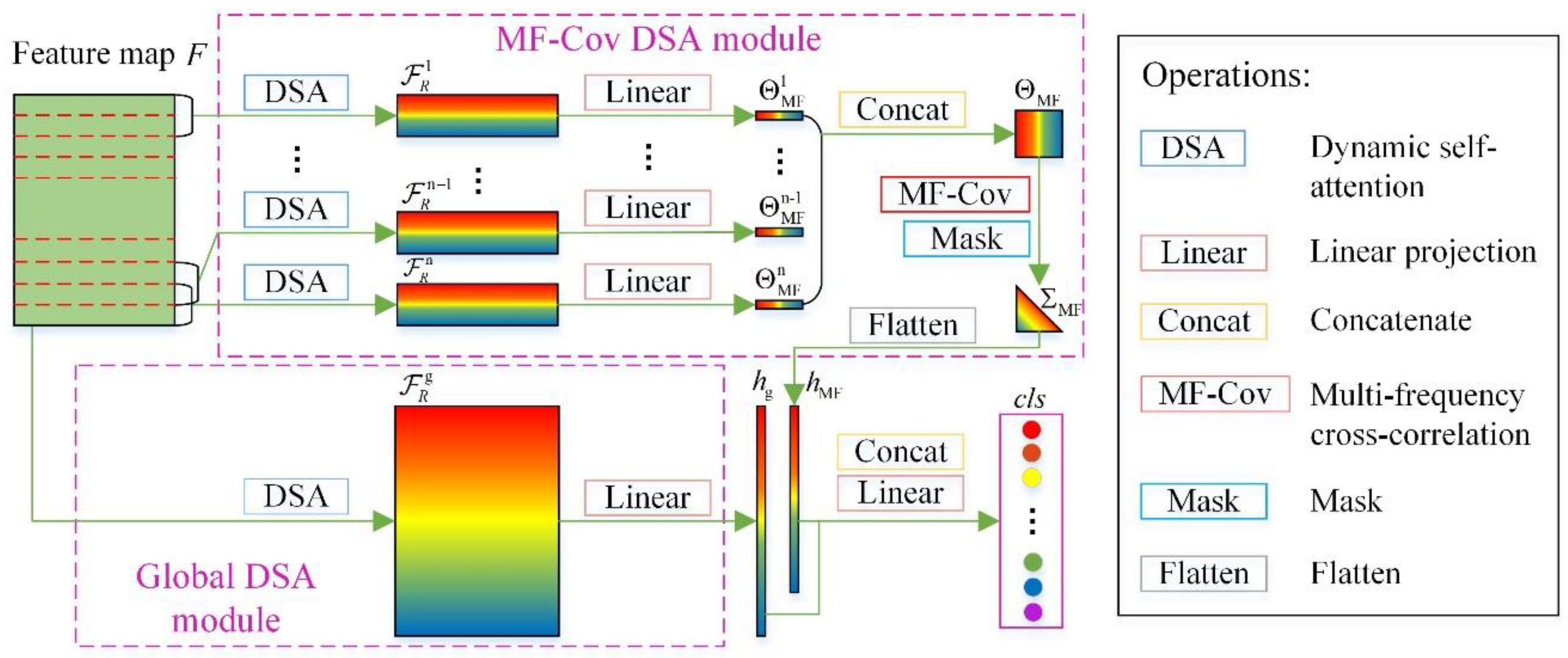
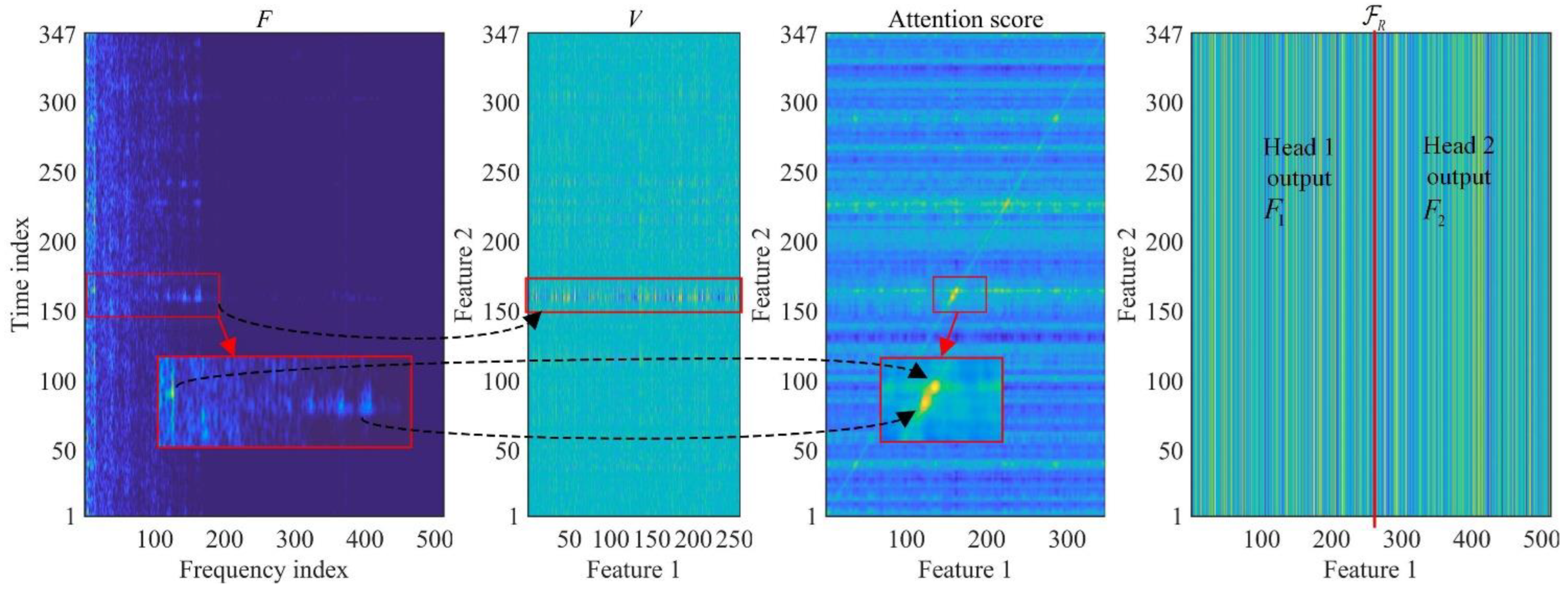
2.4.2. Multi-Frequency Cross-Correlation Dynamic Self-Attention
2.4.3. Global Dynamic Self-Attention
2.4.4. Diagnosis Result Output and Loss Function
3. Results and Discussion
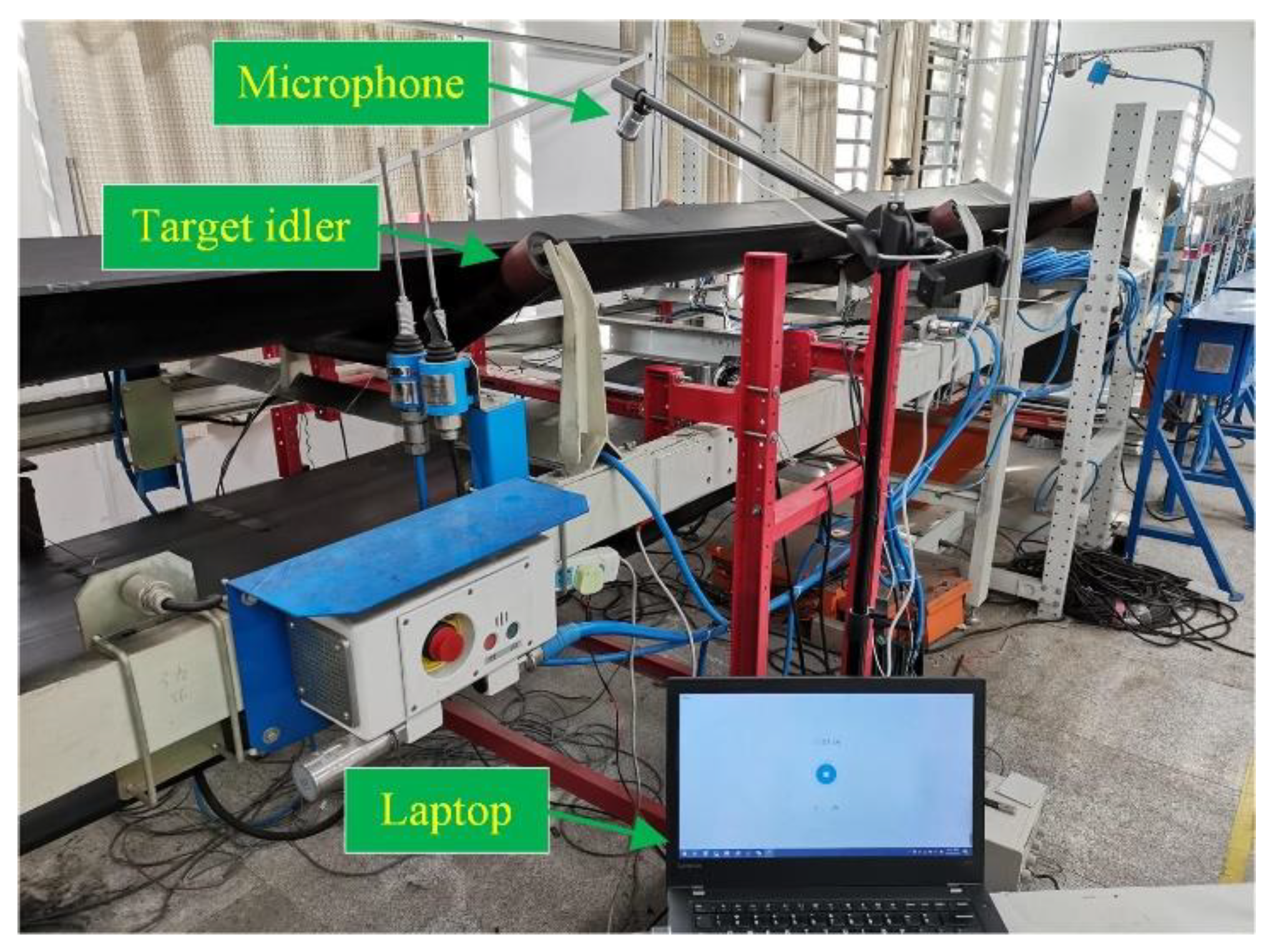
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Data Acquisition
3.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
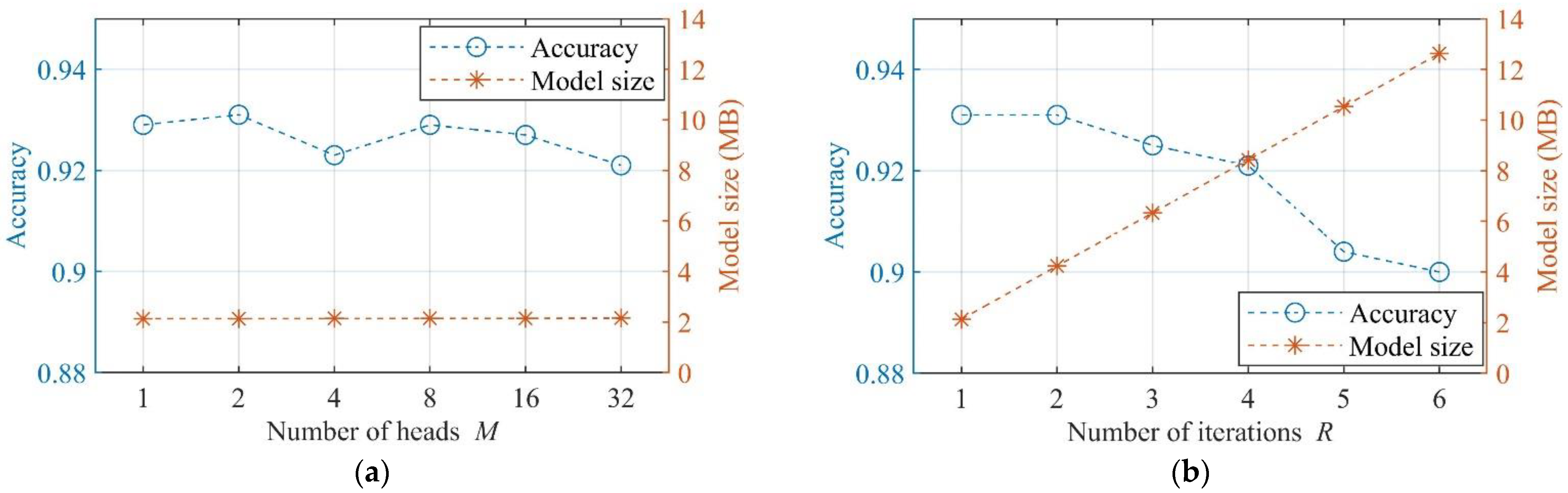
3.3.1. Super Parameters Determination of the Dynamic Self-Attention Block
3.3.2. Weighting Method
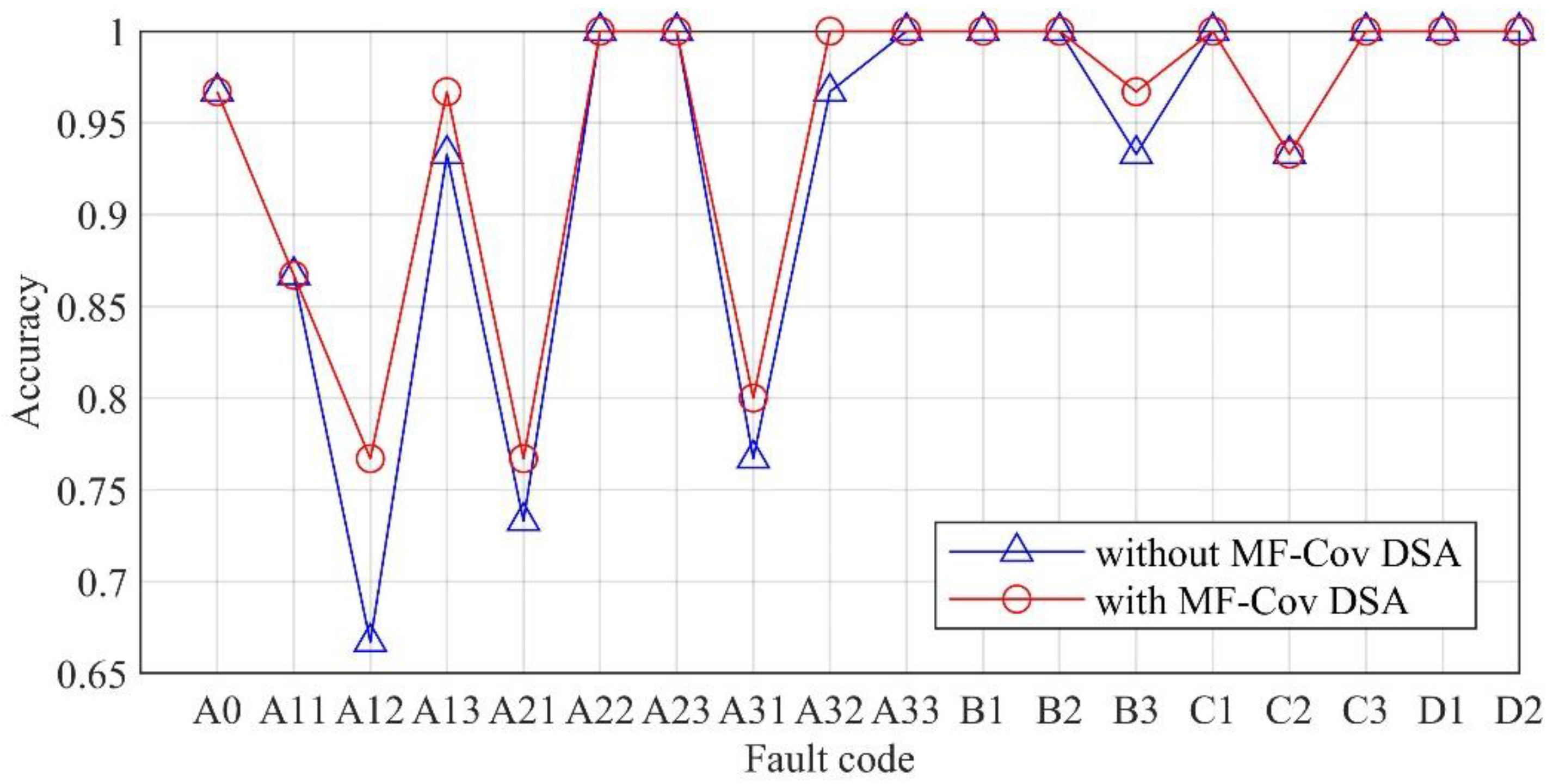
3.3.3. Performance Comparison and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Miao, C.Y. The conveyor belt longitudinal tear on-line detection based on improved SSR algorithm. Optik 2016, 127, 7395–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, C.Y.; Li, X.G.; Xu, G.W. Research on deviation detection of belt conveyor based on inspection robot and deep learning. Complexity 2021, 2021, 3734560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, M.; Stojanović, B.; Blagojević, M. Failure analysis of idler roller bearings in belt conveyors. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharana, V.; Ravikumarb, S.; Kangasabapathy, H. Condition monitoring of self aligning carrying idler (SAI) in belt-conveyor system using statistical features and decision tree algorithm. Measurement 2014, 58, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, S.; Kanagasabapathy, H.; Muralidharan, V. Fault diagnosis of self-aligning troughing rollers in belt conveyor system using k-star algorithm. Measurement 2019, 133, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, Z.P.; Yang, M.J.; Fei, M.R.; Wang, Y.L. An audio-based intelligent fault diagnosis method for belt conveyor rollers in sand carrier. Control Eng. Pract. 2020, 105, 104650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.J.; Zhou, W.J.; Song, T.X. Audio-based fault diagnosis for belt conveyor rollers. Neurocomputing 2020, 397, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Pei, D.L.; Lodewijks, G.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Mei, J. Acoustic signal based fault detection on belt conveyor idlers using machine learning. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.R.; Qiao, T.Z.; Pang, Y.S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.T. Research on ADCN method for damage detection of mining conveyor belt. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8662–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.H.; Ma, H.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, G.M. An improved skewness decision tree SVM algorithm for the classification of steel cord conveyor belt defects. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Qiao, T.Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Pang, Y.S. Longitudinal tear detection method of conveyor belt based on audio-visual fusion. Measurement 2021, 176, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, W.C.; Li, J.Y. Edge detection for conveyor belt based on the deep convolutional network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Qiao, T.Z.; Zhang, H.T.; Yang, Y.; Pang, Y.S.; Wei, H.Y. A contactless measuring speed system of belt conveyor based on machine vision and machine learning. Measurement 2019, 139, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutomi, A.Y.; Enoki, H. Localization of inspection device along belt conveyors with multiple branches using deep neural networks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 5, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.Y.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Liang, K.X. A comprehensive review on convolutional neural network in machine fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2020, 417, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.W.; Ma, X.H. A fault diagnosis method of rolling bearings based on parameter optimization and adaptive generalized S-Transform. Machines 2022, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Qiu, D.Y.; Chen, F.A. Support vector machine with parameter optimization by a novel hybrid method and its application to fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2015, 149, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.Q.; He, H.B.; Yan, J.; Xie, P. Multiscale convolutional neural networks for fault diagnosis of wind turbine gearbox. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3196–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Q.; Li, X. Diagnosing rotating machines with weakly supervised data using deep transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2020, 16, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Lei, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, F. Distribution-invariant deep belief network for intelligent fault diagnosis of machines under new working conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshrefzadeh, A. Condition monitoring and intelligent diagnosis of rolling element bearings under constant/variable load and speed conditions. Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 2021, 149, 107153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.12872. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Guo, T.Y.; Xu, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Gao, W. Pre-trained image processing transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.00364. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.P.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Liu, M.; Dai, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. CvT: Introducing convolutions to vision transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15808. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.K.; Garcia, N.; Chu, C.H.; Otani, M.; Nakashima, Y.; Takemura, H. A comparative study of language transformers for video question answering. Neurocomputing 2021, 445, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, M.; Yoon, S.J.; Kang, B.; Lee, J. Perceptual image quality assessment with transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.14730. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, C.Y.; Li, X.G.; Ji, J.H.; Meng, D.J. Research on the fault analysis method of belt conveyor idlers based on sound and thermal infrared image features. Measurement 2021, 186, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JJG-2002; Metrological Verification Regulation of P.R. China, Verification Regulation of Sound Level Meters. China Institute of Metrology: Beijing, China, 2002.
- GB 8923-88; National Standards of P.R. China, Rust Grades and Preparation Grades of Steel Surfaces before Application of Paints and Related Products. National Bureau of Standards: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.06993. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.W.; Lin, C.J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Santen, J.; Mobius, B.; Olive, J. Formant tracking using context-dependent phonemic information. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2005, 13, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

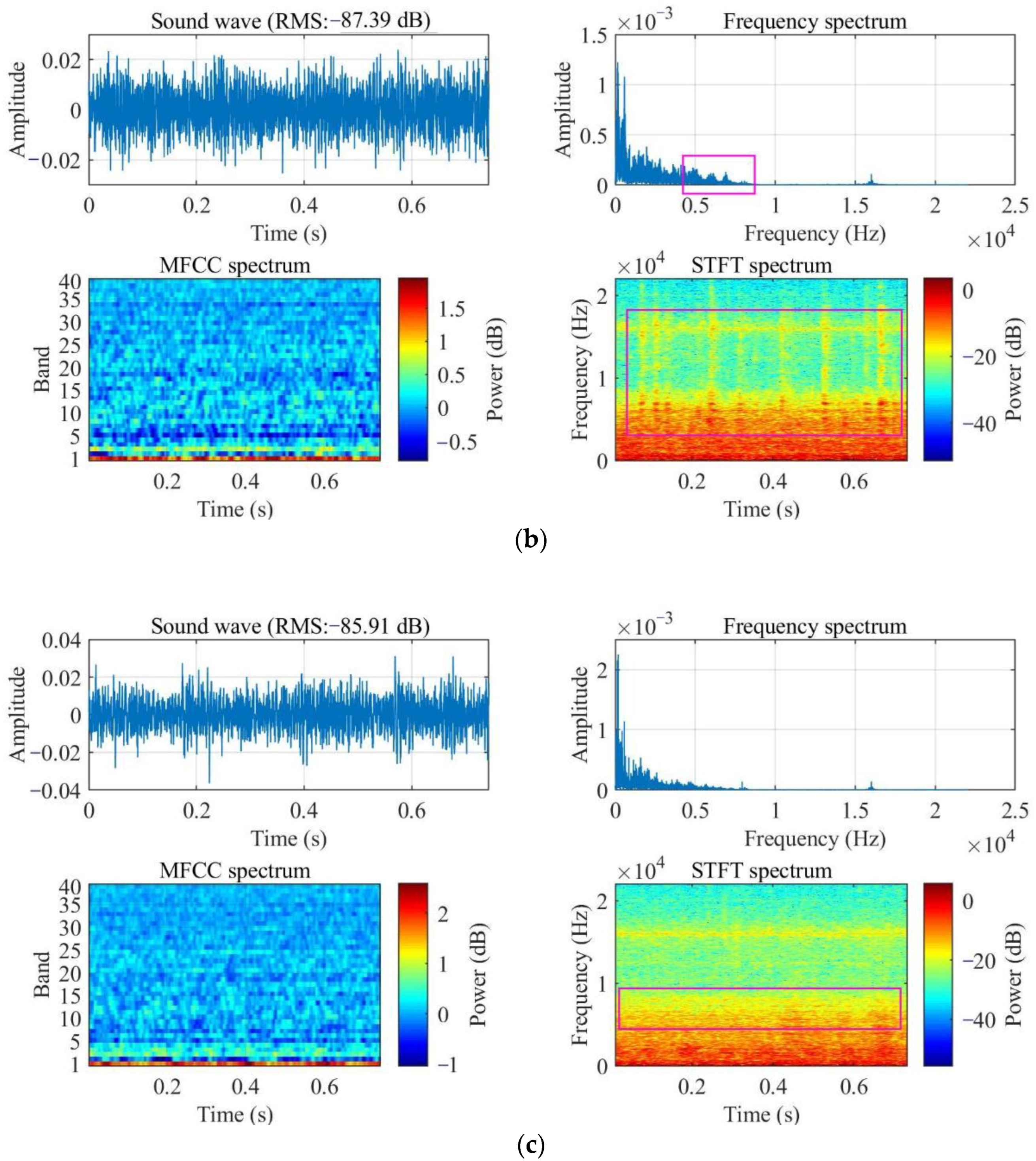



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Length (mm) | 375 |
| Diameter (mm) | 89 |
| Bearing type | 6204 |
| Number of rolling elements | 8 |
| Contact angle (°) | 10 |
| Stage | Code | Manifestation | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | A0 | Normal | - |
| Incipient | A11/A12/A13 | Pits on inner ring/outer ring/rolling element | Diameter: 1 mm, depth: 0.5 mm |
| A21/A22/A23 | Diameter: 2 mm, depth: 0.5 mm | ||
| A31/A32/A33 | Diameter: 3 mm, depth: 1.0 mm | ||
| Final | B1 | Bearing filled with coal particles | Particle diameter < 1 mm |
| B2 | Rustiness | Level B [31] | |
| B3 | Eccentric rotation | Radial runout tolerance: 2 mm | |
| C1 | Cage damaged | Fracture: 3/8 | |
| C2 | Filled with metal debris | Thickness < 0.1 mm | |
| C3 | Raceway wear through | Slot size: 5 × 1 mm | |
| Catastrophic | D1 | Jamming | Speed: 0 rpm |
| D2 | Roller wear through | Speed: 0 rpm, fissure size: 30 × 1.5 cm |
| Algorithm | Feature | Accuracy | Latency (ms) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM-Linear | MFCC | 78.7% | 450.0 | 75.0 |
| SVM-RBF | 71.1% | 480.0 | 79.0 | |
| RF | 64.8% | 5.2 | 2.7 | |
| ResNet-18 | 77.6% | 19.2 | 44.8 | |
| Densenet-121 | 63.9% | 53.0 | 30.4 | |
| Ours | 90.2% | 1.2 | 0.02 | |
| SVM-Linear | STFT spectrum | 68.3% | 450.9 | 71.6 |
| SVM-RBF | 38.0% | 515.6 | 73.6 | |
| RF | 68.1% | 6.3 | 2.0 | |
| ResNet-18 | 89.8% | 23.0 | 44.8 | |
| Densenet-121 | 81.9% | 54.4 | 30.4 | |
| Ours | 94.6% | 27.8 | 3.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Miao, C.; Li, X.; Ji, J.; Meng, D.; Wang, Y. A Dynamic Self-Attention-Based Fault Diagnosis Method for Belt Conveyor Idlers. Machines 2023, 11, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020216
Liu Y, Miao C, Li X, Ji J, Meng D, Wang Y. A Dynamic Self-Attention-Based Fault Diagnosis Method for Belt Conveyor Idlers. Machines. 2023; 11(2):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020216
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi, Changyun Miao, Xianguo Li, Jianhua Ji, Dejun Meng, and Yimin Wang. 2023. "A Dynamic Self-Attention-Based Fault Diagnosis Method for Belt Conveyor Idlers" Machines 11, no. 2: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020216
APA StyleLiu, Y., Miao, C., Li, X., Ji, J., Meng, D., & Wang, Y. (2023). A Dynamic Self-Attention-Based Fault Diagnosis Method for Belt Conveyor Idlers. Machines, 11(2), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020216





